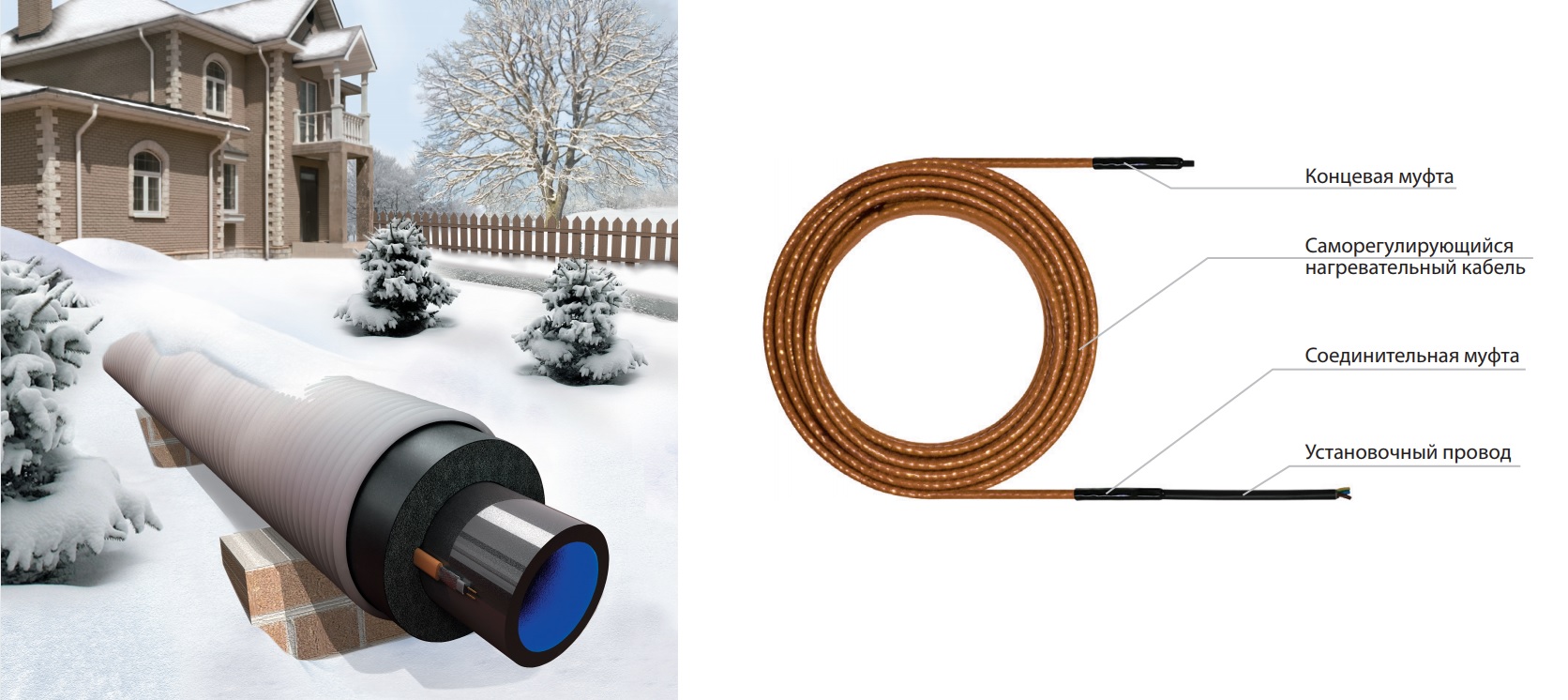
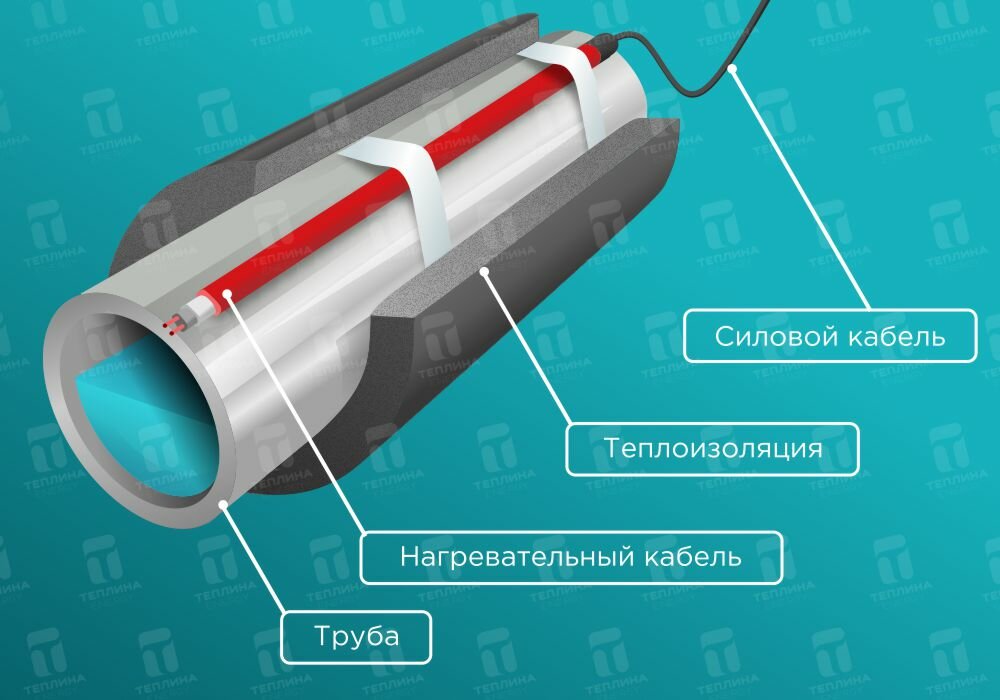
- Types of heating cables for pipes
- Resistive heating cable
- Self-regulating heating cable
- 2. What parameters influence the choice?
- Types of pipeline heating
- Resistive option for heating
- Semiconductor self-adjusting
- How to choose the right cable?
