- Basic Methods
- Punching
- Horizontal Directional Drilling
- Ground puncture
- Laying steps
- Varieties
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Hidden laying method: technology features
- Trenchless cable laying technology
- HDD method
- Technology Benefits
- Features of the open method of laying pipelines
- Closed laying
- Technology
- Features for HDPE pipes
- Profitable option
- Does it make sense to do the work yourself?
- backfilling
- A bit about history: how the HDD method originated
- Features of trenchless technology
- Advantages of the method
- Cons of technology
- Areas of use
- Equipment, materials for laying
- Choice of equipment for puncture
- Special equipment
- SNiP 3.05.04-85
- Notes
Basic Methods
For trenchless pipe laying, the following most popular and popular methods are used:
- sanitation,
- punching,
- horizontal directional drilling,
- soil puncture.
It should be remembered that, just as with open laying, it is imperative to adhere to the distance between pipes in the trench established by SNiP, so with the trenchless method, these rules must be observed.
Trenchless pipe laying technology can be viewed here.
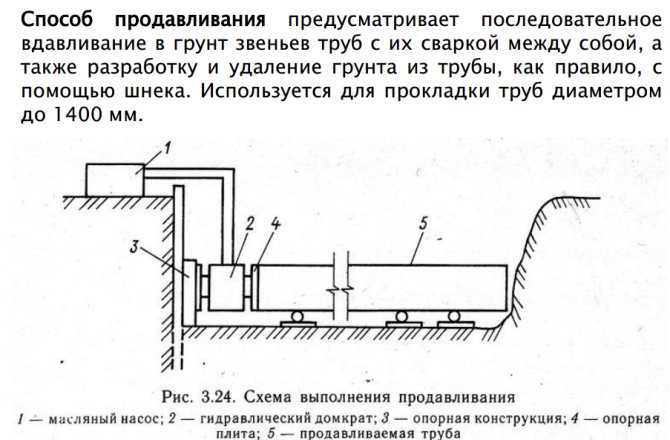
Translated from Latin means recovery, treatment.This procedure is used only on an existing section of the pipeline and consists in replacing old pipes with new ones. This can be done in two ways - relining and renovation.
Relining is a common rehabilitation method in which a new polyethylene pipe of a smaller diameter is laid in an old, for example, steel pipe. At the same time, it is necessary to carefully examine the internal state of the old pipe, choose the right diameter for the new one, and attach a hydraulic calibrator to the end of which, which will move forward along the old line, making room for the new pipe.
Renovation is used if the old pipeline has become obsolete, so it is completely destroyed, and a new one is laid in its place.
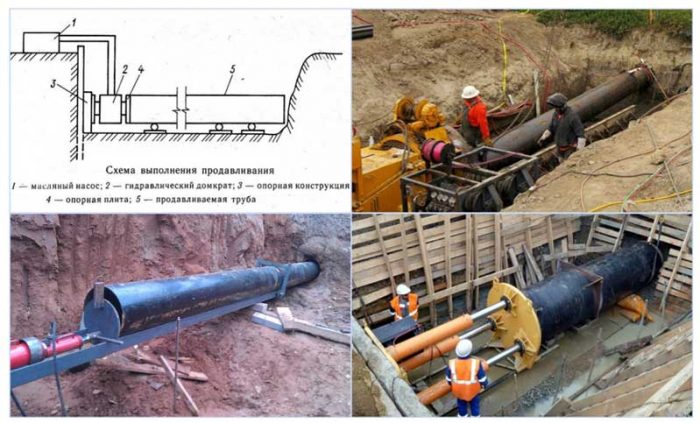
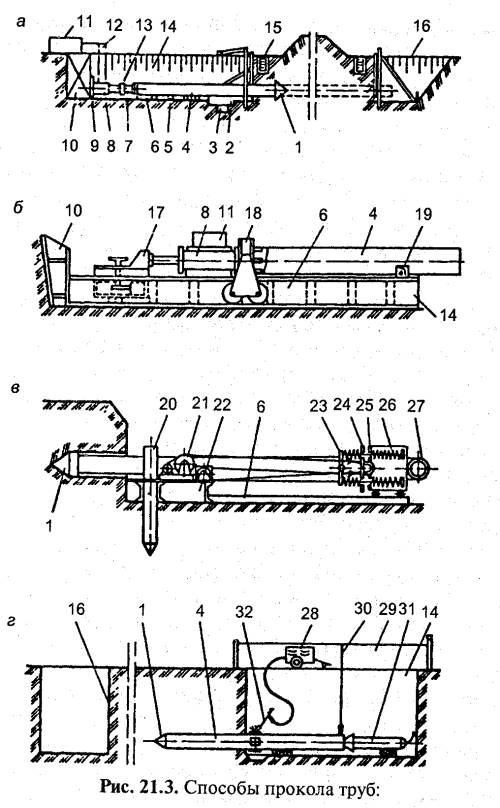
Punching
This method is used for laying large diameter pipes. At the same time, they are pressed into the ground using a hydraulic jack and a vibro-impact mechanism. The soil, preferably sandy and loose, is removed by compressed air to the outside through the pipe itself.
