- How to find out the gas consumption for heating a house
- How to reduce gas consumption
- How to calculate main gas consumption
- Calculation for liquefied gas
- How to reduce gas consumption
- Determinants of gas mixture consumption
- Advantages of gas for heating
- Determination of annual gas consumption
- Calculation of gas flow from a gas tank
- Calculation of the consumption of liquefied gas
- Methods for calculating natural gas
- For central strapping
- For autonomous heating on an area of 50, 60, 80 sq. m and 400m2
- By heat loss
- According to the power of the gas boiler
- We calculate how much gas a gas boiler consumes per hour, day and month
- Table of consumption of known models of boilers, according to their passport data
- Quick Calculator
- Method of calculation for natural gas
- We calculate the gas consumption by heat loss
- Heat loss calculation example
- Boiler power calculation
- By quadrature
- Calculation of natural gas consumption
- The boiler is connected to the main gas pipeline
- Calculation of gas consumption in formulas
- Using formulas by example
- How much gas is used on average per month, day and hour
- How to calculate the expense
How to find out the gas consumption for heating a house
How to determine the gas consumption for heating a house 100 m 2, 150 m 2, 200 m 2?
When designing a heating system, you need to know what it will cost during operation.
That is, to determine the upcoming fuel costs for heating. Otherwise, this type of heating may subsequently be unprofitable.
How to reduce gas consumption
A well-known rule: the better the house is insulated, the less fuel is spent on heating the street. Therefore, before starting the installation of the heating system, it is necessary to perform high-quality thermal insulation of the house - the roof / attic, floors, walls, replacing windows, hermetic sealing contour on the doors.
You can also save fuel by using the heating system itself. Using warm floors instead of radiators, you will get more efficient heating: since heat is distributed by convection currents from the bottom up, the lower the heater is located, the better.
In addition, the normative temperature of floors is 50 degrees, and radiators - an average of 90. Obviously, floors are more economical.
Finally, you can save gas by adjusting the heating over time. It makes no sense to actively heat the house when it is empty. It is enough to withstand a low positive temperature so that the pipes do not freeze.
Modern boiler automation (types of automation for gas heating boilers) allows remote control: you can give a command to change the mode through a mobile provider before returning home (what are Gsm modules for heating boilers). At night, the comfortable temperature is slightly lower than during the day, and so on.
How to calculate main gas consumption
The calculation of gas consumption for heating a private house depends on the power of the equipment (which determines the gas consumption in gas heating boilers). Power calculation is performed when choosing a boiler. Based on the size of the heated area.It is calculated for each room separately, focusing on the lowest average annual temperature outside.
To determine the energy consumption, the resulting figure is divided approximately in half: throughout the season, the temperature fluctuates from a serious minus to plus, gas consumption varies in the same proportions.
When calculating the power, they proceed from the ratio of kilowatts per ten squares of the heated area. Based on the foregoing, we take half of this value - 50 watts per meter per hour. At 100 meters - 5 kilowatts.
Fuel is calculated according to the formula A = Q / q * B, where:
- A - the desired amount of gas, cubic meters per hour;
- Q is the power required for heating (in our case, 5 kilowatts);
- q - minimum specific heat (depending on the brand of gas) in kilowatts. For G20 - 34.02 MJ per cube = 9.45 kilowatts;
- B - the efficiency of our boiler. Let's say 95%. The required figure is 0.95.
We substitute the numbers in the formula, we get 0.557 cubic meters per hour for 100 m 2. Accordingly, gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m 2 (7.5 kilowatts) will be 0.836 cubic meters, gas consumption for heating a house of 200 m 2 (10 kilowatts) - 1.114, etc. It remains to multiply the resulting figure by 24 - you get the average daily consumption, then by 30 - the average monthly.
Calculation for liquefied gas
The above formula is also suitable for other types of fuel. Including for liquefied gas in cylinders for a gas boiler. Its calorific value, of course, is different. We accept this figure as 46 MJ per kilogram, i.e. 12.8 kilowatts per kilogram. Let's say the boiler efficiency is 92%. We substitute the numbers in the formula, we get 0.42 kilograms per hour.
Liquefied gas is calculated in kilograms, which are then converted to liters.To calculate the gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m 2 from a gas tank, the figure obtained by the formula is divided by 0.54 (the weight of one liter of gas).
Further - as above: multiply by 24 and by 30 days. To calculate the fuel for the entire season, we multiply the average monthly figure by the number of months.
Average monthly consumption, approximately:
- consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house of 100 m 2 - about 561 liters;
- consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house of 150 m 2 - approximately 841.5;
- 200 squares - 1122 liters;
- 250 - 1402.5 etc.
A standard cylinder contains about 42 liters. We divide the amount of gas required for the season by 42, we find the number of cylinders. Then we multiply by the price of the cylinder, we get the amount needed for heating for the entire season.
How to reduce gas consumption
A well-known rule: the better the house is insulated, the less fuel is spent on heating the street. Therefore, before starting the installation of the heating system, it is necessary to perform high-quality thermal insulation of the house - the roof / attic, floors, walls, replacing windows, hermetic sealing contour on the doors.

