- The principle of operation of the fire RCD
- How to connect RCD correctly
- Where is RCD used?
- Where to put?
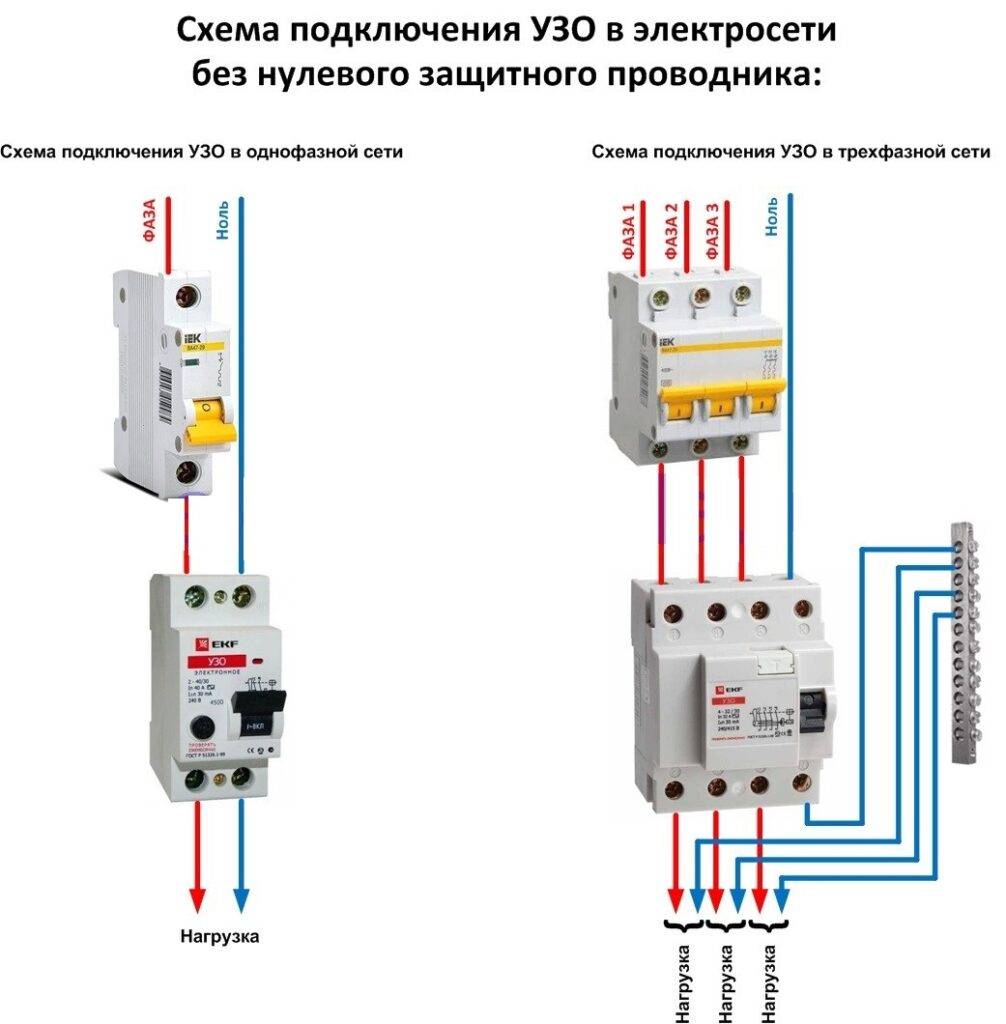
- RCD connection diagrams in a single-phase network
- In custody
- Causes of an electrical fire
- Where is the fire protection RCD installed?
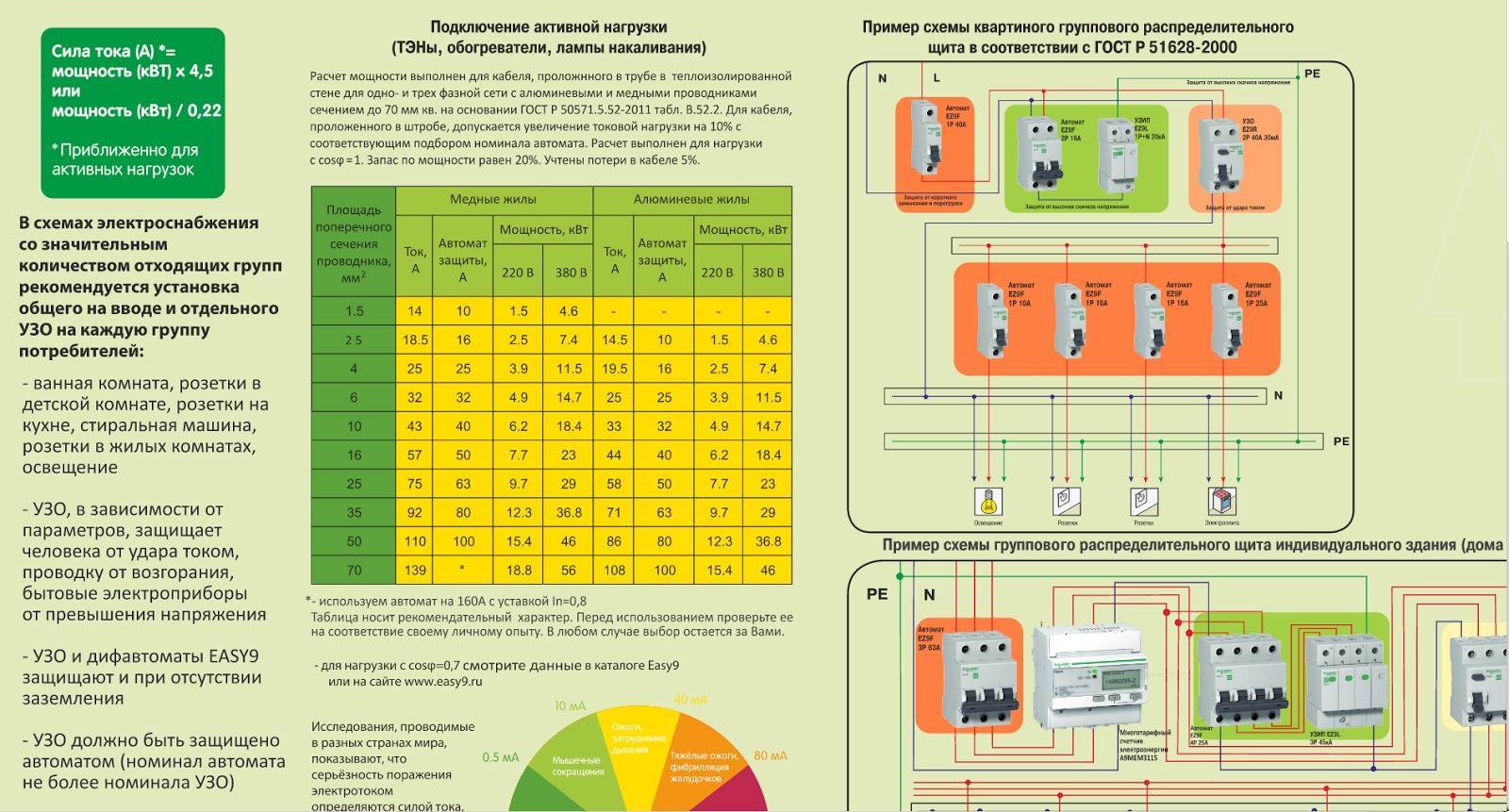
- The choice of automatic devices, UZO and wire sections - quickly and accurately!