- Types of heating cable
- Type #1 - resistive
- Type #2 - self-adjusting
- Advantages of a heating cable
- Types of heating cable
- Self-regulating heating cable
- Resistive heating cable
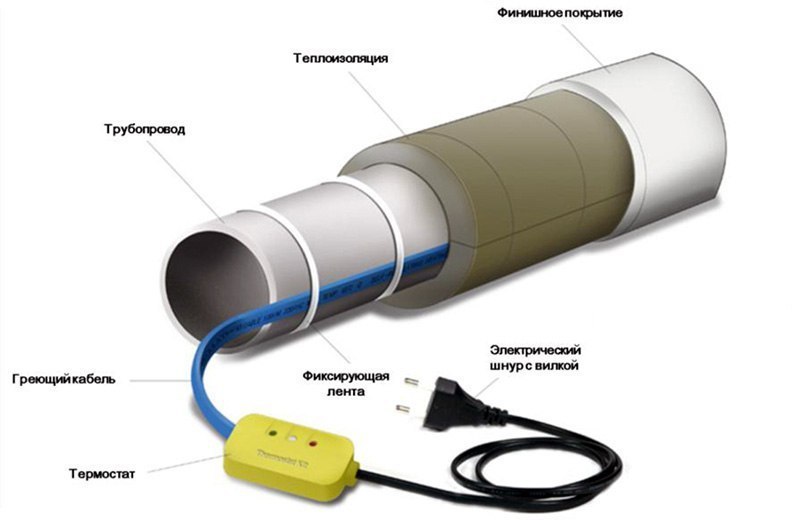
- How to lay the heating cable outside the pipe
- Finally
Types of heating cables for pipes
Let us consider in more detail the types of heating cables.
Resistive heating cable
 The most simple and cheap are resistive cables. The principle of their operation is similar to the principle of operation of an electric heating coil, which heats up when electricity passes through it.
The most simple and cheap are resistive cables. The principle of their operation is similar to the principle of operation of an electric heating coil, which heats up when electricity passes through it.
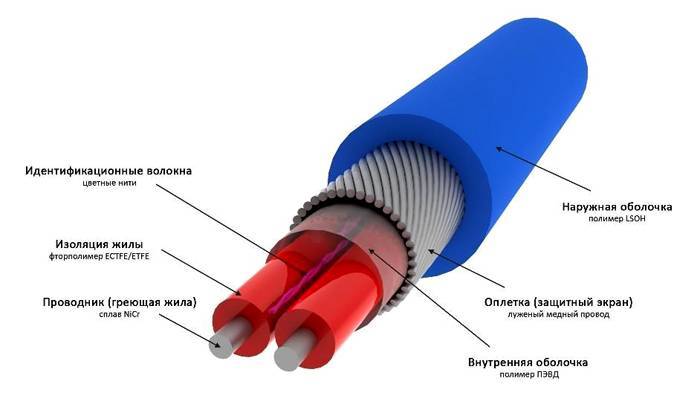
The basis of these cables is a heating core, mostly nichrome, covered with a two-layer insulation, ground shield, which also performs a reinforcing function. On top of this "pie" is closed with a protective shell. The mandatory presence of grounding is due to strict safety requirements in case of violation of the integrity of the wire.
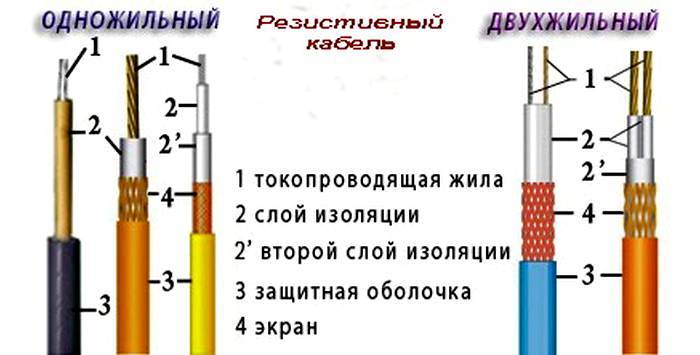
Manufacturers offer single-core and two-core types of resistive cables.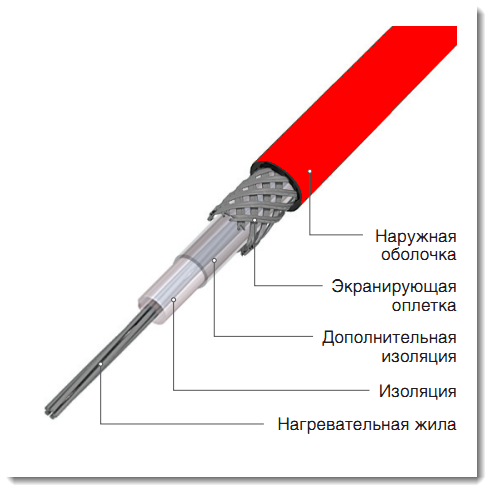
In order for the heating to function, it is necessary to loop the electrical circuit, that is, connect the power to both ends of the wire. In the case of a single-core system, connection difficulties may arise. You can fold the cable in two, but then the material consumption, and, accordingly, the costs, will increase exactly twice. Therefore, two-core cables are most widely used.
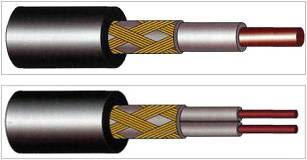
The loopback here is provided by a contact sleeve, which is installed at the end of the wire and closes the circuit. The biggest disadvantage of this option is that this same coupling can only be installed in the factory, so only pieces of the sizes offered by the manufacturers are on sale. It is strictly forbidden to cut the cable yourself. The disadvantages include the fact that in order to reduce energy consumption, the purchase and installation of an additional equipment as a system automatic control and management, maintaining a given temperature regime.
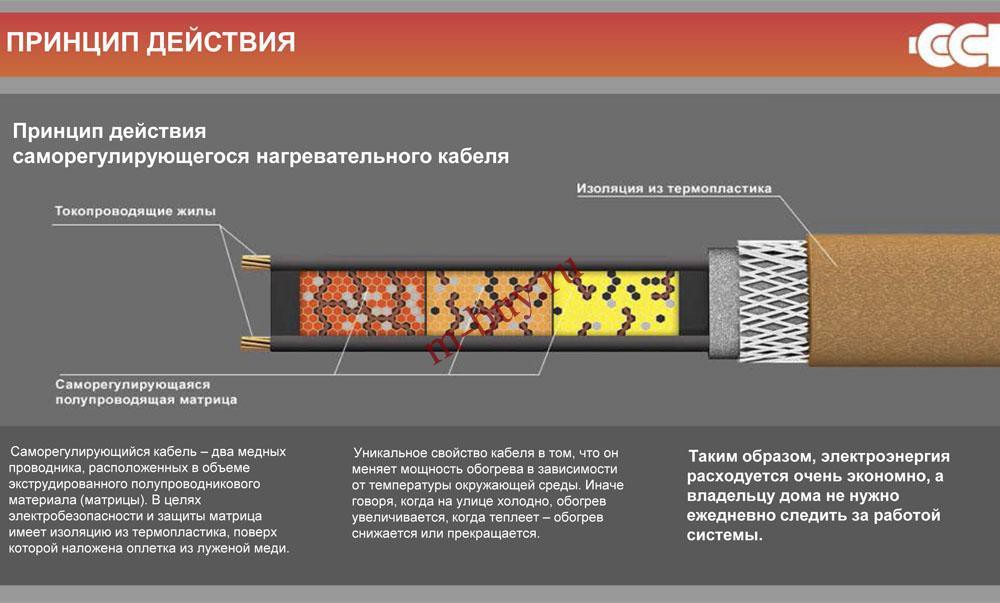
Self-regulating heating cable
There are also self-regulating semiconductor heating cables, which are the most economical and fundamentally differ in both the principle of operation and their device.
