- What is unit power?
- Electric power of air conditioner
- Air conditioner cooling capacity
- Calculation of power for a household air conditioner
- What is an online calculator for?
- Counting methods
- The necessary conditions
- Calculation by quadrature
- Volume calculation
- The final selection stage
- How to calculate the power of the air conditioner?
- Calculation methods
- Operations based on room squares
- Calculation with additional parameters
- Calculation technique and formulas
- What to count?
- Calculation of power consumption and electricity costs
- Types of air conditioners by power
What is unit power?
First of all, it is necessary to distinguish between the concept of the consumed electric power of the air conditioner and the so-called cooling power. Usually both of these parameters are indicated on the packaging, as well as on the device case. They are related, but not equal. When discussing the issue of the power of the cooling unit, be sure to specify what kind of power is in question.

So, what is this difference between these capacities, we will understand further.
Electric power of air conditioner
This is the energy that the air conditioner consumes from the electrical network in your home. In other words, this is the power that is expressed in kilowatts per hour (kW / h).It is for her that you will have to pay the bills of the utility organization.
It should be understood that the indicated electrical power describes the electrical power consumption during continuous operation of the cooling unit for an hour. In reality, air conditioners use much less energy because they work intermittently. When the temperature in the room reaches a certain point, the device turns off and stops consuming electricity. If the thermal insulation of the building is good, then the coolness will last for a long time.
Air conditioner cooling capacity
This is the rate at which the air conditioner cools your home. It is measured in the so-called British Thermal Units (BTU) or British Thermal Unit (BTU). One BTU equates to 0.3 conventional electrical watts (W). As a rule, the number of thousand BTUs is indicated in the index. For example, if “BTU 5” is written on the package, this means that this unit consumes 5000 * 0.3 = 1.5 kilowatts from the mains per hour of continuous operation, which is not so much.
The higher the BTU, the more energy your device needs to operate, and this figure increases in a linear relationship, but the degree of cooling of the room also increases.
An air conditioner with a specified power up to "12 BTU" does not require an additional separate power supply, because it consumes about 3.5 kW from the network. This can be equated to the work of heating elements of a modern washing machine or a powerful boiler. Ordinary residential wiring should be sufficient.

Of course, you should not load one line (socket) at the same time with an air conditioner, microwave and electric oven, for example. The wires in the wall from such a load can overheat and simply burn out.Finding the place of the cliff will be very difficult, and eliminating the cliff is even more difficult. You will have to tear off the wallpaper or open the tile, break part of the wall, connect the wires, and then restore everything back.
Calculation of power for a household air conditioner
 types of air conditioners
types of air conditioners
Why is it so important to correctly calculate and choose an air conditioner in terms of power (cooling capacity)?
Insufficient optimal power entails the operation of the device in non-stop mode - it will try to reach the required temperature in the room. With an excess of optimal power, the air conditioner will operate in constant start / stop mode and produce too strong cooled air flows that cannot be distributed normally around the entire perimeter. Both the one and the other options instantly wear out the compressor.
Having made the correct calculation of the air conditioner power, after reaching the set temperature, the compressor turns off, and then only the room unit functions. As soon as the parameters have increased by a couple of degrees, a command is sent to the compressor through the temperature sensors, and it turns on again.
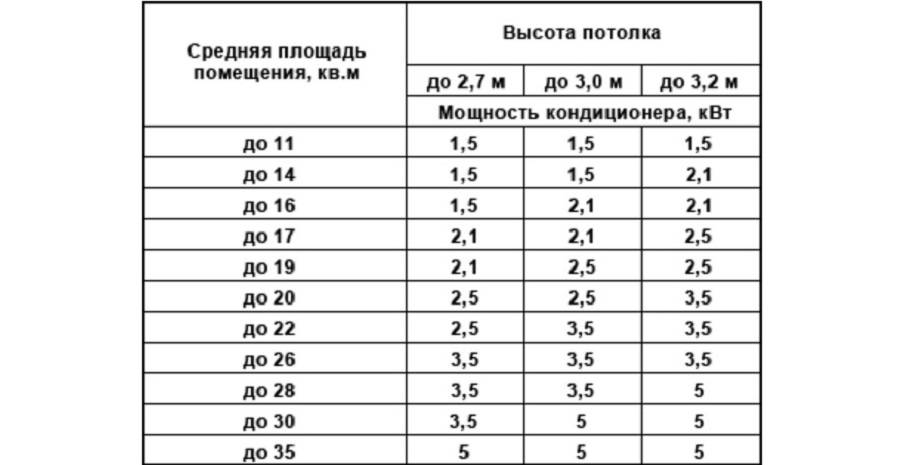
When buying a household split system or monoblock, you can make a lightweight power calculation, taking into account only the area of \u200b\u200bthe room.
