- Factors affecting gas consumption
- How to calculate gas consumption for home heating
- Method of calculation for natural gas
- Gas consumption for DHW
- Liquefied gas
- Calculation of gas consumption for heating a living space of 100 m²
- Why do we need to calculate the use of liquefied or natural gas
- How to find out the gas consumption for heating a house
- How to reduce gas consumption
- How to calculate main gas consumption
- Calculation for liquefied gas
- What to do if the gas consumption for heating seems excessive?
Factors affecting gas consumption
The gas holder has the form of a volumetric tank, which is filled with liquefied hydrocarbon gas (LHG). It is a mixture of two gases - propane and butane.
Autonomous heating schemes with gas extraction from a gas tank and a gas boiler in the system have become a modern alternative to heating houses from solid fuel or diesel boilers
Storage of gas in such tanks, with its further use for heating a house, may be due to the following factors:
- the inability to tie into the main gas pipe or the high cost of such a connection;
- constant and unsolvable gas services problems with gas pressure in the central pipeline.
For the normal operation of most gas boilers, the gas pressure in the pipeline must be at least 35 mbar.This norm is often not maintained in the main gas pipelines and is only from 8 to 22 mbar.
To determine the volume of liquefied gas in the tank, there are mechanical level gauges or more modern remote telemetry systems. Such equipment can be supplied with the tank or purchased separately. The average daily gas consumption can also be determined by the difference in the readings of the gas meter, if any.
But, a more accurate answer to the question of how much gas in a gas tank is enough to heat a home, what is its consumption and how to minimize its costs, mathematical calculations will help. And this is despite the fact that objectively such a calculation will be of an average nature.
Fuel in an independent gas supply from a gas tank is consumed not only for heating. Although in much smaller volumes, it is also spent on heating water, the operation of a gas stove and other household needs.
It should be taken into account that the following factors influence the gas consumption:
- the climate of the region and the wind rose;
- the quadrature of the house, the number and degree of thermal insulation of windows and doors;
- material of walls, roofs, foundations and the degree of their insulation;
- the number of residents and the mode of their stay (permanently or periodically);
- technical characteristics of the boiler, the use of additional gas appliances and auxiliary equipment;
- the number of heating radiators, the presence of a warm floor.
These and other conditions make the calculation of fuel consumption from a gas tank a relative value, which is based on average accepted indicators.
How to calculate gas consumption for home heating
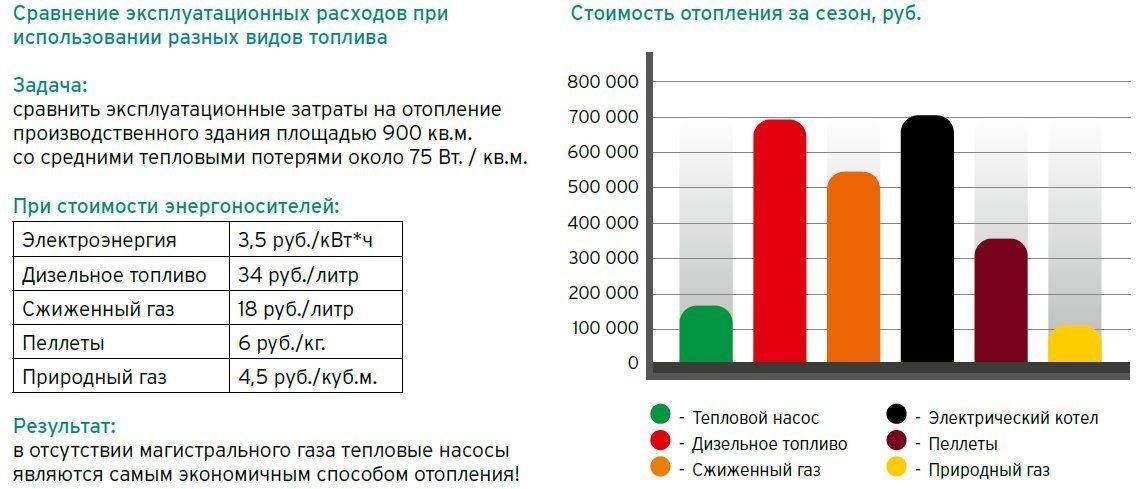
Gas is still the cheapest type of fuel, but the cost of connection is sometimes very high, so many people want to first assess how economically justified such costs are. To do this, you need to know the gas consumption for heating, then it will be possible to estimate the total cost and compare it with other types of fuel.
