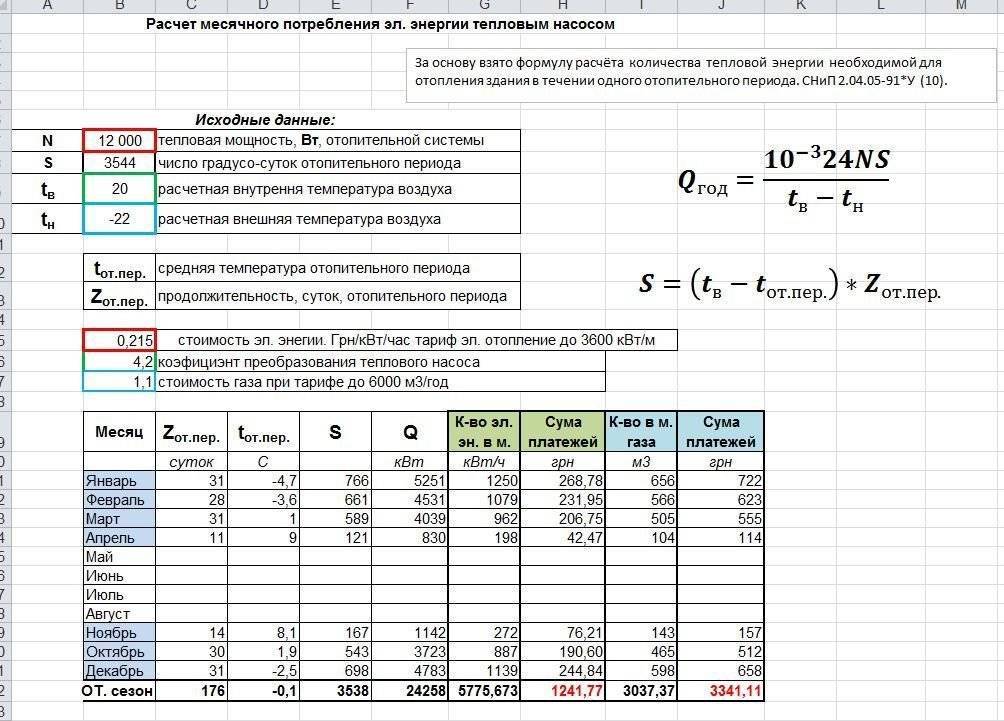
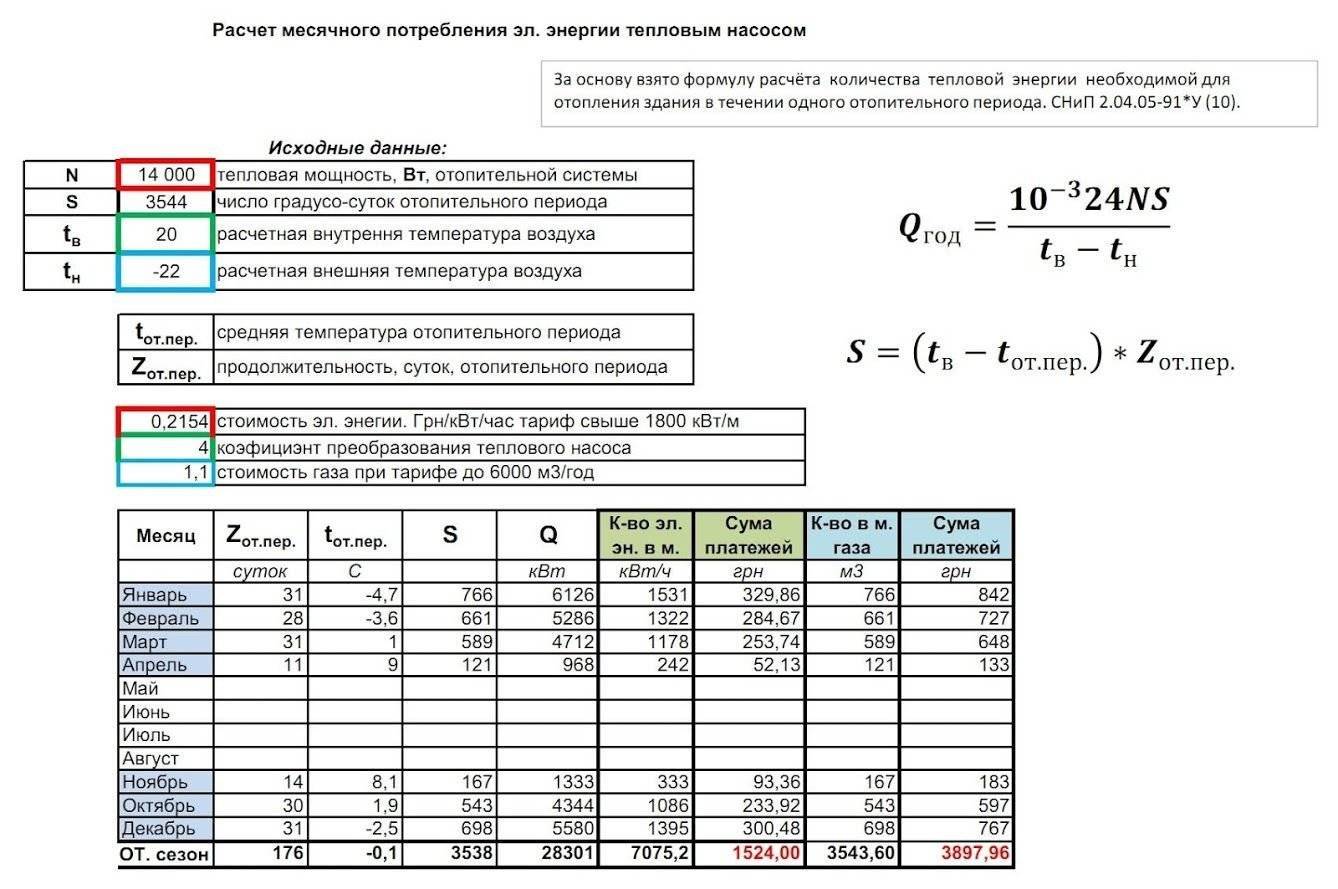
- Types of radiators
- Aluminum
- cast iron
- Bimetallic
- Possible changes
- Selection of a circulation pump for various heating systems
- Calculation of the pump for the heating system
- The principle of operation and purpose of the pump
- When should a pump be used?
