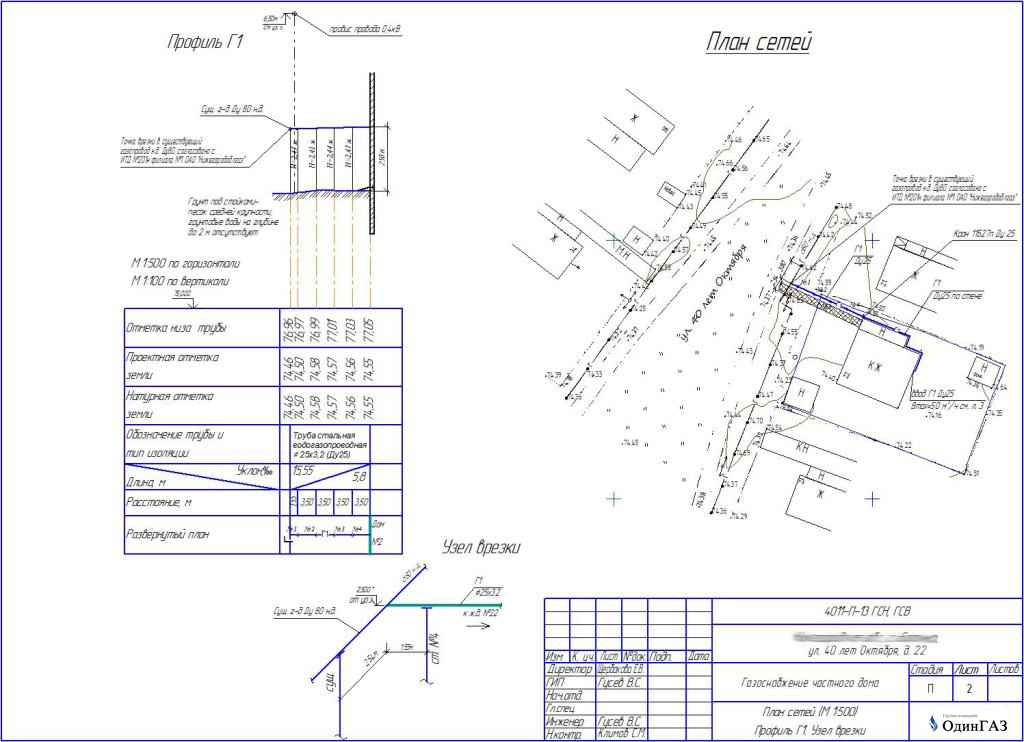
- Punching method
- Calculation of the cost of gas connection
- What factors affect the cost
- Where should you start?
- Norms for the installation of a gas pipeline
- The process of laying above-ground systems
- Outdoor piping
- Benefits and subsidies for conducting gas to a private house
- Trench for gas pipeline
- Categories of gasified objects
- Installation rules
- Rules for the location of pipes and gas equipment in the kitchen
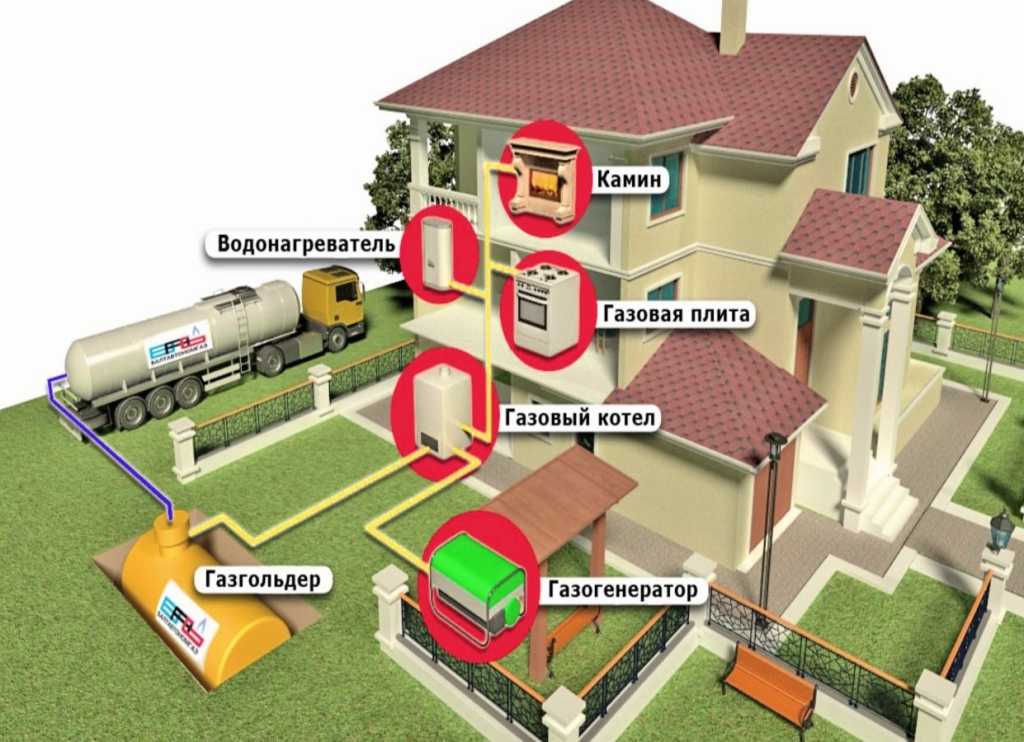
- Boiler with gas
- Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
- Second phase
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Punching method
The punching method is designed for laying metal pipes of large diameter (from 800 mm). And one of its main features is the absence of the need to dig a trench. This method is used for pipelines no longer than 80 meters. The essence of the method is that hydraulic jacks press a steel case with a knife at the end into the ground. It is poured into the pipes, then they must be cleaned manually.

This method is widely used when laying pipelines under various structures, highways and rails. He is also involved in the conduct of water, oil and gas pipelines, installation of sewers.In addition to the fact that large diameter pipes can be used in this way, there are other advantages: relatively low costs and speed of work.
Calculation of the cost of gas connection
How much does it cost to install gas in a private house? The answer to this question depends on several factors.
The complex of works on gasification includes several stages - from the creation of a technical project to the actual installation of the pipeline. At the same time, pipes are laid by various methods, and the complex of works is divided between the GDO and the contractor - the first pull the network to the site, the second - across the territory and inside the house.
The final cost also depends on the regional and territorial features of the location of the site.
What factors affect the cost
The overall estimate, as a rule, is formed by the contractor involved in the drafting of the project.
You need to understand that, in addition to the costs of materials and construction and installation work (and they are affected by both the layout and the number of floors), it includes:
- preparation, development and approval of project documentation;
- registration of the project in the municipal organization;
- expenses for GDO services for laying and tie-in to the main highway;
- costs for system acceptance and subsequent commissioning.
It is impossible to derive a single tariff in such a situation - each site and house has individual characteristics and requires a separate expert assessment.
Where should you start?
You need to know that work on the design of gas supply can only be started after the technical conditions have been agreed and received, or as they are also called TU for the gas supply of an object.
This is a significant special document, only a gas distribution organization has the right to issue it.Obtaining technical specifications gives the owner of the site the opportunity to order the development of the project.

Obtaining the Technical Specifications allows the owner of a house or a plot for its construction to order a gasification project. Without technical specifications, such a project cannot be developed.
To obtain technical conditions, it is necessary to provide the following documentation package to the local gas service:
- Application for obtaining TU. It can only be written by the owner of the land plot allocated for construction, or by the homeowner if the building has already been erected.
- A copy of a document that can verify the identity of the applicant. Usually it is a passport.
- Original documents that confirm the applicant's ownership of the house. You will also need a document that confirms the legality of the building. This may be a purchase / sale agreement, as well as an act of acceptance of the building into operation or a technical passport from the BTI.
- If construction is still underway, it is necessary to provide documentation confirming the applicant's ownership of the site. This may be a lease or purchase / sale of a plot, as well as a certificate confirming the registration of ownership.
