- The structure of the register
- Decreased heat transfer.
- Methods for calculating the heat transfer of heating pipes
- Instructions for self-production of registers
- Work order
- How to weld a heating register
- Welding technology
- Ratio of metal thickness to electrode diameter
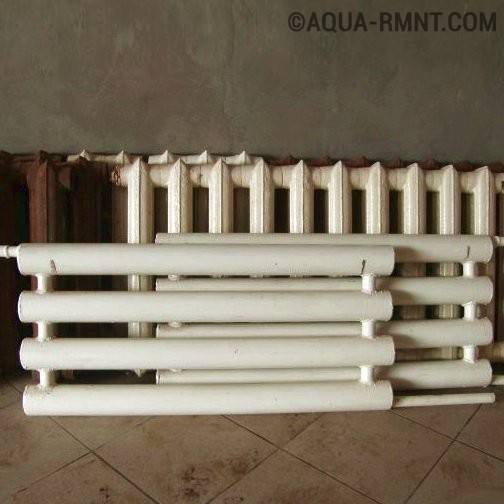
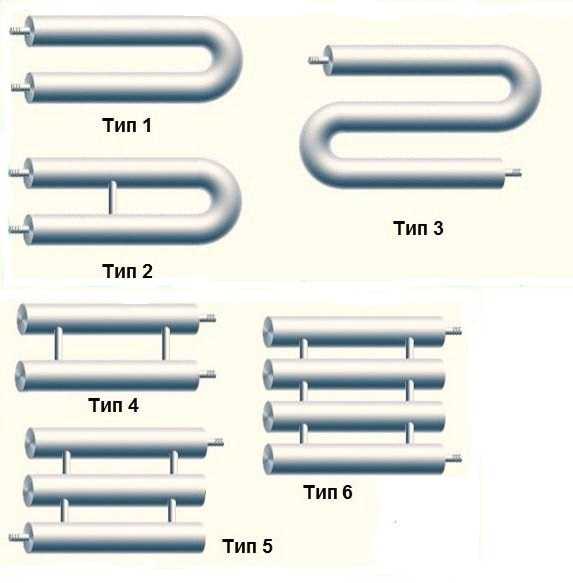
- Varieties of heating registers
- Materials for manufacturing
- Design
- Mounting methods: welding or threading?
- Classic designs of heating registers
- Option #1 - horizontal register
- Option #2 - vertical registers
- How to set the heating register
- We make a register with our own hands
- Main advantages
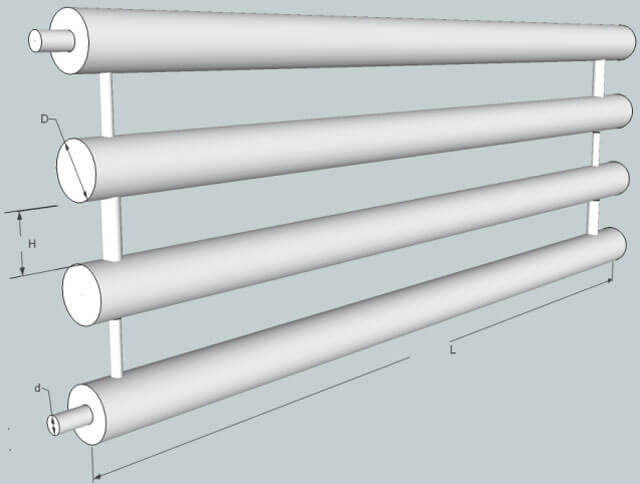
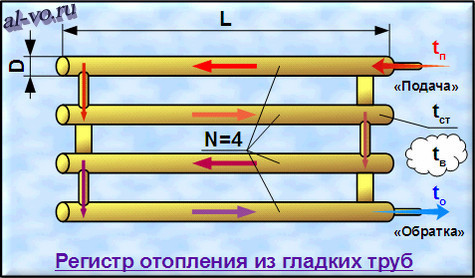
The structure of the register

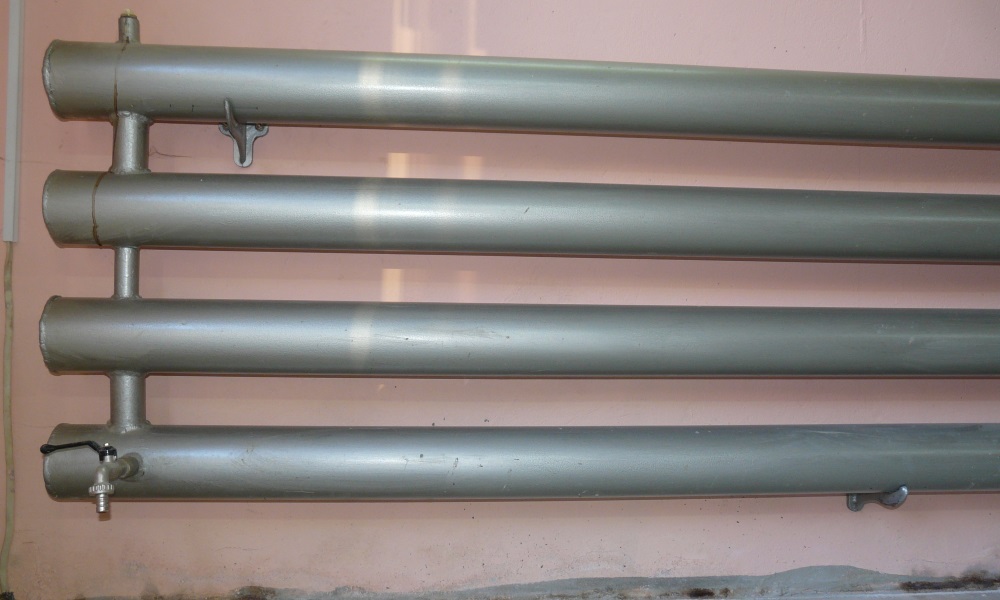
For the manufacture of heating registers, smooth carbon steel pipes with a round section, as well as square and rectangular ones, are used. Their combined use is possible. Stainless and galvanized steel, aluminum, copper, brass can also be good materials for registers, but they are much more expensive and more difficult to do it yourself.