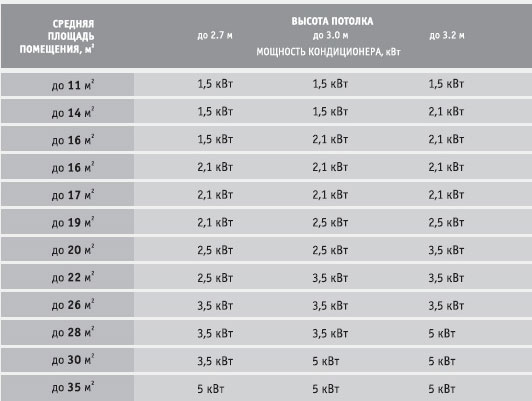
It is generally accepted that on average 1 kW = 10 m². Therefore, a 17 m² room requires a cooling capacity of 1.7 kW. Air conditioners with a power of 1.5 kW or more are produced, but not all manufacturers have such low-power models. And the next value is usually 2 kW. If the side is sunny, the room is equipped with a large amount of equipment, and several people are regularly there, then it is better to give preference to higher values - 2 kW or 7 BTU.
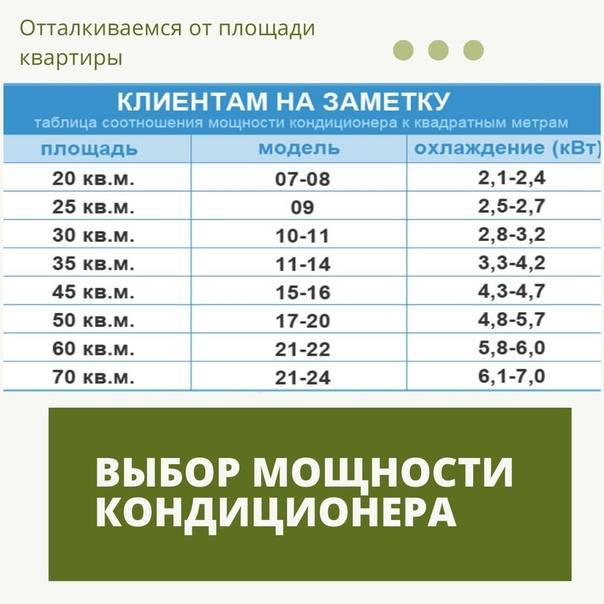
Small air conditioners comply with the following table of values:
| Area, m² | power, kWt | Power, Btu/h |
| 15 | 1,5 | 5 |
| 20 | 2 | 7 |
| 25 | 2,5 | 9 |
| 35 | 3,5 | 12 |
| 45 | 4,5 | 14-15 |
| 50 | 5,0 | 18 |
| 60 | 6,0 | 21 |
| 70 | 7,0 | 24 |
A typical calculation of power over the area of \u200b\u200bthe room is done according to the generally accepted scheme:
Q1 = S * h * q / 1000
where Q is the power when working in cold (kW), S is the area (m²), h is the height of the ceilings (m), q is a coefficient equal to 30 - 40 W / m³:
q = 30 for the shadow side;
q = 35 for normal light hit;
q = 40 for the sunny side.
Q2 is the total value of heat surpluses from people.
Heat surpluses from an adult:
0.1 kW - with minimal activity;
0.13 kW - with low or medium activity;
0.2 kW - with increased activity;
Q3 is the total value of heat gains from household appliances.
Heat surpluses from household appliances:
0.3 kW - from PC;
0.2 kW - from TV;
For other devices, there is a value in the calculation of 30% of the maximum power consumption.
The climate control power must be in the range Qrange from -5% to +15% of the calculated power Q.
What is an online calculator for?
Today, many online storefronts offer a service such as a calculator for calculating the power of an air conditioner, which easily determines the exact value of cooling capacity, taking into account all the features of the room. This is very convenient - even a simple layman can use it without special knowledge in the field of air conditioning systems. Why would such a skill be needed? So that an unscrupulous seller does not try to mislead a person by trying to sell him a device of inadequate power that has been stale in the warehouse.
At the end of the article, you can watch a video with detailed instructions on how to use the calculator for calculating the power of an air conditioner for an ordinary buyer.
It is worth remembering that these types of standard calculations are only suitable for household and administrative premises with an area of \u200b\u200bno more than 70-80 m², without additional technical equipment and large crowding of people on the territory
Of no small importance is the type / type of compressor. This is also taken into account when choosing an air conditioning system for an apartment or office.
Thus, with the calculation of the power of the air conditioner by the area of the room, everything is clear - its results are rather arbitrary, and they are unsuitable for multi-systems or centralized air conditioning systems in industrial buildings.
Counting methods
There are several methods for calculation.
- You can calculate the power of the air conditioner using a special calculator, which is located on the developer's Internet resource.
- The calculation is carried out according to the quadrature of the room.
- You can calculate the power of the equipment using the formula using the data on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and the source of warm air in it.
- Calculation of the heat gain of the protective building for the summer period using an additional supply of warm air.
The latter is usually used by engineers who are involved in construction projects.
