- How to choose the section of the duct?
- Air heating technique
- How to make air heating with your own hands?
- One-pipe heating scheme
- Estimation
- An example of calculating the heat loss of a house
- Additional elements of the system
- Air heating of industrial premises
- Stage three: linking branches
- Linkage Criteria
- What is the difference between solid fuel boilers
- DIY installation recommendations
- Application of thermal air curtains
- An example of calculating the heat loss of a house
How to choose the section of the duct?
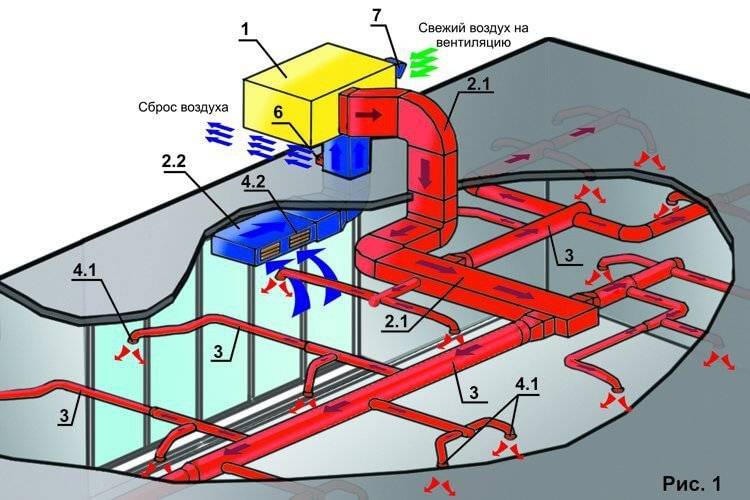
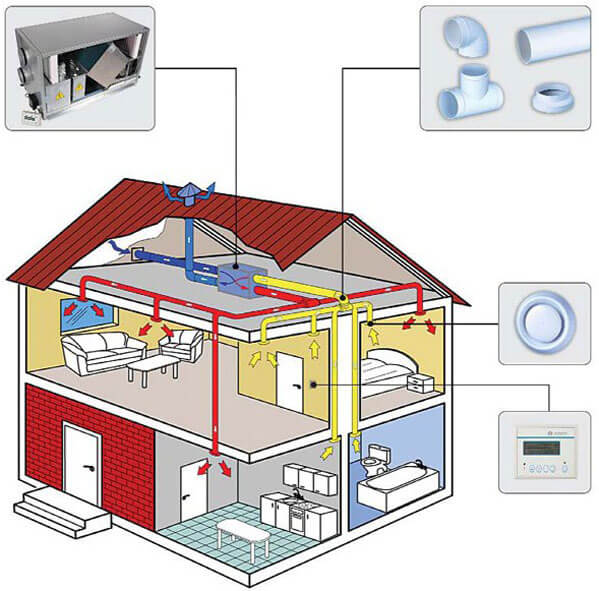
The ventilation system, as you know, can be ducted or ductless. In the first case, you need to choose the right section of the channels. If it is decided to install structures with a rectangular section, then the ratio of its length and width should approach 3:1.

The length and width of rectangular ducts should be three to one to reduce noise
The standard speed of movement of air masses along the main ventilation duct should be about five meters per second, and on branches - up to three meters per second. This will ensure that the system operates with a minimum amount of noise. The speed of air movement largely depends on the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe duct.
To select the dimensions of the structure, you can use special calculation tables.In such a table, you need to select the volume of air exchange on the left, for example, 400 cubic meters per hour, and select the speed value on top - five meters per second.
Then you need to find the intersection of the horizontal line for air exchange with the vertical line for speed.
Using this diagram, the cross section of the ducts for the duct ventilation system is calculated. The speed of movement in the main canal should not exceed 5 m/s
From this point of intersection, a line is drawn down to a curve from which a suitable section can be determined. For a rectangular duct, this will be the area value, and for a round duct, this will be the diameter in millimeters. First, calculations are made for the main duct, and then for branches.
Thus, calculations are made if only one exhaust duct is planned in the house. If it is planned to install several exhaust ducts, then the total volume of the exhaust duct must be divided by the number of ducts, and then calculations should be carried out according to the above principle.
This table allows you to choose the cross section of the duct for duct ventilation, taking into account the volume and speed of movement of air masses
In addition, there are specialized calculation programs with which you can perform such calculations. For apartments and residential buildings, such programs can be even more convenient, since they give a more accurate result.
Normal air exchange is influenced by such a phenomenon as reverse thrust, with the specifics of which and how to deal with it, the article recommended by us will acquaint you.
