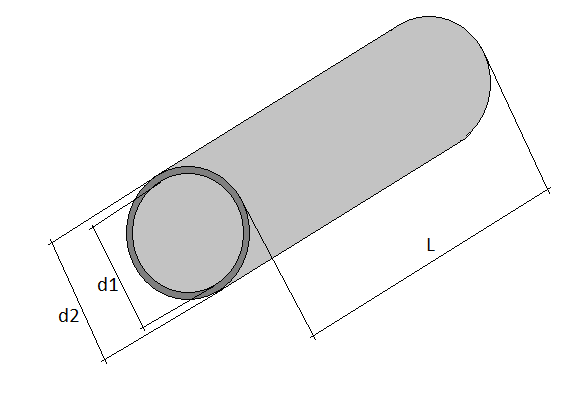
- Geometrical parameters of pipes
- Obtaining a result by an experimental method
- Instructions for the calculator for calculating the area and volume of a pipe by diameter
- Pipe Volume and Area Calculator
- Instructions for an online calculator for calculating the area and volume of a pipe
- GOST and SNiP requirements
- Calculation of the volume of a steel pipe
- A little about the design of the engine Lada 21083 8 valves
- The formula for calculating the volume of a pipe
- Calculation of the volume of water in the pipe and system
- Pipe Volume Calculation
- Determine the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe pipe
- The formula for calculating the volume of a pipe
- The volume of the water supply in liters
- Methods for calculating specific gravity
- Determination of the specific gravity of the pipe by the formulas
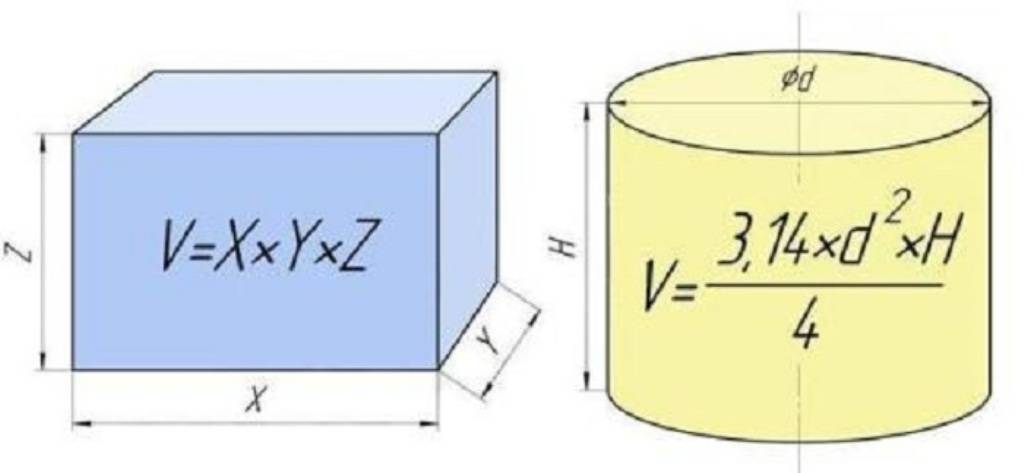
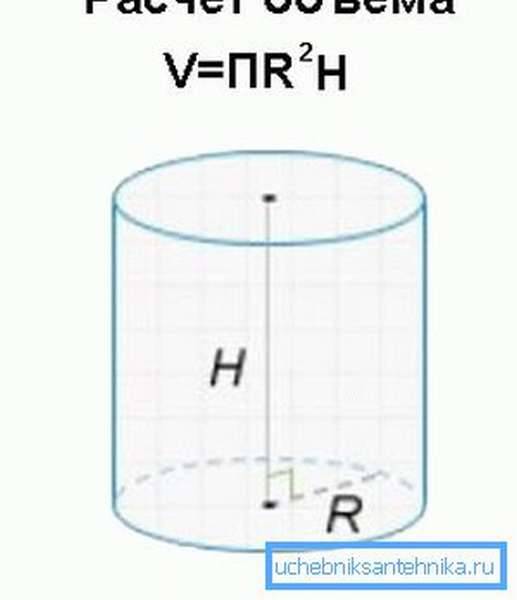
Geometrical parameters of pipes
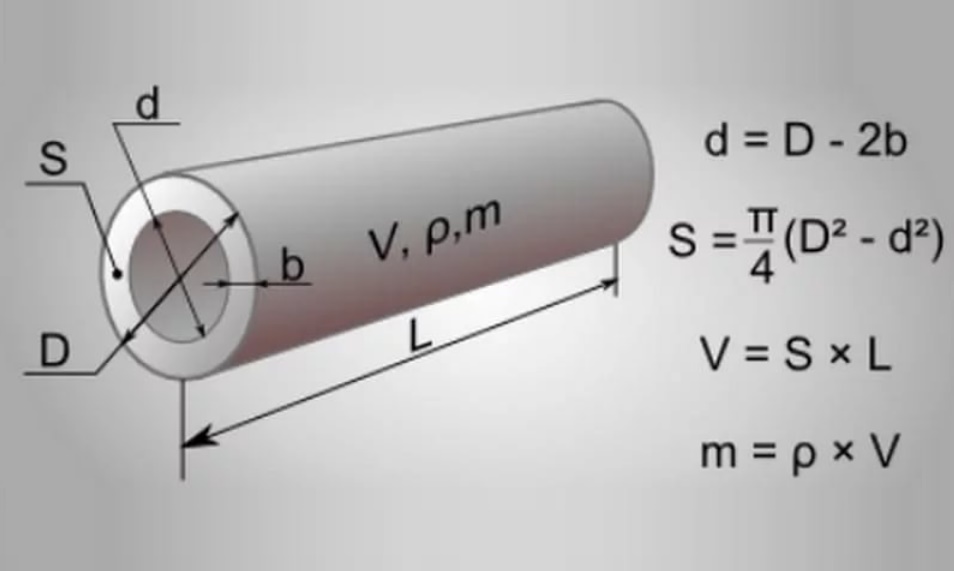
To determine the volume of a pipe, it is necessary and sufficient to know only two of its indicators: length and internal (actual) diameter
It is important not to confuse the last parameter with the external size, which is given for the correct selection of fittings and connecting elements.
If the wall thickness is not known, then DN (diameter of the internal passage) can be used instead of the calculated internal diameter. They are approximately equal, and the DN value is usually indicated on the marking, which is placed on the outside of the product.
The standard range of polypropylene pipes contains outside diameter and thickness walls in millimetres.From these two parameters, you can calculate the inner diameter
Before trying to calculate the volume of any pipe, it is necessary to avoid a common mistake and bring all parameters to a single measurement system. The fact is that the length is usually expressed in meters, and the diameter - in millimeters. The ratio of these two units is as follows: 1 m = 1000 mm.
In fact, you can bring the parameters to intermediate values \u200b\u200b- centimeters or decimeters. Sometimes it is even convenient, given that in this case the number of decimal places or, conversely, zeros, will not be very large.
