- Natural ventilation and ventilation with a heat exchanger on the example of the Murator house project
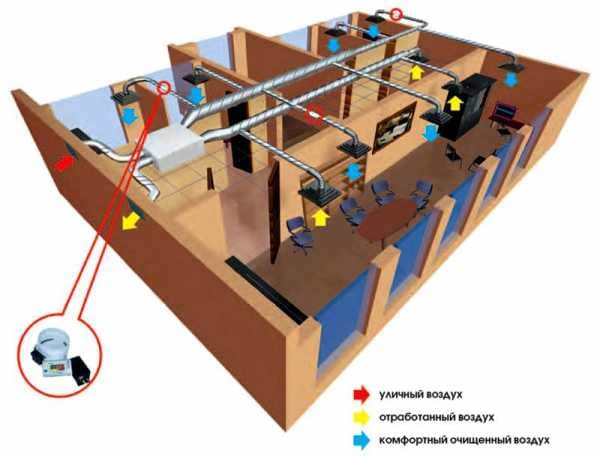
- Air supply systems with recuperation
- What is hidden behind the concept of "recovery"
- What is an air recuperator
- Why choose heat recovery ventilation
- How is a rotary heat exchanger arranged?
- Principle of operation
- Types of coating of a rotary drum
- Types by area of application
- Control scheme
- Specifications
- Prices for recuperators
- What you need to consider in the operation of various models of equipment
- Plate heat exchanger
- Rotor system
- Liquid heat exchanger in an office building
- breather
- Compact recuperator model
- Types of recuperators
- Rotary
- lamellar
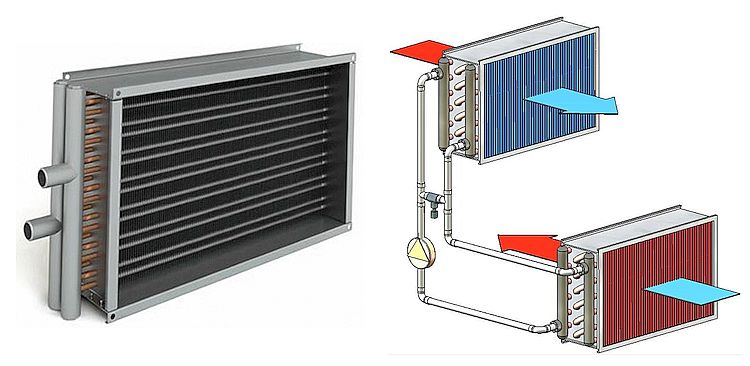
- Recirculating water
- Chamber
- Freon
- Recuperator - heat pipes
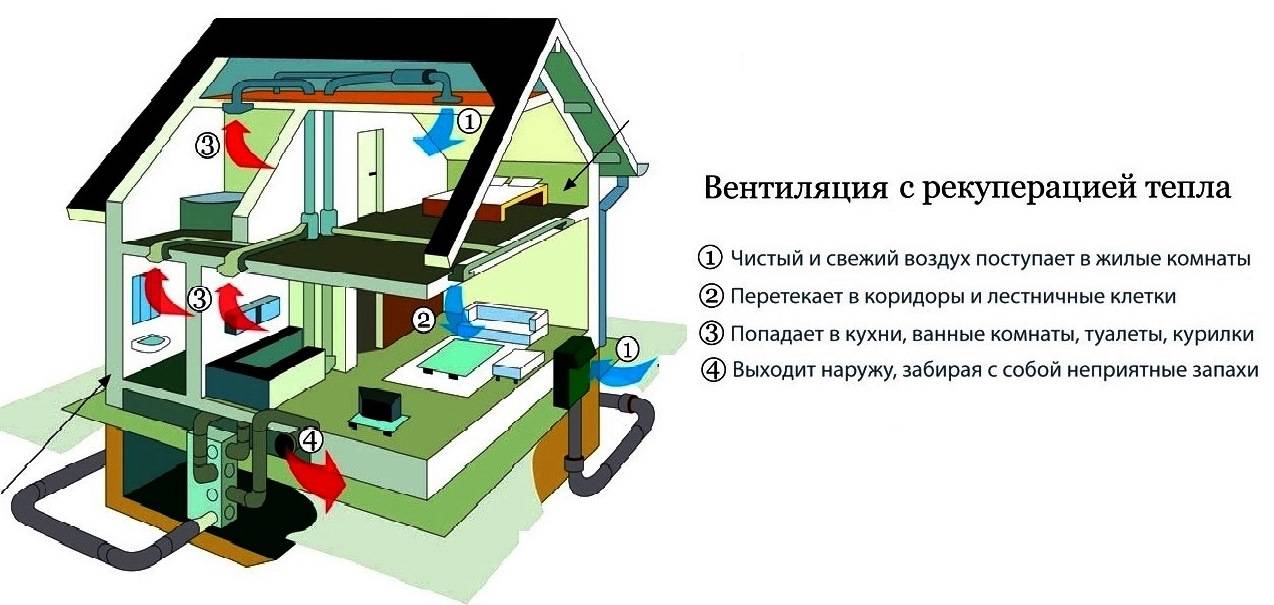
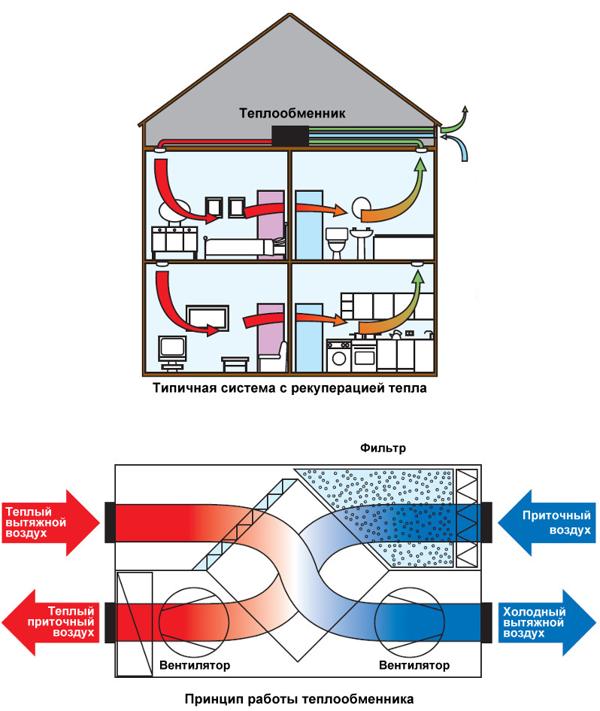
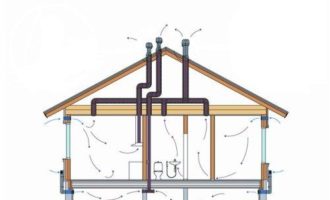
Natural ventilation and ventilation with a heat exchanger on the example of the Murator house project
 The assessment of both types of ventilation is presented on the example of house designs offered in natural ventilation (Murator M93a) and heat recovery (Murator EM93a) versions. House "Autumn Dream" from the Murator collection has 155 sq. m of living space and a typical layout of modern single-family houses.For heating in the house, this is a solid fuel boiler, there is also a fireplace, so regardless of the ventilation system chosen, you need to build two chimneys. It is said that the use of ventilation with heat recovery saves on chimneys - our example shows that this is not always the case.
