- Conditionally schematic power calculation
- Reasons for possible errors
- Calculation of steel radiators
- An example of calculating a steel radiator
- Scheme of connection and placement of radiators
- Approximate calculation of bimetallic radiators
- Initial data for calculations
- We mark on the project the results of previous calculations, heating batteries and other devices of the system
- Useful tips for the proper arrangement of the heating system
- Glazing, area and orientation of windows
- Steel plate heating radiators
- How to calculate the number of heating radiator sections
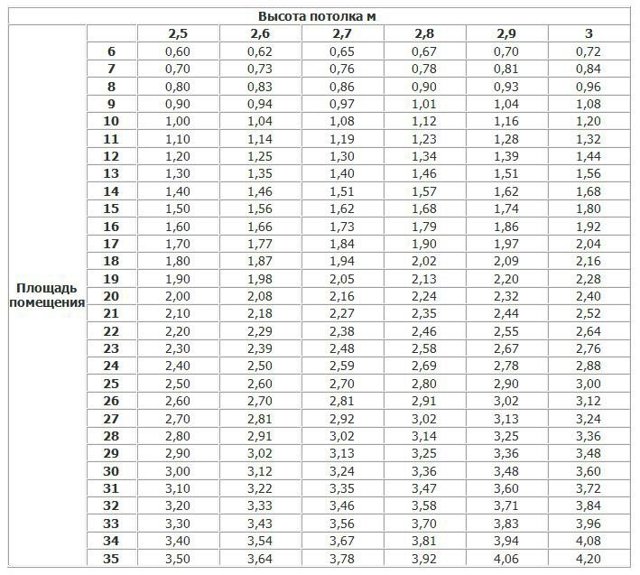
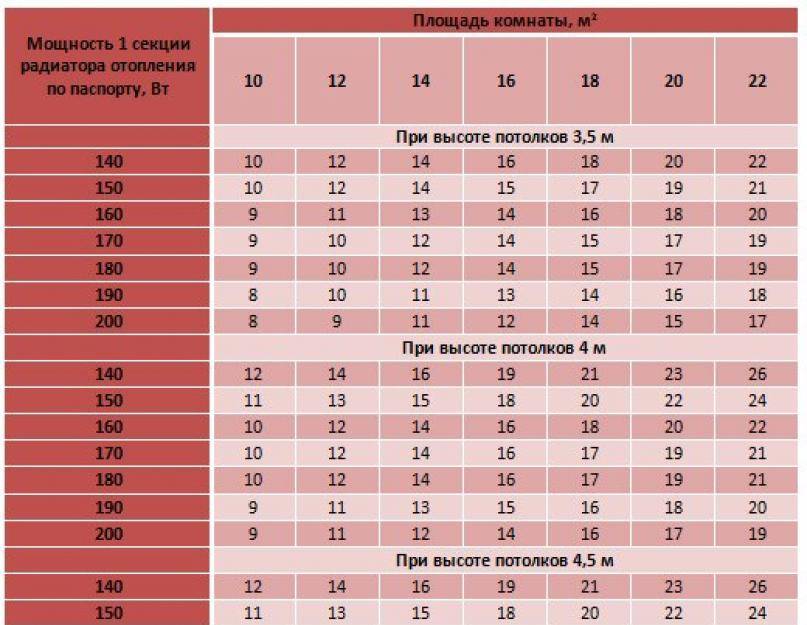
- Calculation based on room area
- Calculation of the number of sections in radiators, based on the volume of the room
- What does it depend on?
- How to calculate the number of radiators for a single pipe circuit
Conditionally schematic power calculation
In the temperate climate zone (the so-called middle climatic zone), the accepted norms regulate the installation of heating radiators with a capacity of 60 - 100 W per square meter of the room. This calculation is also called area calculation.
In the northern latitudes (meaning not the Far North, but the northern regions that lie above 60 ° N), power is taken in the range of 150 - 200 W per square meter.
The power of the heating boiler is also determined based on these values.