The relationship of volume units. When translating from one value to another, it is necessary to avoid an error in the number of zeros or, conversely, decimal places
For pipes not produced in Russia (and not for Russia), the diameter can be expressed in inches. In this case, it is necessary to recalculate, taking into account that 1″ = 25.4 mm.
This is interesting: Mini-factory for foam blocks
Obtaining a result by an experimental method
In practice, problematic situations arise when the hydraulic system has a complex structure or some of its fragments are laid in a secret way. In this case, it becomes impossible to determine the geometry of its parts and calculate the total volume. Then the only way out is to conduct an experiment.
Using a collector and laying pipes under the screed is an advanced way of secretly supplying hot water to heating radiators. It is impossible to accurately calculate the length of communications in the absence of a plan
It is necessary to drain all the liquid, take some measuring container (for example, a bucket) and fill the system to the desired level. Filling occurs through the highest point: an open-type expansion tank or an upper release valve.In this case, all other valves must be open to avoid the formation of air pockets.
If the movement of water along the circuit is carried out by the pump, then you need to let it work for an hour or two without heating the coolant. This will help expel residual air pockets. After that, you need to add fluid to the circuit again.
This method can also be used for individual parts of the heating circuit, for example, a warm floor. To do this, you need to disconnect it from the system and “spill” it in the same way.
Instructions for the calculator for calculating the area and volume of a pipe by diameter
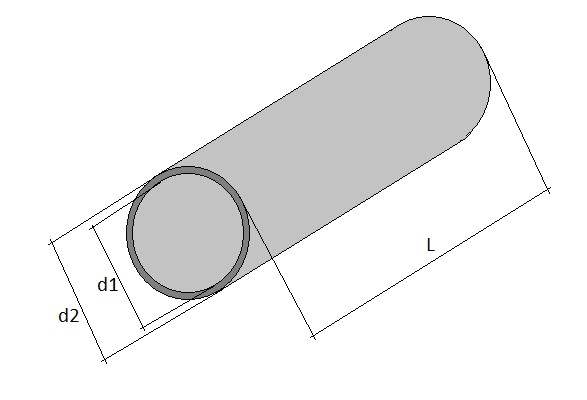
Enter dimensions in millimeters:
d1 - The inner diameter of the pipe is determined by its purpose. The internal diameters of commonly used pipes are 6, 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65, 80, 100, 110, 125, 200mm.
d2 - External diameter, depends on the type and application of the pipe.
