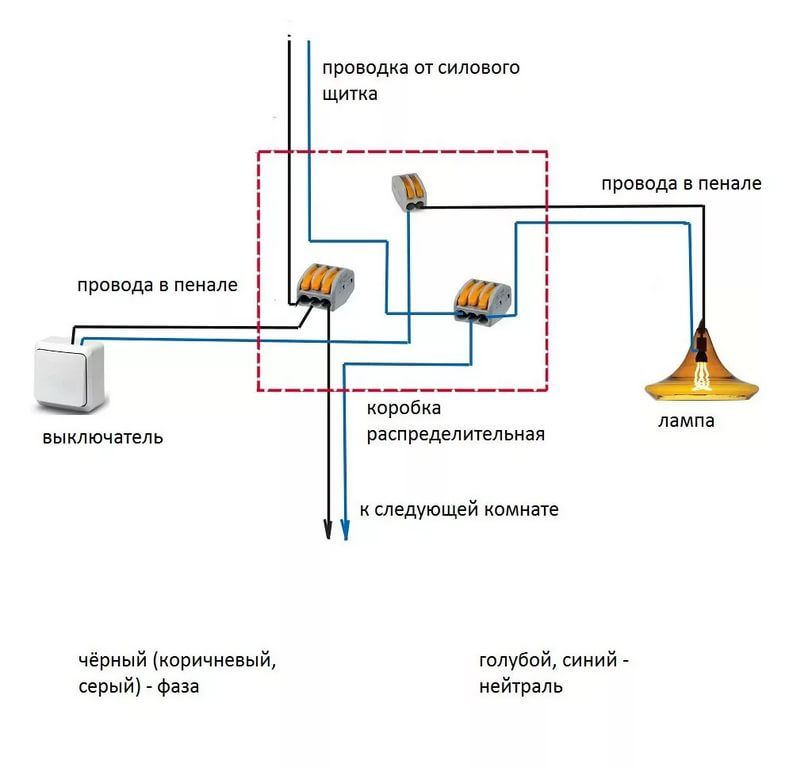
- CABLE SECTION
- Cable recommendation
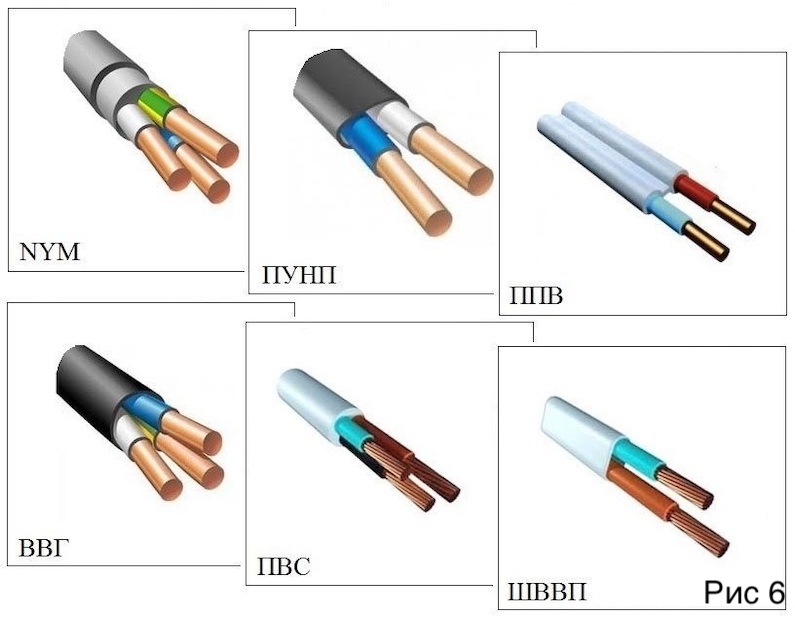
- VVG
- NYM
- PVA
- What wires do not fit?
- Product # 1 - PVC wire
- Product # 2 - wires SHVVP, PVVP
- Air cable entry
- Video description
- Cable calculation
- Briefly about the main
- What wires do not fit?
- Product # 1 - PVC wire
- Product # 2 - wires SHVVP, PVVP
- Section calculation
- Cable brand
- For concealed wiring
- For open wiring
- For wiring outside the home
- For a bath
- Letter designations
- Important characteristics when choosing a wire
- Device and material
- Cable section
- Insulation and sheath thickness
- Cable marking
- Core colors
- Marking
- What to use - wire or cable?
