- How to calculate the number of heating radiator sections
- Calculation based on room area
- Calculation of the number of sections in radiators, based on the volume of the room
- The importance of correct calculation
- By area of the room
- By room size
- Use of coefficients
- Types of radiators
- Rooms with standard ceiling heights
- Rooms with a ceiling height of more than 3 meters
- An example of calculating the power of heating batteries
- Heat transfer rates for space heating
- Full formula for accurate calculation
- How to calculate heat losses for a private house and apartment
- Peculiarities
- Battery types
- Steel
- Cast iron
- Aluminum
- Bimetallic
How to calculate the number of heating radiator sections
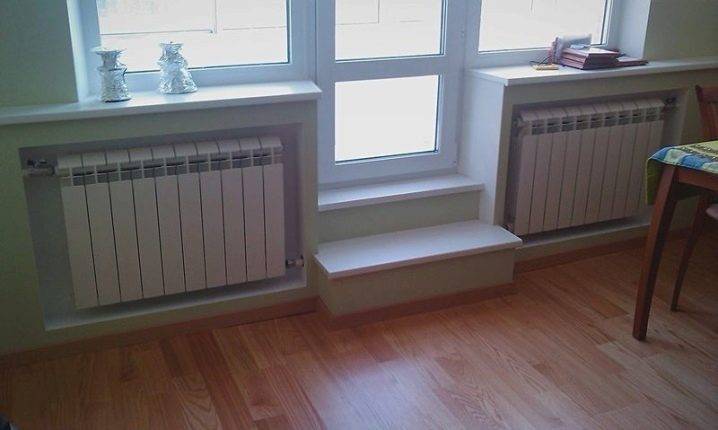
In order for heat transfer and heating efficiency to be at the proper level, when calculating the size of radiators, it is necessary to take into account the standards for their installation, and by no means rely on the size of the window openings under which they are installed.
Heat transfer is not affected by its size, but by the power of each individual section, which are assembled into one radiator. Therefore, the best option would be to place several small batteries, distributing them around the room, rather than one large one. This can be explained by the fact that heat will enter the room from different points and evenly warm it up.
Each separate room has its own area and volume, and the calculation of the number of sections installed in it will depend on these parameters.
Calculation based on room area
To correctly calculate this amount for a certain room, you need to know some rules:
You can find out the required power for heating a room by multiplying by 100 W the size of its area (in square meters), while:
- The radiator power is increased by 20% if two walls of the room face the street and there is one window in it - this can be an end room.
- You will have to increase the power by 30% if the room has the same characteristics as in the previous case, but it has two windows.
- If the window or windows of the room face the northeast or north, which means that there is a minimum amount of sunlight in it, the power must be increased by another 10%.
- The radiator installed in a niche under the window has a reduced heat transfer, in this case it will be necessary to increase the power by another 5%.

Niche will reduce the energy efficiency of the radiator by 5%
If the radiator is covered with a screen for aesthetic purposes, then the heat transfer is reduced by 15%, and it also needs to be replenished by increasing the power by this amount.

