- PS for sewerage
- Capacity of the water pipe
- Passability of the pipe depending on the diameter
- Table of pipe capacity by coolant temperature
- Pipe capacity table depending on the coolant pressure
- The procedure for laying a gas pipeline
- Installation of the riser and preparation of the premises
- The subtleties of the construction of the internal system
- Welding, assembly and acceptance rules
- Reducing gas consumption
- Insulation of walls, roofs, ceilings
- window replacement
- other methods
- Laying methods
- Gas pipe classification
- Dimensional parameters
- Calculation of gas consumption
- By boiler power
- By quadrature
- Depending on the pressure
- Diameter calculation
- Taking into account heat losses
- By counter and without
- What documents will be needed?
- Why gasify the house?
- Code of Practice for Design and Construction general provisions for the design and construction of gas distribution systems from metal and polyethylene pipes the general provision and construction gas distribution system from steel and
PS for sewerage
Substation for sewerage depends on the sewage disposal system used: pressure or gravity. The definition of PS is based on the laws of the science of hydraulics. To calculate the PS of the sewer system, you will need not only complex formulas for calculation, but also tabular information.
To determine the volumetric flow rate of a liquid, a formula of the following type is taken:
q=a*v;
where, a is the flow area, m2;
v is the speed of movement, m/s.
The flow area a is the section perpendicular at each point to the velocity of the particles of the fluid flow. This value is also known under such a name as the free flow area. To determine the indicated value, the formula is used: a = π*R2. The value of π is constant and equals 3.14. R is the pipe radius squared. To find out the speed at which the flow moves, you will need to use the following formula:
v = C√R*i;
where, R is the hydraulic radius;
С – wetting coefficient;
I - slope angle.
To calculate the slope angle, you need to calculate I=v2/C2*R. To determine the wetting coefficient, you need to use the following formula: C=(1/n)*R1/6. The value of n is the coefficient of roughness of pipes, equal to 0.012-0.015. To determine R, the formula is used:
R=A/P;
where, A is the cross-sectional area of the pipeline;
P is the wetted perimeter.
The wetted perimeter is the line along which the flow in cross section comes into contact with the solid walls of the channel. To determine the value of the wetted perimeter in a round pipe, you will need to use the following formula: λ=π*D.
The table below shows the parameters for calculating the PS of waste sewer pipelines of a non-pressure or gravity method. Information is selected depending on the diameter of the pipe, after which it is substituted into the appropriate formula.
If you need to calculate the PS of the sewer system for pressure systems, then the data is taken from the table below.
Capacity of the water pipe
Water pipes in the house are used most often.And since they are subjected to a large load, the calculation of the throughput of the water main becomes an important condition for reliable operation.
Passability of the pipe depending on the diameter
Diameter is not the most important parameter when calculating pipe patency, but it also affects its value. The larger the inner diameter of the pipe, the higher the permeability, as well as the lower the chance of blockages and plugs. However, in addition to the diameter, it is necessary to take into account the coefficient of friction of water on the pipe walls (table value for each material), the length of the line and the difference in fluid pressure at the inlet and outlet. In addition, the number of bends and fittings in the pipeline will greatly affect the patency.
Table of pipe capacity by coolant temperature
The higher the temperature in the pipe, the lower its capacity, as the water expands and thereby creates additional friction.
For plumbing, this is not important, but in heating systems it is a key parameter
There is a table for calculations of heat and coolant.
Table 5. Pipe capacity depending on the coolant and the heat given off
| Pipe diameter, mm | Bandwidth | |||
| By warmth | By coolant | |||
| Water | Steam | Water | Steam | |
| Gcal/h | t/h | |||
| 15 | 0,011 | 0,005 | 0,182 | 0,009 |
| 25 | 0,039 | 0,018 | 0,650 | 0,033 |
| 38 | 0,11 | 0,05 | 1,82 | 0,091 |
| 50 | 0,24 | 0,11 | 4,00 | 0,20 |
| 75 | 0,72 | 0,33 | 12,0 | 0,60 |
| 100 | 1,51 | 0,69 | 25,0 | 1,25 |
| 125 | 2,70 | 1,24 | 45,0 | 2,25 |
| 150 | 4,36 | 2,00 | 72,8 | 3,64 |
| 200 | 9,23 | 4,24 | 154 | 7,70 |
| 250 | 16,6 | 7,60 | 276 | 13,8 |
| 300 | 26,6 | 12,2 | 444 | 22,2 |
| 350 | 40,3 | 18,5 | 672 | 33,6 |
| 400 | 56,5 | 26,0 | 940 | 47,0 |
| 450 | 68,3 | 36,0 | 1310 | 65,5 |
| 500 | 103 | 47,4 | 1730 | 86,5 |
| 600 | 167 | 76,5 | 2780 | 139 |
| 700 | 250 | 115 | 4160 | 208 |
| 800 | 354 | 162 | 5900 | 295 |
| 900 | 633 | 291 | 10500 | 525 |
| 1000 | 1020 | 470 | 17100 | 855 |
Pipe capacity table depending on the coolant pressure
There is a table describing the throughput of pipes depending on the pressure.