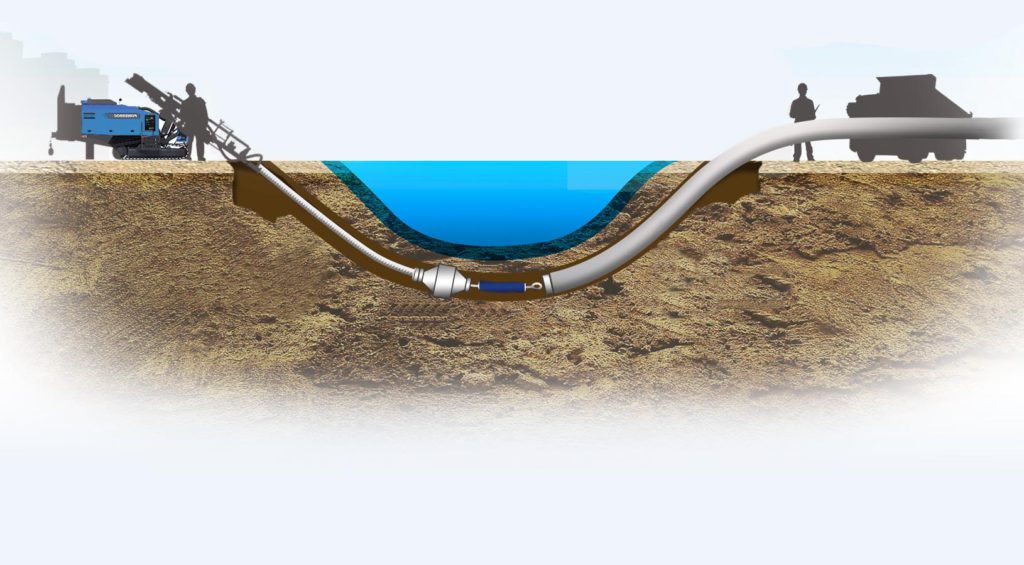
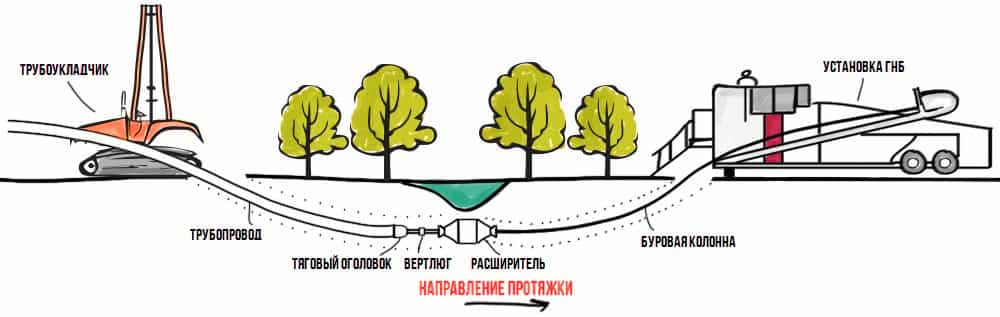
Horizontal Directional Drilling
The most expensive, but at the same time the most versatile method of trenchless pipeline laying, since it can cope with soils of any density, even rocks, and lay a pipeline up to 100 meters long. The drilling process is carried out using installations for trenchless pipe laying - drilling machines. At a depth of up to 15 m in a given direction, a small well is drilled. The drilling head is connected to a drive rod, therefore it is able to bypass underground obstacles, clearly adhere to a given trajectory. The resulting well is expanded and a working pipeline is dragged through it.

Drilling machines are used for trenchless pipe laying by the HDD method.
Ground puncture
This method is effective on clay and loamy soils when laying pipes with a diameter of up to 15 cm is required. The essence of the method is that a steel pipe with a cone is pushed through the thickness of the soil. The earth is not brought out, but compacted with the help of hydraulic jacks. A polyethylene pipe is then introduced into the formed well.

Soil piercing method
Trenchless pipeline laying is the future. We hope that we will soon forget about the unpleasant traces that remain from repair work on heating mains and other city communications.
- Royal Pipe Works (KTZ)
- Chelyabinsk Pipe Insulation Plant (ChZIT)
- Kstovo Pipe Plant
- Engels Pipe Plant (ETZ)
- Naberezhnye Chelny Pipe Plant "TEM-PO"
Add company
- We carry out calculations for the pipe deflection independently
- Features of insertion into gas pipes
- Dealing with condensate from chimneys
- Ways to fix leaking pipes under pressure
- How to make a fungus on a chimney pipe with your own hands
TrubSovet .ru We know everything about pipes
2015–2017 All rights reserved
When copying materials from the site, be sure to place a back link to
Laying steps
Pierced sewerage is
procedure in several steps:
- site preparation for equipment. Her size
is 10 × 15 m; - installation of a pilot rod that plunges into
soil at the entry point of the drill head; - drilling a pilot well. This is the main stage
works. A well is made with a given configuration, its diameter is 100 mm.
