- Versions
- lamellar
- With heat pipes
- Rotary
- Intermediate coolant
- What is recuperative ventilation
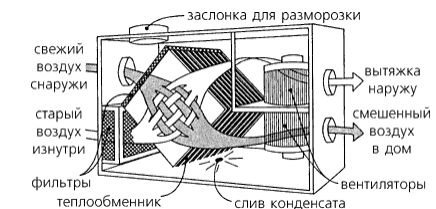
- The main elements of ventilation systems
- Specifications
- What are there?
- Spiral
- Rotary heat exchangers
- Plate heat exchanger
- Finned plate heat exchanger
- Industrial and domestic recuperators - what are the differences?
- The concept of recovery: the principle of operation of the heat exchanger
- Equipment installation procedure
- Control scheme
- Making an air recuperator for the home with your own hands
- Main technical parameters
- Efficiency
- Ventilation system performance
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Versions
How can a heat recovery ventilation system work? We list the main schemes with their brief description.
lamellar
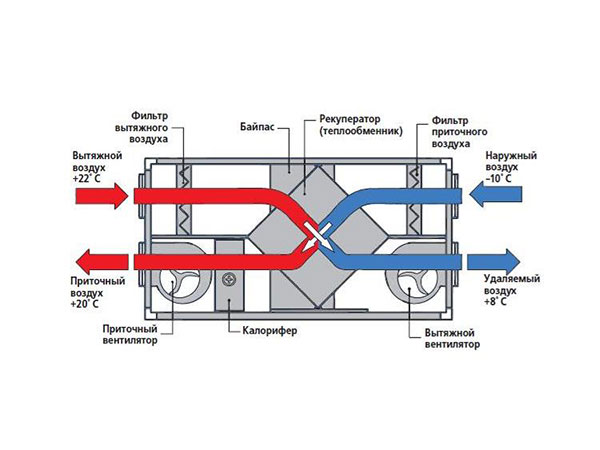
The exhaust and supply channels pass through a common housing, separated by a partition. The partition is pierced with heat exchanger plates - most often aluminum, less often copper.
Operation of a plate heat exchanger.
Heat is transferred between the channels due to the thermal conductivity of the plates. Obviously, in this case, the problem of condensate will rise to its full height. How is she resolved?
The heat exchanger is equipped with a simple icing sensor (usually thermal), on the signal from which the relay opens the bypass valve. Cold air from the street begins to flow bypassing the heat exchanger; warm flow in the exhaust channel quickly melts the ice on the surface of the plates.
This class of devices belongs to the lowest price category; the retail price depends almost linearly on the size of the duct. Here are the prices of the Ukrainian online store Rozetka at the time of writing:
| Model | Ventilation duct size | Price |
| Vents PR 160 | Diameter 160 mm | 20880 r. |
| PR 400x200 | 400x200 mm | 25060 r. |
| PR 600x300 | 600x300 mm | 47600 r. |
| PR 1000x500 | 1000x500 mm | 98300 r. |
With heat pipes
The recuperator device is completely identical to that described above. The only difference is that the heat exchanger plates do not penetrate the partition between the channels; they are pressed onto the heat pipes passing through the baffle.
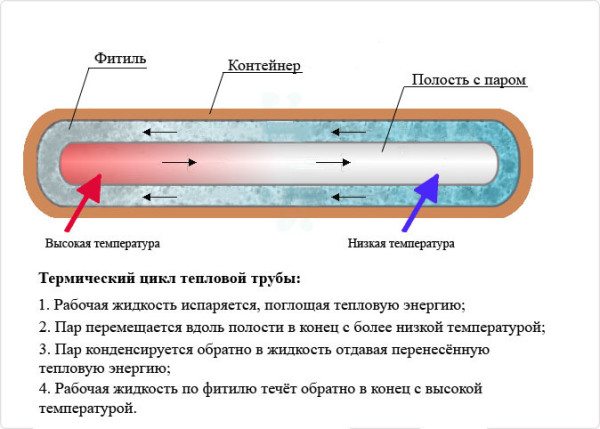
Heat pipe.
Thanks to the heat pipes, the parts of the heat exchanger can be separated by some distance.
Rotary
At the boundary between the supply and exhaust channels, a rotor with lamellar fins slowly rotates. Plates heated in one of the channels give off heat in the second channel.
Rotary recuperator.
What gives rotary heat recovery in ventilation systems in practical terms?
- Increase in efficiency from 40-50% typical for lamellar devices to 70-75%.
- Solving the problem of condensation. Moisture that has settled on the rotor plates in warm air is completely evaporated when heat is transferred to the cold air stream. At the same time, the problem of low humidity in winter is solved.
Alas, the scheme also has several drawbacks.
- Greater design complexity means reduced fault tolerance.
- For damp rooms, the rotary circuit is not suitable.
- The heat exchanger chambers are separated by a non-hermetic partition. If so, odors from the exhaust duct can enter the supply duct.
Intermediate coolant
For heat transfer, a classic water heating system with a circulation pump and convectors is used. The complexity and rather low efficiency (usually no more than 50%) justify themselves only in cases where the supply and exhaust channels are separated by a considerable distance due to the architectural features of the structure.
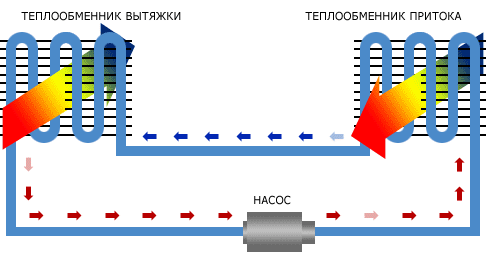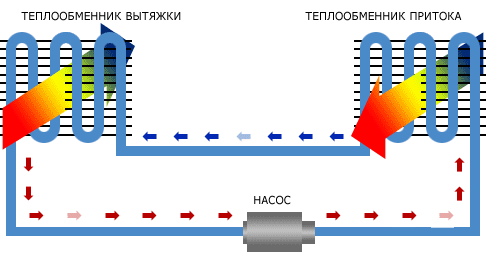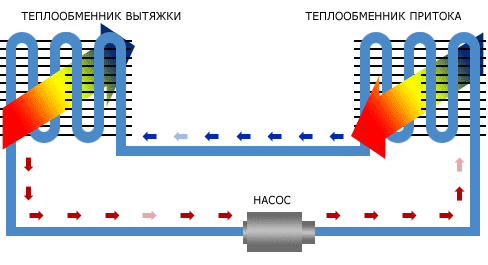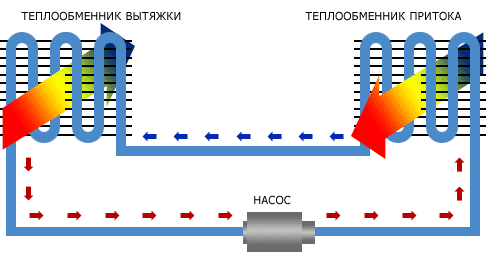
Scheme with a coolant.
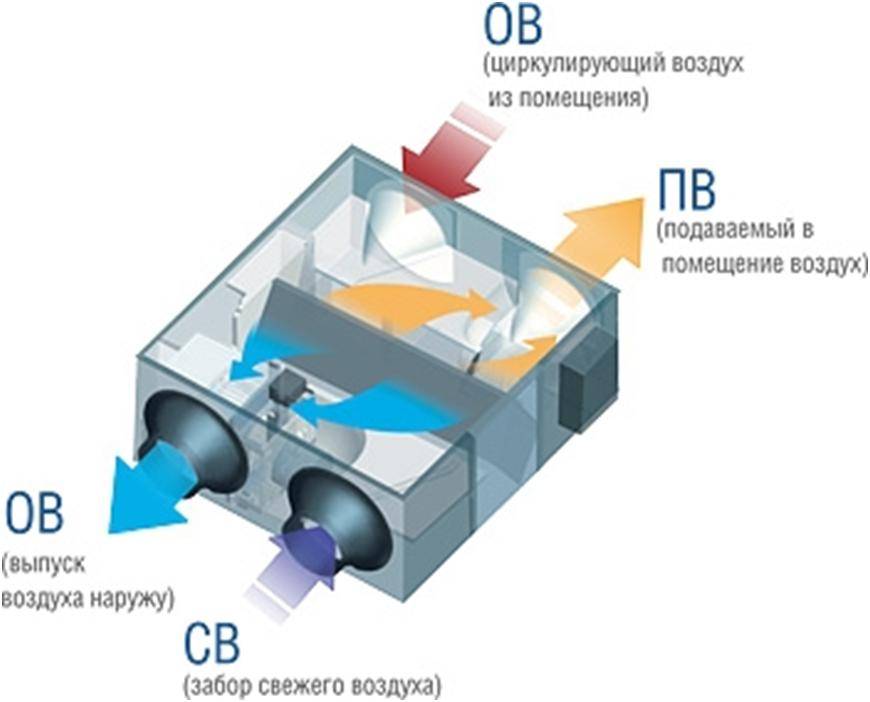
What is recuperative ventilation
Ventilation in the premises can be natural, the principle of which is based on natural phenomena (spontaneous type) or on air exchange provided by specially made openings in the building (organized ventilation). However, in this case, despite the minimum material costs, the dependence on the season, climate, and the lack of the ability to purify the air do not fully meet the needs of people.
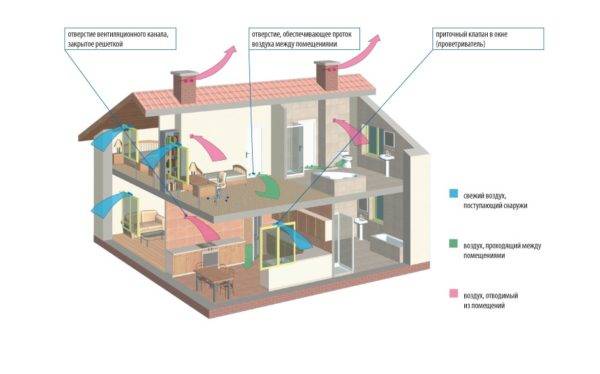 Supply and exhaust ventilation, air exchange
Supply and exhaust ventilation, air exchange
Artificial ventilation allows you to provide more comfortable conditions for those in the premises, but its installation requires certain financial investments. It is also quite energy intensive. To compensate for the pros and cons of both types of ventilation systems, their combination is most often used.