L - Length of the pipe, here specify the length of the pipe billet.
The main parameters of pipes d1, d2, L can be gleaned from the following regulatory documents:
GOST 24890-81 “Welded pipes made of titanium and titanium alloys. Specifications"; GOST 23697-79 “Welded straight-seam pipes made of aluminum alloys. Specifications"; GOST 167-69 “Lead pipes. Specifications"; GOST 11017-80 “High pressure seamless steel pipes. Specifications"; GOST R 54864-2011 “Seamless hot-formed steel pipes for welded steel building structures. Specifications"; GOST R 54864-2016 “Seamless hot-formed steel pipes for welded steel building structures. Specifications"; GOST 5654-76 “Seamless hot-formed steel pipes for shipbuilding. Specifications"; GOST ISO 9329-4-2013 “Seamless steel pipes for work under pressure.Specifications"; GOST 550-75 “Seamless steel pipes for the oil refining and petrochemical industries. Specifications"; GOST 19277-73 “Seamless steel pipes for oil and fuel pipelines. Specifications"; GOST 32528-2013 “Seamless hot-formed steel pipes. Specifications"; GOST R 53383-2009 “Seamless hot-formed steel pipes. Specifications"; GOST 8731-87 “Seamless hot-formed steel pipes. Specifications"; GOST 8731-74 “Seamless hot-formed steel pipes. Technical requirements” and GOST 8732-78 “Seamless hot-formed steel pipes. Assortment".
It is important to know that 1 inch is approximately equal to 2.54 cm, since the system for measuring pipe diameters in inches is very often used. Click Calculate. Click "Calculate"
Click Calculate.
An online calculator will help you calculate the volume of pipes from various materials. This will make it possible to make more accurate design calculations, taking into account the capacity of the pipe section. And it will allow you to choose the optimal parameters of water supply (calculate the pressure in the system) or heating pipes (to achieve uniform heating of the room). You can also calculate the volume and surface area of the pipe in m3 by its diameter, which will allow you to find out the painting area and purchase the necessary amount of paint and varnish materials to cover and prevent pipe rusting.
Pipe Volume and Area Calculator
Instructions for an online calculator for calculating the area and volume of a pipe
All parameters are indicated in mm
L - Pipe in length.
D1 - Diameter on the inside.
D2 - Diameter on the outer part of the pipe.
With this program, you can calculate the volume of water or any other liquid in the pipe.
To accurately calculate the volume of the heating system, it is necessary to add the volume of the heating boiler and radiators to the result obtained. As a rule, these parameters are indicated in the passport on the product.
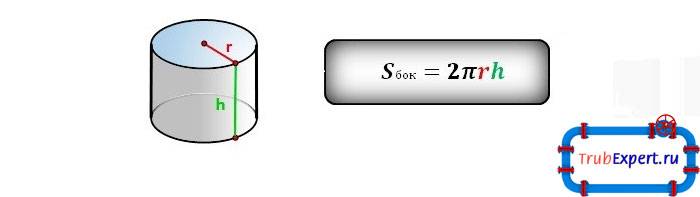
According to the results of calculations, you will find out the total volume of the pipeline, per linear meter, the surface area of the pipe. As a rule, the surface area is used to calculate the required amount of coating material.
When calculating, you must specify the outer and inner diameter of the pipeline and its length.
The program performs pipe surface calculations according to the following formula P=2*π*R2*L.
Pipe volume calculations are performed using the formula V=π*R1^2*L.
Where,
L is the length of the pipeline.
R1 is the inner radius.
R2 is the outer radius.