- Choice of fire protection device
- RCD leakage current
- Electronic or mechanical device
- Conventional RCD or selective
- In the apartment
- Kinds
- How to properly connect wires to machines
- Ferrules for flexible wire
- arcuate bend
- Non-breaking jumpers
- Rated breaking current RCD
- General functions of the differential switch
- How can an RCD prevent a fire?
The principle of operation of the fire RCD
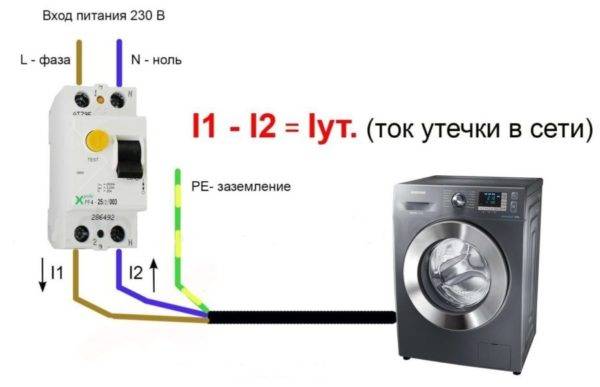
The principle of operation of both fire-fighting and conventional RCDs is the same based on the constant comparison of the current vectors flowing through the phase and neutral conductors.
 The principle of operation of the RCD
The principle of operation of the RCD
Let's consider this mechanism in detail:
- In the normal power supply mode, when the current vectors are equal, the induced magnetic fluxes from each wire, adding up in the magnetic circuit, destroy each other.
- When a leakage occurs, the current in the working neutral conductor decreases by its value.
- The total magnetic flux changes proportionally to the leakage. It induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the magnetic circuit coil.
- Under the influence of EMF, the KL output relay is activated. It completely removes power from the protected line.
The RCD of general application, having a high speed, is designed to protect a person from the effects of electric current. The fire RCD has an increased trip setting of 100 or 300 milliamps and, accordingly, lower speed. This difference is clearly shown in the following graph:
| Time-current characteristics of the RCD | |
| 1 - time-current characteristic of RCD type "S" (IΔn = 300 mA) | 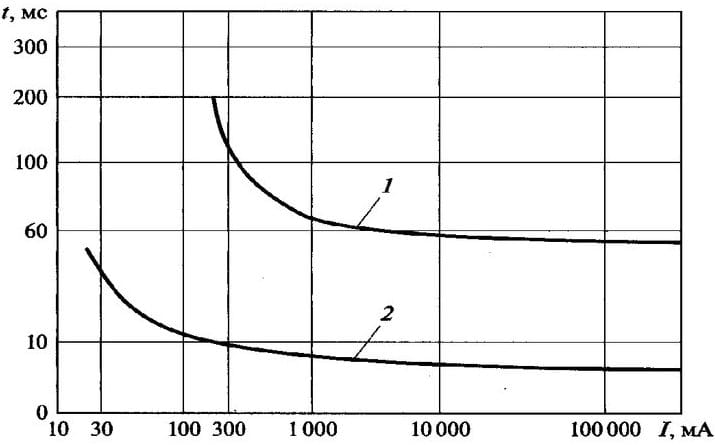 |
| 2 - time-current characteristic of RCDs for general use (IΔn = 30 mA) |
A fire protection RCD with a sensitivity of 100 - 300 mA will prevent a short circuit and prevent fire by de-energizing the entire building until the current leakage is eliminated. And such devices with a rough cutoff, first of all, cover those sections of the network that are not protected by general-purpose RCDs.
How to connect RCD correctly
The RCD connection scheme is selected separately for each electrical network. The connection must be made in such a way that it is located as close as possible to the input of the electrical network. In this case, reliable protection of the network from possible current leakage into the ground is provided. A specific connection scheme is determined on site in order to take into account all the parameters of a given network, the power of connected devices, and others.
Connection methods are divided into two types:
- An economical way is when one protective shutdown is installed on the entire electrical network. With such an installation, if the RCD trips, the entire electrical network will be turned off, the leakage current should not exceed 30 mA. It can be difficult to pinpoint the location of the breakdown.
- Most often, a different method is used.Here, residual current devices are installed on each line individually. During operation, only the damaged line is disconnected. The disadvantage of this method is the high cost, it requires much more free space in the electrical panel or, in general, a separate shield located in the apartment.
Different types of RCDs have their own characteristics when connected. All RCDs are divided by their types into single-phase, two-phase and three-phase, having different connection schemes. Let's look at specific examples of how single-phase and three-phase devices are connected.