The necessary conditions
When calculating the power of the air conditioner, the following factors are taken into account:
- floor of the house;
- the presence of windows of non-standard shape;
- device location;
- frequency of airing the room;
- the number of household appliances in the home or office;
- ceiling height, distortions, etc.
Calculation by quadrature
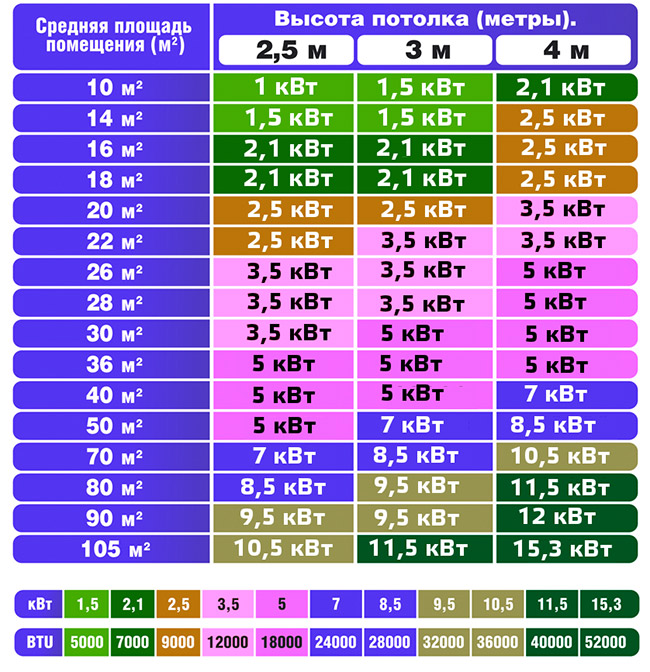
The essence of this calculation of the power of the air conditioner is as follows: if the height of the ceilings in the building is up to 3 m, then 100 W of cold energy should go out per 1 square meter.Therefore, for an area of 20 m2, an air conditioner with a capacity of 2 kW is required. When the ceilings are higher than 3 m, the cooling capacity is taken not 100 W, but more. Visual table:
| Ceiling size | Refrigeration power |
| 3 to 3.4 m | 120 W/m2 |
| 3.4–4 m | 140 W/m2 |
| More than 4 m | 160 W/m2 |
In addition, it is necessary to add to the number of cold for the entire size of the room the force of replenishing the heat input from people who are often in the room, as well as from working equipment. It is recommended to take the number of heat input:
- 1 person - 300 W;
- 1 unit of equipment - 300 W.
This means that in a building of 20 m2 there is always 1 person who works all day at the computer, and therefore 600 watts are added to the purchased 2 kW. The result is 2.6 kW.
Calculation of power by quadrature and number of people
Volume calculation
The calculation of the power of the air conditioner can be calculated by a separate cold number with room parameters from 1 m3. To correctly calculate the strength of the air conditioner, you need to take separate data that are equal to:
- in dark rooms - 30 W / m3;
- average lighting in the building - 35 W/m3;
- light area of the building - 40 W / m3.
The required power to replenish the heat supply through building structures is calculated using the following formula: Q1 = q x V, where V is the parameters of the room in m3.
As for technology, here the figure depends on its features. If this is a computer, then you need to add 250-300 watts. From any other equipment - in the amount of 30% of the amount of energy consumed. After that, everything can be calculated according to the formula. In order to determine the required value, the number of people and equipment is added to the volume of the room (Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3).

Bright rooms require more power
The final selection stage
The number that came out of the formula above is not final. According to the instructions for using the device, it is forbidden to keep it turned on all day. In order for the work force to be minimal, and the device to be able to serve for many more years, it is necessary to stock up on the auxiliary power of the air conditioner.