- The principle of operation of the device
- The main types of pumps for heating
- Wet equipment
- "Dry" variety of devices
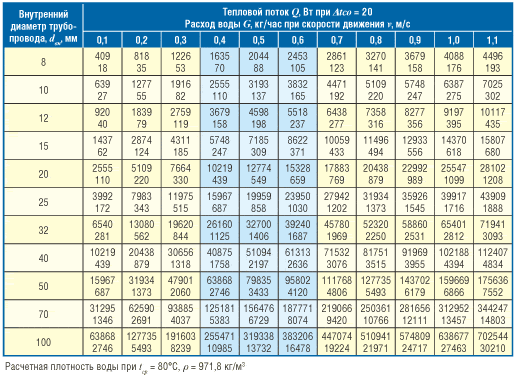
- Calculation of the required feed
- Required supply
- How to correctly determine the type of heating boiler and calculate its power
- When calculating it, you must take into account:
- Selection of a circulation pump for a heating system
- Theory of hydraulic calculation of the heating system.
- Recommendations for calculating the pump power for water wells.
- Why are heating system pump calculations necessary?
Types of radiators
The most popular among the total number of convectors are three types:
- Aluminum radiator;
- Cast iron battery;
- Bimetal radiator.
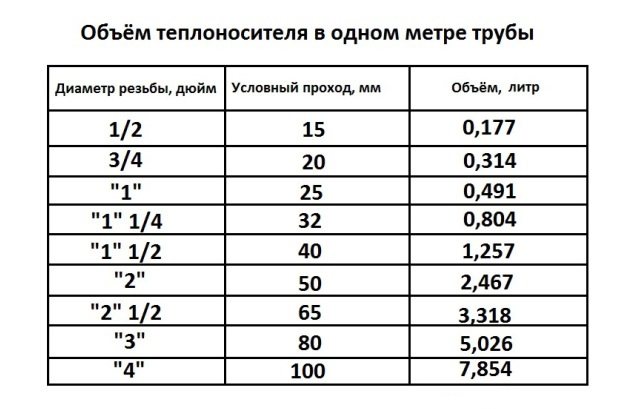
If you know which convector is installed in your home and are able to count the number of sections, then it will not be difficult to make simple calculations. Next, calculate volume of water in the radiator, table and all the necessary data are presented below. They will help to accurately calculate the amount of coolant in the entire system.
| Convector type | Average volume of water liter/section |
| Aluminum | |
| Old cast iron | |
| New cast iron |

Bimetallic
Aluminum
Although in some cases the internal heating system of each battery may differ, there are generally accepted parameters that allow you to determine the amount of liquid that fits into it. With a possible error of 5%, you will know that one section of an aluminum radiator can contain up to 450 ml of water
It is worth paying attention to the fact that for other coolants the volumes can be increased
cast iron
Calculating the amount of liquid that fits in a cast-iron radiator is a little more difficult. An important factor will be the novelty of the convector. In new imported radiators, there are much fewer voids, and due to the improved structure, they heat no worse than the old ones.
The new cast iron convector holds about 1 liter of liquid, the old one will fit 700 ml more.
Bimetallic
These types of radiators are quite economical and productive. The reason why filling volumes can change lies only in the features of a particular model and pressure spread. On average, such a convector is filled with 250 ml of water.
Possible changes
Each battery manufacturer sets its own minimum / maximum allowable standards, but the volume of coolant in the inner tubes of each model may change based on pressure increases. Usually, in private houses and new buildings, an expansion tank is installed on the basement floor, which allows you to stabilize the pressure of the liquid even when it expands when heated.
The parameters are also changing on outdated radiators. Often, even on non-ferrous metal tubes, growths form due to internal corrosion. The problem can be impurities in the water.
Due to such growths in the tubes, the amount of water in the system must be gradually reduced. Considering all the features of your convector and the general data from the table, you can easily calculate the required amount of water for the heating radiator and the entire system.
The circulation pump is selected according to two main characteristics:
G* - flow rate, expressed in m 3 / hour;
H - head, expressed in m.
*To record the flow rate of the coolant, manufacturers of pumping equipment use the letter Q. Manufacturers of valves, for example, Danfoss, use the letter G to calculate the flow rate. In domestic practice, this letter is also used. Therefore, as part of the explanations of this article, we will also use the letter G, but in other articles, going directly to the analysis of the pump operation schedule, we will still use the letter Q for flow.