 Organization of air exchange
Organization of air exchange
Any artificial ventilation system according to its purpose is divided into supply or exhaust. In the first case, the equipment must provide forced air supply to the room. At the same time, the exhaust air masses are brought out in a natural way.
air ducts through which air moves;
fans responsible for its inflow;
sound absorbers;
filters;
air heaters that provide air supply of a certain temperature, which is especially important in the cold season.
Supply and exhaust ventilation
In addition to the above, the system can be equipped with additional modules to ensure a comfortable microclimate.
The exhaust system, which functions simultaneously with natural ventilation, is designed to remove exhaust air masses. The main component of such equipment is exhaust fans.
The best option for a ventilation device is supply and exhaust equipment, the installation of which helps to create the necessary conditions for people in the premises. Such a scheme is especially useful in buildings whose finishing materials do not have vapor permeability, which is not uncommon today.
 Supply and exhaust equipment
Supply and exhaust equipment
 Ventilation with supply and exhaust devices
Ventilation with supply and exhaust devices
 Ventilation system
Ventilation system
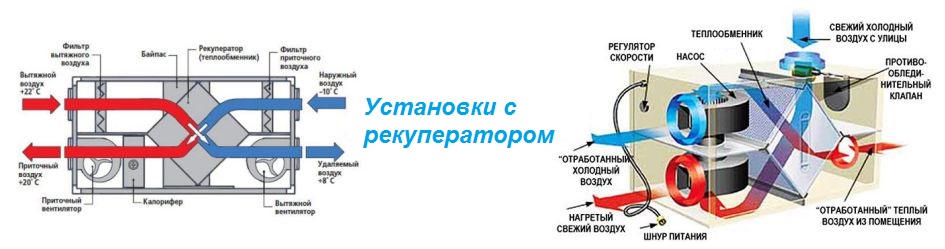
There is one significant drawback in the operation of the supply and exhaust ventilation - heated air is removed outside, and air masses that have the temperature of the external environment enter. For heating, a large amount of electricity is consumed (this is especially noticeable during the cold period). To reduce unjustified costs, recuperators are used.
Recuperation (in relation to ventilation) - the return of part of the thermal energy of the exhaust air in the room for use in the technological process. It can be used in centralized and local systems.
 Ventilation scheme
Ventilation scheme
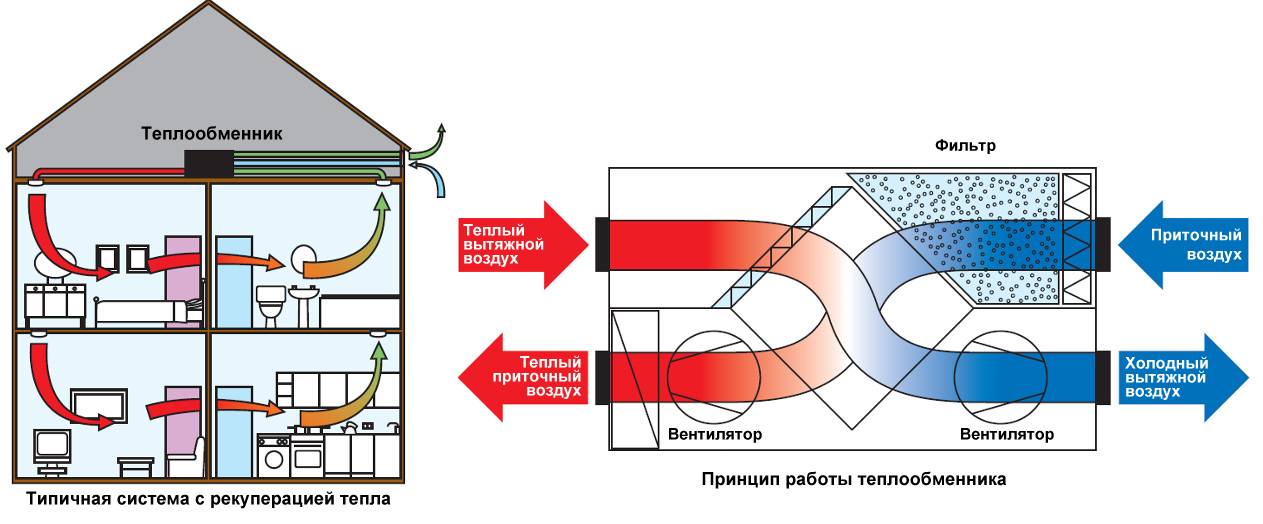
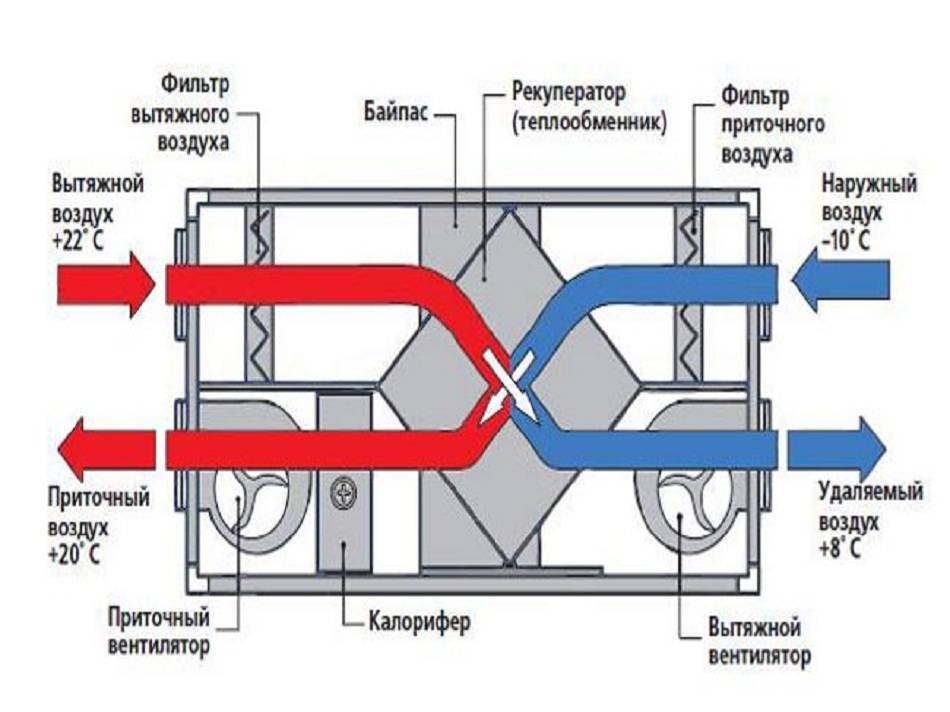
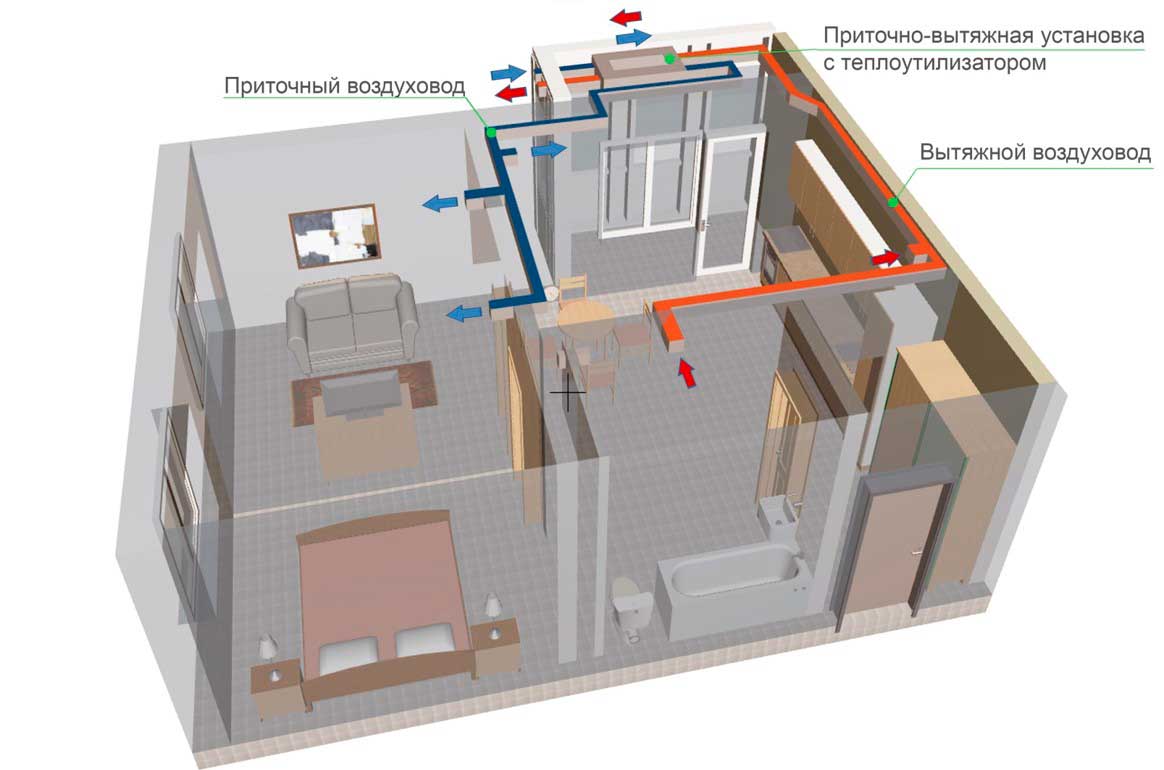
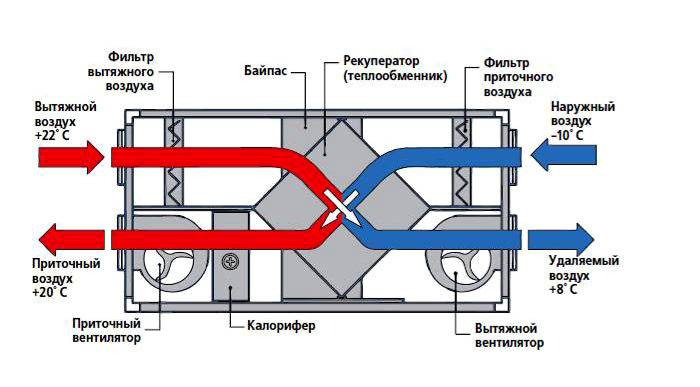
The recuperation process is carried out in special heat exchangers (recuperators), to which supply and exhaust channels are connected.The air masses taken out of the room, passing through the heat exchanger, give off part of the heat to the air coming from the street, but do not mix with it. Such a scheme can significantly reduce the cost of heating the supply air flow.