You can also save fuel by using the heating system itself. Using warm floors instead of radiators, you will get more efficient heating: since heat is distributed by convection currents from the bottom up, the lower the heater is located, the better.
In addition, the normative temperature of floors is 50 degrees, and radiators - an average of 90. Obviously, floors are more economical.
Finally, you can save gas by adjusting the heating over time. It makes no sense to actively heat the house when it is empty. It is enough to withstand a low positive temperature so that the pipes do not freeze.
Modern boiler automation (types of automation for gas heating boilers) allows remote control: you can give a command to change the mode through a mobile provider before returning home (what are Gsm modules for heating boilers). At night, the comfortable temperature is slightly lower than during the day, and so on.
Determinants of gas mixture consumption
Home heating using natural gas is considered the most popular and convenient today. But due to the rise in the price of "blue fuel", the financial costs of homeowners have increased significantly. That is why most zealous owners today are worried about the average gas consumption for heating a house.
The main parameter in calculating the consumption of fuel consumed for heating a country house is the heat loss of the building.
It is good if the owners of the house took care of this even when designing. But in most cases, in practice, it turns out that only a small part of homeowners knows the heat loss of their buildings.
The consumption of the gas mixture directly depends on the efficiency and power of the boiler.
The following also have an impact:
- climatic conditions of the region;
- structural features of the building;
- the number and type of installed windows;
- the area and height of the ceilings in the premises;
- thermal conductivity of the applied building materials;
- quality of insulation of the outer walls of the house.
Please note that the recommended nameplate power of the installed unit demonstrates its maximum capabilities. It will always be slightly higher than the performance of the unit operating in normal mode when heating a particular building.

The power of the installed unit is calculated in strict accordance with the current regulatory requirements, taking into account all of the above factors
For example, if the nameplate power of the boiler is 15 kW, then the system will actually function effectively at a thermal power of about 12 kW. A power reserve of about 20% is recommended by specialists in case of accidents and extremely cold winters.
Therefore, when calculating fuel consumption, one should be guided precisely by real data, and not be based on maximum values calculated for short-term action in an emergency mode.
It is recommended to buy a gas unit with a power reserve of about 20% in case of emergencies and cold winters. For example, if the calculated thermal power is 10 kW, then it is recommended to purchase equipment with a nameplate power of 12 kW
Advantages of gas for heating
The undoubted and most important advantage of gas heating is its availability and cost, gas is much cheaper than electricity, fuel oil, diesel fuel and pellets. The exception is coal, but taking into account the labor costs for its delivery and the dirt after its use, the choice of most consumers remains with the main gas.
Using natural gas, you will save about 30% of your money compared to diesel fuel, electricity will cost you twice as much. When using diesel fuel, coal and when using bottled gas boilers, funds are spent on delivery, purchase of a storage container.
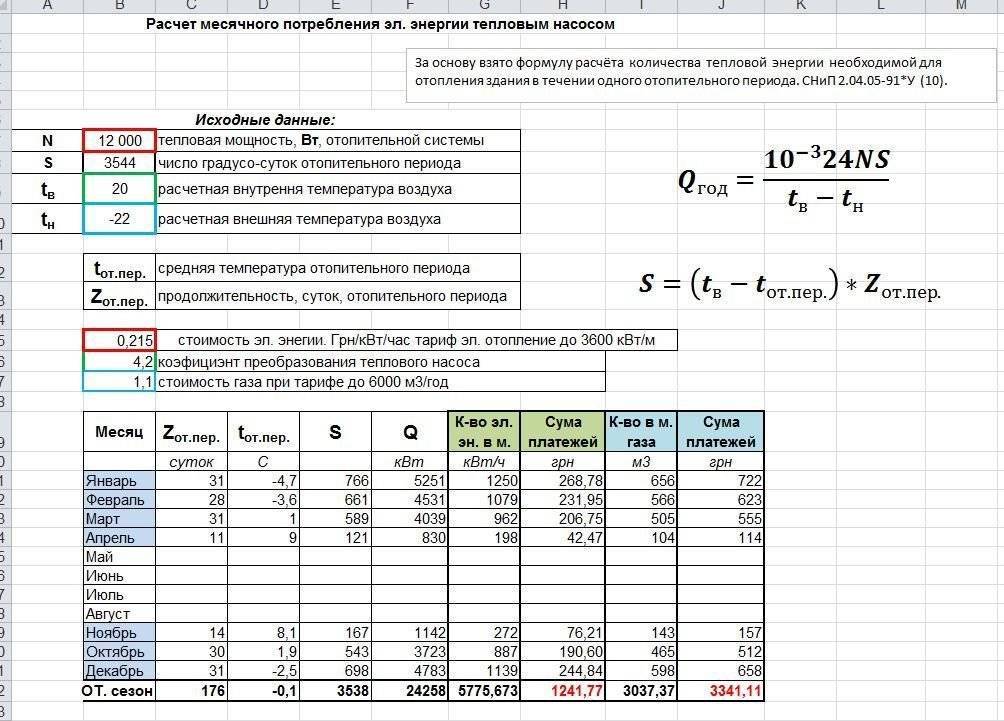
Determination of annual gas consumption
annual
gas costs Qyear,
m3/year,
for household needs is determined by the number
population of the city (district) and norms
gas consumption per person,
and for public utilities - depending on
from the throughput of the enterprise
and gas consumption rates according to the formula:
(3.1)
Where:
q
- the rate of heat consumption per one calculated
unit, MJ/year;
N
– number of accounting units;
– lower calorific value of gas on dry
mass, MJ/m3.