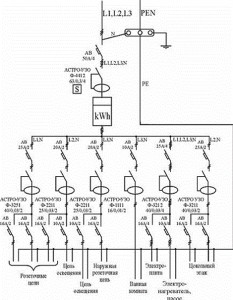
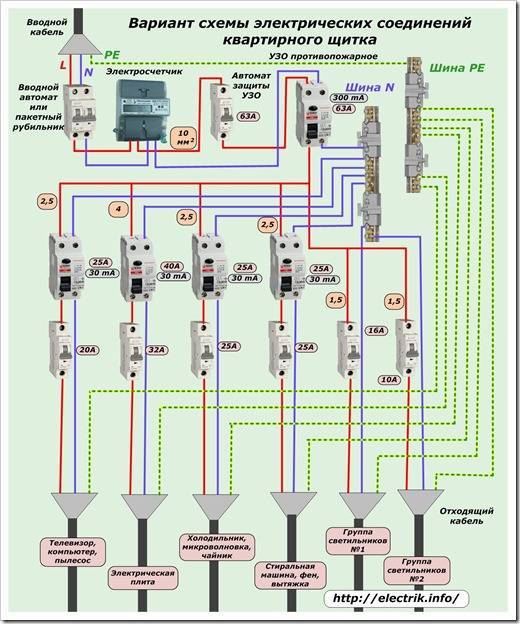
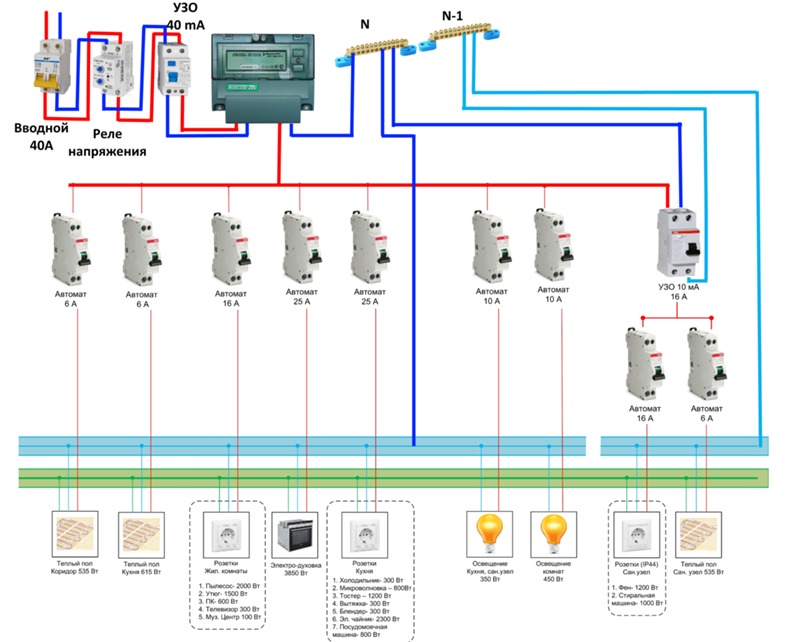
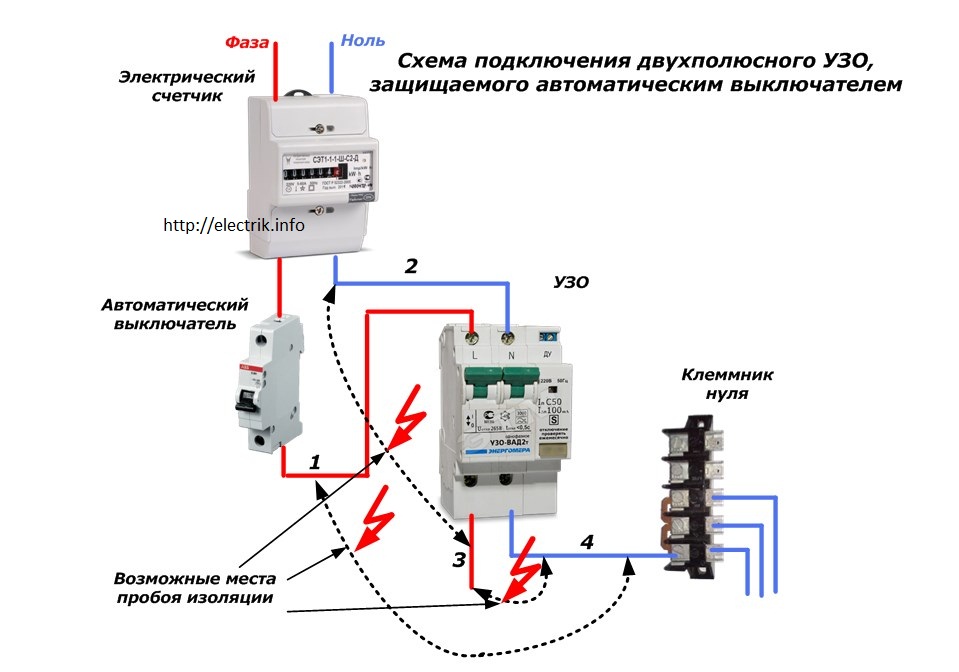
The switching circuit of a single-phase RCD, as a rule, includes separated zero and ground buses. With this option, it is installed behind the introductory circuit breaker. Then, after that, circuit breakers are additionally installed, which are used to protect and switch individual loops.
When using a circuit for three-phase RCDs, simultaneous protection of single-phase and three-phase consumers is ensured. Zero and ground tires are combined in this circuit. With this connection, the electricity meter is installed between the residual current device and the introductory circuit breaker.
It is necessary to check the operability of the RCD monthly. The easiest way is to press the "test" button located on the device. Such a check can be done by an ordinary user, without qualification. A more serious test - a trial current leakage - is quite complicated and is carried out only by a qualified specialist.
Where is RCD used?