Screens on radiators are beautiful, but they will take up to 15% of the power
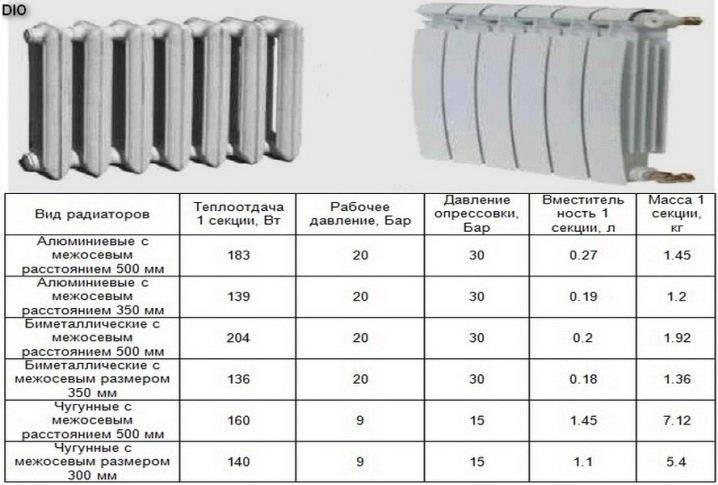
The specific power of the radiator section must be indicated in the passport, which the manufacturer attaches to the product.
Knowing these requirements, it is possible to calculate the required number of sections by dividing the resulting total value of the required thermal power, taking into account all the specified compensating corrections, by the specific heat transfer of one section of the battery.
The result of the calculations is rounded up to an integer, but only up. Let's say there are eight sections.And here, returning to the above, it should be noted that for better heating and heat distribution, the radiator can be divided into two parts, four sections each, which are installed in different places in the room.
Each room is calculated separately
It should be noted that such calculations are suitable for determining the number of sections for rooms equipped with central heating, the coolant in which has a temperature of no more than 70 degrees.
This calculation is considered quite accurate, but you can calculate in another way.
Calculation of the number of sections in radiators, based on the volume of the room
The standard is the ratio of thermal power in 41 W per 1 cube. meter of the volume of the room, provided that it contains one door, window and external wall.
To make the result visible, for example, you can calculate the required number of batteries for a room of 16 square meters. m and a ceiling, 2.5 meters high:
16 × 2.5 = 40 cubic meters
Next, you need to find the value of thermal power, this is done as follows
41 × 40=1640 W.
Knowing the heat transfer of one section (it is indicated in the passport), you can easily determine the number of batteries. For example, heat output is 170 W, and the following calculation is made:
1640 / 170 = 9,6.
After rounding, the number 10 is obtained - this will be the required number of sections of heating elements per room.
There are also some features:
- If the room is connected to the adjacent room by an opening that does not have a door, then it is necessary to calculate the total area of the two rooms, only then the exact number of batteries for heating efficiency will be revealed.
- If the coolant has a temperature below 70 degrees, the number of sections in the battery will have to be proportionally increased.
- With double-glazed windows installed in the room, heat losses are significantly reduced, therefore the number of sections in each radiator can be less.
- If old cast-iron batteries were installed in the premises, which coped well with creating the necessary microclimate, but there are plans to change them to some modern ones, then it will be very simple to calculate how many of them will be needed. One cast-iron section has a constant heat output of 150 watts. Therefore, the number of installed cast iron sections must be multiplied by 150, and the resulting number is divided by the heat transfer indicated on the sections of new batteries.
The importance of correct calculation
From the correct calculation of sections of bimetallic heating batteries depends on how comfortable it will be indoors in winter. This number is influenced by the following factors:
- Temperature. If there are not enough sections, then in winter it will be cold in the room. If there are too many of them, then there will be too hot and dry air.
- Expenses. The more sections you buy, the more expensive it will be to replace the batteries.
Calculating the number of sections of bimetallic batteries is quite difficult. When calculating take into account:
- fans that remove part of the heat from the room;
- exterior walls - it is colder in the corner rooms;
- Are heat packs installed?
- whether there is thermal insulation of the walls;
- what are the minimum winter temperatures in the region of residence;
- whether steam is used for heating, which increases heat transfer;
- whether it is a living room, a corridor or a warehouse;
- what is the ratio of the area of walls and windows.
In this video you will learn how to calculate the actual amount of heat
By area of the room
