- The boiler is connected to the main gas pipeline
- Calculation of gas consumption in formulas
- Using formulas by example
- Calculation of gas consumption
- Heat Load and Gas Flow Formulas
- Calculation of the planned maximum hourly gas consumption
- Varieties of gas
- Liquefied gas
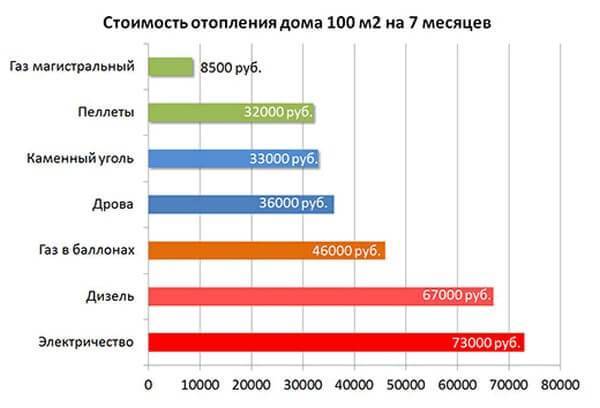
- Calculation of gas consumption for heating a living space of 100 m²
- Volume flow
- The value of pressure and velocity in the flow
- Types of gas, liquid and steam flow
- Calculation of the consumption of liquefied gas
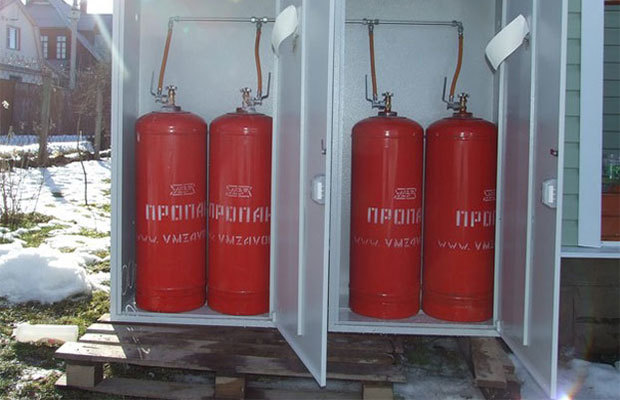
The boiler is connected to the main gas pipeline
Let us analyze the calculation algorithm that allows us to accurately determine the consumption of blue fuel for a unit installed in a house or apartment with a connection to centralized gas supply networks.
Calculation of gas consumption in formulas
For a more accurate calculation, the power of gas heating units is calculated by the formula:
Boiler power = Qt * TO,
where Qt — planned heat losses, kW; K - correction factor (from 1.15 to 1.2).
The planned heat loss (in W), in turn, is calculated as follows:
Qt = S * ∆t * k / R,
where
S is the total area of enclosing surfaces, sq. m; ∆t — indoor/outdoor temperature difference, °C; k is the scattering coefficient; R is the value of the thermal resistance of the material, m2•°C/W.
Dissipation factor value:
- wooden structure, metal structure (3.0 - 4.0);
- one-brick masonry, old windows and roofing (2.0 - 2.9);
- double brickwork, standard roof, doors, windows (1.1 - 1.9);
- walls, roof, floor with insulation, double glazing (0.6 - 1.0).
The formula for calculating the maximum hourly gas consumption based on the received power:
Gas volume = Qmax / (Qр * ŋ),
where Qmax — equipment power, kcal/h; QR — calorific value of natural gas (8000 kcal/m3); ŋ - boiler efficiency.
In order to determine the consumption of gaseous fuel, you just need to multiply the data, some of which must be taken from the data sheet of your boiler, some from building guides published on the Internet.
Using formulas by example
Suppose we have a building with a total area of 100 square meters. Building height - 5 m, width - 10 m, length - 10 m, twelve windows measuring 1.5 x 1.4 m. Indoor / outdoor temperature: 20 ° C / - 15 °C.
We consider the area of \u200b\u200benclosing surfaces:
- Floor 10 * 10 = 100 sq. m
- Roof: 10 * 10 = 100 sq. m
- Windows: 1.5*1.4*12pcs = 25.2 sq. m
- Walls: (10 + 10 + 10 + 10) * 5 = 200 sq. m Behind the windows: 200 - 25.2 = 174.8 sq. m
The value of thermal resistance of materials (formula):
R = d / λ, where d is the thickness of the material, m λ is the thermal conductivity of the material, W/.
