- How to choose the section of the duct?
- The fourth way (see Figure 14) .
- Room ventilation calculation by specific formulas
- The formula for calculating the ventilation of a room by the multiplicity
- Formula for calculating the number of people
- Ventilation design contract
- We work with objects
- Text from the document "1. Calculation of ventilation"
- DEPARTMENT "Ecology and life safety"
- 2 Factors affecting the quality of air exchange
- Why is it profitable to order ventilation design in IS Ecolife
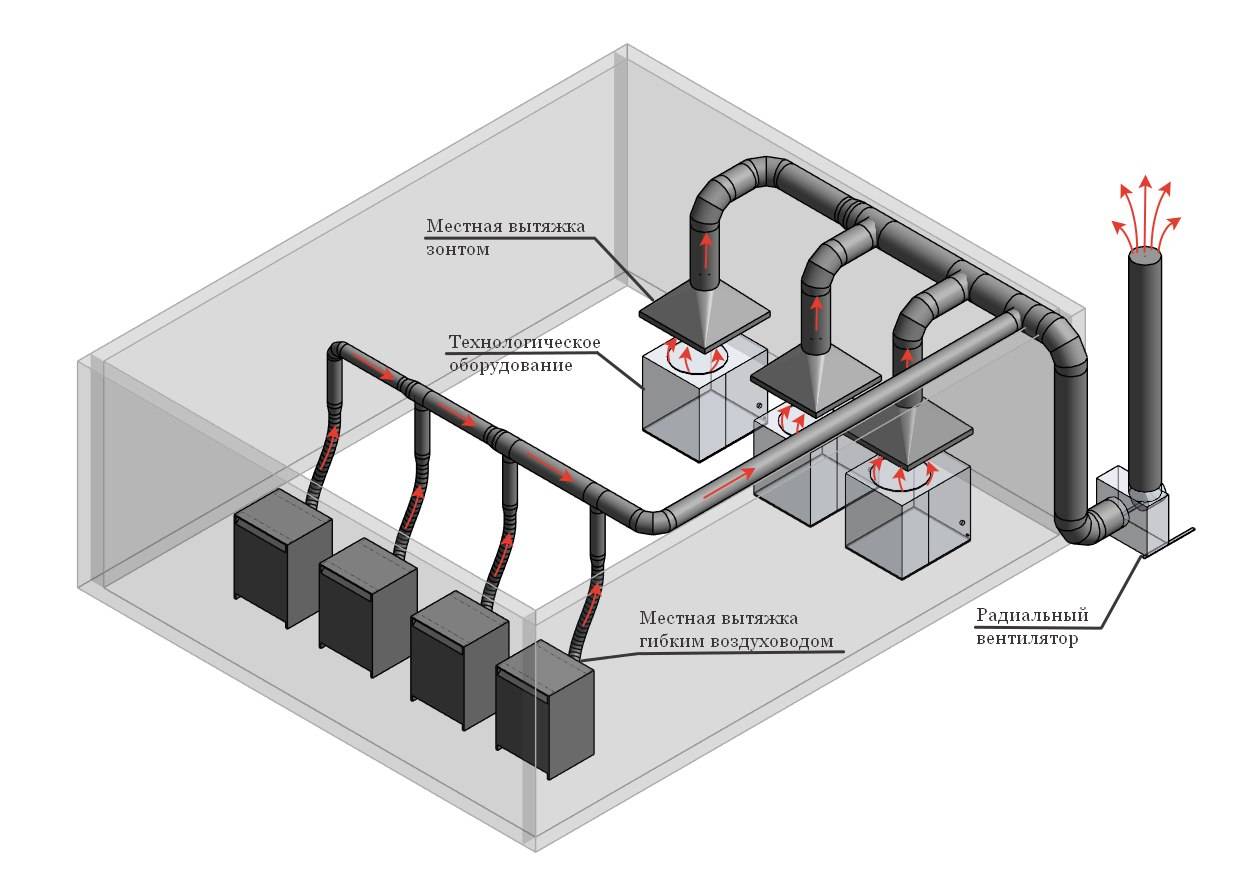
- Calculation of duct diameters and air duct sections
- 4 General ventilation
How to choose the section of the duct?