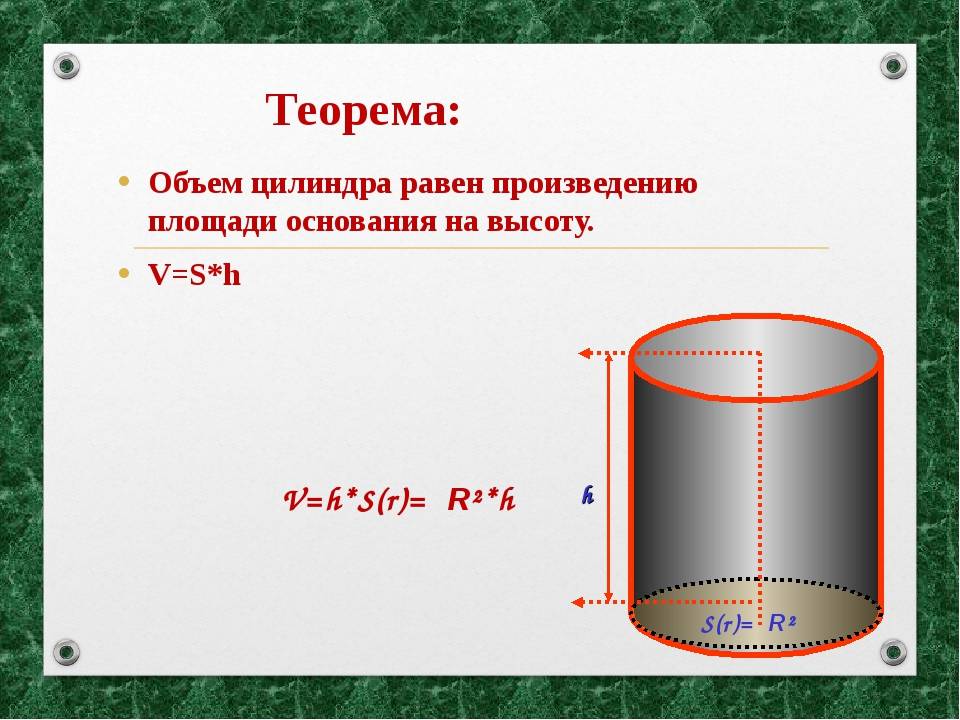
How to correctly calculate the volume of bodies
Calculating the volume of a cylinder, pipes and other physical bodies is a classic problem from applied science and engineering. As a rule, this task is not trivial. According to analytical formulas for calculating the volume of liquids in various bodies and containers, it can be very difficult and cumbersome. But, in general, the volume of simple bodies can be calculated quite simply. For example, using a few mathematical formulas, you can determine the volume of the pipeline. As a rule, the amount of liquid in the pipes is determined by the value of m3 or cubic meters. However, in our program, you get all calculations in liters, and the surface area is determined in m2 - square meters.
Useful information
The dimensions of steel pipelines for gas supply, heating or water supply are indicated in whole inches (1″.2″) or fractions (1/2″, 3/4″). For 1 ″, according to generally accepted standards, 25.4 millimeters are taken. To date, steel pipes can be found in reinforced (double-walled) or in the usual version.
For reinforced and conventional pipelines, the inner diameters differ from the standard ones - 25.4 millimeters: for example, in a reinforced one, this parameter is 25.5 millimeters, and in a standard or ordinary one - 27.1 millimeters. It follows that, slightly, but these parameters differ, which should also be taken into account when choosing pipes for heating or water supply. As a rule, specialists do not really delve into these details, since for them an important condition is Du (Dn) or conditional passage. This value is dimensionless. This parameter can be determined using special tables. But we do not need to go into these details.
Docking of various steel pipes, the size of which is presented in inches with aluminum, copper, plastic and others, the data of which are presented in millimeters, special adapters are provided.
As a rule, this type of pipe calculation is necessary in the process of calculating the size of the expansion tank for the heating system. The volume of water in the heating system of a room or house is calculated using our program online. However, often, inexperienced specialists simply neglect this data, which should not be done. Since, for the efficient functioning of the heating system, it is necessary to take into account all the parameters in order to choose the right boiler, pump and radiators.Also, the volume of liquid in the pipeline will be important in the case when antifreeze is used instead of water in the heating system, which is quite expensive and overpayments in this case will be unnecessary.
To determine the volume of liquid, it is necessary to correctly measure the outer and inner diameters of the pipeline.
An approximate calculation can be performed based on the proportion of 15 liters of liquid per 1 kW of heating boiler power
For example, you have a 4 kW boiler, from here we get the volume of the entire system is 60 liters (4x15)
We have given the exact values of the volume of liquid for different radiators in the heating system.
Water volume:
- old cast-iron battery in 1 section - 1.7 liters;
- new cast-iron battery in 1 section - 1 liter;
- bimetallic radiator in 1 section - 0.25 liters;
- aluminum radiator in 1 section - 0.45 liters.
Conclusion
Now you know how to correctly and quickly calculate the volume of a pipe for a water supply or heating system.
GOST and SNiP requirements
In modern multi-storey buildings, the heating system is installed based on the requirements of GOST and SNiP. The regulatory documentation specifies the temperature range that central heating must provide. This is from 20 to 22 degrees C with humidity parameters from 45 to 30%.
