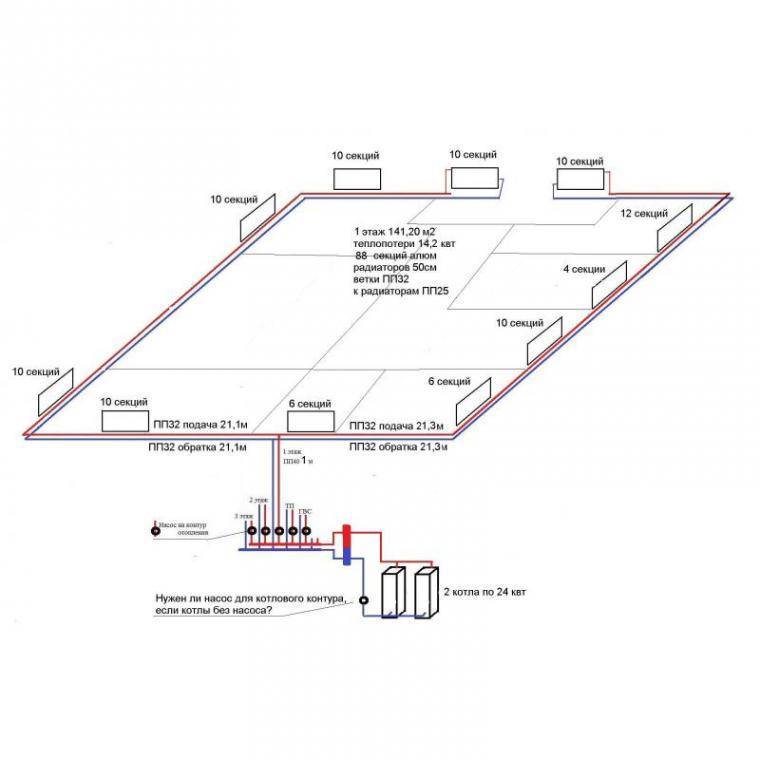
- Hydraulic calculation of water supply
- Boiler power determination
- Calculation of the thermal power of the heating system
- Thermal calculation of the house
- Thermotechnical calculation taking into account the heat losses of the house
- Calculation of heat loss at home
- Overview of programs for hydraulic calculations
- Oventrop CO
- Instal-Therm HCR
- HERZ C.O.
- Features of the selection of a circulation pump
- Expansion tank volume
- Let's talk about the amount of pumped fluid in more detail.
- Calculation of heat loss and boiler for home heating online
- How to work on the calculator
- Classification of heating systems of a private house
- Heating element selection
- Boiler power determination
- Eventually
Hydraulic calculation of water supply
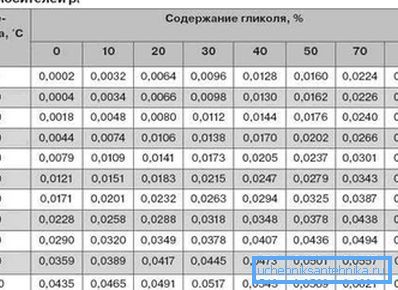
Of course, the “picture” of calculating heat for heating cannot be complete without calculating such characteristics as the volume and speed of the coolant. In most cases, the coolant is ordinary water in a liquid or gaseous state of aggregation.

The actual volume of the coolant is recommended to be calculated by summing up all the cavities in the heating system. When using a single-circuit boiler, this is the best option. When using double-circuit boilers in the heating system, it is necessary to take into account the consumption of hot water for hygienic and other domestic purposes
The calculation of the volume of water heated by a double-circuit boiler to provide residents with hot water and heat the coolant is made by summing the internal volume of the heating circuit and the actual needs of users in heated water.
The volume of hot water in the heating system is calculated by the formula:
W=k*P, where
- W is the volume of the heat carrier;
- P is the power of the heating boiler;
- k is the power factor (the number of liters per unit of power is 13.5, the range is 10-15 liters).
As a result, the final formula looks like this:
W=13.5*P
The coolant velocity is the final dynamic assessment of the heating system, which characterizes the rate of fluid circulation in the system.
This value helps to evaluate the type and diameter of the pipeline:
V=(0.86*P*μ)/∆T, where
- P - boiler power;
- μ – boiler efficiency;
- ∆T is the temperature difference between the supply water and the return water.