Trajectory control is carried out every 3 m of length; - extraction of the drill head and expansion of the well
by pulling the rimmer. This is a tool that is installed on a flexible
the rod and forcefully pull in the direction opposite to the drilling of the pilot well; - a string of pipelines is attached behind the rimmer,
which, immediately after the expansion of the well, is drawn into it in the direction towards
drilling rig.
Sewer puncture device requires
constant trajectory control. This is done by an operator who oversees
progress on the receiver display. The signal to it comes from the sensors of the drilling rig.
heads. If it is necessary to change the trajectory, he gives the driller a command to
feed stop and sets the desired angle of rotation. For any size, the head
rotate only clockwise so that the connection of the drilling
rods.
Varieties
Sewerage by puncture method -
it is an efficient and promising technology. Since its inception, developed
three work options:
- hydropuncture;
- vibropuncture;
- punching.
Each of these methods is designed
to work under certain conditions. For example, the hydraulic method is good in
clay viscous soils, vibration is more effective in dense rocks with
numerous rock inclusions. Punching is used on soft
soils that do not require significant effort to drill a well.
Either technique requires a significant axial force to be applied in the direction of penetration. Powerful hydraulic jacks are used to create it. The load on the axle of the rod is large - from 30 to 400 tons, which provides an effective and quick solution to the problem.
Advantages and disadvantages

Sewerage device method
HDB has a number of advantages:
- the cost of laying the network is reduced;
- technology is less labor intensive than traditional
methodology; - line construction time is reduced by approx.
by 30%; - no need to restore landscape, elements
surface improvement; - there are practically no restrictions on the venue
works. Can be laid on the territory of historical monuments, industrial
enterprises in the zone of dense building; - the fertile layer is not removed and does not deteriorate
soil; - during the execution of work is not necessary
block the movement of vehicles, stop production or take
other restrictions.
Disadvantages of HDD technology:
- technique is not suitable for creating extended
wells or for laying pipelines at great depths; - the maximum length of one line is
300-400 m. If you need a longer system, you will have to make intermediate
pits and pass repeated wells.
Certain difficulties arise if a gravity sewerage device is made using the HDD method. To do this, it is necessary to provide a height difference between the entry and exit points of the well. If a pipe with a diameter of 160-200 mm is used, a slope of 8 or 7 mm is required for each meter of length. For a line length of 400 m (maximum), the height difference will be 3.2 m. In addition, avoiding obstacles in the vertical plane becomes impossible. If large inclusions appear on the way of the well, you will have to make a horizontal bypass without changing the given angle of inclination. This may require more piping, which will increase the cost and time of system assembly.
Hidden laying method: technology features
The technology for assembling highways is selected, among other things, depending on which pipes are used from what material. Polymeric pipes are welded in several pieces (up to a length of 18-24 m) directly near the storage facility, and then delivered to the laying site.Here, in the summer, they are collected in a continuous thread, after which they are placed in a trench. Installation is carried out using mobile welding units. In winter, pipes are laid in a trench one at a time and connected by gluing or using rubber rings.
The construction of ceramic pipelines along the slope is carried out from top to bottom. Before installation, the pipes are inspected for chips. They are connected by a socket method with a bituminous strand seal and a cement mortar lock. Concrete pipes are laid in much the same way. In this case, a rubber ring can be used as a seal.
Asbestos-cement main pipelines with pressure up to 0.6 MPa are assembled using double-shoulder asbestos-cement couplings, and with pressure up to 0.9 MPa - using cast-iron flanges. Non-pressure pipelines are carried out using cylindrical couplings. Steel lines are laid using welding.

Trenchless cable laying technology
 Laying a cable line without a trench is used in almost any project for the installation of electrical networks, where there are no obstacles, engineering structures and underground telecommunications.
Laying a cable line without a trench is used in almost any project for the installation of electrical networks, where there are no obstacles, engineering structures and underground telecommunications.
For this, special special equipment with movable and traction mechanisms is used.
In this article, we will consider the existing methods of trenchless cable laying, as well as provide the technology for carrying out the work.
HDD method
Horizontal directional drilling is carried out from the surface of the earth. The well is formed by drilling a pilot channel with its further expansion.
The main feature of this method is the ability to control the direction of the drilling itself, that is, a certain trajectory of the well is developed.
Trenchless laying of a HDD cable involves the formation of a pilot channel, which is performed by drilling a steel shaft into the ground, at which a drill head is located at the end.
With HDD technology, a special solution is injected into the channel. This solution (concrete) does not allow the rock to collapse. This procedure is done under high pressure.
Once the pilot hole is completed, a reamer is attached to the wellbore in place of the drill head. With the help of a swivel, a polyethylene pipe is attached to the expander, which is called a case, a cable line is pulled through it.
A steel cable is pre-installed in this case, with which the cable will be pulled.