This is a simplified calculation bimetallic heating radiators per square meter.It gives a fairly correct result only for rooms with a height of no more than 3 m. According to plumbing standards, for heating one square meter of a room located in central Russia, a heat output of 100 W is required. With this in mind, the calculation is made as follows:
- determine the area of \u200b\u200bthe room;
- multiply by 100 W - this is the required heating power of the room;
- the product is divided by the heat transfer of one section (it can be recognized by the radiator passport);
- the resulting value is rounded up - this will be the desired number of radiators (for the kitchen, the number is rounded down).
 You can calculate the number of sections by the area of \u200b\u200bthe room
You can calculate the number of sections by the area of \u200b\u200bthe room
This method cannot be considered completely reliable. The calculation has many disadvantages:
- it is suitable only for rooms with low ceilings;
- can only be used in central Russia;
- does not take into account the number of windows in the room, the material of the walls, the degree of insulation and many other factors.
By room size
This method gives a more accurate calculation, since it takes into account all three parameters of the room. It is based on a sanitary heating norm for one cubic meter of space, equal to 41 watts. To calculate the number of sections of a bimetallic radiator, perform the following steps:
- Determine the volume of the room in cubic meters, for which its area is multiplied by the height.
- The volume is multiplied by 41 W and the heating power of the room is obtained.
- The resulting value is divided by the power of one section, which is recognized from the passport. The number is rounded - this will be the required number of sections.
Use of coefficients
Their application allows to take into account many factors. The coefficients are used as follows:
- If the room has an additional window, 100 watts are added to the heating power of the room.
- For cold regions, there is an additional factor by which the heating power is multiplied. For example, for the regions of the Far North it is 1.6.
- If the room has bay windows or large windows, then the heating power is multiplied by 1.1, for a corner room - by 1.3.
- For private houses, the power is multiplied by 1.5.
Correction factors help to more accurately calculate the number of battery sections. If the selected bimetallic radiator consists of a certain number of sections, then you need to take the model in which it exceeds the calculated value.
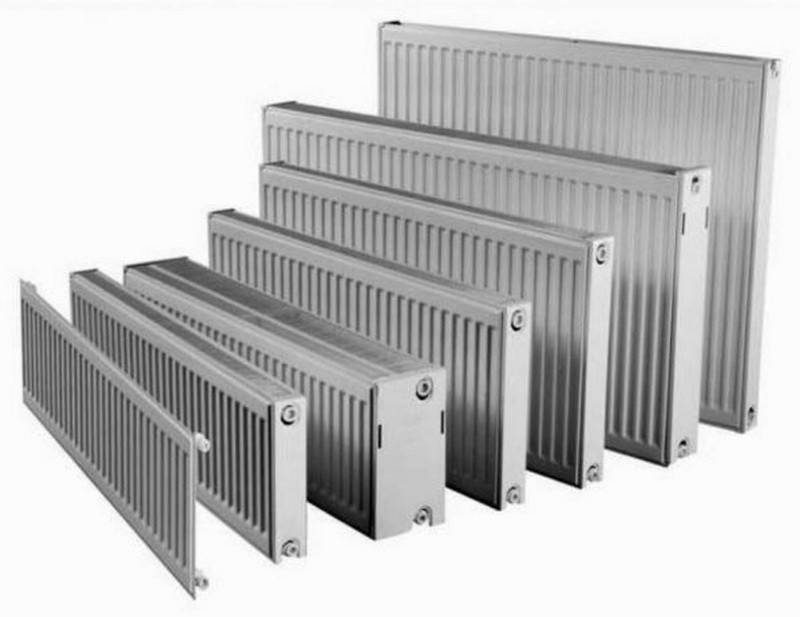
Types of radiators
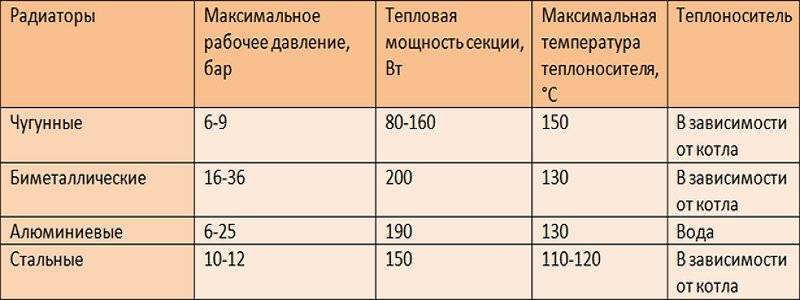
The first thing you need to know is the type and material from which your radiators are made, and their number depends on this in particular. On sale there are both already familiar cast-iron types of batteries, but significantly improved, as well as modern specimens made of aluminum, steel and the so-called bimetallic radiators made of steel and aluminum.
Modern battery options are made in a variety of designs and have numerous shades and colors, so you can easily choose those models that are more suitable for a particular interior. However, we must not forget about the technical characteristics of the devices.
Bimetallic batteries have become the most popular of modern radiators. They are arranged according to the combined principle and consist of two alloys: they are steel on the inside, aluminum on the outside. They attract with their aesthetic appearance, economy in use and ease of operation.
Modern bimetallic battery for 10 sections
But they also have a weak side - they are acceptable only for heating systems with sufficiently high pressure, which means for buildings connected to central heating in apartment buildings. For buildings with autonomous heating supply, they are not suitable and it is better to refuse them.
It is worth talking about cast iron radiators. Despite their great "historical experience", they do not lose their relevance. Moreover, today you can buy cast-iron options made in various designs, and you can easily choose them for any design. Moreover, such radiators are produced that may well become an addition or even decoration to the room.