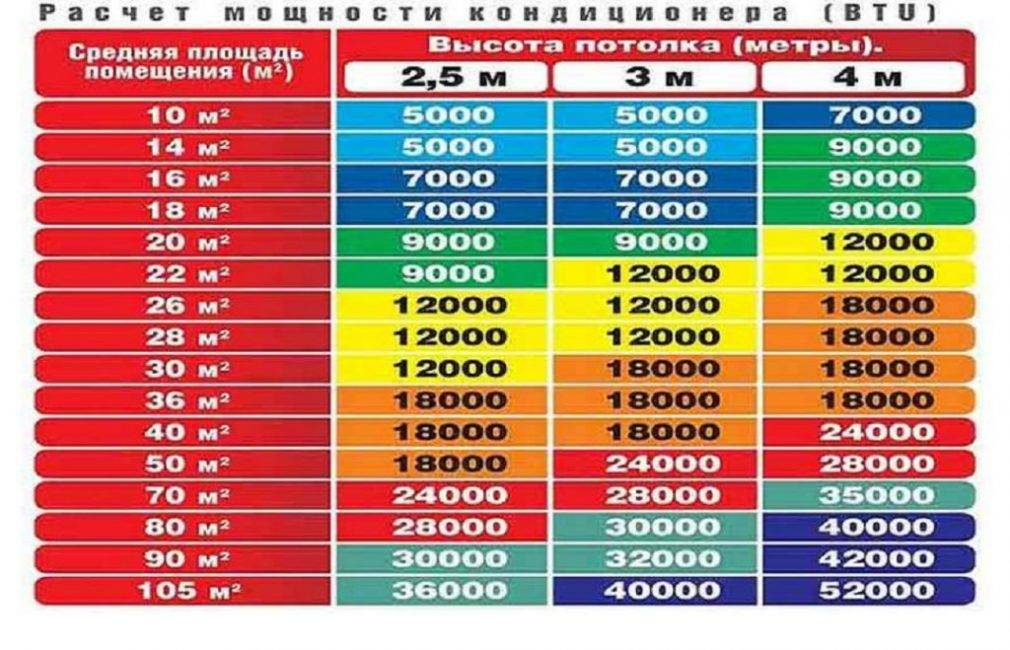
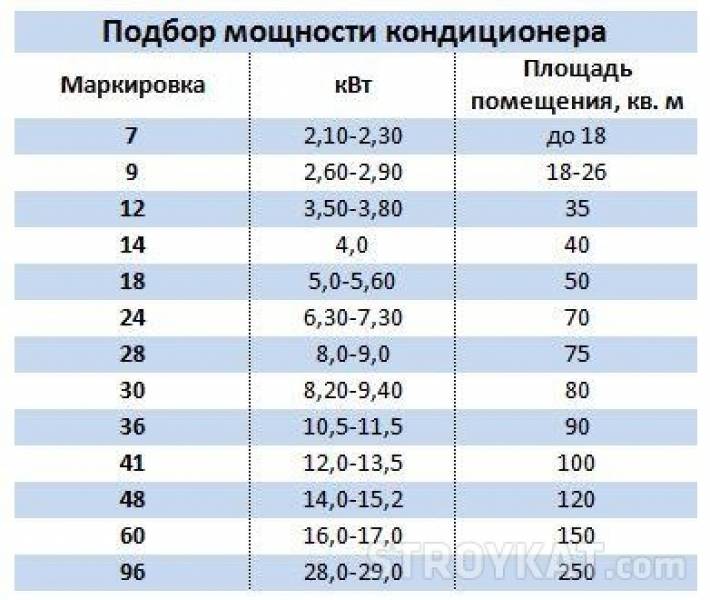
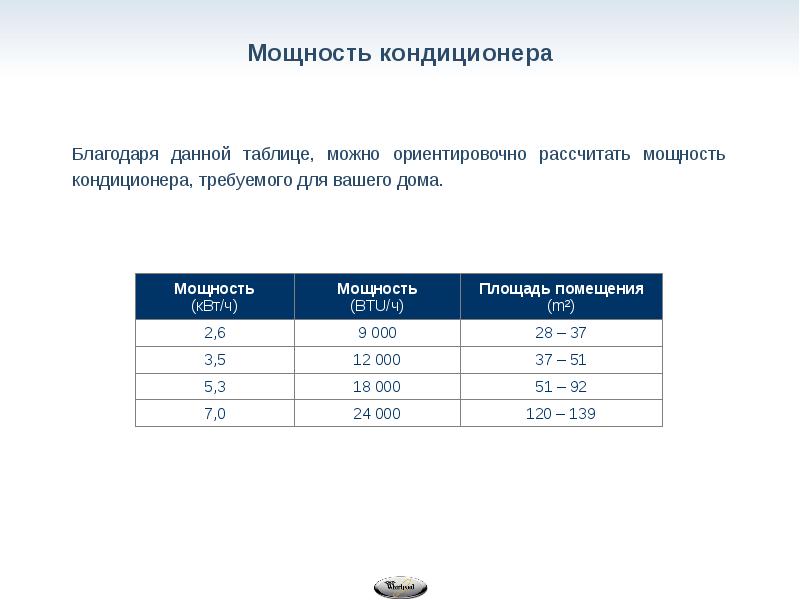
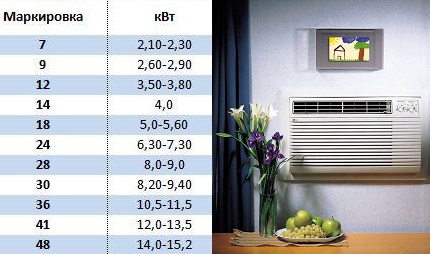
Almost always, it is taken in the number of 15–20% of the calculated value of the air conditioner. Most developers produce product lines according to the gradation rules adopted in the USA. They are specified in BTU. Since the gradation starts at 7, it means 7000 BTU or 2.1 air conditioner power in kW. Using the table below, you can choose an air conditioner with a suitable power for certain room area parameters.
| Btu | 7 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 24 |
| Air conditioner power calculation | 2,1 | 2,6 | 3,5 | 5,2 | 7 |
| Building area m2 | up to 20 | 20–25 | 25–35 | 35–50 | More than 50 |
Before buying an air conditioning system, you need to know that, unlike other heating and cooling systems, the used energy output of the air conditioner does not correspond to the power of the refrigeration. At the time of calculating the strength of the air conditioner for inexperienced people, the resulting figure can be very confusing. Therefore, it is worth knowing that the information of refrigeration devices is effective due to the formation of vaporization and freon condensate. Split systems consume several times less power than indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging, so do not be surprised at the small numbers received.