Selection of a circulation pump for various heating systems
The pump for heating is selected based on the size of the heating system, the number and types of heating equipment.
The pump must be selected according to the second (!) Speed. Then, if there is an error in the calculations, then at the third (highest) speed, the pump will still work normally.
Below is a selection of a heating pump for various heating systems.
The 25/40 pump is the weakest of the pumps and is usually used to heat the boiler: this power is enough to create a flow through the boiler coil. Or with a very small system (for example, a solid fuel boiler plus 5-6 radiators).
Important! The system must be assembled correctly, otherwise the pump will not “push through” the system (moreover, any pump, and not just the lowest power one).The 25/60 pump is the most common pump in use and is installed in most cases. It can be installed on a radiator heating system for 10 ... 15 radiators
Also in water heated floors with an area of 80 ... 100 m2. (Some believe that it goes to a floor area of 130 ... 150 m2., And for radiator systems it can be safely used on an area up to 250 m2. I would recommend checking these statements in the program so as not to be fooled.)
It can be installed on a radiator heating system for 10 ... 15 radiators. Also in water heated floors with an area of 80 ... 100 m2. (Some believe that it goes to a floor area of 130 ... 150 m2., And for radiator systems it can be safely used on an area up to 250 m2. I would recommend checking these statements in the program so as not to be fooled.)
The 25/60 pump is the most common pump in use and is installed in most cases. It can be installed on a radiator heating system for 10 ... 15 radiators. Also in water heated floors with an area of 80 ... 100 m2. (Some believe that it goes to a floor area of 130 ... 150 m2., And for radiator systems it can be safely used on an area up to 250 m2. I would recommend checking these statements in the program so as not to be fooled.)
Again, the system must be assembled correctly.
Pump 25/80. Such a pump is installed for sufficiently large areas of underfloor heating (120 ... 150 m2). Or on two floors of a house with a total area of 200 ... 250 m2 with a radiator system.
But if you have two floors and a radiator heating system, then it is better to put separate pumps on each floor. In this case, it is possible to provide for the option when one of the pumps fails, and the second one is connected to service the entire house, both floors.In addition to such duplication in case of an emergency, two pumps make it possible to organize floor-to-floor climate control: each pump will operate according to its own room thermostat.
Here, in fact, is the whole selection of a pump for heating. However, if you have little or no experience in installing heating systems, then it’s better not to be lazy, but check yourself again by calculating the hydraulic resistance in the program, which is described in the next article and video. And then compare your calculations with the pump selection recommendations above.
selection of pump for heating
Calculation of the pump for the heating system
Selection of a circulation pump for heating
The type of pump must be necessarily circulation, for heating and withstand high temperatures (up to 110 ° C).
The main parameters for selecting a circulation pump:
2. Maximum head, m
For a more accurate calculation, you need to see a graph of the pressure-flow characteristic

Pump characteristic is the pressure-flow characteristic of the pump. Shows how the flow rate changes when exposed to a certain pressure loss resistance in the heating system (of a whole contour ring). The faster the coolant moves in the pipe, the greater the flow. The greater the flow, the greater the resistance (pressure loss).
Therefore, the passport indicates the maximum possible flow rate with the minimum possible resistance of the heating system (one contour ring). Any heating system resists the movement of the coolant. And the larger it is, the less will be the overall consumption of the heating system.
Intersection point shows the actual flow and head loss (in meters).
System characteristic - this is the pressure-flow characteristic of the heating system as a whole for one contour ring. The greater the flow, the greater the resistance to movement. Therefore, if it is set for the heating system to pump: 2 m 3 / hour, then the pump must be selected in such a way as to satisfy this flow rate. Roughly speaking, the pump must cope with the required flow. If the heating resistance is high, then the pump must have a large pressure.
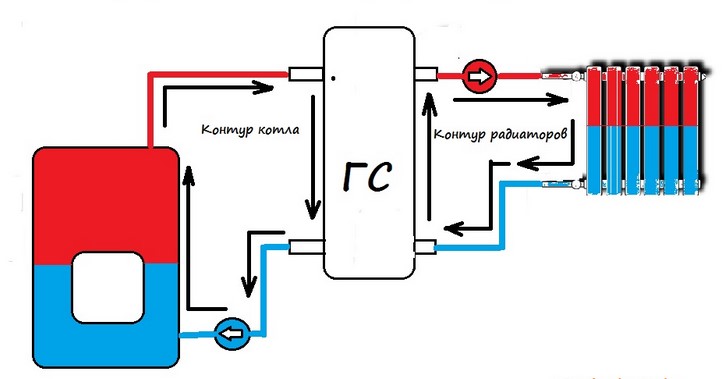
In order to determine the maximum pump flow rate, you need to know the flow rate of your heating system.
In order to determine the maximum pump head, it is necessary to know what resistance the heating system will experience at a given flow rate.
heating system consumption.
The consumption strictly depends on the required heat transfer through the pipes. To find the cost, you need to know the following:
2. Temperature difference (T1 and T2) supply and return pipelines in the heating system.
3. The average temperature of the coolant in the heating system. (The lower the temperature, the less heat is lost in the heating system)
Suppose that a heated room consumes 9 kW of heat. And the heating system is designed to give 9 kW of heat.