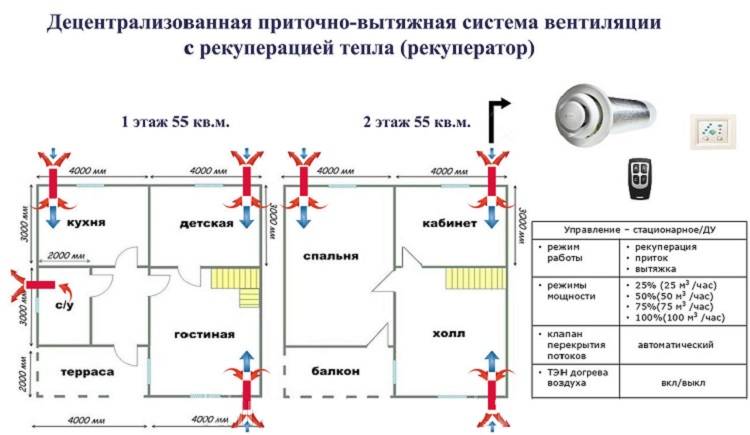
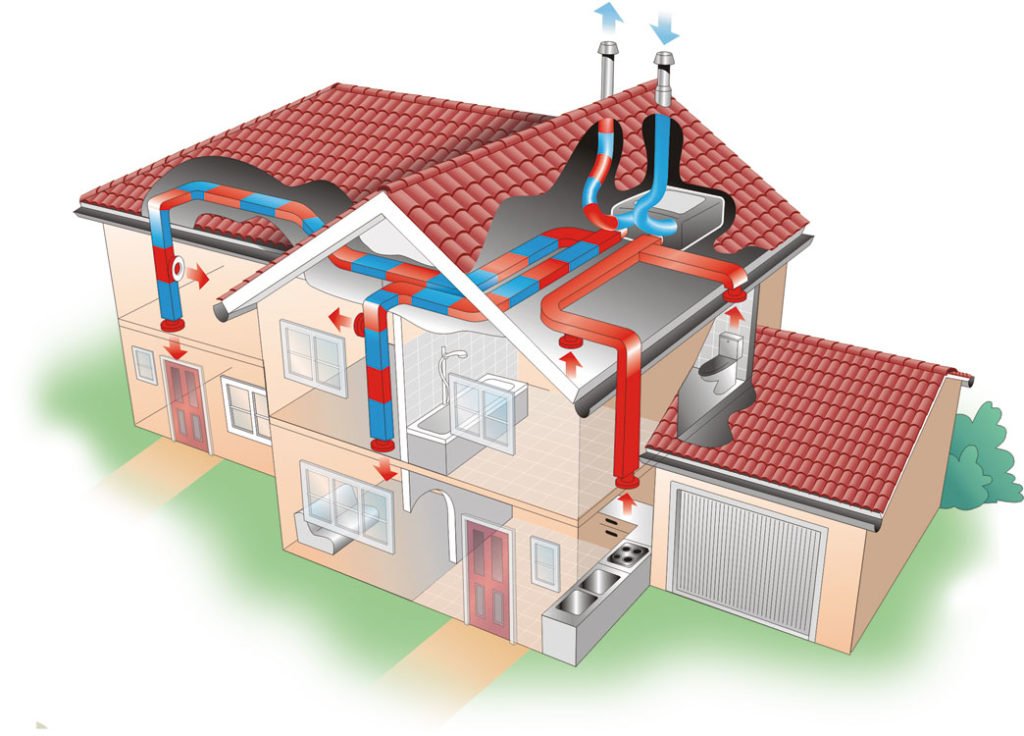
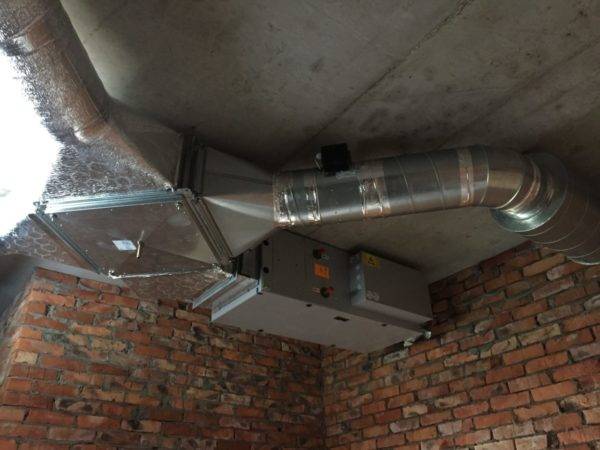
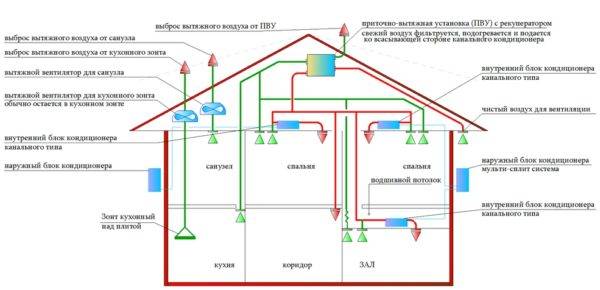
Recuperators can be installed on various parts of the building: ceilings, walls, floors or roofs. They can also be mounted outside the building. The equipment is either a monoblock or individual modules.
 Daikin HRV plus (VKM)
Daikin HRV plus (VKM)
When designing a ventilation system, many factors are taken into account:
- dimensions and number of rooms;
- the purpose of the building;
- air flow.
The efficiency of the installed system depends on this and on the type of recuperator chosen. Efficiency when using heat energy recovery can vary within 30 ... 90%. But even the installation of equipment characterized by minimal efficiency brings tangible benefits.
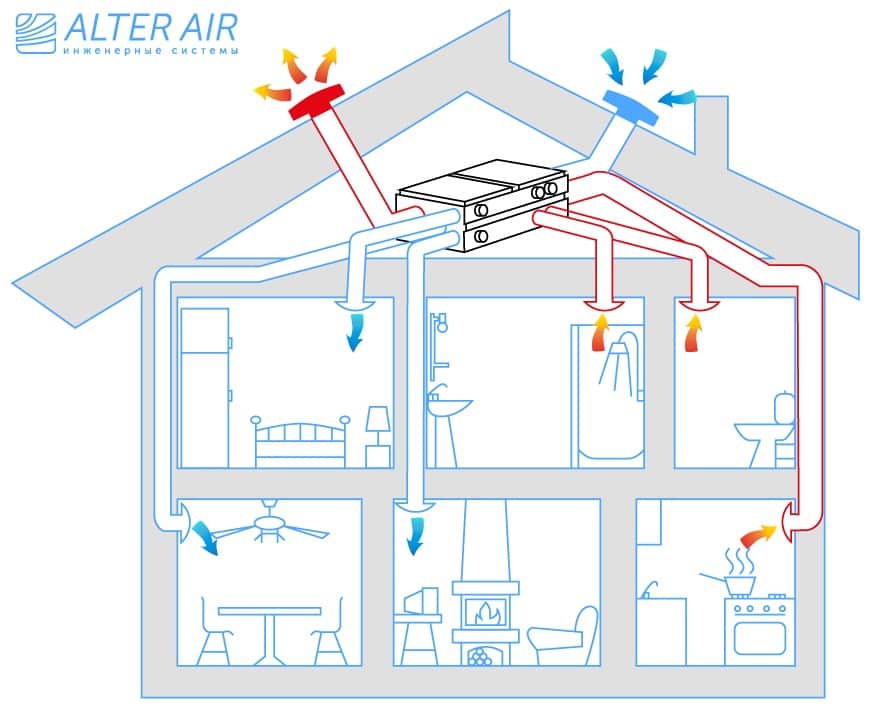
How is the circulation of air masses when installing supply and exhaust ventilation with a heat exchanger:
- with the help of air intakes, air is taken from the room and disposed of through the air ducts to the outside;
- before leaving the building, the air flow passes through the heat exchanger (heat exchanger), leaving part of the thermal energy there;
- through the same heat exchanger, cold air is sent from outside, which is heated by heat and supplied to the room.