Table
3.1 Annual gas consumption for domestic
and household needs
| Purpose | Index | Quantity | Norm | Annual | results, |
| Quarters with gas stoves and centralized | |||||
| On the | On the | population | 2800 | 6923067,49 | |
| Hospitals | On the | 1637,131 | 367911,5 | ||
| Polyclinics | On the | 3547,117 | 5335,796 | ||
| Canteens | On the | 14938822 | 1705670,755 | ||
| TOTAL: | 9348138,911 | ||||
| Quarters (2nd | |||||
| On the | On the | population | 8000 | 31787588,63 | |
| Hospitals | On the | 2630,9376 | 591249,1485 | ||
| Polyclinics | On the | 5700,3648 | 8574,702 | ||
| Canteens | On the | 24007305 | 2741083,502 | ||
| TOTAL: | 36717875,41 | ||||
| annual | |||||
| Baths | On the | 3698992,9 | 2681524,637 | ||
| Laundries | On the | 25964,085 | 8846452,913 | ||
| bakery | On the | 90874,298 | 8975855,815 |
annual
gas costs for technological and
energy needs of industrial,
household and agricultural
enterprises are determined by specific
fuel consumption standards, the volume of produced
products and the value of the actual
fuel consumption. Gas consumption
determined separately for each
enterprises.
Annual
gas consumption for the boiler room is added up
from gas expenses for heating, hot
water supply and forced ventilation
buildings throughout the area.
Annual
gas consumption for heating
, m3/year,
residential and public buildings are calculated
according to the formula:
(3.1)
Where:
a
= 1.17 - correction factor is accepted
depending on the outside temperature
air;
qa–
specific heating characteristic
buildings are accepted 1.26-1.67 for residential
buildings depending on the number of storeys,
kJ/(m3×h×aboutFROM);
tin
– temperature
internal air, C;
tcpfrom
– average outdoor temperature
air during the heating season, °С;
Pfrom
\u003d 120 - the duration of the heating
period, days ;
VH–
external building volume of heated
buildings, m3;
–inferior
calorific value of gas on a dry basis,
kJ/m3;
ή
– efficiency of the heat-using plant,
0.8-0.9 is accepted for heating
boiler room.
Outer
construction volume of heated buildings
can be determined
how
(3.2)
Where:
V–
volume of residential buildings per person, accepted
equal to 60 m3/person,
if there is no other data;
Np—
number of inhabitants in the region, people
Table
3.2 Correction factor values
a
temperature dependent
outdoor
air
| ,°C | -10 | -15 | -20 | -25 | -30 | -35 | -40 | -50 |
| a | 1,45 | 1,20 | 1,17 | 1,08 | 1,00 | 0,95 | 0,85 | 0,82 |
Annual
gas consumption for centralized hot
water supply (DHW)
,
m3/year,
boiler rooms are determined by the formula:
(3.3)
Where:
qDHW
\u003d 1050 kJ / (person-h) - an aggregated indicator
average hourly heat consumption for domestic hot water
1 person;
N
– number
residents using the centralized
DHW;
tchl,txs–
cold water temperature in summer and
winter period, °С, accepted tchl
\u003d 15 ° С,tx=5
°C;
–inferior
calorific value of gas on a dry basis,
kJ/m3;
–
reduction factor
hot water consumption in summer
depending on the climate zone
taken from 0.8 to 1.
m3/year
Annual
gas consumption for forced ventilation
public buildings
,
m3/year,
can be determined from the expression
(3.4)
Where:
qin–
specific ventilation characteristic
building, 0.837 kJ/(m3×h×°С);
fcp.in.–
average outdoor temperature
for calculation of ventilation, °С, (permissible
accepttcp
in.=tcpom).
By
area annual gas consumption consumed
low pressure networks
,
m3/year,
equals
(3.5)
m3/year
Annual
gas consumption by large household
consumers
, m3/year,
equals:
(3.6)
m3/year
Total
for utilities and household
needs spent
,
m3/year,
gas
(3.7)
m3/year
General
annual gas consumption by the region
,
m3/year,
without industrial consumers is:
(3.8)
m3/year.
Calculation of gas flow from a gas tank
The calculation of the consumption for heating of the mixture from the gas storage used in the heat supply system of the house has its own characteristics and differs from the calculation of the consumption of the main natural gas.