To achieve these indicators, it is necessary to calculate all the nuances in the operation of the system even during the development of the project. The task of a heat engineer is to ensure the minimum difference in the pressure values of the liquid circulating in the pipes between the lower and last floors of the house, thereby reducing heat loss.
| number of storeys | Working pressure, atm |
| Up to 5 floors | 2-4 |
| 9-10 floors | 5-7 |
| From 10 and up | 12 |
The following factors influence the actual pressure value:
- The condition and capacity of the equipment supplying the coolant.
- The diameter of the pipes through which the coolant circulates in the apartment. It happens that wanting to increase the temperature indicators, the owners themselves change their diameter upwards, reducing the overall pressure value.
- The location of a particular apartment. Ideally, this should not matter, but in reality there is a dependence on the floor, and on the distance from the riser.
- The degree of wear of the pipeline and heating devices. In the presence of old batteries and pipes, one should not expect that the pressure readings will remain normal. It is better to prevent the occurrence of emergency situations by replacing your old heating equipment.
How pressure changes with temperature Check the operating pressure in a high-rise building using tubular strain gauges. If, when designing the system, the designers laid down automatic pressure control and its control, then sensors of various types are additionally installed. In accordance with the requirements prescribed in the regulatory documents, control is carried out in the most critical areas:
- at the coolant supply from the source and at the outlet;
- before the pump, filters, pressure regulators, mud collectors and after these elements;
- at the outlet of the pipeline from the boiler room or CHP, as well as at its entry into the house.
Please note: 10% difference between standard working pressure on the 1st and 9th floor is normal
Calculation of the volume of a steel pipe

Pipes made of steel are ordinary or reinforced. Regular pipes have an internal diameter of 27.1 mm, while the reinforced type has an internal diameter of 25.5 mm. But experts in their calculations use the value of the conditional passage Du (Dn). This value is considered dimensionless and convenient for calculations, since with differences in pipe diameter, the entire amount of work becomes more complicated.Therefore, all the difficulties were reduced to one denominator, which requires special tables and subtleties of calculations. In cases of joining pipes made of steel (inch) with plastic or aluminum (mm), specialized fittings are used in practice - connections.
The calculation of the volume of the pipeline in the heating system is necessary, for example, to determine the size of the membrane (expansion) tank. The total volume of water in the heating system is also quite easy to calculate, but there is no need for this, but antifreeze requires calculations, because each liter of it costs additional costs. For calculations, you will also need to find out what material the radiator sections are made of, their distance between them and the number of sections in each radiator. It is better to indicate the final result in liters, since the volumes of liquids are usually measured in liters. To do this, the resulting total in cubic centimeters is divided by 1000. The amount of coolant in the boiler will only need to be added, this will turn out the volume of the pipeline.
Most ordinary people do not really understand how important it is to calculate the volume of the pipe. But professional experts will confirm the need for calculations. Since in their practice they were faced with the fact that the pipe can be closed on the other side (cylinder) or there is a need for an accurate idea of the pressure created, because it can be optimized by changing the volume of the pipe in a particular section
Since in their practice they were faced with the fact that the pipe can be closed on the other side (cylinder) or there is a need for an accurate idea of the pressure created, because it can be optimized by changing the volume of the pipe in a particular section.
A little about the design of the engine Lada 21083 8 valves
The insufficient power of the 1.3-liter internal combustion engine of the eighth family required the creation of a larger power unit. The designers bored out the base block for 82 mm pistons, thereby increasing the working volume by 200 cubes. As a result, the resulting motor added 9 hp. and 11 Nm of torque.
It was on this engine that AvtoVAZ engineers first applied cylinder honing, which allowed them to practically abandon the mandatory engine break-in. And also the diameter of the intake valves was increased from 35 mm to 37 mm. The timing drive remained unchanged, however, when the belt breaks, the valve does not bend.
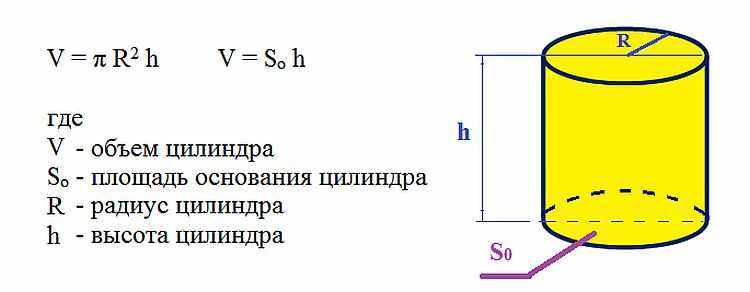
The formula for calculating the volume of a pipe
To start the calculations, you should find out the initial data. For example, you need a pipe radius. From here you can get an indicator of how much the pipe takes or how much it holds in itself. For our case (determining the capacity of water), the second option is suitable.