In order to answer where it is necessary to use an RCD, we turn to the EIC (7th edition), namely paragraphs 7.1.71-7.1.85. Let's make a "squeeze" of these requirements:
- RCD is necessary to disconnect damaged sections of the circuit and to prevent electric shock to a person or wiring fire;
- RCD is used on group lines that supply socket outlets for portable electrical receivers;
- In residential buildings, RCDs are recommended to be installed on apartment shields; they can be installed on floor shields. For a private house - in a switchboard or ASU;
- It is recommended to use an RCD with an overcurrent shutdown function (differential automatic) for lines supplying socket outlets. If there are many such lines, in order to save money, a group of circuit breakers can be used after the RCD. (clause 7.1.79);
- For lines supplying socket outlets, it is necessary to use an RCD with a differential. operating current not more than 30 mA. (clause 7.1.79). 300 mA RCDs are used for fire protection. Such an RCD is installed after the meter, before distribution to outgoing lines;
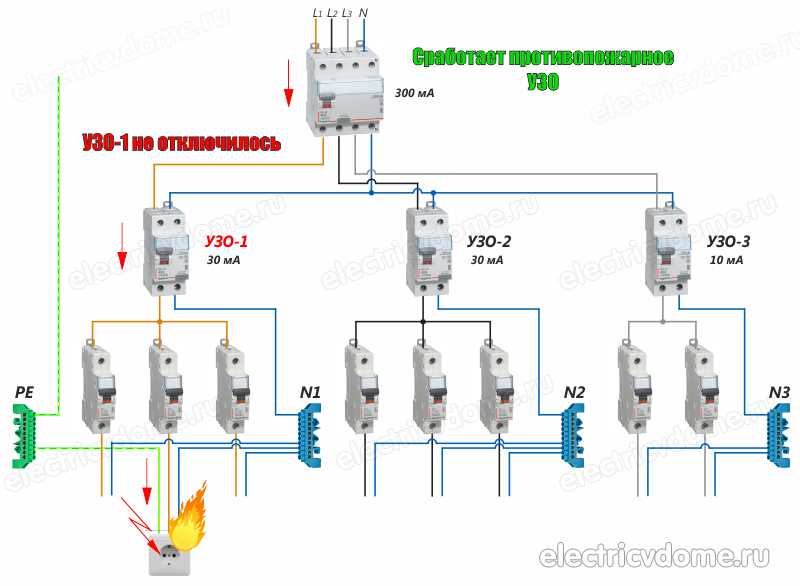
- The setting (maximum allowable value of the parameter) in time for the input RCD should be 3 times greater than the RCD setting on the outgoing lines. This will provide protection selectivity. That is, in case of damage on the outgoing line, the introductory RCD will not have time to work, and only the damaged section will turn off. (clause 7.1.73);
- The RCD should not trip in the event of a power failure.
Where to put?
We put in the distribution boards of apartments and boards of private houses on the lines that feed the sockets. For three-phase receivers (for example, three-phase machines), we use a four-pole (3-phase) RCD, for single-phase receivers - a two-pole (single-phase) RCD. It is impossible to use a 3-phase RCD for 3 outgoing lines. An asymmetric load will cause false tripping of the RCD (for example, after a 3-phase RCD, the phases went to different buildings).
RCD connection diagrams in a single-phase network
The industry produces residual current devices designed to operate in a single-phase or three-phase network. Single-phase devices have 2 poles, three-phase - 4. Unlike circuit breakers, neutral conductors must be connected to disconnecting devices in addition to phase wires. The terminals to which the zero conductors are connected are designated by the Latin letter N.
To protect people from electric shock, RCDs are most often used that respond to leakage currents of 30 mA. In damp rooms, basements, children's rooms, devices set to 10 mA are used. Disconnecting devices designed to prevent fires have a trip threshold of 100 mA or more.
In addition to the trip threshold, the protective device is characterized by a rated switching capacity. This term refers to the maximum current that the breaking device can withstand indefinitely.
Watch this video on YouTube
An important condition for the reliable functioning of protection against leakage currents is the grounding of metal cases of electrical apparatus. TN grounding can be done with a separate wire or through the grounding contact of the mains socket.
In practice, two methods are used to include residual current devices in an electrical circuit:
- RCD connection diagram with individual protection;
- group consumer protection scheme.
The first switching method is most often used to protect powerful consumers of electricity. It can be applied to electric stoves, washing machines, air conditioners, electric heating boilers or water heaters.
Individual protection provides for the simultaneous connection of the RCD and the machine, the circuit is a serial connection of two protective devices. They can be placed in a separate box in the immediate vicinity of the electrical receiver. The choice of the disconnecting device is carried out according to the rated and differential current. It will be better if the rated breaking capacity of the protective device is one step higher than the rating of the circuit breaker.
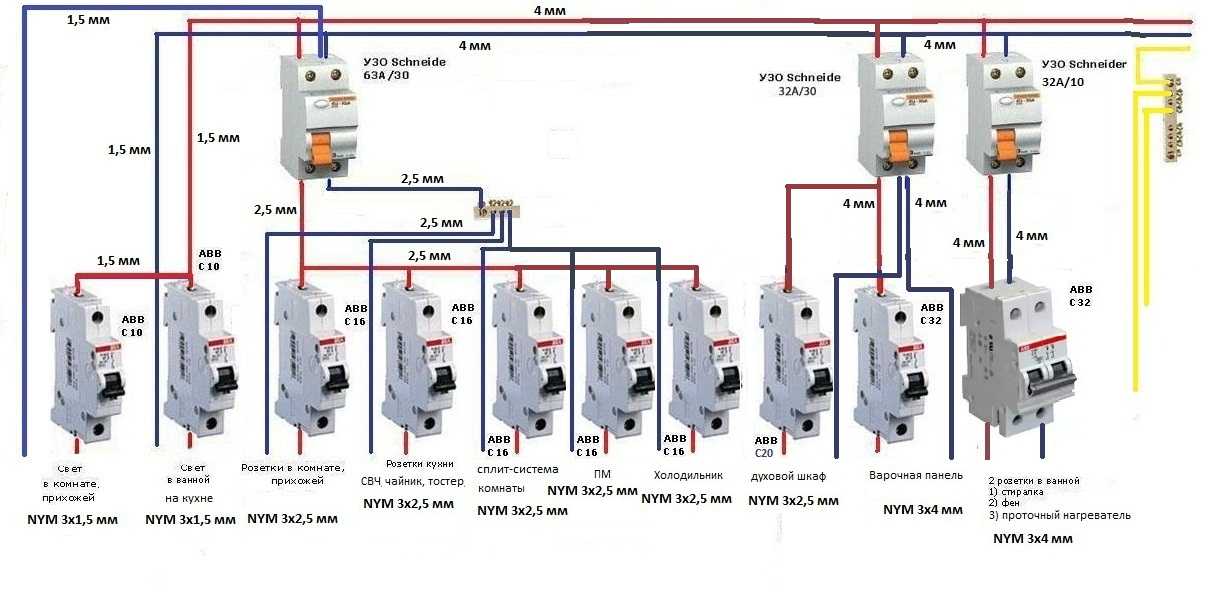
With group protection, a group of automata supplying different loads is connected to the RCD. In this case, the switches are connected to the output of the leakage current protection device. Connecting an RCD in a group circuit reduces costs and saves space in switchboards.