Using the above methods of hydraulic calculation, it will be possible to obtain real parameters that are the “foundation” of the future heating system.
Boiler power determination
To maintain the temperature difference between the environment and the temperature inside the house, an autonomous heating system is needed that maintains the desired temperature in every room of a private house.
The basis of the heating system are different types of boilers: liquid or solid fuel, electric or gas.
The boiler is the central node of the heating system that generates heat. The main characteristic of the boiler is its power, namely the rate of conversion of the amount of heat per unit of time.
Having calculated the heat load for heating, we obtain the required nominal power of the boiler.
For an ordinary multi-room apartment, the boiler power is calculated through the area and specific power:
Rboiler=(Spremises*Rspecific)/10, where
- Spremises- the total area of the heated room;
- Rspecific– specific power relative to climatic conditions.
But this formula does not take into account heat losses, which are sufficient in a private house.
There is another ratio that takes this parameter into account:
Rboiler=(Qlosses*S)/100, where
- Rboiler– boiler power;
- Qlosses– heat loss;
- S - heated area.
The rated power of the boiler must be increased. The reserve is necessary if it is planned to use the boiler for heating water for the bathroom and kitchen.

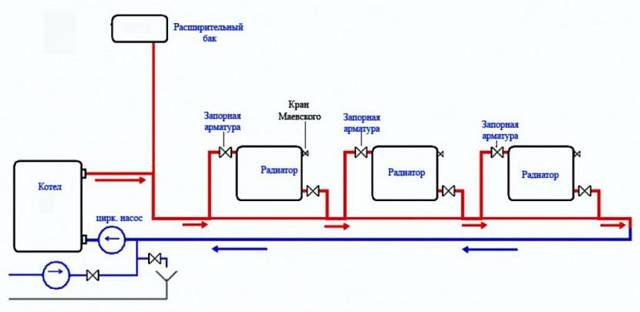
In most heating systems of private houses, it is recommended to use an expansion tank, in which the supply of coolant will be stored. Every private house needs hot water supply
In order to provide for a boiler power reserve, the safety factor K must be added to the last formula:
Rboiler=(Qlosses*S*K)/100, where
K - will be equal to 1.25, that is, the design power of the boiler will be increased by 25%.
Thus, the power of the boiler makes it possible to maintain the standard air temperature in the rooms of the building, as well as to have an initial and additional volume of hot water in the house.
Calculation of the thermal power of the heating system
The thermal power of the heating system is the amount of heat that needs to be generated in the house for comfortable life during the cold season.
Thermal calculation of the house
There is a relationship between the total heating area and the boiler power. At the same time, the power of the boiler must be greater than or equal to the power of all heating devices (radiators).The standard heat engineering calculation for residential premises is as follows: 100 W of power per 1 m² of heated area plus 15 - 20% of the reserve.
The calculation of the number and power of heating devices (radiators) must be carried out individually for each room. Each radiator has a certain heat output. In sectional radiators, the total power is the sum of the power of all used sections.
In simple heating systems, the above methods for calculating power are sufficient. The exception is buildings with non-standard architecture, large glass areas, high ceilings and other sources of additional heat loss. In this case, a more detailed analysis and calculation using multiplying factors will be required.
Thermotechnical calculation taking into account the heat losses of the house
Calculation of heat loss at home must be performed for each room separately, taking into account windows, doors and external walls.
In more detail, the following data are used for heat loss data:
- Thickness and material of walls, coatings.
- Roof structure and material.
- Foundation type and material.
- Glazing type.
- Floor screed type.
To determine the minimum required power of the heating system, taking into account heat losses, you can use the following formula:
Qt (kWh) = V × ΔT × K ⁄ 860, where:
Qt is the heat load on the room.
V is the volume of the heated room (width × length × height), m³.
ΔT is the difference between the outdoor air temperature and the required indoor temperature, °C.
K is the heat loss coefficient of the building.
860 - conversion of the coefficient to kWh.
The heat loss coefficient of the building K depends on the type of construction and the insulation of the room:
| K | Construction type |
| 3 — 4 | A house without thermal insulation is a simplified structure or a structure made of corrugated metal sheet. |
| 2 — 2,9 | House with low thermal insulation - simplified building structure, single brickwork, simplified window and roof construction. |
| 1 — 1,9 | Medium Insulation - Standard Construction, Double Brickwork, Few Windows, Standard Roof. |
| 0,6 — 0,9 | High thermal insulation - improved construction, thermally insulated brick walls, few windows, insulated floor, high quality thermally insulated roofing pie. |
The difference between the outdoor air temperature and the required indoor temperature ΔT is determined based on the specific weather conditions and the required level of comfort in the house. For example, if the outside temperature is -20 °C, and +20 °C is planned inside, then ΔT = 40 °C.