Table 6. Pipe capacity depending on the pressure of the transported liquid
| Consumption | Bandwidth | ||||||||
| DN pipe | 15 mm | 20 mm | 25 mm | 32 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm | 65 mm | 80 mm | 100 mm |
| Pa/m – mbar/m | less than 0.15 m/s | 0.15 m/s | 0.3 m/s | ||||||
| 90,0 – 0,900 | 173 | 403 | 745 | 1627 | 2488 | 4716 | 9612 | 14940 | 30240 |
| 92,5 – 0,925 | 176 | 407 | 756 | 1652 | 2524 | 4788 | 9756 | 15156 | 30672 |
| 95,0 – 0,950 | 176 | 414 | 767 | 1678 | 2560 | 4860 | 9900 | 15372 | 31104 |
| 97,5 – 0,975 | 180 | 421 | 778 | 1699 | 2596 | 4932 | 10044 | 15552 | 31500 |
| 100,0 – 1,000 | 184 | 425 | 788 | 1724 | 2632 | 5004 | 10152 | 15768 | 31932 |
| 120,0 – 1,200 | 202 | 472 | 871 | 1897 | 2898 | 5508 | 11196 | 17352 | 35100 |
| 140,0 – 1,400 | 220 | 511 | 943 | 2059 | 3143 | 5976 | 12132 | 18792 | 38160 |
| 160,0 – 1,600 | 234 | 547 | 1015 | 2210 | 3373 | 6408 | 12996 | 20160 | 40680 |
| 180,0 – 1,800 | 252 | 583 | 1080 | 2354 | 3589 | 6804 | 13824 | 21420 | 43200 |
| 200,0 – 2,000 | 266 | 619 | 1151 | 2486 | 3780 | 7200 | 14580 | 22644 | 45720 |
| 220,0 – 2,200 | 281 | 652 | 1202 | 2617 | 3996 | 7560 | 15336 | 23760 | 47880 |
| 240,0 – 2,400 | 288 | 680 | 1256 | 2740 | 4176 | 7920 | 16056 | 24876 | 50400 |
| 260,0 – 2,600 | 306 | 713 | 1310 | 2855 | 4356 | 8244 | 16740 | 25920 | 52200 |
| 280,0 – 2,800 | 317 | 742 | 1364 | 2970 | 4356 | 8566 | 17338 | 26928 | 54360 |
| 300,0 – 3,000 | 331 | 767 | 1415 | 3076 | 4680 | 8892 | 18000 | 27900 | 56160 |
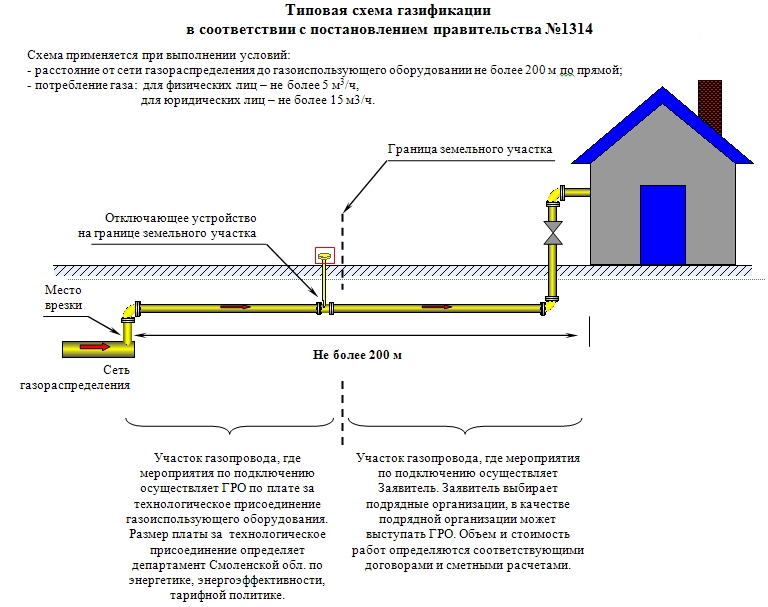
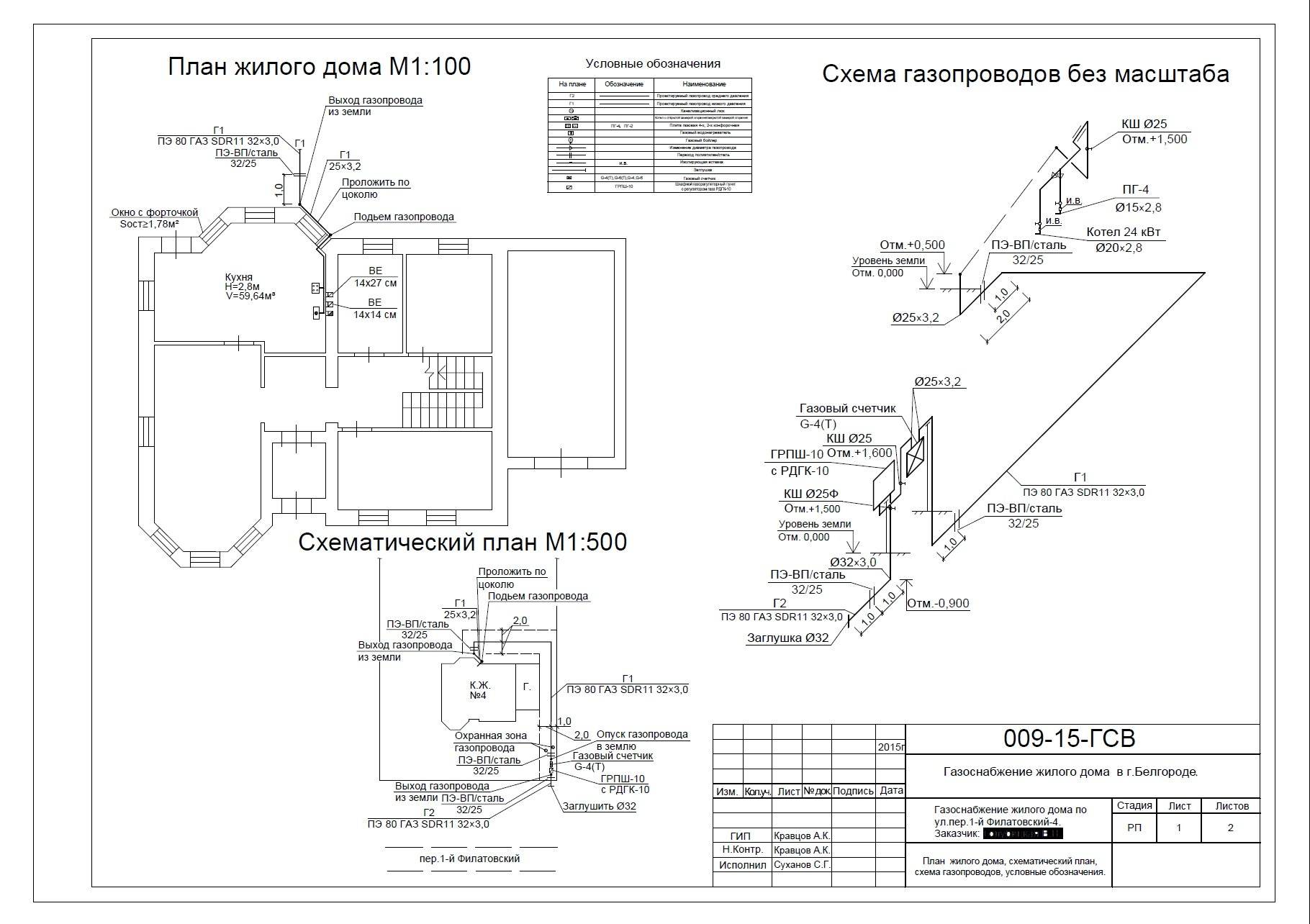
The procedure for laying a gas pipeline
Despite the fact that the installation of pipes should be carried out exclusively by professionals with the necessary qualifications, each owner of a private house should familiarize himself in detail with the procedure for carrying out the work. This will avoid trouble and the appearance of unplanned financial expenses.