 Recuperator
Recuperator
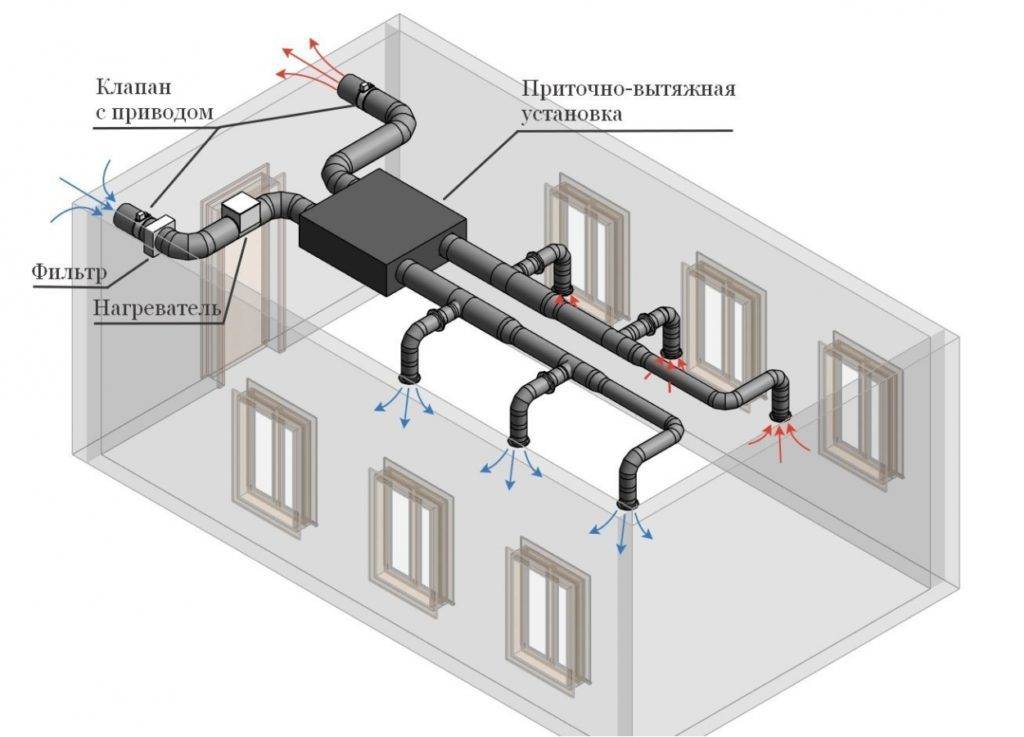
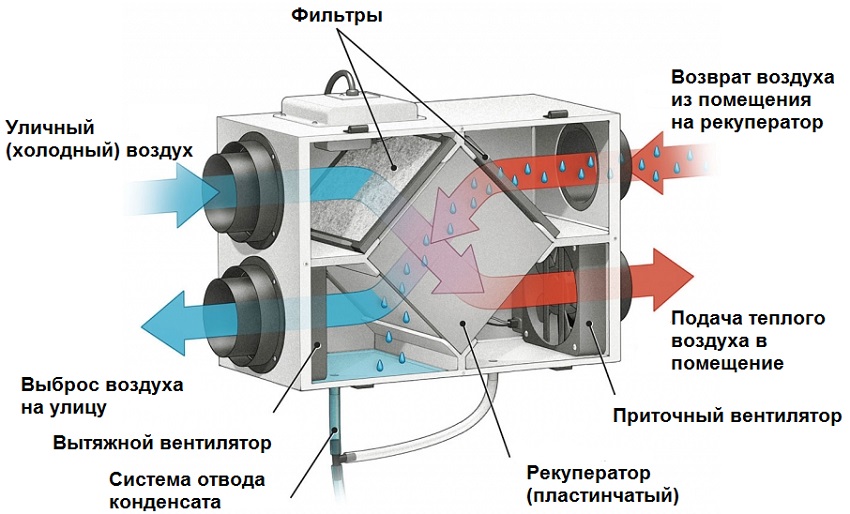
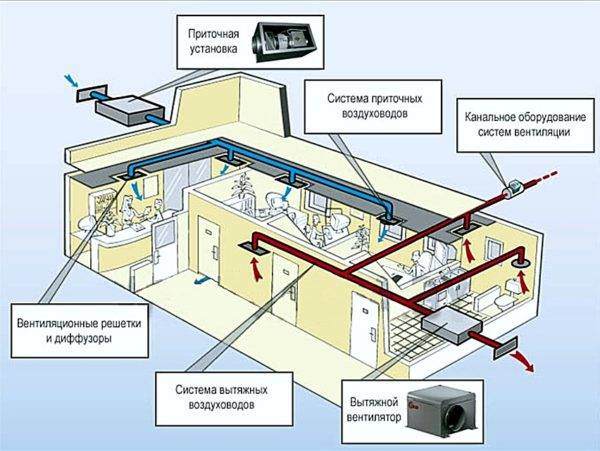
The main elements of ventilation systems
 Recuperator in the ventilation system
Recuperator in the ventilation system
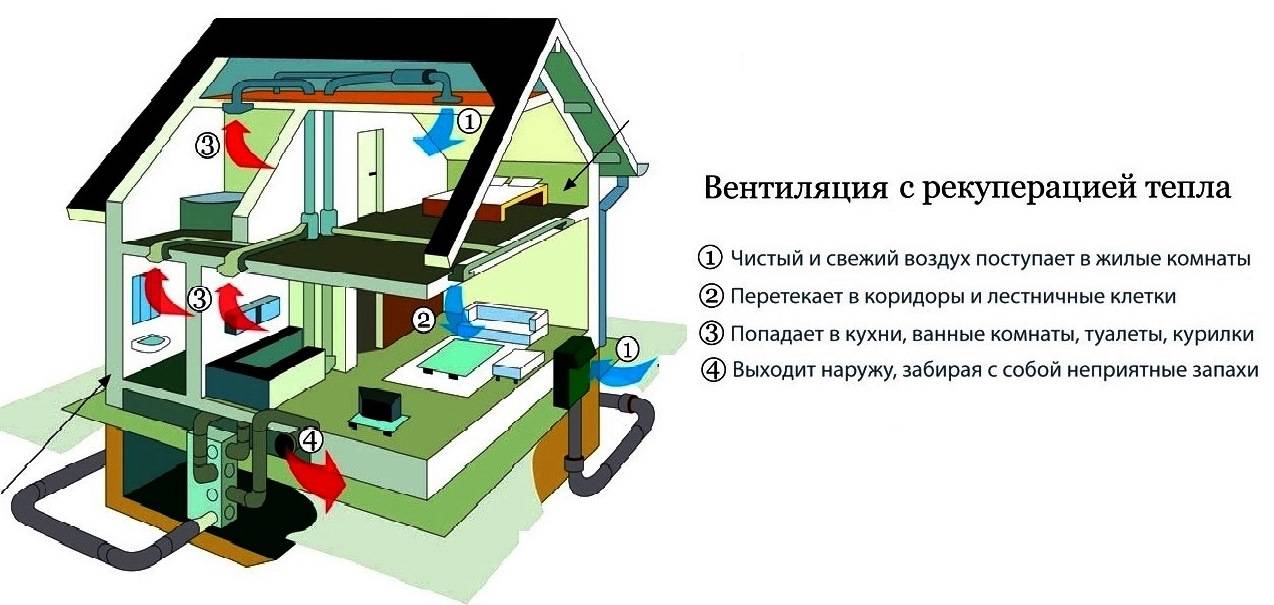
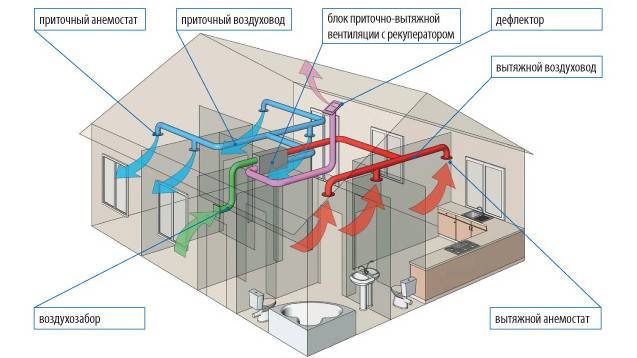
Ventilation with heat recovery in a private house consists not only of a heat exchanger unit.
The system includes:
- protective grilles;
- air ducts;
- valves;
- fans;
- filters.
- automation and control bodies.
The grids protect against accidental entry into the system of large objects, birds and rodents, which can cause accidents. This option is possible when a foreign object falls on the fan impeller. The consequence may be:
- deformed blades and increased vibration (noise);
- jamming of the fan rotor and combustion of the motor windings;
- an unpleasant odor from dead and decaying animals.
Air ducts and fittings (turns, tees, adapters) are bought at the same time, they try to purchase products from the same manufacturer. The difference in size leads to gaps at the joints, disruption of flow and turbulence.
 In severe frost, you can close the supply valve temporarily
In severe frost, you can close the supply valve temporarily
Do not use corrugated air ducts for ventilation with a heat exchanger, which create resistance to air flows and increased noise during operation.
Air valves are needed to temporarily change the parameters of air movement, for example, they can be used to close the inlet channel in a particularly frosty period of time when the heat exchanger cannot cope with heating the air to the required temperature.
Filters are installed in all models of ventilation with recuperation. They protect the equipment from street dust and tree fluff, which quickly clog the heat exchangers.