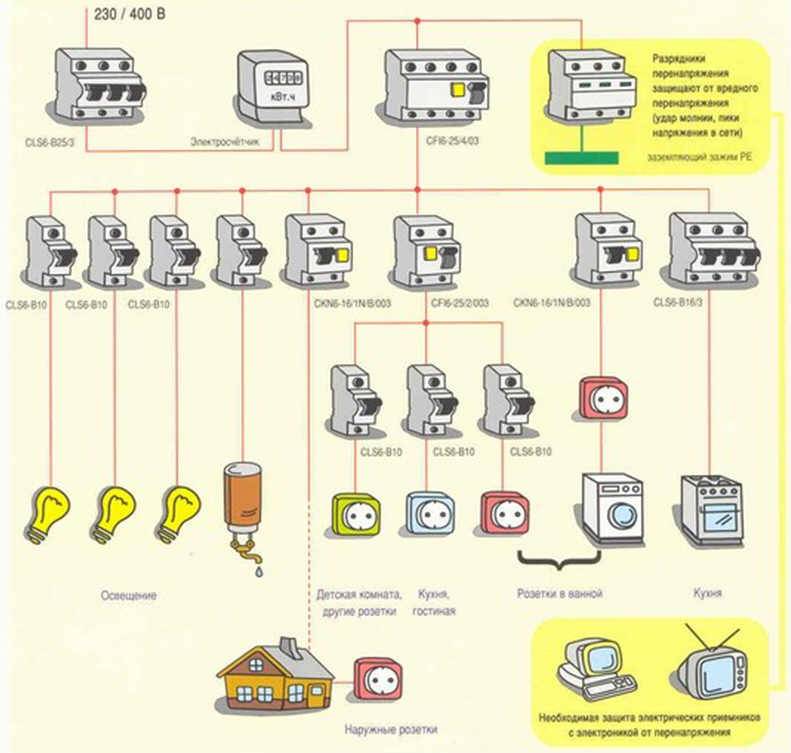
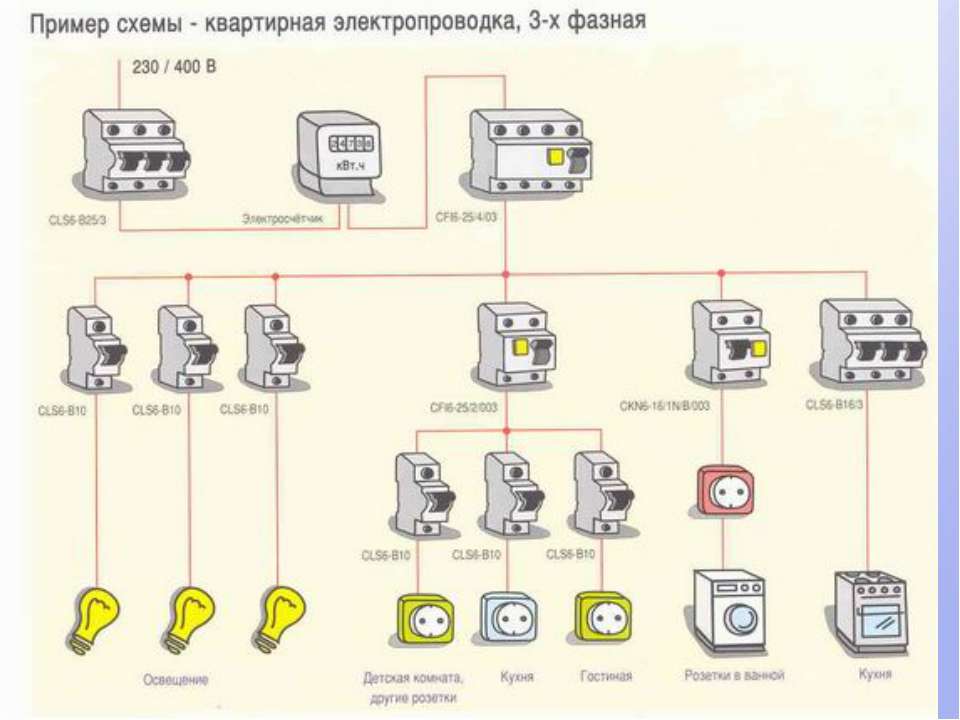
CABLE SECTION
When choosing the cross section of electrical cables for wiring an apartment or a private house, we are primarily guided by the same PUE 7.1.34., Which states that the minimum allowable cross section of a copper cable should be 1.5 mm2. Each line of electrical wiring must be calculated separately according to the load, depending on this, the cross section of the cable cores is selected.
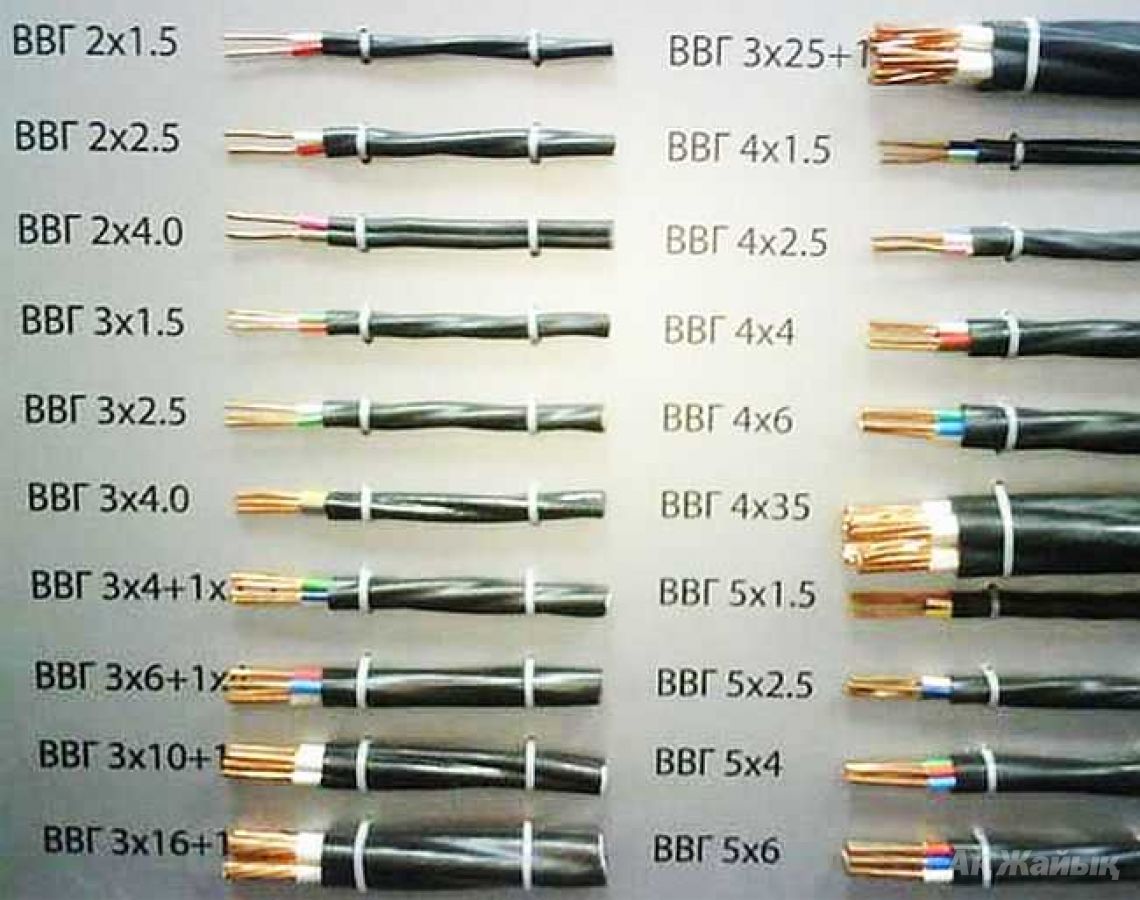
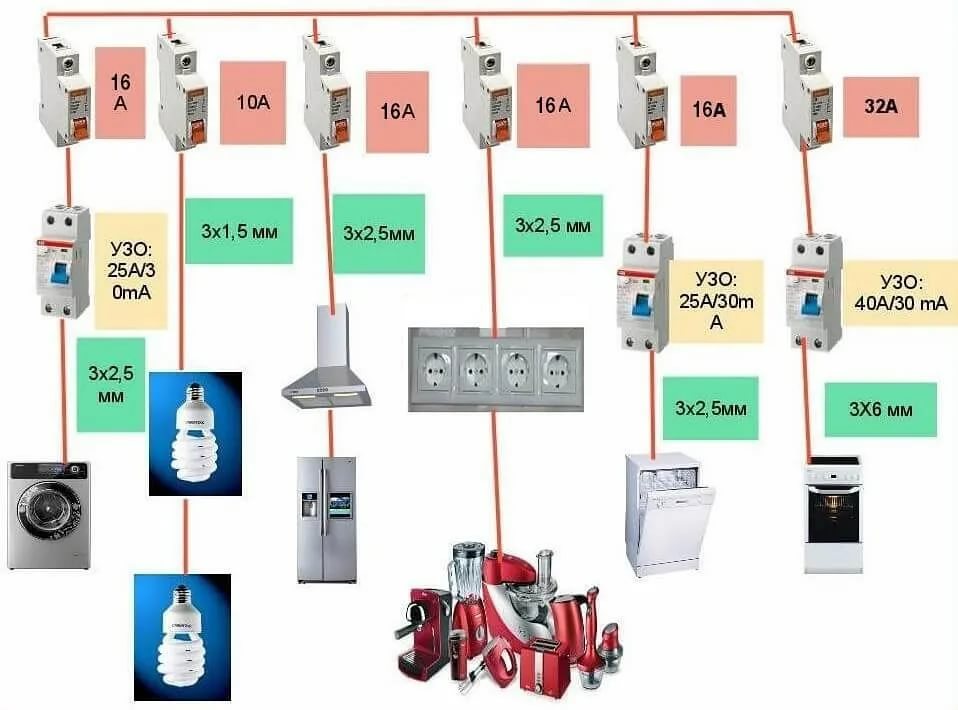
Most often, in residential buildings, it is enough to use cables of the following sections (for example, VVGngLS):
VVGngLS 3x1.5 mm.kv - For lighting groups, maximum power up to 4.1 kW, recommended rating of the protective circuit breaker 10A (2.3kW)
VVGngLS 3x2.5 mm.kv - For groups of sockets, maximum power up to 5.9 kW, recommended rating of the protective circuit breaker 16A (3.6kW)