Installation of the riser and preparation of the premises
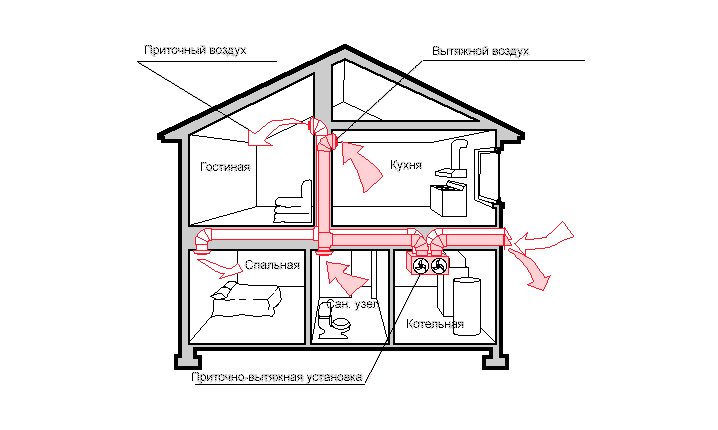
If a private house is gasified in order to organize heating, then you need to take care of the arrangement of the premises. The room with all equipment should be separate and fairly well ventilated. After all, natural gas is not only explosive, but also toxic to the human body.

The boiler room must have a window. This will provide the opportunity to ventilate the room at any time, which will avoid fuel vapor poisoning.
As for the dimensions, the ceiling height in the room should be at least 2.2 m. For a kitchen where a stove with two burners will be installed, an area of 8 m2 will be enough, and for a four-burner model - 15 m2.
If equipment with a capacity of more than 30 kW is used to heat the house, then the boiler room should be moved outside the house and be a separate building.
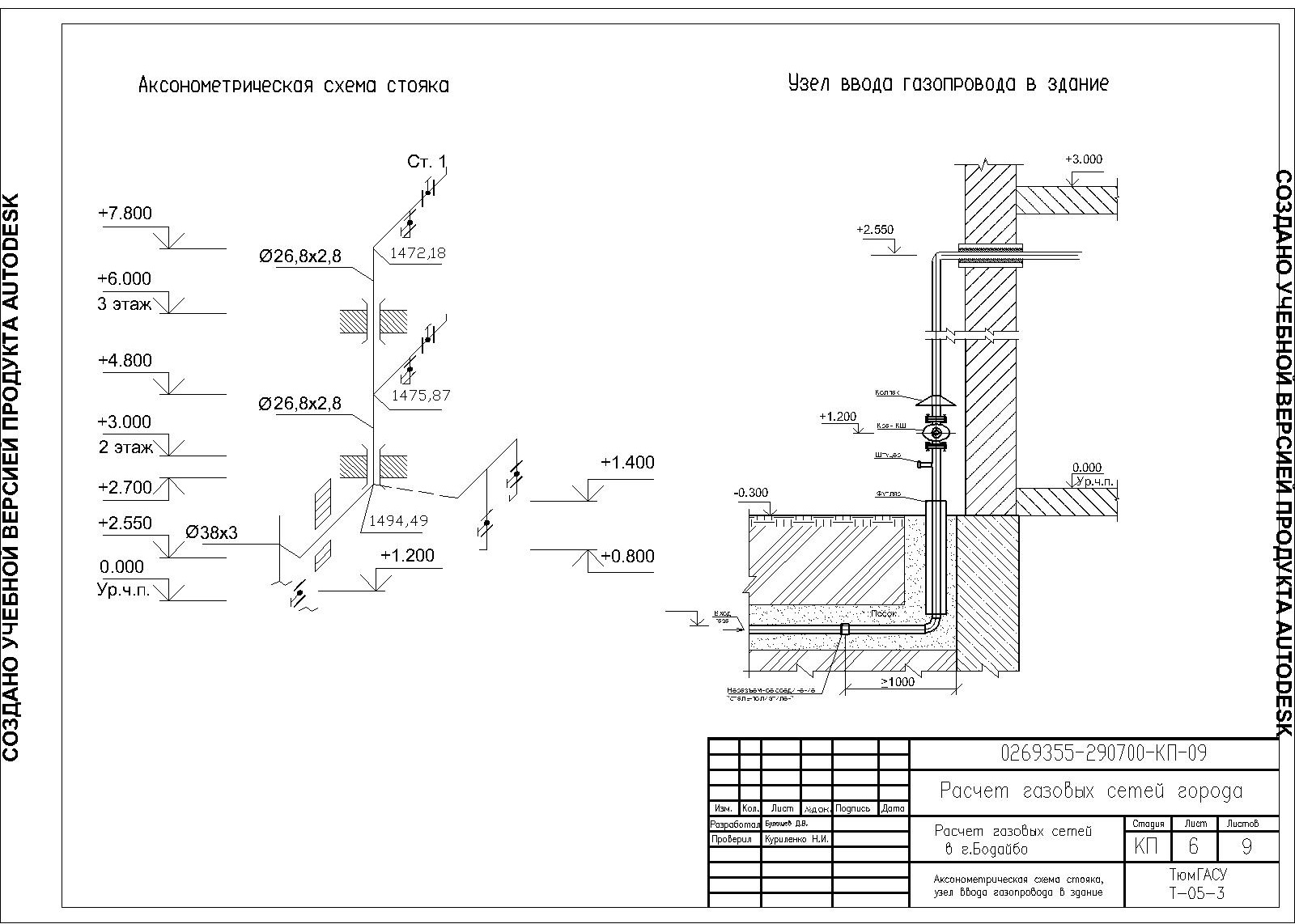
Gas is supplied to the cottage through an input device, which is a hole above the foundation. It is equipped with a special case through which the pipe passes. One end is connected to the riser, and the other is part of the internal gas supply system.
The riser is mounted exactly vertically and the structure must be at least 15 cm away from the wall. The reinforcement can be fixed using special hooks.
The subtleties of the construction of the internal system
During the installation of the pipeline in the wall, all its parts must be passed through the sleeves. In this case, the entire structure must be covered with oil paint. The free space present between the pipe and the sleeve is filled with tarred tow and bitumen.

It is necessary to ensure that during the installation of the pipeline, as few threaded and welded connections as possible are used. This approach will make the whole structure as reliable as possible. Accordingly, for this it is necessary to select pipes of maximum length