Method of calculation for natural gas
The approximate gas consumption for heating is calculated based on half the capacity of the installed boiler. The thing is that when determining the power of a gas boiler, the lowest temperature is laid. This is understandable - even when it is very cold outside, the house should be warm.

You can calculate the gas consumption for heating yourself
But it is completely wrong to calculate the gas consumption for heating according to this maximum figure - after all, in general, the temperature is much higher, which means that much less fuel is burned. Therefore, it is customary to consider the average fuel consumption for heating - about 50% of the heat loss or boiler power.
We calculate the gas consumption by heat loss
If there is no boiler yet, and you estimate the cost of heating in different ways, you can calculate from the total heat loss of the building. They are most likely familiar to you. The methodology here is as follows: they take 50% of the total heat loss, add 10% to provide hot water supply and 10% to heat outflow during ventilation. As a result, we get the average consumption in kilowatts per hour.
Then you can find out the fuel consumption per day (multiply by 24 hours), per month (by 30 days), if desired - for the entire heating season (multiply by the number of months during which the heating works). All these figures can be converted into cubic meters (knowing the specific heat of combustion of gas), and then multiply cubic meters by the price of gas and, thus, find out the cost of heating.
Heat loss calculation example
Let the heat loss of the house be 16 kW / h. Let's start counting:
- average heat demand per hour - 8 kW / h + 1.6 kW / h + 1.6 kW / h = 11.2 kW / h;
- per day - 11.2 kW * 24 hours = 268.8 kW;
- per month - 268.8 kW * 30 days = 8064 kW.

The actual gas consumption for heating still depends on the type of burner - modulated are the most economical
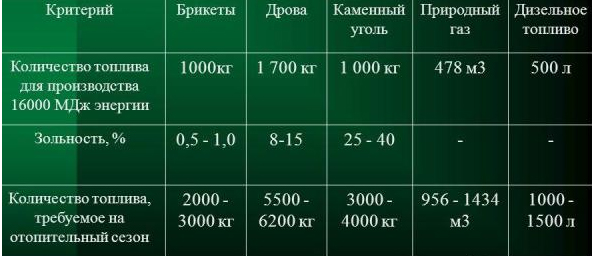
Convert to cubic meters. If we use natural gas, we divide the gas consumption for heating per hour: 11.2 kW / h / 9.3 kW = 1.2 m3 / h. In calculations, the figure 9.3 kW is the specific heat capacity of natural gas combustion (available in the table).
By the way, you can also calculate the required amount of fuel of any type - you just need to take the heat capacity for the required fuel.
Since the boiler has not 100% efficiency, but 88-92%, you will have to make more adjustments for this - add about 10% of the figure obtained. In total, we get the gas consumption for heating per hour - 1.32 cubic meters per hour. You can then calculate:
- consumption per day: 1.32 m3 * 24 hours = 28.8 m3/day
- demand per month: 28.8 m3 / day * 30 days = 864 m3 / month.
The average consumption for the heating season depends on its duration - we multiply it by the number of months that the heating season lasts.
This calculation is approximate. In some month, gas consumption will be much less, in the coldest - more, but on average the figure will be about the same.
Boiler power calculation
Calculations will be a little easier if there is a calculated boiler capacity - all the necessary reserves (for hot water supply and ventilation) are already taken into account. Therefore, we simply take 50% of the calculated capacity and then calculate the consumption per day, month, per season.