Technology Benefits
So, the main advantages of trenchless cable laying are:
- the cost per workflow is reduced;
- the natural landscape, where the work is carried out, will remain unchanged;
- the power grid is laid using fewer special equipment and workers;
- engineering communications are installed in a short time;
- there is no need to stop transport or block highways;
- saving time and volume of work on organizational approvals of various technical issues.
Finally, we recommend watching a demo video, which clearly demonstrates the procedure for laying an electrical cable using HDD technology:
Now you know how trenchless cable laying in the ground is performed. We hope that the information provided was interesting for you!
We also recommend reading:
Features of the open method of laying pipelines
Using this technique, pipelines for heating, water supply, sewerage, etc. can be laid. The use of impassable channels for highways in comparison with the trench method has one indisputable advantage. The pipes laid in them are not subjected to soil pressure during heaving or movement, and therefore, they last longer. The disadvantage of this technique is considered to be difficult access to highways if they need to be repaired.
Laying the pipeline in through channels is more expensive. However, in this case, the specialists of the service companies have the opportunity to access the highways without the need for earthworks.
Above the ground, pipes are usually laid only in disadvantaged areas of settlements, as temporary highways, etc. Various kinds of concrete and metal structures, flyovers, walls of structures, etc. can serve as supports for them.

Ways of laying pipelines in cities can be different. But in any case, the highways through settlements pull outside the zone of pressure in the soil from structures and buildings. This contributes to the preservation of foundations in the event of a breakthrough. All underground city engineering communications are divided into three large groups: main, transit and distribution. The first variety includes all the main communication networks of the settlement. Transit pipelines pass through the city, but are not used in any way. Distribution lines are called highways that extend from the main one directly to the buildings.

Closed laying
In a closed way, pipes are laid without opening the soil, such laying is called "trenchless" and is carried out by one of the following methods:
- puncture;
- vibropuncture by vibration installations;
- hydropuncture (driven and manual piercers);
- mechanical puncture with a jack;
- puncture with a screw soil piercer (mechanized);
- pneumatic punching with the help of a pneumatic punch;
- punching;
- drilling:
- drilling by rolling the soil with a drifter;
- directional drilling;
- horizontal drilling;
- vibration drilling;
- microtunnelling;
- penetration:
- panel board;
- adit.
The choice of a trenchless method of laying pipes depends on the diameter and length of the pipeline, the physical and mechanical properties and hydrogeological conditions of the developed soils and the equipment used.
Closed pipe laying can be used under water, in swamps and in other conditions where access to pipes after laying is impossible or difficult.
Recommended methods of trenchless laying of pipelines:
| Way | Best soil application conditions | Penetration speed, m/h | Required pressing force, t | Restriction on the use of the method | ||
| Diameter, mm | Length, m | |||||
| Puncture: mechanical with a jack | 50-500 | 80 | Sandy and clay without solid inclusions | 306 | 15-245 | Does not apply to rocky and siliceous soils |
| Hydroprocol | 100-200 | 30-40 | Sandy and sandy | 1,6-14 | 25-160 | The method is possible in the presence of water sources and places for pulp discharge |
| 400-500 | 20 | |||||
| Vibropuncture | 500 | 60 | Incoherent sandy, sandy and quicksand | 3,5-8 | 0,5-0,8 | Not suitable for hard and rocky soils |
| Ground piercer | 89-108 | 50-60 | clayey | 1,5-2 | — | Same |
| Pneumatic punch | 300-400 | 40-50 | Soft soils up to group III | 30-40 (without expanders) | 0,8-2,5 | Not applicable in soils with high water saturation |
| Punching | 400-2000 | 70-80 | In soils of groups I-III | 0,2-1,5 | 450 | In floating soils, the method is not applicable. In hard rocks, it can only be used for punching pipes of maximum diameter. |
| Horizontal drilling | 325-1720 | 40-70 | In sandy and clay soils | 1,5-19 | — | In the presence of groundwater, the method is not applicable. |
Technology
There are rules that must be followed at the facility when laying the pipeline in a trench:
- For lowering pipes into trenches, special pipe-laying cranes are used.
- During the procedure, the pipeline should not suffer from kinks, overvoltages or dents.
- The integrity of the insulating material must not be compromised.
- The pipeline must be completely adjacent to the bottom of the trench.
- The position of the pipeline must comply with the design documentation.
Before laying, a rejection is carried out: all pipes with defects cannot be laid in a trench. Prepare the base, if necessary - make the strengthening of the walls. With the help of a pipe-laying crane or manually, if the diameter allows, pipes are laid. Sometimes vertical shields, horizontal runs, and spacer frames are used.
Features for HDPE pipes
Under all polyethylene pipes at the bottom, a sand cushion should be organized. This is a mandatory requirement that must be observed by technology. The pillow should have a height of 10 to 15 cm. It is not compacted, but should be as flat as possible. If the bottom is flat and soft, then a pillow is not required.
The pipes are connected by butt welding. Before installation, the entire system is checked for leaks. The minimum laying depth must be at least 1 meter.
Profitable option
Trenchless laying is necessary in two cases: when laying a new pipeline to replace a failed pipeline or to replace a damaged, clogged old pipeline.