The assessment of both types of ventilation is presented on the example of house designs offered in natural ventilation (Murator M93a) and heat recovery (Murator EM93a) versions. House "Autumn Dream" from the Murator collection has 155 sq. m of living space and a typical layout of modern single-family houses.For heating in the house, this is a solid fuel boiler, there is also a fireplace, so regardless of the ventilation system chosen, you need to build two chimneys. It is said that the use of ventilation with heat recovery saves on chimneys - our example shows that this is not always the case.
In the variant with mechanical ventilation, the boiler room, tightly separated from the residential part of the house, is naturally ventilated, so that the operation of the boiler does not interfere with the operation of the heat exchanger. Natural ventilation is also in the garage. The air for the fireplace is supplied by a special cable from the outside directly into the combustion chamber. It is equipped with a cartridge with a sealed door. In the naturally ventilated version, air is supplied through fans on the windows in each room and exits the kitchen, pantry, sanitary areas, wardrobe and laundry room through ventilation ducts in two chimneys.
Air supply systems with recuperation
The air handling unit with heat recovery is becoming increasingly popular among private homeowners. And its merits, especially in the cold season, are very high.
As you know, there are many ways to provide a living space with the necessary ventilation. This is the natural circulation of air, which is mainly carried out by ventilating the rooms. But you must admit that it is simply impossible to use this method in winter, since all the heat will quickly leave the living quarters.