For example, the design capacity of the boiler is 24 kW.To calculate the gas consumption for heating, we take half: 12 k / W. This will be the average need for heat per hour. To determine the fuel consumption per hour, we divide by the calorific value, we get 12 kW / h / 9.3 k / W = 1.3 m3. Further, everything is considered as in the example above:
- per day: 12 kW / h * 24 hours = 288 kW in terms of the amount of gas - 1.3 m3 * 24 = 31.2 m3
- per month: 288 kW * 30 days = 8640 m3, consumption in cubic meters 31.2 m3 * 30 = 936 m3.

You can calculate gas consumption for heating a house according to the design capacity of the boiler
Next, we add 10% for the imperfection of the boiler, we get that for this case the flow rate will be slightly more than 1000 cubic meters per month (1029.3 cubic meters). As you can see, in this case everything is even simpler - fewer numbers, but the principle is the same.
By quadrature
Even more approximate calculations can be obtained by the quadrature of the house. There are two ways:
Gas consumption for DHW
When water for household needs is heated using gas heat generators - a column or a boiler with an indirect heating boiler, then to find out the fuel consumption, you need to understand how much water is required. To do this, you can raise the data prescribed in the documentation and determining the rate for 1 person.
Another option is to turn to practical experience, and it says the following: for a family of 4 people, under normal conditions, it is enough to heat 80 liters of water once a day from 10 to 75 ° C. From here, the amount of heat required for heating water is calculated according to the school formula:
Q = cmΔt, where:
- c is the heat capacity of water, is 4.187 kJ/kg °С;
- m is the mass flow rate of water, kg;
- Δt is the difference between the initial and final temperatures, in the example it is 65 °C.
For the calculation, it is proposed not to convert volumetric water consumption into mass water consumption, assuming that these values are the same.Then the amount of heat will be:
4.187 x 80 x 65 = 21772.4 kJ or 6 kW.
It remains to substitute this value in the first formula, which will take into account the efficiency of the gas column or heat generator (here - 96%):