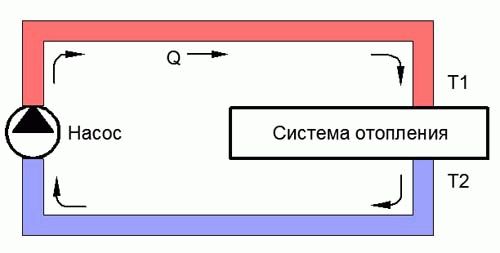
This means that the coolant, passing through the entire heating system (three radiators), loses its temperature (See image). That is, the temperature at point T1 (in service) always over T2 (on the back).
The greater the coolant flow through the heating system, the lower the temperature difference between the supply and return pipes.
The higher the temperature difference at a constant flow rate, the more heat is lost in the heating system.
C - heat capacity of the water coolant, C \u003d 1163 W / (m 3 • ° C) or C \u003d 1.163 W / (liter • ° C)
Q - consumption, (m 3 / hour) or (liter / hour)
t1 – Supply temperature
t2 – The temperature of the cooled coolant
Since the loss of the room is small, I suggest counting in liters. For large losses, use m 3
It is necessary to determine what the temperature difference will be between the supply and the cooled coolant. You can choose absolutely any temperature, from 5 to 20 °C. The flow rate will depend on the choice of temperatures, and the flow rate will create some coolant velocities. And, as you know, the movement of the coolant creates resistance. The greater the flow, the greater the resistance.
For further calculation, I choose 10 °C. That is, on the supply 60 ° C on the return 50 ° C.
t1 – Temperature of the giving heat carrier: 60 °C
t2 – Temperature of the cooled coolant: 50 °С.
W=9kW=9000W
From the above formula I get:
Answer: We got the required minimum flow rate of 774 l/h
heating system resistance.
We will measure the resistance of the heating system in meters, because it is very convenient.
Suppose we have already calculated this resistance and it is equal to 1.4 meters at a flow rate of 774 l / h
It is very important to understand that the higher the flow, the greater the resistance. The lower the flow, the lower the resistance.
Therefore, at a given flow rate of 774 l / h, we get a resistance of 1.4 meters.
And so we got the data, this is:
Flow rate = 774 l / h = 0.774 m 3 / h
Resistance = 1.4 meters
Further, according to these data, a pump is selected.
Consider a circulation pump with a flow rate of up to 3 m 3 / hour (25/6) 25 mm thread diameter, 6 m - head.
When choosing a pump, it is advisable to look at the actual graph of the pressure-flow characteristic.If it is not available, then I recommend simply drawing a straight line on the chart with the specified parameters
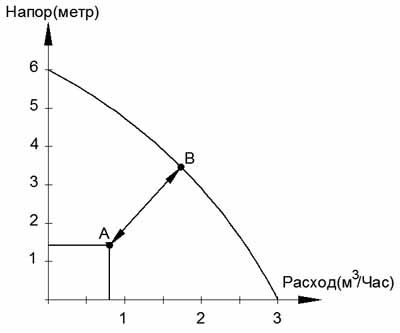
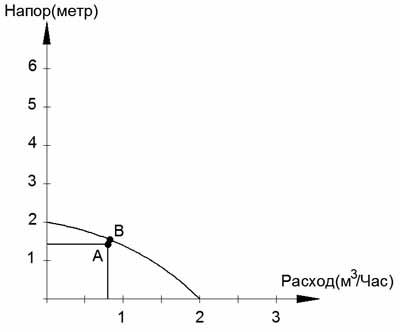
Here the distance between points A and B is minimal, and therefore this pump is suitable.
Its parameters will be:
Maximum consumption 2 m 3 / hour
Max head 2 meters
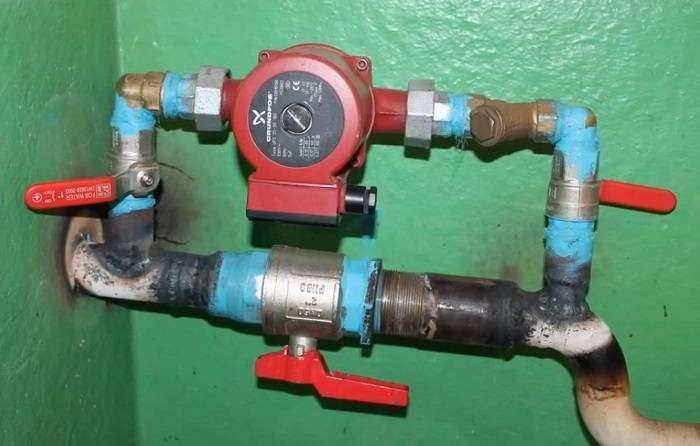
The principle of operation and purpose of the pump
The main problem for residents of the last floors of an apartment building and owners of country cottages is cold batteries. In the first case, the coolant simply does not reach their homes, and in the second, the furthest sections of the pipeline are not heated. And all this because of insufficient pressure.
When should a pump be used?