VVGngLS 3x6 mm.kv - For powering an electric hob or electric stove, maximum power up to 10.1 kW, recommended rating of the protective circuit breaker 32A. (7.3 kW)
The input cable to the apartment is selected according to the power allocated to the apartment, but it is recommended to use at least 3x6mm.kv, it is better if 3x10mm.kv.
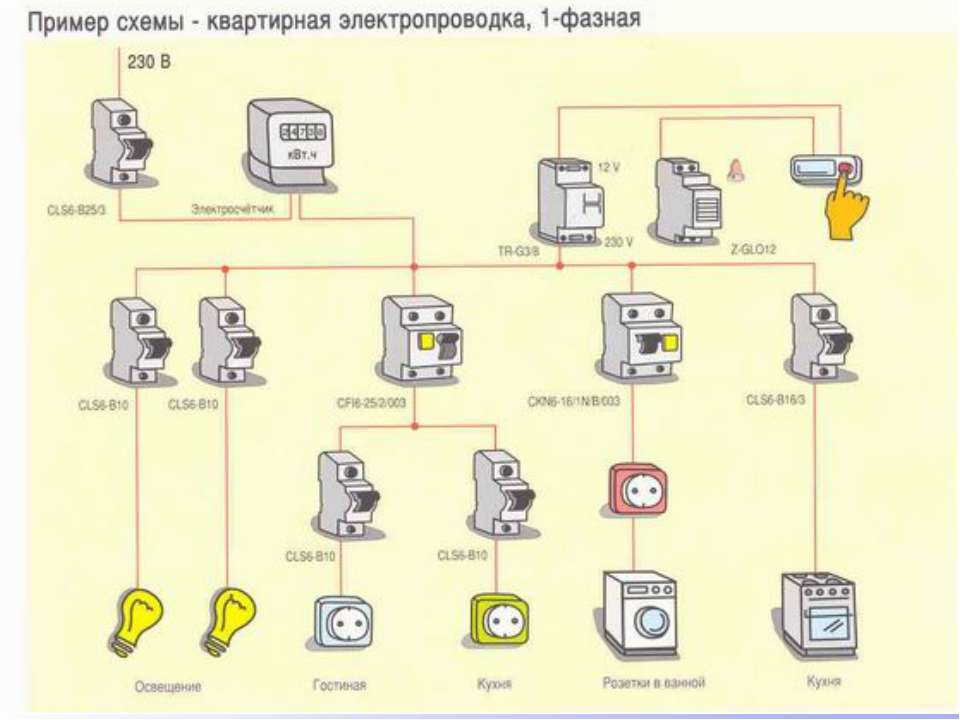
Cable recommendation
For intra-apartment wiring (lighting lines, connecting sockets), it is advisable to use the following brands of cable products. These are not the only options, although they are the most used.
VVG
For wiring in a hidden way - an excellent choice. External and internal insulation - vinyl, sufficient flexibility (see the decoding of the marking above).

If the first letter is "A", then the conductors are made of aluminum (AVVG)
Such products are in less demand, so sellers often position them as absolutely identical to copper cable and recommend them to buyers, while focusing on a lower price. The difference in the materials of the lived has already been said, and this must be taken into account.