2 id="kak-rasschitat-moschnost-konditsionera">How to calculate the power of an air conditioner?
The calculation of the electricity consumption of an air conditioner depends on many indicators, including:
- the number of square meters in the room;
- the number of people and pets living in the room;
- thermal insulation of the room;
- the degree of exposure to sunlight in the room;
- volumetric characteristics of the conditioned area;
- geometry and configuration;
- number and power of electrical appliances in the room:
- presence and number of door and window openings.
In order to determine the required power of the device, special calculation formulas are used that measure thermal energy in watts.
Industry experts are of the opinion that the general standard recommended air cooling capacity for every 10 square meters of area is 1kW. Also, for each person living there, another 0.1 kW is added.
Calculation methods
Professionals distinguish between accurate and approximate calculation of the power of the air conditioner. First, an approximate calculation is made, and already at the installation site they make the final revision. It should be noted that only one room can be considered correct calculations. In the case when the device must serve adjacent rooms, a misalignment of the temperature regime and ventilation inevitably occurs: a draft walks near the air conditioner, and stuffiness remains in remote places.
It should also be borne in mind that perfect calculations are relevant only for medium-sized, up to 70-80 square meters, premises in capital buildings: cottages, city apartments in high-rise buildings, offices.
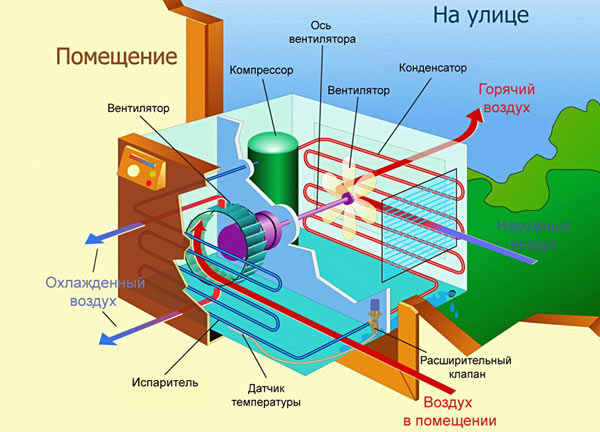
The method for calculating the cooling capacity contains the Q factor, which is based on the summation of all possible heat sources:
Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3,
The first indicator Q1 is the heat entering the room from the window, ceiling, walls and floor. We calculate by the formula: Q1 = S * h * q / 1000, where
h is the height of the room (m);
S - room area (sq. m);
q - variable coefficient, which ranges between 30 - 40 W / m?:
- average illumination = 35;
- shaded room - q = 30;
- bright rooms with a lot of sunlight q = 40.
The second indicator Q2 is the heat gain from the people present in the air-conditioned room:
- passive state - 0.10 kW;
- when walking - 0.13 kW;
- when performing active actions - 0.20 kW.
Q3 are the heat gains generated by household appliances in total terms:
0.3 kW - the value obtained from a personal desktop computer;
0.2 kW - the value obtained from the LCD TV.
Air conditioner installers take into account all electrical appliances in the room. It is believed that any unit allocates a third of the power consumed to the external environment.
So, we begin the calculation of the power of the air conditioner. It consists of several stages:
- Determine the height of the ceiling. If this parameter is standard 2.50-2.70 meters, then the formula does not require adjustment.
- Determine the area of the room. Everything is as always: the width of the room is multiplied by its length.
Now we calculate:
Q (heat gains) = S (room area) * h (room height) * q (average coefficient 35 - 40 W / sq. m).
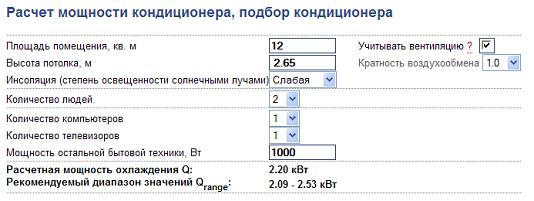
Given: a room with an area of, for example, 20 square meters and a ceiling at a height of 2.7 meters, windows on the south side, 3 people live or often visit, while the room has a floor lamp with one bulb and a plasma TV, we calculate:
Q total \u003d 20x2.7x40 + 3x130 + 200 + 300 \u003d 2100 + 390 + 500 \u003d 2990 W
Answer: The cooling capacity should be 2.99 kW or 2990 W
To choose the optimal model of equipment for a given room, you should focus on a slightly higher power, for example, an air conditioner with a power parameter of 3.5 kW.
