- PC calculation option
- Calculation of the volume of water present in the entire system
- How are mass and quality related?
- Advantages and disadvantages of steel pipe rolling
- Pipe Volume Calculation
- Determine the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe pipe
- The formula for calculating the volume of a pipe
- The volume of the water supply in liters
- Inner and outer diameter, wall thickness, radius
- Simplified method for calculating the weight of pipes
- Why do we need pipe parameters calculations
- 4 Calculation of the weight of a profile pipe according to the formula
- Why you may need to calculate the water in the pipe
- For sewerage
- The volume of the wedge and obelisk
- Formulation of the problem
PC calculation option
Performing the calculus using a computer is the least laborious - all that is required of a person is to insert the necessary data into the appropriate columns.
Therefore, a hydraulic calculation is done in a few minutes, and this operation does not require a large stock of knowledge, which is necessary when using formulas.
For its correct implementation, it is necessary to take the following data from the technical specifications:
- gas density;
- coefficient of kinetic viscosity;
- gas temperature in your region.
The necessary technical conditions are obtained from the city gas department of the settlement where the gas pipeline will be built.Actually, the design of any pipeline begins with the receipt of this document, because it contains all the basic requirements for its design.
The use of special programs is the simplest method of hydraulic calculation, excluding the search and study of formulas for calculations.
Next, the developer needs to find out the gas consumption for each device that is planned to be connected to the gas pipeline. For example, if the fuel will be transported to a private house, then stoves for cooking, all kinds of heating boilers are most often used there, and the necessary numbers are always in their passports.
In addition, you will need to know the number of burners for each stove that will be connected to the pipe.
At the next stage of collecting the necessary data, information about the pressure drop at the installation sites of any equipment is selected - this can be a meter, a shut-off valve, a thermal shut-off valve, a filter, and other elements.
In this case, it is easy to find the necessary numbers - they are contained in a special table attached to the passport of each product.
The designer should pay attention to the fact that the pressure drop at maximum gas consumption should be indicated.
From a special table attached to the product passport, you can find out information about the pressure loss when connecting devices to the network
At the next stage, it is recommended to find out what the blue fuel pressure will be at the tie-in point. Such information may contain the technical specifications of your Gorgaz, a previously drawn up scheme of the future gas pipeline.
If the network will consist of several sections, then they must be numbered and indicate the actual length.In addition, for each, all variable indicators should be prescribed separately - this is the total flow rate of any device that will be used, the pressure drop, and other values.
A simultaneity factor is required. It takes into account the possibility of joint operation of all gas consumers connected to the network. For example, all heating equipment located in an apartment building or a private house.
Such data is used by the hydraulic calculation program to determine the maximum load in any section or in the entire gas pipeline.
For each individual apartment or house, the specified coefficient does not need to be calculated, since its values are known and are indicated in the table below:
A table with simultaneity coefficients, the data from which is used in any type of calculation. It is enough to select the column corresponding to a particular household appliance and take the desired number
If at some facility it is planned to use more than two heating boilers, furnaces, storage water heaters, then the simultaneity indicator will always be 0.85. Which will need to be indicated in the corresponding column used for the calculation of the program.
Next, you should specify the diameter of the pipes, and you will also need their roughness coefficients, which will be used in the construction of the pipeline. These values are standard and can be easily found in the Rulebook.
Calculation of the volume of water present in the entire system
To determine such a parameter, it is necessary to substitute the value of the inner radius into the formula. However, a problem immediately appears. And how to calculate the total volume of water in the pipe of the entire heating system, which includes:
- Radiators;
- Expansion tank;
- Heating boiler.
First, the volume of the radiator is calculated. To do this, its technical passport is opened and the values \u200b\u200bof the volume of one section are written out. This parameter is multiplied by the number of sections in a particular battery. For example, one is equal to 1.5 liters.
When a bimetal radiator is installed, this value is much less. The amount of water in the boiler can be found in the device passport.
To determine the volume of the expansion tank, it is filled with a pre-measured amount of liquid.
It is very easy to determine the volume of pipes. The available data for one meter, a certain diameter, simply needs to be multiplied by the length of the entire pipeline.