NYM
Import analogue of VVG. The main difference is only in price - a German-made cable is more expensive. It can be added that it is more flexible, but for intra-apartment wiring, a small difference in this parameter is not important.

"Noodles" is not used as often. Basically, when reinstalling the outlet to another place.

PVA
Conductors are stranded.Basically, the PVA wire is used to connect fixed-mounted household and lighting fixtures to the line, connect sockets, and independently manufacture carriers (extension cords).

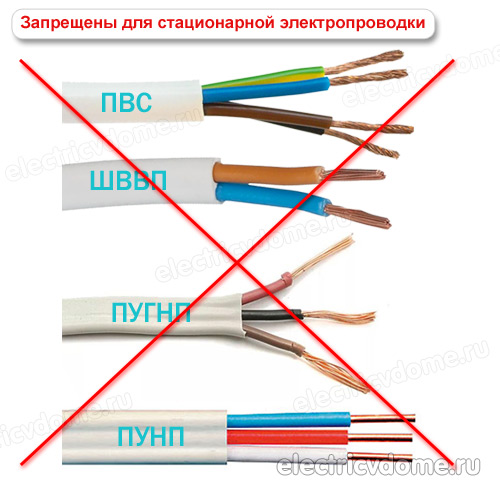
What wires do not fit?
There are product options that are strictly forbidden to be used for laying electrical networks, even in the most extreme cases. These include the following types of products.
Product # 1 - PVC wire
Connecting copper element, sheathed and insulated with PVC. It has a stranded design with 2-5 conductors 0.75-10 sq. mm.
A wire rated at 0.38 kW can be used to connect household electrical appliances to the mains and for the manufacture of extension cords.
PVS is not suitable for laying wiring for the following reasons:
- It has a multi-wire core structure, so tinning and soldering is necessary to connect the ends, which requires a lot of time and a lot of experience.
- The product poses a fire hazard: the wire strands heat up the cable more, causing the insulation to wear out faster, which can lead to a short circuit.
- PVS cannot be laid in a bundle, while almost all cable models are suitable for this. Due to the fact that the wiring lines must be at some distance from each other, it will be necessary to make strobes in the wall for each of them.
Thus, even the low price of such wires cannot compensate for the high costs of installation, and the quality of the installed electrical network will not be too high.
Product # 2 - wires SHVVP, PVVP
Cords or cables having single or stranded copper conductors can be used to connect household appliances and electrical equipment.
However, they are not suitable for stationary electrical communications, since these products do not have non-combustible insulation.
 Although a flat cord with polyvinyl chloride sheaths (SHVVP) is not recommended for laying electrical networks, it is quite suitable for organizing low-current lighting up to 24V, namely for laying wiring from a transformer to LEDs
Although a flat cord with polyvinyl chloride sheaths (SHVVP) is not recommended for laying electrical networks, it is quite suitable for organizing low-current lighting up to 24V, namely for laying wiring from a transformer to LEDs
In addition, the service life of SHVVP and VPPV is quite short, and the stranded structure requires processing of terminations and soldering during installation.
It is also worth mentioning PUNP (universal flat wire), which was banned for laying electrical networks in an apartment back in 2007.
This outdated product has poor insulation and low power, which is why it cannot withstand modern loads.
Air cable entry
Connecting electricity to a country house from a pole can be done using an air inlet. This method involves tensioning the cable from the power line to the shield using anchor bolts on the support. The wire entry must be done no lower than 2 m 75 cm above the ground, and if the height of the structure is insufficient, special pipe racks are used. It can be curved ("gander") or straight.
If the height of the house meets the standards, then a shield with a residual current device is installed on the wall. The space from the pole to the entry point should be up to 10 m. If it is larger, then an additional support is required, which will be mounted at a distance of up to 15 m from the power line.
The branch from the pole is made with a wire with a copper core and with a cross section from 4 mm² (length up to 10 m) to 6 mm² (from 10 to 15 m) and 10 mm² with a cable length of more than 25 m. If the core of the wire consists of aluminum, then its diameter must be at least 16 mm.If SIP is used to enter electricity into the house, then special fittings and an insulator made of glass, polymer or porcelain are required to connect it.
Video description
How the introductory cable is laid along overhead lines is shown in the video:
The first is needed to protect the cable from snow melting or falling trees. In these incidents, the armature breaks, but the cable remains intact. An insulator is required to protect the jumpers, since due to the rigidity of the SIP, it cannot be directly connected to the shield. To do this, a softer cable is attached to it. Also, when connecting aluminum and copper wires, it is forbidden to twist. To do this, all jumpers must be made from terminal boxes, and insulators must be used to protect them.
When tensioning the cable, it should be taken into account that its height above the pedestrian zone should be at least 3.5 m, and above the carriageway, a distance from the ground of 5 m is required. The tension force must be adjusted using a dynamometer. The advantage of aerial laying is that it requires few resources to connect the cable, and it is also possible to quickly change the wire.
The disadvantage of this type of entry is that the wiring is exposed and can be damaged by trees, weather, or other mechanical means. Also, hanging wires prevent the entrance of large vehicles (truck cranes, aerial platforms, fire trucks).