Each of the nodes is assembled at the bottom, and at a height only fasteners of pre-preparatory components are carried out. If the diameter of the pipes does not exceed 4 cm, then they can be fixed with clamps or hooks. For all others, it is recommended to use brackets or hangers.
Welding, assembly and acceptance rules
The following article will acquaint you with the specifics of organizing autonomous gas heating, which analyzes in detail the options for heating units. Independent craftsmen will need the boiler piping schemes given in the material we recommend.
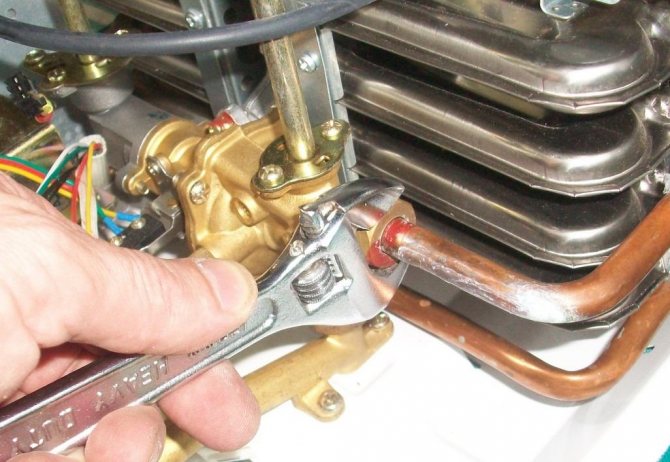
All components of the pipeline are interconnected by welding. In this case, the seam must be of high quality and reliable. To achieve this, you must first level the end of the pipe and strip about 1 cm on each side of it.
As for the assembly of threaded connections, for this you need to use a special technique. First, the joint is processed with whitewash. The next step is to wind long-staple flax or a special tape. Only then can the threaded connection be tightened.
As soon as the masters finish the work, a commission should come to the house.She carries out pressure testing of the gas pipeline and checks the quality of installation. Moreover, without fail, the owner is instructed on the rules for using the gas pipeline. Employees will also tell you how to properly operate equipment that consumes blue fuel.
Reducing gas consumption
Saving gas is directly related to the reduction of heat losses. Enclosing structures such as walls, ceiling, floor in the house must be protected from the influence of cold air or soil. Automatic adjustment of the operation of heating equipment is used for the effective interaction of the outdoor climate and the intensity of the gas boiler.
Insulation of walls, roofs, ceilings
 You can reduce gas consumption by insulating walls
You can reduce gas consumption by insulating walls
The outer heat-shielding layer creates a barrier for surface cooling in order to consume the least amount of fuel.