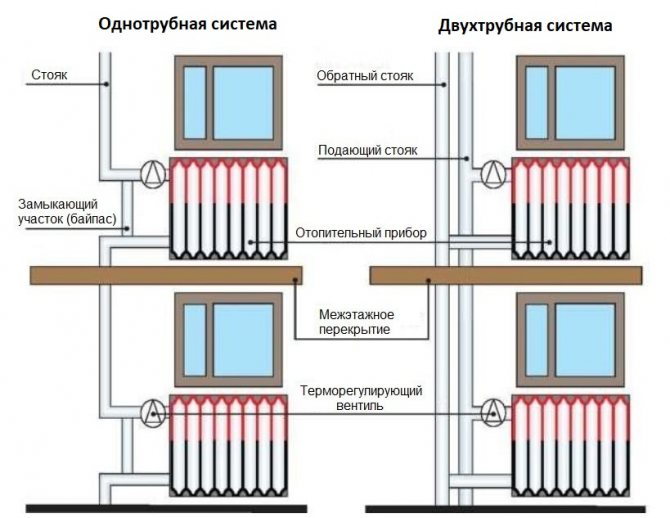
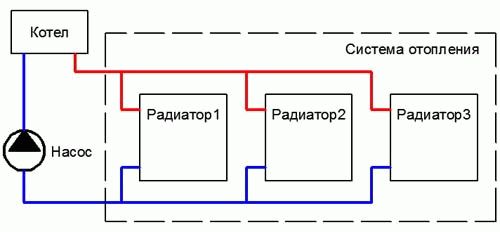
The only correct solution in a situation with insufficient pressure will be the modernization of the heating system with a coolant circulating under the influence of gravity. This is where pumping comes in handy. Basic organization schemes heating with pump circulation reviewed here.
This option will also be effective for owners of private houses, allowing you to significantly reduce heating costs. A significant advantage of such circulating equipment is the ability to change the speed of the coolant. The main thing is not to exceed the maximum allowable readings for the diameter of the pipes of your heating system in order to avoid excessive noise during the operation of the unit.
So, for living rooms with a nominal pipe diameter of 20 mm or more, the speed is 1 m / s. If you set this parameter to the highest value, then you can warm up the house in the shortest possible time, which is important in the case when the owners were away and the building had time to cool down. This will allow you to get the maximum amount of heat with minimal time.
The pump is an important element of the home heating system. It helps to increase its efficiency and reduce fuel consumption.
The principle of operation of the device
The circulation unit is powered by an electric motor. It takes the heated water from one side and pushes it into the pipeline on the other. And from this side again comes a new portion and everything repeats.
It is due to centrifugal force that the heat carrier moves through the pipes of the heating system. The operation of the pump is a bit like the operation of a fan, only it is not the air that circulates through the room, but the coolant through the pipeline.
The body of the device is necessarily made of corrosion-resistant materials, and ceramics are usually used to make the shaft, rotor and wheel with blades.
This is interesting: Designing heating for a country house: how to foresee everything?
The main types of pumps for heating
All equipment offered by manufacturers is divided into two large groups: "wet" or "dry" type pumps. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which must be taken into account when choosing.
Wet equipment
Heating pumps, called "wet", differ from their counterparts in that their impeller and rotor are placed in a heat carrier. In this case, the electric motor is in a sealed box where moisture cannot get.
This option is an ideal solution for small country houses. Such devices are distinguished by their noiselessness and do not require thorough and frequent maintenance. In addition, they are easily repaired, adjusted and can be used with a stable or slightly changing level of water flow.

A distinctive feature of modern models of "wet" pumps is their ease of operation. Thanks to the presence of "smart" automation, you can increase productivity or switch the level of windings without any problems.
As for the disadvantages, the above category is characterized by low productivity. This minus is due to the impossibility of ensuring high tightness of the sleeve separating the heat carrier and the stator.
"Dry" variety of devices
This category of devices is characterized by the absence of direct contact of the rotor with the heated water it pumps. The entire working part of the equipment is separated from the electric motor by rubber protective rings.
The main feature of such heating equipment is high efficiency. But from this advantage follows a significant disadvantage in the form of high noise. The problem is solved by installing the unit in a separate room with good sound insulation.
When choosing, it is worth considering the fact that the “dry” type pump creates air turbulence, so small dust particles can rise, which will negatively affect the sealing elements and, accordingly, the tightness of the device.
Manufacturers solved this problem this way: when the equipment is operating, a thin water layer is created between the rubber rings. It performs the function of lubrication and prevents the destruction of sealing parts.
Devices, in turn, are divided into three subgroups:
- vertical;
- block;
- console.
The peculiarity of the first category is the vertical arrangement of the electric motor.Such equipment should be bought only if it is planned to pump a large amount of heat carrier. As for block pumps, they are installed on a flat concrete surface.

Block pumps are intended for use in industrial purposes, when large flow and pressure characteristics are required
Console devices are characterized by the location of the suction pipe on the outside of the cochlea, while the discharge pipe is located on the opposite side of the body.
Calculation of the required feed
New house
The parameters of the heating system of a new house are determined with the help of computer-aided design with a high level of accuracy. The heat consumption of the house and the performance of the pump are determined by the standards. Losses due to friction in pipelines (in units of pressure - mbar or GPa) are determined by non-standardized, but standardized calculation method used for the calculation of pipeline systems. This method also allows you to calculate the pump head in meters.
old house
Since the design documentation of old buildings, as a rule, is not stored for a long time, and the technical characteristics of the pipelines of such houses (for example, diameter, laying paths, etc.) are almost impossible to determine, when they are restored or re-equipped, one has to rely on a rough estimate and calculations.
Required supply

The required flow of the pump is calculated by the formula: hour
- where Q is the heat consumption of the house, kW;
- 1.163 – specific heat capacity of water, Wh/(kg K);
- ∆υ - temperature difference between the supply and return water flows, K
The use of circulation pumps in new homes
Calculations according to the above formula are carried out automatically within the calculation program.According to the building heat consumption standards, this is the sum of the heat consumption of individual rooms. Heat loss due to the influence of cold outside air is no more than 50% of the total, since the wind blows only one side of the house. However, increasing these losses by adding a heat transfer share may result in choosing a larger boiler and pump than necessary. If the heat consumption of a room is calculated according to this recommendation as for an apartment with “partially limited heating”, then a temperature difference of 5 K is taken into account for each heated neighboring room (Fig. 3).