Wire laid on overhead lines
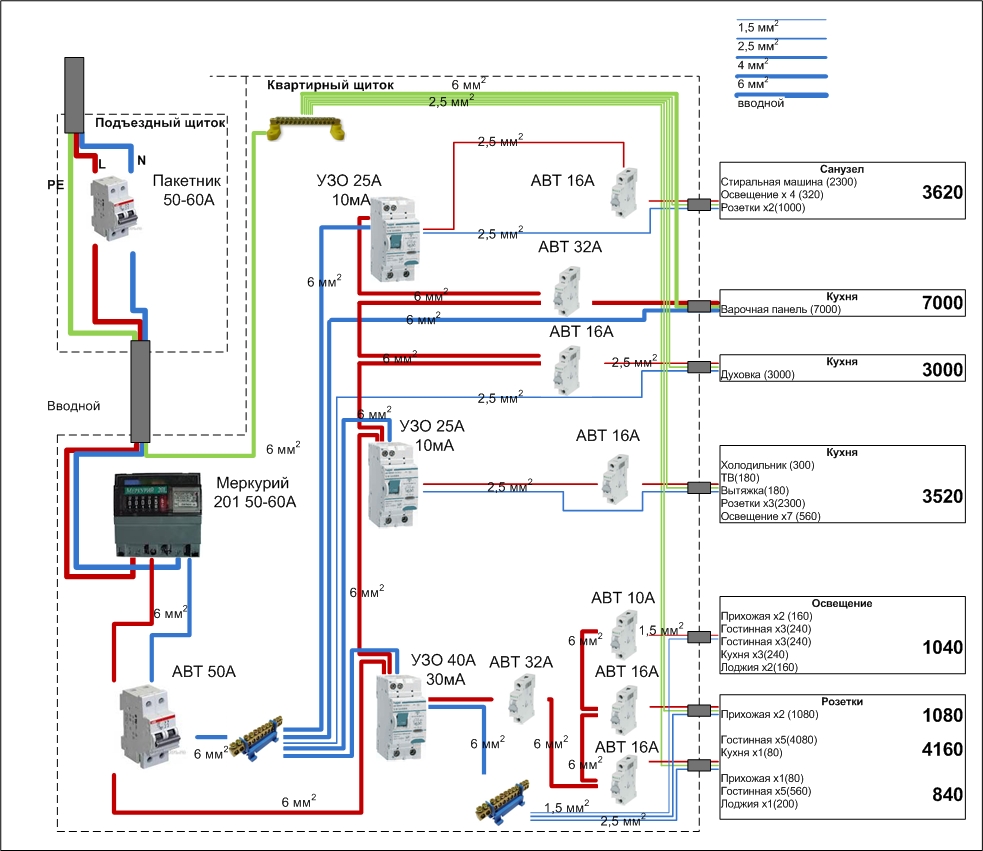
Cable calculation
It is required to know what section is needed for 15 kW and 380 to enter the house, since with an aluminum and copper core it has different characteristics, and also differs with different connection methods. For open introduction at a voltage of 380 V and a power of 15 kW, a copper conductor with a cross section of 4 mm² and capable of withstanding a current of 41 A is required, and for an aluminum wire - from 10 mm² and a current of 60 A.
For cables laid in the pipe, copper conductors must have a cross section of 10 mm², and for aluminum - from 16 mm². The length of the cable depends on the distance of the entry point from the pole, as well as the presence of additional fasteners or props.

First of all, the wire is brought to the electricity meter
Briefly about the main
A cable for laying in the ground for 15 kW of network power must be taken with protection or laid in a pipe. The cross section of such a wire should be from 10 mm².
Cables are available for air and underground placement.
It is necessary to pass the cable through the wall in a metal pipe at a slight slope.
The cross section of the cable directly depends on the method of its input, as well as the material from which it is made.
For a network of 15 kW with a voltage of 380 V, an additional three-band machine is required.
What wires do not fit?
There are product options that are strictly forbidden to be used for laying electrical networks, even in the most extreme cases. These include the following types of products.
Product # 1 - PVC wire
Connecting copper element, sheathed and insulated with PVC. It has a stranded design with 2-5 conductors with a cross section of 0.75-10 square millimeters.
A wire rated at 0.38 kW can be used to connect household electrical appliances to the mains and for the manufacture of extension cords.
PVS is not suitable for laying wiring for the following reasons:
- It has a multi-wire core structure, so tinning and soldering is necessary to connect the ends, which requires a lot of time and a lot of experience.
- The product poses a fire hazard: the wire strands cause the product to heat up more, causing the insulation to wear faster, which can lead to a short circuit.
- PVS cannot be laid in a bundle, while almost all cable models are suitable for this. Due to the fact that the wiring lines must be at some distance from each other, it will be necessary to make strobes in the wall for each of them.
Thus, even the low price of such wires cannot compensate for the high costs of installation, and the quality of the installed electrical network will not be too high.
Product # 2 - wires SHVVP, PVVP
Cords or cables having single or stranded copper conductors can be used to connect household appliances and electrical equipment.
However, they are not suitable for stationary electrical communications, since these products do not have non-combustible insulation.
Although a flat cord with polyvinyl chloride sheaths (SHVVP) is not recommended for laying electrical networks, it is quite suitable for organizing low-current lighting up to 24V, namely for laying wiring from a transformer to LEDs
In addition, the service life of SHVVP and VPPV is quite short, and the stranded structure requires processing of terminations and soldering during installation.
It is also worth mentioning PUNP (universal flat wire), which was banned for laying electrical networks in an apartment back in 2007.
This outdated product has poor insulation and low power, which is why it cannot withstand modern loads.
Section calculation
Section calculation
First, the rated load current is determined by the formula: I = W / 220 where,
- W is the power of the electrical receiver, W;
- 220 - voltage in a single-phase network, V.
So, a 3 kW water heater consumes current I = 3000 / 220 = 13.6 A. Then, according to the table, the cable section is selected. It depends not only on the rated current, but also on the material and method of laying (the cable cools better when open).