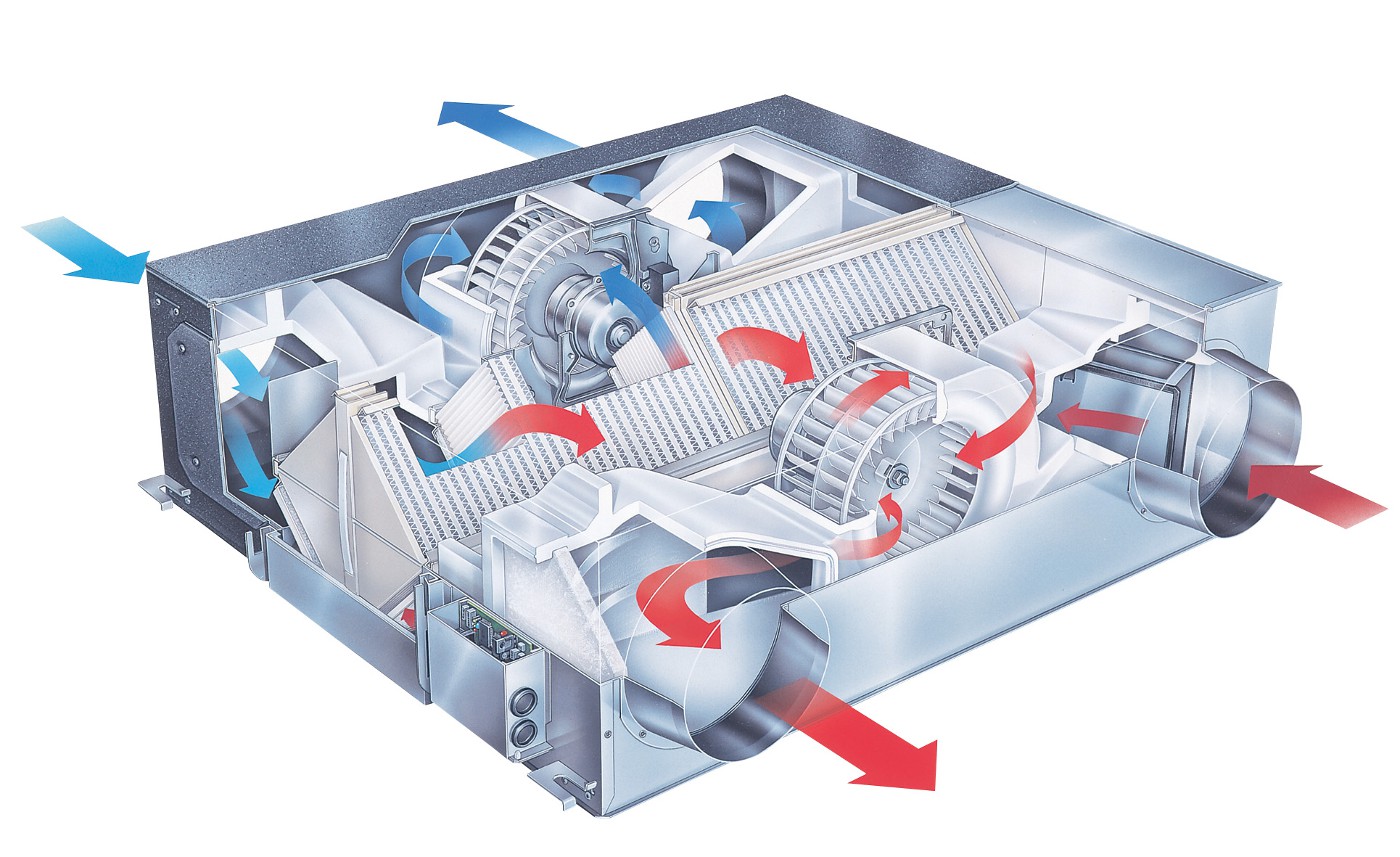
Fans can be built into the heat exchanger unit or installed in ducts. When calculating, it is necessary to determine the required power of the device.
Specifications
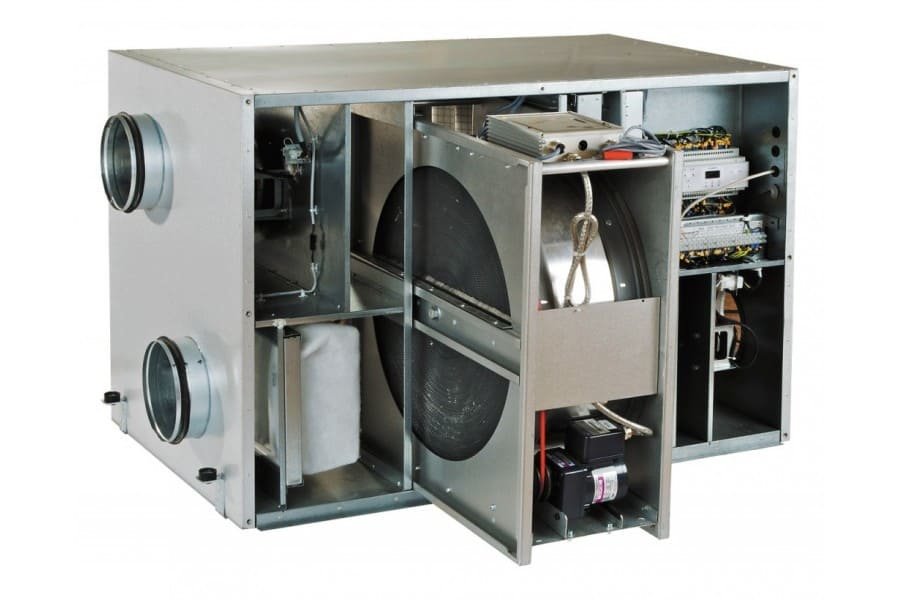
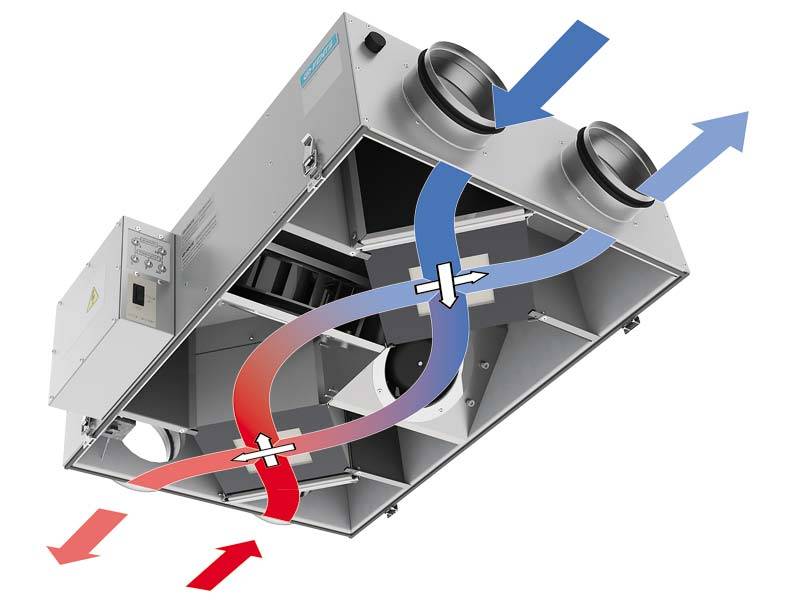
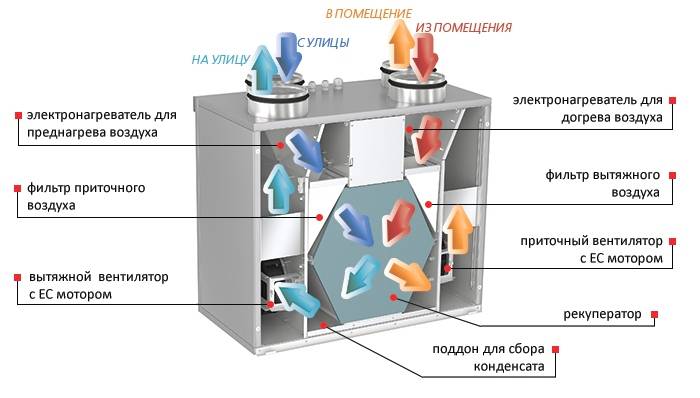
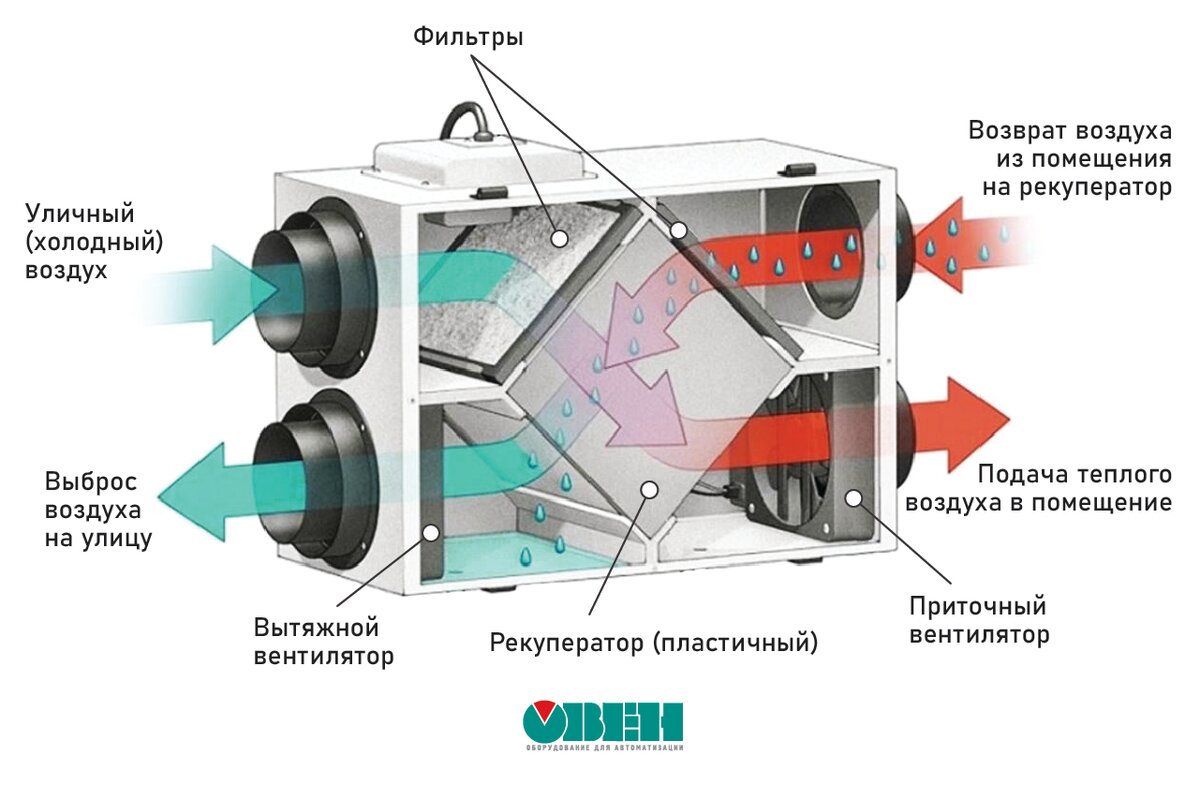
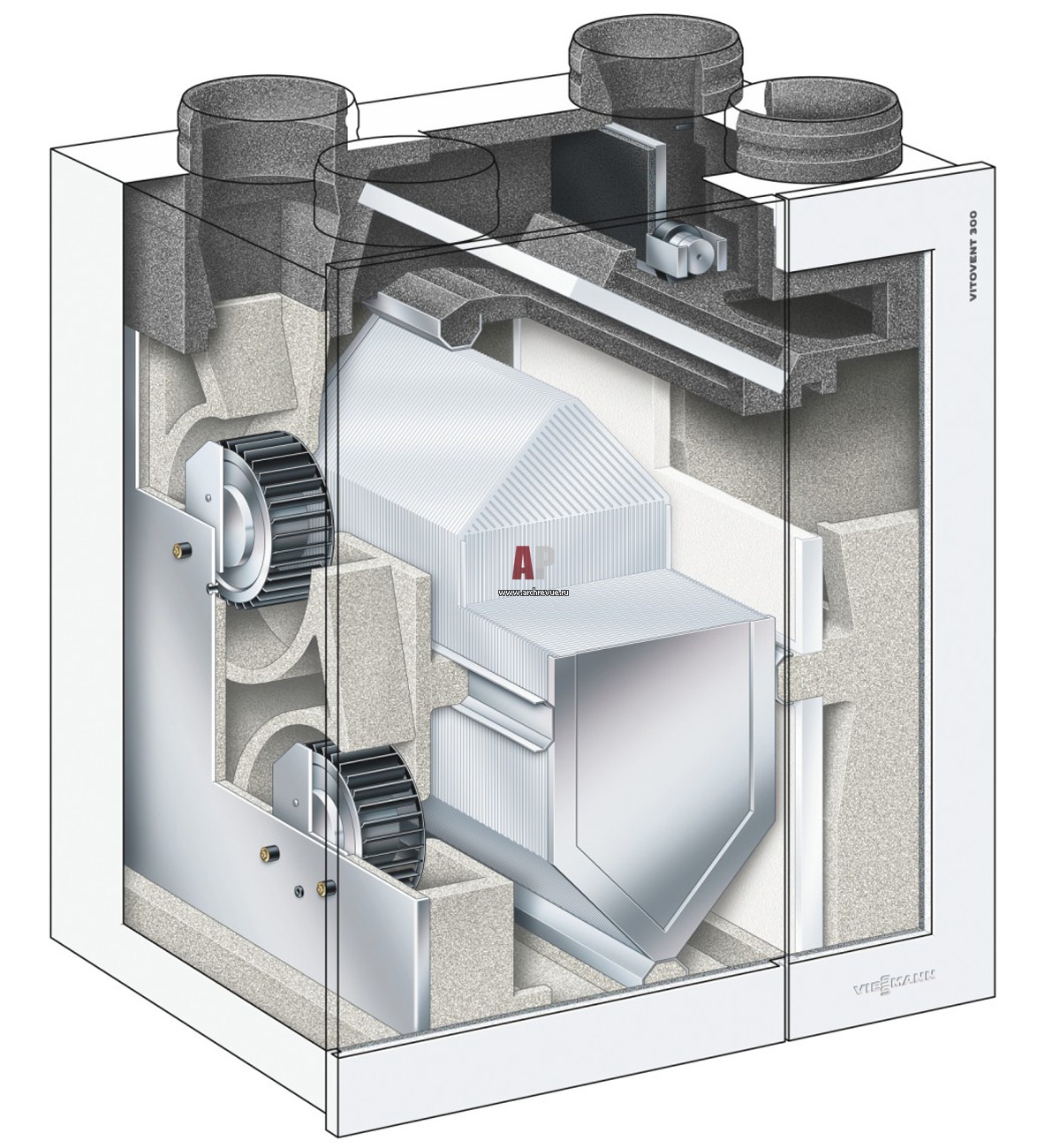
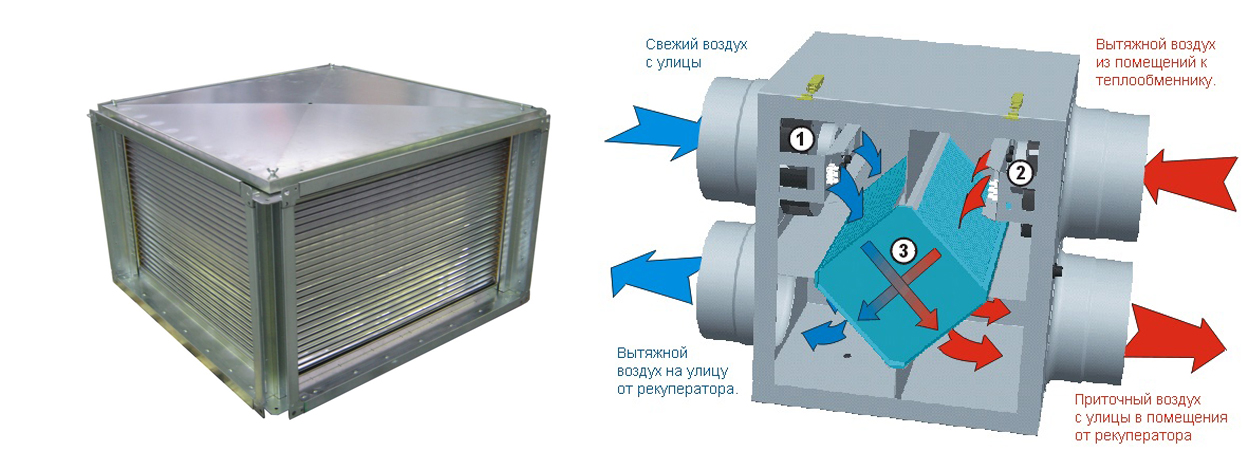
The heat recuperator consists of a housing, which is covered with heat and noise insulating materials and is made of sheet steel.The case of the device is strong enough and able to withstand weight and vibration loads. There are inflow and outflow openings on the case, and air movement through the device is provided by two fans, usually of axial or centrifugal type. The need for their installation is due to a significant slowdown in the natural circulation of air, which is caused by the high aerodynamic resistance of the heat exchanger. In order to prevent the suction of fallen leaves, small birds or mechanical debris, an air intake grille is installed on the inlet located on the street side. The same hole, but from the side of the room, is also equipped with a grill or diffuser that evenly distributes air flows. When installing branched systems, air ducts are mounted to the holes.
In addition, the inlets of both streams are equipped with fine filters that protect the system from dust and grease drops. This prevents the heat exchanger channels from clogging and significantly extends the life of the equipment. However, the installation of filters is complicated by the need for constant monitoring of their condition, cleaning, and, if necessary, replacing them. Otherwise, a clogged filter will act as a natural barrier to air flow, as a result of which the resistance to them will increase and the fan will break.
In addition to fans and filters, recuperators include heating elements, which can be water or electric. Each heater is equipped with a temperature switch and is able to automatically turn on if the heat leaving the house cannot cope with the heating of the incoming air.The power of the heaters is selected in strict accordance with the volume of the room and the operating performance of the ventilation system. However, in some devices, the heating elements only protect the heat exchanger from freezing and do not affect the temperature of the incoming air.