Cast iron radiator in modern style
These batteries are suitable for both autonomous and central heating, and for any coolant. They warm up longer than bimetallic ones, but also cool down for a longer time, which contributes to greater heat transfer and heat retention in the room. The only condition for their long-term operation is high-quality installation during installation.
Steel radiators are divided into two types: tubular and panel.

Tubular steel radiators
Tubular options are more expensive, they heat up more slowly than panel ones, and, accordingly, keep the temperature longer.

These characteristics of both types of steel batteries will directly affect the number of points for their placement.
Steel radiators have a respectable appearance, so they fit well into any style of interior design. They do not collect dust on their surface and are easily put in order.
Aluminum radiators have good thermal conductivity, so they are considered quite economical. Thanks to this quality and modern design, aluminum batteries have become leaders in sales.

Lightweight and efficient aluminum heatsinks
But, when purchasing them, it is necessary to take into account one of their drawbacks - this is the exactingness of aluminum to the quality of the coolant, so they are more suitable only for autonomous heating.
In order to calculate how many radiators will be needed for each of the rooms, you will have to take into account many nuances, both related to the characteristics of the batteries, and others that affect the preservation of heat in the premises.
Rooms with standard ceiling heights
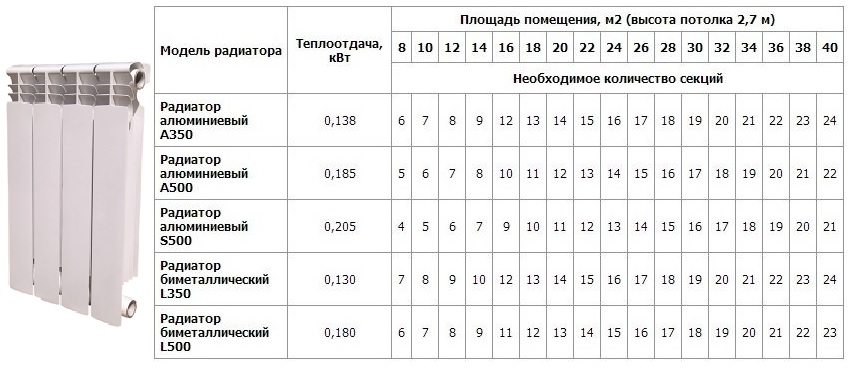
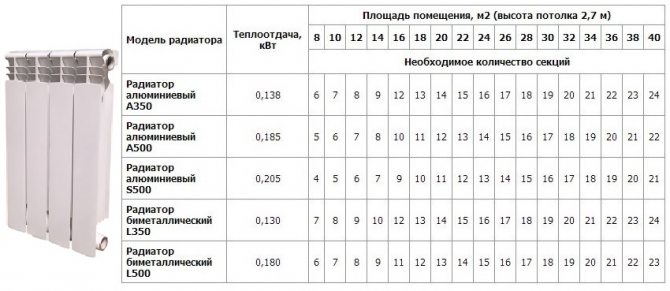
The calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators for a typical house is based on the area of the rooms. The area of a room in a typical house is calculated by multiplying the length of the room by its width. To heat 1 square meter, 100 watts of heater power is required, and to calculate the total power, you need to multiply the resulting area by 100 watts. The value obtained means the total power of the heater. The documentation for the radiator usually indicates the thermal power of one section. To determine the number of sections, you need to divide the total capacity by this value and round the result up.
A room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with the usual height of the ceilings. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts. Find the number of sections.
- We determine the area of \u200b\u200bthe room by multiplying its length by its width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the total power of heating devices 14 100 \u003d 1400 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1400/160 = 8.75. Round up to a higher value and get 9 sections.
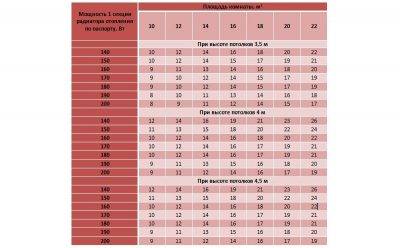
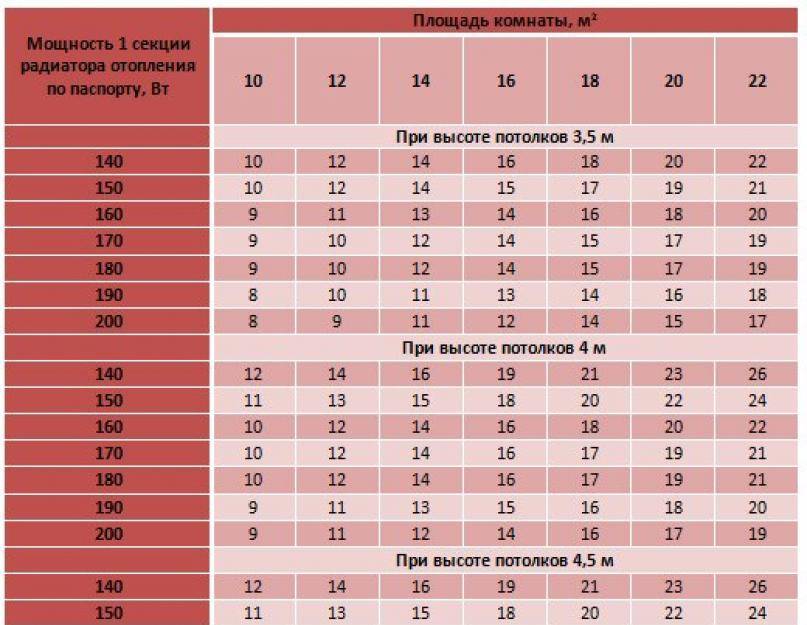
You can also use the table:
Table for calculating the number of radiators per M2