AT single-phase network connection of one RCD for several consumers requires the calculation of the rated current of the protective device. Its load capacity must be equal to or greater than the sum of the ratings of the connected circuit breakers. The choice of the differential protection threshold is determined by its purpose and the hazard category of the premises. The protective device can be connected in the switchboard in the stairwell or in the switchboard inside the apartment.
The scheme for connecting RCDs and machines in an apartment, individual or group, must comply with the requirements of the PUE (Electrical Installation Rules). The rules unequivocally prescribe the grounding of electrical installations protected by RCDs. Failure to comply with this condition is a gross violation and may lead to negative consequences.
In custody
When choosing which RCD to install in a private house, be guided by the characteristics in the complex.
It is important to consider the number of household appliances that will work simultaneously. The higher the value, the more expensive
These expenses are not always necessary.
Before installation, study the color marking of electrical wires. This will help to avoid errors when installing the RCD.

RCD power for an apartment - up to 30 mA
As for manufacturers, quality products can be found from domestic companies. Foreign products are not always designed to work with our networks
That is why before buying it is so important to study all the features of the product, how it works, equipment passport
You can also learn about the choice of RCD from the video:
Watch this video on YouTube
Causes of an electrical fire
Electrical fires can be caused by:
- Heating of conductors (local or extended) due to overload.
- Sparking at the place of poor electrical contact (in connections, at the terminals of electrical appliances and apparatus)
- Leakage from non-insulated sections of the circuit (in junction, branch and feed-through boxes, switchboards, electrical apparatus).
- The burning of an electric arc in any part of the circuit, caused by a short circuit current.
- Cable insulation damage.
Damage to the cable insulation can occur for the following reasons:
- Electrical - from overvoltage and overcurrents.
- Mechanical - impact, pressure, squeezing, bending, damage by a foreign body.
- Environmental influences - humidity, heat, radiation (ultraviolet), aging, chemical attack.
The development of a short circuit from the leakage current, leading to fire, occurs as follows:
- In the place of microdamage of the insulation between the conductors under voltage, an extremely small point current begins to flow.
- Under the influence of humidity, pollution, dust penetration over time, a conductive bridge is formed, through which the leakage current flows.
- As the insulation deteriorates, starting from a current value of approximately 1 mA, the conductive channel is gradually carbonized, a “carbon bridge” appears, and the current continuously increases.
- With leakage current values of 150 mA, which corresponds to a power of 33 W, there is a real risk of fire due to the heating of various flammable materials by the heat generated at the insulation fault.
Where is the fire protection RCD installed?
To increase the level of protection against fire in case of short circuits to grounded parts, when the current is insufficient to operate the overcurrent protection, it is recommended to install an RCD with a trip current of 100 mA at the input to the apartment (house). Devices with a setting of 300 mA are suitable for use in large facilities with many electrical panels and long cable lines.
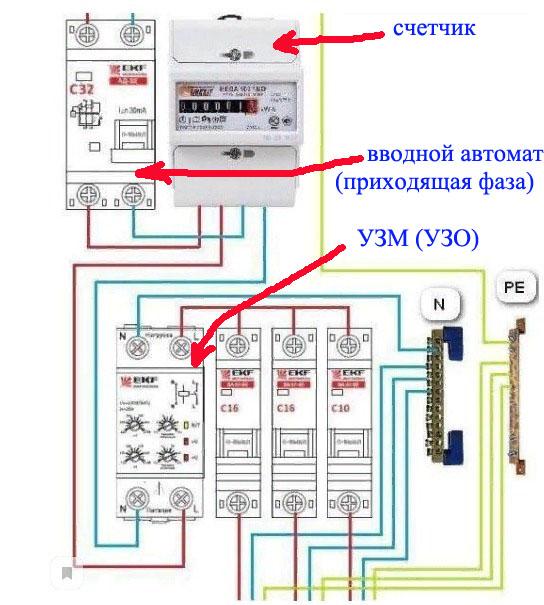
The protective device is used in multi-level (multi-stage, cascade) circuits as the first stage of differential protection. It is placed in metering boards or in floor switchboards after the meter. At the same time, from the introductory machine, the phase and working neutral conductor are connected directly to the metering device (electric meter). Further, after the metering device, a fire-fighting RCD is installed.
The choice of automatic devices, UZO and wire sections - quickly and accurately!
Hello dear readers of my site!
This time I will show you how to quickly and accurately select a circuit breaker, RCD (residual current device) and the required wire cross-section when repairing or installing electrical wiring.
And an excellent program called “Electrician” will help us with this.
I have repeatedly told how to use this program, read:
“Electric Program. Voltage loss. Where does the electricity go in the wires?
“How much money do you need for electrical wiring?”
“Don't know how to choose a machine? Use the Electrician program!”
So, how can "Electrician" help us? We look.
Open the program and click on the “Apartment” button at the bottom.
In the window that opens, you will see a ready-made version of a single-line wiring diagram in the house. Who does not know what it is and what they eat it all with - do not be alarmed, there is nothing complicated!)))
note
Here we indicate that the material of the electrical wiring we have is copper, the type of conductor is a cable and the number of cores is three-core. On the choice of the scheme a little later.
The input to the house is shown in the upper part of the diagram, that is, the direction of power is from top to bottom. The input cable is three-core, two cable cores are connected to the AB circuit breaker (the first one, if counted from top to bottom).
Two strokes on the cable means two cores. These are phase (L) and zero (N), and the earth conductor (PE) is shown to the right.
From the introductory machine, the phase and zero go to the electric meter Wh.
And then the wiring is “divided” into several groups.
The program "Electrician" offers as many options for single-line diagrams - 4 options. They differ in the number and composition of the groups. For example, I showed the difference between Scheme #1 and Scheme #2:
Here they are - all 4 options for schemes:
Further, after selecting the scheme, it is necessary to indicate in the corresponding field the power of the connected electrical appliances and their power factor.
This can be seen either in the passport for the electrical appliance or on its case. The program “Electrician” can also help us with this.
To do this, click "Select power" and in the window that opens, click once on the desired electrical appliance. You can select several devices, the program automatically sums up the power.