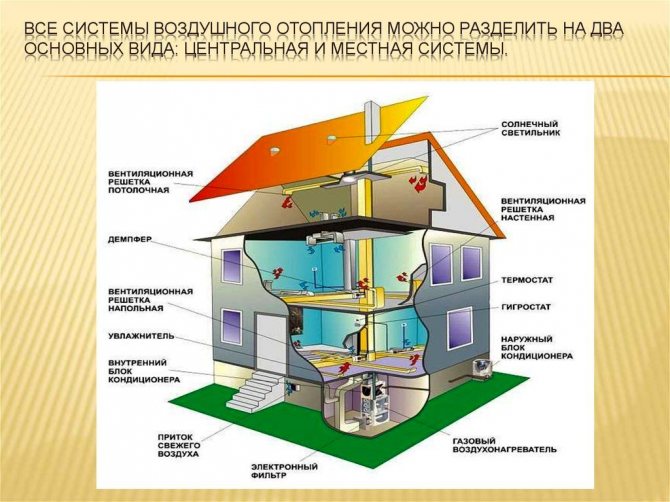
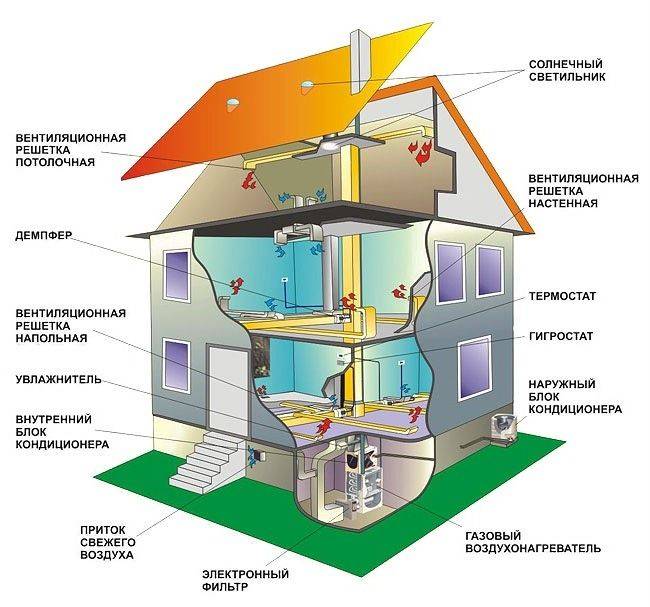
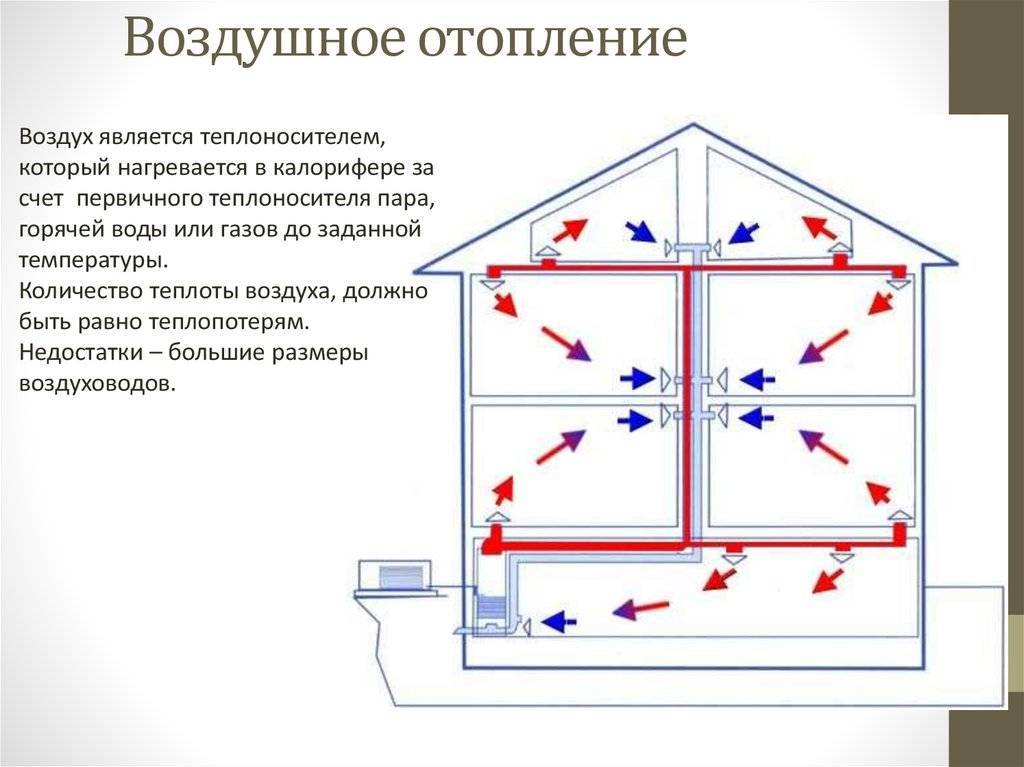
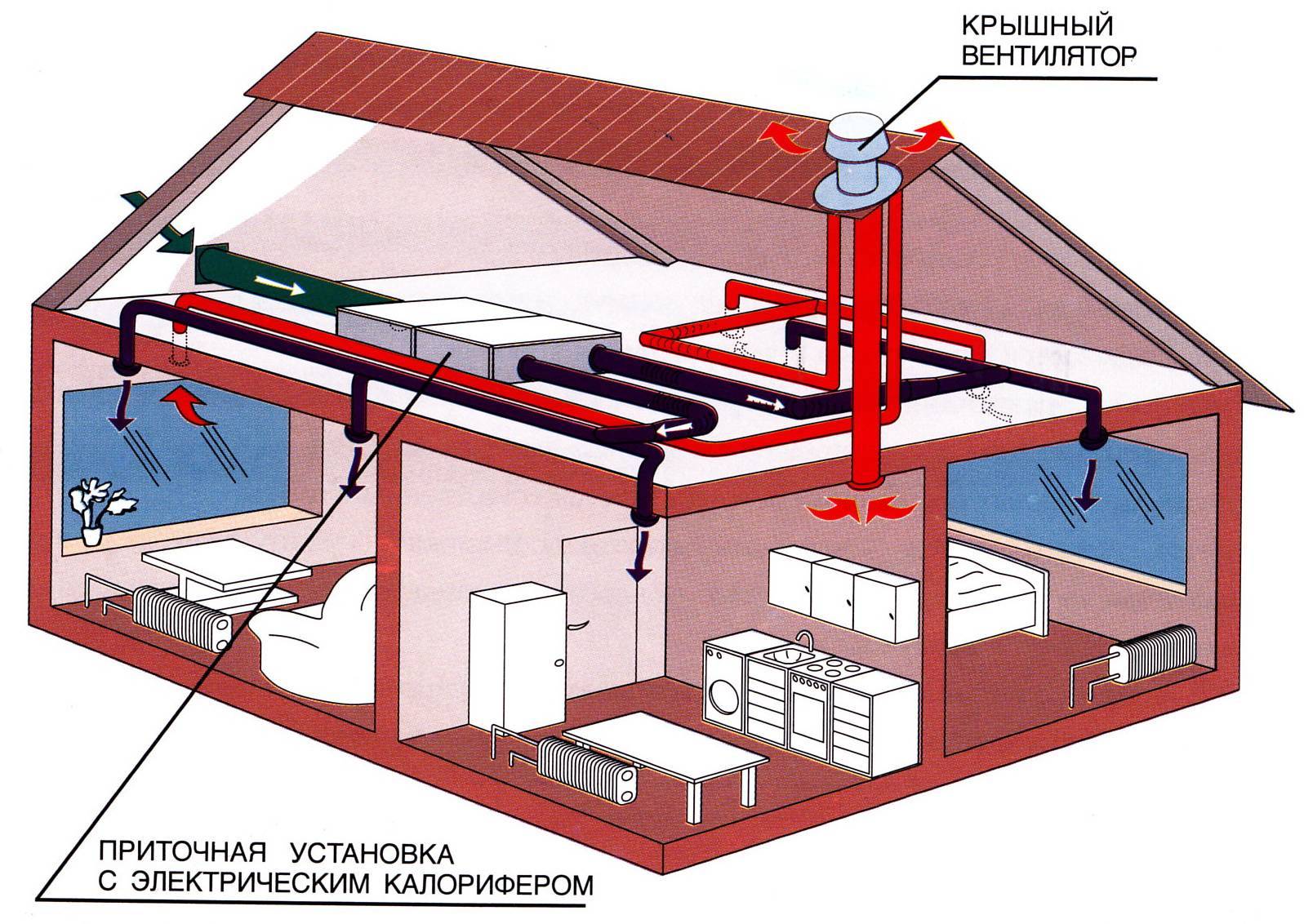
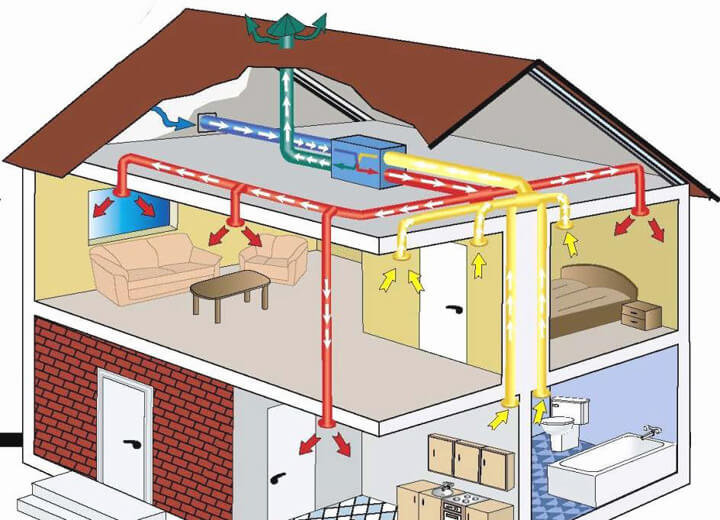
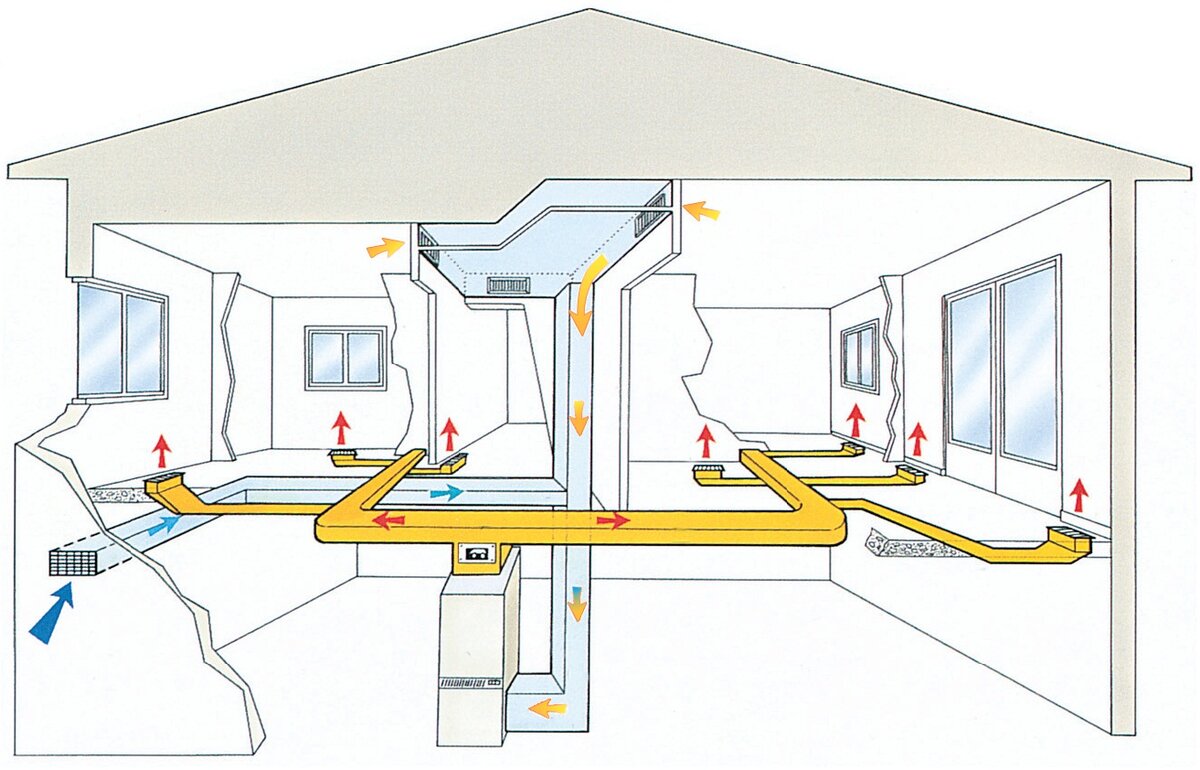
Air heating technique
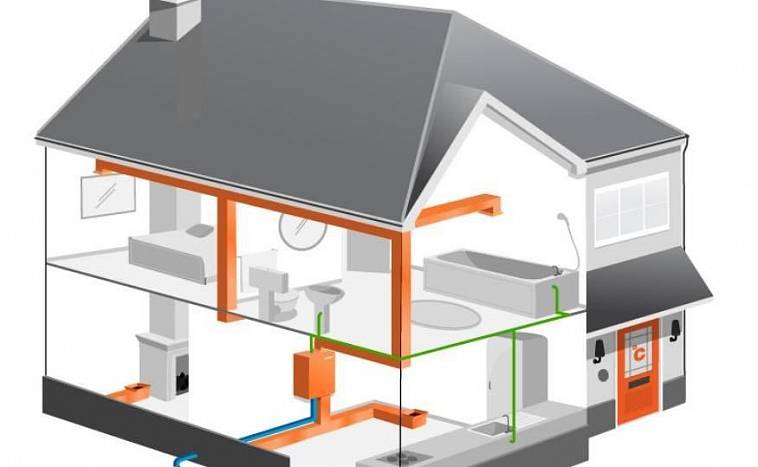
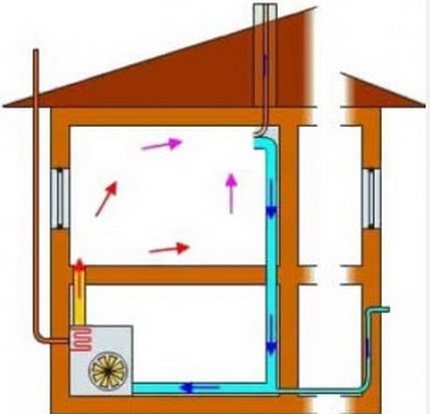
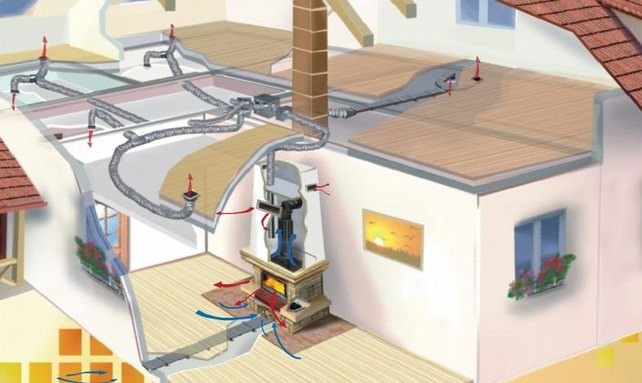
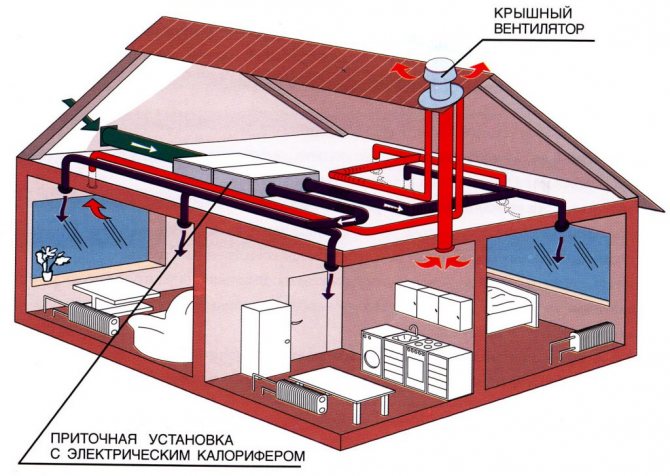
Air is a very efficient coolant. The most simplified example of an air heating system is a conventional fan heater.This mechanism is able to warm up a small room in a few minutes. But in order to organize air heating of a country house, the use of more serious equipment is required.