Calculate R:
- For the floor (concrete screed 8 cm + mineral wool 150 kg / m3 x 10 cm) R (floor) \u003d 0.08 / 1.75 + 0.1 / 0.037 \u003d 0.14 + 2.7 \u003d 2.84 (m2• °C/W)
- For roofing (12 cm mineral wool sandwich panels) R (roofing) = 0.12 / 0.037 = 3.24 (m2•°C/W)
- For windows (double glazing) R (windows) = 0.49 (m2•°C/W)
- For walls (12 cm mineral wool sandwich panels) R (walls) = 0.12 / 0.037 = 3.24 (m2•°C/W)
The values of thermal conductivity coefficients for different materials were taken from the handbook.
 Get in the habit of regularly taking meter readings, writing them down and doing a comparative analysis, taking into account the intensity of the boiler, weather conditions, etc. Operate the boiler in different modes, look for the best load option
Get in the habit of regularly taking meter readings, writing them down and doing a comparative analysis, taking into account the intensity of the boiler, weather conditions, etc. Operate the boiler in different modes, look for the best load option
Now let's calculate the heat loss.
Q (floor) \u003d 100 m2 * 20 ° C * 1 / 2.84 (m2 * K) / W \u003d 704.2 W \u003d 0.8 kW Q (roof) \u003d 100 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 3, 24 (m2 * K) / W \u003d 1080.25 W \u003d 8.0 kW Q (windows) \u003d 25.2 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 0.49 (m2 * K) / W \u003d 1800 W \u003d 6, 3 kW Q (walls) \u003d 174.8 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 3.24 (m2 * K) / W \u003d 1888.3 W \u003d 5.5 kW
Heat loss of enclosing structures:
Q (total) \u003d 704.2 + 1080.25 + 1800 + 1888.3 \u003d 5472.75 W / h
You can also add heat loss for ventilation. To heat 1 m3 of air from -15°С to +20°С, 15.5 W of thermal energy is required. A person consumes approximately 9 liters of air per minute (0.54 cubic meters per hour).
Suppose there are 6 people in our house. They need 0.54 * 6 = 3.24 cu. m of air per hour. We consider the heat loss for ventilation: 15.5 * 3.24 \u003d 50.22 W.
And the total heat loss: 5472.75 W / h + 50.22 W = 5522.97 W = 5.53 kW.
After conducting a heat engineering calculation, we first calculate the boiler power, and then the gas consumption per hour in a gas boiler in cubic meters:
Boiler power \u003d 5.53 * 1.2 \u003d 6.64 kW (round up to 7 kW).
To use the formula for calculating gas consumption, we translate the resulting power indicator from kilowatts to kilocalories: 7 kW = 6018.9 kcal. And let's take the boiler efficiency = 92% (manufacturers of modern gas floor boilers declare this indicator within 92 - 98%).
Maximum hourly gas consumption = 6018.9 / (8000 * 0.92) = 0.82 m3/h.
Calculation of gas consumption
Knowing the total heat loss, you can quite simply calculate the required consumption of natural or liquefied gas for heating a house with an area of 200 m2.
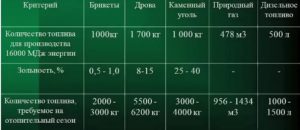
The amount of energy released, in addition to the volume of fuel, is affected by its heat of combustion. For gas, this indicator depends on the humidity and chemical composition of the mixture supplied. Distinguish higher (Hh) and lower (Hl) calorific value.
The lower calorific value of propane is less than that of butane. Therefore, in order to accurately determine the calorific value of liquefied gas, you need to know the percentage of these components in the mixture supplied to the boiler
To calculate the amount of fuel that is guaranteed to be enough for heating, the value of the net calorific value, which can be obtained from the gas supplier, is substituted into the formula. The standard unit for calorific value is “mJ/m3” or “mJ/kg”. But since the units of measurement and power of boilers and heat losses operate in watts, and not joules, it is necessary to perform a conversion, given that 1 mJ = 278 Wh.
If the value of the net calorific value of the mixture is unknown, then it is permissible to take the following average figures:
- for natural gas Hl = 9.3 kWh/m3;
- for LPG Hl = 12.6 kWh / kg.
Another indicator required for calculations is the boiler efficiency K. It is usually measured as a percentage. The final formula for gas consumption over a period of time E (h) is as follows:
V = Q × E / (Hl ×K/100).
The period when centralized heating is turned on in houses is determined by the average daily air temperature.