The ventilation system, as you know, can be ducted or ductless. In the first case, you need to choose the right section of the channels.
If it is decided to install structures with a rectangular section, then the ratio of its length and width should approach 3:1.
The length and width of rectangular ducts should be three to one to reduce noise
The speed of movement of air masses along the main highway should be about five meters per hour, and on branches - up to three meters per hour.
This will ensure that the system operates with a minimum amount of noise. The speed of air movement largely depends on the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe duct.
To select the dimensions of the structure, you can use special calculation tables. In such a table, you need to select the volume of air exchange on the left, for example, 400 cubic meters per hour, and select the speed value on top - five meters per hour.
Then you need to find the intersection of the horizontal line for air exchange with the vertical line for speed.
Using this diagram, the cross section of the ducts for the duct ventilation system is calculated. The speed of movement in the main canal should not exceed 5 km/h
From this point of intersection, a line is drawn down to a curve from which a suitable section can be determined. For a rectangular duct, this will be the area value, and for a round duct, this will be the diameter in millimeters.
First, calculations are made for the main duct, and then for the branches.
Thus, calculations are made if only one exhaust duct is planned in the house. If it is planned to install several exhaust ducts, then the total volume of the exhaust duct must be divided by the number of ducts, and then calculations should be carried out according to the above principle.
This table allows you to choose the cross section of the duct for duct ventilation, taking into account the volume and speed of movement of air masses
In addition, there are specialized calculation programs with which you can perform such calculations. For apartments and residential buildings, such programs can be even more convenient, since they give a more accurate result.
The fourth way (see Figure 14) .
The use of honeycomb humidifiers makes it possible to solve the problem of air humidification in the most optimal way in terms of energy costs. Given the frontal speed Vf = 2.3 m/s of supply air in a honeycomb humidifier, it is possible to achieve a relative humidity of the supply air:
- with a honeycomb nozzle depth of 100 mm - φ = 45%;
- with a honeycomb nozzle depth of 200 mm - φ = 65%;
- with a honeycomb nozzle depth of 300 mm - φ = 90%.
1. We select the parameters of internal air from the zone of optimal parameters:
- temperature - maximum tAT = 22°С;
- relative humidity - minimum φAT = 30%.
2. Based on two known parameters of indoor air, we find a point on the J-d diagram - (•) B.
3. The temperature of the supply air is assumed to be 5°C lower than the temperature of the indoor air
tP = tAT - 5, ° С.
On the J-d diagram, we draw the supply air isotherm - tP.
4. Through a point with the parameters of internal air - (•) B we draw a process ray with a numerical value heat-humidity ratio
ε = 5 800 kJ/kg N2O
to the intersection with the supply air isotherm - tP.
We get a point with the supply air parameters - (•) P.
5. From a point with outdoor air parameters - (•) H we draw a line of constant moisture content - dH = const.
6. From a point with supply air parameters - (•) P we draw a line of constant heat content - JP = const before crossing with lines:
relative humidity φ = 65%.
We get a point with the parameters of humidified and cooled supply air - (•) O.
constant moisture content of the outside air - dН = const.
We get a point with the parameters of the supply air heated in the air heater - (•) K.
7. Part of the heated supply air is passed through the honeycomb humidifier, the rest of the air is passed through the bypass, bypassing the honeycomb humidifier.
eight.We mix the humidified and cooled air with the parameters at the point - (•) O with the air passing through the bypass, with the parameters at the point - (•) K in such proportions that the mixture point - (•) C coincides with the supply air point - (• ) P:
- line KO - total supply air - GP;
- line KS - the amount of humidified and cooled air - GO;
- CO line - the amount of air passing through the bypass - GP — GO.
9. Outdoor air treatment processes on the J-d diagram will be represented by the following lines:
- line NK - the process of heating the supply air in the heater;
- line KS - the process of humidification and cooling of part of the heated air in the honeycomb humidifier;
- CO line - bypassing heated air, bypassing the honeycomb humidifier;
- KO line - mixing of humidified and cooled air with heated air.