Statistics show that part of the heated air leaves through the structures:
- roof - 35 - 45%;
- uninsulated window openings - 10 - 30%;
- thin walls - 25 - 45%;
- entrance doors - 5 - 15%.
The floors are protected by a material that has an acceptable moisture permeability according to the norm, because when wet, the thermal insulation characteristics are lost. It is better to insulate the walls from the outside, the ceiling is insulated from the side of the attic.
window replacement
 Plastic windows let in less heat in winter
Plastic windows let in less heat in winter
Modern metal-plastic frames with two- and three-circuit double-glazed windows do not allow air flow and prevent drafts. This leads to a reduction in losses through the gaps that were in the old wooden frames. For ventilation, tilt-and-turn sash mechanisms are provided, which contribute to the economical use of internal heat.
Glasses in structures are pasted over with a special energy-saving film, which allows ultraviolet and infrared rays to pass inside, but prevents their reverse penetration. Glasses are supplied with a network of elements that heat the area to thaw snow and ice. Existing frame structures are additionally insulated with polyethylene film on the outside or thick curtains are used.
other methods
It is advantageous to use modern gas-fired condensing boilers and install an automated coordination system. Thermal heads are installed on all radiators, and a hydraulic arrow is mounted on the unit piping, which saves 15 - 20% of heat.
Laying methods
The technical characteristics of the gas pipeline are regulated by the relevant GOST. The material is selected based on the category of the system, that is, the magnitude of the supply pressure, and the installation method: underground, above ground or installation inside the building.
- Underground is the safest, especially when it comes to high pressure lines. Depending on the class of the transferred gas mixture, laying is carried out either below the freezing level of the soil - wet gas, or from 0.8 m to the ground level - dry gas.
- Aboveground - implemented with unremovable obstacles: residential buildings, ravines, rivers, canals, and so on. This method of installation is allowed on the territory of factories.
- The gas pipeline in the house - the installation of the riser, as well as the gas pipe in the apartment, is carried out only in an open way. It is allowed to place communications in strobes, but only if they are interrupted by easily removable shields. Easy and quick access to any part of the system is a prerequisite for security.

Gas pipe classification
For systems of different classes, different pipes are used.The state regulations for them are as follows:
- for gas pipelines with low or medium pressure, electric-welded longitudinal pipes of general purpose are used;
- for systems with a high, electric-welded longitudinal and seamless hot-rolled are allowed.
The choice of material is also influenced by the method of installation.
- For underground communications, both steel and polyethylene products are the norm.
- For aboveground, only steel ones are allowed.
- The house, both private and multi-storey, uses steel and copper pipelines. The connection is supposed to be welded. Flanged or threaded is allowed only in the areas of installation of valves and devices. Copper piping allows connection to press fittings.

The photo shows an example.
Dimensional parameters
GOST allows two types of gas pipes in the apartment. Products belong to general-purpose products, since complete gas tightness and mechanical strength are important here, while resistance to pressure is of little importance: 0.05 kgf / cm2 is a modest value.
- The steel pipeline parameters are as follows.
- The outer diameter of the steel pipe can range from 21.3 to 42.3 mm.
- The conditional pass makes the range from 15 to 32 mm.
- The choice is made depending on the scope of delivery: a gas appliance in an apartment or a riser in a house.
- The diameter of the copper pipeline is selected in the same way. The advantage of this option is easier installation - with press fittings, anti-corrosion material and attractive appearance. According to the norm, copper products must comply with GOST R 50838-95, other materials are not allowed.
- The diameter of gas pipes for pipelines with pressure from 3 to 6 kgf / cm2 varies in a much larger range - from 30 to 426 mm. The wall thickness in this case depends on the diameter: from 3 mm for small sizes, up to 12 mm for diameters over 300 mm.
- When constructing an underground gas pipeline, GOST allows the use of low-pressure polyethylene gas pipelines. The material is designed for pressure up to 6 kgf/cm2. The diameter of the plastic pipe varies from 20 to 225 mm. In the photo - a gas pipeline from HDPE.
The pipeline is laid in the trench only in ready-made sections, so the installation of the pipeline is an expensive and time-consuming work. When turning, steel gas pipelines are cut and connected through special elements. Polyethylene allow bends: for systems with a pressure of 3 to 6 kgf / cm2 up to 25 outer diameters, with a value of up to 0.05 kgf / cm2 - up to 3. Together with greater lightness and high anti-corrosion, this makes the option with a plastic pipeline more and more attractive .
Calculation of gas consumption
The power of the boiler or convector depends on the heat loss in the building. The average calculation is carried out taking into account the total area of \u200b\u200bthe house.
When calculating the gas consumption, the norms of warming up per square meter are taken into account with a ceiling height of up to 3 m:
- in the southern regions, 80 W / m² is taken;
- in the northern ones - up to 200 W / m².
The formulas take into account the total cubic capacity of individual rooms and premises in the building. 30 - 40 W are allocated for heating each 1 m³ of the total volume, depending on the area.
By boiler power
 Bottled and natural gas are calculated in different units
Bottled and natural gas are calculated in different units
The calculation is based on the power and heating area. An average consumption rate is used - 1 kW per 10 m². It should be clarified that it is not the electric power of the boiler that is taken, but the thermal power of the equipment.Often such concepts are replaced, and an incorrect calculation of gas consumption in a private house is obtained.
The volume of natural gas is measured in m³ / h, and liquefied gas - in kg / h. Practice shows that 0.112 m³ / h of the main fuel mixture is consumed to obtain 1 kW of thermal power.