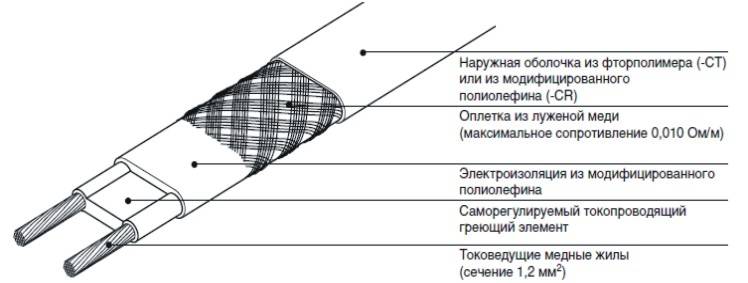
Metal conductors are interconnected by a semiconductor jumper, which is the heating element. Due to the unique characteristics of a semiconductor, its electrical conductivity is directly dependent on the ambient temperature. As the temperature drops, the resistance drops and heat generation increases, and as the temperature rises, the power consumption decreases accordingly.But the most interesting is the fact that temperature self-regulation is carried out throughout the entire cable at each point, so different sections have different degrees of heating and the temperature rises only where necessary, therefore, electricity consumption is minimized.
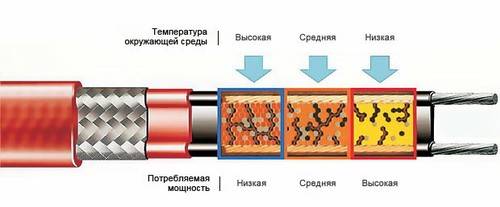
In addition to being economical, the advantage of the semiconductor type is that the cable can be purchased in any required length, it has cut lines at small intervals.
Its biggest drawback, of course, is its rather high cost. Although everyone makes their own choice between high price and low power consumption.
We invite you to watch a video review of a self-regulating heating tape:
2. What parameters influence the choice?
Before you purchase the right amount of cable, you need to clearly determine which type is right for your needs. The whole variety of this product differs in five main features:
- By type - the cable can be self-regulating or resistive. At the same time, the principle of operation for both heaters is the same. Heating occurs due to the current that flows through the internal veins;
- According to the material of the outer insulation. The possibility of application under certain conditions depends on this criterion. For example, to organize a heating system for sewers or drains, it is necessary to choose cables with a polyolefin coating. Fluoropolymer insulation is available for cable that will be installed on the roof or used in industrial applications where additional UV protection is needed.If the cable is laid in the inner cavity of the water pipes, then it is better to choose a food-grade coating, that is, fluoroplast insulation. This will prevent the change in taste of the water, which is sometimes the case;
- Absence or presence of a screen (braid). The braid makes the product stronger, more resistant to various mechanical influences, in addition, the screen performs the function of grounding. The absence of this element indicates that you have a product that belongs to the budget category;
- According to the temperature class - there are low-, medium- and high-temperature heaters. This indicator is very important in the arrangement of the heating system for water supply and drainage. Low-temperature elements are heated up to +65°C, power does not exceed 15 W/m and is suitable for heating pipes of small diameter. Medium-temperature conductors are heated up to a maximum of +120 ° C, the power reaches 10-33 W / m, they are used to prevent freezing of pipes of medium diameter or to heat the roof. High-temperature thermal cables are capable of heating up to +190°C and have a specific power from 15 to 95 W/m. This type is advisable to use for industrial purposes or in the presence of pipes of large diameter. For domestic use, such conductors are considered too powerful and expensive;
- By power. The power characteristics of the coolant must be taken into account without fail. If you pick up a low power conductor, you simply will not achieve the desired result. Exceeding the required indicator can lead to too high a level of energy consumption, which in practice will be unjustified. The choice of the required power level primarily depends on the diameter of the heated pipe.According to the recommendations of experts, for pipes with a diameter of 15-25 mm, a power of 10 W / m is sufficient, for a diameter of 25-40 mm - 16 W / m, for a pipe with a size of 60-80 mm - 30 W / m, for those that exceed 80 mm in diameter, - 40 W / m.
Types of pipeline heating
Heating wires are classified according to the heat dissipation scheme into self-regulating and resistive systems. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Resistive option for heating
The principle of operation of such a cable is to heat an insulated metal core, and it is important to monitor the temperature in order to prevent combustion of the heating element. According to the type of construction, such a cable can be with one or two cores. The first option is rarely used, as it requires the circuit to be closed. When heating pipes, such a system is sometimes impossible at all.
When heating pipes, such a system is sometimes not possible at all.
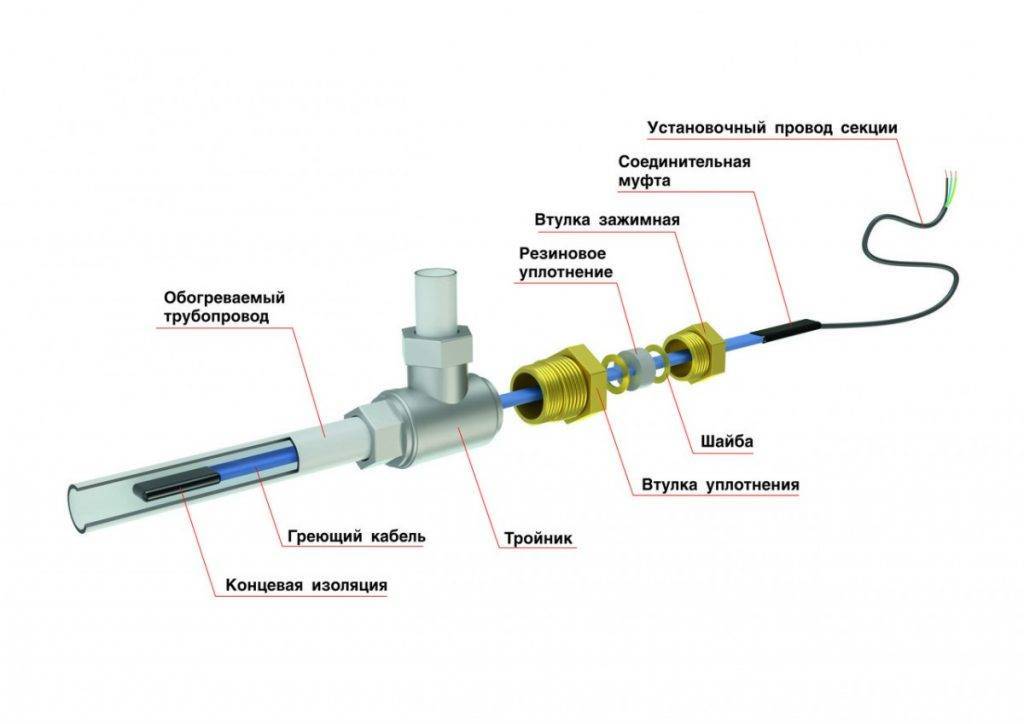
Resistive cable device
A two-core wire is more practical - one end of the cable is connected to the network, a contact sleeve is installed on the other, which ensures closure. One conductor can serve as a heat source, then the second one serves only for the necessary conductivity. Sometimes both conductors are used, increasing the power of the heating itself.