The predicted volume of gas consumption is calculated by the formula:
V = Q / (q × η), where
V is the calculated volume of LPG, measured in m³/h;
Q is the calculated heat loss;
q - the smallest specific value of the heat of combustion of gas or its calorie content. For propane-butane, this value is 46 MJ/kg or 12.8 kW/kg;
η - efficiency of the gas supply system, expressed in absolute value to unity (efficiency / 100).Depending on the characteristics of the gas boiler, the efficiency can range from 86% for the simplest to 96% for high-tech condensing units. Accordingly, the value of η may be from 0.86 to 0.96.
Assume that the heating system is planned to be equipped with a modern condensing boiler with an efficiency of 96%.
Substituting in the original formula the values \u200b\u200baccepted for calculation, we obtain the following averaged volume of gas consumed for heating:
V \u003d 9.6 / (12.8 × 0.96) \u003d 9.6 / 12.288 \u003d 0.78 kg / h.
Since a liter is considered to be a LPG filling unit, it is necessary to express the volume of propane-butane in this unit of measurement. To calculate the number of liters in the mass of a liquefied hydrocarbon mixture, kilograms must be divided by density.
The table shows the values of the test density of liquefied gas (in t / m3), at various average daily air temperatures and in accordance with the ratio of propane to butane expressed as a percentage
The physics of the transition of LPG from liquid to vapor (working) state is as follows: propane boils at minus 40 ° C and above, butane - from 3 ° C with a minus sign. Accordingly, a 50/50 mixture will begin to pass into the gaseous phase at a temperature of minus 20 °C.
For mid-latitudes and a gas tank buried in the ground, such proportions are sufficient. But, in order to protect yourself from unnecessary troubles, it will be optimal in winter conditions to use a mixture with at least 70% propane content - “winter gas”.
Taking for the calculated density of LPG equal to 0.572 t / m3 - a mixture of propane / butane 70/30 at a temperature of -20 ° C), it is easy to calculate the gas consumption in liters: 0.78 / 0.572 \u003d 1.36 l / h.
Daily consumption with such a selection of gas in the house will be: 1.36 × 24 ≈ 32.6 liters, during the month - 32.6 × 30 = 978 liters. Since the obtained value is calculated for the coldest period, then, adjusted for weather conditions, it can be divided in half: 978/2 \u003d 489 liters, on average per month.
The duration of the heating season is calculated from the moment when the average temperature during the day outside does not exceed +8 degrees Celsius for 5 days. This period ends in spring, with stable warming.
In the area that we took as an example (Moscow region), such a period averages 214 days.
Gas consumption for heating during the year, when calculated, will be: 32.6 / 2 × 214 ≈ 3488 l.
Calculation of the consumption of liquefied gas
Many boilers can run on LPG. How beneficial is it? What will be the consumption of liquefied gas for heating? All this can also be calculated. The technique is the same: you need to know either heat loss or boiler power. Next, we translate the required amount into liters (a unit of measurement of liquefied gas), and if desired, we consider the number of required cylinders.
Let's look at the calculation with an example. Let the boiler power be 18 kW, respectively, the average heat demand is 9 kW / h. When burning 1 kg of liquefied gas, we get 12.5 kW of heat. So, to get 9 kW, you need 0.72 kg (9 kW / 12.5 kW = 0.72 kg).
Next, we consider:
- per day: 0.72 kg * 24 hours = 17.28 kg;
- per month 17.28 kg * 30 days = 518.4 kg.
Let's add a correction for the efficiency of the boiler. It is necessary to look in each specific case, but let's take 90%, that is, add another 10%, it turns out that the monthly consumption will be 570.24 kg.

Liquefied gas is one of the heating options
To calculate the number of cylinders, we divide this figure by 21.2 kg (this is how much, on average, there is a kg of gas in a 50 liter cylinder).
The mass of liquefied gas in various cylinders
In total, this boiler will require 27 cylinders of liquefied gas. And consider the cost yourself - prices vary by region. But don't forget about shipping costs. By the way, they can be reduced by making a gas tank - a sealed container for storing liquefied gas, which can be refueled once a month or less - depending on the storage volume and needs.
And again, do not forget that this is only an approximate figure. In cold months, gas consumption for heating will be more, in warm months - much less.
P.S. If it is more convenient for you to calculate the consumption in liters:
- 1 liter of liquefied gas weighs approximately 0.55 kg and, when burned, gives approximately 6500 kW of heat;
- There are about 42 liters of gas in a 50 liter bottle.
Methods for calculating natural gas
There are four types of gas flow calculations: by heater power, heat loss or type of heating system.
For central strapping

The formula is quite simple:
V = N / (Q * J), where:
- N is the power required for the premises.
- Q is the heat of combustion of the fuel.
- J is the efficiency of the heater.
Q for G20 gas is taken equal to 34.02 MJ per cubic meter, for G30 - 45.65. And there is also G31, which has slightly better characteristics than G30.