How to find the radius? It is enough to know the diameter of the pipe, which must be divided by two. In our case, we are talking about the inner diameter. If for some reason this parameter is unknown, then you can navigate along the circumference. To do this, using a flexible meter, we measure this indicator, and then divide it by 2Pi, which is approximately equal to 6.28.
You will also need to determine the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe product. To do this, we again use the number Pi, which must be multiplied by the square of the radius.In this case, we will receive this parameter in the same unit of measurement in which the radius was taken. This means that if the radius was presented in meters, then we will get the cross-sectional area in square meters.
As a result, it remains to substitute the obtained values \u200b\u200bin the main formula, multiplying the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe pipe by the length.
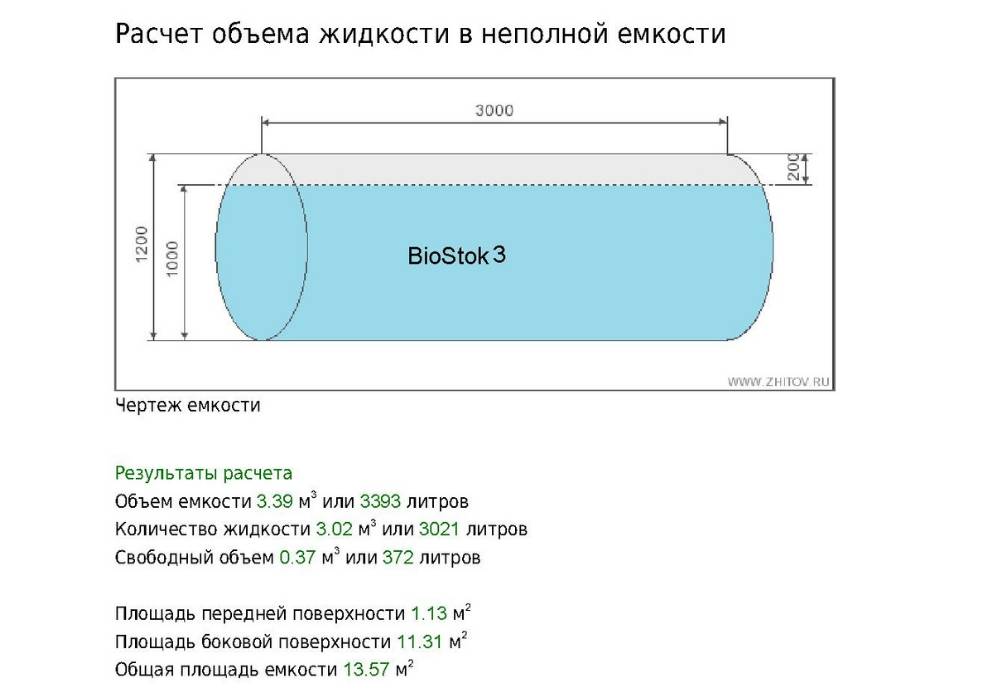
Calculation of the volume of water in the pipe and system
To determine this parameter, you need to substitute the data of the inner radius of the pipe into the above formula. But what if you need to calculate the entire volume of the heating system, which also consists of radiators, and a heating boiler, and an expansion tank?
You need to calculate the volume of the radiator. To do this is quite simple. You need to find out from the technical data sheet what is the volume of one section, and then multiply this number by the number of sections in a particular battery. So, often in cast-iron radiators this figure for one section is about 1.5 liters. If the radiator is bimetallic, then this figure can be ten times less.
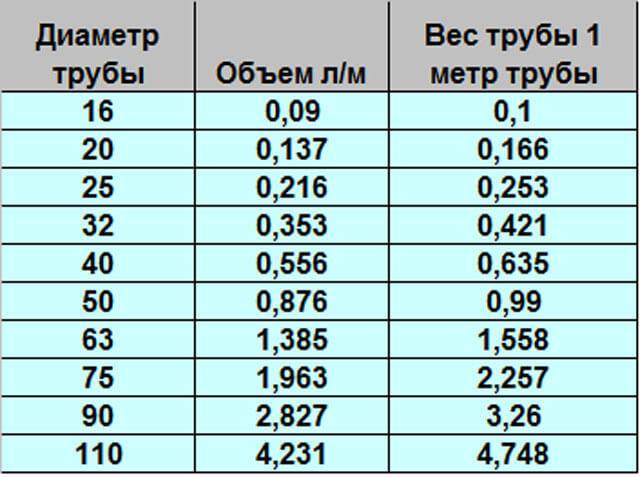
Pipe calculation - weight, mass, diameter
As for the volume of water in the boiler, these data are also available in the passport.