The technology of the procedure for the operation of the heating system with the help of air is as follows. The heat generator heats the air masses that enter the premises of the building through a pipe system. Here, air currents mix with the air space of the rooms, thereby raising the temperature. The cooled air rushes down, from where it enters a special pipeline and is redirected through it to the heat generator for heating.
This heating system of a private house involves the use of specially designed thermoregulation, in which the air is first heated to the required temperature, and then transfers its heat to the room, warming all objects around. The heating of air masses is carried out without intermediaries in the form of a system of pipes and batteries, so there are simply no irrational heat losses here.
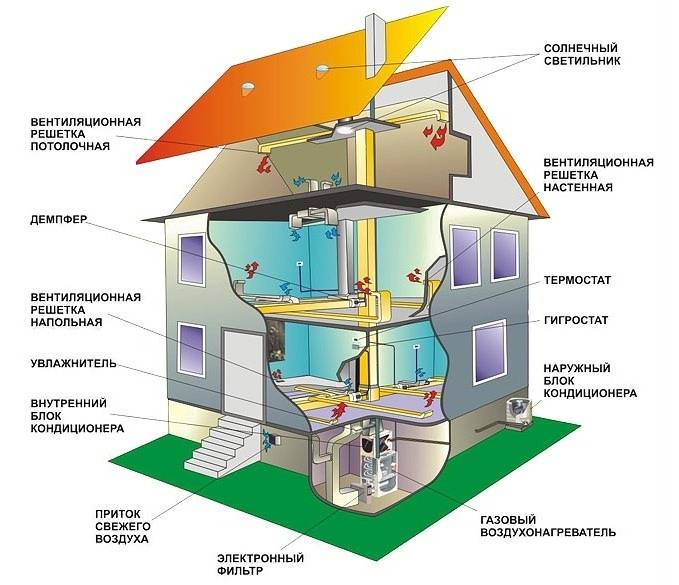
Such heating is usually used for frame structures, which are widespread in Canada, hence the name of the technology. The fact is that frame buildings, unlike brick buildings, are not able to effectively retain heat from radiators, and heating with air creates an acceptable microclimate with low financial costs.
How to make air heating with your own hands?
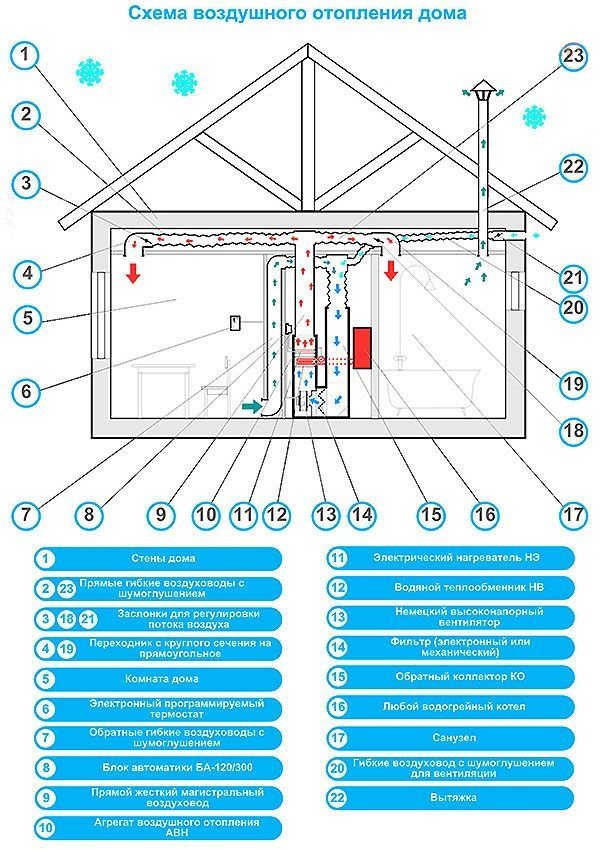
After receiving all the necessary calculations, you can begin preparing for the installation of the selected system, because it is not so difficult to organize air heating of a private house with your own hands. First you need to draw a diagram of the approximate passage of the air ducts and their connections with each other.