If over the past five days it does not exceed “+ 8 ° С”, then according to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 307 of 05/13/2006, heat supply to the house must be ensured. For private houses with autonomous heating, these figures are also used when calculating fuel consumption.
The exact data on the number of days with a temperature not higher than “+ 8 ° С” for the area where the cottage was built can be found in the local department of the Hydrometeorological Center.
If the house is located close to a large settlement, then it is easier to use the table. 1. SNiP 23-01-99 (column No. 11). Multiplying this value by 24 (hours per day) we get the parameter E from the gas flow calculation equation.
According to climatic data from Table. 1 SNiP 23-01-99 construction organizations carry out calculations to determine the heat loss of buildings
If the volume of air inflow and the temperature inside the premises are constant (or with slight fluctuations), then the heat loss through the building envelope and due to the ventilation of the premises will be directly proportional to the outdoor temperature.
Therefore, for the parameter T2 in the equations for calculating heat loss, you can take the value from column No. 12 of Table. 1. SNiP 23-01-99.
Heat Load and Gas Flow Formulas
Gas consumption is conventionally denoted by the Latin letter V and is determined by the formula:
V = Q / (n/100 x q), where
Q - heat load on heating (kW / h), q - calorific value of gas (kW / m³), n - Gas boiler efficiency, expressed as a percentage.
Main gas consumption is measured in cubic meters per hour (m³ / h), liquefied gas - in liters or kilograms per hour (l / h, kg / h).

Gas consumption is calculated before designing the heating system, choosing a boiler, energy carrier, and then easily controlled using meters
Let us consider in detail what the variables in this formula mean and how to define them.
The concept of "heat load" is given in the federal law "On Heat Supply". Having slightly changed the official wording, let's just say that this is the amount of thermal energy transferred per unit of time to maintain a comfortable indoor air temperature.
In the future, we will also use the concept of "thermal power", so at the same time we will give its definition in relation to our calculations. Thermal power is the amount of thermal energy that a gas boiler can produce per unit of time.
Thermal load is determined in accordance with MDK 4-05.2004 by means of thermal engineering calculations.
Simplified formula:
Q = V x ΔT x K / 860.
Here V is the volume of the room, which is obtained by multiplying the height of the ceiling, the width and length of the floor.
ΔT is the difference between the air temperature outside the building and the required air temperature in the heated room. For calculations, the climatic parameters given in SP 131.13330.2012 are used.

To get the most accurate gas consumption indicators, formulas are used that even take into account the location of windows - the sun's rays warm up the room, reducing heat loss
K is the heat loss coefficient, which is the most difficult to determine accurately due to the influence of many factors, including number and position of external walls regarding the cardinal points and wind regime in winter; number, type and dimensions of windows, entrance and balcony doors; the type of building and thermal insulation materials used, and so on.

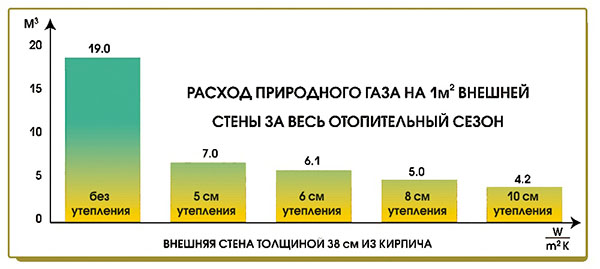
On the building envelope of the house there are areas with increased heat transfer - cold bridges, due to which fuel consumption can increase significantly
If necessary, perform a calculation with an error within 5%, it is better to conduct a thermal audit of the house.
If the calculation requirements are not so stringent, you can use the average values of the heat loss coefficient:
- increased degree of thermal insulation - 0.6-0.9;
- thermal insulation of an average degree - 1-1.9;
- low thermal insulation - 2-2.9;
- lack of thermal insulation - 3-4.
Double brickwork, small windows with triple glazing, insulated roofing system, strong foundation, thermal insulation with materials with low thermal conductivity - all this indicates a minimum heat loss coefficient for your home.
With double brickwork, but conventional roofing and double-framed windows, the coefficient rises to average values. The same parameters, but single brickwork and a simple roof are a sign of low thermal insulation. The lack of thermal insulation is typical for country houses.

It is worth taking care of saving thermal energy already at the stage of building a house by insulating walls, roofs and foundations and installing multi-chamber windows
Having chosen the value of the coefficient that is most appropriate for the thermal insulation of your home, we substitute it into the formula for calculating the heat load. Further, according to the formula, we calculate the gas consumption to maintain a comfortable microclimate in a country house.