To measure the capacity of the expansion tank, you need to fill it with the measured amount of water.
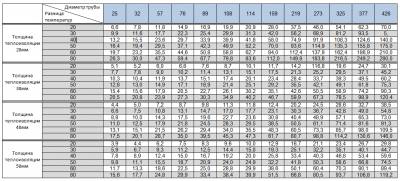
With pipes, as already mentioned, it is also simple. The values obtained for each meter of a certain diameter need only be multiplied by the footage of this pipe diameter. It should be noted that in the relevant literature, as well as on the Web, there are special tables that allow you to determine the data based on other parameters, taking into account the material and features of the products. It is only necessary to understand that these figures are indicative. However, the error will be insignificant if we take them to calculate the volume of water.
It is impossible not to note one characteristic feature in this issue. Steel pipes of larger diameter pass less water than polypropylene pipes of the same diameter. This is due to the fact that the latter have a smoother inner surface, while steel ones have a rougher one. However, at the same time, steel products have a larger volume of water than in other types of pipes similar in terms of throughput.
Calculation of the volume of the heating system is necessary to determine the volume of the expansion tank, select a heating boiler or determine the required amount of coolant.
Calculating the volume of the heating system is quite simple, for this it is necessary to sum the internal volume of all elements of the system
. The problem arises precisely in determining the volume of internal elements, in order not to re-read GOSTs and passports for heating devices, this article contains all the necessary information. It will greatly simplify the calculation of your heating system.
Pipe Volume Calculation
To calculate the volume of a pipe, you need to use school knowledge of geometry. There are several ways: 1. Multiplying the cross-sectional area of the figure by its length in meters, the result will be meters cubed. 2. It is possible to find out the size of the water supply in liters. To do this, the volume is multiplied by 1000 - this is the number of liters of water in 1 cubic meter. 3. The third option is to immediately count in liters. You will need to make measurements in decimeters - the length and area of \u200b\u200bthe figure. This is a more complicated and inconvenient way.
To calculate manually - without a calculator, you will need a caliper, ruler and calculator. To facilitate the process of determining the size of the volume of the pipe, you can use the online calculator.
Determine the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe pipe
To know the exact value, you must first calculate the cross-sectional area. To do this, you should use the formula:
S = R2 x Pi
Where R is the radius of the pipe and Pi is 3.14. Since liquid containers are usually round, R is squared.
Consider how you can make calculations, having a product diameter of 90 mm:
- We determine the radius - 90 / 2 = 45 mm, in terms of centimeters 4.5.
- We square 4.5, it turns out 2.025 cm2.
- We substitute the data into the formula - S \u003d 2 x 20.25 \u003d 40.5 cm2.
If the product is profiled, then it must be calculated according to the rectangle formula - S \u003d a x b, where a and b are the size of the sides (length). When determining the size of a profile section with a side length of 40 and 50, 40 mm x 50 mm = 2000 mm2 or 20 cm2 is required.
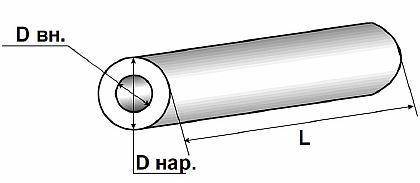
To calculate the section, it is necessary to know the inner diameter of the pipe, which is measured with a caliper, but this is not always possible. If only the outer diameter is known, and we do not know the thickness of the walls, then more complex calculations will be required. The standard thickness is 1 or 2 mm, for large diameter products it can reach 5 mm.
Important! It is better to start the calculation if there are accurate indicators of the thickness of the walls and the inner radius
The formula for calculating the volume of a pipe
Calculate the volume of the pipe in m3, you can use the formula:
V = S x L
That is, you only need to know two values: the cross-sectional area (which was determined in advance) (S) and the length (L).
For example, the length of the pipeline is 2 meters, and the cross-sectional area is half a meter. To calculate, you need to take the formula by which the area of \u200b\u200bthe circle is determined, and insert the external size of the metal crossbar:
S \u003d 3.14 x (0.5 / 2) \u003d 0.0625 sq.m.