V \u003d 6 / (9.2 x 96 / 100) \u003d 6 / 8.832 \u003d 0.68 m³ of natural gas 1 time per day will be spent on heating water. For a complete picture, here you can also add the consumption of a gas stove for cooking at the rate of 9 m³ of fuel per 1 living person per month.
Liquefied gas
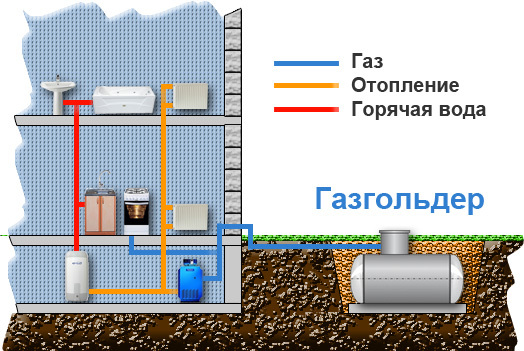
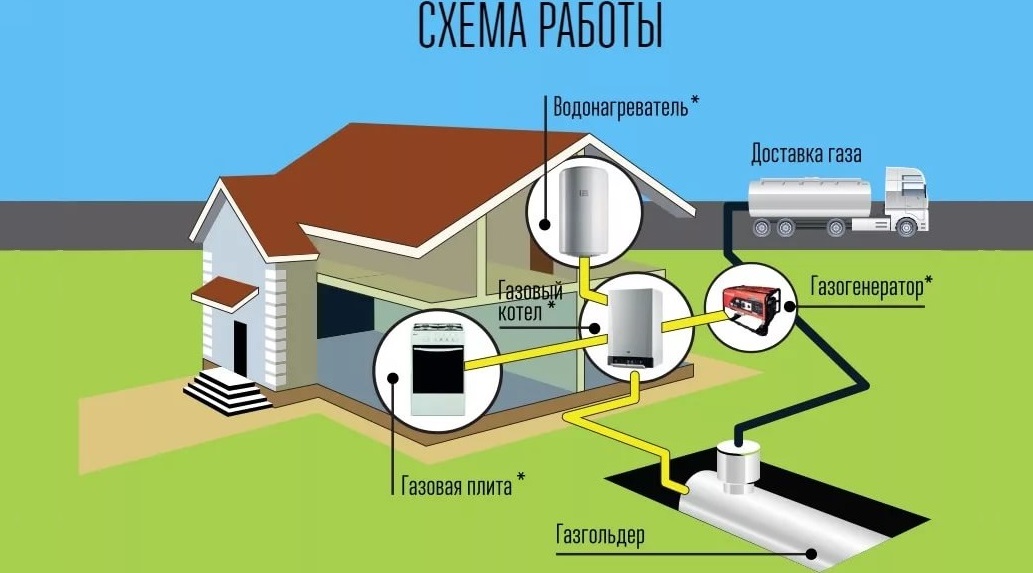
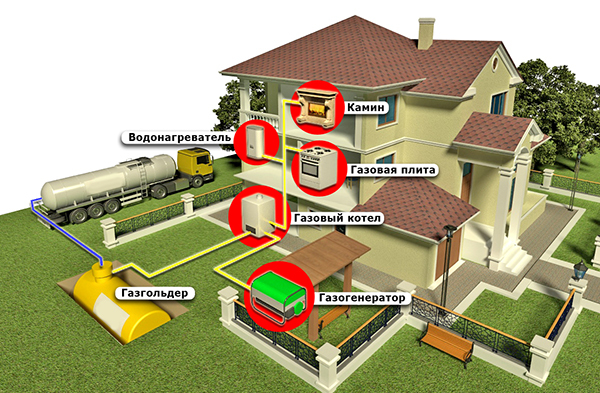
Many boilers are made in such a way that the same burner can be used when changing fuel. Therefore, some owners choose methane and propane-butane for heating. This is a low density material. During the heating process, energy is released and natural cooling occurs under the influence of pressure. The cost depends on the equipment. Autonomous supply includes the following elements:
- A vessel or cylinder containing a mixture of butane, methane, propane - a gas holder.
- Devices for management.
- A communication system through which fuel moves and is distributed inside a private house.
- Temperature sensors.
- Stop valve.
- Automatic adjustment devices.
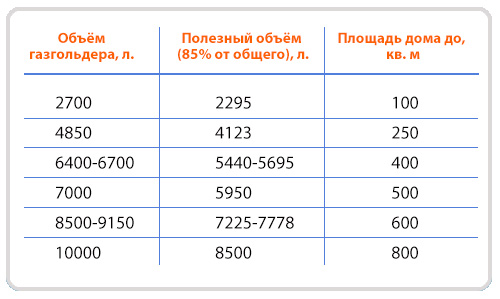
The gas holder must be located at least 10 meters from the boiler room. When filling a cylinder of 10 cubic meters, to service a building of 100 m2, you will need equipment with a capacity of 20 kW. Under such conditions, it is enough to refuel no more than 2 times a year. To calculate the approximate gas consumption, you need to insert the value for the liquefied resource into the formula R \u003d V / (qHxK), while the calculations are carried out in kg, which are then converted to liters. With a calorific value of 13 kW / kg or 50 mJ / kg, the following value is obtained for a house of 100 m2: 5 / (13x0.9) \u003d 0.427 kg / hour.
Since a liter of propane-butane weighs 0.55 kg, the formula comes out - 0.427 / 0.55 = 0.77 liters of liquefied fuel in 60 minutes, or 0.77x24 = 18 liters in 24 hours and 540 liters in 30 days. Given that there are about 40 liters of resource in one container, the consumption during the month will be 540/40 = 13.5 gas cylinders.
How to reduce resource consumption?
In order to reduce the cost of space heating, homeowners take various measures. First of all, it is necessary to control the quality of window and door openings. If there are gaps, heat will escape from the rooms, which will lead to more energy consumption.