If, however, in a house in which air circulation is carried out only naturally, there is no more efficient system, then it turns out that in cold weather the rooms do not receive the necessary volume of fresh air and oxygen, respectively, which further negatively affects the well-being of all family members.
And here the best option would be heat recovery in ventilation systems. Ideally, it is desirable to purchase a unit that could also provide moisture recovery.
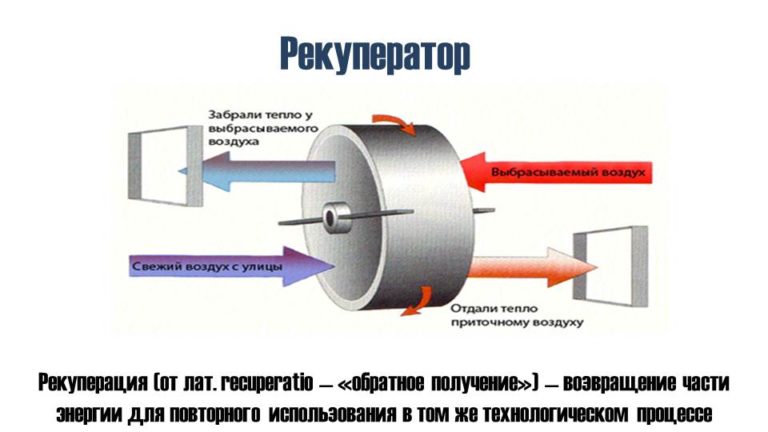
What is hidden behind the concept of "recovery"
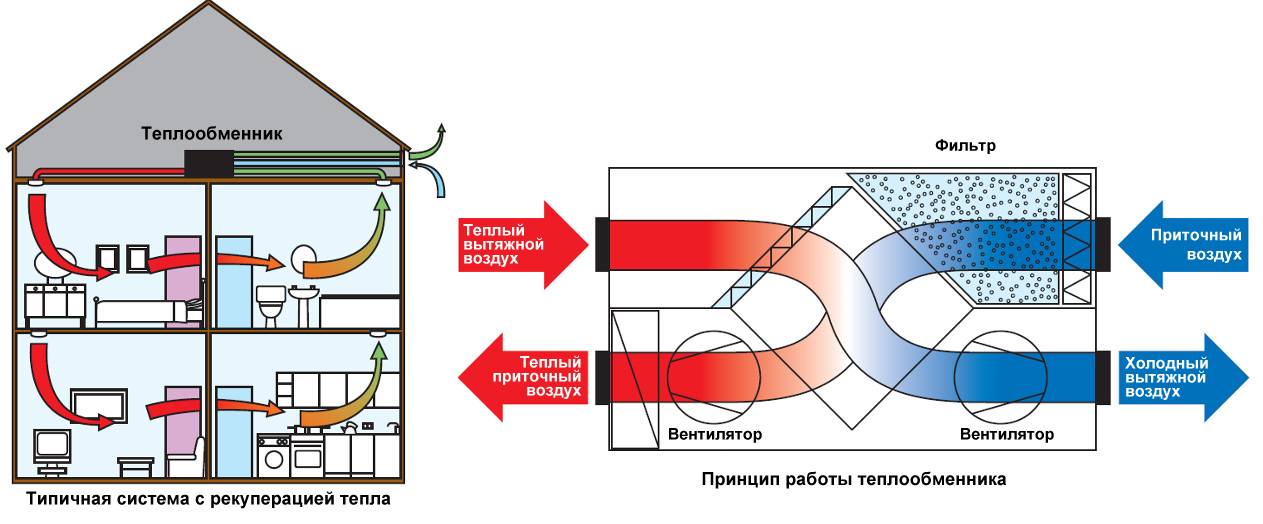
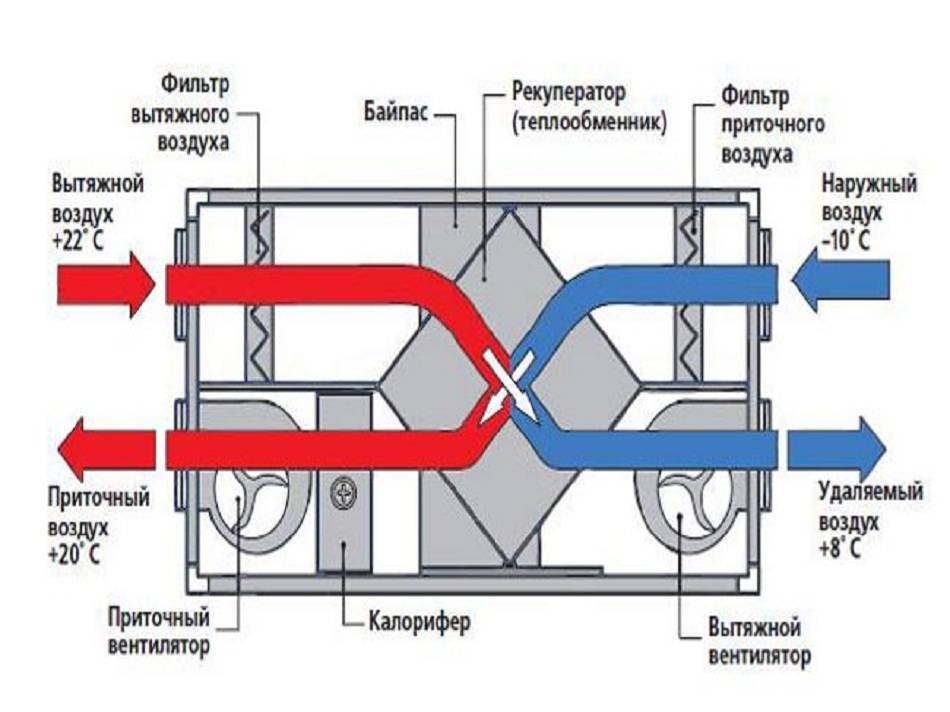
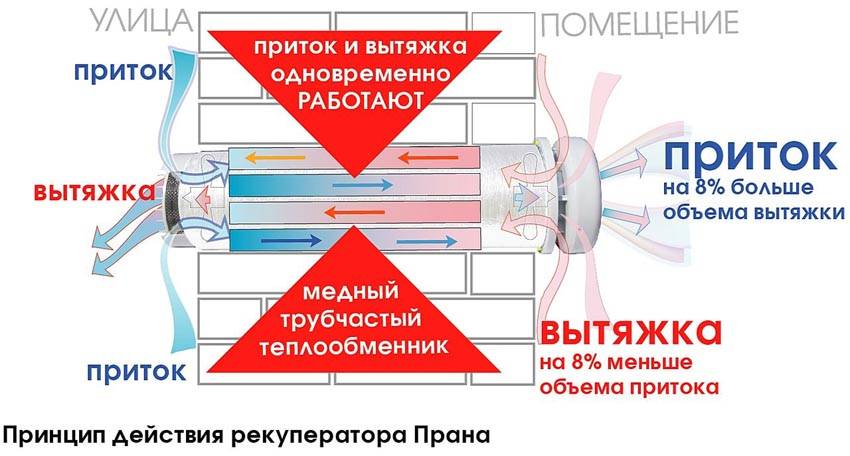
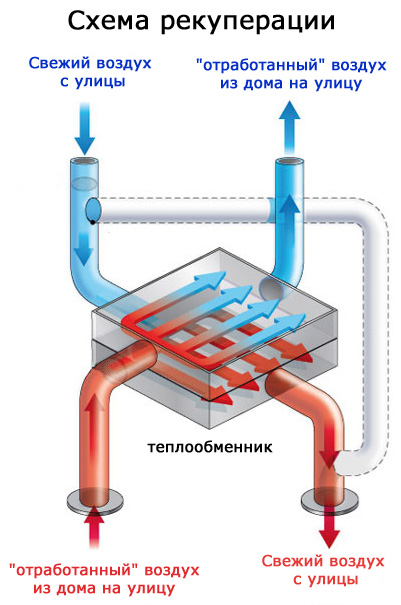
In simple words, recovery is identical to the word "preservation". Heat recovery is the process of storing thermal energy. This is due to the fact that the flow of air that leaves the room cools or heats the air entering inside. Schematically, the recovery process can be represented as follows:
The ventilation with heat recovery takes place according to the principle that the flows must be separated by the design features of the heat exchanger in order to avoid mixing. However, for example, rotary heat exchangers do not make it possible to completely isolate the supply air from the exhaust air.
What is an air recuperator
By its design, an air-to-air heat exchanger is a unit for heat recovery of the output air mass, which allows the most efficient use of heat or cold.
Why choose heat recovery ventilation
Ventilation, which is based on heat recovery, has a very high efficiency. This indicator is calculated by the ratio of the heat that the heat exchanger actually produces to the maximum amount of heat that can only be stored.
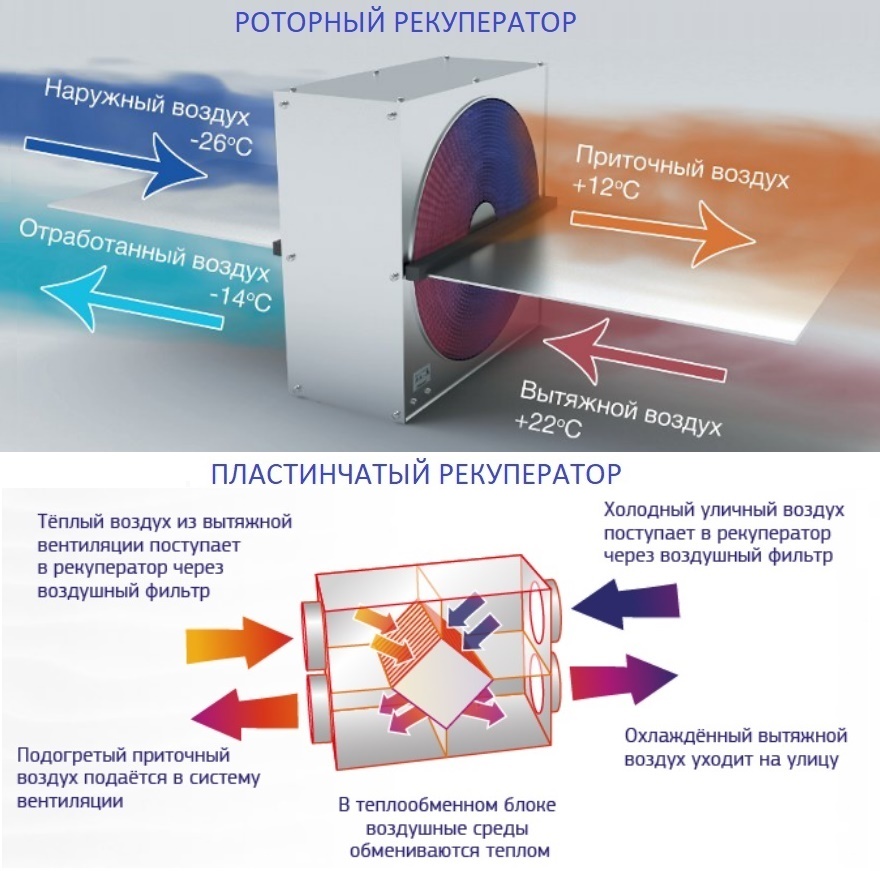
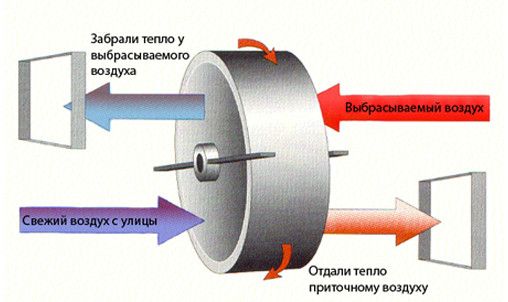
How is a rotary heat exchanger arranged?