Important
After you have selected electrical appliances in this window, do NOT close the window! And click the left mouse once in the cell of power that you were looking for:
In a similar way, fill in all the power cells
With the cosine phi parameters, I suggest not to bother, this is not very important, you can specify the value 0.9 in all cells
If you look carefully, you will see that in the background in the main window of the program the total power of the indicated electrical circuits is also indicated:
After all the fields are filled in, click on the "Calculate" button and the program starts to select the ratings of circuit breakers. RCD and wire section.
After a couple of seconds, you're done!
This is how the Electrician program can help in choosing machines. ouzo and wire cross-sections for electrical wiring.
As you can see, for the power that I indicated on a single-line diagram with such powerful electrical appliances as an electric stove of 6 kW, and even allocated 8.5 kW to the kitchen with plumbing equipment, an input cable of 25 sq. mm for copper and a 100 ampere input machine are required.
Of course, in reality this is not the case, the energy supply organization will never allow the use of such power with a current of 100 amperes for an apartment, and even in one phase ...
But here it should also be taken into account that this is the MAXIMUM possible power if you turn on ALL electrical appliances at once, in reality, of course, no one does this)))
Advice
Therefore, in the example I have given, I would set the input to a 40 ampere machine, a santekh AV circuit machine. I would replace the equipment with 20A, leave the rest as is.
What would you do?
As advertising:
If you are interested in the repair or manufacture of high-pressure hoses, then all this can be ordered at a specialized service center where you can make a competent repair of hoses.
I would be glad for your comments, if there are any technical questions, then please ask them on the forum, it is there that I answer questions - FORUM.
Subscribe to my YouTube video channel!
Choice of fire protection device
There are a huge number of different models of RCDs. Each of them is optimally suited for a specific task. For example, single-phase protective devices are used to protect ordinary apartments, and a three-phase device is already useful for a small workshop.

The difference also exists in the maximum currents that the RCD is capable of passing. For an apartment, a device of 25-32 A is enough. For industrial facilities, as a rule, a device of at least 63 A is required, which corresponds to a consumer with a power of about 15 kW.
Therefore, there are a number of criteria by which a residual current device should be selected. The most significant of them are:
- leakage current. For fire-fighting models, it lies in the range of 100-300 milliamps.
- Electronic or electromechanical RCD. This factor affects the reliability of the device.
- Selective or non-selective device.Depends on the scale and complexity of the scheme.
RCD leakage current
Typical values are 100-300 mA. The choice should be based on two factors:
- Branching of electrical wiring. The larger it is, the higher the leakage.
- State of isolation. The older, damper and dirtier it is, the stronger the leaks.
For an apartment, an RCD of 100 mA is used. This is explained by the small branching and the total length of the wiring. After all, the larger the area of the cables laid in the walls, the easier it is for the current to find a weak spot in the insulation and leak to nearby grounded structures.

Large industrial consumers have more extensive power supply routes. They also have great length. Therefore, it is easier for the current to find weak insulation and leave the current-carrying core.
Additional Information. It is worth emphasizing here that current leakage and a short circuit to ground are two different things. During a short circuit, the insulation resistance drops to almost zero. Therefore, huge and destructive fault currents occur, accompanied by sparks and arcing. Leakage of current through insulation is a common and normal phenomenon. Within reasonable limits, it is present even in new electrical cables.
Another important factor that increases the leakage current is the condition of the insulation. Moisture, dirt particles, metal dust and cracks reduce the resistance of the protective layer. This usually happens with old wiring. As a result, leakage current increases. Therefore, if the wiring is old or is in a humid environment, then it is advisable to choose an RCD designed for large leaks.
Electronic or mechanical device
The fire protection devices on sale are divided into 2 types according to their design:
- Electronic. Contain a small printed circuit board that controls the contacts.
- Electromechanical. They work without complicated electronics.
Electronic devices have a disadvantage. For their operation, voltage is required in the protected line. Therefore, if the neutral conductor breaks in front of the RCD, then it loses its operability and does not work if the insulation is damaged.
Electromechanical devices are more reliable in this regard. They are not so critical to the quality of the supply voltage and are less susceptible to its surges and drawdowns.
Conventional RCD or selective
Conventional protective devices are suitable for small consumers. They are suitable for apartments with a small number of rooms and reliable wiring insulation. The main disadvantage of such devices is the inability to quickly find out exactly where the current leakage occurred. That is, if the insulation is damaged somewhere in the apartment, then the power supply to the entire area will be turned off.
Selective RCDs are used to form selective protection. Usually these are category S devices. Their use allows you to localize the place of insulation damage and disconnect only the problem area from the power supply.
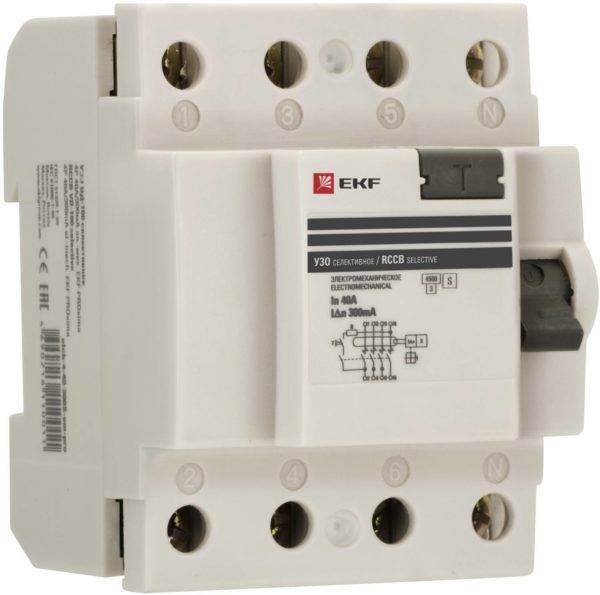 Selective device EKF
Selective device EKF
Selective residual current devices are installed at the input to the electrical panel. They are suitable for large branched consumers or multi-room apartments, in which the search for a current leakage point can take too long.