For rooms located at the end of the building, the calculated number of radiators must be increased by 20%.
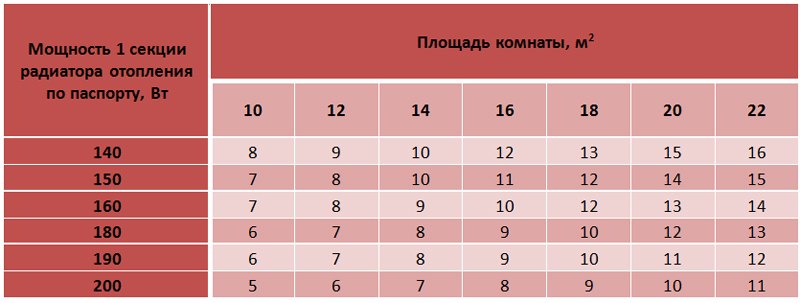
Rooms with a ceiling height of more than 3 meters
The calculation of the number of sections of heaters for rooms with a ceiling height of more than three meters is based on the volume of the room. Volume is the area multiplied by the height of the ceilings. To heat 1 cubic meter of a room, 40 W of the heat output of the heater is required, and its total power is calculated, multiplying the volume of the room by 40 W. To determine the number of sections, this value must be divided by the power of one section according to the passport.
A room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with a ceiling height of 3.5 m. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts. It is necessary to find the number of sections of heating radiators.
- We find the area of the room by multiplying its length by the width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the volume of the room by multiplying the area by the height of the ceilings: 14 3.5 \u003d 49 m 3.
- We find the total power of the heating radiator: 49 40 \u003d 1960 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1960/160 = 12.25. Round up and get 13 sections.
You can also use the table:
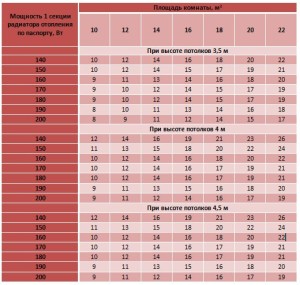
As in the previous case, for a corner room, this figure must be multiplied by 1.2. It is also necessary to increase the number of sections if the room has one of the following factors:
- Located in a panel or poorly insulated house;
- Located on the first or last floor;
- Has more than one window;
- Located next to unheated premises.
In this case, the resulting value must be multiplied by a factor of 1.1 for each of the factors.
Corner room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with a ceiling height of 3.5 m. Located in a panel house, on the ground floor, has two windows. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts. It is necessary to find the number of sections of heating radiators.
- We find the area of the room by multiplying its length by the width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the volume of the room by multiplying the area by the height of the ceilings: 14 3.5 \u003d 49 m 3.
- We find the total power of the heating radiator: 49 40 \u003d 1960 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1960/160 = 12.25. Round up and get 13 sections.
- We multiply the resulting amount by the coefficients:
Corner room - coefficient 1.2;
Panel house - coefficient 1.1;
Two windows - coefficient 1.1;
First floor - coefficient 1.1.
Thus, we get: 13 1.2 1.1 1.1 1.1 = 20.76 sections. We round them up to a larger integer - 21 sections of heating radiators.
When calculating, it should be borne in mind that different types of heating radiators have different thermal output. When choosing the number of heating radiator sections, it is necessary to use exactly those values that correspond to the selected type of batteries.