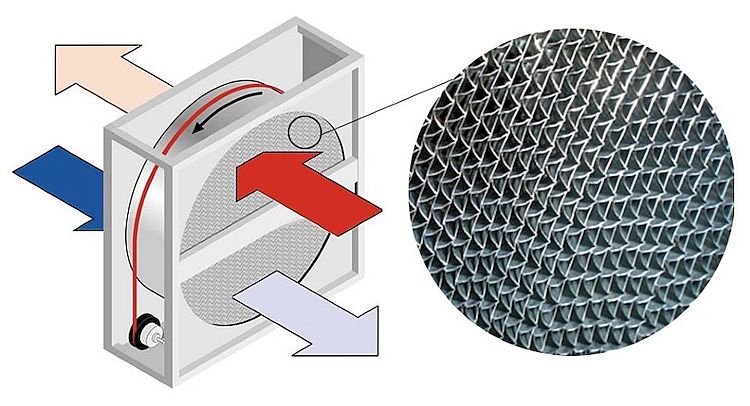
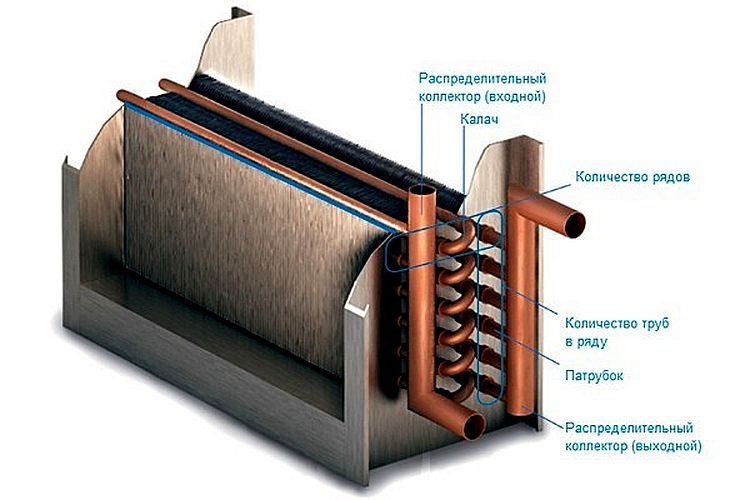
This device is a cylinder in shape and consists of the main element - an aluminum rotor, completed from flat and corrugated plates. The aluminum rotor is covered with a housing made of galvanized steel.
 Rotary air recuperator
Rotary air recuperator
In addition, the device includes a drive mechanism with a belt for rotation, as well as axial bearings, a sensor (sensor) for controlling the rotation of the rotor itself and a sealing tape. The latter is designed to isolate air masses.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of the device is quite simple. The device is put into operation by engaging a V-belt drive. If the product is operated at high temperatures, then the electric motor is mounted outside the body of the heat exchanger. Also in this case, a chain is used instead of a belt.
Inside the rotary heat exchanger, heat is transferred from the heated gas to the cold one. Responsible for this is a rotating rotor-cylinder, which is made of small metal plates. Subsequently, the hot gas heats up these plates, and then the plates go into the cooled gas flow, after which they transfer thermal energy to it.
Types of coating of a rotary drum
There is a classification of recuperators according to the type of coating of the rotor drum. There are currently five types of products:
- condensation type - in this case, an aluminum drum acts as a rotor, which has no coating and can only remove the thermal energy of air masses, but it is not able to move the heat of moisture in air masses;
- hygroscopic view - in this case, the drum is covered with a special hygroscopic coating that has sorbing properties - the drum collects moisture during operation, after which it transfers it from stream to stream, during which both moisture and latent heat of air masses are removed;
- sorption type - in this case we are talking about a modification of the hygroscopic type using a silica gel coating - this sorbent has a huge surface area, approximately 800 m2 / g, which makes it an extremely powerful agent for absorbing moisture;
- epoxy type - such a coating is used in cases where it is necessary to additionally protect the aluminum drum from possible destructive effects of chemical compounds in the treated air (for example, if the air in the room contains chlorine or various vapors, such as ammonia);
- antibacterial look - in this case, the drum is protected by an antibacterial coating that can resist about six hundred types of pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms (usually such a coating is required for enthalpy rotors).
Types by area of application
Now there are three main types of air mass recuperators, differing in the scope of operation and additional "stuffing".
Product types:
- Standard view. In this case, there is a division of the regenerator into several sector parts (from 4 to 12). This type of device is used to remove excess heat from the exhaust air. Also, such a device transfers moisture when working out air flows below the dew point temperature.
- High temperature look. This type of device is used to remove heated air flows, the initial temperature of which reaches approximately +250 degrees.
- Enthalpy view. This device is used to remove the full thermal energy, but in addition to this, the device also transfers moisture.