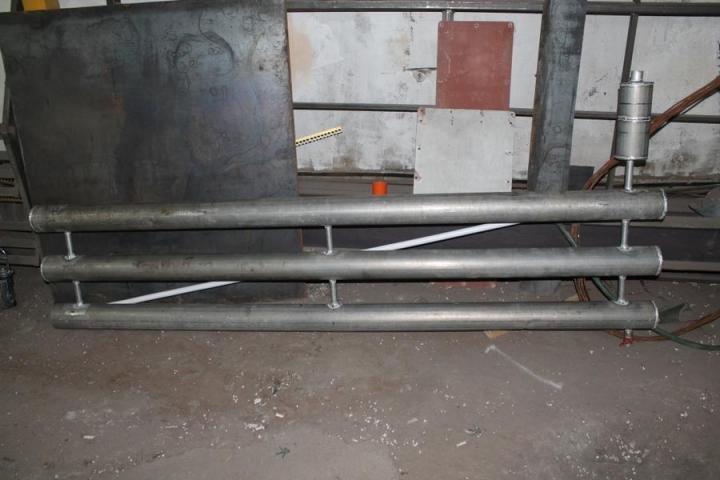
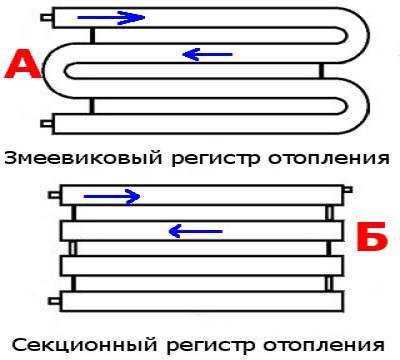
The most simple to implement are heating registers from steel profile pipe. They can be performed in two main configurations: sectional type and serpentine (S-shaped).

In a sectional type register, several sections of profiled rolled metal with plugged ends are arranged in parallel and connected to each other by round tubes of a smaller cross section. Jumpers provide filling of the rows of the device with coolant from both sides at the same time. At the same time, the closer the adapter pipes are installed to the edge, the higher the heat transfer of the device.
In the serpentine register, the liquid passes in an S-shape through the rows of shaped pipes, gradually cooling down. To give the structure rigidity, additional deaf jumpers are used. Horizontal rows are connected in pairs by a snake using tubes of a smaller section, as in sectional models, or segments of the main profile. The latter option is preferable because of the lower hydraulic resistance and greater heat transfer.

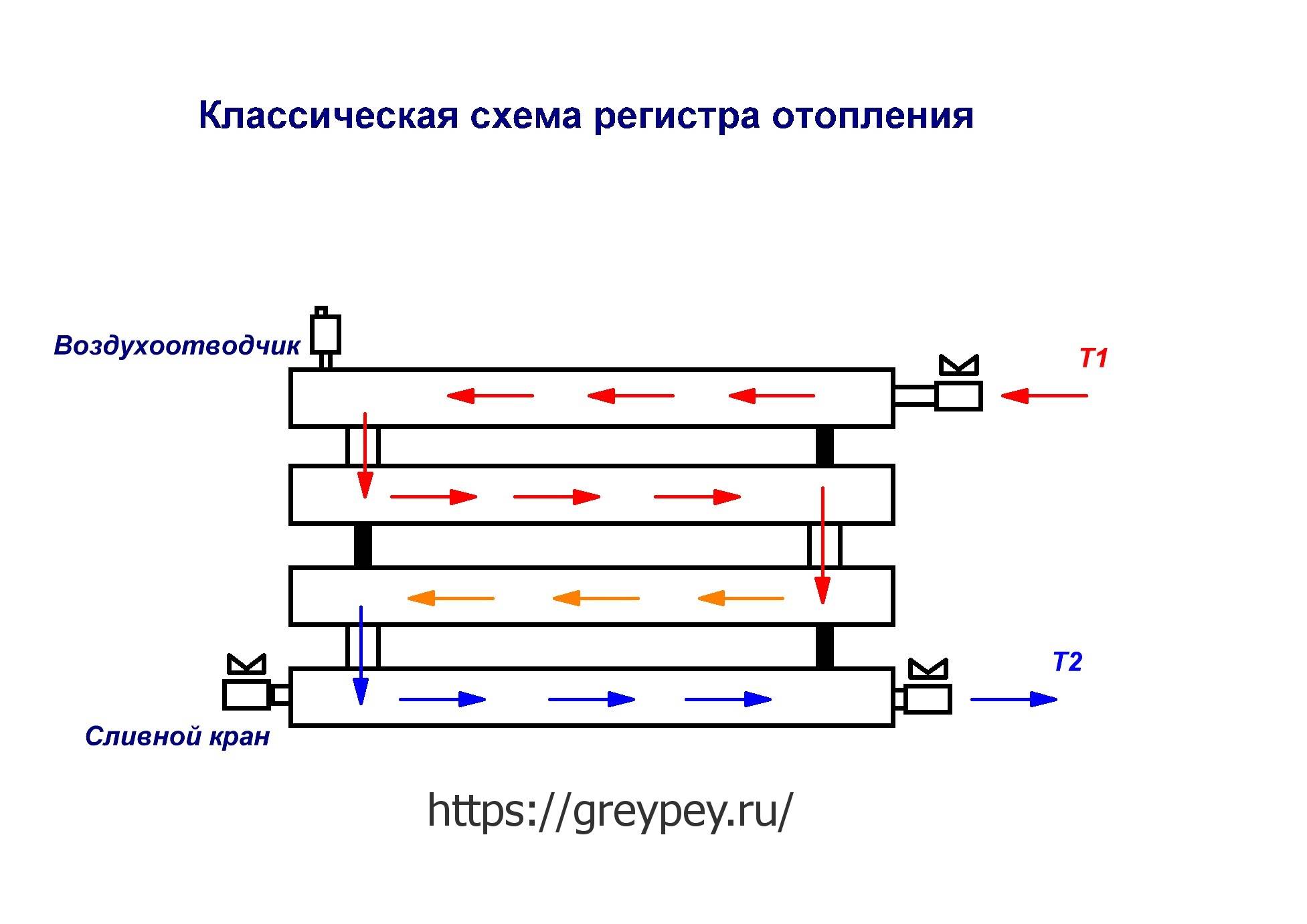
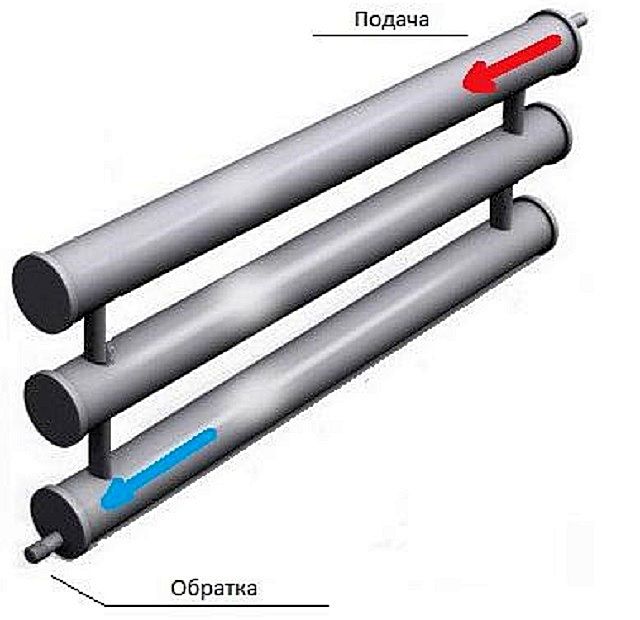
Connection pipes are made with threads or for welding. The most effective option for connecting a heater is a top-down scheme. For low models and in the case of forced circulation of the coolant, it may be justified to enter and exit from below.