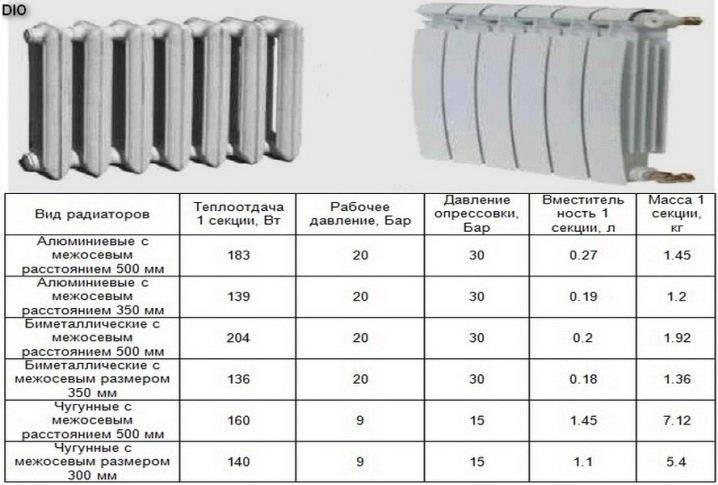
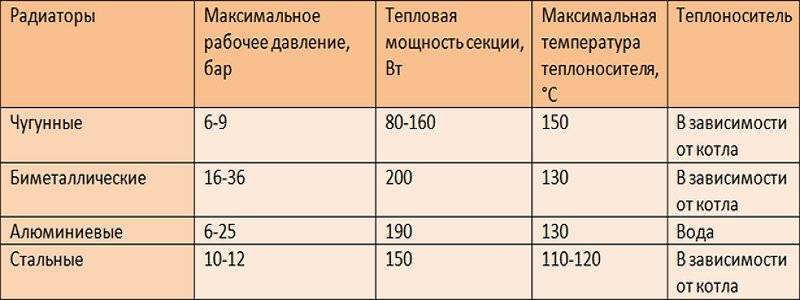
- The calculation of the power of heating radiators is carried out exactly according to this method. This is the power that radiators should have. The heat transfer values of cast iron batteries are in the range of 125 - 150 W per section. In other words, a room of fifteen square meters can be heated (15 x 100 / 125 = 12) by two six-section cast-iron radiators;
- Bimetallic radiators are calculated in a similar way, since their power corresponds to the power of cast-iron radiators (in fact, it is a little more). The manufacturer must indicate these parameters on the original packaging (in extreme cases, these values are given in standard tables for technical specifications);
- The calculation of aluminum heating radiators is carried out in the same way. The temperature of the heaters themselves is largely related to the temperature of the coolant inside the system and the heat transfer values of each individual radiator. Related to this is the overall price of the device.
There are simple algorithms, which are called by a common term: a calculator for calculating heating radiators, which uses the above methods. Do-it-yourself calculation using such algorithms is quite simple.
Reasons for possible errors
Manufacturers try to indicate the maximum heat transfer rates in the documents for batteries. They are possible only if the temperature of the water in the heating is at the level of 90 C (the heat head is indicated in the passport as 60 C).
In reality, such values are not always achieved by heating networks. This means that the capacity of the section will be lower, and more sections are needed. The heat output of one section can be 50-60 against the declared 180 W!
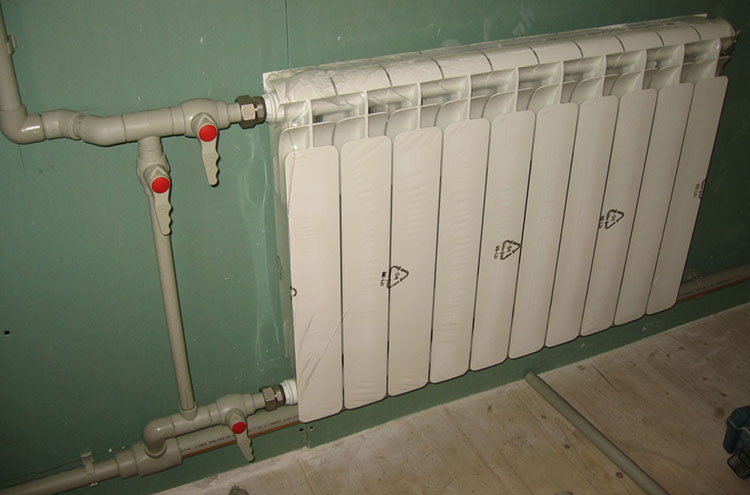

Lateral connection of heating radiators
If the accompanying document to the radiator indicates the minimum value of heat transfer, it is better to rely on this indicator in calculating the heat transfer of the radiator of heating batteries.
Another circumstance that affects the power of the radiator is its connection diagram. If, for example, a long radiator of 12 sections is connected sideways, the far sections will always be much colder than the first ones. So, the power calculations were in vain!
Long radiators need to be connected diagonally, short batteries will suit any option.