- Explication of the building on the ground.
It must be understood that the proposed connection to the gas main will be allowed only if the area where the house is built is included in the gasification plan.
It is important that there is a technical possibility of connection. This assumes that the volume of gas in the existing pipeline allows one more point of consumption to be added.
Gas is a potentially dangerous type of fuel, so only professionals can deal with the design of gas networks
In terms of time, the preparation of technical specifications takes about a month.When connecting to a gas main, certain requirements must be met. For example, a building can be removed from the gas pipeline by no more than 200 m.
In this case, the design area of the building should not be more than 250 square meters. m. Such houses belong to the first group of gas consumers. They have the right to consume gas at a rate of not more than 5 cubic meters per hour.
If the area of \u200b\u200bthe house is larger, connection is also possible, but obtaining technical specifications will become much more complicated, since it will be necessary to additionally coordinate the transfer of the consumer from the second group to the first.
To obtain technical conditions, you can use the services of special companies, but this will be expensive. Therefore, it makes sense to do the paperwork yourself.
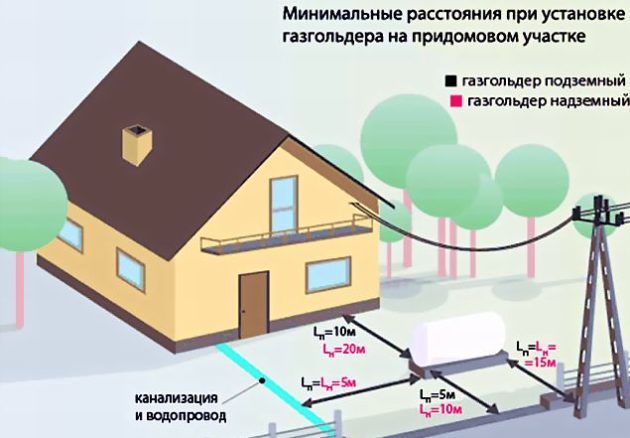
Norms for the installation of a gas pipeline
The gas pipeline is one of the most important parts of the house. Thanks to him, heating appears in the room, with the help of gas appliances you can cook food and heat water for hot water supply. But if used incorrectly, gas can become a serious problem leading to tragedy. To avoid this, the standards used in the installation of the gas pipeline were invented. They ensure the safety and correct operation of the devices.
Basic Rules:

- It is not allowed to cross the gas pipeline and window openings, doors and ventilation.
- The distance from the pipe to the electrical panel must be at least half a meter.
- There must be at least 25 cm between the gas system and electrical communications.
- The gas pipeline should be at a height of 220 mm from the floor, in rooms with a sloping ceiling this distance is 200 mm.
- A flexible hose with a diameter of 10 mm can be connected to the gas equipment.
- Water heaters cannot be installed in the bathroom.
- High humidity creates back draft, due to which the room is filled with carbon monoxide and can cause poisoning.
- The distance between the plate and the pipe must be maintained, it must exceed 80 cm.
- After metering devices, a pipe slope of 3% should begin.
- The metering device should be located at a height of 1600 mm from the floor.
- The meter should be located at a distance of 80 cm from the heating equipment or stove.
- To install the gas pipeline in the wall, it is necessary to make a hole in the wall separate from the ventilation.
- It is necessary to provide access to communications. You can put them in a box, but it must be equipped with a lid for access.
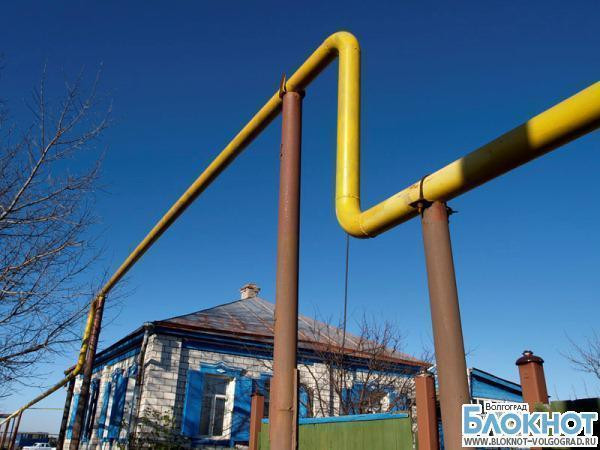
The process of laying above-ground systems
The above-ground laying of the gas pipeline system requires less material costs compared to the previous option. The main support for the pipes are special supports, which are placed first. It is easier for specialists to control the state of a structure or repair work. The risk of fire and damage to citizens of housing facilities is reduced.
Fig 6. Above-ground laying
During the creation of an elevated view, it is necessary to create maximum protection for pipes from mechanical damage and temperature changes. Depending on the climatic zone in which it is planned to create a highway, the type of protection is selected.
It is important to note that when creating an above-ground system, it will be necessary to constantly monitor its condition in order to prevent premature wear. Compared to underground, it is less reliable due to close contact with the environment.Professionals must comply with the rules and regulations to create a quality source of fuel transportation
Professionals must necessarily comply with the rules and regulations in order to create a quality source of fuel transportation.
During installation, certain distances between the supports must be maintained, taking into account the diameter of the pipes, as well as above the ground:
| Ground Distance | Between supports |
| To ensure the passage of specialists from 2.2 m | Minimum span 100m with maximum pipe diameter 30cm |
| In places where the motorway is located 5m | With a diameter of up to 60cm - 200m |
| Where do trolleybuses and trams from 7.1m pass | More than 60 cm from 300m |
Also, the thickness of the pipes is taken into account, the minimum figure is from 2m.