The design of the register necessarily provides for a Mayevsky crane or an automatic air vent. It is located at the end of the top row on a threaded fitting to enable replacement. A prerequisite for installation is the observance of a slope of 0.05% in the direction of the movement of the coolant.
Registers are both stationary and portable. The former work as elements of a general heating system, the latter perform the task of local heating. The heat source for a separate mobile register is a heating element with a power of 1.5-6 W, built into the housing.

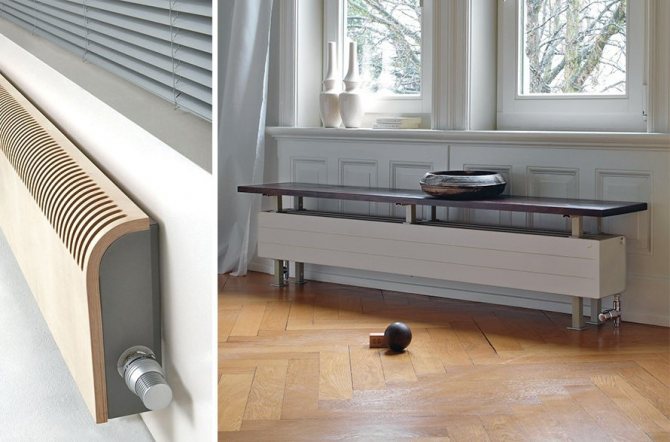
In addition to large horizontal registers, small vertical models are also in demand. With careful work, you can get home-made cheap radiators from shaped pipes, almost as good as modern sectional radiators in terms of aesthetics.
In some cases, steel registers can be a good addition to the heaters already installed in the room. Despite lower heat dissipation than similarly sized radiators, their use may be more appropriate due to their lower cost.

High vertical registers are very convenient for high rooms or near high window openings. They can successfully fit into the interiors of rooms with unusual design solutions. With a little experimenting with color and shape, you can get a creative decoration from simple heating devices.
Decreased heat transfer.
In order to save energy, it becomes relevant to reduce the heat transfer of pipes in those sections of communications that are not used for their intended purpose, for example, when moving from one building to another or in an unheated room.
To do this, there are many options for using thermal insulation materials. Manufacturers present a fairly wide range to choose from, ranging from cheap fiberglass to more expensive types of expanded polystyrene. You can purchase pipes with insulation elements already built into it.
Summing up, we conclude that the use of such calculations helps to significantly save and avoid many technical obstacles in the design of water and heat supply systems.
In fact, you are a desperate person if you decide on such an event.The heat transfer of a pipe, of course, can be calculated, and there are a great many works on the theoretical calculation of the heat transfer of various pipes.
To begin with, if you started heating the house with your own hands, then you are a stubborn and purposeful person. Accordingly, a heating project has already been drawn up, pipes have been selected: either these are metal-plastic heating pipes or steel heating pipes. Heating radiators are also already looked after in the store.
But, before acquiring all this, that is, at the design stage, it is necessary to make a conditionally relative calculation. After all, the heat transfer of heating pipes, calculated in the project, is a guarantee of warm winters for your family. You can't go wrong here.
Methods for calculating the heat transfer of heating pipes
Why is the emphasis usually placed on the calculation of heat transfer of heating pipes. The fact is that for industrial heating radiators, all these calculations have been made, and are given in the instructions for the use of products. Based on them, you can easily calculate the required number of radiators depending on the parameters of your house: volume, coolant temperature, etc.
Tables. This is the quintessence of all the necessary parameters, collected in one place. Today, a great many tables and reference books are posted on the Web for online calculation of heat transfer from pipes. In them you will find out what is the heat transfer of a steel pipe or cast-iron pipe, the heat transfer of a polymer pipe or copper.
All that is needed when using these tables is to know the initial parameters of your pipe: material, wall thickness, internal diameter, etc. And, accordingly, enter the query "Table of heat transfer coefficients of pipes" into the search.
In the same section on determining the heat transfer of pipes, one can also include the use of manual Handbooks on the heat transfer of materials. Although they are getting harder and harder to find, all the information has migrated to the Internet.
Formulas. The heat transfer of a steel pipe is calculated by the formula
Qtp=1.163*Stp*k*(Twater - Tair)*(1-pipe insulation efficiency), W where Stp is the surface area of the pipe, and k is the heat transfer coefficient from water to air.
The heat transfer of a metal-plastic pipe is calculated using a different formula.
Where - temperature on the inner surface of the pipeline, ° С; t c - temperature on the outer surface of the pipeline, ° С; Q- heat flow, W; l — pipe length, m; t— coolant temperature, °C; t vz is the air temperature, °С; a n - coefficient of external heat transfer, W / m 2 K; d n is the outer diameter of the pipe, mm; l is the coefficient of thermal conductivity, W/m K; d in — pipe inner diameter, mm; a vn - coefficient of internal heat transfer, W / m 2 K;
You perfectly understand that the calculation of the thermal conductivity of heating pipes is a conditionally relative value. The average parameters of certain indicators are entered into the formulas, which can and do differ from the real ones.
For example, as a result of the experiments, it was found that the heat transfer of a polypropylene pipe located horizontally is slightly lower than that of steel pipes of the same inner diameter, by 7-8%. It is internal, since polymer pipe wall thickness A bit more.
Many factors affect the final figures obtained in tables and formulas, which is why the footnote "approximate heat transfer" is always made. After all, the formulas do not take into account, for example, heat losses through building envelopes made of different materials. For this, there are corresponding Tables of amendments.
However, using one of the methods for determining the heat output of heating pipes, you will have a general idea of \u200b\u200bwhat kind of pipes and radiators you need for your home.
Good luck to you, builders of your warm present and future.