Calculation of heat loss at home
These data will be needed to determine the required power of the heating system, i.e. the boiler, and the heat output of each radiator separately. To do this, you can use our online heat loss calculator. They need to be calculated for each room in the house that has an outer wall.
Examination. The calculated heat loss of each room is divided by its quadrature and we get the specific heat loss in W/sq.m. They usually range from 50 to 150 W/sq. m. If your figures are very different from those given, then perhaps a mistake was made. The heat losses of the rooms of the upper floor are the largest, followed by the heat losses of the first floor and the least they are in the rooms of the middle floors.
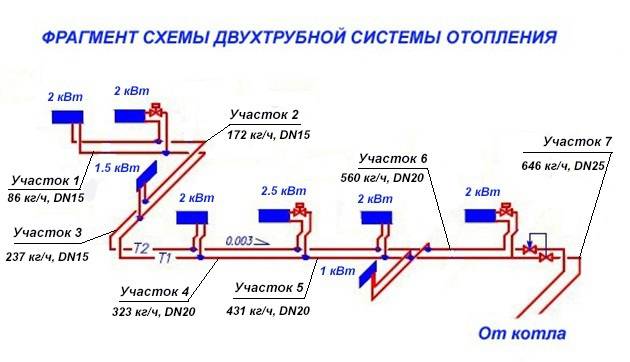
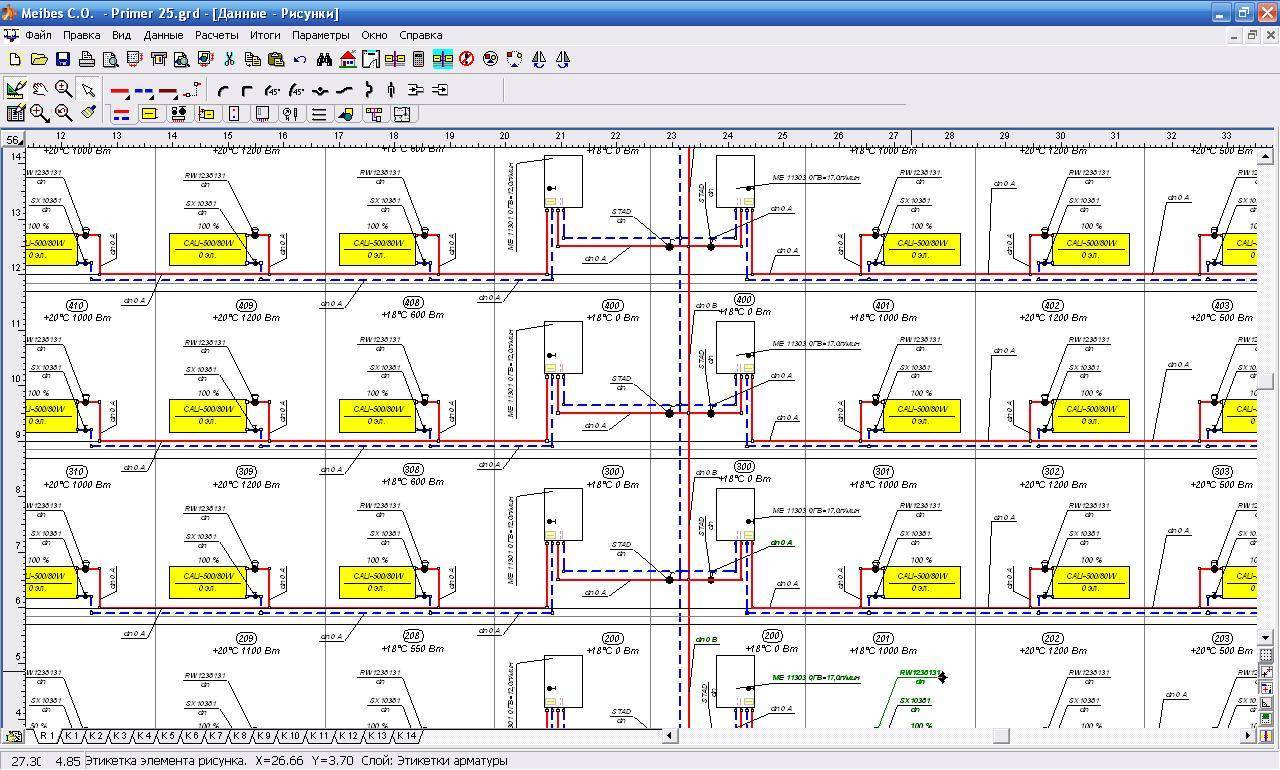
Overview of programs for hydraulic calculations
In essence, any hydraulic calculation of water heating systems is considered a difficult engineering task. To solve it, a number of software packages have been developed that facilitate the implementation of such a procedure.