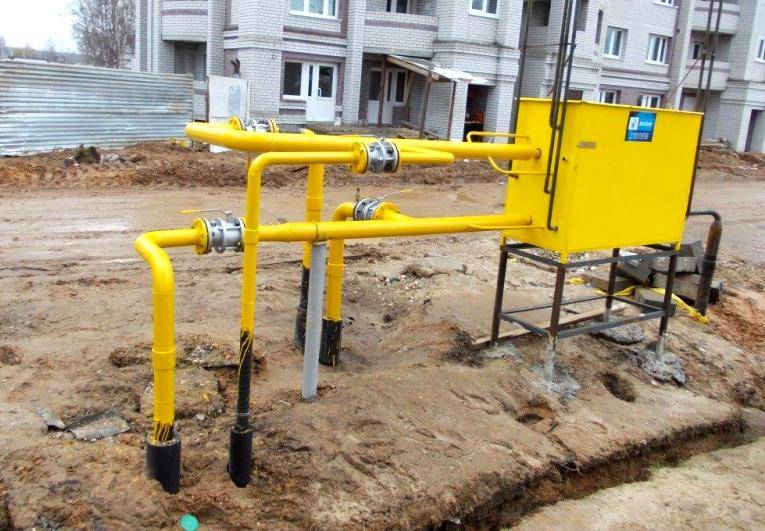
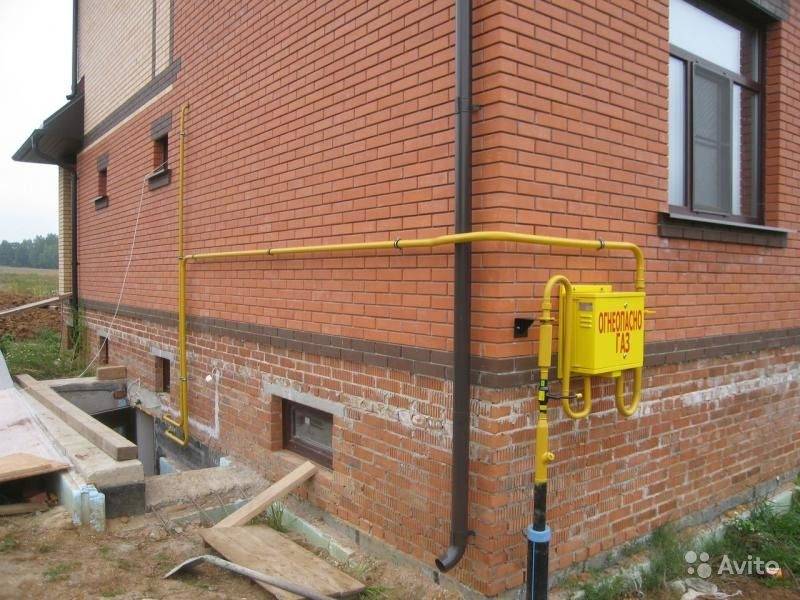
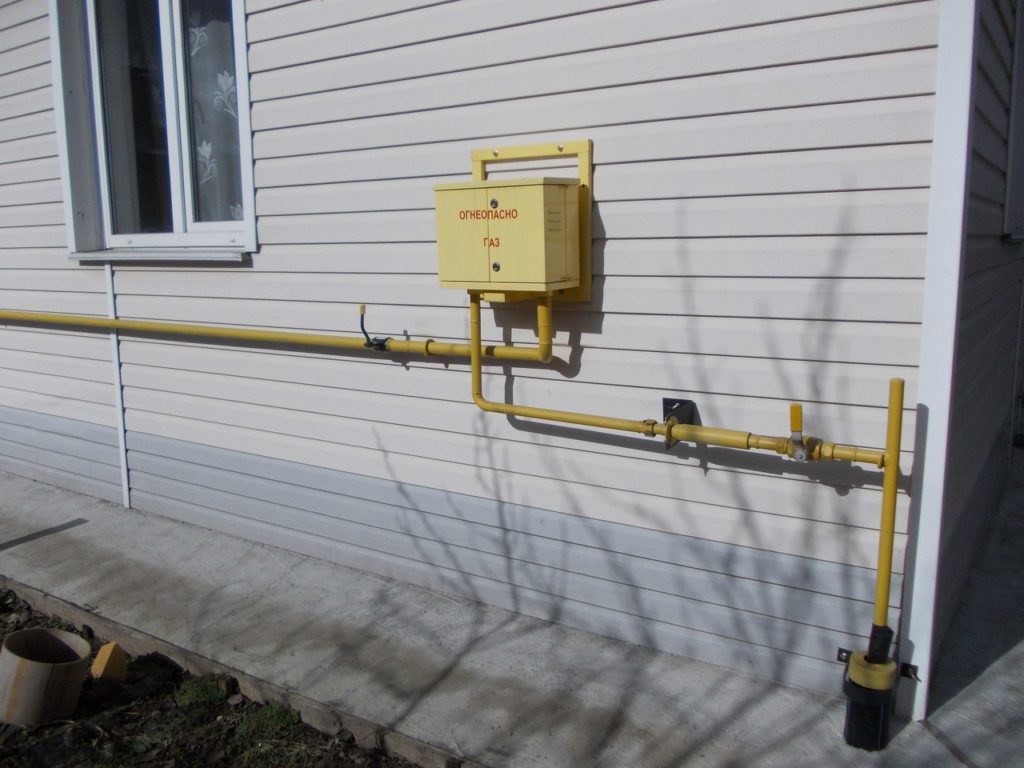
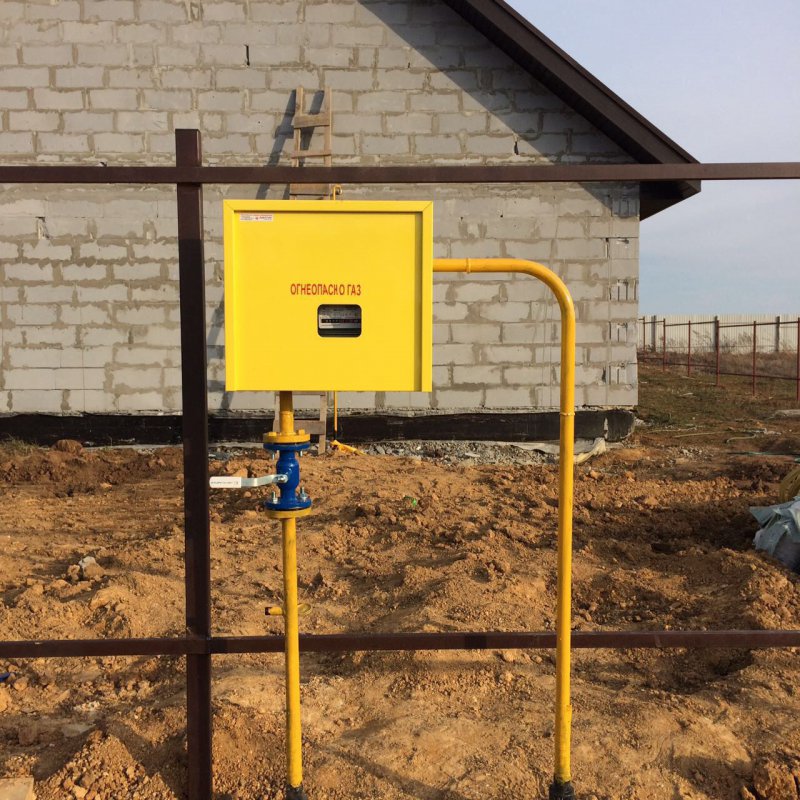
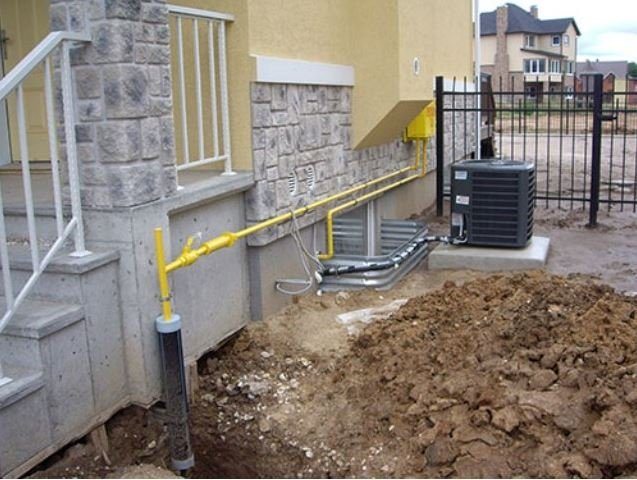
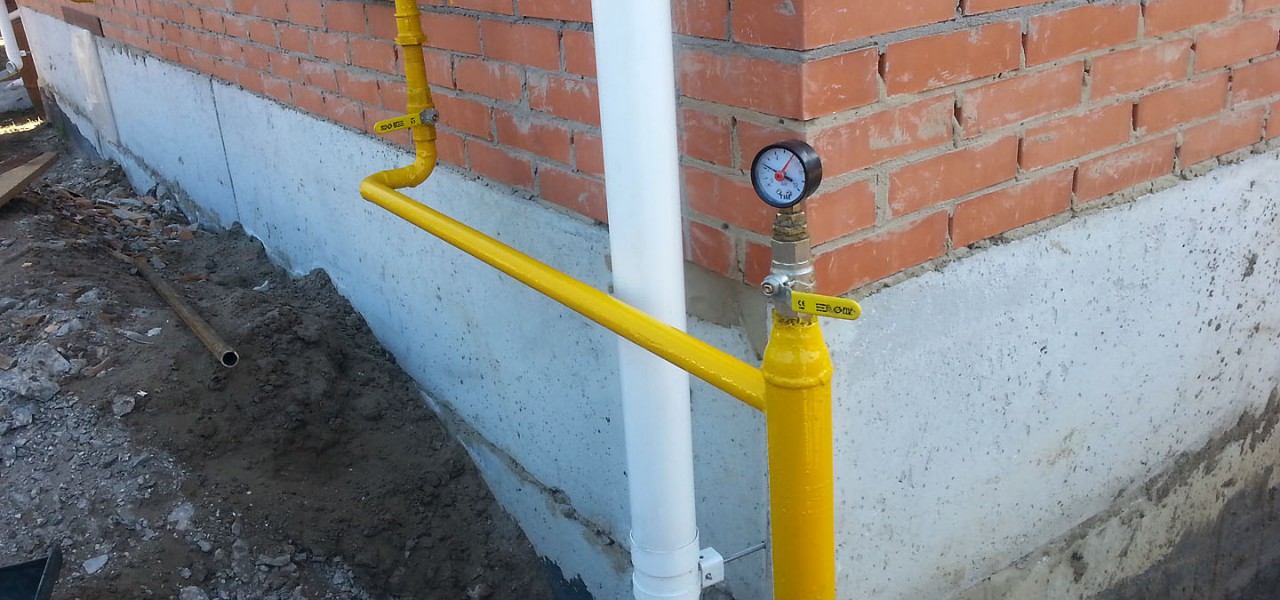
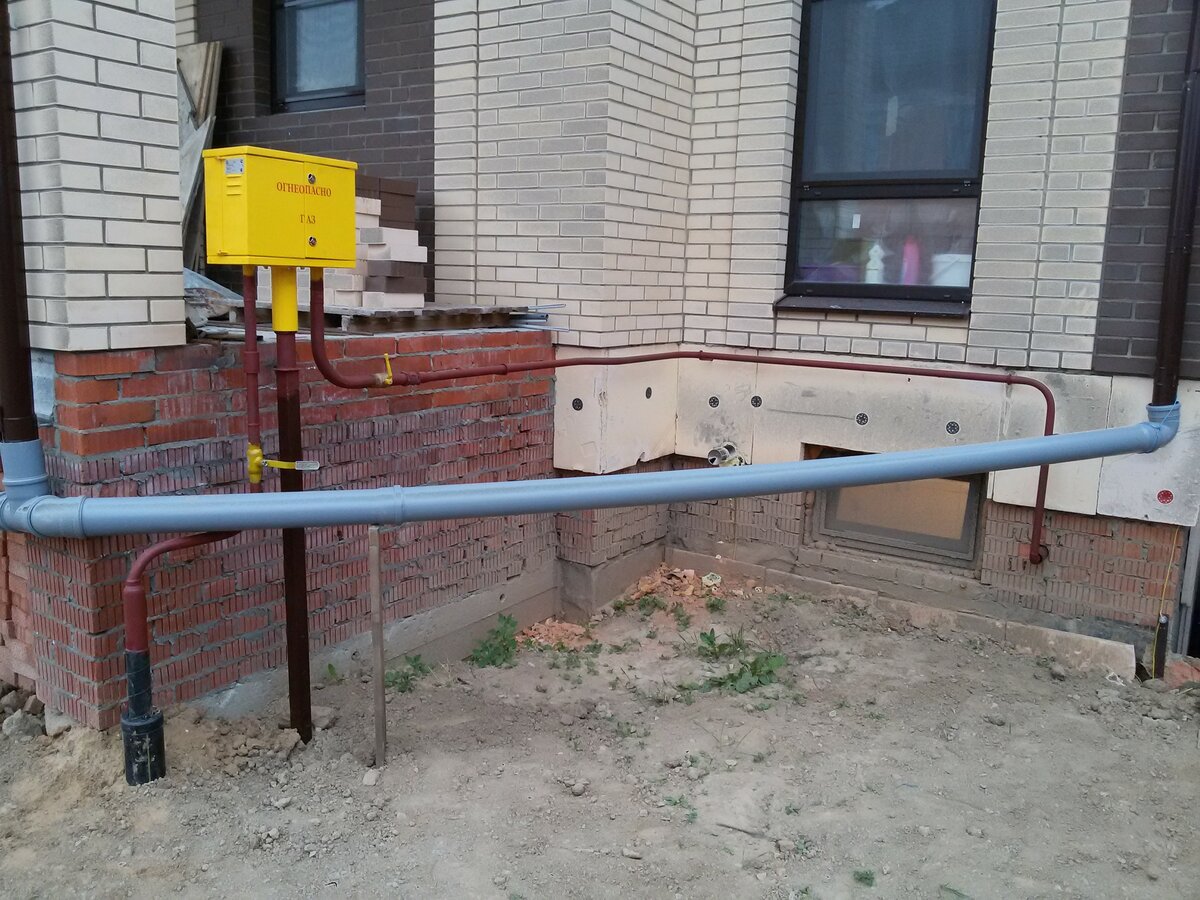
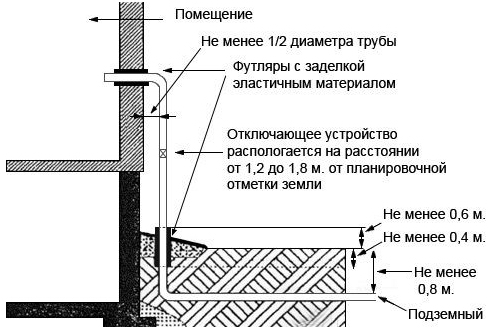
Outdoor piping
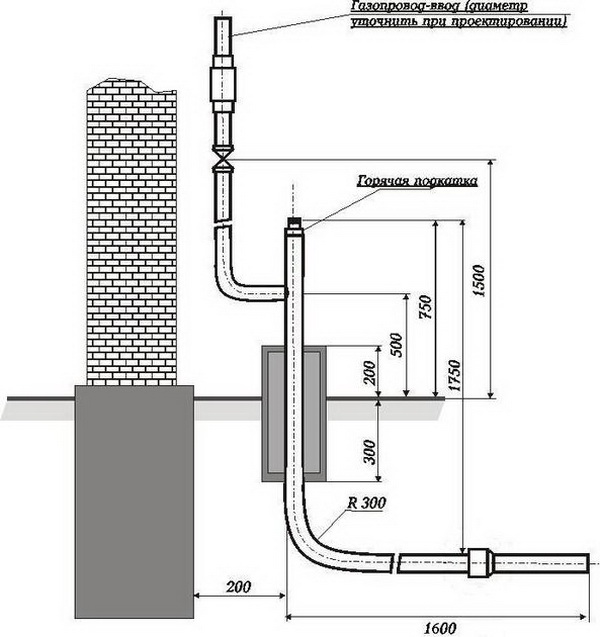
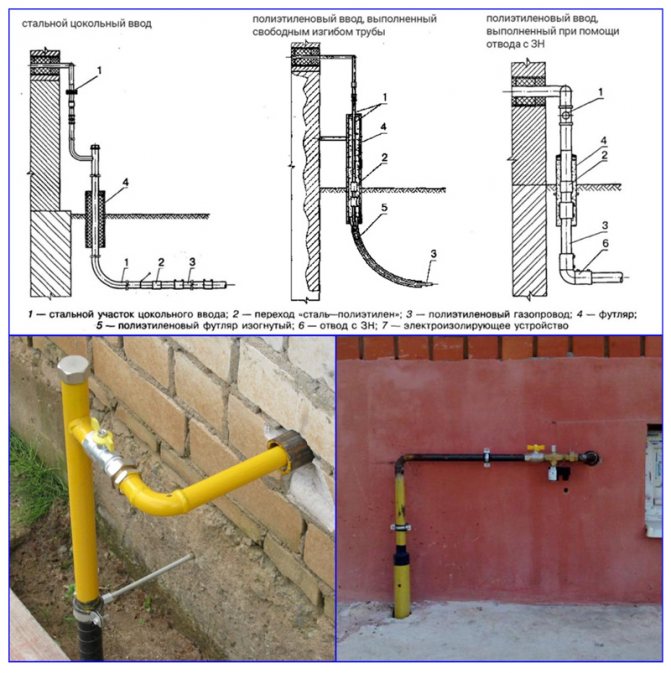
The external pipeline, from the connection point to the entrance to the house, can be either above-ground, metal (pipe on racks and clamps along the wall), or underground, both metal and polymer (PE pipe laid in a trench way). If an underground pipe is brought into the house in a basement, a so-called "basement entry" is required - an integral connection between the steel and polyethylene pipes. Such connections are sold ready-made, and the price of the issue is quite acceptable, it is convenient that they already come with a case (sleeve) for wiring.
kam711 Member
I am going to go through the installation of a gas consumption network with my own hands. I think it will be useful for many.