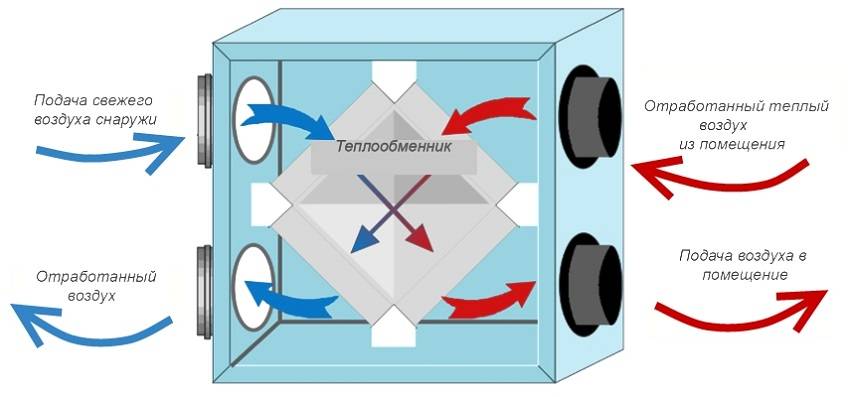
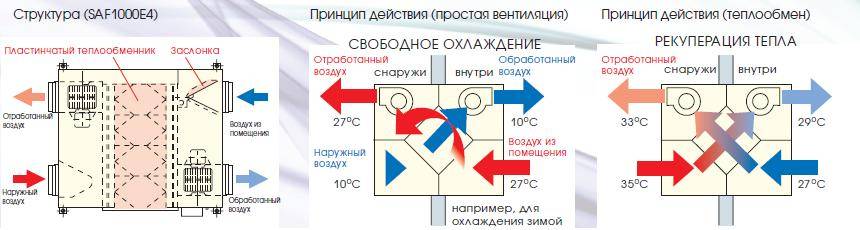
 The principle of operation of the air recuperator
The principle of operation of the air recuperator
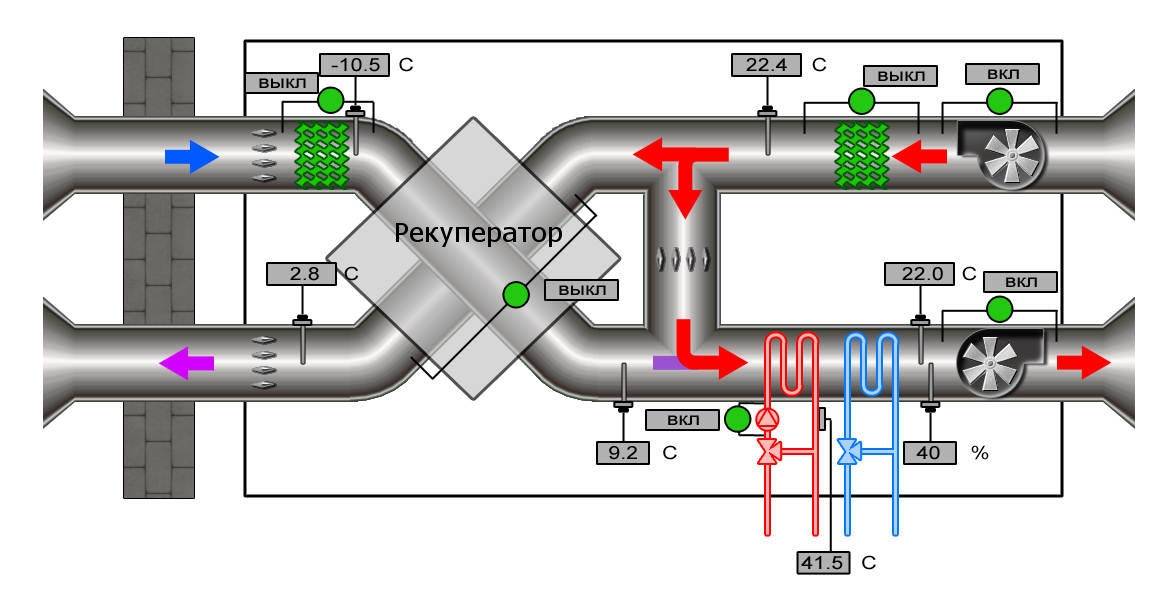
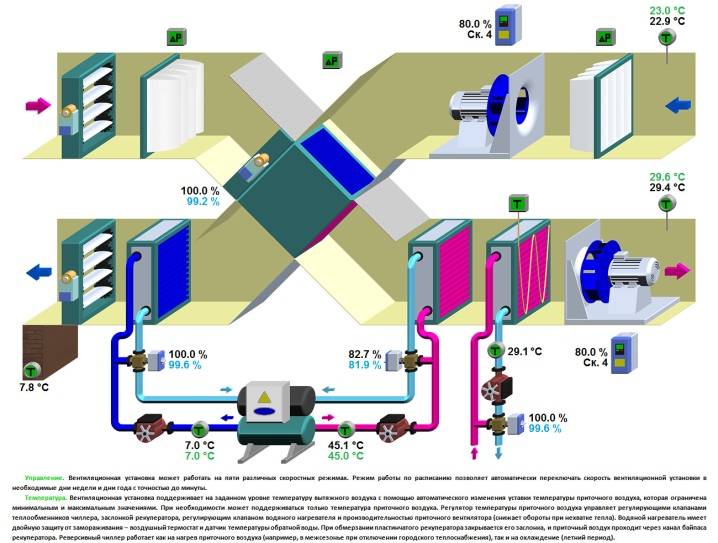
Control scheme
All components of the air handling unit must be properly integrated into the system of operation of the unit, and perform their functions in the proper amount. The task of controlling the operation of all components is solved by an automated process control system. The installation kit includes sensors, analyzing their data, the control system corrects the operation of the necessary elements. The control system allows you to smoothly and competently fulfill the goals and tasks of the air handling unit, solving complex problems of interaction between all elements of the unit.
Ventilation control panelDespite the complexity of the process control system, the development of technology makes it possible to provide an ordinary person with a control panel from the unit in such a way that from the first touch it is clear and pleasant to use the unit throughout its service life.
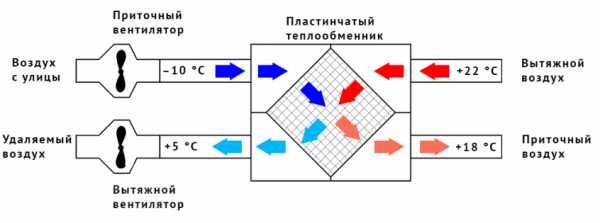
Example. Heat Recovery Efficiency Calculation: Calculates the efficiency of using a heat recovery heat exchanger compared to using only an electric or only water heater.
Consider a ventilation system with a flow rate of 500 m3/h. Calculations will be carried out for the heating season in Moscow. From SNiPa 23-01-99 "Construction climatology and geophysics" it is known that the duration of the period with an average daily air temperature below +8°C is 214 days, the average temperature of the period with an average daily temperature below +8°C is -3.1°C .
Calculate the required average heat output: In order to heat the air from the street to a comfortable temperature of 20°C, you will need:
N=G*Cp *p(in-ha) *(text-tWed )= 500/3600 * 1.005 * 1.247 * = 4.021 kW
This amount of heat per unit of time can be transferred to the supply air in several ways:
- Supply air heating by an electric heater;
- Heating of the supply heat carrier removed through the heat exchanger, with additional heating by an electric heater;
- Heating of outdoor air in a water heat exchanger, etc.