You can try to perform a hydraulic calculation of the heating system in the Excel shell, using ready-made formulas. However, the following problems may occur:
- Big error. In many cases, one or two pipe schemes are taken as an example of a hydraulic calculation for heating systems. Finding the same calculations for the collector is problematic;
- To correctly take into account the resistance in terms of the hydraulics of the pipeline, reference data is needed, which are not available in the form. They need to be searched and entered additionally.
Oventrop CO
The most simple and clear program for the hydraulic calculation of the heat network. An intuitive interface and flexible settings can help you quickly deal with the invisible moments of data entry. Small problems may appear during the first setup of the complex. You will need to enter all the parameters of the system, starting from the pipe material itself and ending with the placement of the heating elements.
It is distinguished by the flexibility of settings, the ability to make the simplest hydraulic calculation of heat supply both for a new heating network and for upgrading an old one. It stands out from substitutes with a good graphical interface.
Instal-Therm HCR
The software package is calculated for professional resistance in terms of heating system hydraulics. The free version has a lot of contraindications. The scope of use is the design of heat supply in large public and industrial buildings.
In practical conditions, for autonomous heat supply of private apartments and houses, hydraulic calculation is not always done. However, this can lead to a deterioration in the operation of the heating system and a quick breakdown of its components - heaters, pipes and a boiler. To avoid this, it is necessary to calculate the system parameters in time and compare them with the actual ones for the subsequent optimization of the heat supply operation.
HERZ C.O.
It is characterized by flexibility of settings, the ability to make a simplified hydraulic calculation of heating both for a new heat supply system and for upgrading an old one. Differs from analogues in a convenient graphical interface.
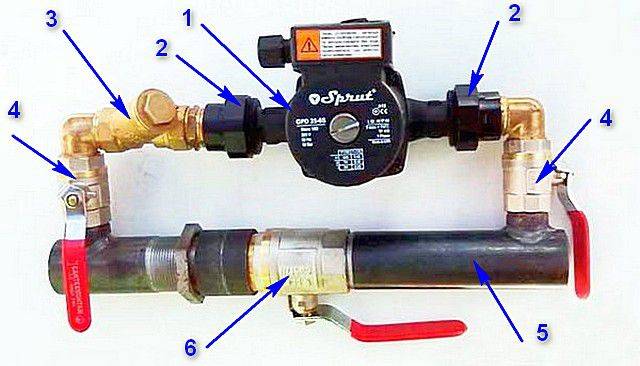
Features of the selection of a circulation pump
The pump is selected according to two criteria:
- The amount of liquid pumped, expressed in cubic meters per hour (m³/h).
- Head expressed in meters (m).
With pressure, everything is more or less clear - this is the height to which the liquid must be raised and is measured from the lowest to the highest point or to the next pump, if the project provides for more than one.
Expansion tank volume
Everyone knows that a liquid tends to increase in volume when heated. So that the heating system does not look like a bomb and does not flow at all seams, there is an expansion tank into which the displaced water from the system is collected.
What volume should be purchased or made a tank?
It's simple, knowing the physical characteristics of water.
The calculated volume of coolant in the system is multiplied by 0.08. For example, for a coolant of 100 liters, the expansion tank will have a volume of 8 liters.
Let's talk about the amount of pumped fluid in more detail.