Calculation of steel radiators
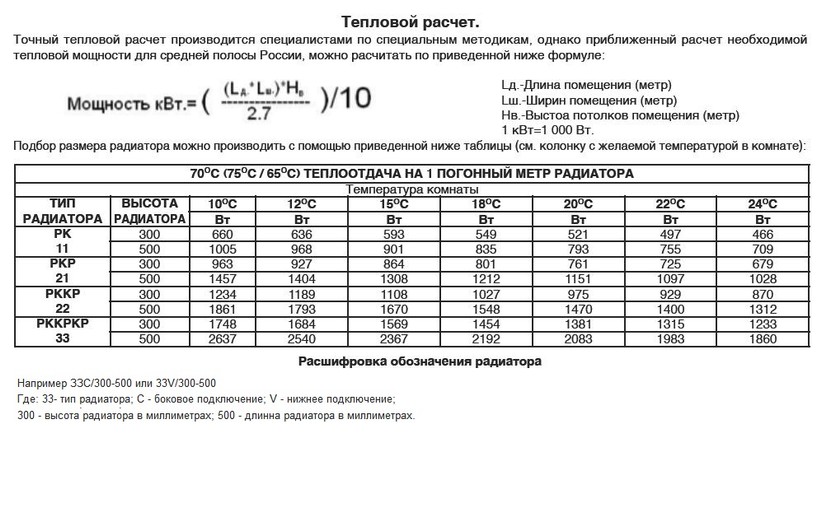
In order to calculate the power of steel radiators, you must use the formula:
Pst \u003d TPtotal / 1.5 x k, where
- Рst - power of steel radiators;
- TPtot - the value of the total heat loss in the room;
- 1.5 - coefficient for reducing the length of the radiator, taking into account operation in the temperature range of 70-50 ° C;
- k - safety factor (1.2 - for apartments in a multi-storey building, 1.3 - for a private house)

steel radiator
An example of calculating a steel radiator
We proceed from the conditions that the calculation is performed for a room in a private house with an area of 20 square meters with a ceiling height of 3.0 m, which has two windows and one door.
The instruction for calculation prescribes the following:
- TPtotal \u003d 20 x 3 x 0.04 + 0.1 x 2 + 0.2 x 1 \u003d 2.8 kW;
- Рst \u003d 2.8 kW / 1.5 x 1.3 \u003d 2.43 m.
The calculation of steel heating radiators according to this method leads to the fact that the total length of the radiators is 2.43 m. Given the presence of two windows in the room, it would be advisable to choose two radiators of a suitable standard length.
Scheme of connection and placement of radiators
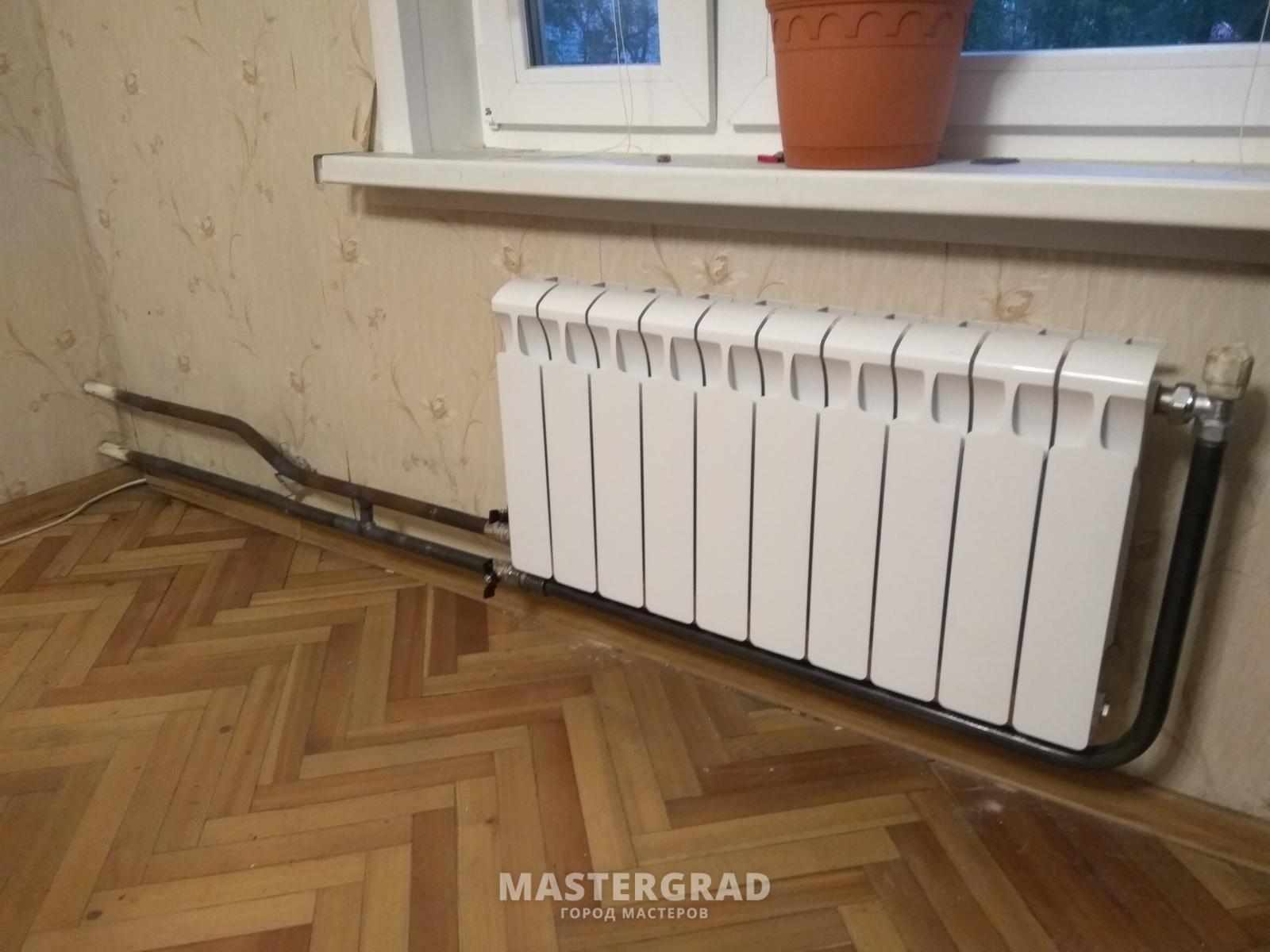
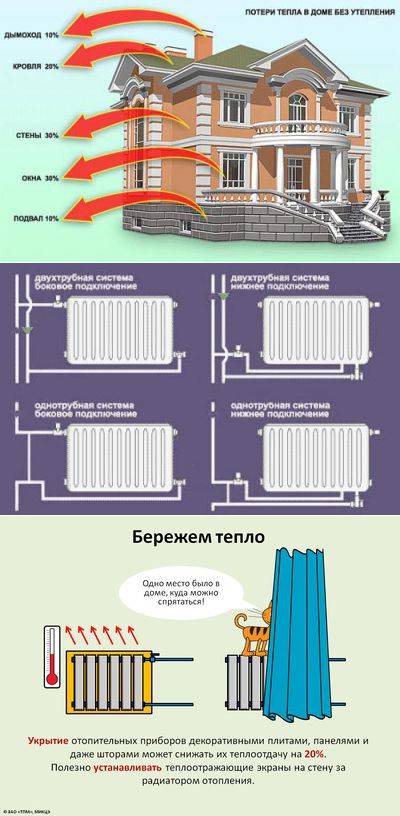
Heat transfer from radiators also depends on where the heater is located, as well as the type of connection to the main pipeline.
First of all, heating radiators are placed under the windows. Even the use of energy-saving double-glazed windows does not make it possible to avoid the greatest heat losses through the light openings. The radiator, which is installed under the window, heats the air in the room around it.

Photo of a radiator in the interior