Attention! The efficiency depends on the specific device and other factors, for example, the presence of insulation
For autonomous heating on an area of 50, 60, 80 sq. m and 400m2
Three indicators take part in the calculations: the area of \u200b\u200bthe building, the recommended power of the boiler and its efficiency. Any values in Joules are converted to Watts: 1 W = 3.6 kJ. The calorific value of gas is 9.45 kW. Recommended power - the amount of energy needed to heat the house during the heating season.

Since heating is not required in summer, only half the value is used. Suppose you need 10 kW: in the calculation we use five: V \u003d 5 / (9.45 * 0.9) \u003d 0.588 cubic meters per hour.
Thus, 14.11 m3 will be needed per day. The heating season lasts about 7 months: from October to April. In 213 days, 3,006 cubic meters of natural gas will be consumed.
This calculation is made for a house with a total area of 100 square meters. Depending on the actual value, the calculation changes:
- Building 50 squares will require half the fuel, and 60 - 40%.
- A house with an area of 80 m2 will take 2405 cubic meters of gas, and a 400 m2 house will take a little more than 12 thousand.
The calculations are approximate, since they do not take into account various factors. For example, some days are warmer and require less fuel, while others are the opposite. The result also depends on the gas used. In the calculation presented, G 20 is used.
By heat loss
You need to know the amount of heat that leaves the room per hour. Let's assume the value is 16 kWh. For calculations, take 70% of the indicator. Thus, the house needs 11 kWh, 264 per day and 7920 per month. To convert to cubic meters, it is enough to divide the value by 9.3 kW / m3 - the specific heat of combustion of natural gas.
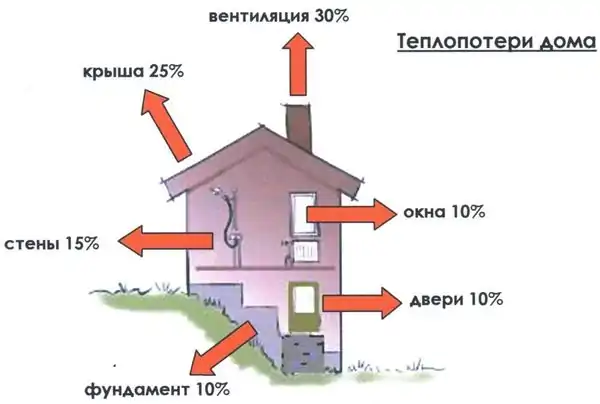
Photo 1. Heat loss at home through its various parts. They affect the gas consumption of the heating boiler.
And you also need to correct for efficiency by dividing the number by the passport indicator. In the proposed example, the gas consumption for one month will be 864 cubic meters. This is an average value, which is enough to multiply by the number of months in the heating season.
According to the power of the gas boiler
The simplest calculation among those presented. It is enough to find out in the passport the power of the heater. The indicator is divided in half and proceed to the calculations. This is related to the actual consumption: the heating season lasts 7 full months out of 12. In especially cold winters, much more heat will be required.
Let's say that the boiler creates 24 kW of energy. Half - 12 kW. We take the need for heat as this value. To determine the fuel consumption, this indicator is divided by the specific heat of combustion of the fuel. For natural gas - 9.3 kW / m3. It turns out that about 1.3 cubic meters of fuel is needed per hour, 31.2 per day, and 936 per month. The resulting value is divided by the efficiency factor and the actual result is obtained.
Photo 2. Consumption of gas consumption per hour and per season, depending on the power of the heating boiler.
We calculate how much gas a gas boiler consumes per hour, day and month
In the design of individual heating systems for private houses, 2 main indicators are used: the total area of \u200b\u200bthe house and the power of the heating equipment. With simple averaged calculations, it is considered that for heating every 10 m2 of area, 1 kW of thermal power + 15-20% of the power reserve is sufficient.
How to calculate the required boiler outputIndividual calculation, formula and correction factors
It is known that the calorific value of natural gas is 9.3-10 kW per m3, hence it follows that about 0.1-0.108 m3 of natural gas is needed per 1 kW of thermal power of a gas boiler. At the time of writing, the cost of 1 m3 of main gas in the Moscow region is 5.6 rubles / m3 or 0.52-0.56 rubles for each kW of boiler heat output.
But this method can be used if the passport data of the boiler are unknown, because the characteristics of almost any boiler indicate the gas consumption during its continuous operation at maximum power.
For example, the well-known floor-standing single-circuit gas boiler Protherm Volk 16 KSO (16 kW power), running on natural gas, consumes 1.9 m3 / hour.
- Per day - 24 (hours) * 1.9 (m3 / hour) = 45.6 m3. In value terms - 45.5 (m3) * 5.6 (tariff for MO, rubles) = 254.8 rubles / day.
- Per month - 30 (days) * 45.6 (daily consumption, m3) = 1,368 m3. In value terms - 1,368 (cubic meters) * 5.6 (tariff, rubles) = 7,660.8 rubles / month.
- For the heating season (suppose, from October 15 to March 31) - 136 (days) * 45.6 (m3) = 6,201.6 cubic meters. In value terms - 6,201.6 * 5.6 = 34,728.9 rubles / season.