Calculation of the planned maximum hourly gas consumption
Application for the calculation of the planned maximum hourly gas consumption (download)
REQUEST FORM providing specifications for connection (technological connection) of capital construction facilities to gas distribution networks (download)
To determine the technical feasibility of connecting a capital construction facility to gas distribution networks, a preliminary assessment of gas consumption is required.
If the estimated maximum hourly gas consumption, according to a preliminary estimate, does not exceed 5 cubic meters. meters / hour, then the provision of the calculation is optional. For Applicants who connect individual housing construction objects, the consumption is up to 5 cubic meters. meters / hour is determined by the heated area of a residential building up to 200 square meters. m and installed gas-using equipment - a heating boiler with a capacity of 30 kW and a household four-burner stove with an oven.
If the maximum hourly gas consumption exceeds 5 cubic meters. meters / hour, the calculation is required.
LLC Gazprom Gas Distribution Samara accepts applications for the issuance of technical conditions in accordance with the requirements of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 30, 2013 N1314 “On approval of the Rules for connection (technological connection) of capital construction facilities to gas distribution networks, as well as on the amendment and invalidation of certain acts of the Government of the Russian Federation”. (download)
The issuance of technical specifications is carried out without charging a fee on the basis of an application for the issuance of technical specifications.
To obtain technical specifications, you must:
- Fill in the Request form for the provision of technical conditions for connection (download).
- Prepare and attach the required documents to the request form
Maximum hourly gas consumption calculator
A single-circuit gas boiler is capable of providing only space heating.
A double-circuit gas boiler includes the ability to provide both heating and hot water supply.
calculate according to:
heated area of premises
maximum power according to the technical characteristics of gas equipment indicated in the passport.
Varieties of gas
A large amount of fuel is required to heat private houses and cottages with an area of more than 150 square meters. For this reason, when choosing a suitable coolant, one should take into account not only the degree of its heat transfer, but also the economic benefits from its use, the profitability of equipment installation. Gas most of all meets the listed parameters.

For a larger area of the room, more fuel is needed
Varieties of gas:
- Natural. It combines hydrocarbons of various types with a predominant share of methane CH4 and impurities of non-hydrocarbon origin. When burning one cubic meter of this mixture, more than 9 kW of energy is released. Since gas in nature is located underground in the layers of certain rocks, special pipelines are laid for its transportation and delivery to consumers. In order for natural gas to enter the house and heat it, it is necessary to connect to such a pipeline. All connection work is carried out exclusively by gas service specialists. Their work is highly valued, so a tie-in to a gas main can cost a large amount.
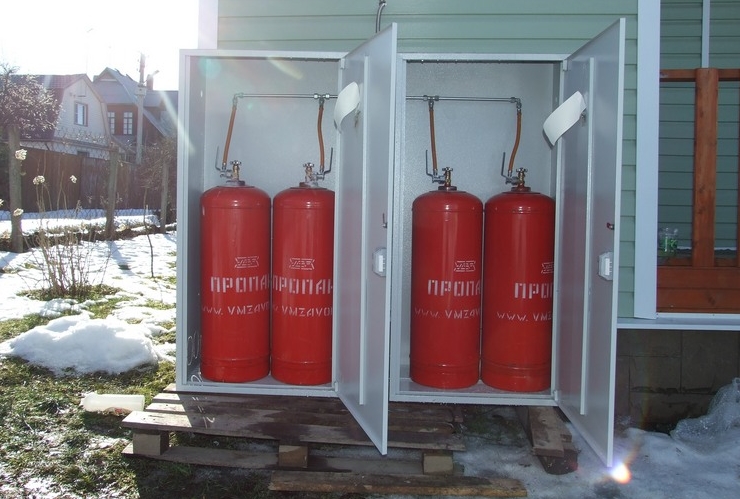
- Liquefied. Includes substances such as ethylene, propane and other combustible additives. It is customary to measure it not in cubic meters, but in liters. One liter, burning, gives about 6.5 kW of heat.Its use as a heat carrier does not imply an expensive connection to the main pipeline. But for the storage of liquefied fuel, it is necessary to equip a special container. As gas is consumed, its volumes will have to be replenished in a timely manner. To the cost of permanent purchase must be added the cost of transportation.
You will see the principles of heating with liquefied gas cylinders in this video:
Liquefied gas
Many boilers are made in such a way that the same burner can be used when changing fuel. Therefore, some owners choose methane and propane-butane for heating. This is a low density material. During the heating process, energy is released and natural cooling occurs under the influence of pressure. The cost depends on the equipment. Autonomous supply includes the following elements:
- A vessel or cylinder containing a mixture of butane, methane, propane - a gas holder.