Note that in the global network and reference literature, you can see special tables. They show indicative product data. The error of the given data is quite small, so the values \u200b\u200bgiven in the table can be safely used to calculate the volume of water.
I must say that when calculating the values, you need to take into account some characteristic differences. Metal pipes with a large diameter pass the amount of water much less than the same polypropylene pipes.
The reason lies in the smoothness of the surface of the pipes. In steel products, it is made with a large roughness. PPR pipes do not have roughness on the inner walls. However, at the same time, steel products have a larger volume of water than in other pipes of the same section. Therefore, to make sure that the calculation of the volume of water in the pipes is correct, you need to double-check all the data several times and back up the result with an online calculator.
How are mass and quality related?
By the weight of the measured segment, you can understand: did the manufacturer of this product cheat, did he save on the production process, does the pipe comply with GOST. After all, the density of the pipe is a constant value, and the volume of metal used to manufacture the product is determined by GOST and the conscience of the manufacturer.
And if the mass of the measured segment, determined by multiplying the volume of the material by the density, is less than the profile pipe weight table provides, then you can no longer ask about the quality of such products: such a product is only suitable for remelting.
However, it might not be all that bad. After all, the buyer can simply make a mistake in calculating the weight. This situation occurs quite often. Therefore, in order not to blame honest manufacturers unfounded, the buyer of a profile pipe must be aware of the method for calculating the mass of the product. And in this article we will introduce you to several methods that allow you to determine the value of the weight of a profile pipe even in the field.
Advantages and disadvantages of steel pipe rolling
Steel products have many advantages that are recommended to pay attention to. First of all, it should be noted that parts made of this alloy are distinguished by high strength characteristics.
It is this fact that determines their wide distribution in the construction industry, where the strength of products is one of the main indicators. A wide range of parts is also considered an important advantage, as it allows you to expand their operational scope. In the construction market, you can easily choose parts that are suitable in shape and technical characteristics.

Metal pipes are characterized by high strength characteristics
All steel pipes can be divided into three categories:
- round;
- profiled (square and rectangular);
- non-standard (multifaceted).
A serious advantage inherent in these products is that they have a high resistance to mechanical stress. Steel pipes perfectly tolerate pressure and shock. It is worth noting that they have an acceptable cost and belong to the middle price segment.
A wide variety of types of parts allows them to be used in various fields: construction, household, etc. Steel products have a small linear expansion
This is a very important advantage, since many pipes expand when heated, and if they are placed in a screed, this can lead to cracks.
In order to answer the question of how to calculate the weight of a pipe, you need to get to know all the methods that allow you to make this calculation. Knowledge of the mass of steel products is required at all stages, from their acquisition to installation.

A wide variety of steel pipes allows them to be used in various areas of life.
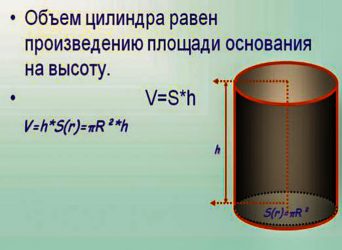
Pipe Volume Calculation
To calculate the volume of a pipe, you need to use school knowledge of geometry. There are several ways: 1. Multiplying the cross-sectional area of the figure by its length in meters, the result will be meters cubed. 2. It is possible to find out the size of the water supply in liters. To do this, the volume is multiplied by 1000 - this is the number of liters of water in 1 cubic meter. 3. The third option is to immediately count in liters. You will need to make measurements in decimeters - the length and area of \u200b\u200bthe figure. This is a more complicated and inconvenient way.
To calculate manually - without a calculator, you will need a caliper, ruler and calculator. To facilitate the process of determining the size of the volume of the pipe, you can use the online calculator.
Determine the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe pipe
To know the exact
value, you must first calculate the cross-sectional area. For this,
formula should be used:
S = R2 x Pi
Where R is the radius of the pipe and Pi is 3.14. Since liquid containers are usually round, R is squared.
Let's see how we can
make calculations, having a product diameter of 90 mm:
- Determine the radius - 90 / 2 = 45 mm, in
in terms of centimeters 4.5. - We square 4.5, it turns out 2.025 cm2.
- We substitute the data into the formula - S \u003d 2 x 20.25
= 40.5 cm2.