Having drawn an approximate procedure for connecting the system, it is better to discuss it with professionals, even if you already have personal experience in this matter, so that a person from the outside can give an objective assessment and find hidden flaws that can lead to vibration, draft and extraneous noise during operation of the equipment.
An experienced expert can assist with the selection of a suitable heat generator model that can ensure that the air is heated to the required temperature and does not overheat during increased activity. If the unit is quite large, it is better for it to allocate a separate extension adjacent to the house.
Heat generators are of two types:
- Stationary. They usually use gas fuel, due to their impressive dimensions and for safety reasons, they must be installed exclusively in separate rooms. They are mainly used to heat huge buildings, they are also often placed in factory floors.
- Mobile. Convenient for those who have dachas and country cottages, they are more compact than stationary counterparts. Their combustion chamber is isolated, but to ensure safety, these structures must be located in rooms with a built-in chimney system. This type is also known as calorific.
The process of self-installation of equipment for air heating consists of several stages:
- Install the boiler and heat exchanger. The first is mounted almost always in the basement. It is forbidden to connect its gas version on its own, this must be agreed with the relevant services.
- Make holes in the wall of the room where the heat exchanger is located for the outlet of the air outlet sleeve.
- Connect the heat exchanger to the air supply pipe.
- Install a fan under the combustion chamber. Supply to its outer side of the return pipe.
- Carry out the wiring of air vents and their fastening. Usually, they are selected with a circular cross section, for which you need to select special brackets.
- Connect the supply channels and the return air duct, insulate them.
It is relatively easy to equip the system with your own hands, but it is unlikely that it will be possible to carry out all the calculations correctly. Possible errors will lead to a decrease in the efficiency of the structure, constant drafts and other unpleasant consequences. Therefore, it is better to get a professionally prepared project and, if you wish, bring it to life on your own.
Air heating of the house is an efficient and profitable way of heating, which is more efficient than traditional water and gas systems. An air heating system can significantly improve the quality of life in a private house. This heating option is one of the safest, most economical, extremely durable and reliable systems. Therefore, it is becoming more and more popular.
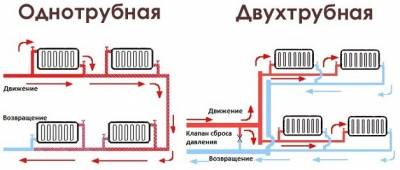
One-pipe heating scheme
From the heating boiler, you need to draw the main line representing the branching. After this action, it contains the required number of radiators or batteries. The line, drawn according to the design of the building, is connected to the boiler. The method forms the circulation of the coolant inside the pipe, heating the building completely. The circulation of warm water is adjusted individually.
A closed heating scheme is planned for Leningradka.In this process, a single-pipe complex is mounted according to the current design of private houses. At the request of the owner, elements are added to:
- Radiator controllers.
- Temperature controllers.
- balancing valves.
- Ball valves.
Leningradka regulates the heating of certain radiators.
Estimation
If you are going to do air heating at home with your own hands, it is very important to correctly make all the calculations before starting work. Things to consider:
- Estimated heat loss in each individual room.
- The required power of the heat generator and its type.
- How much air will be heated.
- Calculation of the area of air ducts, their length and diameter.
- Determine possible air pressure losses.
- Calculate the correct speed of air movement in the room so that there are no drafts and at the same time the circulation of air masses in the house takes place effectively and it is evenly heated.
A mistake made during the planning stage of the air system will result in a loss of time and serious amounts of money if the heating does not work properly and everything has to be redone.
The engineer will offer several options for the air heating system. It remains to choose the right one.
Only after making accurate calculations and drawing up a project, they begin to purchase a heater and all necessary materials.
An example of calculating the heat loss of a house
The house in question is located in the city of Kostroma, where the temperature outside the window during the coldest five-day period reaches -31 degrees, the ground temperature is + 5 ° C. The desired room temperature is +22°C.
We will consider a house with the following dimensions:
- width - 6.78 m;
- length - 8.04 m;
- height - 2.8 m.
The values will be used to calculate the area of the railings.
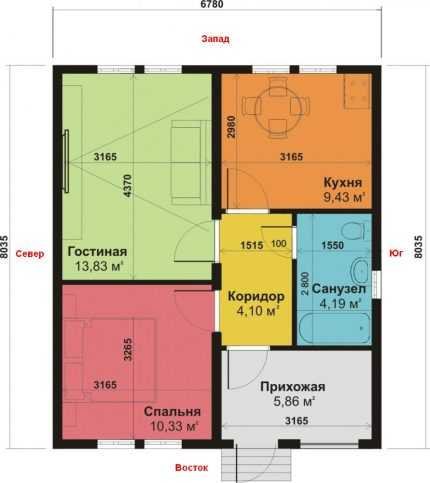
For calculations, it is most convenient to draw a house plan on paper, indicating on it the width, length, height of the building, the location of windows and doors, their dimensions
The walls of the building are:
- aerated concrete thickness B=0.21 m, thermal conductivity coefficient k=2.87;
- foam B=0.05 m, k=1.678;
- facing brick B=0.09 m, k=2.26.
When determining k, information from the tables should be used, or better, information from the technical data sheet, since the composition of materials from different manufacturers may differ, therefore, have different characteristics.
Reinforced concrete has the highest thermal conductivity, mineral wool slabs have the lowest, so they are most effectively used in the construction of warm houses
The floor of the house consists of the following layers:
- sand, V=0.10 m, k=0.58;
- crushed stone, V=0.10 m, k=0.13;
- concrete, B=0.20 m, k=1.1;
- ecowool insulation, B=0.20 m, k=0.043;
- reinforced screed, B=0.30 m k=0.93.
In the above plan of the house, the floor has the same structure throughout the area, there is no basement.
The ceiling is made up of:
- mineral wool, V=0.10 m, k=0.05;
- drywall, B=0.025 m, k= 0.21;
- pine shields, H=0.05 m, k=0.35.
The ceiling has no access to the attic.
There are only 8 windows in the house, all of them are two-chamber with K-glass, argon, D=0.6. Six windows have dimensions of 1.2x1.5 m, one - 1.2x2 m, one - 0.3x0.5 m. The doors have dimensions of 1x2.2 m, the D value according to the passport is 0.36.