Water heater elements are more economical. This is due to the fact that the coolant, which moves through the copper coil, enters it from the heating system of the house. From the coil, the plates are heated, which, in turn, give off heat to the air flow. The water heater regulation system is represented by a three-way valve that opens and closes the water supply, a throttle valve that reduces or increases its speed, and a mixing unit that regulates the temperature. Water heaters are installed in a system of air ducts with a rectangular or square section.
Electric heaters are often installed on air ducts with a circular cross section, and a spiral acts as a heating element. For the correct and efficient operation of the spiral heater, the air flow velocity must be greater than or equal to 2 m/s, the air temperature must be 0-30 degrees, and the humidity of the passing masses must not exceed 80%. All electric heaters are equipped with an operation timer and a thermal relay that turns off the device in case of overheating.
In addition to the standard set of elements, at the request of the consumer, air ionizers and humidifiers are installed in the recuperators, and the most modern samples are equipped with an electronic control unit and a function for programming the operating mode, depending on external and internal conditions.Dashboards have an aesthetic appearance, allowing the heat exchangers to organically fit into the ventilation system and not disturb the harmony of the room.
What are there?

Units are divided into the following types:
- By type of construction - shell-and-tube, spiral, rotary, lamellar, lamellar finned.
- By appointment - air, gas, liquid. The air unit is understood as a ventilation unit, the task of which is ventilation with heat recovery. In gas-type appliances, smoke is used as a heat carrier. Liquid recuperators - spiral and coil - are often installed in swimming pools.
- According to the temperature of the coolant - high-temperature, medium-temperature, low-temperature. Heat exchangers are called high-temperature heat exchangers, the heat carriers of which reach 600C and above. Medium temperature - these are devices with coolant characteristics in the region of 300-600C. The temperature of the coolant of the low-temperature unit is below 300C.
- According to the method of media movement - direct-flow, counter-flow, cross-flow. They differ depending on the direction of air flow. In cross-flow units, the flows are perpendicular to each other, in counter-flow units, the inflow and exhaust are opposite to each other, and in direct-flow units, the flows are unidirectional and parallel.
Spiral
In spiral models, heat exchangers look like two spiral channels through which media move. Made from rolled material, they are wound around a dividing wall located in the center.