The conductors are protected by multilayer insulation, which has a grounding in the form of a loop (screen). To protect against mechanical damage, the outer contour is made of a PVC sheath.
Cross section of two types of resistive cable
Such a system has its positive and negative sides. The first ones include:
- High power and heat transfer, which is necessary for a pipeline with an impressive diameter or with a considerable number of style details (tees, flanges, etc.)
- Simplicity of design at an affordable cost. Such a cable for heating a water pipe with a minimum power costs 150 rubles per meter.
The disadvantages of the system include the following:
- For correct operation, it is necessary to purchase additional elements (temperature sensor, control unit for automatic control).
- The cable is sold with a certain footage, and the end contact sleeve is mounted in production conditions. Do-it-yourself cutting is prohibited.
For more economical operation, use the second option.
Semiconductor self-adjusting
This system self-regulating heating cable for water pipes completely different in principle from the first option. Two conductors (metal) are separated by a special semiconductor matrix, which acts as a heating source. This ensures high current conductivity at low temperatures. At the same time, when the temperature rises, the consumption of electricity decreases markedly.
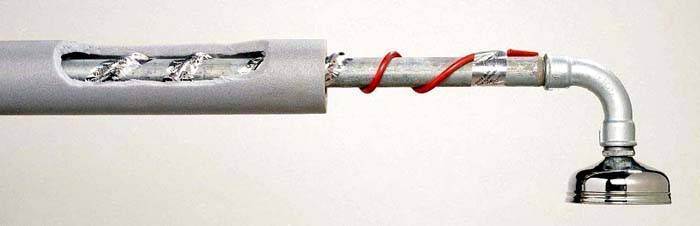
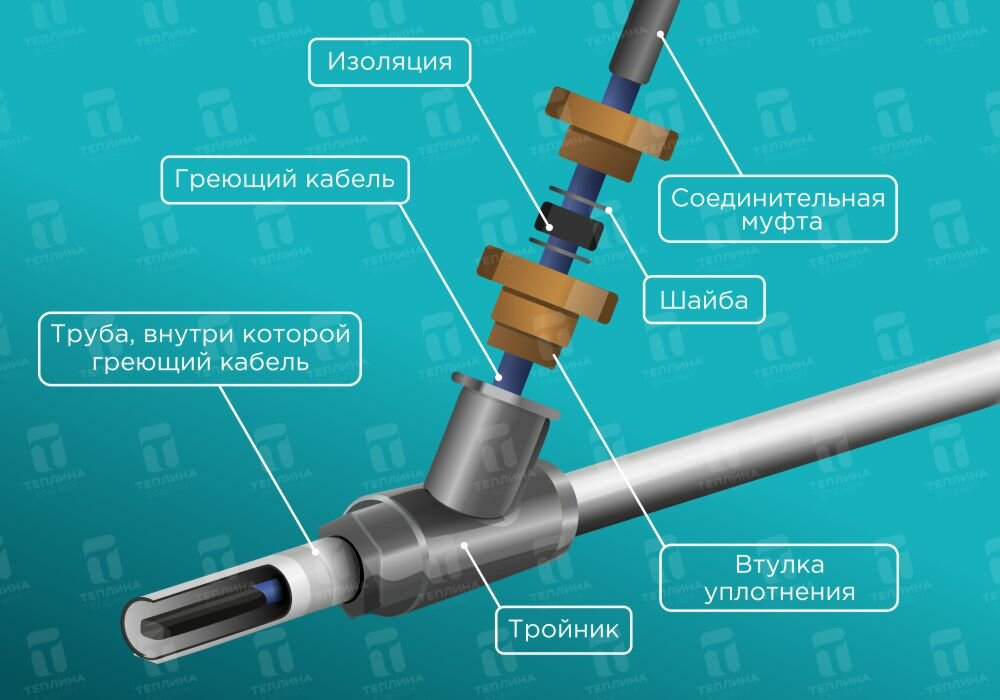
Installation option
Such features allow you to achieve the highest temperatures in more vulnerable areas. Does this cable system have for heating water pipes its advantages:
- Energy savings increase, as the system reduces power when the ambient temperature rises.
- You can buy the required length, cut places are provided in increments of 20 or 50 cm.
There is also a negative side - the high cost of the cable itself.Even for simple varieties, the price is about 300 rubles per meter, and the most “advanced” models are estimated at over 1000 rubles.
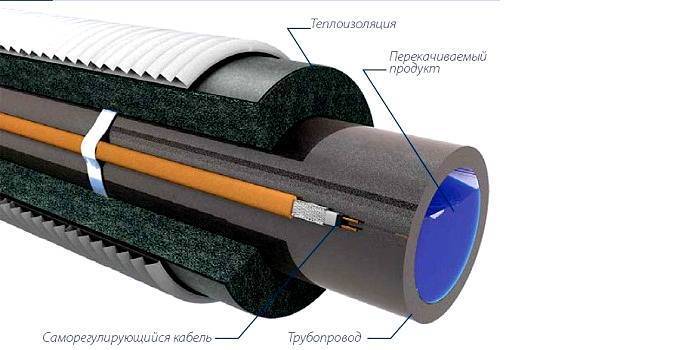
Sectional variant with self-regulating heating wire
Any system can be installed inside or outside the pipe. Each technology has its own characteristics that should be considered during installation. So, for an external structure, it is better to choose models with a flattened section, since a large surface of the cable will be in contact with the pipe, which will increase heat transfer. The power limit is wide, you can pick up from 10 to 60 watts per linear meter.
How to choose the right cable?