Additional elements of the system
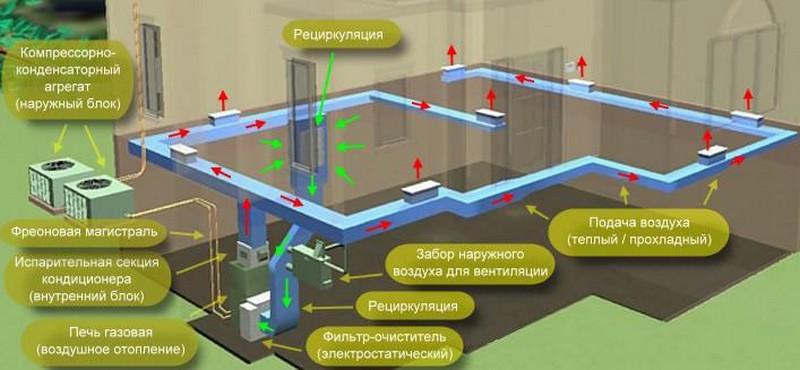
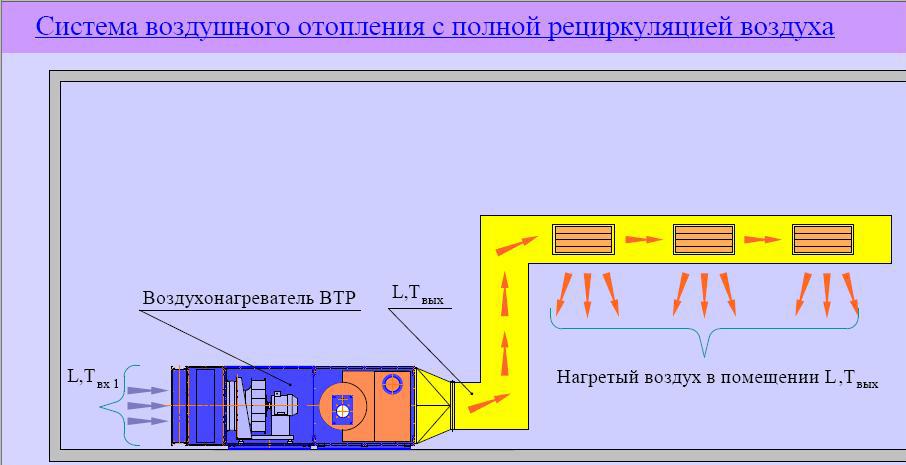
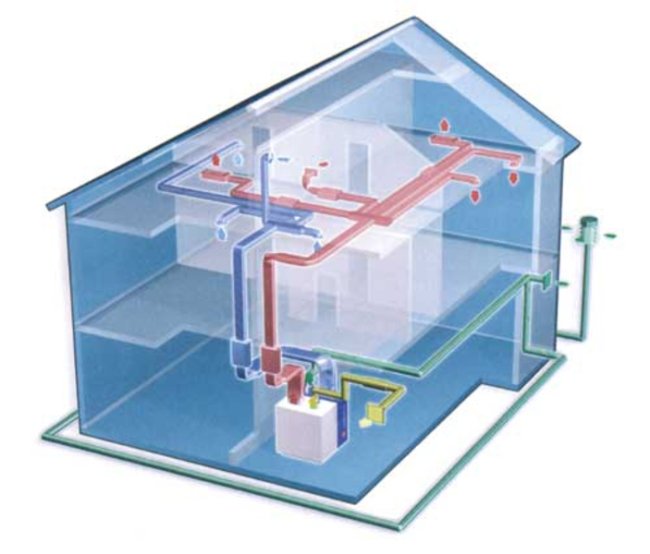
It is irrational to use the air system only for heating, it can be used to make a universal device for creating a microclimate in the house. To do this, an air cooling unit and an air conditioning unit are built into the device.
Such a system provides heating in winter and cooling in summer, maintaining a pleasant temperature inside the house, regardless of the weather outside. In addition, the system is supplemented with some more useful equipment:
- Electronic filter. It consists of removable cassettes that purify the incoming air by ionizing it. Filter plates trap microparticles of dust. Cassettes can be easily removed and cleaned by rinsing under running water.
- Humidifier. It is an evaporative unit with flowing water. Hot air, passing through this block, contributes to the active evaporation of moisture. Thus, the air is actively humidified.
- The desired level of moisture is controlled by a special humidity sensor with a regulator.
- UV lamp for air purification. Disinfects pathogenic bacteria in the air with ultraviolet light.
- Programmable thermostat. Controls the entire heating and cooling system. Connects to the Internet, thanks to which the temperature control in the house can be controlled from anywhere. Has 4 programmed modes.
- Electronic ventilation control unit. Allows you to control the ventilation system autonomously or completely turn it off if necessary.
WATCH VIDEO
A properly designed and well-made air heating system at home will delight residents with a pleasant microclimate for more than one year.
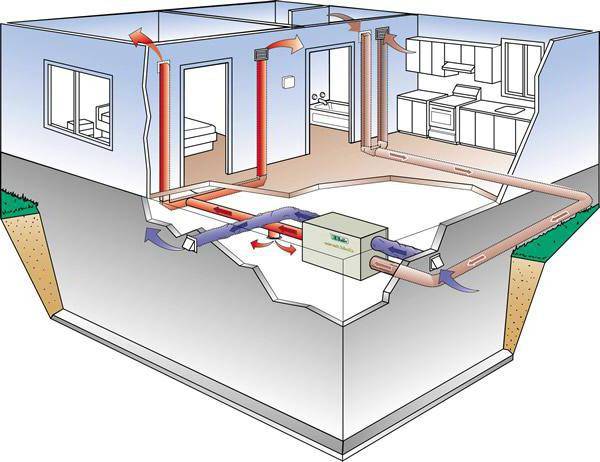
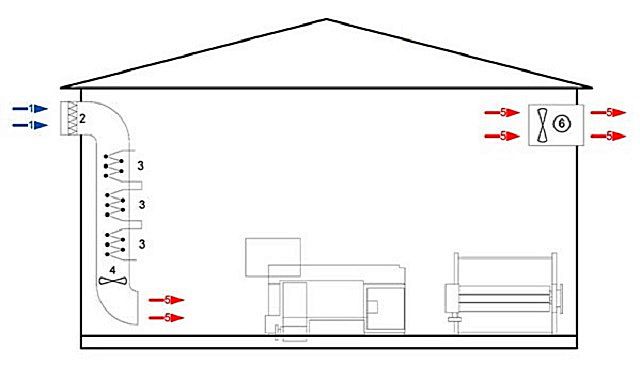
Air heating of industrial premises

Through the system of air ducts, heat is distributed throughout the territory of the production workshop
The air heating system at each specific industrial enterprise can be used as the main one, or as an auxiliary one.In any case, installation of air heating in a workshop is cheaper than water heating, since there is no need to install expensive boilers for heating industrial premises, lay pipelines and mount radiators.