Option 1
- A ready-made basement input is bought (preferably in an office where there is welding).
- 50 m of PE pipes are welded onto it immediately (right in the office) and direct entry into the house.
- A trench is being dug, sand is everything, a pipe is being laid.
- All wiring in the house is done by MP compipe-gas, up to the counter with threaded connections to an anaerobic sealant.
- Representatives of the GRO are invited to review creativity.
Option 2
All the same, but without a trench and a PE pipe.
When wiring underground, before backfilling, the line must be tested for leaks (air under pressure). The outlet of the pipe from the ground is closed with a protective steel sleeve, the cavity is covered with sand or filled with an elastic material.
According to the standards, the above-ground pipeline can be not only steel, but also copper.
AlexeyV888 Member
I have four meters of pipe to the fence, not much money. GRO will bring under the overhead connection. Why should I mess with the underground? My goal is to ensure that the GRO does not find anything to get to the bottom of. I foresee acceptance through an independent examination and court, and with the subway, they have significantly added opportunities. Simplicity, clarity, and minimum requirements are important to me. The copper connection on the press fittings is just right. About steel and polyethylene requirements of the mountain, a bunch of different tests can be carried out. For press fittings, a certificate and mechanical tests are sufficient. Well, this is how I see it, after reading all the joint ventures and GOSTs on this topic five times. There are examples of such implementation.

Benefits and subsidies for conducting gas to a private house
According to federal law No. 69-FZ (as amended on July 26, 2019), Article 24 approved a list of persons who may be granted benefits and subsidies for connecting gas supply to private households and supplying gas. These include the following categories of citizens:
- pensioners;
- disabled people of I, II, III groups;
- veterans, combatants and their widows;
- large families;
- liquidators of the Chernobyl accident;
- low-income families.
The amount of benefits is regulated at the federal and regional levels. In most cases, 50% is provided concession for gas connection owners of private houses belonging to these categories of citizens. However, the regional authorities of individual subjects of the Russian Federation can return up to 90% of the connection cost. Veterans and invalids of the Great Patriotic War, blockade survivors, as well as persons who have reached the age of 80, can be provided with 100% compensation.
Payments for connecting gas to the house to preferential groups
To apply for compensation, you need to contact the social insurance fund at the place of registration. You need to have with you:
- The passport.
- Documents confirming the ownership of the capital structure.
- Pension certificate (for pensioners).
- Medical documents confirming disability (disabled people of groups I, II, III).
- Information about the composition of the family.
- Income certificate (for low-income citizens).
- An agreement with a gas distribution organization and an agreement for the supply of gas.
- Acts of the work done.
- Payment receipts (to confirm the purchase of gas equipment and connection of gas supply).
In case of providing false information, the presence of debt, lack of documents or an incorrectly completed application, compensation will be denied. Working pensioners may also be denied a subsidy. According to the legislation, privileged categories of citizens are required to annually confirm their status.
In conclusion of the article, it is worth noting that the ease of use and low cost of blue fuel will pay for the troublesome and expensive gasification procedure.
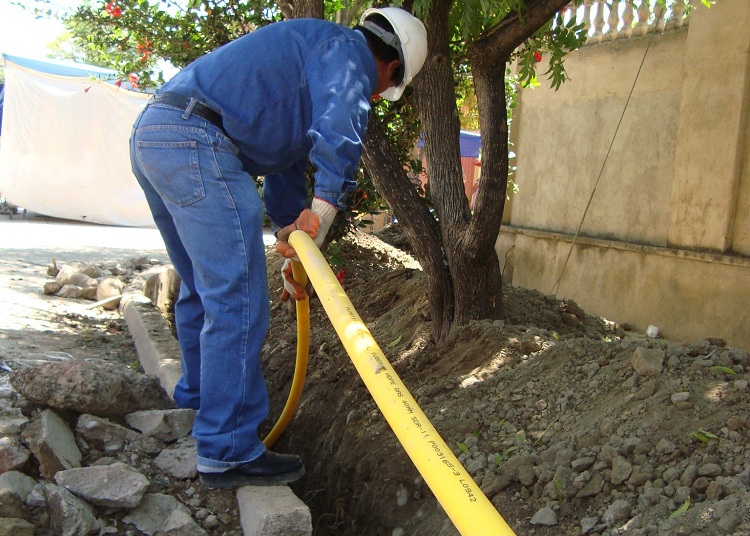
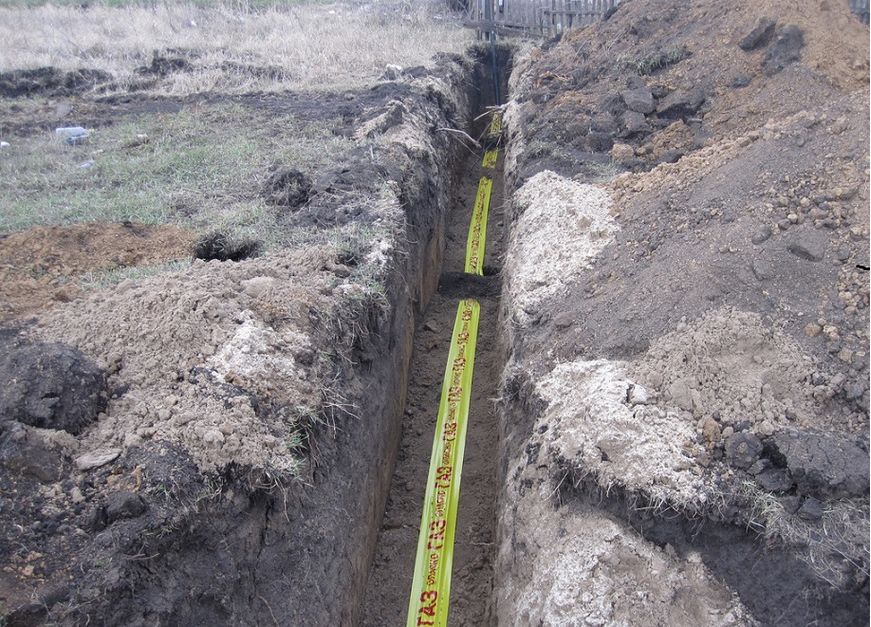
Trench for gas pipeline
The depth of laying (laying) of a low-pressure gas pipeline is determined by the regulatory document “SNiP 42-01-2002.Gas distribution systems” and is described in paragraph 5.2 as follows:
Laying of low-pressure gas pipelines should be carried out at a depth of at least 0.8 m to the top of the gas pipeline or case. In places where the movement of vehicles and agricultural machines is not provided, the depth of laying low-pressure steel gas pipelines can be at least 0.6 m.
When crossing or passing the gas pipeline communication under roads and other places of movement of vehicles, the laying depth must be at least 1.5 meters, to the top point of the gas pipeline, or its case.
Accordingly, the depth of the trench for the gas pipeline is calculated by the following formula: the diameter of the gas pipeline + the thickness of the case + 0.8 meters, and when crossing the road - the diameter of the gas pipeline+ case thickness + 1.5 meters.
When a low-pressure gas pipeline crosses a railway, the laying depth of the gas pipeline from the bottom of the rail or the top of the road surface, and if there is an embankment, from its bottom to the top of the case, must meet safety requirements, but be at least:
in the production of works in an open way - 1.0 m;
when performing work by punching or directional drilling and shield penetration - 1.5 m;
in the production of work by the puncture method - 2.5 m.