The water consumption in the heating system is calculated according to the formula:
G = Q / (c * (t2 - t1)), where:
- G - water consumption in the heating system, kg / s;
- Q is the amount of heat that compensates for heat loss, W;
- c - specific heat capacity of water, this value is known and equal to 4200 J / kg * ᵒС (note that any other heat carriers have worse performance compared to water);
- t2 is the temperature of the coolant entering the system, ᵒС;
- t1 is the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the system, ᵒС;
Recommendation! For a comfortable stay, the temperature delta of the heat carrier at the inlet should be 7-15 degrees. The floor temperature in the "warm floor" system should not be more than 29ᵒ C. Therefore, you will have to figure out for yourself what type of heating will be installed in the house: will there be batteries, a “warm floor” or a combination of several types.
The result of this formula will give the coolant flow rate per second of time to replenish heat losses, then this indicator is converted into hours.
Advice! Most likely, the temperature during operation will vary depending on the circumstances and the season, so it is better to immediately add 30% of the reserve to this indicator.
Consider the indicator of the estimated amount of heat required to compensate for heat losses.
Perhaps this is the most complex and important criterion that requires engineering knowledge, which must be approached responsibly.
If this is a private house, then the indicator can vary from 10-15 W / m² (such indicators are typical for "passive houses") to 200 W / m² or more (if it is a thin wall with no or insufficient insulation).
In practice, construction and trade organizations take as a basis the heat loss indicator - 100 W / m².
Recommendation: Calculate this indicator for a particular house in which a heating system will be installed or reconstructed. To do this, heat loss calculators are used, while losses for walls, roofs, windows, and floors are separately calculated. These data will make it possible to find out how much heat is physically given off by the house to the environment in a particular region with its own climatic regimes.
We multiply the calculated loss figure by the area of \u200b\u200bthe house and then substitute it into the water consumption formula.
Now you should deal with such a question as water consumption in the heating system of an apartment building.
Calculation of heat loss and boiler for home heating online
With the help of our calculator for calculating heating for a private house, you can easily find out the required boiler power to heat your cozy “nest”.
As you remember, in order to calculate the heat loss rate, you need to know several values \u200b\u200bof the main components of the house, which together account for more than 90% of the total losses. For your convenience, we have added to the calculator only those fields that you can fill out without special knowledge:
- glazing;
- thermal insulation;
- the ratio of the area of windows and floor;
- outside temperature;
- the number of walls facing the outside;
- which room is above the calculated one;
- room height;
- room area.
After you get the value of the heat loss at home, a correction factor of 1.2 is taken to calculate the required boiler power.
How to work on the calculator
Remember that the thicker the glazing and the better the thermal insulation, the less heating power will be required.
To get results, you need to answer the following questions:
- Choose one of the proposed types of glazing (triple or double glazing, conventional double glazing).
- How are your walls insulated? Solid thick insulation from a couple of layers of mineral wool, polystyrene foam, EPPS for the north and Siberia. Maybe you live in Central Russia and one layer of insulation is enough for you. Or are you one of those who builds a house in the southern regions and a double hollow brick is suitable for him.
- What is your window-to-floor area ratio, in %. If you do not know this value, then it is calculated very simply: divide the floor area by the window area and multiply by 100%.
- Enter the minimum winter temperature for a couple of seasons and round up. Do not use the average temperature for winters, otherwise you risk getting a smaller boiler and the house will not be heated enough.
- Do we calculate for the whole house or just for one wall?
- What is above our room. If you have a one-story house, select the type of attic (cold or warm), if the second floor, then a heated room.
- The height of the ceilings and the area of the room are necessary to calculate the volume of the apartment, which in turn is the basis for all calculations.
Calculation example:
- one-story house in the Kaliningrad region;
- wall length 15 and 10 m, insulated with one layer of mineral wool;
- ceiling height 3 m;
- 6 windows of 5 m2 from a double-glazed window;
- the minimum temperature for the last 10 years is 26 degrees;
- we calculate for all 4 walls;
- from above a warm heated attic;
The area of our house is 150 m2, and the area of windows is 30 m2. 30/150*100=20% window to floor ratio.
We know everything else, we select the appropriate fields in the calculator and we get that our house will lose 26.79 kW of heat.
26.79 * 1.2 \u003d 32.15 kW - the required heating capacity of the boiler.