When choosing a suitable hot cable, it is necessary to determine not only its type, but also the right power.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account such parameters as:
- the purpose of the structure (for sewerage and water supply, calculations are performed differently);
- the material from which the sewerage is made;
- pipeline diameter;
- features of the area to be heated;
- characteristics of the heat-insulating material used.
Based on this information, heat losses are calculated for each meter of the structure, the type of cable, its power are selected, and then the appropriate length of the kit is determined. Calculations can be performed using a special formula, according to calculation tables or using an online calculator.
The calculation formula looks like this:
Qtr - heat loss of the pipe (W); - coefficient of thermal conductivity of the heater; Ltr is the length of the heated pipe (m); tin is the temperature of the contents of the pipe (C), tout is the minimum ambient temperature (C); D is the outer diameter of communications, taking into account the insulation (m); d - outer diameter of communications (m); 1.3 - safety factor
When heat losses are calculated, the length of the system should be calculated. To do this, the resulting value must be divided by the specific power of the cable of the heating device. The result should be increased, taking into account the heating of additional elements. The power of the cable for sewerage starts from 17 W / m and can exceed 30 W / m.
If we are talking about sewer pipelines made of polyethylene and PVC, then 17 W / m is the maximum power. If you use a more productive cable, then there is a high probability of overheating and damage to the pipe. Information about the characteristics of the product can be found in its technical data sheet.
Using the table, choosing the right option is a little easier. To do this, you first need to find out the diameter of the pipe and the thickness of the thermal insulation, as well as the expected difference between the temperature of the air and the contents of the pipeline. The latter indicator can be found using reference data depending on the region.
At the intersection of the corresponding row and column, you can find the value of heat loss per meter of pipe. Then the total length of the cable should be calculated. To do this, the size of the specific heat loss obtained from the table must be multiplied by the length of the pipeline and by a factor of 1.3.
The table allows you to find the size of the specific heat loss of a pipe of a specific diameter, taking into account the thickness of the heat-insulating material and the operating conditions of the pipeline (+)
The result obtained should be divided by the specific power of the cable. Then you need to take into account the influence of additional elements, if any. On specialized sites you can find convenient online calculators. In the appropriate fields, you need to enter the necessary data, for example, the diameter of the pipes, the thickness of the insulation, ambient and working temperature fluids, region, etc.
Such programs usually offer the user additional options, for example, they help to calculate the required diameter of the sewer, the dimensions of the thermal insulation layer, the type of insulation, etc.
Optionally, you can choose the type of laying, find out the appropriate step when installing the heating cable in a spiral, get a list and the number of components that will be needed for laying the system.
When choosing a self-regulating cable, it is important to correctly consider the diameter of the structure on which it will be installed. For example, for pipes with a diameter 110 mm, it is recommended to take the Lavita GWS30-2 brand or a similar version from another manufacturer
For a 50 mm pipe, the Lavita GWS24-2 cable is suitable, for structures with a diameter of 32 mm - Lavita GWS16-2, etc.
Complex calculations will not be needed for sewers that are not used often, for example, in a summer cottage or in a house that is used only occasionally. In such a situation, they simply take a cable with a power of 17 W / m with a length corresponding to the dimensions of the pipe. A cable of this power can be used both outside and inside the pipe, while installing a gland is not necessary.
When choosing a suitable option for a heating cable, its performance should be correlated with the calculated data on the likely heat loss of the sewer pipe
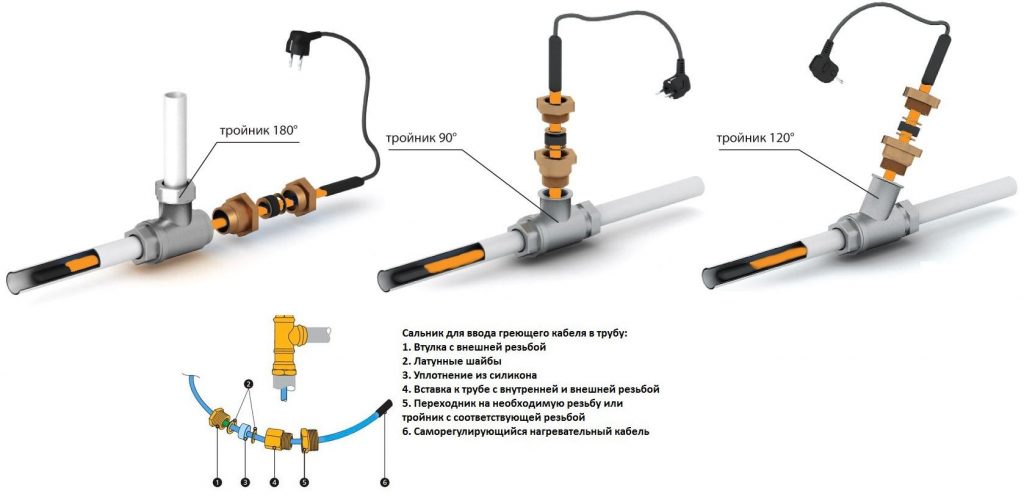
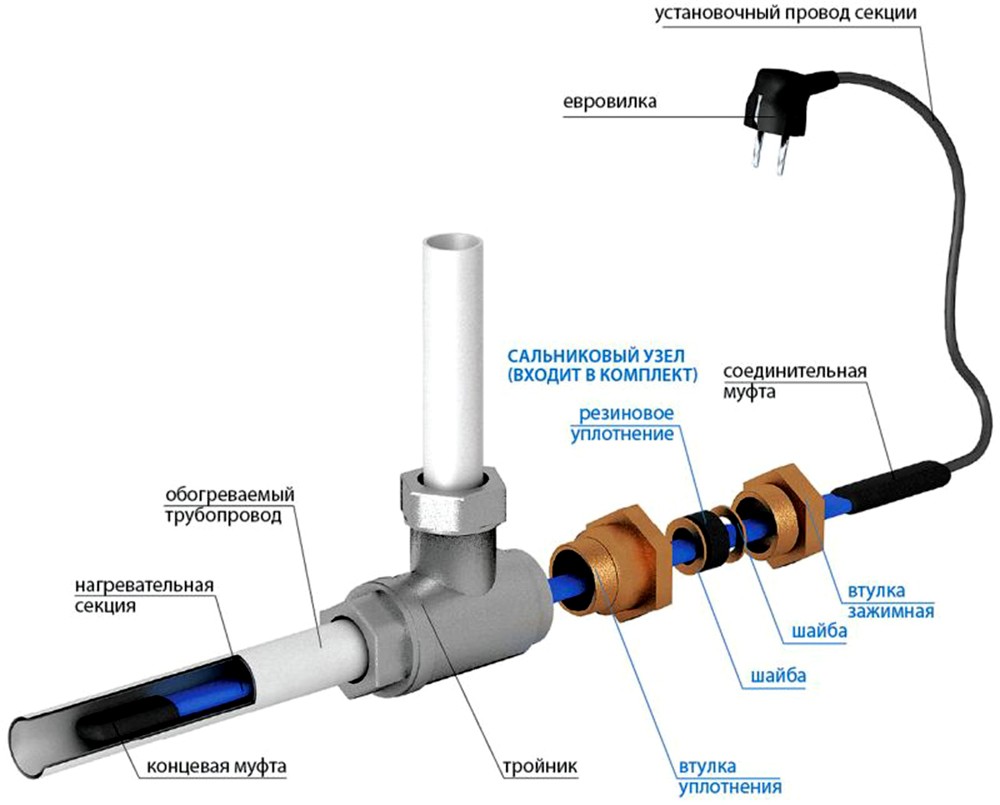
For laying a heating cable inside a pipe, a cable with special protection against aggressive effects, for example, DVU-13, is selected. In some cases, for installation inside, the brand Lavita RGS 30-2CR is used. This is not entirely correct, but a valid solution.