If the product
profiled, then you need to calculate according to the rectangle formula - S \u003d a x b, where a
and b is the size of the sides (length). When determining the size of a profile section with a length
sides 40 and 50, you need 40 mm x 50 mm = 2000 mm2 or 20 cm2.
To calculate the cross section,
you need to know the inner diameter of the pipe, which is measured with a caliper,
but this is not always possible. If only the outer diameter is known, and we do not know
wall thickness, then more complex calculations will be required. Standard Thickness
sometimes 1 or 2 mm, for large diameter products it can reach 5 mm.
Important!
It is better to start the calculation if there are accurate indicators of the thickness of the walls and
inner radius
Formula
pipe volume calculation
Calculate the volume of the pipe in m3,
you can use the formula:
V = S x L
That is, you need to know
only two values: the cross-sectional area (which was determined in advance) (S) and
length (L).
For example, the length
the pipeline is 2 meters, and the cross-sectional area is half a meter. For calculation it is necessary
take the formula for determining the area of a circle and insert the outer dimension
metal cross bars:
S = 3.14 x (0.5 / 2) =
0.0625 sq.m.
The final result will be as follows:
V = HS = 2 x 0.0625 = 0.125
meter cube.
H is the wall thickness
When calculating, it is important
so that all indicators have one unit of measurement, otherwise the result
will turn out wrong. It is easier to take data in cm2
The volume of the water supply in liters
It is easy to calculate the volume of liquid in a pipe without a calculator if you know its inner diameter, but this is not always
can be done when radiators or heating boilers for water have a complex
shape. Today, such products are often used in the construction industry, with
arrangement of warm floors. Therefore, you should first find out the parameters
design, this information can be found in the data sheet or accompanying
documentation. To calculate the size of a non-standard container, you need to fill in
into it water, which is measured in advance.
In addition, the cubic capacity of water will depend
and from the material from which the plumbing is made. For example, a steel
will pass an order of magnitude less water than an equal-sized polypropylene or
plastic. This is affected by the surface from the inside, iron is more rough, which
affects permeability.
Therefore, it is necessary to do
calculations for each container if it is made of a different material, and
then add up all the scores. You can use special
service programs or calculators, today there are a lot of them on the Internet, they
greatly facilitate the process of determining the amount of water in the system.
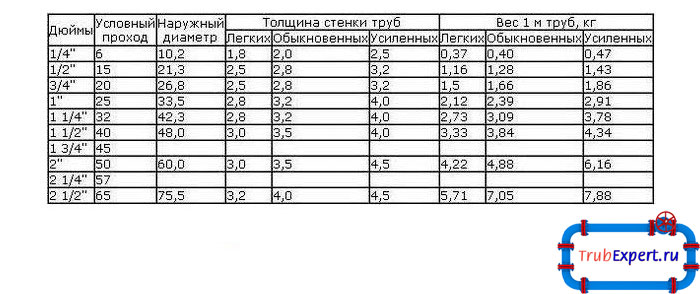
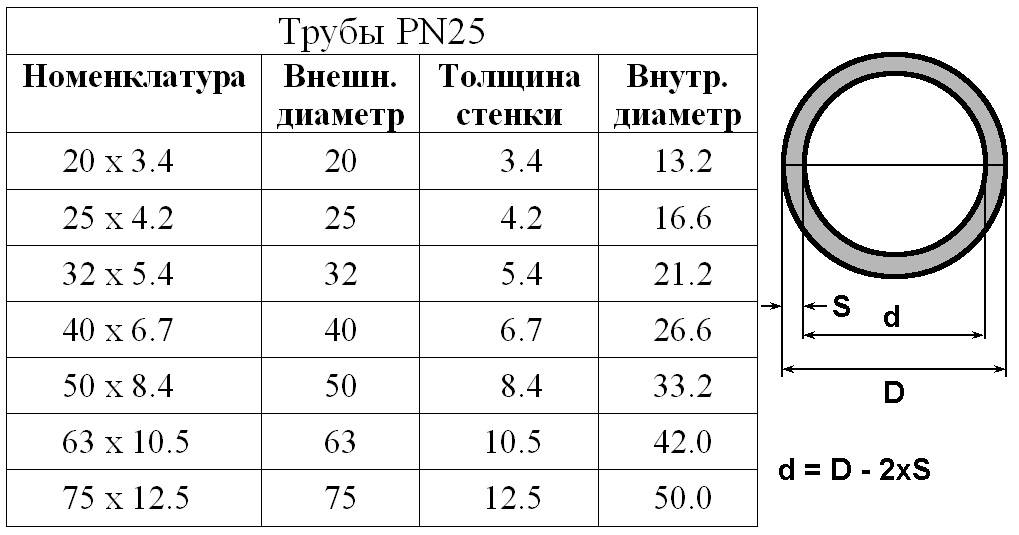
Inner and outer diameter, wall thickness, radius
Pipes are a specific product. They have an inner and outer diameter, since their wall is thick, its thickness depends on the type of pipe and the material from which it is made. The technical specifications often indicate the outer diameter and wall thickness.