Calculation 1: Heat is transferred to the supply air by means of an electric heater. The cost of electricity in Moscow S=5.2 rubles/(kW*h). Ventilation works around the clock, for 214 days of the heating period, the amount of money, in this case, will be equal to:1\u003d S * 24 * N * n \u003d 5.2 * 24 * 4.021 * 214 \u003d 107,389.6 rubles / (heating period)
Calculation 2: Modern recuperators transfer heat with high efficiency. Let the recuperator heat the air by 60% of the required heat per unit time. Then the electric heater needs to spend the following amount of power: N(el.load) = Q - Qrivers \u003d 4.021 - 0.6 * 4.021 \u003d 1.61 kW
Provided that the ventilation will work for the entire period of the heating period, we get the amount for electricity:2 = S * 24 * N(el.load) * n = 5.2 * 24 * 1.61 * 214 = 42,998.6 rubles / (heating period) Calculation 3: A water heater is used to heat outdoor air. Estimated cost of heat from technical hot water per 1 Gcal in Moscow: Sg.w.\u003d 1500 rubles / gcal. Kcal \u003d 4.184 kJ For heating, we need the following amount of heat: Q(GV) = N * 214 * 24 * 3600 / (4.184 * 106) = 4.021 * 214 * 24 * 3600 / (4.184 * 106) = 17.75 Gcal :C3 = S(GV) *Q(GV) \u003d 1500 * 17.75 \u003d 26,625 rubles / (heating period)
The results of calculating the costs of heating the supply air for the heating period of the year:
| Electric heater | Electric heater + recuperator | Water heater |
|---|---|---|
| RUB 107,389.6 | RUB 42,998.6 | 26 625 rubles |
From the above calculations, it can be seen that the most economical option is to use the hot service water circuit. In addition, the amount of money required to heat the supply air is significantly reduced when using a recuperative heat exchanger in the supply and exhaust ventilation system in comparison with using an electric heater. air, which allows to reduce the energy costs for heating the supply air, therefore, the cash costs for the operation of the ventilation system are reduced. The use of the heat of the removed air is a modern energy-saving technology and allows you to get closer to the "smart home" model, in which any available type of energy is used to the fullest and most useful.
Get a free consultation with a heat recovery ventilation engineer
Get!
Specifications
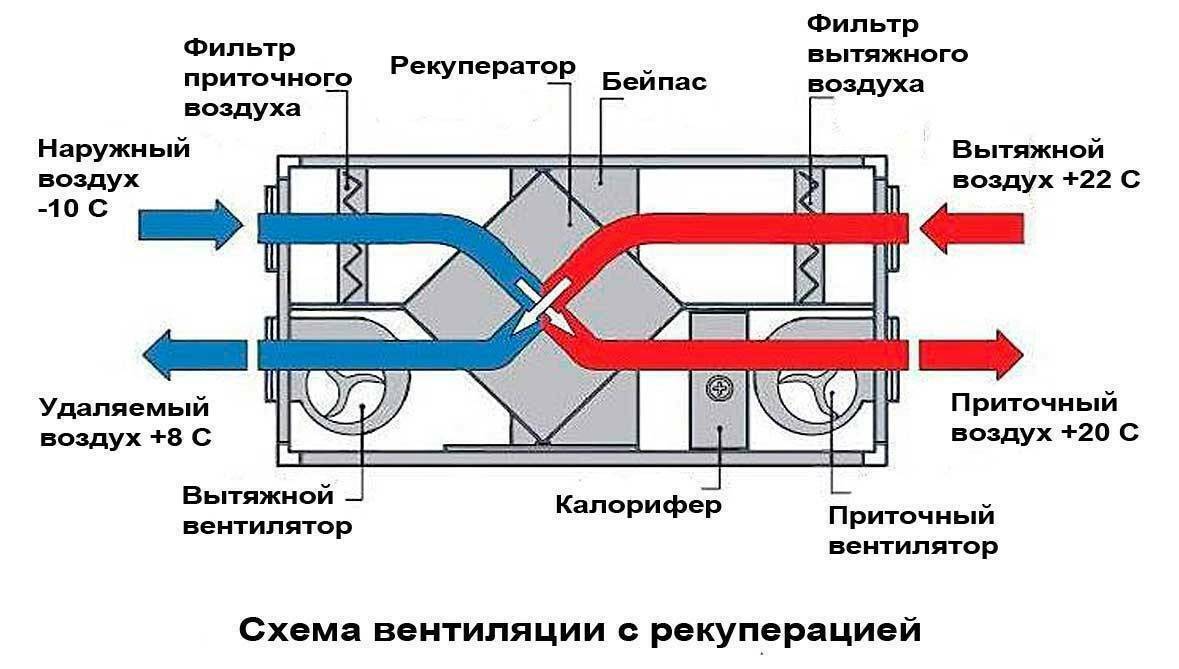
The heat recuperator consists of a housing, which is covered with heat and noise insulating materials and is made of sheet steel.The case of the device is strong enough and able to withstand weight and vibration loads. There are inflow and outflow openings on the case, and air movement through the device is provided by two fans, usually of axial or centrifugal type. The need for their installation is due to a significant slowdown in the natural circulation of air, which is caused by the high aerodynamic resistance of the heat exchanger. In order to prevent the suction of fallen leaves, small birds or mechanical debris, an air intake grille is installed on the inlet located on the street side. The same hole, but from the side of the room, is also equipped with a grill or diffuser that evenly distributes air flows. When installing branched systems, air ducts are mounted to the holes.
In addition, the inlets of both streams are equipped with fine filters that protect the system from dust and grease drops. This prevents the heat exchanger channels from clogging and significantly extends the life of the equipment. However, the installation of filters is complicated by the need for constant monitoring of their condition, cleaning, and, if necessary, replacing them. Otherwise, a clogged filter will act as a natural barrier to air flow, as a result of which the resistance to them will increase and the fan will break.
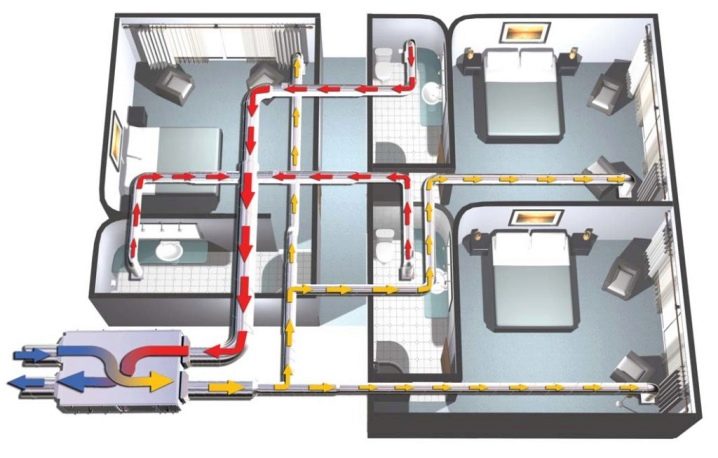
In addition to fans and filters, recuperators include heating elements, which can be water or electric. Each heater is equipped with a temperature switch and is able to automatically turn on if the heat leaving the house cannot cope with the heating of the incoming air.The power of the heaters is selected in strict accordance with the volume of the room and the operating performance of the ventilation system. However, in some devices, the heating elements only protect the heat exchanger from freezing and do not affect the temperature of the incoming air.