Instructions for self-production of registers
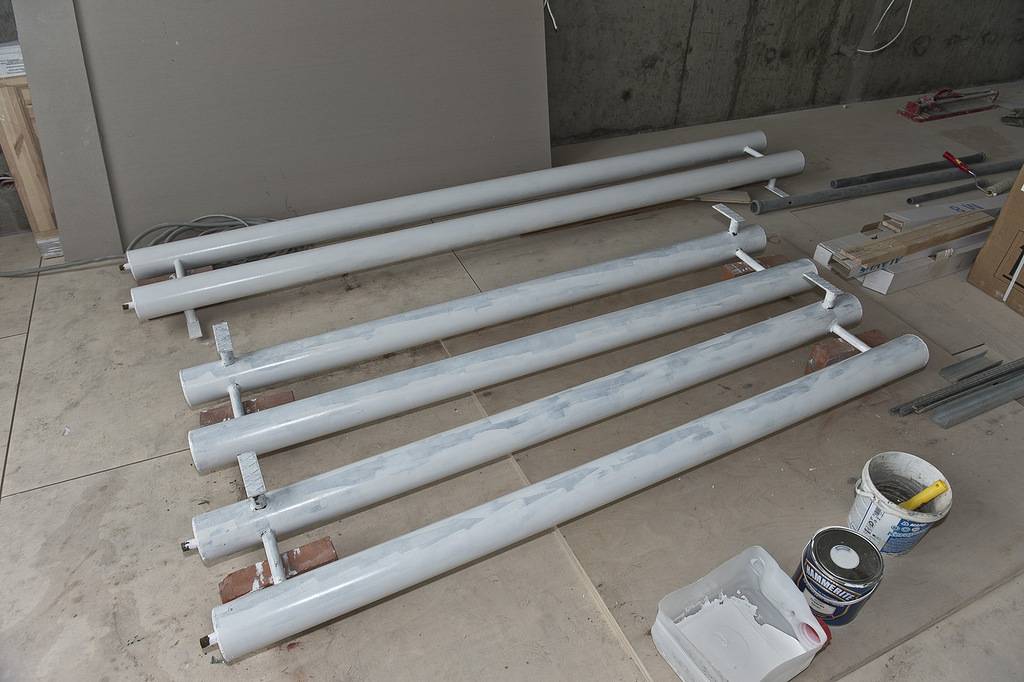
It is easiest to make a steel heat exchanger with your own hands, although its assembly will require skills in working with welding and grinding equipment and compliance with certain rules.
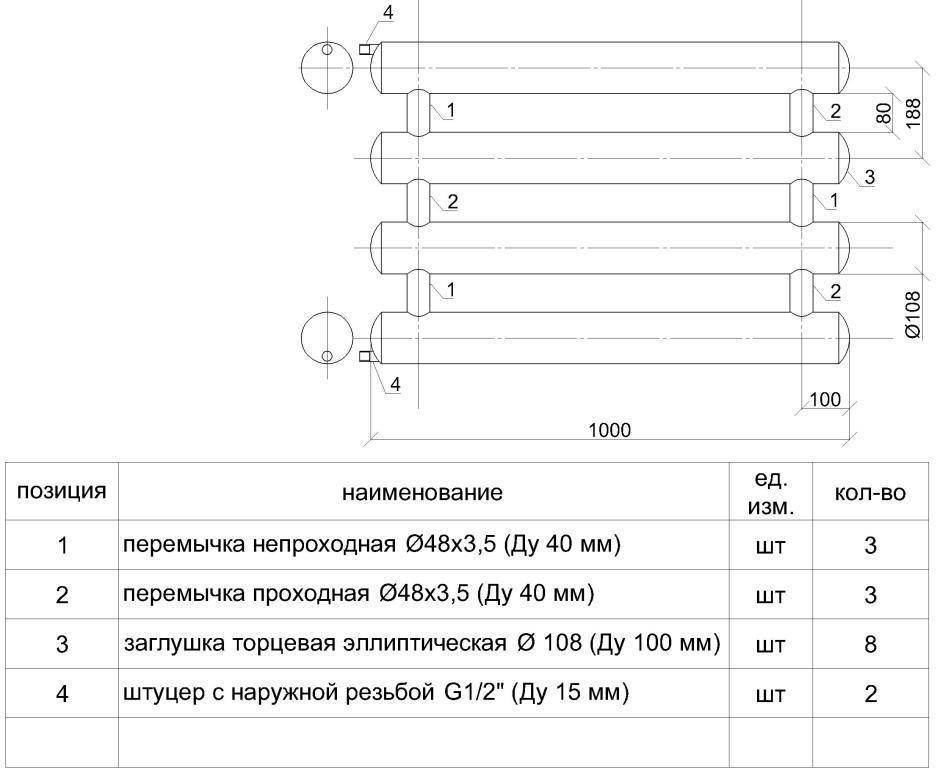
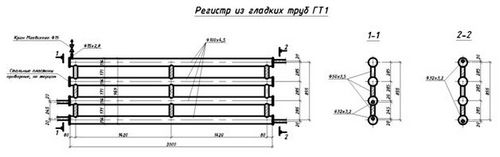
- Before installation, it is necessary to perform calculations and a drawing, which will indicate the dimensions of pipes and connecting elements, the location of fittings and connection points. The drawing will help to accurately calculate the number and parameters of consumables.
- The clearance between the sections is taken as 1.5D or D + 0.5 cm, where D is the diameter of the pipe. The distance between the parallel sections of the serpentine register is calculated depending on the arc element used or the turning radius (R) when using a pipe bender. In the first case, the distance is equal to twice the difference between the height of the arc element (F) and the diameter: 2(F-D). In the second case, the distance will be equal to 2R-D. With a smaller distance, heat transfer decreases.
- Since welding and grinding equipment is used during installation, it is imperative to wear protective clothing and shoes, and protect your face with a special mask or goggles.
- For the effective operation of the register, strict parallelism of its sections is necessary; a level, a plumb line and a building corner will help to control this parameter during the work.
- At the upper point of the register, the most distant from the supply pipe, an air vent is installed to get rid of air pockets in the circuit. When installing a parallel heat exchanger with manifolds, air vents are placed at the top of each manifold.
- Racks and brackets are required to secure the register. The more massive the structure, the more fasteners will be required.
Work order
- The work area is being cleaned.
- Register elements are marked and cut in accordance with the drawing.
- The inner and outer surfaces of the pipes, as well as the edges of the holes, are cleaned of debris and rust with a steel brush.
- Plugs are cleaned of debris and plaque. Holes are drilled in two plugs for connection to the heating circuit.
- Plugs, jumpers and connecting pipes or manifolds are welded in accordance with the drawing. The parallelism of the sections is checked after attaching each element.
- Welds are cleaned.