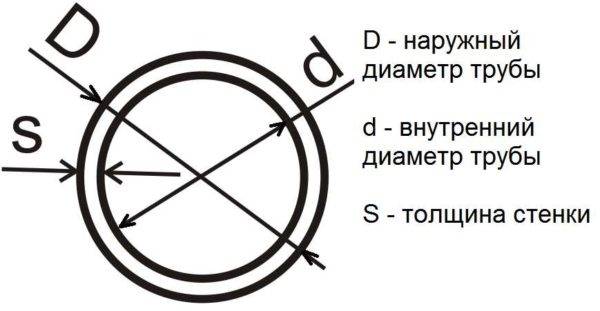
Pipe inner and outer diameter, wall thickness
Having these two values, it is easy to calculate the inner diameter - subtract twice the wall thickness from the outer one: d = D - 2 * S. If you have an outer diameter of 32 mm, a wall thickness of 3 mm, then the inner diameter will be: 32 mm - 2 * 3 mm = 26 mm.
If, on the contrary, there is an inner diameter and wall thickness, but an outer one is needed, we add double the stack thickness to the existing value.
With radii (denoted by the letter R), it is even simpler - this is half the diameter: R = 1/2 D. For example, let's find the radius of a pipe with a diameter of 32 mm. We just divide 32 by two, we get 16 mm.

Caliper measurements are more accurate
What to do if there is no pipe technical data? To measure. If special accuracy is not needed, a regular ruler will do; for more accurate measurements, it is better to use a caliper.
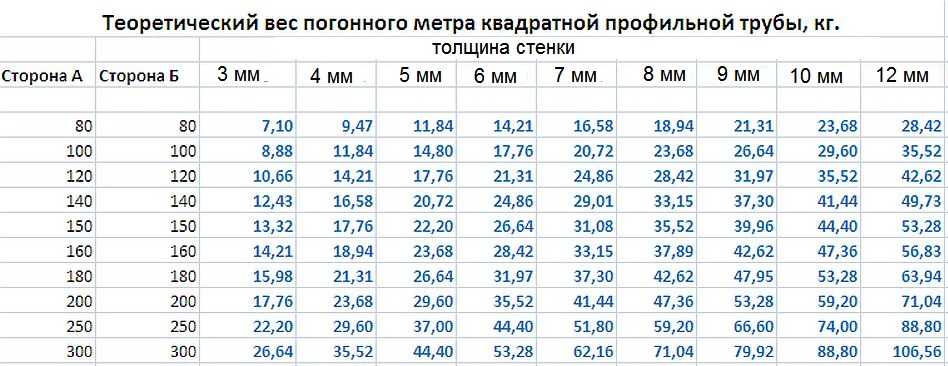
Simplified method for calculating the weight of pipes
Well, at the very end, we will reveal a terrible secret to you: there is a simplified formula for calculating the weight of a profile pipe 1 m long! And this is not even a formula, but a tabular data set.
More detailed information can be found in GOST 8639-82, which contains the value of the mass of a meter segment, calculated for each unit of the assortment of profile pipes. That is, for a simplified calculation, we must take the value of the mass of a meter-long pipe cut and multiply this value by the length of the measured segment of the product. That's all.And no complications!