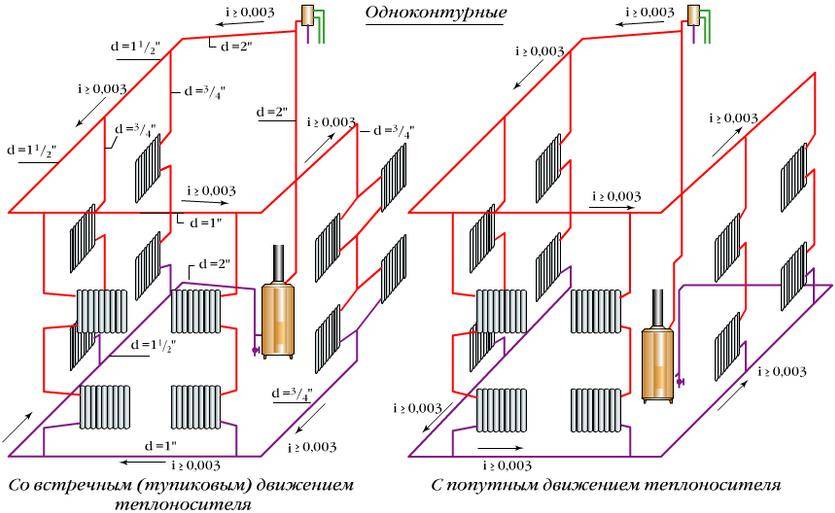
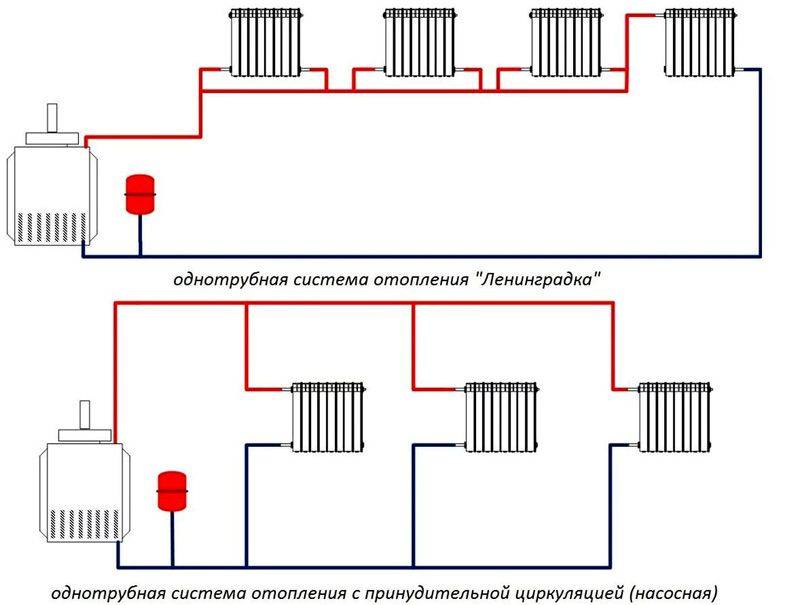
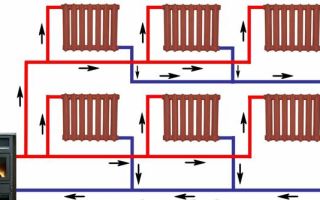
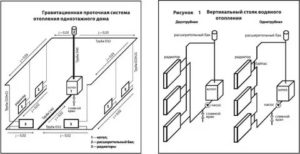
Classification of heating systems of a private house
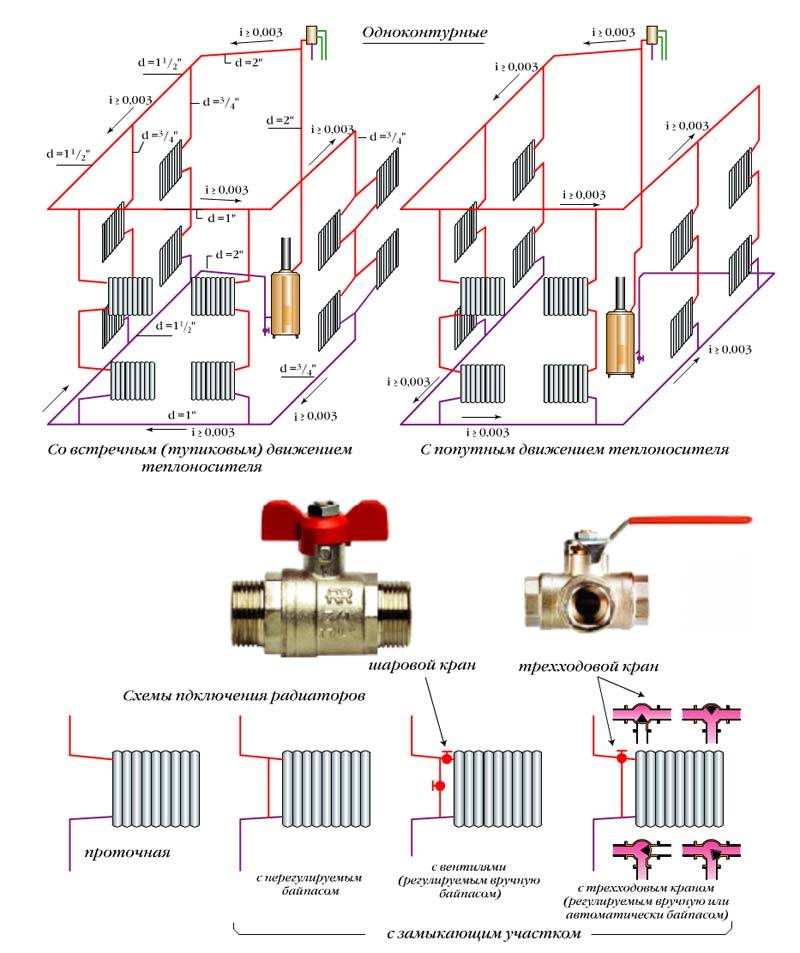
First of all, heating systems differ in the type of coolant and are:
- water, the most common and practical;
- air, a variation of which is an open fire system (i.e. a classic fireplace);
- electric, the most convenient to use.
In turn, water heating systems in a private house are classified according to the type of wiring and are single-pipe, collector and two-pipe. In addition, for them there is also a classification according to the energy carrier required for the operation of the heating device (gas, solid or liquid fuel, electricity), and according to the number of circuits (1 or 2). These systems are also divided by pipe material (copper, steel, polymers).
Heating element selection
Boilers are conditionally divided into several groups depending on the type of fuel used:
- electric;
- liquid fuel;
- gas;
- solid fuel;
- combined.
Among all the proposed models, the most popular are devices operating on gas. It is this type of fuel that is relatively profitable and affordable. In addition, equipment of this kind does not require special knowledge and skills for its maintenance, and the efficiency of such units is quite high, which other units that are identical in functionality cannot boast of. But at the same time, gas boilers are only appropriate if your house is connected to a centralized gas main.
Boiler power determination