This cable is designed for heating roofs or storm drains, so it is not protected against corrosive substances. It can only be considered as a temporary option, since with prolonged use in inappropriate conditions, the Lavita RGS 30-2CR cable will inevitably break.
Types of heating cable
All heating systems are divided into 2 large categories: resistive and self-regulating. Each type has its own area of application. Suppose resistive ones are good for heating short sections of pipes of small cross section - up to 40 mm, and for long sections of the water supply system it is better to use a self-regulating (in other words - self-regulating, "samreg") cable.
Type #1 - resistive
The principle of operation of the cable is simple: a current passes through one or two cores located in an insulating winding, heating it. Maximum current and high resistance add up to a high heat dissipation coefficient. On sale there are pieces of resistive cable of a certain length, having a constant resistance. In the process of functioning, they give off the same amount of heat along the entire length.
Single-core cable, as the name suggests, has one core, double insulation and external protection. The only core acts as a heating element
When installing the system, it must be remembered that a single-core cable is connected at both ends, as in the following diagram:
Schematically, the connection of a single-core type resembles a loop: first it is connected to an energy source, then it is pulled (wound) along the entire length of the pipe and comes back
Closed heating circuits are more often used to heat a roof drainage system or for a “warm floor” device, but an option applicable to plumbing also exists.
A feature of the installation of a single-core cable to the water pipe is laying it on both sides. In this case, only the external connection type is used.
For internal installation, one core is not suitable, since laying the “loop” will take up a lot of internal space, moreover, accidental crossing of wires is fraught with overheating.
A two-core cable is distinguished by the separation of the functions of the cores: one is responsible for heating, the second for supplying energy.
The connection scheme is also different. There is no need for a “loop-like” installation: as a result, the cable is connected at one end to the power source, the other is pulled along the pipe
Two-core resistive cables are used for plumbing systems as actively as samregs. They can be mounted inside pipes using tees and seals.
The main advantage of a resistive cable is its low cost. Many note reliability, long service life (up to 10-15 years), ease of installation. But there are also disadvantages:
- high probability of overheating at the intersection or proximity of two cables;
- fixed length - can neither be increased nor shortened;
- the impossibility of replacing the burned-out area - you will have to change it completely;
- the impossibility of adjusting the power - it is always the same along the entire length.
In order not to spend money on a permanent cable connection (which is impractical), a thermostat with sensors is installed. As soon as the temperature drops to + 2-3 ºС, it automatically starts heating, when the temperature rises to + 6-7 ºС, the energy is turned off.
Type #2 - self-adjusting
This type of cable is versatile and can be used for various applications: heating of roofing elements and water supply systems, sewer lines and liquid containers. Its feature is self-adjustment power and intensity of heat supply. As soon as the temperature drops below the set point (assume + 3 ºС), the cable begins to heat up without outside participation.
Scheme of a self-regulating cable. The main difference from the resistive counterpart is the conductive heating matrix, which is responsible for adjusting the heating temperature. Insulating layers do not differ
The principle of operation of the samreg is based on the property of the conductor to reduce / increase the current strength depending on the resistance. As the resistance increases, the current decreases, which leads to a decrease in power. What happens to the cable when it cools down? The resistance drops - the current strength increases - the heating process begins.
The advantage of self-regulating models is the "zoning" of work. The cable itself distributes its “labor force”: it carefully warms up the cooling sections and maintains the optimum temperature where strong heating is not needed.
The self-regulating cable works all the time, and this is welcome in the cold season. However, during a thaw or in the spring, when frosts stop, it is irrational to keep it on.
To fully automate the process of turning the cable on / off, you can equip the system with a thermostat that is "tied" to the outside temperature.
Advantages of a heating cable
Picture 4. Close up
In practice, buyers already highlight the positive aspects of these products:
- Affordable prices.
- Resistance to influences of any nature - biological, thermal, climatic, chemical. The design will warm under any circumstances.
- No harmful effects on the health of people around.
- Simple operation.
- Long service life of 25 years or more.
- A wide range of applications, which boasts a heating wire.
- Independent control of heat supply. This means that the user himself can turn the system on and off when it is convenient for him.
Types of heating cable
Picture 5. Mounting example
In total, there are two main types of these products:
Resistive heating.
The function of heating elements is performed by current conductors when it comes to these products. For pipes, these types of heaters are used less and less.
Self-regulating heating cables.
The most convenient to use.
Self-regulating heating cable
They consist of one or more cores, which are isolated from each other with the help of special shells. The areas of application of the products are different.
The necessary operating power is maintained independently by the product. The same goes for the amount of heat generated. Most often, the parameters are determined by what weather conditions develop where the system is used.
The operation of the cable depends on the resistance. The current supply is reduced if the resistance is greater. As a result, power is also reduced. Areas where it is necessary to raise or lower the degree are automatically determined by the heating cable.
Resistive heating cable
Consists of one or two conductive wires.They are not subject to self-cutting; they differ from existing analogues in a fixed length.
Without the use of thermostats in this case, it becomes impossible to change the power. Such heating cables are often found inside sewer pipes.
If the product includes two parallel cores through which current passes, then this is a zonal subspecies. A wire attached to the cores at a fixed distance acts as a heating element. Such varieties are supplied with special marks, according to which it is easy to cut when installing the heating cable.