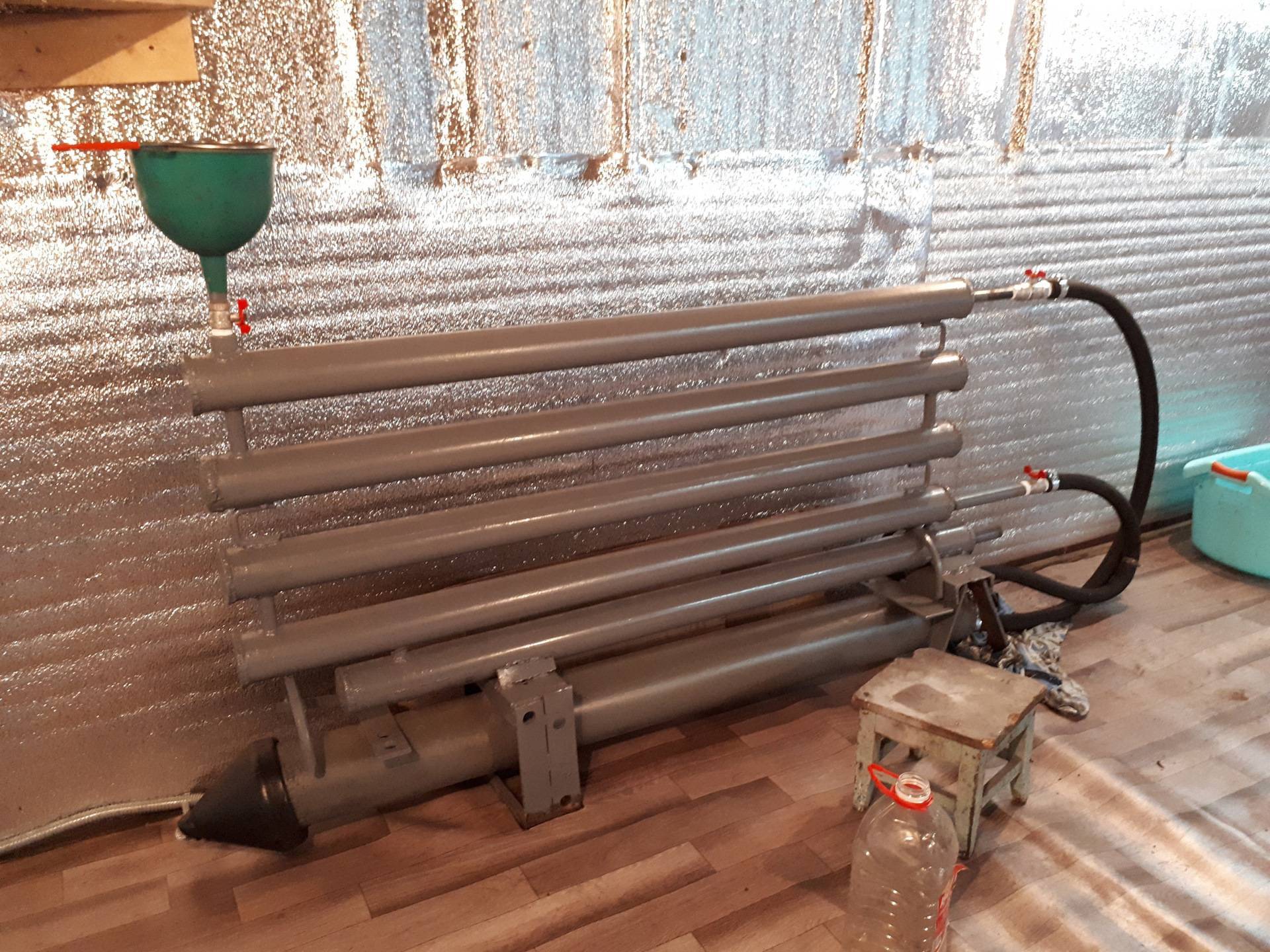
- The tightness of the resulting register is checked: the outlet is hermetically sealed, and water is poured through the inlet under pressure. If even small drops appear on the seams, it is necessary to drain the liquid and additionally boil the seam.
- If necessary, cover the heat exchanger with heat-resistant paint for metal.
- The register is fixed on the supporting and suspension elements.
- Connect to the heating system.
How to weld a heating register
The assembly of individual structural elements together is carried out by welding the metal.This can be done in any way convenient for you. How to weld a heating register? In fact, it all depends on what kind of welding machine you have:
- electric arc (manual, semi-automatic);
- gas.
The most widespread are electric arc manual welding machines, as they are the cheapest and simplest. Such an apparatus can both connect metal parts and cut them. On large parts, you need to cut holes for pipes. This should be done near the edge, stepping back one diameter of the pipe. There will be four holes on the middle section, two on the first and outer sections.

Holes for connecting pipes
After that, on a flat horizontal surface, we lay out all the elements in one structure and make tacks at the base of the nozzles. You need to make either two tacks along the equator of the pipe, or three evenly around the entire circumference, as in the Mercedes badge. If the location of the tacks is incorrect, then the part may lead during welding. After making sure that the geometry of the register is correct, you can proceed to welding.
While working in the melting bath, it is necessary to maintain a high temperature and distribute the molten metal. The electrode must constantly move along a certain trajectory. How to weld a heating register, the simplest electrode movement trajectories:
- left - right (herringbone);
- forward - backward (with an influx).
The most important moment is the formation of the root of the seam on the tack and the exit from the tack. The process is carried out with a break, as the welder needs to change the position of the electrode. Although with proper skill you can cook without interruption. After the seam has cooled, you need to knock down the sludge with a hammer.So, it remains only to weld the ends with plugs, which must first be cut out of metal of the same thickness.
As a result, we got a blank in which holes for supply and return, as well as an air vent, will be cut in the future. The air vent, the same Mayevsky crane, removes air pockets that reduce the efficiency of the heat exchanger. You can also read more about the air in the heating system. Connecting the registers to the heating system is the last stage, after which it is possible to carry out a hydraulic test and put the equipment into operation.
In addition, this blank can be used for the manufacture of a register with an electric heating element. A hole for a heating element is cut out in the lower end, and an open-type expansion tank is installed in the upper part.
Welding technology
Purely technologically, the connection of steel elements is carried out either by electric or gas welding, where the technology is almost the same
When welding registers, please note that in serpentine structures, the joints are vertical seams, and in sectional ones, both vertical and horizontal. It is easier to cook the latter, because they are located in the plane of the table
To technology welding of horizontal seams (section + jumper) the following requirements apply:
- Tacking can be carried out at one or two points, exposing the jumper vertically. Two points are located symmetrically about the jumper installation axis.
- The joint, connected by one point of the tack, is cooked immediately, but the process must be started from the opposite side of the tack.
- The joint, connected by two tack points, is welded from the first point.
- Vertical seams in registers - connection of main pipes with plugs and 90° bends. The requirements for this type of seam are:
- If the pipe thickness is up to 3 mm, then the joint is scalded in one pass with a 2.5 mm electrode.
- If the thickness exceeds 4 mm, then welding is carried out in two passes: with a radical seam, and on top with a facing roller.
- When connecting pipes with a diameter of more than 60 mm, welding is carried out in sections along the entire perimeter of the joint.