Water heater elements are more economical. This is due to the fact that the coolant, which moves through the copper coil, enters it from the heating system of the house. From the coil, the plates are heated, which, in turn, give off heat to the air flow. The water heater regulation system is represented by a three-way valve that opens and closes the water supply, a throttle valve that reduces or increases its speed, and a mixing unit that regulates the temperature. Water heaters are installed in a system of air ducts with a rectangular or square section.


Electric heaters are often installed on air ducts with a circular cross section, and a spiral acts as a heating element. For the correct and efficient operation of the spiral heater, the air flow velocity must be greater than or equal to 2 m/s, the air temperature must be 0-30 degrees, and the humidity of the passing masses must not exceed 80%. All electric heaters are equipped with an operation timer and a thermal relay that turns off the device in case of overheating.


In addition to the standard set of elements, at the request of the consumer, air ionizers and humidifiers are installed in the recuperators, and the most modern samples are equipped with an electronic control unit and a function for programming the operating mode, depending on external and internal conditions.Dashboards have an aesthetic appearance, allowing the heat exchangers to organically fit into the ventilation system and not disturb the harmony of the room.

Prices for recuperators
In search of a recuperator, we will meet devices costing from three to a dozen thousand rubles.
What do we get by paying more? Probably a product of a reputable brand, but this should not be a guarantee that the device will meet our expectations. Pay attention to the details of its implementation. For example, the tightness of its body, its rigidity and good heat and sound insulation are very important.
In this regard, the cheapest products are definitely inferior to the more expensive ones.
The heat exchanger usually works throughout the year without interruption, so be sure to use good quality fans, preferably from a reputable manufacturer. They should not only be durable, but also quiet and energy-saving. It happens that devices are offered at attractive prices that consume so much electricity that its cost cuts the savings from heat recovery by more than half. Of course, how big this saving is depends primarily on the efficiency of the heat exchanger.
I wonder if its value as stated by the seller is reliable. With regard to products of unknown brands, it often happens that no research has been carried out in this direction. Few recuperators are capable of recovering almost 90% of heat and are among the most expensive devices. Cheap products with a claimed efficiency of 90% actually restore almost half as much.
How the heat exchanger is protected from freezing has a big impact on efficiency.In more expensive devices, modern control systems are used for this purpose, due to which the efficiency of heat recovery is reduced at negative temperatures. Paying for this, of course, does not make sense if we intend to create a ground-based heat exchanger. But then you should be prepared for additional costs from four to almost ten thousand rubles, depending on what materials we will do it from (the most expensive are special pipes with an antibacterial coating) and what difficulties associated with geological conditions or a small space we will face.
What you need to consider in the operation of various models of equipment
Each air recovery system for a private home has its own strengths and areas of application.
The ventilation system in a private house with recuperation involves not only maintaining temperature and humidity indicators, but also eliminating unfavorable odors. There are a variety of models on the market, differing in their functional characteristics and installation methods.
For example, an extractor hood installed in the ventilation allows you to remove soot, odor and grease. At the same time, clean air enters the room, and greasy dust does not settle on the furniture. Such conditions have a beneficial effect on well-being, facilitate cleaning of the premises.
Plate heat exchanger
The design of the heat exchanger is such that due to separation by metal plates, air flows do not mix. This simple engineering solution provides more efficient heat transfer. To create such equipment does not require large investments. Due to the absence of moving parts, such a device will last a relatively long time.Currently, the efficiency of such devices reaches 60-65%.
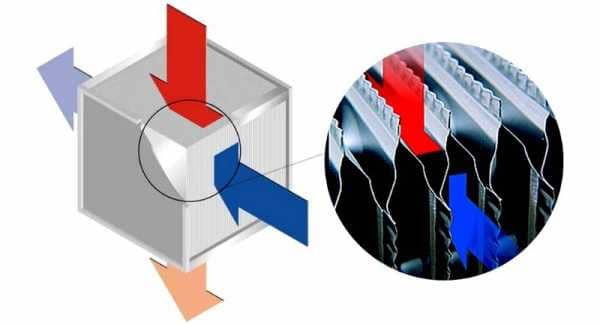
The elements are made of aluminum alloys. They are not subject to corrosive changes and have high heat transfer rates.
Rotor system
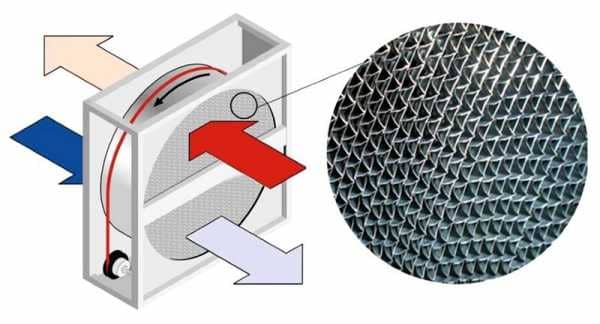
In such equipment, an insignificant part of the air flows is mixed, since the air flow insulator is a brush with fine bristles. The rotor system occupies a larger area than the lamellar system, but also has a high efficiency (up to 86% in the best models). The rotating rotor and the belt that turns it reduce the overall reliability of the device and increase energy consumption for recuperation.
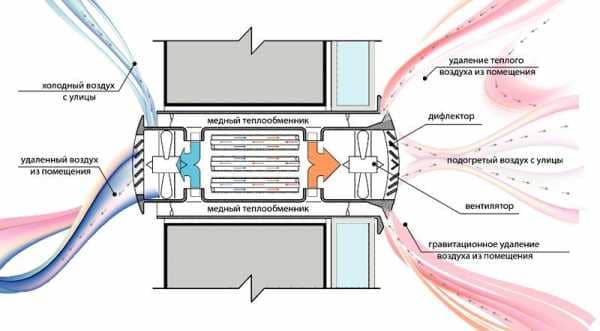
Liquid heat exchanger in an office building
 Scheme of liquid recovery in an office building
Scheme of liquid recovery in an office building
These are expensive models, while their efficiency is not higher than that of similar equipment. The main positive difference is the possibility of placing individual blocks at a great distance from each other. Therefore, liquid heat exchangers are mainly used in large commercial buildings. In private residential areas, a plate or rotary air recuperator for the home is usually used.
breather

The air recovery system for a private house and the breather differ in their purposes. The direct purpose of the breather is to heat the air. There is no heat exchange process in it, so a lot of electricity will be required to raise the air temperature.