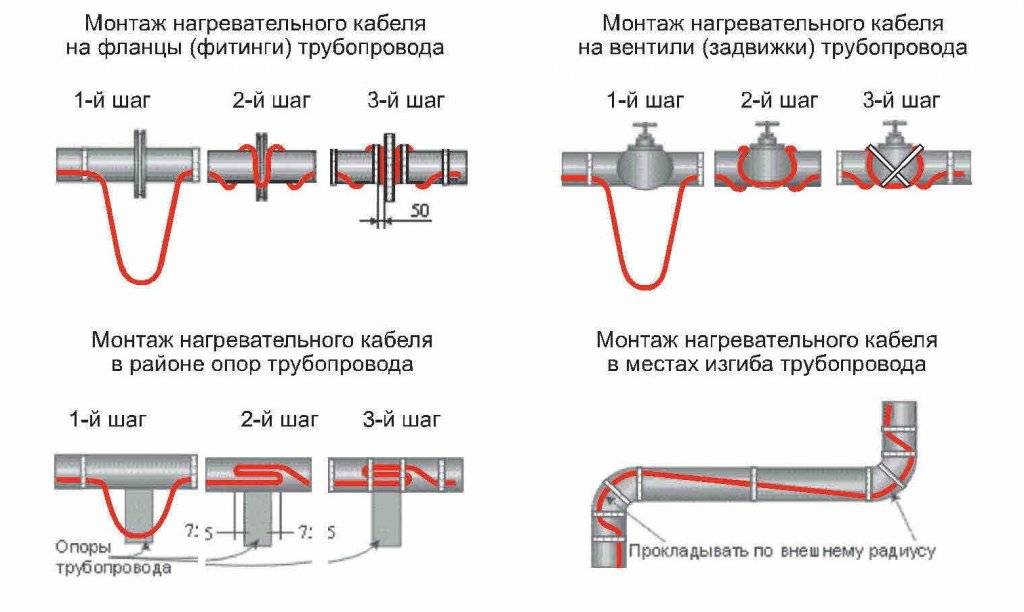
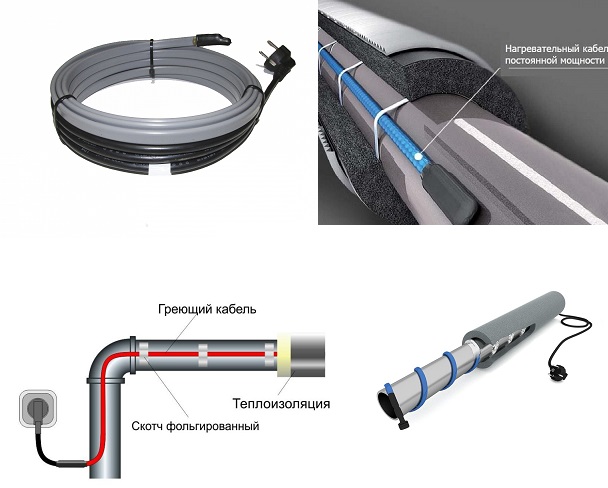
How to lay the heating cable outside the pipe
To mount on the outside you will need:
the cable itself
aluminum tape
It should be tape with a good metallic coating. Cheap lavsan film with a metallized coating will not work.
nylon ties
thermal insulation
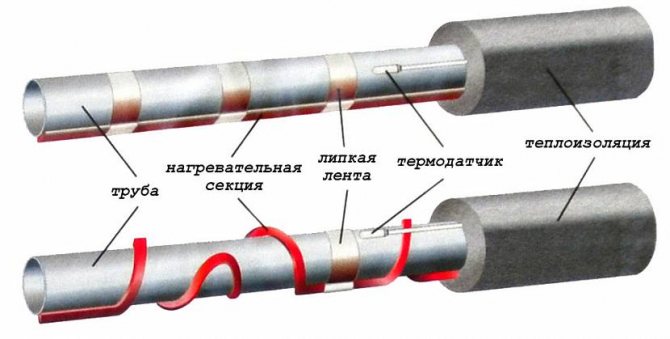
To distribute heat evenly along the entire length, wrap the insulated area with foil tape.
Mistake #6
In this case, there is no need to wrap the entire pipe entirely.
Let's say you have a pipe weaving or more. Glue one strip of tape along it and that's it. It is not necessary to spend the material on the entire surface.
Mistake #7
Steel and copper pipes generally do not need to be wrapped with tape.
This applies equally to metal corrugated. Only the top layer will be enough for them.
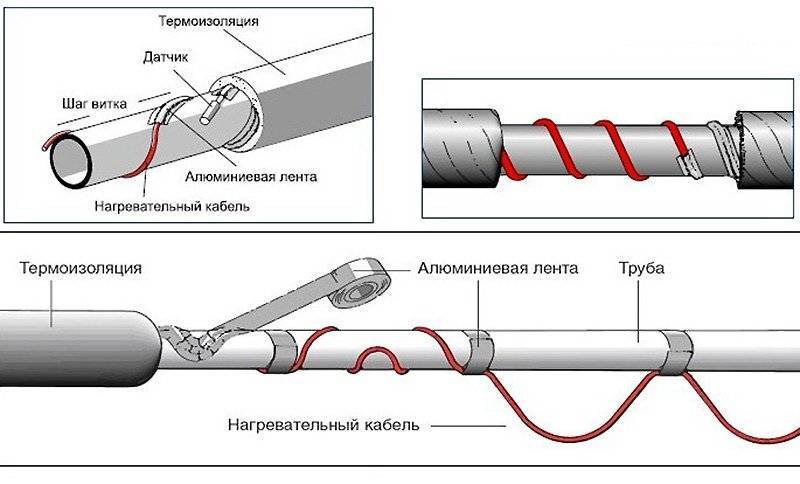
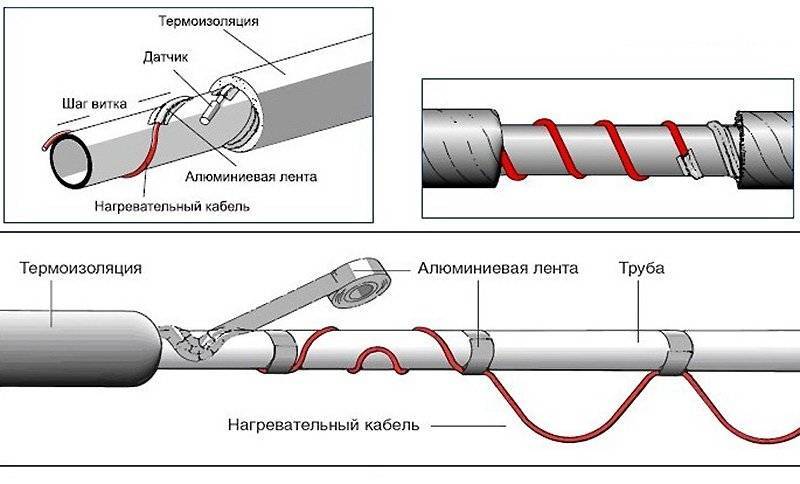
Next, you need to fix the cable.