However, if GOST 8639-82 is not at hand, then the methods described in the previous paragraphs of this article will come in handy. So, either learn to calculate weight from density and volume, or get a reference book. The choice is yours.
Why do we need pipe parameters calculations
In modern construction, not only steel or galvanized pipes are used. The choice is already quite wide - PVC, polyethylene (HDPE and PVD), polypropylene, metal-plastic, corrugated stainless steel. They are good because they do not have such a large mass as steel counterparts. Nevertheless, when transporting polymer products in large volumes, it is desirable to know their mass in order to understand what kind of machine is needed. The weight of metal pipes is even more important - delivery is calculated by tonnage. So it is desirable to control this parameter.

What can't be measured can be calculated
Know the outer surface area pipes needed to buy paint and thermal insulation materials. Only steel products are painted, because they are subject to corrosion, unlike polymer ones. So you have to protect the surface from the effects of aggressive environments. They are used more often for the construction of fences, frames for outbuildings (garages, sheds, gazebos, change houses), so that the operating conditions are difficult, protection is necessary, because all frames require painting. This is where the surface area to be painted is required - the outer area of \u200b\u200bthe pipe.
When constructing a water supply system for a private house or cottage, pipes are laid from a water source (well or well) to the house - underground. And still, so that they do not freeze, insulation is required. You can calculate the amount of insulation knowing the area of the outer surface of the pipeline.Only in this case it is necessary to take material with a solid margin - the joints should overlap with a substantial margin.
The cross section of the pipe is necessary to determine the throughput - whether this product can carry the required amount of liquid or gas. The same parameter is often needed when choosing the diameter of pipes for heating and plumbing, calculating pump performance, etc.
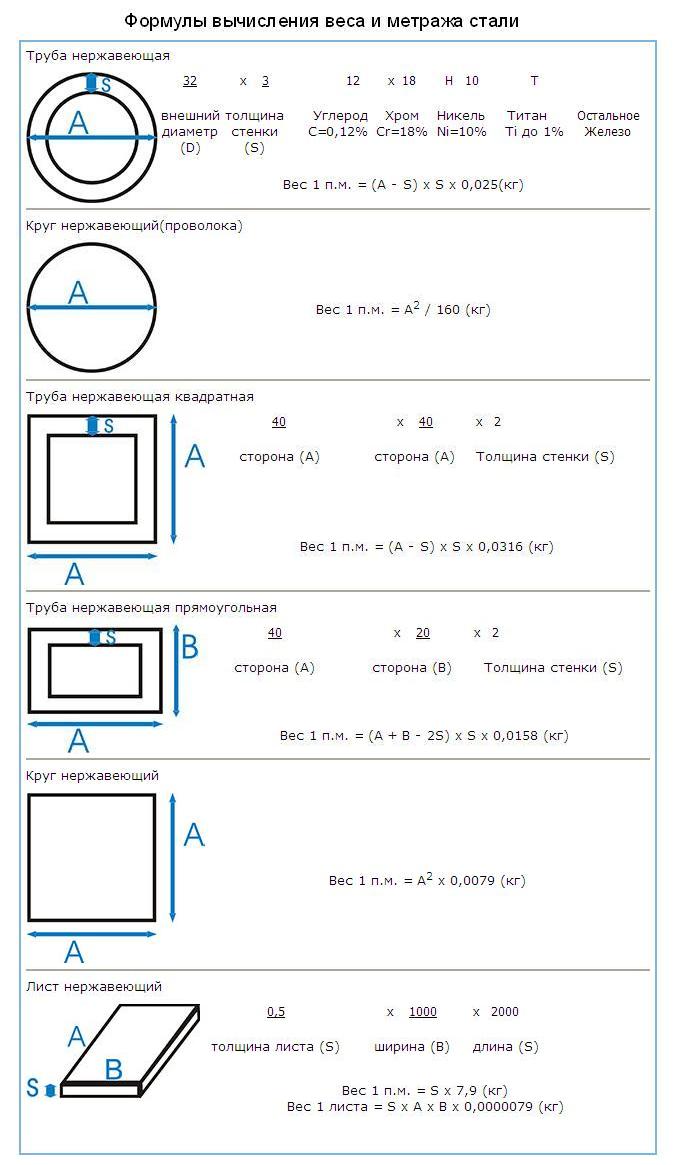
4 Calculation of the weight of a profile pipe according to the formula
The calculation of a profile pipe according to the formula is based on calculating the volume of the metal of the walls of a piece of a product 1 m long. When this value is multiplied by the density of the alloy used for the manufacture of rolled products, the theoretical weight of 1 m of the pipe is obtained. By multiplying this weight by the total length of the product, its mass is determined. The formula for calculating 1 m of profile pipe products is as follows:
m = 2*h*(A+B)*q, where
m is the mass of 1 m of pipe, in kg;
h is the wall thickness of the profile product, in m;
A and B are the lengths of the sides (height, width) of the profile, in m;
q is the density of the metal (steel 7850 kg/m3).