10. Treated outdoor supply air with parameters at the point - (•) P enters the room and assimilates excess heat and moisture along the process beam - the PV line. Due to the increase in air temperature along the height of the room - grad t. Air parameters change. The process of changing parameters occurs along the process beam to the point of outgoing air - (•) U.
11. The amount of air passing through the spray chamber can be determined by the ratio of the segments
12. The required amount of moisture to humidify the supply air in the irrigation chamber
Schematic diagram of the treatment of supply air in the cold season - HP, for the 4th method, see Figure 15.
Room ventilation calculation by specific formulas
To determine the volume of ventilation of the room, you need to calculate:
- By multiplicity
- By number of people
The formula for calculating the ventilation of a room by the multiplicity
Calculation of air exchange by multiplicity means determining the frequency of a complete change of air volume in a room per hour.
Where:
L is the air exchange capacity, which is set in the norms of SNiP 41-01-2003 (m3/h);
n - rate of air exchange;
S - area of the room (m2);
H - the height of this room (m).
Formula for calculating the number of people
In addition, in order to find the optimal indoor air flow it is necessary to determine the air exchange by the number of people.
Where:
L is the air mass exchange capacity for the supply system (m3/h);
N - the number of people who are in the building;
Lnorm is the consumption of air masses per person.

Ventilation design contract
Our company works with legal entities and individuals. We conclude a contract for the design of ventilation, which is a document that clearly defines the cost and timing of the work. Pre-negotiated terms reduce the risks for both parties, as well as ensure the benefits of the transaction for the seller and the buyer.
The signing of acts of work performed and the acceptance and transfer of equipment means the successful completion of work. We provide a full package of documents, including invoices, acts, invoices and cash receipts when paying in cash, commissioning reports, system settings.
After completing the work, we continue to work with you as a consultant and service organization.

We work with objects

* Manufacturing plants, factories, shopping malls
* Restaurants, cafes, and all catering establishments
* Multi-storey and private residential buildings, office complexes
* Polyclinics, hospitals, schools, educational institutions
* Airports, train stations and all government agencies.
Text from the document "1. Calculation of ventilation"
MOSCOW STATE UNIVERSITY OF INSTRUMENT MAKING AND INFORMATION
DEPARTMENT "Ecology and life safety"
V.N. Yemets
LIFE SAFETY
METHODOLOGICAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR CONDUCTING A PRACTICAL LESSON ON THE DISCIPLINE
"LIFE SAFETY" on the topic "CALCULATION OF THE REQUIRED AIR EXCHANGE WITH GENERAL EXCHANGE VENTILATION"
MOSCOW, 2006
MOSCOW STATE UNIVERSITY OF INSTRUMENT MAKING AND INFORMATION
Department of Ecology and Life Safety
EXERCISE
For practical training in the discipline "Life safety"
on the topic: "Calculation of the required air exchange for general ventilation."
The purpose of the practical lesson is to familiarize the student with the method of calculating the required air exchange for designing general ventilation in industrial premises.
Source materials: options for practical exercises and guidelines (Emets V.N. Guidelines for conducting a practical lesson in the discipline "Life Safety" on the topic "Calculation of the required air exchange during general ventilation." - M.: MGUPI, 2006).
Order of execution:
- select an option according to the table of options;
- Familiarize yourself with the method of calculation;
- perform the calculation;
- issue the completed task in the form of a report (A4 format).
Title page of the task:
MOSCOW STATE UNIVERSITY OF INSTRUMENT MAKING AND INFORMATICS Department of Ecology and Life Safety
Settlement and explanatory note "Calculation of the required air exchange for general ventilation."
Full name of the student Group
Student Code Option
Student's signature Teacher's signature
MOSCOW, 2006
2 Factors affecting the quality of air exchange
The quality of the ventilation system depends on the pollution of the air. In rooms for various purposes, various harmful components can be concentrated in the air:
- humidity;
- exhaust gas elements;
- human excretions (breath, sweat, etc.);
- evaporation of harmful substances;
- thermal energy from operating installations.
Purpose of supply and exhaust ventilation:
- purification of exhaust air in the room;
- removal of harmful components and excess moisture from the air;
- absorption of excess thermal energy, regulation of the temperature regime;
- supply of fresh air to the room, its cooling or heating.