There are general rules for welding, which indicate purely technological methods. For example, at the beginning of the seam, its end is necessarily welded, forming a “lock”. If welding is done with two seams, then the second is carried out in the opposite direction of the first.
There are several welding parameters that you need to pay attention to when carrying out welding work. This is the diameter of the electrode, which is selected depending on the thickness of the steel blanks to be welded, this is the current supplied to the electrode from the welding machine, the polarity and voltage of the welding arc
Ratio of metal thickness to electrode diameter
| Metal thickness, mm | 1—2 | 3—5 | 4—10 | 12—24 | 30—60 |
| Electrode diameter, mm | 2—3 | 3—4 | 4—5 | 5—6 | 6 or more |
The current strength is selected depending on the diameter of the selected electrode. The dependence is as follows: I=Kd, where K is the ratio of the electrode diameter.
| Electrode diameter, mm | >2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Coefficient - "K" | 25—30 | 30—35 | 35—40 | 40—45 | 50—60 |
Varieties of heating registers
Heating registers are a group of pipelines located parallel to each other and communicating with each other. They may differ in material, shape and design.
Materials for manufacturing
Most often, heating registers are made of smooth steel pipes according to GOST 3262-75 or GOST 10704-91. The use of electric-welded pipes is preferable because of the ability to withstand higher pressure. However, in practice, water and gas pipes are also quite common, which are operated no less successfully. Such heaters can easily withstand all kinds of mechanical damage and stress, as well as work with any coolant.
There are also stainless steel models. They are installed in rooms with increased requirements for aesthetics and durability. Due to the increased cost, the use of stainless steel registers is most justified in bathrooms. High resistance to corrosion and a variety of configurations of stainless steel heated towel rails allow them to be used even in the most modern bathroom interiors.
Aluminum and bimetallic registers are more efficient in terms of heat transfer. They are distinguished by lightness and aesthetics, they work perfectly in individual heating systems with well-organized water treatment. In other cases, the low quality of the coolant leads to a quick failure of the devices.
Sometimes you can find registers made of copper. Usually they are used in systems where the main wiring is copper. It is convenient to work with them, they are very nice and durable. In addition, the thermal conductivity of copper is about 8 times higher than that of steel, which makes it possible to significantly reduce the size of the heating surface. A common drawback of all devices made of non-ferrous metals - sensitivity to operating conditions - limits the scope of copper registers.
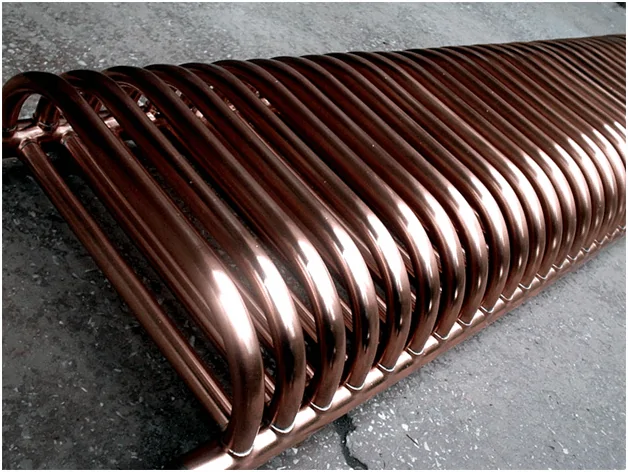

Design
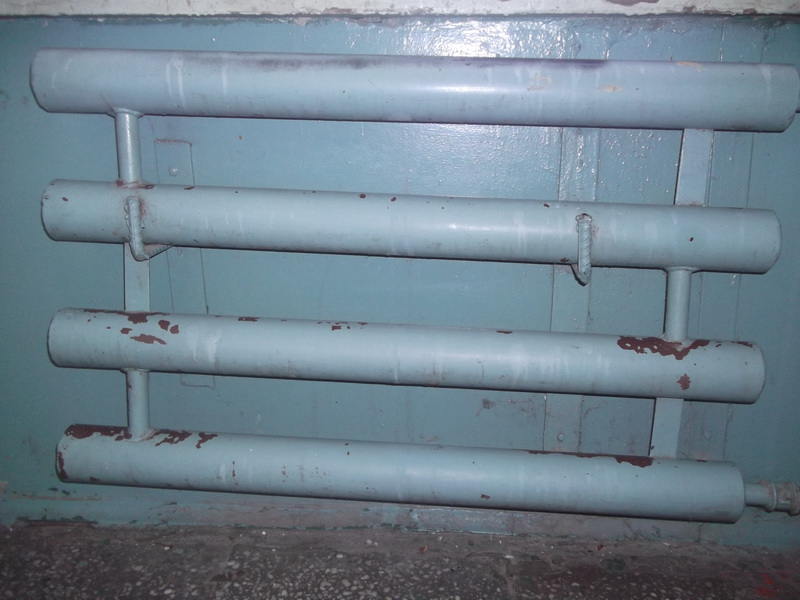
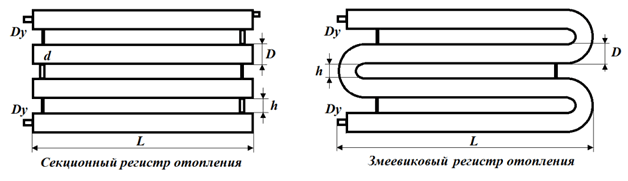
The most characteristic designs of traditional steel registers can be divided into 2 types:
- Sectional;
- Serpentine.
The first is characterized by a horizontal arrangement of pipelines and the use of vertical narrow jumpers between them. The second involves the use of straight and arcuate elements of the same diameter, which are connected by a snake by welding. When using stainless steel or non-ferrous metals, the pipes are simply bent to give the desired configuration.
 There are three options for the execution of connecting pipes:
There are three options for the execution of connecting pipes:
- Threaded;
- Flanged;
- For welding.
They can be located both on one side of the device, and on different sides. The coolant outlet is provided under the supply or diagonally from it. Sometimes there is a lower connection of highways, but in this case heat transfer is significantly reduced.
In sectional registers, 2 types of connections are distinguished depending on the way the jumpers are placed:
- "Thread";
- "Column".