By quadrature
Specific heat consumption is calculated according to the presented formula, if the difference between the outdoor and indoor temperature is approximately 40°C.
The relation V = Q / (g K / 100) is used, where:
- V is the volume of natural gas fuel, m³;
- Q is the thermal power of the equipment, kW;
- g - the smallest calorific value of gas, usually equals 9.2 kW / m³;
- K is the efficiency of the installation.
Depending on the pressure
 The amount of gas is fixed by a meter
The amount of gas is fixed by a meter
The volume of gas passing through the pipeline is measured by a meter, and the flow rate is calculated as the difference between the readings at the beginning and end of the path. The measurement depends on the pressure threshold in the converging nozzle.
Rotary counters are used to measure pressures greater than 0.1 MPa, and the difference between outdoor and indoor temperatures is 50°C. The gas fuel consumption indicator is read under normal environmental conditions. In industry, proportional conditions are considered to be pressure 10 - 320 Pa, temperature difference 20°C and relative humidity 0. Fuel consumption is expressed in m³/h.
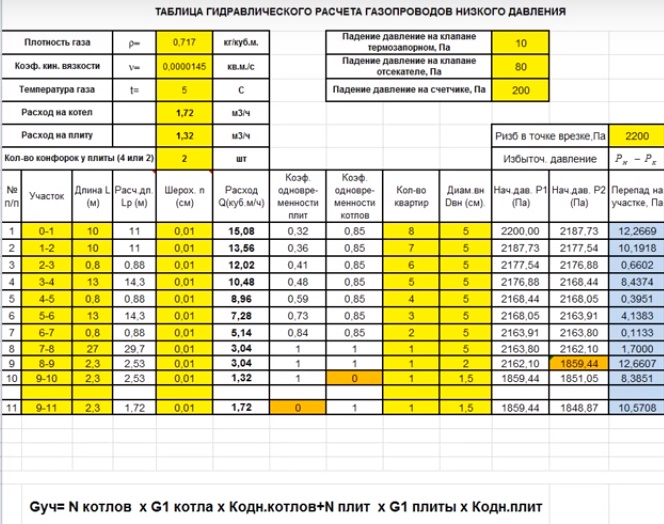
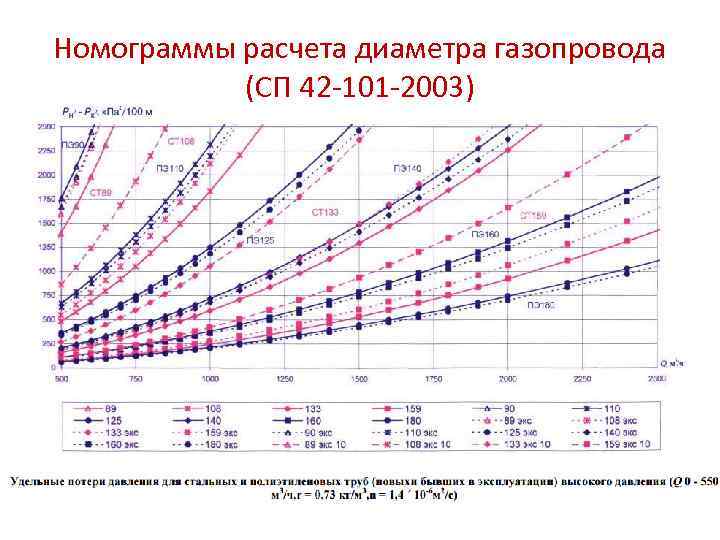
Diameter calculation
 The calculation of the diameter of the gas pipeline is carried out before the start of construction
The calculation of the diameter of the gas pipeline is carried out before the start of construction
The gas velocity in a high pressure gas pipeline depends on collector area and averages 2 - 25 m/s.
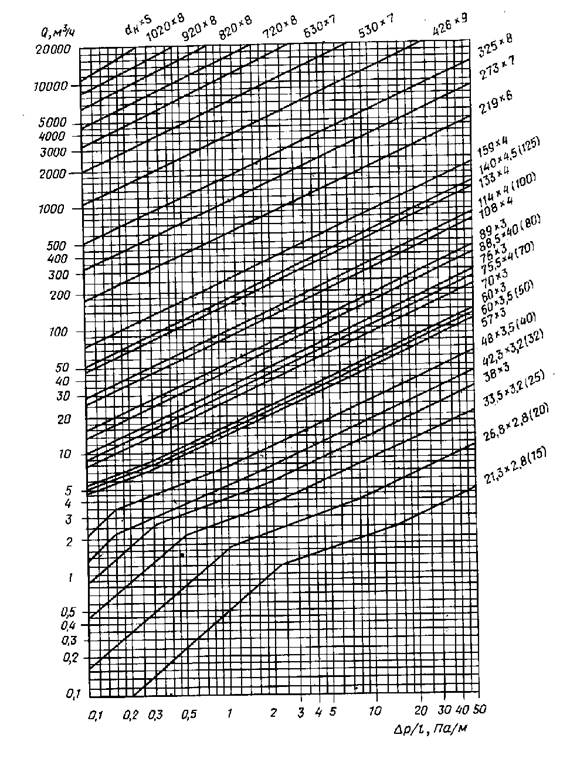
The throughput is found by the formula: Q = 0.67 D² p, where:
- Q is the gas flow rate;
- D is the conditional flow diameter of the gas pipeline;
- p is the working pressure in the gas pipeline or an indicator of the absolute pressure of the mixture.
The value of the indicator is affected by the outside temperature, heating of the mixture, overpressure, atmospheric characteristics and humidity. The calculation of the diameter of the gas pipeline is done when drafting the system.