The heated air rises. At the same time, a layer of warm air creates a thermal curtain in front of the opening, which prevents the movement of cold layers of air from the window.
In addition, cold air flows from the window, mixing with warm upward flows from the radiator, increase the overall convection throughout the entire volume of the room. This allows the air in the room to warm up faster.
In order for such a thermal curtain to be effectively created, it is necessary to install a radiator, which would be at least 70% of the width of the window opening in length.
The deviation of the vertical axes of radiators and windows should not exceed 50 mm.
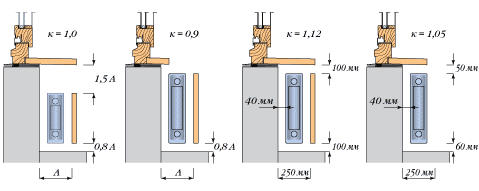
Heat sink placement and correction factors
- When piping radiators that use risers, they must be carried out in the corners of the room (especially in the outer corners of blank walls);
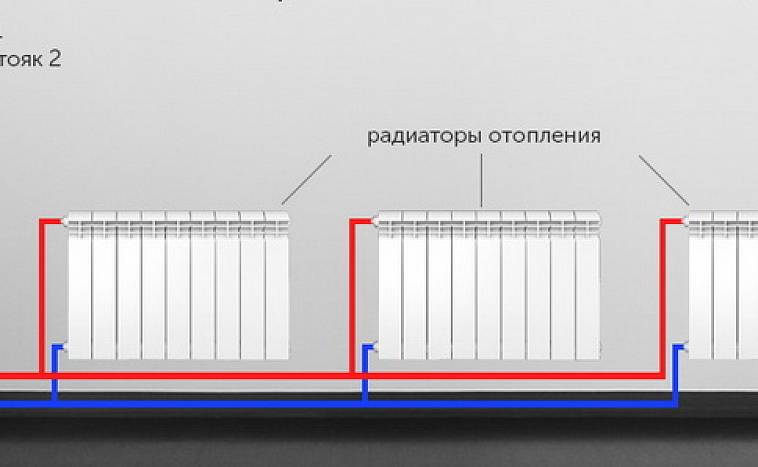
- When heating radiators are connected to the main pipelines from opposite sides, the heat transfer of the devices increases. From a constructive point of view, one-sided connection to pipes is rational.
Wiring diagram
Heat transfer also depends on how the places for the supply and removal of coolant from the heating devices are located. More heat flow will be when the supply is connected to the upper part and removed from the lower part of the radiator.
If the radiators are installed in several tiers, then in this case it is necessary to ensure the sequential movement of the coolant down in the direction of travel.
Video about calculating the power of heating devices:
Approximate calculation of bimetallic radiators
Almost all bimetallic radiators are available in standard sizes. Non-standard must be ordered separately.
This somewhat facilitates the calculation of bimetallic heating radiators.