As for energy consumption, this does not mean that the power of the air conditioning device will be in direct proportion to the level of electricity consumed. Quite the opposite, this device will eat two or even four times less electricity. For example, a selected model with a power of 3.5 kW will require no more than 1.5 kW of electricity.
So, for a room of 20 square meters, the best purchase will be air conditioner line Fujitsu General with the stated power.
In the case when the calculation is made for a production facility or a large office with many employees, it is better to contact specialists, because there you need to take into account the influence of other significant parameters.
If the calculation cannot be done on your own, then you can always use the services of a virtual calculator, the calculations of which turn out to be correct in 99% of cases. Just enter all the required dimensions, characteristics and quantities of units there, and you will get the result in the form of a recommendation.
Operations based on room squares
This technique is held in high esteem by sales representatives. It has some analogies with the calculations of heating equipment in terms of the specific heat parameter.
The essence of the technique: if the ceilings in the room do not reach a height of 3 m, then 100 W of cooling energy should be generated per square meter.
So for a room of 20 sq.m. you need a device with MO 2 kW.
If the ceiling height is more than 3 m, then the specific MO is calculated according to the following table:
To the cold parameter spent on the whole area of the room, it is also necessary to add the power to compensate for heat flows from the inhabitants of the room and household appliances located in it.
Here the calculation is carried out as follows: 300 W of heat comes from one tenant, and 300 W from household units.
It turns out that if in a room of 20 sq.m. 1 tenant constantly stays and he works with a computer, then another 600 watts are added to the calculated 2 kW. Result = 2.6 kW.
In practice, with reference to regulatory documents, if a person is at rest, then heat of 100 watts comes from him. With minor movements - 130 watts. During physical activities - 200 watts. It turns out that in these operations there is some overestimation of thermal parameters from people.
Calculation with additional parameters
The usual calculation of the power of the air conditioner, which is described above, most often gives fairly accurate results, but it would be useful to know about some additional parameters that are sometimes not taken into account, but quite strongly affect the required power of the device. The required power of the air conditioner increases to each of the following factors:
- Fresh air from an open window. The way in which we calculated the power of the air conditioner assumes that the air conditioner will operate with the windows closed, and fresh air will not enter the room. Most often, the operating instructions say that the air conditioner should work with the windows closed, otherwise, if outside air enters the room, an additional heat load will be created.
When the window is open, the situation is different, the air volume entering through it is not normalized and therefore the additional heat load will be unknown. You can try to solve this problem in the following way - the window is set to winter mode ventilation (the window opens a little) and the door closes. Thus, the appearance of drafts in the room will be excluded, but at the same time a small amount of fresh air will fall into the room.

It should be noted that the instruction does not provide for the operation of the air conditioner with the window ajar, therefore, the normal operation of the device cannot be guaranteed in such a situation. If you still use the air conditioner in this mode, then it is worth considering that in this case, electricity consumption will increase by 10-15%.
- Guaranteed 18-20 °C. Most buyers are wondering: is air conditioning dangerous for health? The instructions clearly state that the temperature difference between inside and outside should not be very large. For example, if the temperature outside is 35-40°C, then it is preferable to keep the temperature in the room at least 25-27°C. Based on this, in order for the room to have the minimum possible temperature of 18 ° C, it is necessary that the outside air has a temperature of no more than 28.5 ° C.
- Top floor. In the event that the apartment is located on the top floor and there is no technical floor or attic above it, then the heated roof will transfer heat into the room. A dark-colored horizontal roof receives many times more heat than light-colored walls. Based on this, heat gains from the ceiling will be higher than will be taken into account in the usual calculation, therefore, the power consumption will need to be increased by about 12-20%.
- Increased glass area. During the normal calculation, it is assumed that the room has one standard window (with a glazing area of 1.5-2.0 m2). Based on the degree of sun exposure, the power of the air conditioner changes by 15% up or down from the average. In the event that the size of the glazing is larger than the standard value, then the power of the device should be increased.
Since the standard glazing area (2 * 2) is taken into account in normal calculations, then in order to compensate for additional heat inflows per square meter of glazing more than 2 sq. value of insolation and 50-100 W for shaded rooms.
So, if the room:
- located on the sunny side;
- the room has a large number of office equipment;
- there is a large number of people in it;
- it has panoramic windows,
then an additional 20% of the required power is added.
In the event that, when taking into account additional parameters, the calculated power has increased, it is recommended to choose an inverter air conditioner. Such a unit has a variable cooling capacity and therefore, if installed, it will more effectively cope with a wide range of thermal loads.
Consultants do not recommend choosing a conventional air conditioner with increased power, since in a small room it can create uncomfortable conditions due to the specifics of its work.