| cross section cables, mm2 | open laying | Laying in a pipe | ||||||||||
| copper | aluminum | copper | aluminum | |||||||||
| Current, A | power, kWt | Current, A | power, kWt | Current, A | power, kWt | Current, A | power, kWt | |||||
| 220 V | 380 V | 220 V | 380 V | 220 V | 380 V | 220 V | 380 V | |||||
| 0,5 | 11 | 2,4 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 0,75 | 15 | 3,3 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1,0 | 17 | 3,7 | 6,4 | – | – | – | 14 | 3,0 | 5,3 | – | – | – |
| 1,5 | 23 | 5,0 | 8,7 | – | – | – | 15 | 3,3 | 5,7 | – | – | – |
| 2,5 | 30 | 6,6 | 11,0 | 24 | 5,2 | 9,1 | 21 | 4,6 | 7,9 | 16,0 | 3,5 | 6,0 |
| 4,0 | 41 | 9,0 | 15,0 | 32 | 7,0 | 12,0 | 27 | 5,9 | 10,0 | 21,0 | 4,6 | 7,9 |
| 6,0 | 50 | 11,0 | 19,0 | 39 | 8,5 | 14,0 | 34 | 7,4 | 12,0 | 26,0 | 5,7 | 9,8 |
| 10,0 | 60 | 17,0 | 30,0 | 60 | 13,0 | 22,0 | 50 | 11,0 | 19,0 | 38,0 | 8,3 | 14,0 |
| 16,0 | 100 | 22,0 | 38,0 | 75 | 16,0 | 28,0 | 80 | 17,0 | 30,0 | 55,0 | 12,0 | 20,0 |
| 25,0 | 140 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 105 | 23,0 | 39,0 | 100 | 22,0 | 38,0 | 65,0 | 14,0 | 24,0 |
Typically, copper wires of this section are used in everyday life:
- lighting: 1.5 mm2 (the EMP does not allow using wires of a smaller cross section);
- power section (sockets): 2.5 mm2;
- dishwasher and washing machine, electric stove and other high-power appliances (connected with a separate line): 4 mm2.
The connection of the apartment to the floor shield is carried out using a common cable with a cross section of 6 mm2.
Cable brand
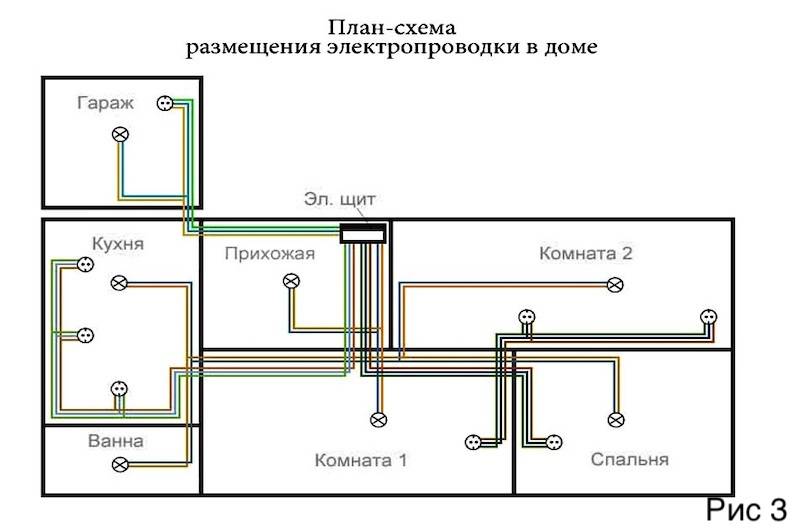
To know which cable to choose for wiring in the house, you need to determine the conditions for its operation. The brand of wire will depend on this. For a private house, three main zones can be distinguished: interior, street, bath. In this case, it is necessary to take into account whether the wiring is hidden or openly mounted.
For concealed wiring
Cables of brands are suitable for kitchen, bedroom and other rooms:
- VVG - a single-core copper conductor or cable with up to four cores. Available in round or flat. A subspecies of the VVGng brand prevents the spread of flame through the wiring, and a conductor marked as VVGng-LS does not burn and emits almost no smoke. Russian production;
- AVVG is a single-core aluminum wire or cable with up to four cores. May be round or flat. The protective shell is incapable of burning. Russian production;
- NYM - German analogue of VVGng, does not burn. Only round. The quality of workmanship is high;
- PVA - multi-stranded copper conductor of round cross section;
- SHVVP is a thin flat multi-strand copper conductor. Only suitable for home electrical and electronic equipment.
There are no specific selection rules. Take what you feel is best. But electricians prefer the German NYM cable. It costs more, but the quality of the wiring will be higher.
For open wiring
In wooden houses, open-type wiring is desired, although no one forbids using it for stone buildings. In this case, the choice of cable determines only its color:
- VVG is painted black;
- NYM grey;
- PVS is performed in white or orange;
- SHVVP is standard white, although other colors are rare. Ask the seller about them.
And what kind of wiring is better to do in a wooden house? It is not the color that is important here, but the fire protection. Only three options are possible here: Russian VVGng-LS or VVGng, as well as German conductors NYM.
For wiring outside the home
If electricity is supplied to the house not by air, but by land, then you need to take AVBBSHV cables if you have aluminum wiring, and VBBSHV if copper. This grade is armored with steel tape, which is applied after the insulating layer. Steel is protected by rubber from groundwater. This design resists mechanical damage, which is possible with inaccurate trench digging and soil movements.
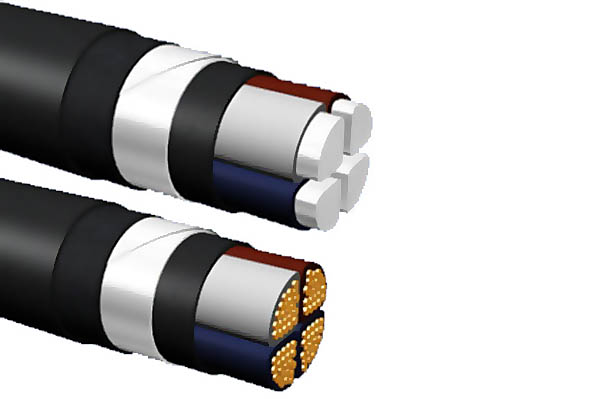
And what cable to use for wiring outdoors, where precipitation, large temperature changes, sun and wind are possible? VVG and AVVG cables are not afraid of this. They can be laid on the roof and wall.
For a bath
It is impossible to conduct sockets and switches in the steam room. The wire in the bath is needed only to provide light. But it has high requirements:
- Moisture resistant;
- Ability to withstand temperatures up to 180 degrees.
These requirements are met by Russian brands RKGM and PVKV, which are protected by a silicon-containing organic shell.