Bimetal radiators
With a standard ceiling height (2.5 - 2.7 m), one section of a bimetallic radiator is taken per 1.8 m2 of a living room.
For example, for a room of 15 m2, the radiator should have 8 - 9 sections:
15/1,8 = 8,33.
For the volumetric calculation of a bimetallic radiator, the value of 200 W of each section for every 5 m3 of the room is taken.
For example, for a room of 15 m2 and a height of 2.7 m, the number of sections according to this calculation will be 8:
15 x 2.7/5 = 8.1

Calculation of bimetallic radiators
Initial data for calculations
The calculation of the heat output of the batteries is carried out for each room separately, depending on the number of external walls, windows and the presence of an entrance door from the street. To correctly calculate the heat transfer indicators of heating radiators, answer 3 questions:
- How much heat is needed to heat a living room.
- What air temperature is planned to be maintained in a particular room.
- The average water temperature in the heating system of an apartment or a private house.

The answer to the first question - how to calculate the required amount of thermal energy in various ways, is given in a separate manual - calculating the load on the heating system.Here are 2 simplified calculation methods: by area and volume of the room.
A common way is to measure the heated area and allocate 100 W of heat per square meter, otherwise 1 kW per 10 m². We propose to clarify the methodology - to take into account the number of light openings and external walls:
- for rooms with 1 window or front door and one outer wall, leave 100 W of heat per square meter;
- corner room (2 external fences) with 1 window opening - count 120 W/m²;
- the same, 2 light openings - 130 W / m².
Distribution of heat losses over the area of a one-story house
With a ceiling height of more than 3 meters (for example, a corridor with a staircase in a two-story house), it is more correct to calculate the heat consumption by cubic capacity:
- a room with 1 window (outer door) and a single outer wall - 35 W/m³;
- the room is surrounded by other rooms, has no windows, or is located on the sunny side - 35 W / m³;
- corner room with 1 window opening - 40 W / m³;
- the same, with two windows - 45 W / m³.
It is easier to answer the second question: the temperature comfortable for living lies in the range of 20 ... 23 ° C. It is uneconomical to heat the air more strongly, it is colder weaker. The average value for calculations is plus 22 degrees.
The optimal mode of operation of the boiler involves heating the coolant to 60-70 ° C. The exception is warm or too cold day when the water temperature has to be reduced or, conversely, increased. The number of such days is small, so the average design temperature of the system is assumed to be +65 °C.
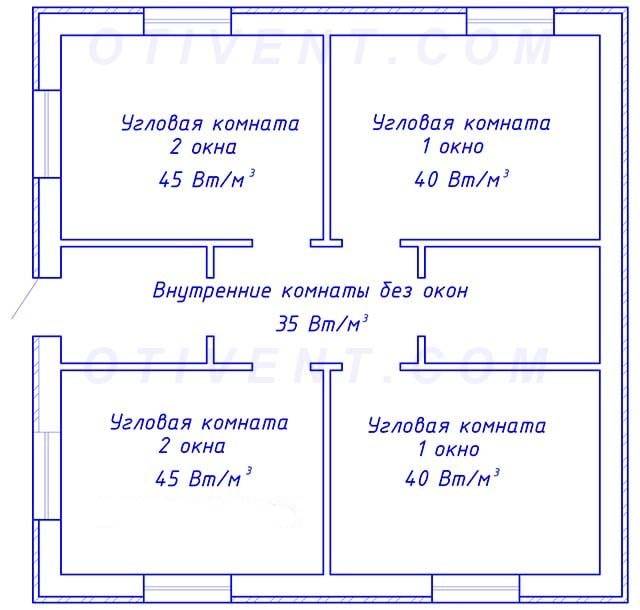
In rooms with high ceilings, we consider the heat consumption by volume
We mark on the project the results of previous calculations, heating batteries and other devices of the system
At the stage of calculating the heat losses of the house, we found out the heat losses for each room. To further make the calculation of heating batteries, it is best to put the data obtained on the plan - for your convenience (in red numbers):
Now you need to “arrange” the radiators, and then calculate the required number of sections (or dimensions, if the radiators are panel).
In the figure below, a plan of the same house, only radiators have been added to the premises (orange rectangles under the windows):
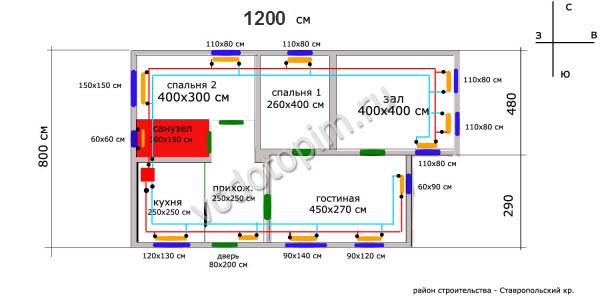
The boiler is marked with a red square. If the boiler is wall-mounted, then it can be installed not in the boiler room, but, for example, in the kitchen. But regardless of the location of the boiler, an exhaust pipe is required, which must be remembered when designing (unless, of course, the boiler is electric).