Also one of the weak points is the roof. Hot air rises and mixes with cold masses, increasing the flow in winter. A rational and inexpensive option would be to provide protection from the cold on the roof with the help of rolls of mineral wool, which is laid between the rafters, without the need for additional fixation
It is important to insulate the walls inside and outside the building. For these purposes, there are a huge number of materials with excellent properties.
For example, expanded polystyrene is considered one of the best insulators that lends itself well to finishing, it is also used in the manufacture of siding.
When installing heating equipment in a country house, it is necessary to calculate the optimal power of the boiler and the system operating on natural or forced circulation. Sensors and thermostats control the temperature, depending on the climatic conditions. Programming will ensure timely activation and deactivation if necessary.A hydraulic arrow for each device with sensors for a single room will automatically determine when it is necessary to start heating the area. The batteries are equipped with thermal heads, and the walls behind them are covered with a foil membrane so that the energy is reflected into the room and does not go to waste. With underfloor heating, the carrier temperature reaches only 50°C, which is also a determining factor in savings.
Plumbers: You'll pay up to 50% LESS for water with this faucet attachment
The use of alternative installations will help reduce gas consumption. These are solar systems and equipment powered by wind power. It is considered most effective to use several options at the same time.
The cost of heating a house with gas can be calculated using a certain formula. Calculations are best done at the design stage of a building, this will help to find out the profitability and feasibility of consumption
It is also important to take into account the number of people living, the efficiency of the boiler and the possibility of using additional alternative heating systems. These measures will save and significantly reduce costs
Calculation of gas consumption for heating a living space of 100 m²
At the first stage of designing a heating system in suburban real estate, it is necessary to determine exactly what the gas consumption will be for heating a house of 100 m², as well as 150, 200, 250 or 300 m². It all depends on the area of the room. Then it will become clear how much liquefied or main fuel is required and what are the cash costs per 1 m². If this is not done, then this type of heating may become unprofitable.
Why do we need to calculate the use of liquefied or natural gas
In the case of heating a cottage, the calculation of gas use is necessary to understand how much fuel is required to heat the house. The storage of heat and, accordingly, its consumption is affected by:
- what region is the property located in?
- what materials it is made of;
- Is it constantly heated or from time to time.
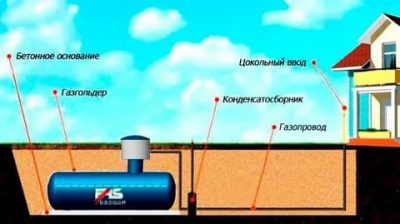
Photo 1. For the safe storage of liquefied fuel, similar devices are used - gas holders.
If it is not natural, but liquefied gas, the calculation helps to determine how many cylinders will be needed and where it would be best to install them. Consideration should also be given to the use of fuel for heating in the case of combined heating: for example, gas and electricity.
How to find out the gas consumption for heating a house
How to determine the gas consumption for heating a house 100 m 2, 150 m 2, 200 m 2?
When designing a heating system, you need to know what it will cost during operation.
That is, to determine the upcoming fuel costs for heating. Otherwise, this type of heating may subsequently be unprofitable.
How to reduce gas consumption
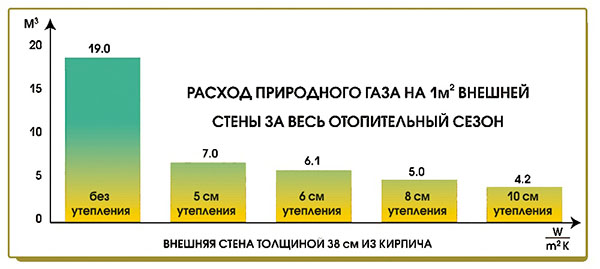
A well-known rule: the better the house is insulated, the less fuel is spent on heating the street. Therefore, before starting the installation of the heating system, it is necessary to perform high-quality thermal insulation of the house - the roof / attic, floors, walls, replacing windows, hermetic sealing contour on the doors.