Before calculating the heating, it is necessary to determine the throughput of the heater, since the efficiency of the thermal installation depends on this indicator. So, a heavy-duty unit will consume a lot of fuel resources, while a low-power unit will not be able to fully provide high-quality space heating. It is for this reason that the calculation of the heating system is an important and responsible process.
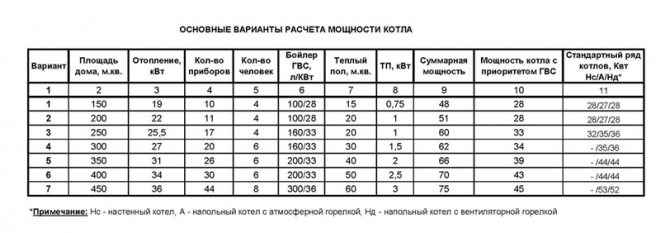
You can not go into complex formulas for calculating the performance of the boiler, but simply use the table below. It indicates the area of \u200b\u200bthe heated structure and the power of the heater, which can create full temperature conditions for living in it.
| The total area of housing in need of heating, m2 | Required performance of the heating element, kW |
| 60-200 | Not higher than 25 |
| 200-300 | 25-35 |
| 300-600 | 35-60 |
| 600-1200 | 60-100 |
Eventually
As you can see, the calculation of the heating capacity comes down to calculating the total value of the four above elements.
Not everyone can determine the required capacity of the working fluid in the system with mathematical accuracy. Therefore, not wanting to perform the calculation, some users act as follows. To begin with, the system is filled by about 90%, after which the performance is checked. Then bleed the accumulated air and continue filling.
During the operation of the heating system, a natural decrease in the level of the coolant occurs as a result of convection processes. In this case, there is a loss of power and productivity of the boiler. This implies the need for a reserve tank with a working fluid, from where it will be possible to monitor the loss of coolant and, if necessary, replenish it.