Taking into account heat losses
To calculate the consumption of the gas mixture, it is required to know the heat losses of the building.
The formula Q = F (T1 - T2) (1 + Σb) n / R is used, where:
- Q - heat loss;
- F is the area of the insulating layer;
- T1 - outdoor temperature;
- T2 - internal temperature;
- Σb is the sum of additional heat losses;
- n is the coefficient of location of the protective layer (in special tables);
- R - resistance to heat transfer (calculated in a specific case).
By counter and without
 Gas consumption depends on the insulation of the walls and the climatic conditions of the region
Gas consumption depends on the insulation of the walls and the climatic conditions of the region
The device determines the gas consumption per month. Standard mix rates apply if no meter is installed. For each region of the country, the standards are set separately, but on average they are taken at the rate of 9 - 13 m³ per month per person.
The indicator is set by local governments and depends on climatic conditions. The calculation is carried out taking into account the number of owners of the premises and the people actually living in the specified living space.
What documents will be needed?
Before proceeding directly to the installation, you will have to start collecting the necessary papers. To do this as soon as possible, you must immediately prepare a passport, as well as documentation that confirms the ownership of the site and the house located on it.
The next step is to submit an application to the relevant service. It expresses a desire to gasify the house.Employees will issue a form that lists all the technical conditions.

The document issued by the gas service is filled in by the specialist involved in the drafting of the project. Choose a qualified designer. After all, the result of work and the safety of residents depend on his competence.
According to the project, the gas network is being installed. Sometimes pipes are laid through the sections of neighbors. In this case, it is necessary to ask them for written permission to carry out such work.
In addition to the papers listed above, you will also need to obtain the following documents:
- the act of commissioning gas-powered equipment;
- agreement on the preparation of technical documentation and work;
- permission to supply natural gas and pay for this service;
- document on the installation of equipment and gasification of the house.
A chimney inspection will also be required. After that, the experts will issue the appropriate act. The last document - permission to gasify a private house - is issued by a local architectural and planning company.
Why gasify the house?
The main reason is cheapness and convenience. The difficult economic situation in the country is forcing the owners of private houses to look for the most affordable option for heating the building. Therefore, it is not at all surprising that over time, the owners of cottages come to the conclusion that it is necessary to gasify the building.
Yes, of course, you can heat your home with electricity. But such a solution is quite expensive, especially if you need to heat several hundred square meters.Yes, and the vagaries of nature in the form of a strong wind or a hurricane can break the cables and you will have to sit for who knows how long without heating, food and hot water.

Modern gas pipelines are laid using durable and high-quality pipes and parts. Therefore, natural disasters are unlikely to harm such a structure.
Another alternative to gas is the old and proven method - heating with a fireplace or brick oven. The main disadvantage of this solution is that storing firewood or coal will lead to dirt.
In addition, it will be necessary to allocate additional square meters for their storage. Therefore, blue fuel will hold a leading position for many more years, and the issue of designing a gas pipeline to connect the private sector will be relevant for a very long time.
Code of Practice for Design and Construction general provisions for the design and construction of gas distribution systems from metal and polyethylene pipes the general provision and construction gas distribution system from steel and
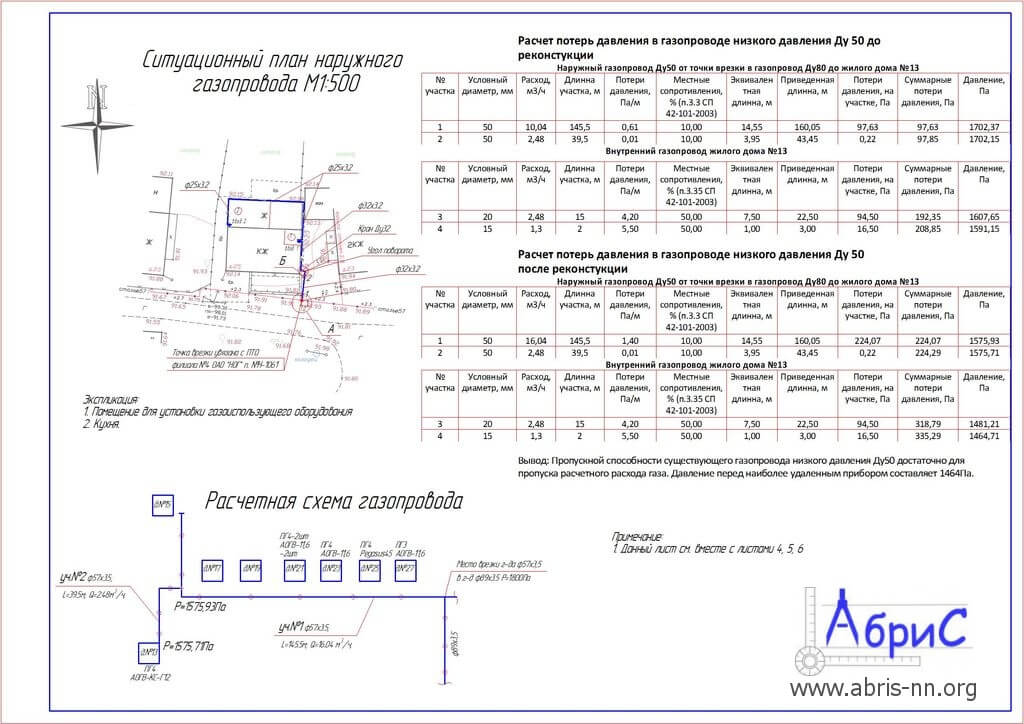
CALCULATION OF GAS PIPELINE DIAMETER AND PERMISSIBLE PRESSURE LOSS
3.21 The throughput capacity of gas pipelines can be taken from the conditions for creating, at the maximum allowable gas pressure loss, the most economical and reliable system in operation, which ensures the stability of the operation of hydraulic fracturing and gas control units (GRU), as well as the operation of consumer burners in acceptable gas pressure ranges.