You can also save fuel by using the heating system itself. Using warm floors instead of radiators, you will get more efficient heating: since heat is distributed by convection currents from the bottom up, the lower the heater is located, the better.
In addition, the normative temperature of the floors is 50 degrees, and the radiators - an average of 90.Obviously, floors are more economical.
Finally, you can save gas by adjusting the heating over time. It makes no sense to actively heat the house when it is empty. It is enough to withstand a low positive temperature so that the pipes do not freeze.
Modern boiler automation (types of automation for gas heating boilers) allows remote control: you can give a command to change the mode through a mobile provider before returning home (what are Gsm modules for heating boilers). At night, the comfortable temperature is slightly lower than during the day, and so on.
How to calculate main gas consumption
The calculation of gas consumption for heating a private house depends on the power of the equipment (which determines the gas consumption in gas heating boilers). Power calculation is performed when choosing a boiler. Based on the size of the heated area. It is calculated for each room separately, focusing on the lowest average annual temperature outside.
To determine the energy consumption, the resulting figure is divided approximately in half: throughout the season, the temperature fluctuates from a serious minus to plus, gas consumption varies in the same proportions.
When calculating the power, they proceed from the ratio of kilowatts per ten squares of the heated area. Based on the foregoing, we take half of this value - 50 watts per meter per hour. At 100 meters - 5 kilowatts.
Fuel is calculated according to the formula A = Q / q * B, where:
- A - the desired amount of gas, cubic meters per hour;
- Q is the power required for heating (in our case, 5 kilowatts);
- q - minimum specific heat (depending on the brand of gas) in kilowatts. For G20 - 34.02 MJ per cube = 9.45 kilowatts;
- B - the efficiency of our boiler. Let's say 95%. The required figure is 0.95.
We substitute the numbers in the formula, we get 0.557 cubic meters per hour for 100 m 2. Accordingly, gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m 2 (7.5 kilowatts) will be 0.836 cubic meters, gas consumption for heating a house of 200 m 2 (10 kilowatts) - 1.114, etc. It remains to multiply the resulting figure by 24 - you get the average daily consumption, then by 30 - the average monthly.
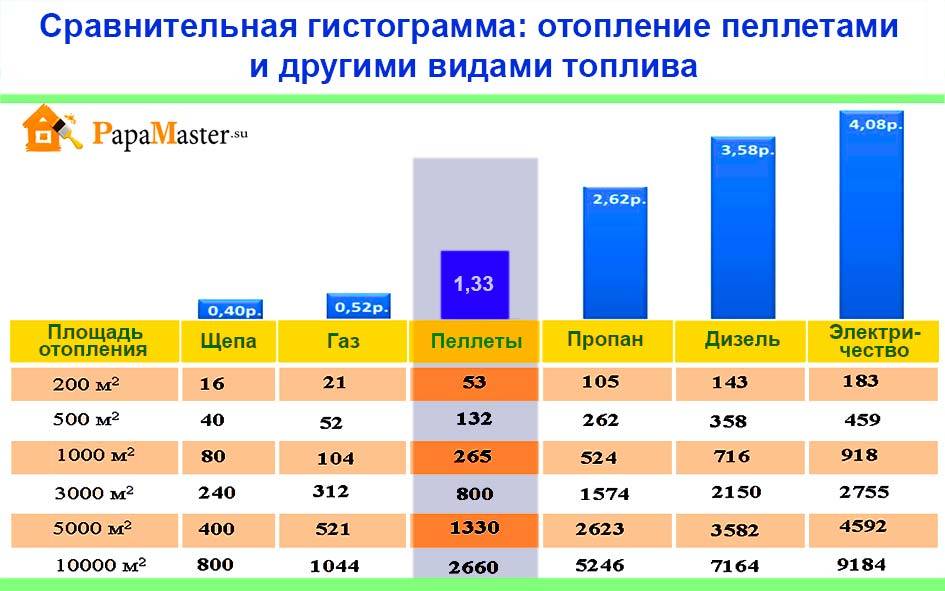
Calculation for liquefied gas
The above formula is also suitable for other types of fuel. Including for liquefied gas in cylinders for a gas boiler. Its calorific value, of course, is different. We accept this figure as 46 MJ per kilogram, i.e. 12.8 kilowatts per kilogram. Let's say the boiler efficiency is 92%. We substitute the numbers in the formula, we get 0.42 kilograms per hour.