It is much cheaper to insert a completely new pipe into an old one and push it to the required distance than to excavate, dismantle the damaged one and lay a new one.
Especially the new way of laying is becoming relevant in urban areas, where the lack of maneuver during work, the side costs associated with the excavation of water pipes, and the great difficulties with traffic flows make the problem simply gigantic.
Trenchless laying makes it possible to install a highway under roads, lawns, various sites without destroying them.
Does it make sense to do the work yourself?
Before making a final decision on how to lay a pipe under the road, one must reflect on the expediency of this enterprise. If the tunnel will have a length of more than 10 meters, then in this case it is better to turn out of the "feat", since the process will take a lot of time and effort.
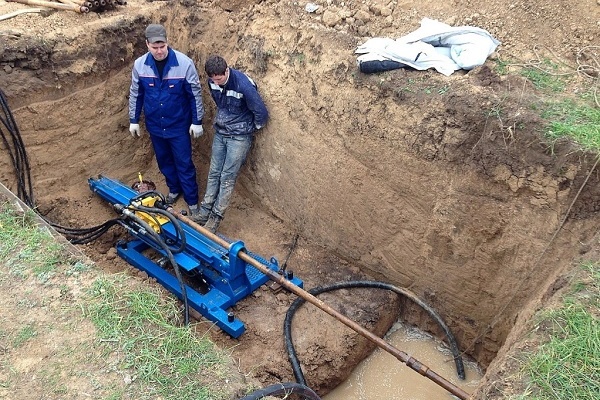

The same conclusion can be drawn if there are other underground communications laid on the site, or there are impassable sections on the territory. Soft soil (sandy, clayey) will somewhat simplify the task, but you need to know well not only your site, but also all the features of the stages.
Do-it-yourself puncture can be considered if:
- there are skills of similar works, and the project has been successfully approved;
- the site is known to the owner in the same way as “their five fingers”;
- the master is confident in his physical strength, and friends will always come to the rescue;
- it is possible to purchase/rent the necessary tools/equipment;
- there are definitely no other underground utilities at the place chosen for work.
If there are any doubts about your own abilities, and the preparatory work, which can take several weeks, does not inspire, then it is better to turn to professionals. They will complete the task within a few days.A 100% guarantee of the safety of the roadway and the track is another advantage, it still cannot be given by independent work.
How to lay a pipe under a road? It is not easy if the master and his assistants have chosen ungrateful manual labor and the same tools. Easy and fast if most of the work is done by special equipment and professionals. Many craftsmen who decide to make a gasket without the help of equipment face unexpected problems. Therefore, it seems that it makes sense to donate a small amount (1000-1500 r), but to avoid unnecessary headaches.
The following video will tell you how to lay pipes under the road with homemade devices:
backfilling
Backfilling of the trench occurs in 2 stages:
- Backfilling of the lower zone with non-frozen soil. It should not include large stones, hard deposits. Backfilling occurs to a height of 0.2-0.5 m above the top of the pipe. The insulation must not be broken. Pressure pipelines are filled up only after testing.
- Backfilling of the upper zone. The soil should not contain inclusions larger than the diameter of the pipe itself. The safety of the pipeline must be observed, and the density of the soil must comply with the design documents.
Most often, trench soil or sand is used for backfilling. It has good water permeability and is not exposed to permafrost. It is necessary to wait for a complete check of the pipes - sewerage, gas pipeline, water supply, only then carry out backfilling.
A bit about history: how the HDD method originated
Appearing in America almost thanks to the observation, enthusiasm and engineering talents of Martin Cherrington (Martin Cherrington), HDD technology has greatly developed, improved and gone far ahead, having won the recognition of builders around the world.
Today, Martin Cherrington is unequivocally recognized as the main inventor of the technology and is sometimes even called the "grandfather of directional drilling." And then, almost 50 years ago, the horizontal drilling industry was developing on several fronts, construction contractors were trying ways to overcome the problems of lack of control and the inability to make trenchless drilling for long distances. It was Cherrington who came up with the idea of combining two already used technologies - directional controlled drilling (it was used in the oil and gas industry) and horizontal drilling (already quite actively used in construction, but was uncontrolled). After several drilling trials, he successfully applied the new idea for the first time to drill a well for a gas pipeline under the Pajero River, which had very high banks with difficult rocky soil. Thus, the solution found was the beginning of a new technique: drilling along a given trajectory, and, if necessary, curvilinear.
BENEFITS AND ADVANTAGES of using HDD as a trenchless method of laying pipes; Areas of use.
The main features of horizontal directional drilling methods are that it allows in cramped urban conditions, or in the presence of highways on the construction path, to carry out trenchless (not damaging the surface) laying of pipes and communications for various purposes.and also solve the problem of overcoming natural barriers in the form of rivers. For clarity, we list the industries in which HDD capabilities have been used for a long time and with great success:
Trenchless pipe laying for transporting liquids and gases during the construction of a water pipeline; sewerage; heating networks; gas pipeline and oil pipeline, as well as other product pipelines.