Normative heat flow in the house
This calculation method is most suitable for calculating the power of a heating radiator, which is necessary to meet the heat demand in each specific case. The resulting indicators boiler output 15-20% are overpriced. Therefore, when determining the parameters of the pump, it is necessary to take into account the following regularity:
Q required consumption=0.85*Q normal consumable
Experts, based on many years of experience, are of the opinion that in the event of a limit value, the smaller of the two pumps should be selected. The reason for this is the deviation of real data from calculated ones.
The use of circulation pumps in old houses
The heat consumption of an old house can only be determined approximately. In this case, the calculation basis is the specific heat consumption per square meter of heated usable area. In a number of normative tables, approximate values of heat consumption of buildings are given, depending on the year of their construction.The HeizAnlV (Germany) regulation states that it is possible to refuse to carry out a thorough calculation of heat consumption if the devices that produce heat are replaced by central heating and their rated heat output does not exceed 0.07 kW per 1 m2 of usable area of the house; for detached houses, consisting of no more than two apartments, this figure is 0.10 kW/m2. Based on the above formula, you can calculate the specific pump flow:
l/(h*m2)
- where V is the specific pump flow, l/(h • m2);
- Q is the specific heat flux, W/m2 (nominal heat output is 70 W/m2 in multi-apartment buildings and 100 W/m2 in individual houses for one or two families).
Taking as an example a heating system in an apartment building with a standard difference between the supply and return temperatures of 20 K, we obtain the following calculations:
V=70 W/m2: (1.63 W*h/(kg*K)*20K)= 3.0[l/(h*m2)]
Therefore, for every square meter of living space, the pump must supply 3 liters of water per hour. Heating engineers should always keep this value in mind. If the value of the temperature difference is different, with the help of calculation tables, you can quickly carry out the necessary recalculations.
Determination of productivity by specific heat consumption
Example
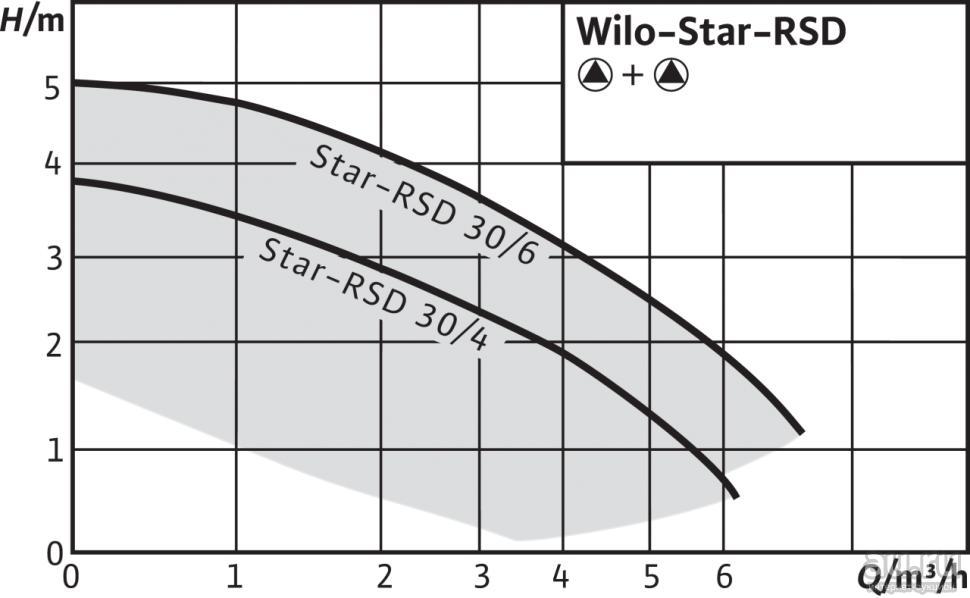
Let's make calculations for a medium-sized house, consisting of 12 apartments of 80 m2 each, with a total area of about 1000 m2. As can be seen from the table, the circulation pump at ∆υ = 20 K must provide a supply of 3m3/h. To meet the demand for heat in such a house, an unregulated pump of the Star-RS 30/6 type is temporarily selected.
A more accurate selection of the appropriate pump is possible only after determining the required pressure.
How to correctly determine the type of heating boiler and calculate its power
In the heating system, the boiler plays the role of a heat generator
When choosing between boilers - gas, electric, liquid or solid fuel, they pay attention to the efficiency of its heat transfer, ease of operation, take into account what type of fuel prevails in the place of residence
The efficient operation of the system and the comfortable temperature in the room directly depend on the power of the boiler. If the power is low, the room will be cold, and if it is too high, fuel will be uneconomical. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a boiler with optimal power, which can be calculated quite accurately.
When calculating it, it is necessary to take into account:
- heated area (S);
- specific power of the boiler per ten cubic meters of the room. It is set with an adjustment that takes into account the climatic conditions of the region of residence (W sp.).
There are established values of specific power (Wsp) for certain climatic zones, which are for:
- Southern regions - from 0.7 to 0.9 kW;
- Central regions - from 1.2 to 1.5 kW;
- Northern regions - from 1.5 to 2.0 kW.