Advantages of the air heating system of the industrial premises:
- saving the area of the working area;
- energy efficient consumption of resources;
- simultaneous heating and air purification;
- uniform heating of the room;
- safety for the well-being of employees;
- no risk of leaks and freezing of the system.
Air heating of a production facility can be:
- central - with a single heating unit and an extensive network of air ducts through which heated air is distributed throughout the workshop;
- local - air heaters (air-heating units, heat guns, air-heat curtains) are located directly in the room.
In the centralized air heating system, to reduce energy costs, a recuperator is used, which partially uses the heat of the internal air to heat the fresh air coming from outside. Local systems do not carry out recovery, they only warm the internal air, but do not provide an inflow of external air. Wall-ceiling air heaters can be used for heating individual workplaces, as well as for drying any materials and surfaces.
By giving preference to air heating of industrial premises, business leaders achieve savings due to a significant reduction in capital costs.
Stage three: linking branches
When all the necessary calculations have been made, it is necessary to link several branches. If the system serves one level, then the branches that are not included in the trunk are linked. The calculation is carried out in the same manner as for the main line. The results are entered into a table. In multi-storey buildings, floor-by-floor branches at intermediate levels are used for linking.
Linkage Criteria
Here, the values of the sum of losses are compared: pressure along the linked segments with a parallel connected main. It is necessary that the deviation is no more than 10 percent. If it is found that the discrepancy is greater, then the linkage can be carried out:
- by selecting the appropriate cross-sectional dimensions of the air ducts;
- by installing diaphragms or throttle valves on the branches.
Sometimes, to carry out such calculations, all you need is a calculator and a couple of reference books. If it is required to carry out an aerodynamic calculation of the ventilation of large buildings or industrial premises, then an appropriate program will be needed. It will allow you to quickly determine the dimensions of the sections, pressure losses both in individual segments and in the entire system as a whole.
The purpose of the aerodynamic calculation is to determine the pressure loss (resistance) to air movement in all elements of the ventilation system - air ducts, their fittings, grilles, diffusers, air heaters and others. Knowing the total value of these losses, you can choose a fan that can provide the required air flow. There are direct and inverse problems of aerodynamic calculation. The direct problem is solved in the design of newly created ventilation systems, which consists in determining the cross-sectional area of all sections of the system at a given flow rate through them.The inverse problem is to determine the air flow rate for a given cross-sectional area of operated or reconstructed ventilation systems. In such cases, to achieve the required flow, it is enough to change the fan speed or replace it with a different size.
By area F
determine the diameterD (for round shape) or heightA and widthB (for a rectangular) duct, m. The values obtained are rounded up to the nearest larger standard size, i.D st ,A st andIn st (reference value).
Recalculate the actual cross-sectional area F
fact and speedv fact .
For a rectangular duct, the so-called. equivalent diameter DL = (2A st * B st ) / (Ast+ Bst), m. Determine the value of the Reynolds similarity test Re = 64100* Dst*v fact. For rectangular shapeD L \u003d D st. Friction coefficient λtr = 0.3164 ⁄ Re-0.25 at Re≤60000, λtr= 0.1266 ⁄ Re-0.167 at Re>60000. Local resistance coefficient λm
depends on their type, quantity and is selected from directories.
Comments:
- Initial data for calculations
- Where to start? Calculation Order
The heart of any ventilation system with mechanical air flow is the fan, which creates this flow in the air ducts. The power of the fan directly depends on the pressure that must be created at the outlet of it, and in order to determine the value of this pressure, it is necessary to calculate the resistance of the entire duct system.
To calculate the pressure loss, you need a diagram and dimensions of the duct and additional equipment.
What is the difference between solid fuel boilers
In addition to the fact that these heat sources produce heat energy by burning various types of solid fuels, they have a number of other differences from other heat generators. These differences are precisely the result of burning wood, they must be taken for granted and always taken into account when connecting the boiler to a water heating system. Features are as follows:
- High inertia. At the moment, there are no ways to abruptly extinguish a burning solid fuel in a combustion chamber.
- Formation of condensate in the firebox. The peculiarity manifests itself when a heat carrier with a low temperature (below 50 °C) enters the boiler tank.
Note. The phenomenon of inertia is absent only in one type of solid fuel units - pellet boilers. They have a burner, where wood pellets are dosed, after the supply is stopped, the flame goes out almost immediately.
The danger of inertia lies in the possible overheating of the water jacket of the heater, as a result of which the coolant boils in it. Steam is formed, which creates high pressure, tearing the body of the unit and part of the supply pipeline. As a result, there is a lot of water in the furnace room, a lot of steam and a solid fuel boiler unsuitable for further operation.
A similar situation may arise when the heat generator is connected incorrectly. After all, in fact, the normal mode of operation of wood-burning boilers is the maximum, it is at this time that the unit reaches its passport efficiency. When the thermostat responds to the heat carrier reaching a temperature of 85 ° C and closes the air damper, combustion and smoldering in the furnace still continues. The temperature of the water rises by another 2-4°C, or even more, before its growth stops.
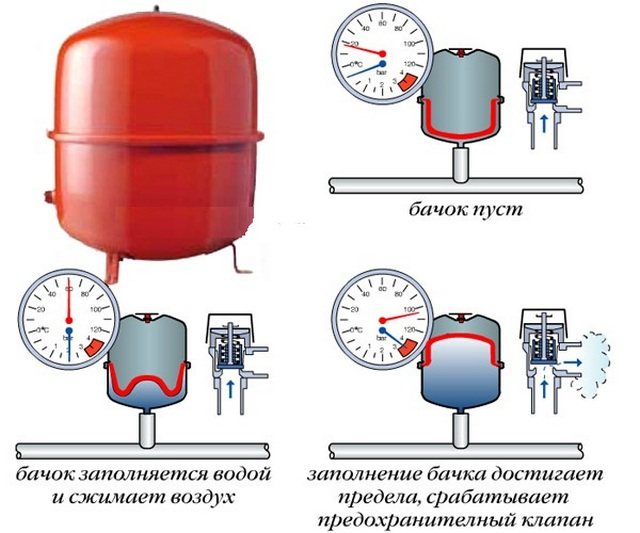
In order to avoid excess pressure and a subsequent accident, an important element is always involved in the piping of a solid fuel boiler - a safety group, more about it will be discussed below.