The final result will be as follows:
V \u003d HS \u003d 2 x 0.0625 \u003d 0.125 cubic meters
H is the wall thickness
When making a calculation, it is important that all indicators have one unit of measurement, otherwise the result will be incorrect. It is easier to take data in cm2
The volume of the water supply in liters
It is easy to calculate the volume of liquid in a pipe without a calculator if you know its inner diameter, but this is not always possible when radiators or heating boilers for water have a complex shape. Today, such products are often used in the construction industry, in the arrangement of underfloor heating. Therefore, you should initially find out the design parameters; this information can be found in the data sheet or accompanying documentation. To calculate the size of a non-standard container, it is necessary to pour water into it, which is measured in advance.
In addition, the cubic capacity of water will also depend on the material from which the water supply is made. For example, a steel product will let in an order of magnitude less water than an equal-sized polypropylene or plastic one. This is affected by the surface from the inside, iron is more rough, which affects the patency.
Therefore, it is necessary to make calculations for each container, if it is made of a different material, and then add up all the indicators. You can use special service programs or calculators, today there are a lot of them on the Internet, they will greatly facilitate the process of determining the amount of water in the system.
Methods for calculating specific gravity
- length;
- height, width or diameter;
- wall thickness.
Therefore, it is indicated as the mass of the volume (in m2) of a profile or cylindrical shape filled with homogeneous steel with the required density (in kg / m3). The length of the pipe when determining its specific gravity is one meter.For steel pipe, in any calculations, the density of the composition from which it is made is constantly taken as 7850 kg / m. cube To determine the weight of one meter of steel pipe (specific gravity), choose one of the following methods:
- according to calculation formulas;
- using tables where the required data are indicated for standard sizes of rolled tubular products.
In any case, the data obtained are only a theoretical calculation. This is due to the following reasons:
- in calculations, it is often necessary to round the calculated values;
- in the calculations, the shape of the pipe is assumed to be geometrically correct, that is, metal sagging at the welding joint, rounding in the corners (for profiled steel), reduction or excess of dimensions relative to the standard ones within the permissible GOST are not taken into account;
- the density of different steel grades differs from 7850 kg/m. cube and for many alloys, the difference is quite significant when determining the weight of a large number of tubular products.
With the help of special tables, the most approximate theoretical indicator of the specific weight of pipe rolling is determined, since complex mathematical formulas were used in their compilation, which took into account the production technology and geometry of the products as much as possible. To use this calculation option, first, according to the available data on pipe rolling, its type is determined. After that, they find in the reference literature a table corresponding to this metal-roll or GOST for this assortment.
The tabular version of the calculation is good because it does not require any calculations, which eliminates the possibility of making a mathematical error in the calculations. But this method implies the availability of special literature.The most universal option is the use of mathematical formulas. This method can be used in any conditions, even, so to speak, "field", far from the possibilities and benefits of civilization.
Determination of the specific gravity of the pipe by the formulas
As mentioned above, the calculation is based on determining the volume of raw materials used to produce one meter of pipe. Then this value must be multiplied by the density of the composition (in the case of steel, by 7850 kg / m3). The desired volume is determined in this way:
- Calculate the volume of a part of a pipe one meter long according to its external dimensions. Why determine the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe pipe, which is multiplied by the length, in our case by 1 meter.
- Calculate the volume of the hollow part of the pipe 1 meter long. Why first determine the dimensions of the cavity (for a round product, the inner diameter is calculated by subtracting double the wall thickness from the outer diameter, and for profiled pipe-rolling, the height and width of the inner diameter are determined, subtracting double the thickness from the outer dimensions). After, according to the results obtained, a calculation is made similar to that indicated in the first paragraph.
- At the end, the second result is subtracted from the first result, this is the volume of the pipe.
All calculations are made only after the conversion of the initial indicators into kilograms and meters. The determination of the volume of a round and cylindrical section of pipes occurs according to the following formula:
V = RxRx3.14xL, where:
- V is the volume;
- R is the radius;
- L is the length.
Another simple formula, but for steel round pipes:
Weight = 3.14x(D - T)xTxLxP, where:
- D is the outer diameter;
- T is the wall thickness;
- L - length;
- P is the density of steel.
data must be converted to millimeters
Specific gravity = (A–T)xTx0.0316
For rectangular pipes:
Specific gravity = (A+B–2xT)xTx0.0158
That is, to determine the exact weight of the material, you can use special tables, which indicate the mass of pipes, taking into account the cross section, diameter and other indicators. If this table is not at hand, then you can always use a special calculator, where to calculate the required values, you just need to enter the necessary data, such as wall thickness and section type of the structure. How to determine the specific gravity, everyone chooses for himself.