In order for the heat transfer from the radiators to be maximum, it is necessary to install them in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations, observing all the distances specified in the passport. This contributes to a better distribution of convective currents and reduces heat loss.
- Consumption of diesel heating boiler
- Bimetal heating radiators
- How to calculate heat for home heating
- Calculation of reinforcement for the foundation
An example of calculating the power of heating batteries
Let's take a room area of 15 square meters and with ceilings 3 meters high. The volume of air to be heated in the heating system will be:
V=15×3=45 cubic meters
Next, we consider the power that will be required to heat a room of a given volume. In our case, 45 cubic meters. To do this, it is necessary to multiply the volume of the room by the power required to heat one cubic meter of air in a given region. For Asia, the Caucasus, this is 45 watts, for the middle lane 50 watts, for the north about 60 watts. As an example, let's take a power of 45 watts and then we get:
45 × 45 = 2025 W - the power required to heat a room with a cubic capacity of 45 meters
Heat transfer rates for space heating

According to practice, for heating a room with a ceiling height not exceeding 3 meters, with one outer wall and one window, 1 kW of heat is enough for every 10 square meters of area.
For a more accurate calculation of the heat transfer of heating radiators, it is necessary to make an adjustment for the climatic zone in which the house is located: for the northern regions, for comfortable heating of 10 m2 of a room, 1.4-1.6 kW of power is needed; for the southern regions - 0.8-0.9 kW. For the Moscow region, amendments are not needed. However, both for the Moscow region and for other regions, it is recommended to leave a power margin of 15% (by multiplying the calculated values by 1.15).
There are more professional valuation methods, described below, but for a rough estimate and convenience, this method is quite sufficient. Radiators may turn out to be slightly more powerful than the minimum standard, however, in this case, the quality of the heating system will only increase: it will be possible to more accurately adjust the temperature and low-temperature heating mode.
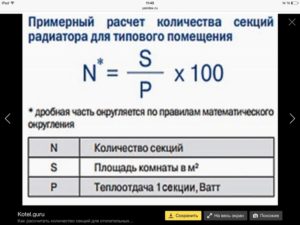
Full formula for accurate calculation
A detailed formula allows you to take into account all possible options for heat loss and the features of the room.
Q = 1000 W/m2*S*k1*k2*k3…*k10,
- where Q is the heat transfer index;
- S is the total area of the room;
- k1-k10 - coefficients that take into account heat losses and installation features of radiators.
Show coefficient values k1-k10
k1 - number of external walls in the premises (walls bordering the street):
- one – k1=1.0;
- two - k1=1,2;
- three - k1-1.3.
k2 - orientation of the room (sunny or shady side):
- north, northeast or east – k2=1.1;
- south, southwest or west – k2=1.0.
k3 - coefficient of thermal insulation of the walls of the room:
- simple, not insulated walls - 1.17;
- laying in 2 bricks or light insulation - 1.0;
- high-quality design thermal insulation - 0.85.
k4 - detailed accounting of the climatic conditions of the location (street air temperature in the coldest week of winter):
- -35°C and less - 1.4;
- from -25°С to -34°С - 1.25;
- from -20°С to -24°С - 1.2;
- from -15°С to -19°С - 1.1;