That is, in practice, depending on the conditions and heating mode, the same Protherm Volk 16 KSO consumes 700-950 cubic meters of gas per month, which is about 3,920-5,320 rubles / month. It is impossible to accurately determine the gas consumption by the calculation method!
To obtain accurate values, metering devices (gas meters) are used, because the gas consumption in gas heating boilers depends on the correctly selected power of the heating equipment and the technology of the model, the temperature preferred by the owner, the arrangement of the heating system, the average temperature in the region for the heating season, and many other factors , individual for each private house.
Table of consumption of known models of boilers, according to their passport data
| Model | power, kWt | Max consumption of natural gas, cubic meters m/hour |
| Lemax Premium-10 | 10 | 0,6 |
| ATON Atmo 10EBM | 10 | 1,2 |
| Baxi SLIM 1.150i 3E | 15 | 1,74 |
| Protherm Bear 20 PLO | 17 | 2 |
| De Dietrich DTG X 23 N | 23 | 3,15 |
| Bosch Gas 2500 F 30 | 26 | 2,85 |
| Viessmann Vitogas 100-F 29 | 29 | 3,39 |
| Navien GST 35KN | 35 | 4 |
| Vaillant ecoVIT VKK INT 366/4 | 34 | 3,7 |
| Buderus Logano G234-60 | 60 | 6,57 |
Quick Calculator
Recall that the calculator uses the same principles as in the example above, the actual consumption data depends on the model and operating conditions of the heating equipment and can only be 50-80% of the data calculated with the condition that the boiler operates continuously and at full capacity .
Method of calculation for natural gas
The approximate gas consumption for heating is calculated based on half the capacity of the installed boiler. The thing is that when determining the power of a gas boiler, the lowest temperature is laid. This is understandable - even when it is very cold outside, the house should be warm.
You can calculate the gas consumption for heating yourself
But it is completely wrong to calculate the gas consumption for heating according to this maximum figure - after all, in general, the temperature is much higher, which means that much less fuel is burned.Therefore, it is customary to consider the average fuel consumption for heating - about 50% of the heat loss or boiler power.
We calculate the gas consumption by heat loss
If there is no boiler yet, and you estimate the cost of heating in different ways, you can calculate from the total heat loss of the building. They are most likely familiar to you. The methodology here is as follows: they take 50% of the total heat loss, add 10% to provide hot water supply and 10% to heat outflow during ventilation. As a result, we get the average consumption in kilowatts per hour.
Then you can find out the fuel consumption per day (multiply by 24 hours), per month (by 30 days), if desired - for the entire heating season (multiply by the number of months during which the heating works). All these figures can be converted into cubic meters (knowing the specific heat of combustion of gas), and then multiply cubic meters by the price of gas and, thus, find out the cost of heating.
| The name of the crowd | unit of measurement | Specific heat of combustion in kcal | Specific heating value in kW | Specific calorific value in MJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural gas | 1 m 3 | 8000 kcal | 9.2 kW | 33.5 MJ |
| Liquefied gas | 1 kg | 10800 kcal | 12.5 kW | 45.2 MJ |
| Hard coal (W=10%) | 1 kg | 6450 kcal | 7.5 kW | 27 MJ |
| wood pellet | 1 kg | 4100 kcal | 4.7 kW | 17.17 MJ |
| Dried wood (W=20%) | 1 kg | 3400 kcal | 3.9 kW | 14.24 MJ |
Heat loss calculation example
Let the heat loss of the house be 16 kW / h. Let's start counting:
- average heat demand per hour - 8 kW / h + 1.6 kW / h + 1.6 kW / h = 11.2 kW / h;
- per day - 11.2 kW * 24 hours = 268.8 kW;
-
per month - 268.8 kW * 30 days = 8064 kW.
Convert to cubic meters. If we use natural gas, we divide the gas consumption for heating per hour: 11.2 kW / h / 9.3 kW = 1.2 m3 / h.In calculations, the figure 9.3 kW is the specific heat capacity of natural gas combustion (available in the table).
Since the boiler has not 100% efficiency, but 88-92%, you will have to make more adjustments for this - add about 10% of the figure obtained. In total, we get the gas consumption for heating per hour - 1.32 cubic meters per hour. You can then calculate:
- consumption per day: 1.32 m3 * 24 hours = 28.8 m3/day
- demand per month: 28.8 m3 / day * 30 days = 864 m3 / month.
The average consumption for the heating season depends on its duration - we multiply it by the number of months that the heating season lasts.
This calculation is approximate. In some month, gas consumption will be much less, in the coldest - more, but on average the figure will be about the same.
Boiler power calculation
Calculations will be a little easier if there is a calculated boiler capacity - all the necessary reserves (for hot water supply and ventilation) are already taken into account. Therefore, we simply take 50% of the calculated capacity and then calculate the consumption per day, month, per season.