So back to the system heating plan.
Radiators are located under the windows; on the scheme, radiators are orange.
On my diagram, a two-pipe heating system. In order not to pull it around the perimeter of the whole house, the pipeline is designed with two loops.
The supply pipe is marked in red, the return pipe in blue. Black dots on the supply and return lines are shutoff valves (radiator taps, thermal heads). Shut-off valves are marked on the supply and return of each radiator. Shut-off valves must be installed - in case the radiator fails, and it will need to be disconnected for replacement / repair without stopping the entire system.
In addition to the shut-off valves on each radiator, the same valves are on the supply for each wing, immediately after the boiler. For what?
As you can see from the diagram, the length of the loops is not the same: the “wing” going down from the boiler (if you look at the diagram) is shorter than the one that goes up. This means that the resistance of a shorter pipeline will be less.Therefore, the coolant can flow more along the shorter “wing”, then the longer “wing” will be colder. Due to the taps on the supply pipe, we can adjust the uniformity of the coolant supply.
The same taps are placed on the return line of both loops - in front of the boiler.
Useful tips for the proper arrangement of the heating system
 Bimetallic radiators come from the factory connected in 10 sections. After calculations, we got 10, but we decided to add 2 more in reserve. So, it's better not to. Factory assembly is much more reliable, it is guaranteed from 5 to 20 years.
Bimetallic radiators come from the factory connected in 10 sections. After calculations, we got 10, but we decided to add 2 more in reserve. So, it's better not to. Factory assembly is much more reliable, it is guaranteed from 5 to 20 years.
The assembly of 12 sections will be done by the store, while the warranty will be less than a year. If the radiator leaks shortly after the end of this period, repairs will have to be carried out on their own. The result is unnecessary problems.
Let's talk about the effective power of the radiator. The characteristics of the bimetallic section, indicated in the product passport, are based on the fact that the temperature difference of the system is 60 degrees.
Such pressure is guaranteed if the battery coolant temperature is 90 degrees, which does not always correspond to reality. It's necessary take into account when calculating room radiator systems.
Here are some tips for installing the battery:
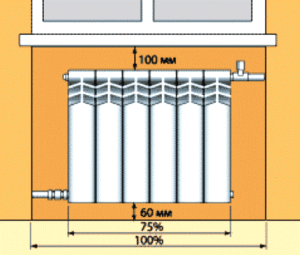
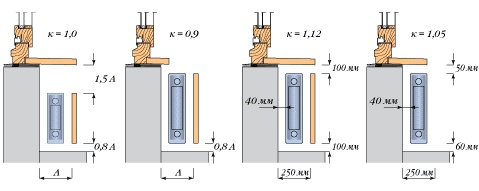
- The distance from the window sill to the top edge of the battery must be at least 5 cm. Air masses can circulate normally and transfer heat to the entire room.
- The radiator needs to lag behind the wall by a length of 2 to 5 cm. If reflective thermal insulation is attached behind the battery, then you need to purchase elongated brackets that provide the specified clearance.
- The bottom edge of the battery is supposed to be indented from the floor equal to 10 cm. Failure to follow the recommendations will worsen heat transfer.
- A radiator mounted against a wall, and not in a niche under a window, must have a gap of at least 20 cm with it. This will prevent dust from accumulating behind it and help heat the room.
It is very important to make such calculations correctly. It depends on how efficient and economical the resulting heating system will be.
All the information given in the article is intended to help the average person with these calculations.
Glazing, area and orientation of windows
Windows can account for 10% to 35% of heat loss. The specific indicator depends on three factors: the nature of the glazing (coefficient A), the area of the windows (B) and their orientation (C).
The dependence of the coefficient on the type of glazing:
- triple glass or argon in a double package - 0.85;
- double glass - 1;
- single glass - 1.27.
The amount of heat loss directly depends on the area of window structures. Coefficient B is calculated based on the ratio of the total area of window structures to the area of the heated room:
- if the windows are 10% or less of the total area of the room, B = 0.8;
- 10-20% – 0,9;
- 20-30% – 1;
- 30-40% – 1,1;
- 40-50% – 1,2.
And the third factor is the orientation of the windows: heat loss in a south-facing room is always lower than in a north-facing room. Based on this, we have two coefficients C:
- windows in the north or west - 1.1;
- windows on the south or east side - 1.
Steel plate heating radiators
How to find out the power of a heating battery if these are plate-type steel radiators, because they do not have sections? In this case, when making calculations, the length of the steel plate heating radiator and the center distance are taken into account
In addition, manufacturers recommend paying attention to the way the battery is connected. The fact is that the option of inserting into the heating system affects the thermal power during the operation of the radiator.
Everyone who is interested in the heat transfer value of steel plate batteries can look at the table of the model range of TM Korad products shown in the photo.