- Devices for management.
- A communication system through which fuel moves and is distributed inside a private house.
- Temperature sensors.
- Stop valve.
- Automatic adjustment devices.
The gas holder must be located at least 10 meters from the boiler room. When filling a cylinder of 10 cubic meters, to service a building of 100 m2, you will need equipment with a capacity of 20 kW. Under such conditions, it is enough to refuel no more than 2 times a year. To calculate the approximate gas consumption, you need to insert the value for the liquefied resource into the formula R \u003d V / (qHxK), while the calculations are carried out in kg, which are then converted to liters. With a calorific value of 13 kW / kg or 50 mJ / kg, the following value is obtained for a house of 100 m2: 5 / (13x0.9) \u003d 0.427 kg / hour.
Since a liter of propane-butane weighs 0.55 kg, the formula comes out - 0.427 / 0.55 = 0.77 liters of liquefied fuel in 60 minutes, or 0.77x24 = 18 liters in 24 hours and 540 liters in 30 days. Given that there are about 40 liters of resource in one container, the consumption during the month will be 540/40 = 13.5 gas cylinders.
How to reduce resource consumption?
In order to reduce the cost of space heating, homeowners take various measures. First of all, it is necessary to control the quality of window and door openings. If there are gaps, heat will escape from the rooms, which will lead to more energy consumption.
Also one of the weak points is the roof. Hot air rises and mixes with cold masses, increasing the flow in winter. A rational and inexpensive option would be to provide protection from the cold on the roof with the help of rolls of mineral wool, which is laid between the rafters, without the need for additional fixation
It is important to insulate the walls inside and outside the building. For these purposes, there are a huge number of materials with excellent properties.
For example, expanded polystyrene is considered one of the best insulators that lends itself well to finishing, it is also used in the manufacture of siding.
When installing heating equipment in a country house, it is necessary to calculate the optimal power of the boiler and the system operating on natural or forced circulation. Sensors and thermostats control the temperature, depending on the climatic conditions. Programming will ensure timely activation and deactivation if necessary. A hydraulic arrow for each device with sensors for a single room will automatically determine when it is necessary to start heating the area.The batteries are equipped with thermal heads, and the walls behind them are covered with a foil membrane so that the energy is reflected into the room and does not go to waste. With underfloor heating, the carrier temperature reaches only 50°C, which is also a determining factor in savings.
Plumbers: You'll pay up to 50% LESS for water with this faucet attachment
The use of alternative installations will help reduce gas consumption. These are solar systems and equipment powered by wind power. It is considered most effective to use several options at the same time.
The cost of heating a house with gas can be calculated using a certain formula. Calculations are best done at the design stage of a building, this will help to find out the profitability and feasibility of consumption
It is also important to take into account the number of people living, the efficiency of the boiler and the possibility of using additional alternative heating systems. These measures will save and significantly reduce costs
Calculation of gas consumption for heating a living space of 100 m²
At the first stage of designing a heating system in suburban real estate, it is necessary to determine exactly what the gas consumption will be for heating a house of 100 m², as well as 150, 200, 250 or 300 m². It all depends on the area of the room. Then it will become clear how much liquefied or main fuel is required and what are the cash costs per 1 m². If this is not done, then this type of heating may become unprofitable.
Volume flow
Volumetric flow is the amount of liquid, gas or steam passing through a given point in a certain period of time, measured in units of volume such as m3/min.
The value of pressure and velocity in the flow
Pressure, which is usually defined as force per unit area, is an important characteristic of flow.The figure above shows two directions in which the flow of liquid, gas or vapor, moving, exerts pressure in the pipeline in the direction of the flow itself and on the walls of the pipeline. It is the pressure in the second direction that is most often used in flow meters, in which, based on the reading of the pressure drop in the pipeline, the flow is determined
It is the pressure in the second direction that is most often used in flow meters, in which, based on the reading of the pressure drop in the pipeline, the flow is determined
The figure above shows two directions in which the flow of liquid, gas or vapor, moving, exerts pressure in the pipeline in the direction of the flow itself and on the walls of the pipeline. It is the pressure in the second direction that is most often used in flow meters, in which the flow is determined based on the indication of the pressure drop in the pipeline.