For example, the design capacity of the boiler is 24 kW. To calculate the gas consumption for heating, we take half: 12 k / W. This will be the average need for heat per hour. To determine the fuel consumption per hour, we divide by the calorific value, we get 12 kW / h / 9.3 k / W = 1.3 m3. Further, everything is considered as in the example above:
- per day: 12 kW / h * 24 hours = 288 kW in terms of the amount of gas - 1.3 m3 * 24 = 31.2 m3
-
per month: 288 kW * 30 days = 8640 m3, consumption in cubic meters 31.2 m3 * 30 = 936 m3.
Next, we add 10% for the imperfection of the boiler, we get that for this case the flow rate will be slightly more than 1000 cubic meters per month (1029.3 cubic meters).As you can see, in this case everything is even simpler - fewer numbers, but the principle is the same.
By quadrature
Even more approximate calculations can be obtained by the quadrature of the house. There are two ways:
- It can be calculated according to SNiP standards - for heating one square meter in Central Russia, an average of 80 W / m2 is required. This figure can be applied if your house is built according to all requirements and has good insulation.
- You can estimate according to the average data:
- with good house insulation, 2.5-3 cubic meters / m2 are required;
-
with average insulation, gas consumption is 4-5 cubic meters / m2.
Each owner can assess the degree of insulation of his house, respectively, you can estimate what gas consumption will be in this case. For example, for a house of 100 sq. m. with average insulation, 400-500 cubic meters of gas will be required for heating, 600-750 cubic meters per month for a house of 150 square meters, 800-100 cubic meters of blue fuel for heating a house of 200 m2. All this is very approximate, but the figures are based on many factual data.
Calculation of natural gas consumption
At first glance, the calculation method looks quite simple - it is enough to take half the power of the gas boiler, and the resulting value will give an answer to the question, what is the gas flow rate of the gas boiler. This technique is based on the fact that the power of any gas equipment is determined at the lowest temperature. This is not without meaning, because even in the coldest weather, the house must be fully heated.
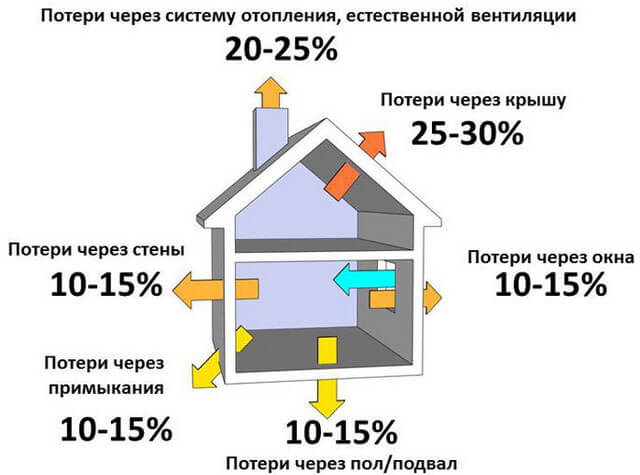
Another thing is that often the temperature is above the calculated mark most of the time, and the gas consumption for heating the house is significantly less. That is why, with a simplified calculation of fuel consumption, half of the boiler power is simply subtracted.
The boiler is connected to the main gas pipeline
Let us analyze the calculation algorithm that allows us to accurately determine the consumption of blue fuel for a unit installed in a house or apartment with a connection to centralized gas supply networks.
Calculation of gas consumption in formulas
For a more accurate calculation, the power of gas heating units is calculated by the formula:
Boiler power \u003d Qt * K,
where Qt is the planned heat loss, kW; K - correction factor (from 1.15 to 1.2).
The planned heat loss (in W), in turn, is calculated as follows:
Qt = S * ∆t * k / R,
where
S is the total area of enclosing surfaces, sq. m; ∆t — indoor/outdoor temperature difference, °C; k is the scattering coefficient; R is the value of the thermal resistance of the material, m2•°C/W.
Dissipation factor value:
wooden structure, metal structure (3.0 - 4.0);
one-brick masonry, old windows and roofing (2.0 - 2.9);
double brickwork, standard roof, doors, windows (1.1 - 1.9);
walls, roof, floor with insulation, double glazing (0.6 - 1.0).
The formula for calculating the maximum hourly gas consumption based on the received power:
Gas volume = Qmax / (Qр * ŋ),
where Qmax is the power of the equipment, kcal/h; Qр is the calorific value of natural gas (8000 kcal/m3); ŋ - boiler efficiency.
In order to determine the consumption of gaseous fuel, you just need to multiply the data, some of which must be taken from the data sheet of your boiler, some from building guides published on the Internet.
Using formulas by example
Suppose we have a building with a total area of 100 square meters. The height of the building is 5 m, the width is 10 m, the length is 10 m, twelve windows are 1.5 x 1.4 m in size.Internal/external temperature: 20°C/-15°C.
We consider the area of \u200b\u200benclosing surfaces:
- Floor 10 * 10 = 100 sq. m
- Roof: 10 * 10 = 100 sq. m
- Windows: 1.5*1.4*12pcs = 25.2 sq. m
- Walls: (10 + 10 + 10 + 10) * 5 = 200 sq. m Behind the windows: 200 - 25.2 = 174.8 sq. m
The value of thermal resistance of materials (formula):
R = d / λ, where d is the thickness of the material, m λ is the thermal conductivity of the material, W/.