Letter designations
"A", standing first - the conductor is made of aluminum; if there is no letter, the conductor is made of copper. The following letters explain the material from which the upper insulating layer is formed:
- "P" - polyethylene insulation;
- "B" - from polyvinyl chloride;
- "R" - made of rubber;

The presence of the letter “K” in the combination indicates the presence of a control cable, the letters “VSh” indicate a sealed coating.

The most common types of wires for electrical wiring in rooms are as follows:
- VVG - wiring with a copper conductor, made in a round or flat shape. Fireproof varieties of these wires have been developed.
- AVVG - made of aluminum, resistant to fire.
- NYM - copper wiring in a round base with one core. It has a reduced flammability and smoke emission.
- PVS - copper cable with several core components; used in the installation work of devices or wires inside apartments.
- ShVVP - wiring with a flattened copper conductor, have a stranded conductor; needed to connect electrical appliances.

Groups of electrical cables are classified by color. VVG wire comes in black; PVA-orange or white; SHVVP-are usually performed in white.

 If you need to perform installation work on laying electrical wiring in the apartment, you should contact an electrician. They will help determine which wires should be used in a given apartment, help calculate the cross-section of wires, the required amount of wiring and its types.
If you need to perform installation work on laying electrical wiring in the apartment, you should contact an electrician. They will help determine which wires should be used in a given apartment, help calculate the cross-section of wires, the required amount of wiring and its types.

The correct choice and competent installation of wiring will ensure the safe use of electrical appliances in life, help to avoid fire hazards.

Important characteristics when choosing a wire
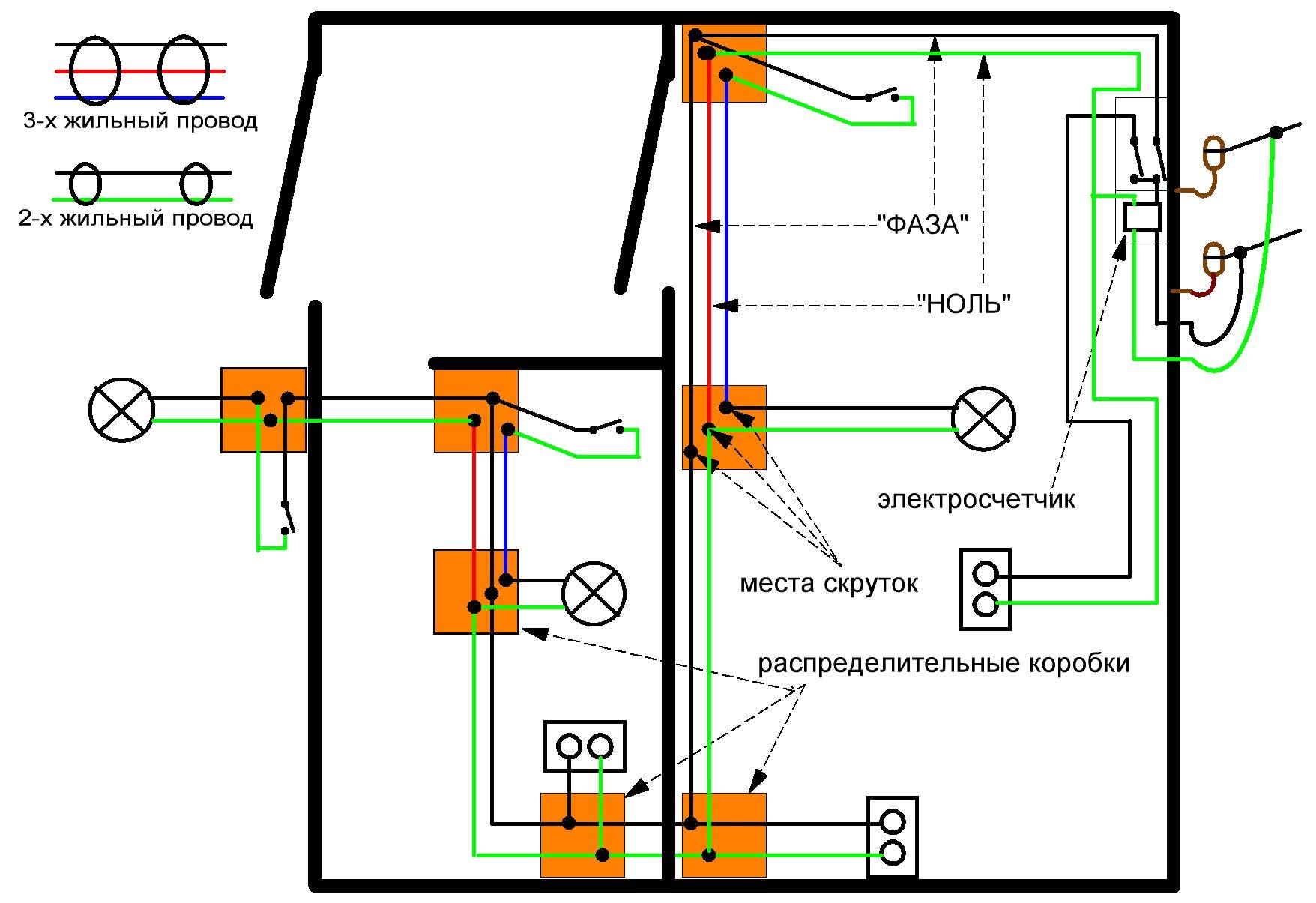
It is necessary to take into account the number of lived. In houses where a ground loop is installed, a 3-core one is used, and where not, a 2-core one. Most often, wiring is reconstructed when it is replaced in old houses. It makes no sense to use expensive material there.
Pay attention to the type of cable cores, which can consist of 1 conductor or several twisted wires
A solid core has less resistance than a multi-wire one, but it is difficult to lay wiring for lighting in an apartment with such a cable. Another type is flexible, it is easy to mount it in the voids of concrete floors or other hard-to-reach places.
Having a greater resistance, the wire heats up, and when the load increases, the insulation melts or ignites. Therefore, a flexible cable with a non-combustible coating is used.