The speed at which a liquid, gas, or vapor flows has a significant effect on the amount of pressure exerted by the liquid, gas, or vapor on the pipeline walls; as a result of a change in speed, the pressure on the walls of the pipeline will change. The figure below graphically depicts the relationship between the flow rate of a liquid, gas or steam and the pressure that the liquid flow exerts on the pipeline walls.
As can be seen from the figure, the diameter of the pipe at point "A" is larger than the diameter of the pipe at point "B". Since the amount of liquid entering the pipeline at point "A" must equal the amount of liquid leaving the pipeline at point "B", the rate at which the liquid flows through the narrower part of the pipe must increase.As the fluid velocity increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid on the pipe walls will decrease.
In order to show how an increase in the flow rate of a fluid can lead to a decrease in the amount of pressure exerted by the flow of fluid on the walls of the pipeline, a mathematical formula can be used. This formula takes into account only velocity and pressure. Other indicators such as: friction or viscosity are not taken into account
If these indicators are not taken into account, then the simplified formula is written as follows: PA + K (VA) 2 = PB + K (VB) 2
The pressure exerted by the fluid on the pipe walls is denoted by the letter P. PA is the pressure on the pipeline walls at point "A" and PB is the pressure at point "B". The fluid velocity is denoted by the letter V. VA is the velocity of the fluid through the pipeline at point "A" and VB is the velocity at point "B". K is a mathematical constant.
As already formulated above, in order for the amount of gas, liquid or steam that passed through the pipeline at point "B" to be equal to the amount of gas, liquid or steam that entered the pipeline at point "A", the velocity of the liquid, gas or steam at point " B" should increase. Therefore, if PA + K (VA)2 should equal PB + K (VB)2, then as the speed VB increases, the pressure PB should decrease. Thus, an increase in speed leads to a decrease in the pressure parameter.
Types of gas, liquid and steam flow
The speed of the medium also affects the type of flow generated in the pipe. Two basic terms are used to describe the flow of a liquid, gas, or vapor: laminar and turbulent.
laminar flow
Laminar flow is the flow of a gas, liquid, or vapor without turbulence, which occurs at relatively low overall fluid velocities.In laminar flow, a liquid, gas, or vapor moves in even layers. The speed of the layers moving in the center of the flow is higher than the speed of the outer (flowing near the pipeline walls) layers of the flow. The decrease in the speed of movement of the outer layers of the flow occurs due to the presence of friction between the current outer layers of the flow and the walls of the pipeline.
turbulent flow
Turbulent flow is a swirling flow of gas, liquid, or vapor that occurs at higher velocities. In turbulent flow, the layers of the flow move with eddies, and do not tend to a rectilinear direction in their flow. Turbulence can adversely affect the accuracy of flow measurements by causing different pressures on the pipeline walls at any given point.
Calculation of the consumption of liquefied gas
Many boilers can run on LPG. How beneficial is it? What will be the consumption of liquefied gas for heating? All this can also be calculated. The technique is the same: you need to know either heat loss or boiler power. Next, we translate the required amount into liters (a unit of measurement of liquefied gas), and if desired, we consider the number of required cylinders.
Let's look at the calculation with an example. Let the boiler power be 18 kW, respectively, the average heat demand is 9 kW / h. When burning 1 kg of liquefied gas, we get 12.5 kW of heat. So, to get 9 kW, you need 0.72 kg (9 kW / 12.5 kW = 0.72 kg).
Next, we consider:
- per day: 0.72 kg * 24 hours = 17.28 kg;
- per month 17.28 kg * 30 days = 518.4 kg.
Let's add a correction for the efficiency of the boiler. It is necessary to look at each specific case, but let's take 90%, that is, add another 10%, it turns out that per month will be 570.24 kg.
Liquefied gas is one of the heating options
To calculate the number of cylinders, we divide this figure by 21.2 kg (this is how many kg are on average gas in a 50 liter bottle).
The mass of liquefied gas in various cylinders
In total, this boiler will require 27 cylinders of liquefied gas. And consider the cost yourself - prices vary by region. But don't forget about shipping costs. By the way, they can be reduced by making a gas tank - a sealed container for storing liquefied gas, which can be refueled once a month or less - depending on the storage volume and needs.
And again, do not forget that this is only an approximate figure. In cold months, gas consumption for heating will be more, in warm months - much less.
P.S. If it is more convenient for you to calculate the consumption in liters:
- 1 liter of liquefied gas weighs approximately 0.55 kg and, when burned, gives approximately 6500 kW of heat;
- There are about 42 liters of gas in a 50 liter bottle.