Calculate R:
- For the floor (concrete screed 8 cm + mineral wool 150 kg / m3 x 10 cm) R (floor) \u003d 0.08 / 1.75 + 0.1 / 0.037 \u003d 0.14 + 2.7 \u003d 2.84 (m2• °C/W)
- For roofing (12 cm mineral wool sandwich panels) R (roofing) = 0.12 / 0.037 = 3.24 (m2•°C/W)
- For windows (double glazing) R (windows) = 0.49 (m2•°C/W)
- For walls (12 cm mineral wool sandwich panels) R (walls) = 0.12 / 0.037 = 3.24 (m2•°C/W)
The values of thermal conductivity coefficients for different materials were taken from the handbook.
Get in the habit of regularly taking meter readings, writing them down and doing a comparative analysis, taking into account the intensity of the boiler, weather conditions, etc. Operate the boiler in different modes, look for the best load option
Now let's calculate the heat loss.
Q (floor) \u003d 100 m2 * 20 ° C * 1 / 2.84 (m2 * K) / W \u003d 704.2 W \u003d 0.8 kW Q (roof) \u003d 100 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 3, 24 (m2 * K) / W \u003d 1080.25 W \u003d 8.0 kW Q (windows) \u003d 25.2 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 0.49 (m2 * K) / W \u003d 1800 W \u003d 6, 3 kW Q (walls) \u003d 174.8 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 3.24 (m2 * K) / W \u003d 1888.3 W \u003d 5.5 kW
Heat loss of enclosing structures:
Q (total) \u003d 704.2 + 1080.25 + 1800 + 1888.3 \u003d 5472.75 W / h
You can also add heat loss for ventilation. To heat 1 m3 of air from -15°С to +20°С, 15.5 W of thermal energy is required.A person consumes approximately 9 liters of air per minute (0.54 cubic meters per hour).
Suppose there are 6 people in our house. They need 0.54 * 6 = 3.24 cu. m of air per hour. We consider the heat loss for ventilation: 15.5 * 3.24 \u003d 50.22 W.
And the total heat loss: 5472.75 W / h + 50.22 W = 5522.97 W = 5.53 kW.
After conducting a heat engineering calculation, we first calculate the boiler power, and then the gas consumption per hour in a gas boiler in cubic meters:
Boiler power \u003d 5.53 * 1.2 \u003d 6.64 kW (round up to 7 kW).
To use the formula for calculating gas consumption, we translate the resulting power indicator from kilowatts to kilocalories: 7 kW = 6018.9 kcal. And let's take the boiler efficiency = 92% (manufacturers of modern gas floor boilers declare this indicator within 92 - 98%).
Maximum hourly gas consumption = 6018.9 / (8000 * 0.92) = 0.82 m3/h.
How much gas is used on average per month, day and hour
Consumption per day is determined by the formula: Rsut = Rsf × 24.
In the example above, consumption per day would be 1.58 x 24 = 37.92 cubic meters. m.
You can go the other way. A properly selected boiler operates at a nominal capacity of 17-18 hours per day. Let it be decided to install a Protherm Medved 20 PLO heater at 17 kW with a heat loss of 15 kW. For him, the passport gas consumption is 2 cubic meters. m/h During the day, he will spend 34-36 cubic meters. m of fuel, which roughly corresponds to the result obtained above.
Monthly consumption will be: Rm = Rsut × 30 × 0.9, where 30 is the number of days; 0.9 is a reduction factor, taking into account that the lowest temperature lasts an average of 1-2 weeks.
In the above example, Rm = 37.92 × 30 × 0.9 = 1023.84 cu. m.
Consumption for the heating season lasting 7 months: Rsez = Rsut × 30.5 × 7 × 0.6.The latter coefficient is used for the reasons that on average the heater operates at 50-70% of the power required in the coldest period of the year.
For the example above: Pcez = 37.92 x 30.5 x 7 x 0.6 = 4857.6 cu. m.
How to calculate the expense
The characteristics of the device indicate two figures: the maximum consumption of liquefied gas and main. The consumption of liquefied gas in gas heating boilers is expressed in kilograms per hour, main - in cubic meters per hour.
Multiplying the figure by 24 hours and by 30 days, we get the monthly expense. We multiply it by the tariff rate in our region, we get the amount that will have to be spent on heating per month. In fact, the boiler operates at full capacity for only half of this time, i.e. The resulting amount must be divided by two.
For liquefied gas, we divide the monthly consumption in half, then by the amount of gas in the cylinder (about 21 kg), we get the number of cylinders and multiply by the price of refueling.
To get the gas consumption per year for a single-circuit boiler (), you need to multiply the monthly figure by the number of months. The duration of the heating season depends on the climatic features of your area.
For double-circuit boilers, 25 percent must be added to the obtained value (.