- from -10°С to -14°С - 0.9;
- not colder than -10°C - 0.7.
k5 - coefficient taking into account the height of the ceiling:
- up to 2.7 m - 1.0;
- 2.8 - 3.0 m - 1.02;
- 3.1 - 3.9 m - 1.08;
- 4 m and more - 1.15.
k6 - coefficient taking into account the heat loss of the ceiling (which is above the ceiling):
- cold, unheated room/attic - 1.0;
- insulated attic / attic - 0.9;
- heated dwelling - 0.8.
k7 - taking into account the heat loss of windows (type and number of double-glazed windows):
-
ordinary (including wooden) double windows - 1.17;
- windows with double glazing (2 air chambers) - 1.0;
- double glazing with argon filling or triple glazing (3 air chambers) - 0.85.
k8 - taking into account the total area of glazing (total area of windows: area of \u200b\u200bthe room):
- less than 0.1 – k8 = 0.8;
- 0.11-0.2 - k8 = 0.9;
- 0.21-0.3 - k8 = 1.0;
- 0.31-0.4 - k8 = 1.05;
- 0.41-0.5 - k8 = 1.15.
k9 - taking into account the method of connecting radiators:
- diagonal, where the supply is from above, the return from below is 1.0;
- one-sided, where the supply is from above, the return is from below - 1.03;
- double-sided lower, where both the supply and return are from below - 1.1;
- diagonal, where the supply is from below, the return from above is 1.2;
- one-sided, where the supply is from below, the return is from above - 1.28;
- one-sided lower, where both supply and return are from below - 1.28.
k10 - taking into account the location of the battery and the presence of the screen:
- practically not covered by a window sill, not covered by a screen - 0.9;
- covered by a window sill or ledge of the wall - 1.0;
- covered with a decorative casing only from the outside - 1.05;
- completely covered by the screen - 1.15.
After determining the values of all the coefficients and substituting them into the formula, you can calculate the most reliable power level of the radiators. For more convenience, below is a calculator where you can calculate the same values by quickly selecting the appropriate input data.
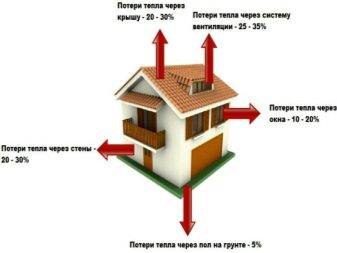
How to calculate heat losses for a private house and apartment
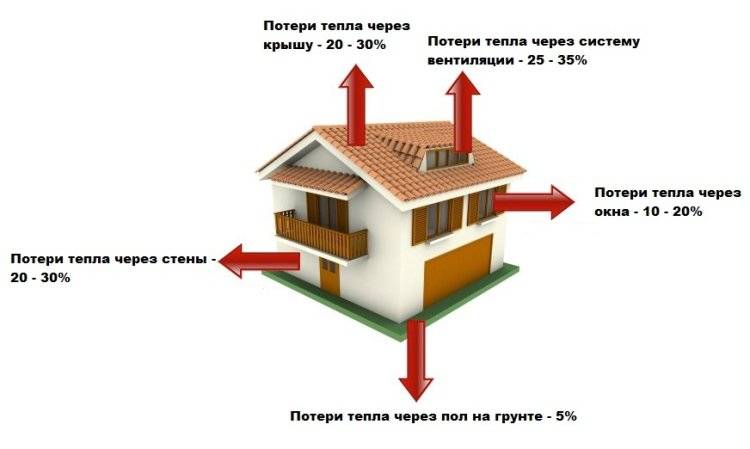

Heat leaves through windows, doors, ceilings, external walls, ventilation systems. For each heat loss, its own coefficient is calculated, which is used in calculating the required power of the heating system.
The coefficients (Q) are determined by the formulas:
- S is the area of a window, door or other structure,
- ΔT is the temperature difference between inside and outside on cold days,
- v is the layer thickness,
- λ is the thermal conductivity of the material.
All obtained Q are added up, summed up with 10-40% of thermal losses through ventilation shafts.The amount is divided by the total area of the house or apartment and added to the estimated capacity of the heating system.
When calculating the area of \u200b\u200bthe walls, the sizes of windows, doors, etc. are subtracted from them. they are counted separately. The biggest heat losses are in rooms on the upper floors with unheated attics and basement levels with a conventional basement.
An important role in the normative calculations is played by the orientation of the walls. The greatest amount of heat is lost by the premises facing the northern and northeastern side (Q = 0.1). Appropriate additives are also taken into account in the described formula.