Rotary heat exchangers
Are established in forced-air and exhaust ventilating systems.The way they operate is based on the passage of supply and exhaust flows through a special rotary heat exchanger of a rotating type.
Plate heat exchanger
It is a heat exchanger where heat is transferred from a hot medium to a cold one by passing through steel, graphite, titanium and copper plates.
Finned plate heat exchanger
Its design is based on thin-walled panels with a ribbed surface, produced using high-frequency welding and connected to each other in turn with a turn of 90. Such a design, as well as a variety of materials used, allows achieving a high temperature of the heating medium, minimum resistance, long service life, high indicators of heat transfer area in relation to the total mass of the heat exchanger. In addition, such devices are inexpensive and are most often used for processing heat from exhaust gas media.
The popularity of ribbed models is based on the following advantages (in comparison with analogues of the rotary and traditional plastic type):
- high operating temperatures (up to 1250C);
- small weight and size;
- more budgetary;
- quick payback;
- low resistance along gas-air paths;
- resistance to slagging;
- ease of cleaning channels from pollution;
- long service life;
- simplified installation and transportation;
- high rates of thermoplasticity.
Industrial and domestic recuperators - what are the differences?

Industrial units are used in industries where there are thermal technological processes.Most often, industrial means precisely traditional plate heat exchangers.
Domestic devices include devices characterized by small dimensions and low productivity. These can be supply and exhaust models, the main task of which is ventilation with heat recovery. Such systems can be implemented in different ways - both in the form of a rotary and in the form of a plate heat exchanger. And each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Next, consider the main selection criteria in order to understand which recuperator is better to buy.
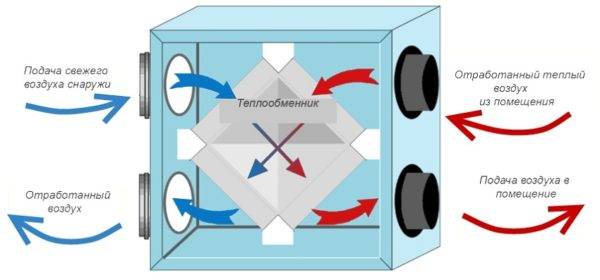
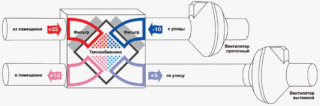
The concept of recovery: the principle of operation of the heat exchanger
Translated from Latin, recuperation means reimbursement or return receipt. With regard to heat exchange reactions, recovery is characterized as a partial return of energy expended on a technological action for the purpose of using it in the same process. In the ventilation system, the principle of recuperation is used to save thermal energy.
By analogy, cooling is recuperated in hot weather - warm supply masses heat the output "working out" and their temperature decreases.
Part of the heat is taken from the exhaust air drawn out to the outside and transferred to the forced fresh jets directed inside the room. This reduces heat loss by up to 70%.
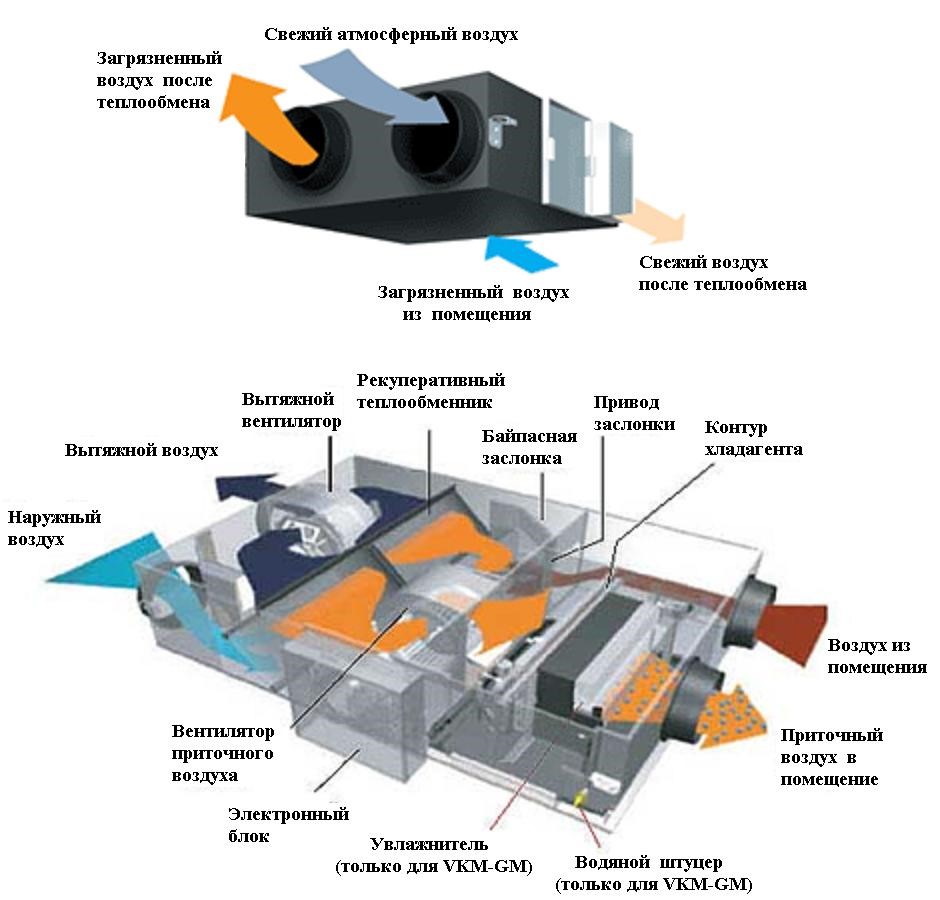
The process of energy recovery is carried out in a recuperative heat exchanger. The device provides for the presence of a heat exchange element and fans for pumping multidirectional air flows. An automation system is used to control the process and control the quality of the air supply.
The design is designed so that the supply and exhaust flows are in separate compartments and do not mix - heat recovery is carried out through the walls of the heat exchanger.
A visual diagram of air circulation will help to understand and understand what ventilation with recuperation is.
Exhaust air is exhausted through hoods in wet rooms (toilet, bathroom, kitchen). Before it goes outside, it passes through the heat exchanger and leaves some of the heat. The supplied air moves in the opposite direction, heats up and enters the living rooms
Equipment installation procedure
Installation of elements of equipment for the supply and exhaust ventilation system of premises is carried out after finishing the walls, before the installation of suspended ceiling panels. The equipment of the ventilation system is installed in a certain order:
- The intake valve is installed first.
- After it - the filter for cleaning the incoming air.
- Then an electric heater.
- Heat exchanger - recuperator.
- Air duct cooling system.
- If necessary, the system is equipped with a humidifier and a fan in the supply duct.
- If the ventilation is of high power, then a noise isolating device is installed.
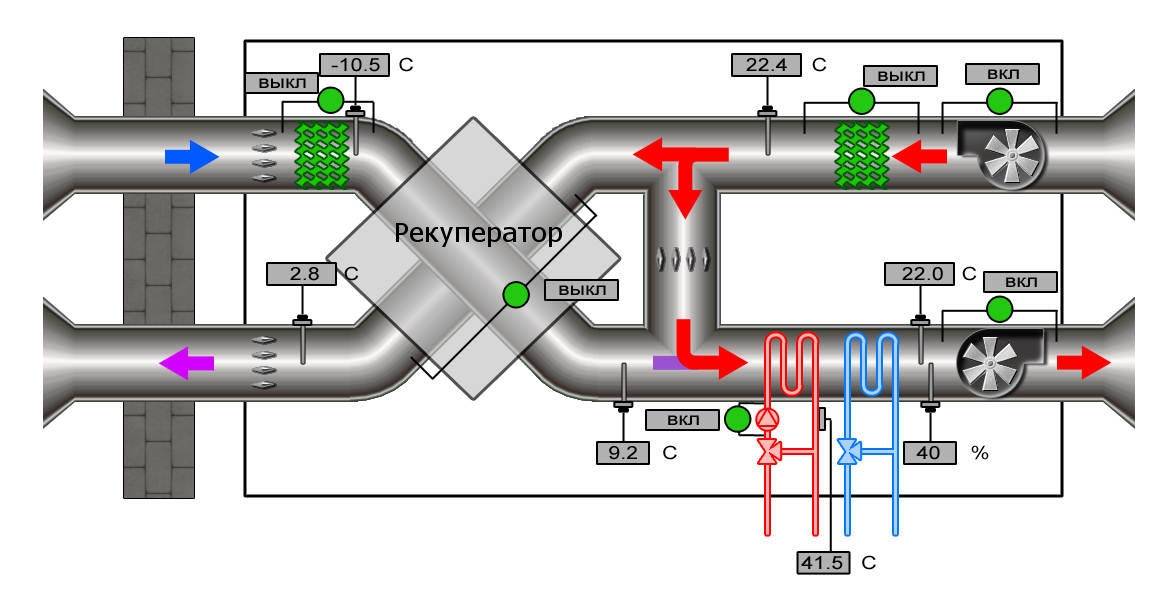
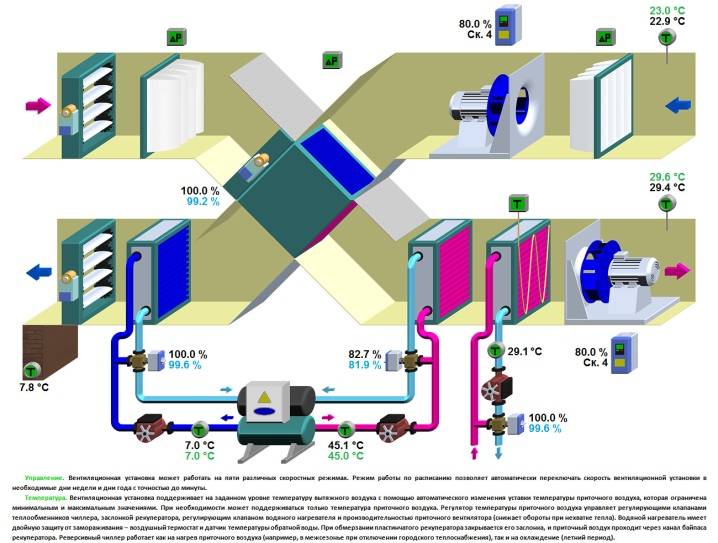
Control scheme
All components of the air handling unit must be properly integrated into the system of operation of the unit, and perform their functions in the proper amount. The task of controlling the operation of all components is solved by an automated process control system. The installation kit includes sensors, analyzing their data, the control system corrects the operation of the necessary elements.The control system allows you to smoothly and competently fulfill the goals and tasks of the air handling unit, solving complex problems of interaction between all elements of the unit.