Thus, the calculation of the power of the air conditioner allows you to choose a device with the optimal cooling capacity to create a comfortable microclimate in the room. The larger the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, the greater the power of the device should be. But the greater its performance, the more electricity the device consumes. Therefore, select equipment with the power necessary and sufficient for efficient work.
Calculation technique and formulas
On the part of a scrupulous user, it is quite logical not to trust the numbers obtained on the online calculator. To check the result of the unit capacity calculation, use the simplified method provided by the refrigeration equipment manufacturers.
So, the required cold performance of a domestic air conditioner is calculated by the formula:
Explanation of designations:
- Qtp - heat flux penetrating into the room from the street through building structures (walls, floors and ceilings), kW;
- Ql - heat dissipation from the residents of the apartment, kW;
- Qbp - heat input from household appliances, kW.
It is easy to find out the heat transfer of household electrical appliances - look at the product passport and find the characteristic of the electrical power consumed. Almost all of the energy used is converted into heat.

The compressor of a home refrigerator converts almost all the consumed electricity into heat, but it works intermittently
Heat gains from people are determined by regulatory documents:
- 100 Wh from a person at rest;
- 130 W / h - in the process of walking or doing light work;
- 200 W / h - with heavy physical exertion.
For calculations, the first value is taken - 0.1 kW.It remains to determine the amount of heat penetrating from the outside through the walls according to the formula:
- S is the quadrature of the refrigerated room, m²;
- h – floor height, m;
- q - specific thermal characteristic, related to the volume of the room, W / m³.
The formula allows you to perform an enlarged calculation of heat gains through the external fences of a private house or apartment using the specific characteristic q. Its values are taken as follows:
- The room is located on the shady side of the building, the window area does not exceed 2 m², q = 30 W/m³.
- With average illumination and glazing area, a specific characteristic of 35 W / m³ is taken.
- The room is located on the sunny side or has a lot of translucent structures, q = 40 W/m³.
Having determined the heat inputs from all sources, add up the figures obtained using the first formula. Compare the results of the manual calculation with those of the online calculator.

A large glass area suggests an increase in the cooling capacity of the air conditioner
When it is necessary to take into account the heat input from the ventilation air, the cooling capacity of the unit increases by 15-30%, depending on the exchange rate. When updating the air environment 1 time per hour, multiply the result of the calculation by a factor of 1.16-1.2.
What to count?
- consumed electric power;
- cooling capacity;
- heating power (for air conditioners with this function).
For many of us, this discrepancy turns out to be a complete surprise, because we know that for electric heaters, whether it be a boiler, an oil radiator or an IR emitter, the heat output is always equal to the electrical power consumed.
The thing is that the air conditioner works according to a slightly different principle: it does not directly convert electricity into one form or another, as heaters do, but uses it as a heat pump drive.
The heat pump itself - and this is its remarkable feature - can pump heat energy from the room to the street (cooling mode) or from the street to the room (heating mode) several times more than the electric energy will be spent for this. That is why it is much more profitable to bask in the off-season with an air conditioner than, say, with a fan heater: for each kilowatt of electricity spent, we will receive 3-4 kW of heat.
From the foregoing, it follows that when choosing an air conditioner, one should first of all take into account its ability to remove heat from the cooled room to the street, that is, the cooling capacity, and the power consumption should be of interest to us only from the point of view of selecting the wiring section and planning the family budget.
Calculation of power consumption and electricity costs
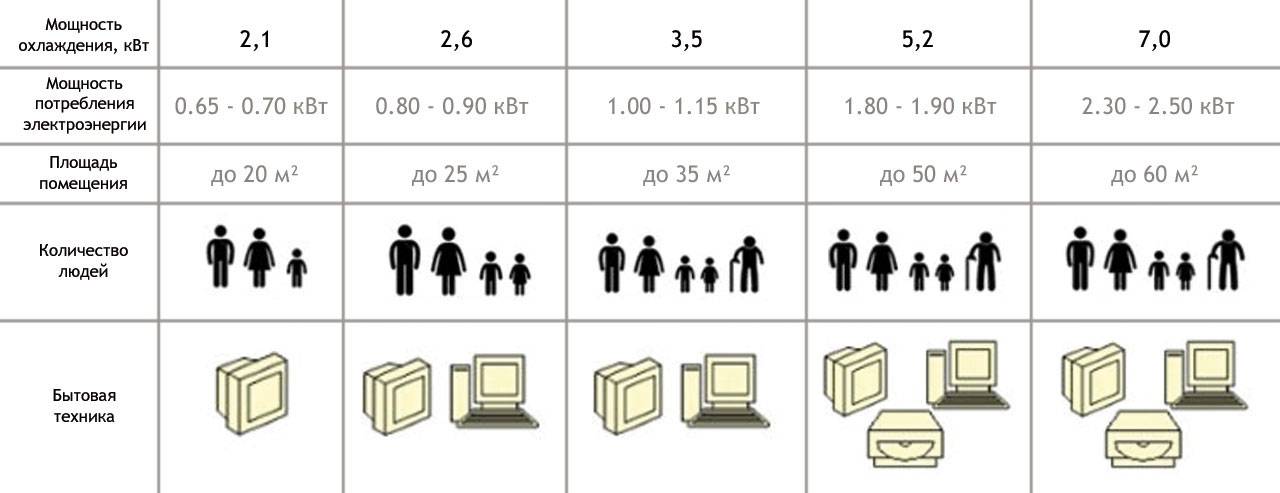
The value of the power consumed by the air conditioner allows you to determine whether it can be connected to a regular outlet or whether you need to pull a separate cable to the electrical panel. In modern houses, electrical wiring and sockets are designed for currents up to 16A, but if the house is old, then the maximum current should not exceed 10A. For safe operation, the current consumed by the split system must be 30% less than the maximum allowable, that is, equipment can be plugged into the outlet, the operating current of which does not exceed 7-11A, which corresponds to the power consumption 1.5–2.4 kW (Note that with such energy consumption, the cooling capacity of the air conditioner will lie in the range of 4.5–9 kW).