Boiler power (Wkot) is calculated by the formula:
W cat. \u003d S * W beats. / ten
Therefore, it is customary to choose the power of the boiler, at the rate of 1 kW per 10 kv. m of heated space.
Not only power, but also the type of water heating will depend on the area of \u200b\u200bthe house. A heating design with natural water movement will not be able to efficiently heat a house with an area of more than 100 square meters. m (due to low inertia). For a room with a large area, a heating system with circular pumps will be required, which will push and accelerate the flow of coolant through the pipes.
Since the pumps operate in non-stop mode, certain requirements are imposed on them - noiselessness, low energy consumption, durability and reliability. On modern gas boiler models, the pumps are already built directly into the body.
Selection of a circulation pump for a heating system
Sometimes a person who has already planted a tree and raised a son is faced with the question - how to choose circulation pump for heating system house being built? And a lot depends on the answer to this question - whether all radiators will be evenly heated, whether the coolant flow rate will be in
the heating system is sufficient, and at the same time not exceeded, whether there will be a rumble in the pipelines, whether the pump will consume excess electricity, whether the thermostatic valves of the heating devices will work correctly, and so on and so forth. After all, the pump is the heart of the heating system, which tirelessly pumps the coolant - the blood of the house, which fills the house with warmth.
Choosing a circulation pump for the heating system of a small building, checking whether the pump is correctly selected by the sellers in the store, or making sure that the pump in the existing heating system is selected correctly is quite simple if you use the enlarged calculation method. The main parameter for selecting a circulation pump is its performance, which must correspond to the thermal power of the heating system it serves.
The required capacity of the circulation pump can be calculated with sufficient accuracy using a simple formula:
where Q is the required pump capacity in cubic meters per hour, P is the thermal power of the system in kilowatts, dt is the temperature delta, the temperature difference between the coolant in the supply and return pipelines. Usually taken equal to 20 degrees.
So let's try. Take, for example, a house with a total area of 200 square meters, the house has a basement, 1st floor and an attic. The heating system is two-pipe. The required thermal power required to heat such a house, let's take 20 kilowatts. We make simple calculations, we get - 0.86 cubic meters per hour. We round up, and take the performance of the required circulation pump - 0.9 cubic meters per hour. Let's remember it and move on. The second most important characteristic of the circulation pump is the pressure. Every hydraulic system has resistance to the flow of water through it. Each corner, tee, reducing transition, each rise - all these are local hydraulic resistances, the sum of which is the hydraulic resistance of the heating system. The circulation pump must overcome this resistance, while maintaining the calculated performance.
The exact calculation of hydraulic resistance is complex and requires some preparation. To approximately calculate the required pressure of the circulation pump, the formula is used:
where N is the number of floors of the building, including the basement, K is the average hydraulic loss per one floor of the building. The coefficient K is taken as 0.7 - 1.1 meters of water column for two-pipe heating systems and 1.16-1.85 for collector-beam systems. Our house has three levels, with a two-pipe heating system.The K coefficient is taken as 1.1 m.v.s. We consider 3 x 1.1 \u003d 3.3 meters of water column.
Please note that the total physical height of the heating system, from the bottom to the top point, in such a house is about 8 meters, and the pressure of the required circulation pump is only 3.3 meters. Each heating system is balanced, the pump does not need to raise water, it only overcomes the resistance of the system, so there is no point in getting carried away with high pressures
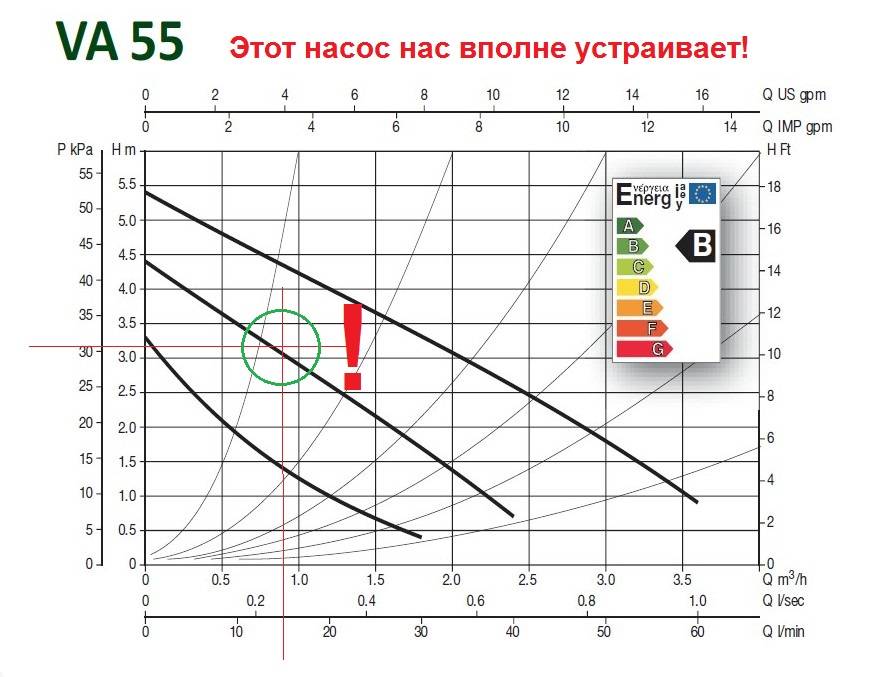
So, we got two parameters of the circulation pump, productivity Q, m / h = 0.9 and head, N, m = 3.3. The point of intersection of the lines from these values, on the graph of the hydraulic curve of the circulation pump, is the operating point of the required circulation pump.