Device and material
According to the requirements of SP 31-110-2003 "Electrical Installations of Residential and Public Buildings", internal electrical wiring must be mounted with wires and cables with copper conductors and should not support combustion. Despite the fact that aluminum is a metal with low resistance, it is a reactive element that quickly oxidizes in air. The resulting film has poor conductivity, and at the point of contact, the wires will heat up as the load increases.
Connecting conductors of different materials (copper and aluminum) leads to a loss of contact and a break in the circuit. During operation, structural changes occur in the metal, as a result of which strength is lost. With aluminum, this happens faster and stronger than with copper.
By design, cable products are:
- single-core (single-wire);
- stranded (stranded).
 Cable laying for lighting has its own specifics due to increased fire safety requirements.
Cable laying for lighting has its own specifics due to increased fire safety requirements.
Single-core wires are more rigid, it is difficult to bend them if they have a large cross section. Multi-wire cables are flexible, they can be used both in outdoor wiring and laid under plaster. But single-core conductors are rarely used for arranging a lighting network in residential premises. For indoor installation in apartment buildings and private houses, 3-core single-wire cables are used. Multi-wire products for these purposes are prohibited due to the high fire hazard.
Cable section
The value is measured in mm² and serves as an indicator of the ability of the conductor to pass electric current. A copper conductor with a cross section of 1 mm² can withstand a load of 10 A without heating above the permissible norm. For wiring, the cable should be selected with a margin for power, because. a layer of plaster reduces heat removal, as a result of which the insulation may be damaged. The cross section of the wire is determined by the formula for calculating the area of a circle. In a stranded conductor, this value must be multiplied by the number of wires.
Insulation and sheath thickness
Each conductor in a multicore wiring cable has an insulating sheath. It is made of PVC-based materials and serves to protect the core from damage. Simultaneously creates a dielectric layer in the bundle of conductors. The coating thickness is standardized and should not be less than 0.44 mm. For cables with a cross section of 1.5-2.5 mm², this value is 0.6 mm.
 The choice and installation of the cable must be trusted to professionals.
The choice and installation of the cable must be trusted to professionals.
The sheath serves to accommodate the cores, fix them and protect them from mechanical damage. It is made of the same material as the conductor insulation, but has a greater thickness: for single-core cables - 1.4 mm, and for stranded cables - 1.6 mm. For indoor wiring, the presence of double insulation is a mandatory requirement. This protects the wire from damage and ensures the safety of the occupants.
Cable marking
It is applied to the cable sheath along the entire length at short intervals. It should be legible and contain the following information:
- wire brand;
- name of the manufacturer;
- release date;
- the number of cores and their cross section;
- voltage value.
Knowing the product designation, you can choose the product you need for the job.Knowing the product designation, you can choose the right equipment.
Core colors
The color of the conductor insulation is needed for ease of installation. Wires in the same sheath have a different color, which is the same along the entire length. Depending on the manufacturer, they may vary, but the color of the ground wire does not change. In a 3-core cable, most often the phase wire is red or brown, the neutral wire is blue or black, and the ground wire is yellow-green.
 Electrical wire colors regulated by regulations.
Electrical wire colors regulated by regulations.
Marking
Mark - a short alphanumeric designation that provides basic information about a cable or wire. The brand of aluminum cable begins with the letter "A". Any other letter in the first place means that the cable is copper.
 Other letters mean:
Other letters mean:
- purpose, for example, "K" - control, "M" - assembly, etc .;
- insulation and sheath material, for example, "B" - polyvinyl chloride (PVC), "P" - polyethylene, "R" - rubber, etc.;
- the presence of armor (letter "B");
- the presence of a filler ("E").
The numbers indicate the number and cross section of the cores, the rated voltage.
For example, a VVG 4x2.5-380 cable has 4 cores with a cross section of 2.5 square meters. mm and PVC insulation, designed for a voltage of 380 V. The fact that the insulation is made of a slow-burning material and does not spread combustion in the bundle (neighboring cables do not ignite) is indicated by the letter combination “ng”. About insulation with reduced smoke emission - “ls” or “ls” (low smoking).
What to use - wire or cable?
"What's the difference" - many will ask, because these are practically synonyms?
Not certainly in that way. There is a difference, and a very significant one.
By wire it is customary to understand a solid or stranded conductor, which may have insulation or be produced without it at all (for example, for use in power lines). Most often, the wire sheath does not have additional protective functions, but is designed exclusively for insulating purposes. Resistance to external influences or to an aggressive environment is not the highest or is completely absent.
Even the combination of several insulated conductors under a common additional external insulation does not make the wire a cable at all.
A cable is a collection of several high-quality insulated wires, united by an outer sheath, which is assigned not so much insulating as protective functions. There can be several such braids, they can be multilayered - polymer, metal, fiberglass. Additional filling of the space between the wires under the outer sheath is also practiced.
The presence of a protective sheath allows you to lay cables for the most difficult operating conditions. Well, in the context of this publication, the following can be noted. For laying hidden wiring, where it will be walled up in walls, that is, to experience mechanical, chemical, and thermal loads (due to the lack of a normal heat sink), only cables should be used. Wires are acceptable for switching in switchboards or on groups of sockets, for connecting household appliances and lighting equipment, including in the form of power cords with plugs for plugging into sockets.
It should be noted that the difference described above is very difficult to understand.In particular, products are produced that practically do not differ at first glance in appearance. But the manufacturer positions one as a cable, and the other is still called a wire.
On the left is the VVGng 3 × 2.5 cable, on the right is the PUMP wire with the same number of cores and their cross section. The cable is suitable for laying hidden wiring, and the wire is completely unsuitable for this.
A classic example of such a pair is the VVG cable and the PUMP wire. With all the external similarity, for example, an equal number of conductors and their cross section, the first one can be used for hidden wiring, and the second one definitely cannot, which has been proven more than once by sad practice. But some electricians still continue to "dabble" in this - it's understandable, since the wire is always cheaper than the cable. But both the internal insulation of the conductors and the outer sheath do not at all reach the levels of protection and fire safety required for the cable.
So, when purchasing materials, it is always worth clarifying how this type of product passes according to the available official certification, whether it is a cable or a wire.