It should be borne in mind that in apartments several sockets are connected to one cable, therefore, to calculate the actual load, it is necessary to sum up the power of all electrical appliances connected to the sockets of one line.
The exact value of the power consumed by the air conditioner and its operating current is indicated in the catalog. Since we do not know which model will be chosen, we calculate these parameters based on the average value of the coefficient .
Knowing the power consumption, we can estimate the cost of electricity. To do this, you need to set the average operating time of the air conditioner per day at a certain power, for example, 2 hours at 100%, 3 hours at 75%, 5 hours at 50% and 4 hours at 25% (this mode of operation is typical for hot weather). After that, you can determine the average energy consumption per day and, by multiplying it for the number of days in a month and the cost of kWh, get the cost of electricity consumed per month. The average daily energy consumption of an air conditioner depends on the air temperature set by the user, the nature of the weather and other factors that are difficult to take into account, so our calculation does not claim to be highly accurate.
After choosing a specific model of a split system, you will be able to clarify the estimated energy consumption (how to do this is described in the section).
| Types of air conditioners | Functions and characteristics |
Types of air conditioners by power
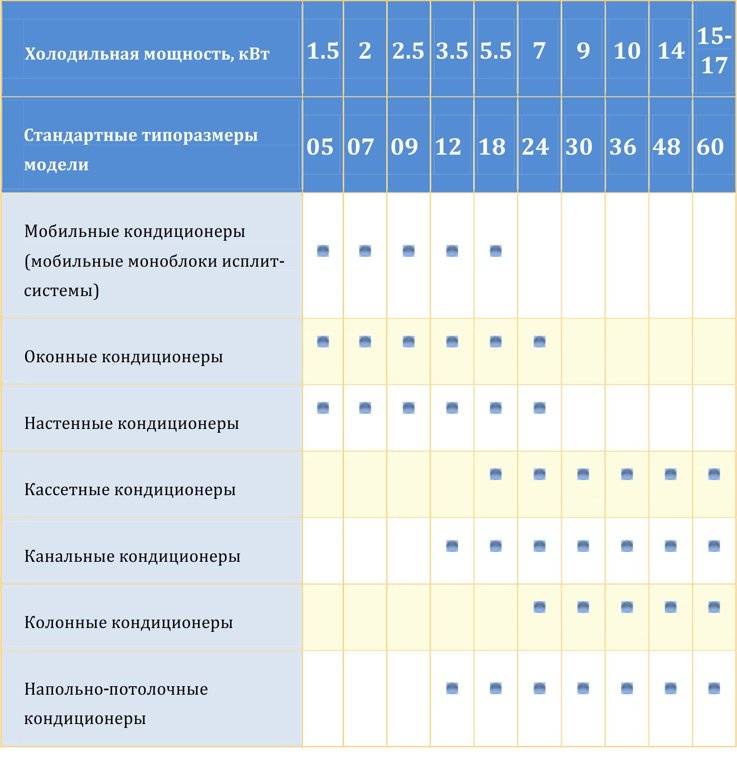
Depending on the room in which air conditioners are used, they are divided into industrial, semi-industrial and household appliances.
Each type of air conditioning device has its own power ratings. For example, household air conditioners have an estimated power of 1.5–8 kW.Knowing how to calculate an air conditioner for an apartment, we can easily calculate that for standard one-three-room living quarters in our houses, air conditioners with a capacity of only 2 kW to 5 kW will suffice. If we are talking about an apartment with a very large footage, then it is advisable to use several low-power devices in different rooms, or install a powerful semi-industrial device.
The most accurate calculation of the cooling capacity of the air conditioner is extremely significant, since only in the summer heat can you check the efficiency of your device. And if you installed the device at the end of summer or autumn, then it will be possible to test its operation only after a year. Therefore, it will be too late to make claims to anyone.