The formula for calculating the supply ventilation of a room:
Lots \u003d 3600 * F * Wо, where:
- F is the total area of openings (sq. m).
- Wo is the average speed of the air mass being drawn in (the parameter depends on air pollution and directly on the operation being performed).
It is strictly forbidden to use the recycling method at industrial facilities where harmful substances of hazard class 1-3, explosive components are concentrated in the air.
Why is it profitable to order ventilation design in IS Ecolife
| VENTILATION SYSTEM FROM A TO Z We are focused on building the entire engineering infrastructure on a turnkey basis. Design, supply of equipment, installation and provision of services are carried out without the involvement of related contractors. High speed of work. Turning to us, you will save not only your money, but also time. | |
| REAL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE RESULT IS Ecolife has a fully equipped production base, a staff of engineers and installers. We carry out all stages of work on our own, provide end-to-end quality control and are 100% responsible for the result. The company provides a guarantee for all work performed and is interested in long-term trouble-free operation of your equipment without downtime and emergency situations. | |
| ZERO PROBLEMS DURING INSPECTIONS We provide all the norms indicated in SanPin, SNiP, NPB, etc. You are protected from sudden orders and sanctions from supervisory authorities, save on fines and other fees. | |
| BEST PRICE We select decent equipment within even a small budget. You get equipment according to the principle "high quality - not necessarily expensive". The calculation of the estimate for services is made immediately after receiving the necessary information. Our principle is full transparency of the cost of work. The amount specified in the contract is a fixed price that will not be changed by us unless you yourself want to revise the estimate. For regular customers there are special discounts and delivery terms. | |
| CONVENIENCE 100% operation outsourced. You can outsource the maintenance of all engineering networks of the facility to one contractor - the company "Ecolife". We work officially under the contract and close all questions on the operation, both planned and urgent, and it is convenient for you to ask from one contractor. |
Ecolife Engineering Systems Company is a team of experienced and licensed specialists for installation and maintenance all types of engineering systems with the subsequent execution of the entire package of documents.
• 5 years on the market of Moscow and the Moscow region
• 7 specialized licenses and certificates
• 40 employees, 4 service vehicles and 3 work crews for prompt execution of orders
• 2 sets of TV inspection and professional European equipment
• We will reduce your costs by 20%. The prices for our services are below the market average without any loss in the quality of work and service.
| Quality assurance |
| Installation of the ventilation system | Ventilation maintenance | Repair of the ventilation system | Installation of the air conditioning system |
Calculation of duct diameters and air duct sections
Determining the total diameter of the air channels, their external sections and the dimensions of individual parts, chimney units must begin with the choice of the geometry of the structure.
The most common configurations are:
- a circle;
- square;
- rectangle;
- oval.
The larger the shaft, the lower the speed of air movement in it. At the same time, the noise that this air produces is also reduced. Such considerations must be taken into account when the necessary optimal parameters are determined. In practice, most people use modern software, because without it only a small circle of experienced designers can determine the required values. You should not be afraid of using remote calculators - they are compiled taking into account the recommendations that special design organizations have been working on for years.
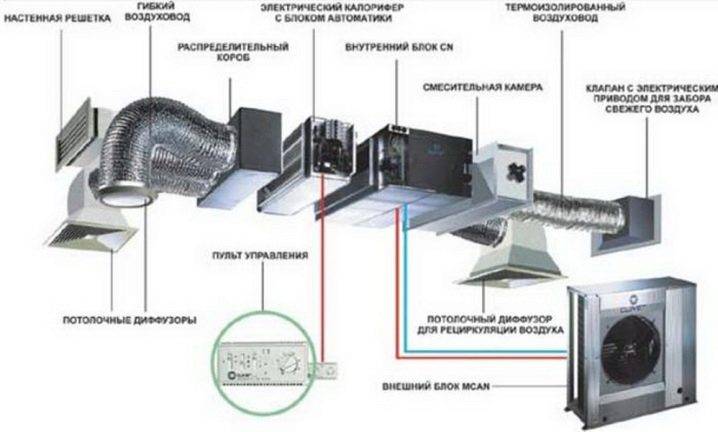
But in the first approximation, you can estimate the necessary values yourself. In this case, the actual diameter of the duct and its outer section will be obtained by rounding the calculated figure to the nearest existing standard size.The most accurate answer can only be obtained by contacting a specialized bureau.