When crossing other communications with a low-pressure gas pipeline - water pipelines, high-voltage cables, sewerage and other gas pipelines, it will be necessary to go deeper below these communications in the place where they pass, by at least 0.5 meters, or you can go above them if they lie at a depth of at least 1.7 meters.
The depth of laying low-pressure gas pipelines in soils of varying degrees of heaving, as well as in bulk soils, should be taken up to the top of the pipe - at least 0.9 of the standard freezing depth, but not less than 1.0 m.
With uniform heaving of soils, the depth of laying the gas pipeline to the top of the pipe should be:
not less than 0.7 of the standard freezing depth, but not less than 0.9 m for medium heaving soils;
not less than 0.8 of the standard freezing depth, but not less than 1.0 m for heavily and excessively heaving soils.
Categories of gasified objects
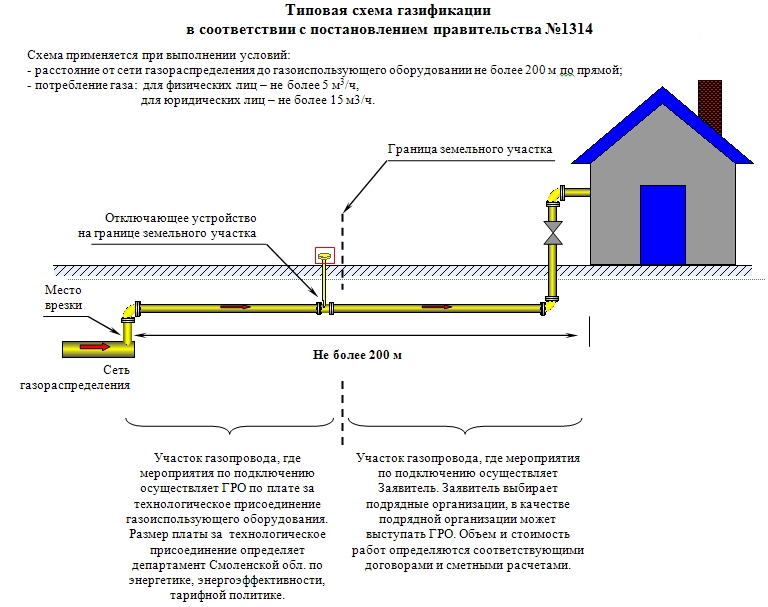
According to Decree No. 1314 of the Government of Russia, homeowners need to find out how much it costs now to bring gas into their homes by contacting the regional gas distribution service.
First of all, household expenses for technological connection depend on the volume of gasification works. In this regard, three categories of capital objects have been identified.
The first category of objects. The first category includes private households whose total consumption of natural gas does not exceed 5 m³/h.
Small businesses are equated to them, the technological equipment of which consumes no more than 15 m³ / h of a mixture of propane and butane. Those. the lowest fee for connection to the gas distribution network is charged for cottages with an area of less than 300 m² and small businesses from the public utility area.
The installation work on the supply of the gas pipeline will be completed at the border of the site. The layout of the gas pipe for the consuming equipment of the household on its territory is carried out according to a separate project
The possible scope of work on laying connecting gas communications to the household of the first category is limited:
- the greatest distance from the main gas distributor to the equipment consuming gas is less than 200 m;
- gas pressure in the gas supply source - up to 0.3 MPa.
In addition, the laying of introductory gas pipelines is carried out without the construction of reduction points (pressure reduction) of the main natural gas.
The fee for connecting the gas pipeline for objects of the first category is 20,000-50,000 rubles (clause 8 of the appendix to the order of the Federal Tariff Service of the Russian Federation No. 101-e / 3 of 04/28/2014). The exact price is determined by the local GDO according to the conditions in the given territory, but cannot exceed 50,000 rubles.
The second category of objects. Among the objects of the second category are households, the connection of which requires distribution gas pipelines and / or the creation of points for reducing the main gas. Their estimated gas consumption is higher than the norm for objects of the first category, a higher gas supply pressure is required (i.e. 0.6 MPa or more), etc.
Compliance with the cost of connection in the first category is observed if the pipeline is inserted into a low-pressure gas pipeline. If gas reduction is required, the connection price will exceed 50 thousand rubles.
In the private housing sector, objects falling under the second category usually have an area of more than 300 m². For their gasification, standardized tariff rates are applied, calculated according to the methodology developed by the Federal Tariff Service of the Russian Federation (Appendix to Order No. 101-e / 3 of April 28, 2014).
It should be noted that applicants for consumption volumes of natural or artificial gas from 300 m³/h and above are required to coordinate gas connections with the GDS, which has a technological connection with the contractor's gas pipeline.
Approval of the amounts of tariffs for connecting gas to households of the second category is made by the local executive authority of the REC (ie the regional energy commission).
The third category of objects. The capital construction objects of the third category include farms that need an individual gasification project. For them, the amount is determined according to the design and estimate documentation, which has previously passed the examination.
The amount of expenses for gasification for households of the third category is established by the REC, related to the location of the economy connected to the main gas.
The prices for laying the gas pipeline along the section from the border entrance are not the same for different companies. However, it is worth considering the need for numerous gas project approvals. Full-fledged gasification will happen faster with an experienced contractor
The following conditions are considered to be characteristic features of the applicants' facilities in need of gasification:
- planned consumption of natural gas from 500 m³/h;
- work on connection to the gas pipeline requires the pipeline to be laid out through the forest fund, along rocky soils, swamps and water obstacles;
- gas pipeline installation work requires passing through obstacles that force the use of horizontal directional drilling.
Those. According to Government Decree No. 1314, there are actually no rigid prices for the technological connection of applicants to the gas network.The cost of gasification works depends on a number of conditions that determine its size in the framework of the relevant methods of the Federal Tariff Service of the Russian Federation.
Installation rules
Pipes for gas are connected by welding;
- Control, disconnecting, regulating devices are connected by thread or flanges. Distortions in connections are unacceptable;
- Pipe joints cannot be hidden in a strobe or box;
- Connections need direct access;
- Pipes need to be painted;
- When closing pipes with a box, from gas. pipes to the box should be at least 10-11 cm;
- 10-15 cm should separate the weld from the passage through the wall and basement of the house;
- For convenient installation and dismantling of taps, inlets, branches, you need to install spurs with lock nuts;
- Usually, the distance from the gas pipes to the walls of the house is indicated in the gasification project for the house. If this is not the case, a distance not less than the diameter of the gas pipe is taken.

Rules for the location of pipes and gas equipment in the kitchen
Special rules also exist for the location of pipes and a gas stove in the kitchen. It is forbidden to place pipes of the gas supply system:
- at a distance of less than 25 cm from the power cable;
- closer than 50 cm from the shield, which is part of the power supply system of the room or from the outlet;
- at a distance of less than 2 m from the floor;
- the distance between the gas pipes is determined so that there is a free space of at least 7 cm between the stove and the wall;
- from the chimney to the pipes must be at least 80 cm;
- distance from the ceiling to pipes and other gas equipment - at least 10 cm;
- the entrance to the house, as well as, if necessary, the passage through the walls and roof is carried out using a special case, while the distance from the pipe to the building must be at least ½ the diameter of the main.
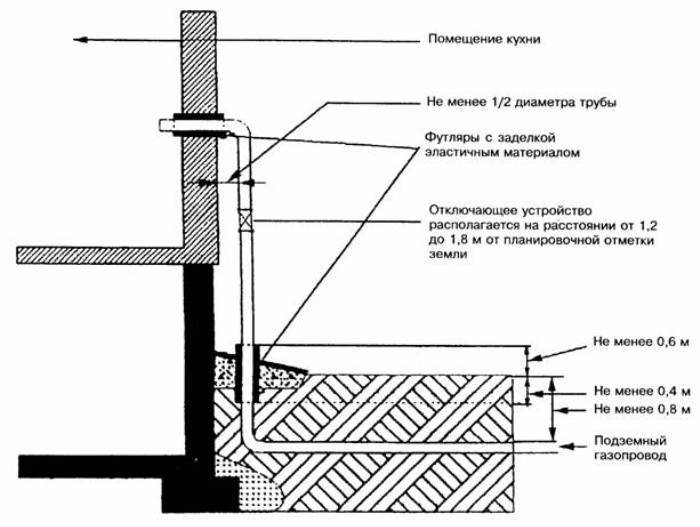
How to properly introduce gas pipes into the house
The introduction of pipes through windows, doors and ventilation shafts is strictly prohibited.