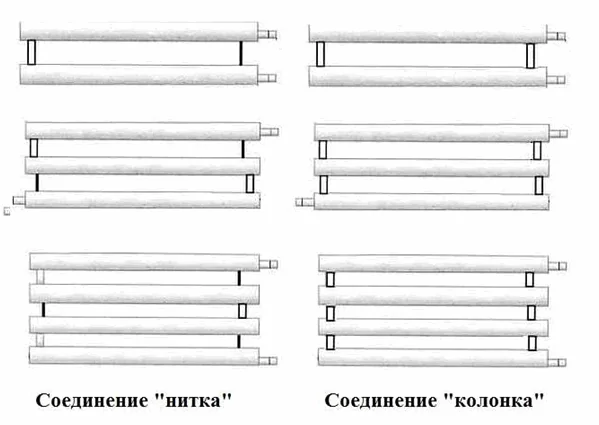
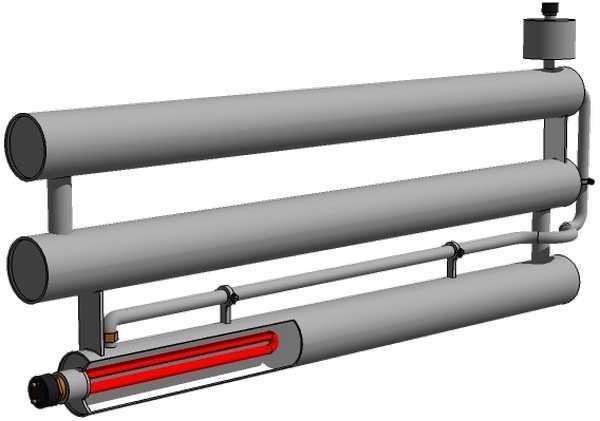
Smooth pipe registers can be used as registers of the main heating system or as separate heaters. For autonomous operation, a heating element of the required power is installed inside the device and connected to the network. As a coolant for portable electric registers made of steel, antifreeze or oil is often used, because. it does not freeze during storage or an emergency power outage.
When used separately from the general heating system, an additional expansion tank must be placed in the upper part of the device. This avoids the increase in pressure due to the increase in volume when heated. The size of the container is selected based on the ability to accommodate about 10% of the total amount of liquid in the heater.
For autonomous use of the register made of steel pipes, legs 200 - 250 mm high are welded to it. If the device is part of the heating circuit, it is not planned to move and the walls are strong enough, then a stationary mount using brackets is used. Sometimes, for very massive registers, a combined installation option is used, i.e. the device is placed on racks and additionally fixed on the wall.
Mounting methods: welding or threading?
The biggest problem when carrying out installation work for assembly and installation heating registers are welding work. Heating devices are assembled from separate parts outdoors, and then, from prepared blanks, the heating system is installed using gas welding. Welds can be replaced with threaded joints, which are inferior in strength and durability to them, but subject to the technology of work and the use of modern materials, they can ensure long-term operation of heating equipment.

The heating register in a garage or warehouse is an independent device that allows you to heat a technical room using electricity
Classic designs of heating registers
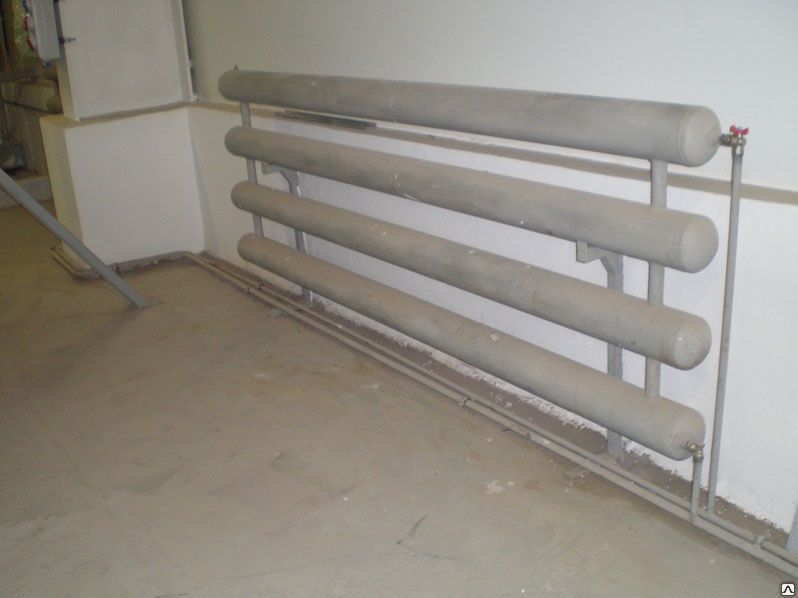
Option #1 - horizontal register
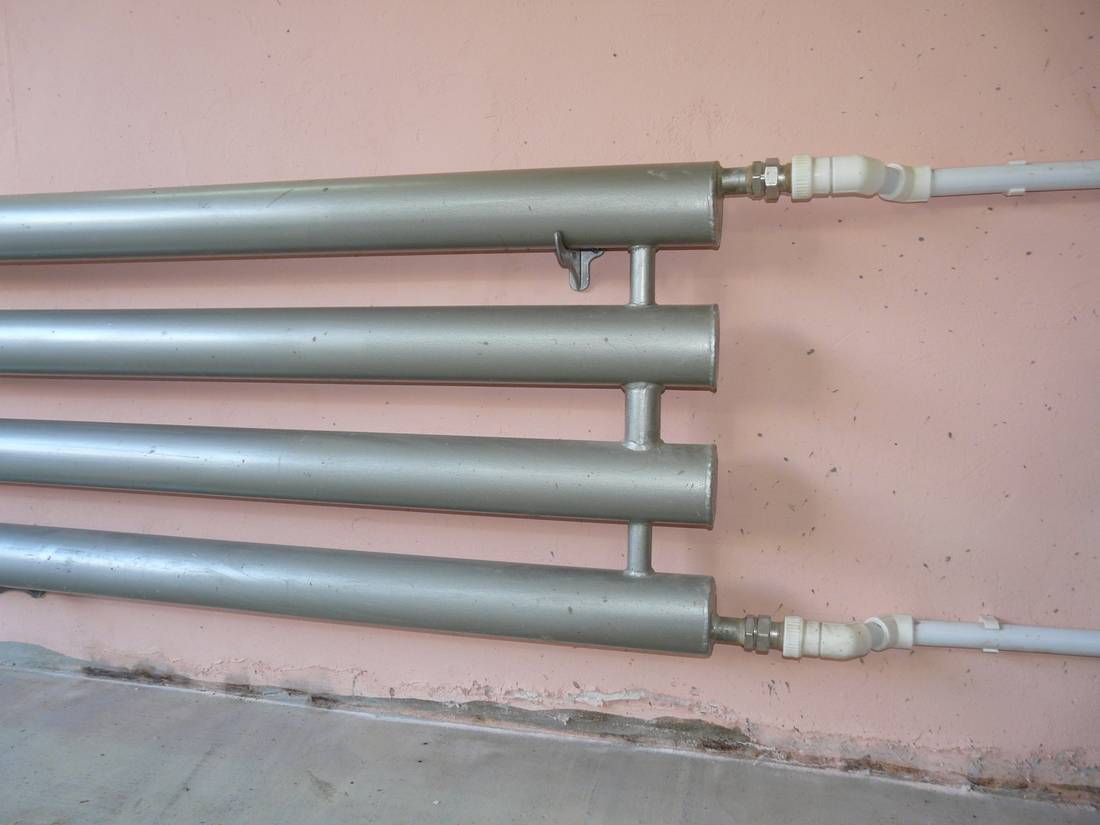
Most often, in the manufacture of a heating register, two or three parallel pipes laid in a horizontal direction are connected. The distance between adjacent sections in the register must necessarily exceed the diameter by 50 mm.Coil designs of registers are also popular, divided into several types depending on the method of connecting devices to the heating system.