How to calculate the number of heating radiator sections
In order for heat transfer and heating efficiency to be at the proper level, when calculating the size of radiators, it is necessary to take into account the standards for their installation, and by no means rely on the size of the window openings under which they are installed.
Heat transfer is not affected by its size, but by the power of each individual section, which are assembled into one radiator. Therefore, the best option would be to place several small batteries, distributing them around the room, rather than one large one. This can be explained by the fact that heat will enter the room from different points and evenly warm it up.
Each separate room has its own area and volume, and the calculation of the number of sections installed in it will depend on these parameters.
Calculation based on room area
To correctly calculate this amount for a certain room, you need to know some rules:
You can find out the required power for heating a room by multiplying by 100 W the size of its area (in square meters), while:
- The radiator power is increased by 20% if two walls of the room face the street and there is one window in it - this can be an end room.
- You will have to increase the power by 30% if the room has the same characteristics as in the previous case, but it has two windows.
- If the window or windows of the room face the northeast or north, which means that there is a minimum amount of sunlight in it, the power must be increased by another 10%.
- The radiator installed in a niche under the window has a reduced heat transfer, in this case it will be necessary to increase the power by another 5%.
Niche will reduce the energy efficiency of the radiator by 5%
If the radiator is covered with a screen for aesthetic purposes, then the heat transfer is reduced by 15%, and it also needs to be replenished by increasing the power by this amount.
Screens on radiators are beautiful, but they will take up to 15% of the power
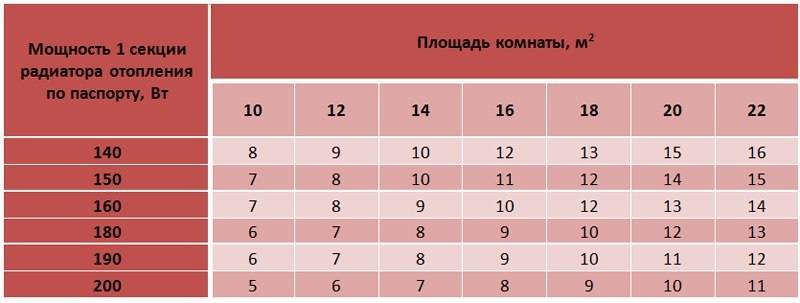
The specific power of the radiator section must be indicated in the passport, which the manufacturer attaches to the product.
Knowing these requirements, it is possible to calculate the required number of sections by dividing the resulting total value of the required thermal power, taking into account all the specified compensating corrections, by the specific heat transfer of one section of the battery.
The result of the calculations is rounded up to an integer, but only up. Let's say there are eight sections. And here, returning to the above, it should be noted that for better heating and heat distribution, the radiator can be divided into two parts, four sections each, which are installed in different places in the room.
Each room is calculated separately
It should be noted that such calculations are suitable for determining the number of sections for rooms equipped with central heating, the coolant in which has a temperature of no more than 70 degrees.
This calculation is considered quite accurate, but you can calculate in another way.
Calculation of the number of sections in radiators, based on the volume of the room
The standard is the ratio of thermal power of 41 W per 1 cubic meter.meter of the volume of the room, provided that it contains one door, window and external wall.
To make the result visible, for example, you can calculate the required number of batteries for a room of 16 square meters. m and a ceiling, 2.5 meters high:
16 × 2.5 = 40 cubic meters
Next, you need to find the value of thermal power, this is done as follows
41 × 40=1640 W.
Knowing the heat transfer of one section (it is indicated in the passport), you can easily determine the number of batteries. For example, heat output is 170 W, and the following calculation is made:
1640 / 170 = 9,6.
After rounding, the number 10 is obtained - this will be the required number of sections of heating elements per room.
There are also some features:
- If the room is connected to the adjacent room by an opening that does not have a door, then it is necessary to calculate the total area of the two rooms, only then the exact number of batteries for heating efficiency will be revealed.
- If the coolant has a temperature below 70 degrees, the number of sections in the battery will have to be proportionally increased.
- With double-glazed windows installed in the room, heat losses are significantly reduced, therefore the number of sections in each radiator can be less.
- If old cast-iron batteries were installed in the premises, which coped well with creating the necessary microclimate, but there are plans to change them to some modern ones, then it will be very simple to calculate how many of them will be needed. One cast-iron section has a constant heat output of 150 watts. Therefore, the number of installed cast iron sections must be multiplied by 150, and the resulting number is divided by the heat transfer indicated on the sections of new batteries.
What does it depend on?
The accuracy of the calculations also depends on how they are made: for the entire apartment or for one room.Experts advise choosing a calculation for one room. Let the work take a little longer, but the data obtained will be the most accurate. At the same time, when purchasing equipment, you need to take into account about 20 percent of the stock. This reserve is useful if there are interruptions in the operation of the central heating system or if the walls are paneled. Also, this measure will save with an insufficiently efficient heating boiler used in a private house.