Trenchless laying of communications all types: pulling an electric cable, laying communication and data cables; other types of communications.
Moreover, pipes are used in almost a variety of ways: from steel, cast iron, concrete, polyethylene, ceramics.
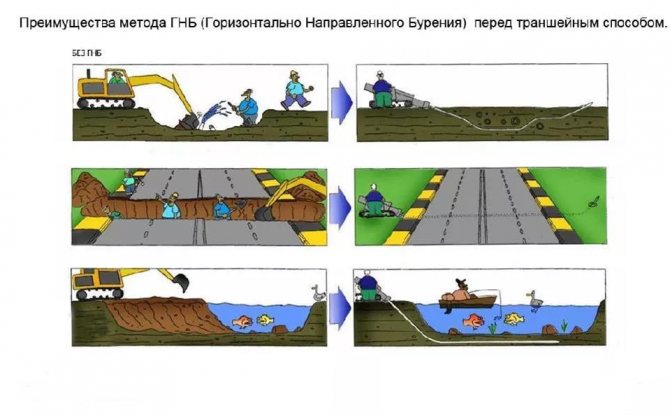
Due to its very essence, the idea of this technique, Trenchless technologies and in particular, HDD technology, contain a whole range of advantages. Let's list them point by point.
The method of HDD implementation does not damage the surface. The integrity of the road pavement is fully preserved and the traffic is not disturbed in any way;
accordingly, coordination with the traffic police, city public transport organizations is dramatically simplified and minimized and their terms are reduced;
The presence of natural barriers, such as rivers, ceases to be a problem for builders, and at the same time, it is not necessary to roughly disturb the landscape with bulky earthworks:
since no tangible harm is done to the ecology of the territory, coordination with environmental organizations also becomes minimal.
In turn, all this significantly reduces the overall time for preparing the construction of networks and communications.
With the trenchless method, the volume of earthworks is significantly reduced, there is no need to remove the soil, as with "ground" technologies for laying trenches;
the amount of equipment and labor required is also decreasing.
Will not affect the landscape - and, therefore, there are no costs for its restoration (including the cost of time)
The accuracy of the gait controlled from the surface makes it possible to exclude “erroneous” exits of the drill at an off-design point and damage to neighboring utilities, which is extremely important in a modern city.
Minimal risks of any emergency situations.
As a result of all of the above, the total financial costs can be reduced in general from 30% and up to 3 times, depending on the object and methodology.
The reduction of construction time is very significant: from 2 to 20 times.
— So, we objectively see a number of undeniable benefits. Thanks to all this, trenchless technology for laying pipes, pipelines and communications has become so popular in all developed countries as a highly efficient, cost-effective, and in a number of complex cases - simply irreplaceable technology. And that is why it is actively developing, conquering new markets.
Features of trenchless technology
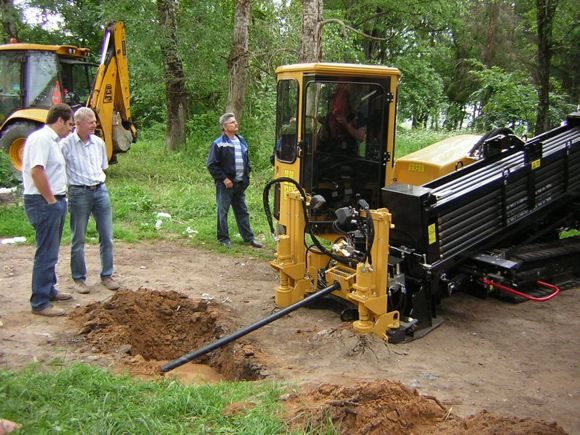

Even from the name it is clear that in this case there is no need to dig trenches. But in this case, we are talking only about crossing a road or railway bed, a reservoir. The pipeline route is brought to the facilities in the traditional way, but there it passes through the ground, so the road surface (or rails, sleepers) remains intact.
Advantages of the method
Trenchless laying of sewers or other engineering systems has undeniable advantages. These include:
- high efficiency;
- relative noiselessness;
- a small amount of preparatory work;
- small number of service personnel;
- no need to block traffic;
- the ability to work at any time of the year;
- complete absence of risk of damage to other communications;
- lower costs when compared with the traditional trench method;
- versatility: the technology makes it possible to lay the track in any area;
- reducing the installation time of systems, as this stage can be completed by professionals within a few days.

The most important advantage of this technology is the absence of serious damage to the environment, because it is not necessary to restore the road surface.
Cons of technology
Are there any disadvantages? They are not, if we consider the method from the point of view of professional builders. Owners of suburban areas can find relative disadvantages even with trenchless laying. This is the need to hire special equipment and labor costs when the operation is carried out without the participation of special equipment.
A small drawback can be considered the novelty of the technology, which in some cases may cause workers to be unaware of its features. Another potential problem is the lack of special equipment, but it is a fixable matter.