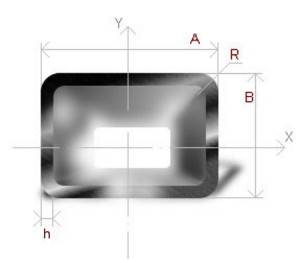
An example of calculating the theoretical weight of profile pipe products. Let's determine the mass of steel products 120x120x7 mm, 200 m long. To do this, we first convert all dimensions into meters. Then A and B will be equal to 0.12 m, and h - 0.007 m.
m \u003d 2 * 0.007 * (0.12 + 0.12) * 7850 \u003d 26.376 kg - the weight of 1 linear meter of pipe 120x120x7.
Determine the total mass for 200 meters:
26.376 * 200 = 5275.2 kg
The theoretical weight of 1 m obtained by the formula differs from the tabular value taken from GOST - 24.18 kg. This discrepancy is due to the fact that the proposed calculation formula does not take into account the external and internal roundings at the corners of the profile of a real pipe.The calculations were carried out for a product of the correct geometric shape (with right angles), but such products are not actually produced. And the theoretical values for the GOST tables were calculated taking into account the actual geometry of the profile of pipe products, so they are more accurate. Since the formulas used in these calculations are much more complicated than those given above and require much more time for calculations, we do not present them. In conditions where the Internet and reference books are not at hand, a simplified quick calculation will be enough to determine the approximate weight of the pipe. And it is better to find out the exact mass by weighing the products.
Why you may need to calculate the water in the pipe
In the plumbing system of a private house there is a pipeline of pipes, radiators, a reservoir for liquid - a membrane tank, as well as boilers, a boiler and other appliances. The heat-insulated floor represents system from the laid out metalplastic highway containing the heat carrier in a certain volume. To completely fill the system and know how much distilled water to buy, you need to calculate its total volume in advance.
When filling the heating system with antifreeze or other non-freezing liquid, in order to save money, it is necessary to know the volume of the pipe. When buying concentrated antifreeze, it will need to be diluted by half, so more liquid will cost more, and the concentration will be calculated incorrectly.
When calculating the volume, use:
- internal diameter of the pipe walls;
- the length of the section or the entire highway.
In the case of a difference in the internal section, each section is calculated separately and then the numbers are summed up.
In addition to the line, the internal volume of the following devices must be taken into account:
- membrane tank. This information can be read in the technical data sheet or checked on your own by pouring a certain amount of liquid into it.
- Radiators. This data is also in the product data sheet. The volume of one section is multiplied by their number throughout the house.
- Various nodes, complex wiring, manifolds also contain a certain volume of liquid, which is difficult to calculate due to the large number of fittings, adapters, and taps.
For sewerage
It is important to calculate the volume of water in the pipe and the potential of the line when arranging a septic tank, since a lack of diameter can lead to poor outflow of liquid from the house and clogging of the sewer. If the number of household appliances in the house exceeds the capacity of sewer pipes in terms of water consumption, the liquid will fill the line completely
If they are not insulated at the same time, in winter the drains inside may freeze and block the line. An ice block can also cause a pipe to break at a weak point, such as at joints or sharp bends. The volume of cast-iron sewer pipes should be larger, since the cast-iron surface is rough from the inside and silt gradually accumulates in it - a layer of organic matter that narrows the clearance and affects the throughput of the highway. Plastic pipes are better in this regard - they are perfectly smooth inside, organic particles cannot attach to the walls, so the calculated volume can not be further increased.