Another unpleasant feature of the operation of the unit on wood is the appearance of condensate on the inner walls of the firebox due to the passage of an unheated coolant through the water jacket. This condensate is not God's dew at all, since it is an aggressive liquid, from which the steel walls of the combustion chamber quickly corrode. Then, having mixed with the ash, the condensate turns into a sticky substance, it is not so easy to tear it off the surface. The problem is solved by installing a mixing unit in the piping circuit of a solid fuel boiler.
Such a deposit serves as a heat insulator and reduces the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler.
It is too early for owners of heat generators with cast-iron heat exchangers that are not afraid of corrosion to breathe a sigh of relief. They can expect another misfortune - the possibility of destruction of cast iron from temperature shock. Imagine that in a private house the electricity was turned off for 20-30 minutes and the circulation pump, which drives water through a solid fuel boiler, stopped. During this time, the water in the radiators has time to cool down, and in the heat exchanger - to heat up (due to the same inertia).
Electricity appears, the pump turns on and sends the cooled coolant from the closed heating system to the heated boiler. From a sharp temperature drop, a temperature shock occurs at the heat exchanger, the cast-iron section cracks, water runs to the floor. It is very difficult to repair, it is not always possible to replace the section.So even in this scenario, the mixing unit will prevent an accident, which will be discussed later.
Emergencies and their consequences are not described in order to scare users of solid fuel boilers or encourage them to purchase unnecessary elements of piping circuits. The description is based on practical experience, which must always be taken into account. With the correct connection of the thermal unit, the likelihood of such consequences is extremely low, almost the same as for heat generators using other types of fuel.
DIY installation recommendations
For laying the main lines of natural circulation, it is better to use polypropylene or steel pipes. The reason is the large diameter, polyethylene Ø40 mm and more is too expensive. We make radiator eyeliners from any convenient material.
An example of installing a two-pipe wiring in a garage
How to make the wiring correctly and withstand all the slopes:
- Start with markup. Designate the battery installation locations, connection points for connections and highway routes.
- Mark the tracks on the walls with a pencil, starting from the distant batteries. Adjust the slope with a long building level.
- Move from the extreme radiators to the boiler room. When you draw all the tracks, you will understand at what level to put the heat generator. The inlet pipe of the unit (for the cooled coolant) must be located at the same level or below the return line.
- If the floor level of the firebox is too high, try moving all the heaters up. Horizontal pipelines will rise next. In extreme cases, make a recess under the boiler.
Laying a return line in a furnace with parallel connection to two boilers
After marking, punch holes in the partitions, cut grooves for the hidden gasket. Then check the traces again, make adjustments and proceed with the installation. Follow the same order: first fix the batteries, then lay the pipes towards the furnace. Install expansion tank with drain pipe.
The gravity pipeline network is filled without problems, Mayevsky's cranes do not need to be touched. Just slowly pump water through the make-up tap at the lowest point, all the air will go into the open tank. If any radiator remains cold after warming up, use the manual air vent.
Application of thermal air curtains
To reduce the volume of air entering the room when opening external gates or doors, in the cold season, special thermal air curtains are used.
At other times of the year they can be used as recirculation units. Such thermal curtains are recommended for use:
- for external doors or openings in rooms with a wet regime;
- at constantly opening openings in the outer walls of structures that are not equipped with vestibules and can be opened more than five times in 40 minutes, or in areas with an estimated air temperature below 15 degrees;
- for external doors of buildings, if they are adjacent to premises without a vestibule, which are equipped with air conditioning systems;
- at openings in internal walls or in partitions of industrial premises in order to avoid the transfer of coolant from one room to another;
- at the gate or door of an air-conditioned room with special process requirements.
An example of calculating air heating for each of the above purposes can serve as an addition to the feasibility study for installing this type of equipment.
The temperature of the air that is supplied to the room by thermal curtains is taken not higher than 50 degrees at external doors, and not more than 70 degrees - at external gates or openings.
When calculating the air heating system, the following values of the temperature of the mixture entering through the external doors or openings (in degrees) are taken:
5 - for industrial premises during heavy work and the location of workplaces no closer than 3 meters to the outer walls or 6 meters from the doors;
8 - for heavy types of work for industrial premises;
12 - during moderate work in industrial premises, or in the lobbies of public or administrative buildings.
14 - for light work for industrial premises.
For high-quality heating of the house, the correct location of the heating elements is necessary. Click to enlarge.
The calculation of air heating systems with thermal curtains is made for various external conditions.
Air curtains at external doors, openings or gates are calculated taking into account wind pressure.
The coolant flow rate in such units is determined from the wind speed and the outside air temperature at parameters B (at a speed of not more than 5 m per second).
In cases where the wind speed at parameters A is greater than at parameters B, then the air heaters should be checked when exposed to parameters A.
The speed of air outflow from slots or external openings of thermal curtains is assumed to be no more than 8 m per second at external doors and 25 m per second at technological openings or gates.
When calculating heating systems with air units, parameters B are taken as the design parameters of the outside air.
One of the systems during non-working hours can operate in standby mode.
The advantages of air heating systems are:
- Reducing the initial investment by reducing the cost of purchasing heating appliances and laying pipelines.
- Ensuring sanitary and hygienic requirements for environmental conditions in industrial premises due to the uniform distribution of air temperature in large premises, as well as preliminary dedusting and humidification of the coolant.
An example of calculating the heat loss of a house
Since the total heat loss of a country house is the sum of the heat loss of windows, doors, walls, ceilings and other elements of the building, its formula is presented as the sum of these indicators. The principle of calculation is as follows:
Qorg.k = Qpol + Qst + Qokn + Qpt + Qdv
It is possible to determine the heat losses of each element, taking into account the features of its structure, thermal conductivity and the heat resistance coefficient indicated in the passport of a particular material.
The calculation of heat loss at home is difficult to consider solely on formulas, so we suggest using a good example.