In the apartment
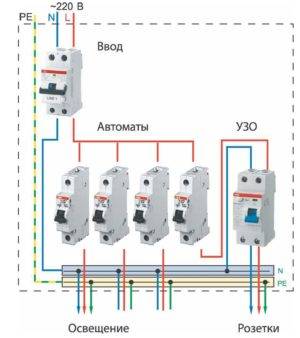 Let us analyze the case when the installation of protection equipment takes place in an apartment panel. Some builders, when renting houses with a free layout, rent housing without wiring an internal electrical network. This is understandable, it is not known where the partitions will stand and, accordingly, sockets and lighting. Therefore, they introduce only cable into the apartment.
Let us analyze the case when the installation of protection equipment takes place in an apartment panel. Some builders, when renting houses with a free layout, rent housing without wiring an internal electrical network. This is understandable, it is not known where the partitions will stand and, accordingly, sockets and lighting. Therefore, they introduce only cable into the apartment.
On the storey electrical panel there is an introductory circuit breaker and an electric meter. The future owner enters into an agreement with another contractor for internal electrical work. The wiring diagram will then change depending on the requirements of the customer. It will depend on the circuit and on the loads which RCD to install. If desired, any man can independently perform these works.
We will assume that the wiring in the apartment corresponds to the protection installation scheme shown in the previous figure. The introductory machine and the counter are located in the floor board, and we will place all other elements in the apartment box. To do this, in the corridor, next to the cable entry point, it is necessary to install an electrical panel. The installation sequence is as follows:
- the input machine is turned off. A sign is posted "Do not turn on, people are working";
- a socket is connected to the cable that was brought into the apartment. It will be needed to connect a working tool and lighting;
- the plate is removed, the machine turns on;
- holes are drilled in the wall with a puncher for the fasteners of the box. Dowels are inserted, and the shield is attached to the wall with screws;
- after that, a metal rail is inserted and fastened to the inner wall of the box with screws.
There should be no difficulties if you follow all the steps consistently and carefully.
Kinds
RCDs are not complex, but at the same time they can be classified according to several criteria. Devices are divided into the following varieties (depending on the type of current leakage):
- Class A. Used for alternating or pulsating electric currents.
- AC class. These devices are designed to operate with alternating current only. They are one of the cheapest and simplest models, used in many apartments.

- Class B.Universal devices for industrial use. They can be used not only for AC, but also for DC or rectified current.
- Sometimes manufacturers add the letter S to the product labeling, which indicates that the device turns off only after a certain period of time. In everyday life, it is not necessary to use such systems together with water heaters, so they are very rare here.
- Class G. These RCDs are similar to S, but their exposure time is much shorter.

Depending on the method of breaking the circuit, RCDs can be divided into the following groups:
- Electronic. They are relatively inexpensive devices that are used in simple systems. Experts do not recommend installing them, as they are powered by the mains. If the user accidentally damages the neutral wire, then the device will simply fail. Another disadvantage can be considered a relatively long period of operation.
- Electromechanical. Switches of this type are not powered by external electrical sources, so they are more reliable and of high quality. The only drawback of such devices can be considered only their inflated price.
How to properly connect wires to machines
There are a large number of devices that will make it easier to connect contacts to automation. In order to choose the appropriate option, we will consider them in detail.
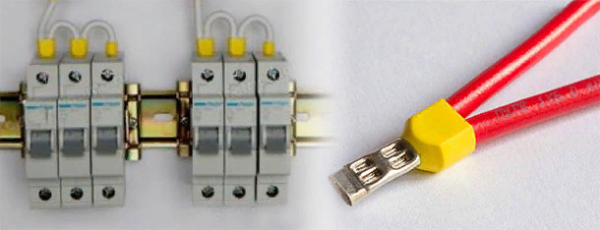
Ferrules for flexible wire
In order to connect the elements of an electrical panel, flexible wires with many wires are often used, because even a beginner can handle connecting such contacts. But at the same time, there is a nuance here.
As we have already discussed above, many masters fix the core with a clamp without termination, due to which the fragile wires begin to break off and the contact weakens.

Sometimes in one clamp it becomes necessary to fix two contacts at once, so double tips were invented for this purpose. They are best suited when you have to install many jumpers.
arcuate bend
Usually, to connect the cores to the clamps, it is required to remove 10 millimeters of the insulating layer - this is enough to form an arc on the messenger, which is then placed in the terminal. As practice shows, most electricians, in the absence of tips, use this method.
As a result, it is possible to obtain a reliable contact that will not weaken over time. This method is suitable if there is a monolithic core at the end.

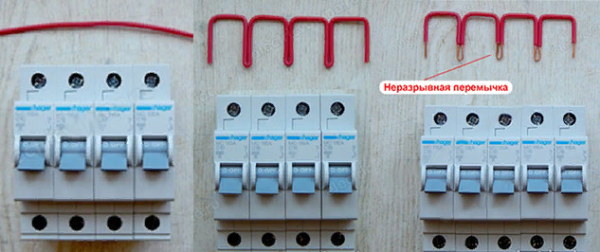
Non-breaking jumpers
When you have to connect several machines with one wire, it becomes necessary to use a comb (tire). However, it is not always at hand, so you can form a home-made comb from a wire of any section.
Bend the wire so that you get a comb. Then, at the bend, it is necessary to strip the wires.
Rated breaking current RCD
The rated RCD breaking current I∆n (setting) is the current at which the RCD trips (tripping). The RCD settings are 10 mA, 30 mA, 100 mA, 300 mA, 500 mA. It should be noted that the non-release current, when a person can no longer unclench his hands and discard the wire, is 30 mA and above. Therefore, to protect a person from electric shock, an RCD with a breaking current of 10 mA or 30 mA is chosen.
RCD rated breaking current I∆n or leakage current is also indicated on the front panel of the RCD.
RCD 10 mA is used to protect electrical receivers in wet rooms or wet consumers, i.e. washing machines and dishwashers, sockets that are inside the bath or toilet, light in the bathroom, underfloor heating in the bathroom or toilet, light or sockets on balconies and loggias.
SP31-110-2003 p.A.4.15 residual current up to 10 mA, if a separate line is allocated to them, in other cases, for example, when using one line for a bathroom, kitchen and corridor, an RCD with a rated differential current of up to 30 mA should be used.
Those. An RCD with a setting of 10 mA is installed on a separate cable, to which only a washing machine is connected. But if other consumers are still powered from the cable line, for example, corridor sockets, kitchens, then in this case an RCD with a trip current (setting) of 30 mA is installed.