If the pipe is round, then the calculation is as follows:
- the size of the diameter is determined, expressed in square meters;
- based on it, through the formula for determining the area of a circle, the diameter of the channel is set;
- for brick shafts located inside the walls and for other situations, the closest possible value is equally selected.
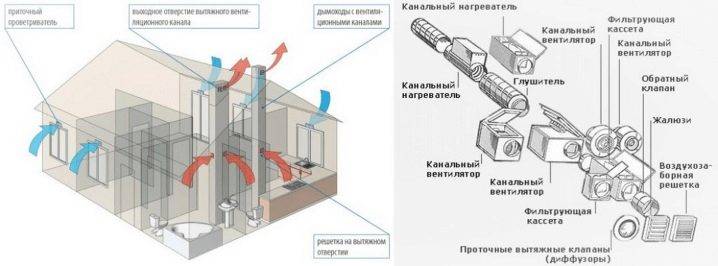
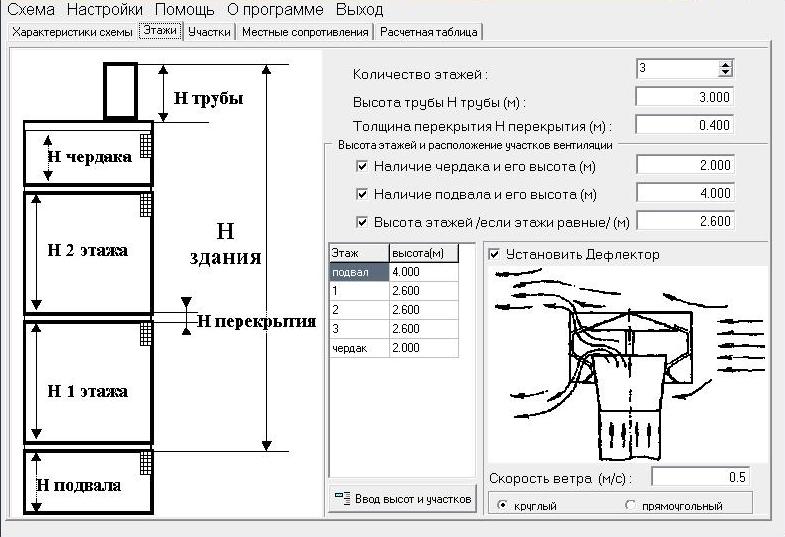
4 General ventilation
Air exchange for general exchange systems is determined depending on the method of removing excess thermal energy from the room and diluting the exhaust air, which contains harmful components, with a clean air stream to the concentration allowed by regulatory documents.
The required volume of supply air to remove excess heat energy is calculated by the formula:
L 1 \u003d Q est. / C * R * (T beats - T pr.), where
- Qsurplus (kJ/h) is the excess amount of thermal energy.
- C (J / kg * K) - heat capacity of air (constant value = 1.2 J / kg * K).
- R (kg/m3) - air density.
- T beats (ºС) is the temperature of the air mass removed from the room.
- T pr. (ºС) - the temperature of fresh air taken from the street.
The ambient temperature depends on the time of year and the geographical location of the industrial facility. The temperature of the exhaust air in the workshop is usually assumed to be 5 ºС higher than the external temperature. The air density is 1.225 kg/m3.
To calculate the ventilation in the room, you need to calculate the required volume of supply air to reduce the concentration of harmful substances in the air mixture to the established standards. This parameter is calculated using the following formula:
L \u003d G / G beats. — G pr., where
- G (mg / h) - the amount of harmful elements released.
- G beats (mg/m3) is the concentration of harmful components in the exhaust air.
- G pr. (mg/m3) - the concentration of harmful components in the supply air.
Any ventilation system can be designed and installed correctly if you approach the matter competently, observing all the requirements established by regulatory documentation.