Let's say you decide to go for the excellent DAB pumps, Italian pumps of excellent quality at a perfectly reasonable price. Using the catalog, or managers of our company, determine the group of pumps, the parameters of which include the required operating point. We decide that this group will be the VA group. We select the most appropriate hydraulic curve diagram, the best suited curve is the pump VA 55/180 X.
The operating point of the pump should be in the middle third of the graph - this zone is the zone of maximum efficiency of the pump. For selection, choose the graph of the second speed, in this case you insure yourself against insufficient accuracy of the enlarged calculation - you will have a reserve for increasing productivity at the third speed and the possibility of reducing it at the first.
Theory of hydraulic calculation of the heating system.
Theoretically, the heating GR is based on the following equation:
∆P = R·l + z
This equality is valid for a specific area.This equation is deciphered as follows:
- ΔP - linear pressure loss.
- R is the specific pressure loss in the pipe.
- l is the length of the pipes.
- z - pressure losses in the outlets, shutoff valves.
It can be seen from the formula that the greater the pressure loss, the longer it is and the more bends or other elements in it that reduce the passage or change the direction of the fluid flow. Let's deduce what R and z are equal to. To do this, consider another equation showing the pressure loss due to friction against the pipe walls:
friction
This is the Darcy-Weisbach equation. Let's decode it:
- λ is a coefficient depending on the nature of the movement of the pipe.
- d is the inner diameter of the pipe.
- v is the velocity of the fluid.
- ρ is the density of the liquid.
From this equation, an important relationship is established - pressure loss on friction is less, the larger the inner diameter of the pipes and the lower the fluid velocity. Moreover, the dependence on speed is quadratic here. Losses in bends, tees and valves are determined by a different formula:
∆Pfittings = ξ*(v²ρ/2)
Here:
- ξ is the coefficient of local resistance (hereinafter referred to as CMR).
- v is the velocity of the fluid.
- ρ is the density of the liquid.
It can also be seen from this equation that the pressure drop increases with increasing fluid velocity. Also, it is worth saying that in the case of using a low-freezing coolant, its density will also play an important role - the higher it is, the harder it is for the circulation pump. Therefore, when switching to “anti-freeze”, it may be necessary to replace the circulation pump.
From the above, we derive the following equality:
∆P=∆Pfriction +∆Pfittings=((λ/d)(v²ρ/2)) + (ξ(v²ρ/2)) = ((λ/α)l(v²ρ/2)) + (ξ*(v²ρ/2)) = R•l +z;
From this we obtain the following equalities for R and z:
R = (λ/α)*(v²ρ/2) Pa/m;
z = ξ*(v²ρ/2) Pa;
Now let's figure out how to calculate the hydraulic resistance using these formulas.
Recommendations for calculating the pump power for water wells.
Sometimes people ask such questions: advise a good well pump, since the old one no longer copes with its task.
The answers to the most common questions will be given below in the form of recommendations from experts.
1. When choosing a pump, try not to give preference to options with vibration, although their price is lower. This type of equipment is more suitable for ordinary wells, since their communications are covered with sand over time.
2. It is better to choose centrifugal type submersible pumps. This will avoid filling the well with sand.
3. To obtain better quality water, install the pump at least 1 m away from the filter.
4. When using water, it is necessary to take into account not only average values, but also peak values. Also make sure that there is enough water for technical purposes (watering the garden, washing the car, etc.).
5. To ensure good water pressure, it is necessary to choose a pump with a power margin of 20% of the selected value. This will create excess pressure in the system and provide excellent water pressure. Pressure reduction is facilitated by factors such as silting of water pipes, the use of filters. It will not work to make this type of calculation without the necessary knowledge and skills, so it is better to turn to professionals for help.
6. Try to lower the pump 1 m below the dynamic water level.By this measure, prevent the engine from being cooled by water that comes in from outside.
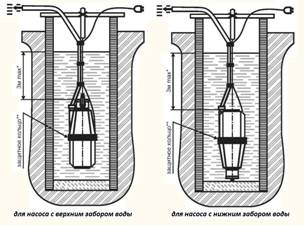
7. To protect against power surges, it is recommended to install stabilizers, since it is very important for a submersible pump that there is a stable voltage and current in the network. Thus, you will additionally protect the equipment and extend its service life.
8. Please note that the diameter of the pump must be at least 1 cm smaller than the diameter of the well itself. This will extend the life of the pump and simplify the installation / dismantling of equipment. For example, if the well is 76 cm in diameter, then the pump must be selected according to a diameter of no more than 74 cm
For example, if the well is 76 cm in diameter, then the pump must be selected according to a diameter of no more than 74 cm.
Why are heating system pump calculations necessary?
Most modern autonomous heating systems used to maintain a certain temperature in living quarters, equipped with centrifugal pumps, which ensure uninterrupted circulation of fluid in the heating circuit.
By increasing the pressure in the system, it is possible to lower the temperature of the water at the outlet of the heating boiler, thereby reducing the daily consumption of the gas consumed by it.
The right choice of the circulation pump model allows you to increase the efficiency of the equipment during the heating season by an order of magnitude and ensure a comfortable temperature in rooms of any size.