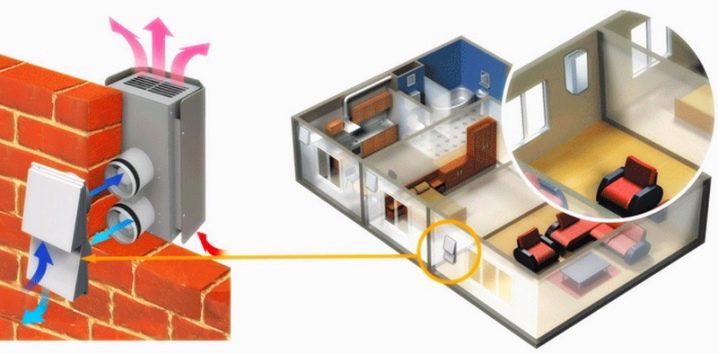
Compact recuperator model
This model is local ventilation with a heat exchanger in a private house. Its use is worth thinking about. Compact models can be installed in the walls of different rooms. They function separately, so they do not require connection to a centralized installation that configures and controls the operation of all devices.
In such models, due to the built-in fans, the synchronous movement of two air streams occurs. The productivity of work is changed by means of the remote control. During the night hours, the device can be set to silent mode.
To prevent freezing, special channels are provided, next to which part of the warm air passes. But the effectiveness of this protection is maintained only up to -15ºС. Activation of the extraction mode helps to eliminate frost and ice from the surface of the heat exchanger. Also, this mode will cope with the purification of the air in the room from suffocating smoke and other contaminants.
The built-in filter protects against the ingress of debris from the street. The size of the filter cells is selected in such a way that it does not create any particular obstacles for air flows, but protects against the penetration of insects and plant fluff. For maintenance, a removable cover is attached to the inside of the heat exchanger.
Types of recuperators
When making a device with your own hands, you should decide on its type. There are several types of recuperators:
- rotary;
- lamellar;
- recirculating water;
- chamber;
- freon.
Rotary
The rotary heat exchanger consists of corrugated steel plates. Externally, the design is a cylindrical container. The rotating drum passes alternately warm and cold streams. During operation, the rotor heats up, which gives off heat to cold air. The rotary apparatus is highly economical.You can set the required number of revolutions of the rotor and adjust the power. The advantage is the possibility of using this type throughout the year, since it does not form an ice crust.
The disadvantages include the overall design. It requires a large ventilation chamber.
lamellar
The plate heat exchanger consists of aluminum, plastic and special paper plates. In some models, the air currents move perpendicular to each other, in others they move in opposite directions.
If aluminum plates are used in the design, then the system is characterized by a low efficiency. This is due to the fact that the device often freezes and needs regular defrosting. Its advantage is its low cost. In addition to aluminum plates, it is allowed to use galvanized steel. Plastic heat exchangers have a greater return, but they are also more expensive.
If the material is special paper, then the return of such equipment is high. However, there is a significant drawback: the device cannot be used in a humid room. The resulting condensate impregnates the paper layers.

Recirculating water
A distinctive feature of this type is the dilution of the supply and exhaust heat exchangers. With the help of antifreeze or water, thermal energy is transferred from the exhaust to the supply.
The system has its advantages:
- no possibility of mixing streams;
- divorced heat exchangers facilitate work at the design stage;
- the ability to combine several supply or exhaust flows into a single one.
Disadvantages:
- the need for a water pump;
- recuperators are capable of only heat exchange, and moisture exchange is impossible.
Chamber
Both streams are sent to a single chamber. It is divided by a partition. After heating one part, the partition is turned. The heated part, which heats the room, begins to receive fresh air. The disadvantage is the high probability of mixing air flows, which leads to their pollution.

Freon
It is based on the physical characteristics of freon, which is located in hermetically sealed tubes. At the beginning of the pipe, the air is heated along with freon, which boils and evaporates. The heat moves on. Freon vapors, in contact with cold streams, condense. Then the cycle repeats.
Recuperator - heat pipes
Such a heat exchanger is a closed system of pipelines pumped with refrigerant, which evaporates as a result of heating by the exhaust air, and condenses again upon contact with cold supply air and takes on a liquid state of aggregation. The efficiency indicator is in the range of 50–70%.
The air recuperator used in the ventilation system allows to achieve a significant reduction in the load on the heating system. However, even the use of a heat exchanger usually requires the use of additional sections in the ventilation system. Electric heating elements or liquid heaters are used to heat the supply air, and central air conditioners or chillers are used to cool the supply air to a predetermined temperature.
The use of classic types of recuperators in ventilation systems makes it possible to reuse from 45% of the exhaust air heat.
However, the development of recuperation systems does not stand still, and the methods and efficiency of exhaust air heat recovery to keep it inside the serviced premises are constantly being improved. The result of this development is, for example, a system with thermodynamic heat recovery (an air-to-air heat pump is used in conjunction with a plate or rotary heat exchanger), which uses a direct expansion heat converter circuit, placed in the form of freon heat exchangers in the exhaust and supply duct -exhaust installation after the classic plate (or rotary) heat exchanger. Such a system, after heat exchange directly in the heat exchanger, makes it possible to obtain some more heat from the exhaust air for transfer to the supply air, bringing the overall efficiency to 95-100%. Thus, it is possible to achieve the most comfortable, that is, the set temperature of the supply air, almost without the consumption of energy resources.

Another indisputable advantage of thermodynamic or active recovery is that the need for additional heating and cooling sections is eliminated.
Currently, units have already been developed and are being manufactured, combining supply and exhaust ventilation devices, a heat exchanger air and heat pump type "air-air" for active recovery. These supply and exhaust recuperative units are an excellent universal solution for organizing a ventilation system in modern buildings and structures.
The entire range of air handling units (SHUs) with heat recovery, according to their characteristics, is optimally suited for the implementation of projects of supply and exhaust ventilation systems of any buildings and premises for domestic, office or industrial purposes due to the use of "active" heat recovery technology (built-in cooling section or heating with an air-to-air heat pump). A significant energy saving effect is demonstrated by industrial versions of the considered installations.
At the same time, the greater the production capacity or the higher the requirements for air exchange, the greater the savings. Suffice it to say that according to the norms of air exchange in a number of industrial industries (metallurgy, chemical production, blacksmith shops) and in aspiration systems, five or even ten times an hourly air exchange is required. Industrial ventilation projects using PES data pay off fairly quickly.
Domestic air handling units use EC coolers, which, having increased air pressure and pumped volume, consume up to a quarter less electrical energy compared to identical asynchronous electric motors.
The industrial range of installations for capacity control is completed with frequency converters.
The models can also be optionally equipped with inverters and additional heat exchangers, perfectly adapting the installation to the requirements of a particular project.