RCD with a leakage current of 10 mA at ABB is released only at 16A. Schneider Electric and Hager have 25/10 mA and 16/10 mA RCDs in their product line.
RCD 30 mA is installed on standard lines, i.e. ordinary household sockets, light in rooms, etc.
PUE p.7.1.79. In group networks supplying socket outlets, RCDs with a rated operating current of not more than 30 mA should be used. It is allowed to connect several group lines to one RCD through separate circuit breakers (fuses).
RCDs 100, 300, 500 mA are called fire-fighting, such RCDs will not save you from a fatal electric shock, but they will save an apartment or a private house from a fire due to faults in the wiring.Such an RCD for 100-500 mA is installed in the input shields, i.e. at the beginning of the line.
In the USA, RCDs with a rated breaking current of 6 mA are used, in Europe up to 30 mA.
It should be noted that the RCD is switched off within the setting of 50-100%, i.e. if we have an RCD of 30 mA, then it should turn off within 15-30 mA.
There are designers who promote double diffs. protection of "wet" consumers. This is when, for example, a washing machine is connected to a 16/10 mA RCD, which in turn is connected to a 40/30 mA group RCD.
In the end, what will we get? At the slightest “sneeze” of the washing machine, we turn off the entire group of machines (kitchen light, boiler and room light), because. in most cases it is not known which RCD 25/30 mA or 16/10 mA will trip, or both will trip.
According to the set of rules for the design of electrical installations of residential and public buildings:
SP31-110-2003 p.A.4.2 When installing RCDs in series, selectivity requirements must be met. With two- and multi-stage circuits, the RCD located closer to the power source must have trip current settings and trip time at least three times longer than that of the RCD located closer to the consumer.
But in fairness, it should be noted that if the electrical wiring is installed with high quality, then the RCDs do not work for years. Therefore, in this case, the last word belongs to the customer.
General functions of the differential switch
In domestic and industrial power networks, several types of protective devices are used to prevent fires and electric shock to people. All of them are designed to operate in case of breakdowns in electrical installations or breakdown of wiring insulation.
The principle of operation, the elements inside and the controlled characteristics are different. However, the task is the same everywhere - if problems arise, quickly break the power supply chain.
You should not confuse the RCD and difavtomat, the device and functionality are different for them. The first device controls only the occurrence of leakage current, and the second is also designed to operate during short circuits and overloads in the network
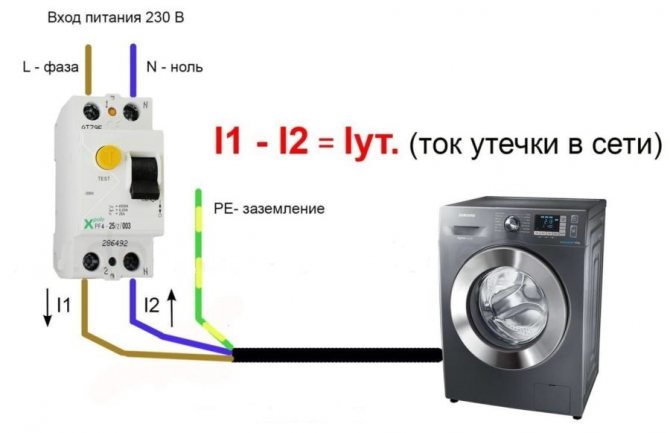
RCD (differential switch) is an electrical device that breaks the power line when a high leakage current appears. The latter occurs during the breakdown of the insulating layer in various thermal electric heaters and wires.
If at this moment a person touches the body of the broken equipment, then the electric current will go through it to the ground. And this is fraught with serious injuries. To prevent this, a residual current device (residual current circuit breaker) is placed in the circuit.
It consists of an RCD conventional and fire-fighting of:
- corps;
- transformer with three windings;
- EMF relay.
In normal operating condition, the electric current passing through the transformer windings forms magnetic fluxes with different poles. Moreover, when they are added, the final zero is obtained. The relay in this state is in the closed state and passes current.
But when a leak occurs, the balance on the windings is disturbed. The automatic switch in question reacts to this, opening the circuit. As a result, the voltage in the network disappears - the broken electrical appliance is de-energized, and nothing threatens the person anymore. The operation of the RCD occurs in just a few milliseconds.
Electrical equipment becomes a source of fire when:
- short circuits;
- overloads in the network and / or the electrical installation itself;
- excess leaks associated with insulation degradation.
In the first two cases, the protective shutdown is performed by a difavtomat (thermal electromagnetic release) or by blowing a fuse. For the third situation, there is precisely the considered RCD for differential current. There are also special insulation control devices, but they are expensive and rarely installed in apartment or house shields.
How can an RCD prevent a fire?
In case of electrical injuries, sparks that can cause a fire are not formed. But a fire in the event of a leakage current can still occur. The point is in the wiring and the electric current passing through the cables. Initially, the conductors are designed for strictly defined voltage values. If these parameters go beyond the design standards, then not for long and before the appearance of an open fire.
If a powerful leakage of electric current begins through the broken insulation, then the metal of the wires, not designed for this, starts to heat up too much - this leads to melting of the insulating braid and heating of surrounding objects
The task of the fire protection RCD is to control this situation and prevent overheating of the wiring. If the insulation is damaged and a leakage current has formed, then the protective device simply disconnects the problem line from the network. If there is a differential switch in the circuit, the matter does not even reach the heating of the metal of the cores and the outbreak of fire.
The leakage current in the range of 300–500 mA and a voltage of 220 V is the heat generated, equal to the heat generated from a lit household lighter. Such heat release inevitably leads to ignition of the wiring and everything nearby.
The main function of the RCD class under consideration is not the protection of a person, but the increase in fire safety. To prevent electric shock, ordinary devices of a smaller rating for leakage current are placed in the circuit after fire protection devices.
Functionally fire protection RCD protects:
- Introductory cable in front of you.
- Wiring a line of consumers after yourself.
- Connected electrical equipment when the downstream standard differential switch fails to trip.
The fire protection RCD is part of the cascade protection of the 220 V electrical network. It is not used in smoke and fire monitoring systems. In them, such protective devices, on the contrary, should not be present. Under certain circumstances, they can turn off such a control system, which is completely unacceptable.