Coil-type heating registers: L - length of the heater, D - pipe diameter, h - distance between pipes (more than diameter by 50 mm)
The length of the heaters is selected in accordance with the dimensions of the room or room in which it is planned to install the heating system. In addition to the listed types of designs of heating registers, there are also:
- single-pipe products;
- four-pipe devices;
- five-pipe models, etc.
The number of pipes used in one heating register depends on the area of \u200b\u200bthe heated room, the quality of the thermal insulation of the object, the presence of other sources of heat in the room, etc. Going through the possible diameters of the pipes, calculate the optimal dimensions of the products at which the optimal temperature will be maintained in the heated room.
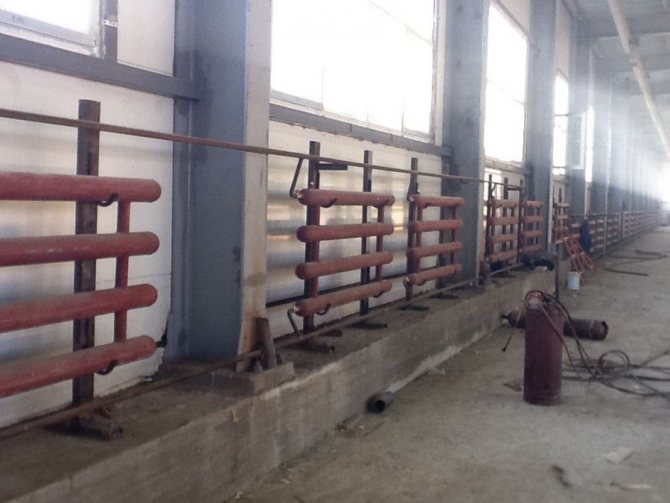
Horizontal heating registers made of smooth pipes use with bottom wiring pipeline. In this case, the products are carefully placed around the perimeter of the room closer to the floor surface. In a residential building, pipes run under the windows. In industrial premises, the location of heating devices depends on the height of the ceilings, the features of the layout of the facility and the placement of industrial equipment.

Heating registers successfully heat social facilities. Caring for such heaters is much easier than for cast iron batteries.
Option #2 - vertical registers
During the redevelopment of apartments and the expansion of their living space due to balconies and loggias, it is necessary to dismantle the batteries installed by the developer during the commissioning of the object.At the same time, the dismantled radiators are replaced by vertical heating registerswelded from a large number of round pipes of small diameter. These heaters are placed in a wall located next to the window opening.
If necessary, vertical heating registers are closed with decorative grilles, which turn an indispensable element of the heating system into an interior decor item. You can disguise the location of the "bundle" of parallel pipes using mirrors, colored glass, mosaics, wrought iron lattice, as well as by placing shelves, hangers, cabinets and other useful items of not bulky furniture.
It is possible to ensure the movement of the coolant in a vertical register installed in an autonomous heating system of a private house using a circulation pump. Horizontal registers are also used in the natural circulation of the coolant, if they are installed with a slight slope (0.05% is enough).
How to set the heating register
Each owner can install a heating register without involving a master in the work. To simplify assembly operations, it is first necessary to prepare each of the elements of the heating system according to the project.
One of the main requirements is a high-quality connection of the register with pipelines. It must withstand the maximum allowable load - 10 MPa. If docking is done by welding, you need to monitor the quality of the seams.
Registers are recommended to be placed along one wall. In this case, a minimum slope in the direction of movement of the coolant is required - up to 0.05% of the length of the device.
It is necessary to have heating registers closer to the floor surface. The larger the diameter of the main pipe, the less resistance for the circulating coolant.

The efficiency of the device depends on a large number of factors, including the heating area, which is directly proportional to the length and diameter of the pipes. The most common in everyday life are models with the following characteristics:
- Recommended pipe diameter - from 25 to 160 mm
- Connecting jumpers for sectional models - from 30 mm
- The distance between the main pipes - from 50 mm
- Maximum pressure - 10 MPa
- Material - high carbon steel
We make a register with our own hands
Anyone who knows how to work with a welding machine is able to make a heating register on their own. A simple design can be filled with antifreeze or oil.
Introductory video for making
To make a heater with your own hands, it is recommended to follow the instructions:
- It is necessary to prepare pipes of suitable diameters and cut blanks
- The inside of the pipe is checked and, if necessary, cleaned to reduce the already high resistance to the circulating coolant
- Plugs are welded from the ends, holes are drilled in some of them

Smaller diameter tubes (vertical) connect thicker ones (horizontal)
It is necessary to install taps to remove air that will accumulate from the edges
All seams are neatly and efficiently cleaned, the surface is painted with oil paints.
In portable structures, it is necessary to install a heating element with a power of 1.5 to 6 W, which will operate from a conventional outlet. If the system is powered by a heating boiler, the efficiency of the registers can be increased by installing a powerful circulation pump.
Main advantages
Among the many advantages of heating registers, it should be noted:
- It is possible to order the manufacture of heating devices according to an individual drawing of the customer
- Inside them, the role of a heat carrier can be performed not only by liquid, but also by hot steam.
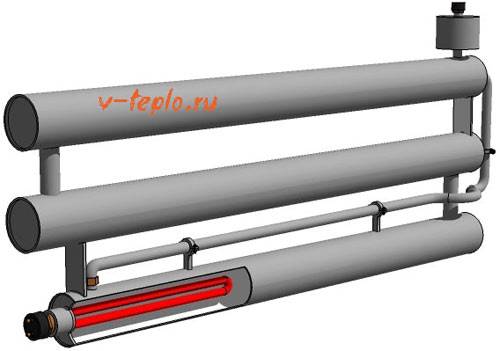
Installation does not require special equipment
They can be installed in rooms with a large area, as they are characterized by efficient heat exchange despite their compact and modest dimensions.
Acceptable cost
In custody
Of course, heating registers are replacing classic heating radiators. In private houses, they can be found in rooms with more aggressive conditions (toilet, bathroom, periodically unheated rooms, etc.). It is not difficult for a good craftsman to make such a device on his own.