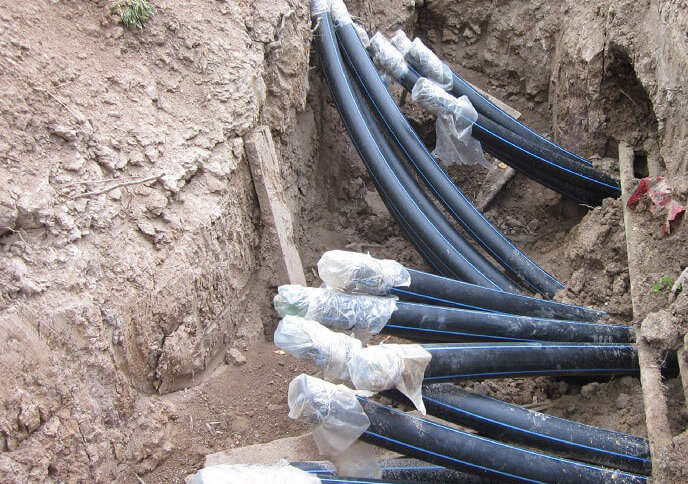
Areas of use
After the invention of new trenchless methods, there was no need for a large amount of earthwork. For this reason, these technologies are widely used. To make sure that the methods are indispensable, it is better to get acquainted with the areas of their application. Types of jobs:

- laying communication cables;
- trenchless sewerage;
- installation of underground heating mains, oil pipelines;
- laying of gas pipelines, water pipelines underground;
- repair or replacement of damaged elements of highways.
One of the types of trenchless laying (HDD) makes it possible to carry out communications in places where the use of other methods is completely excluded. For example, if there is no chance for the entrance of large construction equipment, when there is a high probability of landslides in the area, etc.
Equipment, materials for laying
Despite the fact that there are differences in methods, trenchless laying of sewers or other engineering systems is an operation during which pipeline links are pushed into the ground. Therefore, most often use a certain set of equipment. It includes:
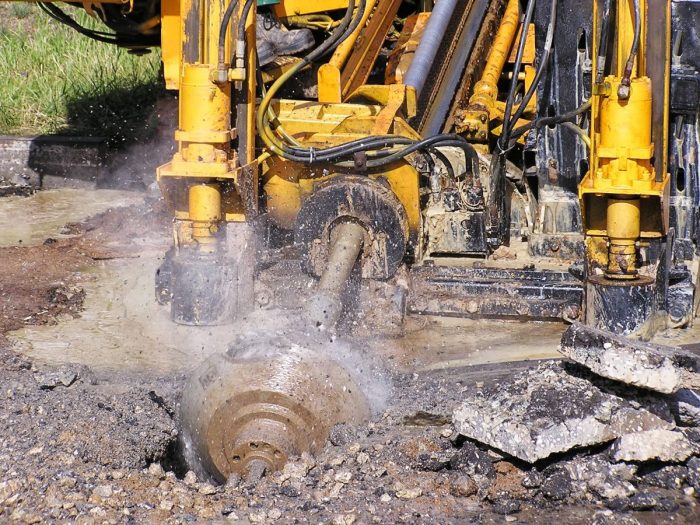

- installations for laying pipes: caterpillar or pneumatic;
- welding equipment for connecting links of the highway;
- pipes, nozzles, drilling heads, augers, rimmers;
- diesel hydraulic stations (oil stations);
- cameras, monitors for surveillance;
- bulldozers, winches, tractors;
- hydraulic jacks.
Each type of trenchless technology may require additional elements, as well as auxiliary equipment. It all depends on the characteristics of the soil, the features and dimensions of the “surmountable obstacle”.
Choice of equipment for puncture
To select the number and type of pressing devices, we make calculations to determine the required pressing force. It depends on:
- pipe diameter;
- the length of the pipeline to be laid;
- type of soil;
- landscape features.
Puncture forces are different and range from 150-2000 kN. Having calculated the required pressing force, we will be able to decide on the type of thrust wall in the excavated pit and the number of jacks for the power plant.
The necessary equipment for a puncture is a pressure pumping jack installation.It consists of GD-170 hydraulic jacks placed on a common frame (one or two paired) with a force of up to 170 tf each. The jack rods have a large stroke amplitude - up to 1.15-1.3 m.
The jacking installation is placed at the bottom of the working pit - a puncture will be carried out from it. Not far from the pit there is a hydraulic pump with a pressure of up to 30 MPa, otherwise 300 kgf / cm2.
Special equipment
Trenchless laying of water pipes implies the use of special equipment and machines. Without it, it is impossible to drill a hole, for example, under a highway (except for external digging).
Thanks to the use of special equipment, work can be carried out at any time of the year with any type of soil.
Use cases and types of equipment:
- Pumping and jacking unit - allows you to make a well, bypassing all obstacles. The kit should include a hydraulic station, expander, rods and cutting heads.
- A hydraulic station is a device that provides power by means of a hydraulic cylinder. Average power - 36 tons.
- With hydropunctures, special devices are used that hit with a powerful directed jet of water. Used on sandy soils. With the use of such equipment, pipes with a diameter of up to 50 cm can be laid. The length of the pipeline is limited to 30 m.