Liquefied gas is calculated in kilograms, which are then converted to liters. To calculate the gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m 2 from a gas tank, the figure obtained by the formula is divided by 0.54 (the weight of one liter of gas).
Further - as above: multiply by 24 and by 30 days. To calculate the fuel for the entire season, we multiply the average monthly figure by the number of months.
Average monthly consumption, approximately:
- consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house of 100 m 2 - about 561 liters;
- consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house of 150 m 2 - approximately 841.5;
- 200 squares - 1122 liters;
- 250 - 1402.5 etc.
A standard cylinder contains about 42 liters. We divide the amount of gas required for the season by 42, we find the number of cylinders. Then we multiply by the price of the cylinder, we get the amount needed for heating for the entire season.
What to do if the gas consumption for heating seems excessive?
It may turn out that either the results of the calculations will immediately seem frighteningly high, or the real consumption will become such that there can be no question of any efficiency in the consumption of energy carriers.
Wait a minute to immediately scold everyone and everything - first of all, you need to figure out what this can be caused by. As a rule, the reasons are quite obvious or hidden, and they will have to be dealt with. And their elimination almost always allows you to bring gas consumption to a completely economical level.
So where to look?
First of all, a large overrun may indicate that there are “holes” in the thermal insulation system of the house. If the building has too much heat loss, then you can really go broke on energy carriers, but without creating a truly comfortable microclimate in the premises. The illustration below shows the possible ways of these losses - all this requires the close attention of the owners.
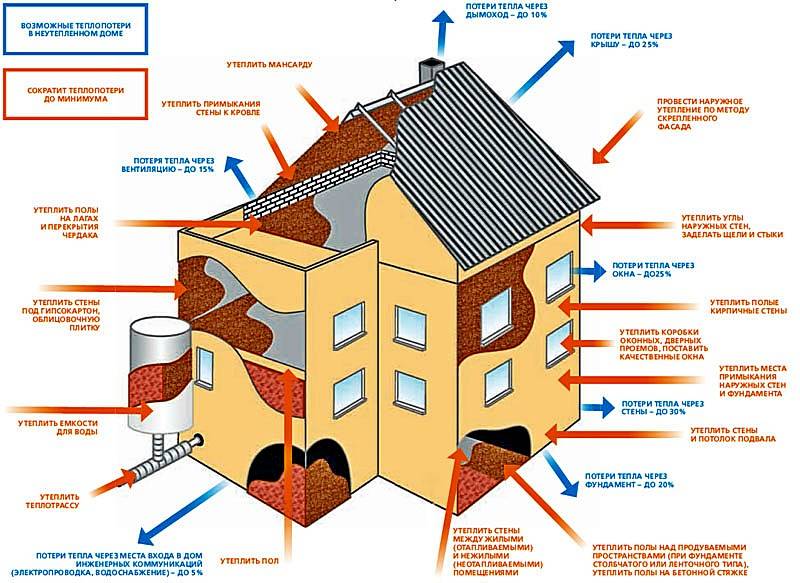
The main ways of heat loss from the house and possible ways to minimize them
At the same time, the issues of housing insulation should not be solved “by eye”. There are certain norms that are tied both to the climatic features of the region of residence and to the type of building structures.