When connecting a private house to gas supply, the following aspects must also be considered:
- gas stoves can only be installed in rooms with a ceiling height of more than 2.2 m. If the kitchen has an inclined ceiling, then the stove is placed anywhere subject to this requirement;
- from the wall on the opposite side to the plate must be at least 100 cm;
- the permissible number of burners of the stove depends on the volume of the kitchen room:
- equipment with 2 burners is installed in a kitchen with a volume of less than 8 m³;
- a stove with 3 burners is used in rooms with a volume of up to 12 m³;
- to install a four-burner stove, a kitchen volume of 15 m³ or more is required;
- from the wall to the gas boiler or to the gas column must also be at least 1 m;
- the kitchen room should be equipped with ventilation and a window with an opening window;
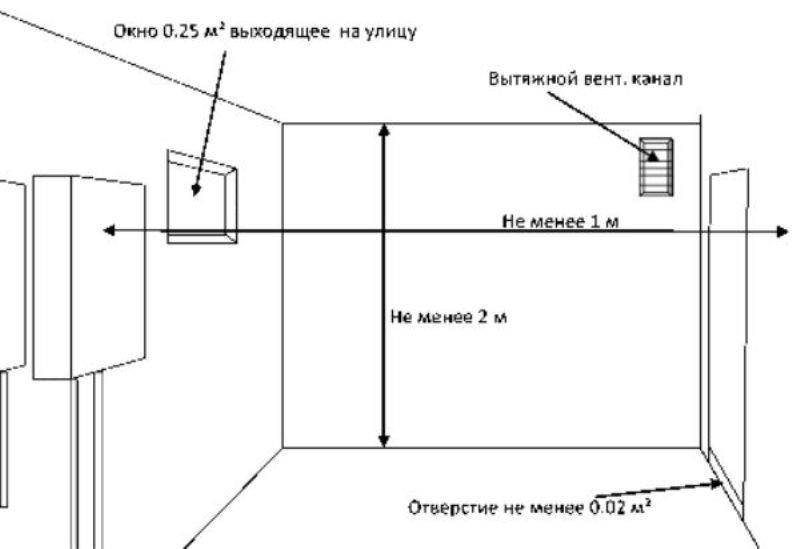
Requirements for the placement of gas equipment
- the gas pipeline fittings, in particular the tap, with which the fuel supply is shut off, must be located at a height of 1.5 m from the floor and at least 20 cm from the stove;
- the length of flexible hoses when connecting gas equipment cannot be more than 3 m;
- walls, floors, furniture adjacent to pipes, stoves or other appliances must be covered with non-combustible materials;
- for additional protection, the pipes that make up the gas supply system of the house must be covered with a layer of paint.
More details about the rules and the process of gasification of private houses are described in the video.
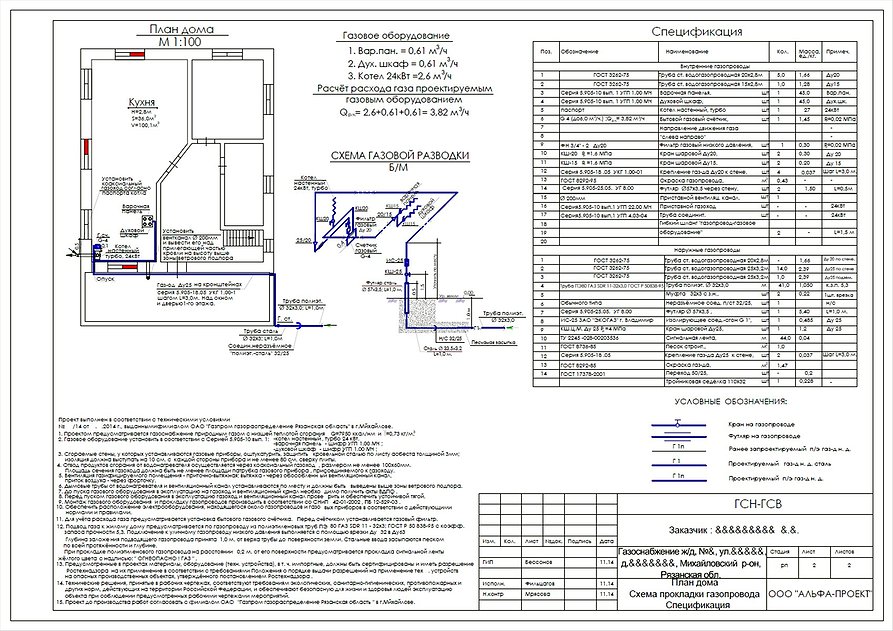
All requirements for the gasification of a separate room, the rules for the location of pipes and the most significant conditions are reflected in the design of the gas system and the accompanying documentation, which is called the technical specifications.
The development of documents takes place before the start of the construction of the gas pipeline and the installation of equipment inside the premises.
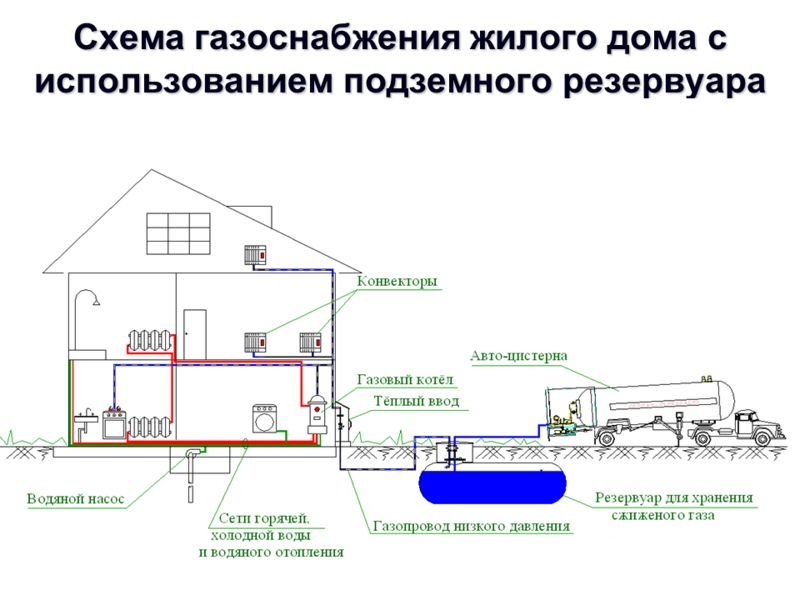
Boiler with gas
This design consists of a centralized boiler that heats the heat-transfer compartment. In this case, the gas is liquefied and distributed through the pipes, thereby ensuring the release of thermal energy. The radiators themselves, being heated to a safe temperature level of 80 degrees, heat the room. In this case, the safest solution would be to use the main gas, since it is located in a special room - the boiler room - and it does not need to be carried out through all the premises of the house.However, heating in a wooden house with gas using a gas boiler has some features that must be considered:
- It is necessary to choose a boiler that works on the principle of convection, since condensing boilers, although they are less expensive, need a low temperature of the pipeline system, which cannot be done while maintaining an optimal level of heat. The underfloor heating system can operate at low temperatures, but it is problematic to install it in wooden houses (in more detail: “Heated floors in a wooden house are a guarantee of comfort”).