- Vibration equipment works on the principle of punching. The installations used in this method have a shock-vibration-indentation principle of operation. In this case, the diameter of the pipes is the same as in the case of hydraulic punctures. But the length of the well is doubled (60m).
- Additional equipment is also used. These can be machines with manipulators, welding, generators, mortar-mixing units.
SNiP 3.05.04-85
What to be guided by when laying a water pipe with your own hands? Basic instructions for laying and designing pipes are contained in SNiP 3.05.04-85 "water supply facilities and external networks and sewerage." Here are some of the requirements of this document.
So, how should pipelines be laid according to SNiP?
- For socket joints with rubber seals, the angle of rotation at each joint should not exceed 2 degrees with a diameter of up to 600 mm and 1 degree with a diameter of 600 mm or more.
- Deviations from the design axis of the pipeline should not be more than 100 mm.
- Rubber seals on socket connections cannot be used frozen.
- Metal and concrete pipelines are protected from corrosion.
- Welding between dissimilar polymer pipes (in particular, HDPE and LDPE) is not allowed.
- Welding of metal pipes can be carried out at a temperature not lower than -50 degrees, polyethylene - not lower than -10 degrees.
Notes
- ↑ "Technology of construction production". Section XII. Laying of engineering networks. Chapter 1. General information. § 2. "Types of pipe laying." Page 383-384. Under the editorship of professors O. O. Litvinov and Yu. I. Belyakov. Kyiv, Head publishing house of the publishing association "Vishcha school". Circulation 20,000, 1985 - 479 pages.
- ↑ "Typical calculations for the construction and repair of gas and oil pipelines (Construction of pipelines)". Chapter 5. Construction of pipeline crossings through natural and artificial obstacles. § 5.3.3 Selection of equipment for the construction of pipeline crossings over roads. — Page 535-550. Ed. d.t.s. prof. L. I. Bykova. — Nedra, p. 824, ill. St. Petersburg, 2006. Circulation 10,000. ISBN 5-94920-038-1.
- ↑ ATR 313.TS-002.000. Typical solutions for laying pipelines of heating networks in polyurethane foam insulation with a diameter of 50-1000 mm.
- I. P. Petrov, V. V. Spiridonov. "Aboveground piping". Publishing house "Nedra". M.: 1965. Circulation 2475 copies. P. 447. Chapter 5. Systems used in above-ground laying of pipelines. §1 Review of constructed overhead pipeline beam systems. Page 97-117.
- M. A. Mokhov, L. V. Igrevsky, E. S. Novik. "Concise electronic guide to the main oil and gas terms with a system of cross-references". - M .: Russian State University of Oil and Gas named after I.M. Gubkin. 2004.
- I. P. Petrov, V. V. Spiridonov. "Aboveground piping". Publishing house "Nedra". M.: 1965. Circulation 2475 copies. P. 447. Chapter 5. Systems used in above-ground laying of pipelines. §2 The main beam systems used in above-ground laying of pipelines. Page 117-119.
- ↑ "Metal structures". In 3 volumes. Volume 3. "Special structures and structures": Proc. for building. universities. Edited by d.t.s. Professor V.V. Gorev. Second edition, corrected. M.: Higher school, 2002. - 544 p.: ill. ISBN 5-06-003787-8 (vol. 3); ISBN 5-06-003697-9. Chapter 5 Pipelines. § 5.4 Design and calculation of underground pipelines. Page 82-85.
- ↑ Chapter 2. Earthworks. § Closed excavation methods. Page 41. "Handbook of the builder: a full range of construction and finishing works for putting the house into operation." A. G. Borisov. — M.: AST: Astrel, 2008. — 327 p. Circulation: 4,000 copies. ISBN 978-5-17-037842-5 (LLC AST Publishing House); ISBN 978-5-271-14158-4 (LLC Astrel Publishing House)
- ↑ Skaftymov N. A. Fundamentals of gas supply. - L .: Nedra, 1975. - 343 p. Circulation 35,000 copies. §IX.4 "Construction of crossings under roads, railway and tram tracks". Page 170-171.
- Fidelev A. S., Chubuk Yu. F. Building machines: Textbook for universities.- 4th ed., revised. and additional - Kyiv: Vishcha school. Head publishing house, 1979, - 336 p. Page 216.
- “Technology of building production. Textbook for universities. Chapter VI. Drilling operations mechanical methods of drilling. S. S. Ataev, N. N. Danilov, B. V. Prykin et al. Stroyizdat, 1984.
- Paragraph 3 "Terms and definitions", SP 86.13330.2014 "Main pipelines". Revision of the updated SNiP III-42-80*.
- ↑
- ↑
- A. G. Kamershtein, V. V. Rozhdestvensky and others “Calculation of pipelines for strength. Reference book. M. - 1969. Circulation 10,000 copies.
- Paragraph 4.15, SP 42.101-2003 "General provisions for the design and construction of gas distribution systems from metal and polyethylene pipes."