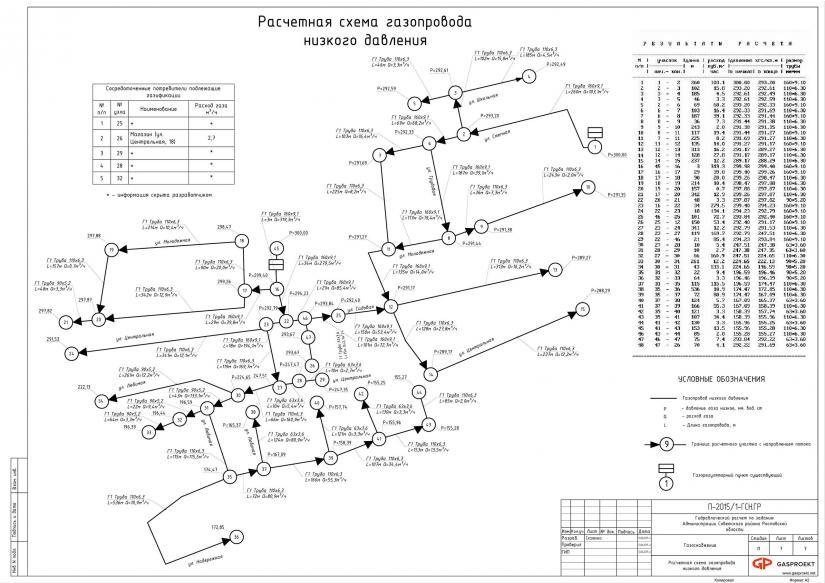
3.22 The calculated internal diameters of gas pipelines are determined based on the condition of ensuring uninterrupted gas supply to all consumers during the hours of maximum gas consumption.
3.23 The calculation of the diameter of the gas pipeline should be performed, as a rule, on a computer with the optimal distribution of the calculated pressure loss between the sections of the network.
If it is impossible or inappropriate to perform the calculation on a computer (lack of an appropriate program, separate sections of gas pipelines, etc.), it is allowed to perform a hydraulic calculation according to the formulas below or according to nomograms (Appendix B) compiled according to these formulas.
3.24 Estimated pressure losses in high and medium pressure gas pipelines are accepted within the pressure category adopted for the gas pipeline.
3.25 Estimated total gas pressure losses in low-pressure gas pipelines (from the gas supply source to the most remote device) are assumed to be no more than 180 daPa, including 120 daPa in distribution gas pipelines, 60 daPa in inlet gas pipelines and internal gas pipelines.
3.26 The values of the calculated pressure loss of gas when designing gas pipelines of all pressures for industrial, agricultural and household enterprises and public utilities are accepted depending on the gas pressure at the connection point, taking into account the technical characteristics of the gas equipment accepted for installation, safety automation devices and process control automation mode of thermal units.
3.27 The pressure drop in the gas network section can be determined:
- for networks of medium and high pressure according to the formula
- for low pressure networks according to the formula
– for a hydraulically smooth wall (inequality (6) is valid):
– at 4000 100000
3.29 Estimated gas consumption in sections of low-pressure distribution external gas pipelines with gas travel costs should be determined as the sum of transit and 0.5 gas travel costs in this section.
3.30 The pressure drop in local resistances (elbows, tees, stop valves, etc.) can be taken into account by increasing the actual length of the gas pipeline by 5-10%.
3.31 For external above-ground and internal gas pipelines, the estimated length of gas pipelines is determined by the formula (12)
3.32 In cases where LPG gas supply is temporary (with subsequent transfer to natural gas supply), gas pipelines are designed with the possibility of their future use on natural gas.
In this case, the amount of gas is determined as equivalent (in terms of calorific value) to the estimated consumption of LPG.
3.33 The pressure drop in the pipelines of the liquid phase of LPG is determined by the formula (13)
Taking into account the anti-cavitation reserve, the average velocities of the liquid phase are accepted: in the suction pipelines - no more than 1.2 m/s; in pressure pipelines - no more than 3 m / s.
3.34 Calculation of the diameter of the LPG vapor phase gas pipeline is carried out in accordance with the instructions for the calculation of natural gas pipelines of the corresponding pressure.
3.35 When calculating internal low-pressure gas pipelines for residential buildings, it is allowed to determine the gas pressure loss due to local resistances in the amount,%:
- on gas pipelines from inputs to the building:
- on the intra-apartment wiring:
3.37 Calculation of ring networks of gas pipelines should be carried out with the linkage of gas pressures at the nodal points of the design rings. The problem of pressure loss in the ring is allowed up to 10%.
3.38 When performing hydraulic calculation of above-ground and internal gas pipelines, taking into account the degree of noise generated by gas movement, it is necessary to take gas movement speeds of no more than 7 m/s for low-pressure gas pipelines, 15 m/s for medium-pressure gas pipelines, 25 m/s for high-pressure gas pipelines pressure.
3.39 When performing hydraulic calculation of gas pipelines, carried out according to formulas (5) - (14), as well as using various methods and programs for electronic computers, compiled on the basis of these formulas, the estimated inner diameter of the gas pipeline should be preliminarily determined by formula (15)