- The heating system should be, as a rule, single-pipe, like a barrack. The main pipe runs along the entire perimeter of the house, and heating radiators cut into the direction of this pipe. All this is suitable for a convection boiler, with heating from 60 degrees and above.
- You can purchase boilers with electronic ignition. That is, they do not need constant maintenance of the burning mode of the main burning part, which in turn increases the level of safety. In the event of frequent power outages, you can simply purchase an uninterruptible power supply system
Big Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
Gas inputs to buildings from the yard line or street network are laid into stairwells or basements. In residential buildings, inputs are arranged separately for each section. When laying pipes through the laying of the foundation, measures are taken to protect them from destruction during the settlement of the building. The pipe located in the wall is wrapped with a pitched rope and placed in a case - a pipe of a larger diameter.
Gas inlets to houses are preferably made basement. The entry of gas pipelines into basements and semi-basements and the laying of gas pipelines along them (if there are no special technical corridors) is prohibited. It is not allowed to install plugs on the basement and intra-house gas pipelines.
Gas input can be made not only in the stairwell, but also in the non-residential basement of the building.
Gas inlets of gas tanks are passed through special chambers, in which shutoff valves, gas tanks, valves for manual discharge and PC for gas discharge into the atmosphere when gas tanks are overfilled, as well as control units for the heating system and valves of non-combustible gas pipelines for purging gas tanks and gas inlets are placed.
Buried steel gas inlets laid under buildings must be enclosed in a gas-tight cartridge. The latter should be included in an accessible and commonly used part of the building.Where the cartridge ends, the annulus between the cartridge and the inlet pipe must be hermetically sealed to prevent gas leakage.
Low-pressure gas inlets of short length (up to 25 m) are allowed to be put into operation without testing them for density under air pressure. In this case, the density of the gas pipeline (inlet) is checked in an unfilled trench under the working pressure of the gas by coating the joints with soapy emulsion or another equivalent method.
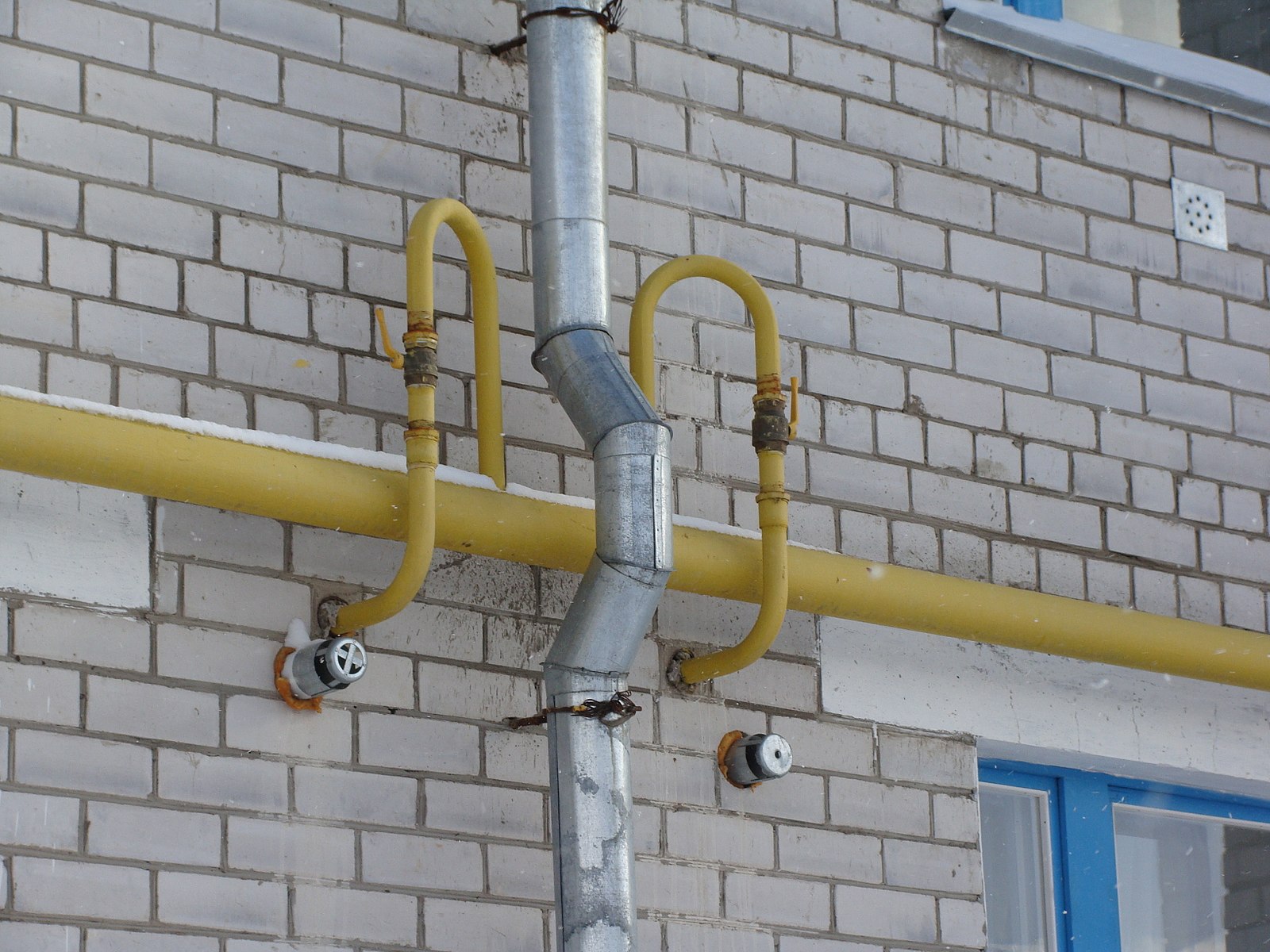
| Scheme of the yard gas pipeline. /, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 - gas risers. |
A gas inlet is a gas pipeline running from the distribution (street) network to the riser of the intra-house gas network.
| Scheme of the yard gas pipeline. 1, 2, h, 4, 5, c, 7 8 - gas risers. |
A gas inlet is a gas pipeline waiting from the distribution (street) network to the riser of the intra-house gas network.
| Scheme of the yard gas pipeline. |
A gas inlet is a gas pipeline running from the distribution (street) network to the riser of the intra-house gas network.
The gas inlets and risers are blown through sequentially, starting from the most distant inlet and riser.
Since there are gas inlets to the building on each of the two stairwells, and the gas pipeline wiring in the left half of the building completely coincides with the wiring in its right half, the gas pipeline scheme can only be drawn up for half of the building.
Pages: 1 2 3 4 5
Second phase
The result of this step should be the conclusion contracts with gas companies for connection. Attached to the application:
- copies of documents for the house and / or land;
- technical conditions;
- situational plan (the same as for obtaining TU);
- topographic plan of the site on a scale of 1:500 (obtained through the State Services free of charge within 10 working days);
- calculation of the hourly maximum gas flow rate, if it is planned to be more than 5 m3/hour;
- the consent of the owner of the gas pipeline to the connection or notification of the concession of capacity.
If it is not the applicant who will submit the papers, prepare a power of attorney in advance. After submitting the documents, the GRO takes time to prepare the contract: a week, if the site already has a network, two weeks in other cases. The timing is relevant for the private sector. You have 10 days to read the terms and conditions.
The price of a gas tie-in is determined individually, for a frequent house it will be from 30 to 50 thousand rubles. Next, you need to order a gasification project if it was not done at the previous stage.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Modern method - trenchless laying and repair:
How to quickly dig a trench:
More about trench pipe laying:
In order to establish an uninterrupted gas supply to the consumer, it is important to choose the right way to install the gas pipeline and carry out the work in accordance with regulatory requirements. For a private household, an underground pipe laying method is preferable, which guarantees maximum protection against accidental damage and third-party interference
If you have your own opinion on this issue, or can add valuable information to our material, please leave your comments in the block below. There you can also ask a question to our experts or participate in the discussion of the material.