Peculiarities
The calculation of heating radiators is made in accordance with the heat loss of a particular room, and also depending on the area of \u200b\u200bthis room. It would seem that there is nothing difficult in creating a proven heating scheme with pipe contours and a carrier circulating through them, however, correct heat engineering calculations are based on the requirements of SNiP. Such calculations are performed by specialists, and the procedure itself is considered extremely complicated. However, with an acceptable simplification, you can perform the procedures yourself. In addition to the area of \u200b\u200bthe heated room, some nuances are taken into account in the calculations.
No wonder experts use various methods to calculate radiators. Their main feature is taking into account the maximum heat loss of the room. Then the required number of heating devices is already calculated, which compensate for these losses.

It is clear that the simpler the method used, the more accurate the final results will be. In addition, for non-standard premises, experts apply special coefficients.

Specialists often use special devices in their projects.For example, a thermal imager can handle the exact determination of the actual heat loss. Based on the data received from the device, the number of radiators is calculated, which accurately compensate for the losses.
This calculation method will show the coldest points of the apartment, the places where the heat will leave most actively. Such points often arise due to construction defects, for example, made by workers, or due to poor quality building materials.
The results of the calculations are closely related to the existing types of heating radiators. To obtain the best result in the calculations, it is necessary to know the parameters of the devices planned for use.
The modern range includes the following types of radiators:
- steel;
- cast iron;
- aluminum;
- bimetallic.
To carry out calculations, we need such device parameters as the power and shape of the radiator, the material of manufacture. The simplest scheme involves placing radiators under each window in the room. Therefore, the calculated number of radiators is usually equal to the number of window openings.

Battery types
There are several types of batteries, and we will list the characteristics of each of them to make it easier for you. select the desired option.
Steel
Not the most common option. The reason for their low popularity is their heat transfer characteristics. Advantages: reasonable price, light weight and easy installation. However, the walls have insufficient heat capacity - they warm up quickly and cool down quickly. In addition, water hammer can cause leaks in places where the sheets are joined. At the same time, inexpensive models (without a protective coating) can rust. Such options serve much less than others and their warranty period is more limited.

It is often difficult to determine the number of steel radiators per room, since their one-piece design does not allow you to add or remove sections. Thermal power must first be taken into account. It all depends on the width and length of the space in which you are going to install them. In some tubular models, segments can be added. Craftsmen make it to order when they make them.

Cast iron
Each of us has seen such products: standard harmonicas. Let their design be extremely simple, but the design made it possible to effectively heat houses and apartments. The heat output of one "accordion" is 160 watts. The calculation of sections of prefabricated cast-iron radiators is simple, since their number could be unlimited. Modern proposals have become improved, they fit into different interiors. There are also exclusive models with embossed patterns. Advantages of cast iron pipes:
- heat is retained for a long time with high returns;
- resistance to water hammer, sudden temperature changes;
- resistant to corrosion.

You can use different coolants, as they are suitable for autonomous and central heating systems. The disadvantages include the fragility of the material (it does not withstand direct impacts), the complexity of installation (due to its large size). In addition, not every wall can support their weight. Before starting the boiler in winter, test the system, fill the pipes with water to determine if there are any malfunctions.

Aluminum
Appeared not so long ago, but quickly became popular. They are relatively inexpensive, minimalistically designed, their material has good heat dissipation. Aluminum models withstand high pressure and temperature.The heat transfer of each section is up to 200 W, but at the same time its weight is small - no more than 2 kg. They do not require large coolants. They are type-setting, so you can add or remove sections of radiators, counting on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. There are also solid models.

Flaws:
- Aluminum is subject to corrosion. There is also a high probability of gas formation, so aluminum pipes are more suitable for an autonomous heating system.
- Non-separable models can leak at the joints, they cannot be repaired, they will have to be replaced completely.

The most durable options are made of anodized metal. They remain resistant to corrosion for a long time.
Their design is roughly similar, and when you make a choice, pay attention to the documents. How to correctly calculate the number of radiator sections per room according to the instructions.

Bimetallic
The model of a bimetallic radiator is no less reliable than a cast iron one. Good heat dissipation makes them better than aluminum. This is facilitated by the features of their design. One segment consists of steel manifolds. They are connected by a metal channel. Masters assemble them using threaded couplings. Due to the aluminum coating, you can get a good thermal return. Pipes don't rust. High strength and wear resistance combined with excellent heat dissipation.