The relationship of the heating system with the type of radiator used must be taken into account first of all. For example, steel devices come in a very elegant shape, but the models are not very popular among buyers. It is believed that the main drawback of such devices is poor-quality heat transfer. The main advantage is an inexpensive price, as well as low weight, which simplifies the work associated with installing the device.
Steel radiators usually have thin walls that heat up quickly but cool down just as quickly. During hydraulic shocks, welded joints of steel sheets leak. Inexpensive options without a special coating corrode. Manufacturers' warranties are usually short term. Therefore, despite the relative cheapness, you will have to spend a lot.


Cast iron radiators are familiar to many because of their ribbed appearance. Such "accordions" were installed both in apartments and in public buildings everywhere. Cast iron batteries do not differ in special grace, but they serve for a long time and with high quality. Some private houses still have them.A positive characteristic of this type of radiators is not only the quality, but also the ability to supplement the number of sections.


Modern cast-iron batteries have slightly modified their appearance. They are more elegant, smoother, they also produce exclusive options with a pattern of cast iron.
Modern models have the properties of previous versions:
- retain heat for a long time;
- not afraid of water hammer and temperature changes;
- do not corrode;
- suitable for all types of coolants.
In addition to the unsightly appearance, cast iron batteries have another significant drawback - fragility. Cast iron batteries are almost impossible to install alone, as they are very massive. Not all wall partitions can support the weight of a cast iron battery.

Aluminum radiators have appeared on the market recently. The popularity of this species contributes to the low price. Aluminum batteries are distinguished by excellent heat dissipation. At the same time, these radiators are light in weight and usually do not require a large volume of coolant.
On sale you can find options for aluminum batteries in both sections and solid elements. This makes it possible to calculate the exact number of products in accordance with the required power.
Like any other product, aluminum batteries have disadvantages, such as susceptibility to corrosion. In this case, there is a risk of gas formation. The quality of the coolant for aluminum batteries must be very high. If aluminum radiators are sectional type, then at the joints they often leak. At the same time, it is simply impossible to repair the battery. The highest quality aluminum batteries are made by anodic oxidation of the metal. However, these designs do not have external differences.
Bimetallic heating radiators have a special design, due to which they have increased heat transfer, and reliability is comparable to cast-iron options. The bimetallic radiator battery consists of sections connected by a vertical channel. The outer aluminum shell of the battery provides high heat dissipation. Such batteries are not afraid of hydraulic shocks, and any coolant can circulate inside them. The only drawback of bimetallic batteries is the high price.

How to calculate the number of radiators for a single pipe circuit
It should be taken into account the fact that all of the above applies to two-pipe heating schemes, assuming the supply of coolant of the same temperature to each of the radiators. Calculating sections of a heating radiator in a single-pipe system is an order of magnitude more difficult, because each subsequent battery in the direction of the coolant is heated by an order of magnitude less. Therefore, the calculation for a single-pipe circuit involves a constant revision of the temperature: such a procedure takes a lot of time and effort.
To facilitate the procedure, such a technique is used when the calculation of heating per square meter is carried out, as for a two-pipe system, and then, taking into account the drop in thermal power, sections are increased to increase the heat transfer of the circuit in general. For example, let's take a single-pipe type circuit that has 6 radiators. After determining the number of sections, as for a two-pipe network, we make certain adjustments.
The first of the heaters in the direction of the coolant is provided with a fully heated coolant, so it can not be recalculated.The supply temperature to the second device is already lower, so you need to determine the degree of power reduction by increasing the number of sections by the obtained value: 15kW-3kW = 12kW (the percentage of temperature reduction is 20%). So, to make up for heat losses, additional sections will be needed - if at first they needed 8 pieces, then after adding 20% we get a final number - 9 or 10 pieces.
When choosing which way to round, take into account the functional purpose of the room. If we are talking about a bedroom or a nursery, rounding up is carried out. When calculating the living room or kitchen, it is better to round down. It also has its share of influence on which side the room is located - south or north (northern rooms are usually rounded up, and south rooms are rounded down).
This method of calculation is not perfect, as it involves increasing the last radiator in the line to a truly gigantic size. It should also be understood that the specific heat capacity of the supplied coolant is almost never equal to its power. Because of this, boilers for equipping single-pipe circuits are selected with some margin. The situation is optimized by the presence of shut-off valves and the switching of batteries through the bypass: thanks to this, the possibility of adjusting the heat transfer is achieved, which somewhat compensates for the decrease in the temperature of the coolant. However, even these methods do not relieve the need to increase the size of the radiators and the number of its sections as they move away from the boiler when using a single-pipe scheme.
To solve the problem of how to calculate heating radiators by area, a lot of time and effort will not be needed
Another thing is to correct the result obtained, taking into account all the characteristics of the dwelling, its dimensions, the method of switching and the location of the radiators: this procedure is quite laborious and lengthy. However, it is in this way that you can get the most accurate parameters for the heating system, which will ensure the warmth and comfort of the premises.