Above, a link was given to go to a publication devoted to calculating the required heat output of a heating system. In the same article there is another interesting section, also equipped with an online calculator - it is possible to independently assess the compliance of the existing insulation with regulatory indicators. So do not be lazy, first check in theory whether everything corresponds to the recommended parameters.And, of course, carry out a practical revision of thermal insulation structures - wear, aging, caking, wetting of heaters is not ruled out.
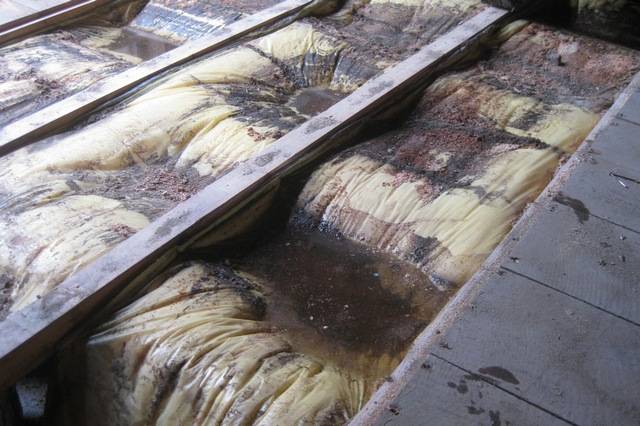

It also happens that the thermal insulation hidden from constant monitoring is so dilapidated or wet that it creates only the illusion of insulation.
In a word, if you want to achieve comfort in the house, combined with economical energy consumption, start by putting the insulation system in order.
- Be very careful about the condition of windows and doors - quite often too much heat leaks through old frames or boxes or through poor-quality glazing, which leads to excessive gas consumption for heating. It may be worth considering replacing windows and doors with new ones.
- The reason may lie in the imperfection of the heating system itself or the equipment installed in it. A personal example - at one time a house was purchased in which heating was carried out from a hefty cast-iron boiler according to the natural circulation scheme. The first winter I had to live with him, and gas bills were just cosmic! It is understandable. The boiler was installed back in the 70s of the last century, when the tariffs were cheap, and there were no gas meters anywhere. The replacement with AOGV-11.6 with simultaneous insertion into the circulation pump circuit reduced consumption by almost four times (!). And all the costs of modernization paid off in record time.
And now the choice of boiler equipment is much richer. Modern heating boilers with high efficiency and a control system thought out to the smallest detail, sensitively monitoring all changes, allow you to use energy resources with maximum efficiency.
It is worth evaluating the correct placement of heat exchange devices (radiators or convectors) in the rooms. Even the connection scheme to the heating circuit has an impact on the efficiency of heat transfer. In addition, there are various tricks, for example, installing reflective screens on the wall behind the batteries - this gives quite a tangible effect.
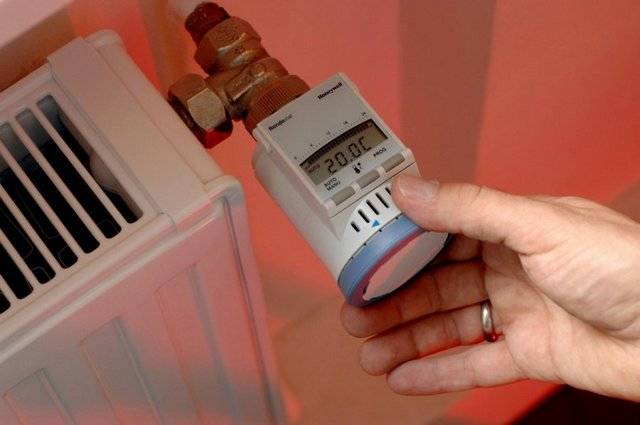

Economical consumption of the thermal energy generated by the boiler can be achieved by installing thermostatic regulators on heating radiators.
Savings can also be achieved by installing thermostatic control devices on radiators - heat will be taken only to the extent that is really necessary for a particular room.
So even the simplest decrease in the temperature in the rooms by a few degrees can lead to quite economical indicators of gas consumption for heating.