The volume of internal sewer pipes should not be greater than the external line.This leads to blockages in the area where the internal and external sewer pipes are joined. The same principle applies to internal wiring - the volume of liquid from household appliances should not exceed the volume that the main riser in the house can accommodate.
The volume of the wedge and obelisk
The wedge in the technique is often a pentahedron, the base of which is a rectangle, and the side faces are isosceles triangles or trapezoids. The formula for calculating the volume of a wedge is:
- a - side of the base of the foot of the wedge;
- a1 is the width of the wedge tip;
- b is the thickness of the wedge;
- h is the height of the wedge.
The obelisk is a hexagon, the base of which are rectangles that are located in parallel planes. The opposite faces are symmetrically inclined towards the base of the obelisk. The volume of this geometric body:
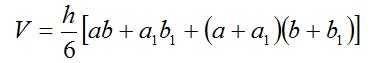
- a and b are the dimensions of the length and width of the larger base of the obelisk;
- a a1 and b1 - the smaller base of the obelisk;
- h is the height of the obelisk.
Formulation of the problem
Hydraulic calculation in the development of a pipeline project is aimed at determining the diameter of the pipe and the pressure drop of the carrier flow. This type of calculation is carried out taking into account the characteristics of the structural material used in the manufacture of the highway, the type and number of elements that make up the pipeline system (straight sections, connections, transitions, bends, etc.), performance, physical and chemical properties of the working environment.
 Many years of practical experience in the operation of pipeline systems has shown that pipes with a circular cross section have certain advantages over pipelines with a cross section of any other geometric shape:
Many years of practical experience in the operation of pipeline systems has shown that pipes with a circular cross section have certain advantages over pipelines with a cross section of any other geometric shape:
- the minimum ratio of the perimeter to the cross-sectional area, i.e. with an equal ability to ensure the consumption of the carrier, the cost of insulating and protective materials in the manufacture of pipes with a cross section in the form of a circle will be minimal;
- a round cross section is most advantageous for moving a liquid or gaseous medium from the point of view of hydrodynamics; the minimum friction of the carrier against the pipe walls is achieved;
- the shape of the section in the form of a circle is as resistant as possible to the effects of external and internal stresses;
- The manufacturing process for round tubes is relatively simple and affordable.
Selection of pipes by diameter and material is carried out on the basis of specified design requirements for a specific technological process. Currently, pipeline elements are standardized and unified in diameter. The determining parameter when choosing a pipe diameter is the allowable working pressure at which this pipeline will be operated.
The main parameters characterizing the pipeline are:
- conditional (nominal) diameter - DN;
- nominal pressure - PN;
- operating allowable (excess) pressure;
- pipeline material, linear expansion, thermal linear expansion;
- physical and chemical properties of the working environment;
- complete set of the pipeline system (branches, connections, expansion compensation elements, etc.);
- pipeline insulation materials.
Nominal diameter (passage) of the pipeline (DN) is a conditional dimensionless value that characterizes the throughput of a pipe, approximately equal to its inner diameter. This parameter is taken into account when fitting related pipeline products (pipes, bends, fittings, etc.).
The nominal diameter can have values from 3 to 4000 and is denoted: DN 80.
The conditional passage, by numerical definition, approximately corresponds to the actual diameter of certain sections of the pipeline. Numerically, it is chosen in such a way that the throughput of the pipe increases by 60-100% when moving from the previous conditional passage to the next one. The nominal diameter is selected according to the value of the internal diameter of the pipeline. This is the value that is closest to the actual diameter of the pipe itself.
Nominal pressure (PN) is a dimensionless value that characterizes the maximum pressure of the working carrier in a pipe of a given diameter, at which long-term operation of the pipeline at a temperature of 20°C is feasible.
Pressure ratings have been established based on long practice and operating experience: from 1 to 6300.
The nominal pressure for a pipeline with given characteristics is determined by the pressure closest to the pressure actually created in it. At the same time, all pipeline fittings for a given line must correspond to the same pressure. The calculation of the pipe wall thickness is carried out taking into account the value of the nominal pressure.