Mistake #8
Most often this is done with the same aluminum tape.

However, this is fraught with the fact that the wire eventually “bulges out” and begins to move away from the wall, which reduces heat transfer by several times.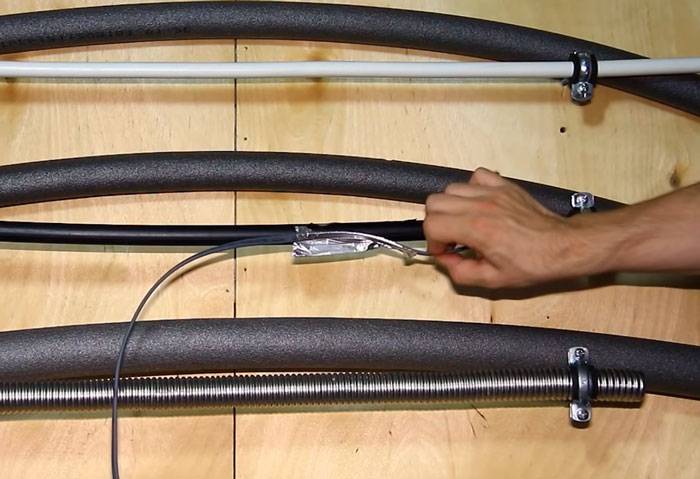
To prevent this from happening, use nylon ties.The distance between the ties is 15-20 cm.
The cable itself can be laid both in a flat strip and in rings around. The first option is considered more rational for sewers and pipes of small diameter.
In this case, the overlapping spiral gasket will cost you a pretty penny. But often only this method allows you to normally warm up a large-section pipe in severe frosts.
Mistake #9
When laying the cable in a straight line, it must be placed not on top or side, but on the bottom of the pipe.
The warmer the water, the lower its density, which means that when heated, it will rise up. If installed incorrectly, the bottom of the pipe may turn out to be cold, and this is fraught with freezing, especially in sewer systems.
They have water flowing underneath them. In addition, such pipes are never full.
Another layer of foil tape is glued over the cable.
After that, thermal insulation in the form of foamed polyethylene is put on all this “pie” (pipe-adhesive-cable-screed-adhesive tape).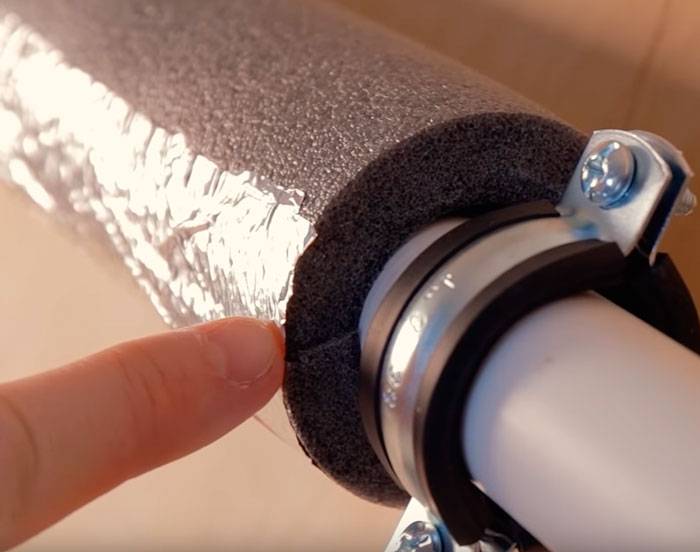
Its use is mandatory. It keeps all the heat inside and reduces energy consumption.
The heat-insulating seam is sealed with reinforcing tape.
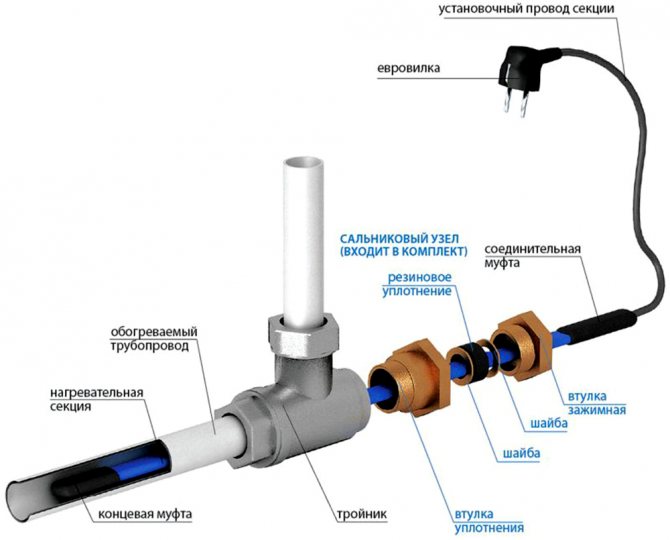
Otherwise, maximum tightness cannot be achieved. If you have a ready-made kit with a plug at the end of the cable, then, in principle, the entire installation is over. Plug the cable into the outlet and forget what freezing pipes are, once and for all.
Finally
The problem of uninterrupted water supply to a private house remains relevant today. When laying pipelines, everyone thinks that he has done everything to the water in the pipes did not freeze, but winter comes and it becomes clear that not everything is thought out to the end. Heating in pipes in the most vulnerable places is a kind of insurance for all occasions.As a rule, each winter is characterized by certain periods when sub-zero temperatures reach peak values. Therefore, heating can be turned on precisely during such peak periods, turning off at the rest, and the temperature can be monitored on the Internet according to the weather forecast. As a rule, most of the forecasts are absolutely real, so you can always rely on them. To be safe, you can turn on the heating only at night, and in the daytime, when the temperature rises, the heating can be turned off. In this case, you will not have to pay a lot for electricity, but water will be supplied to the house on an ongoing basis.

As for colder regions, when cold frosty weather lasts for a long time, this problem becomes more urgent. In such conditions, heating of water pipes is indispensable. Under such conditions, the earth freezes deep enough, so it makes no sense to dig too deep, especially since in any case you will have to bring water into the dwelling, and this is already a big risk. The best option to protect the water supply system from freezing is the organization of pipe heating and reliable thermal insulation. The main thing is to do everything correctly and in a timely manner.
How to choose a heating cable inside a pipe

Watch this video on YouTube




























![[instruction] do-it-yourself toilet installation | video](https://fix.housecope.com/wp-content/uploads/e/0/5/e05c3aaa569c15a65a76abf551b1139c.jpg)