Ventilation control panelDespite the complexity of the process control system, the development of technology makes it possible to provide an ordinary person with a control panel from the unit in such a way that from the first touch it is clear and pleasant to use the unit throughout its service life.
Example. Heat Recovery Efficiency Calculation: Calculates the efficiency of using a heat recovery heat exchanger compared to using only an electric or only water heater.
Consider a ventilation system with a flow rate of 500 m3/h. Calculations will be carried out for the heating season in Moscow. From SNiPa 23-01-99 "Construction climatology and geophysics" it is known that the duration of the period with an average daily air temperature below +8°C is 214 days, the average temperature of the period with an average daily temperature below +8°C is -3.1°C .
Calculate the required average heat output: In order to heat the air from the street to a comfortable temperature of 20°C, you will need:
N=G*Cp *p(in-ha) *(text-tWed )= 500/3600 * 1.005 * 1.247 * = 4.021 kW
This amount of heat per unit of time can be transferred to the supply air in several ways:
- Supply air heating by an electric heater;
- Heating of the supply heat carrier removed through the heat exchanger, with additional heating by an electric heater;
- Heating of outdoor air in a water heat exchanger, etc.
Calculation 1: Heat is transferred to the supply air by means of an electric heater.The cost of electricity in Moscow S=5.2 rubles/(kW*h). Ventilation works around the clock, for 214 days of the heating period, the amount of money, in this case, will be equal to:1\u003d S * 24 * N * n \u003d 5.2 * 24 * 4.021 * 214 \u003d 107,389.6 rubles / (heating period)
Calculation 2: Modern recuperators transfer heat with high efficiency. Let the recuperator heat the air by 60% of the required heat per unit time. Then the electric heater needs to spend the following amount of power: N(el.load) = Q - Qrivers \u003d 4.021 - 0.6 * 4.021 \u003d 1.61 kW
Provided that the ventilation will work for the entire period of the heating period, we get the amount for electricity:2 = S * 24 * N(el.load) * n = 5.2 * 24 * 1.61 * 214 = 42,998.6 rubles / (heating period) Calculation 3: A water heater is used to heat outdoor air. Estimated cost of heat from technical hot water per 1 Gcal in Moscow: Sg.w.\u003d 1500 rubles / gcal. Kcal \u003d 4.184 kJ For heating, we need the following amount of heat: Q(GV) = N * 214 * 24 * 3600 / (4.184 * 106) = 4.021 * 214 * 24 * 3600 / (4.184 * 106) = 17.75 Gcal :C3 = S(GV) *Q(GV) \u003d 1500 * 17.75 \u003d 26,625 rubles / (heating period)
The results of calculating the costs of heating the supply air for the heating period of the year:
| Electric heater | Electric heater + recuperator | Water heater |
|---|---|---|
| RUB 107,389.6 | RUB 42,998.6 | 26 625 rubles |
From the above calculations, it can be seen that the most economical option is to use the hot service water circuit.In addition, the amount of money required to heat the supply air is significantly reduced when using a recuperative heat exchanger in the supply and exhaust ventilation system in comparison with using an electric heater. air, which allows to reduce the energy costs for heating the supply air, therefore, the cash costs for the operation of the ventilation system are reduced. The use of the heat of the removed air is a modern energy-saving technology and allows you to get closer to the "smart home" model, in which any available type of energy is used to the fullest and most useful.
Get a free consultation with a heat recovery ventilation engineer
Get!
Making an air recuperator for the home with your own hands
A simple plate heat exchanger can be made by hand.
For work you need to prepare:
- four square meters of sheet material: iron, copper, aluminum or textolite;
- plastic flanges;
- a box made of tin or plywood, MDF;
- sealant and mineral wool;
- corners and hardware;
- cork sheets on an adhesive basis.
Heat exchanger device
Sequencing:
- From sheet material, you need to make square plates measuring 200 by 300 millimeters. In total, seven dozen blanks will be required. The main thing at this stage is accuracy and exact observance of the parameters.
- A cork coating is glued to the blanks on one side. One blank remains uncoated.
- The blanks are assembled into a cassette, turning each subsequent ninety degrees. The plates are held together with glue. The uncoated plate is the last one.
- The cassette needs to be fastened with a frame, for this a corner is used.
- All joints are carefully treated with silicone.
- Flanges are attached to the sides of the cassette, a drainage hole is drilled at the bottom and a tube is inserted to remove moisture.
- So that the device can be periodically removed, guides for the corners are made on the walls of the case.
- The resulting device is inserted into the housing, the walls of which are insulated with mineral wool material.
- It remains only to insert the air exchanger into the ventilation system.
Main technical parameters
Knowing the required performance of the ventilation system and the heat exchange efficiency of the heat exchanger, it is easy to calculate the savings on air heating for a room under specific climatic conditions. By comparing the potential benefits with the costs of purchasing and maintaining the system, you can reasonably make a choice in favor of a heat exchanger or a standard heater.
Often, equipment manufacturers offer a model line in which ventilation units with similar functionality differ in air exchange volume. For residential premises, this parameter must be calculated according to Table 9.1. SP 54.13330.2016
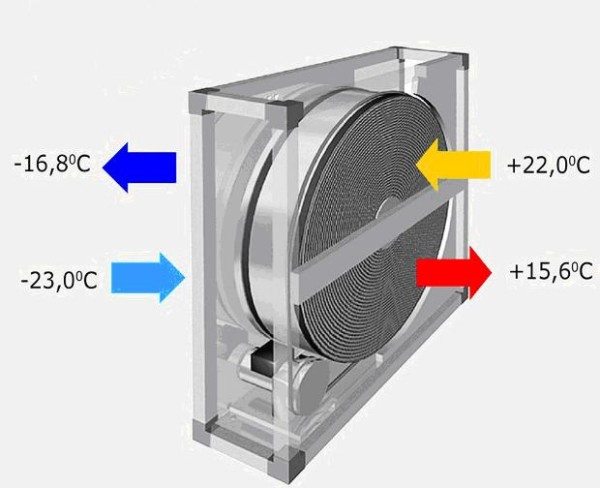
Efficiency
Under the efficiency of the heat exchanger understand the efficiency of heat transfer, which is calculated by the following formula:
K = (TP - Tn) / (Tin - Tn)
Wherein:
- TP - the temperature of the incoming air inside the room;
- Tn – outdoor air temperature;
- Tin - the air temperature in the room.
The maximum efficiency value at a nominal air flow rate and a certain temperature regime is indicated in the technical documentation of the device. His real figure will be slightly less. In the case of self-manufacturing of a plate or tube heat exchanger, in order to achieve maximum heat transfer efficiency, it is necessary to adhere to the following rules:
- The best heat transfer is provided by countercurrent devices, then by cross-flow devices, and the smallest - with unidirectional movement of both flows.
- The intensity of heat transfer depends on the material and thickness of the walls separating the flows, as well as on the duration of the presence of air inside the device.
Knowing the efficiency of the heat exchanger, it is possible to calculate its energy efficiency at various outdoor and indoor air temperatures:
E (W) \u003d 0.36 x P x K x (Tin - Tn)
where Р (m3/h) – air consumption.
The calculation of the efficiency of the heat exchanger in monetary terms and comparison with the costs of its purchase and installation for a two-story cottage with a total area of 270 m2 shows the feasibility of installing such a system
The cost of recuperators with high efficiency is quite high, they have a complex design and large dimensions. It is sometimes possible to circumvent these problems by installing several simpler devices in such a way that the incoming air passes through them in series.
Ventilation system performance
The volume of air passed through is determined by the static pressure, which depends on the power of the fan and the main components that create aerodynamic resistance.As a rule, its exact calculation is impossible due to the complexity of the mathematical model, therefore, experimental studies are carried out for typical monoblock structures, and components are selected for individual devices.
The fan power must be selected taking into account the throughput of any type of heat exchangers installed, which is indicated in the technical documentation as the recommended flow rate or the amount of air passed by the device per unit of time. As a rule, the permissible air velocity inside the device does not exceed 2 m/s.
Otherwise, at high speeds, a sharp increase in aerodynamic resistance occurs in the narrow elements of the recuperator. This leads to unnecessary energy costs, inefficient heating of the outside air and a shortened life of the fans.
The graph of dependence of pressure loss on air flow rate for several models of high-performance heat exchangers shows a non-linear increase in resistance, therefore, it is necessary to adhere to the requirements for the recommended air exchange volume indicated in the technical documentation of the device
Changing the direction of the air flow creates additional aerodynamic drag. Therefore, when modeling the geometry of an indoor air duct, it is desirable to minimize the number of pipe turns by 90 degrees. Diffusers to disperse air also increase resistance, so it is advisable not to use elements with a complex pattern.
Dirty filters and gratings create significant flow problems and must be cleaned or replaced periodically.One of the effective ways to assess clogging is to install sensors that monitor the pressure drop in the areas before and after the filter.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Comparison of the operation of natural ventilation and a forced system with recuperation:
The principle of operation of a centralized heat exchanger, calculation of efficiency:
The device and operation of a decentralized heat exchanger using the Prana wall valve as an example:
About 25-35% of the heat leaves the room through the ventilation system. To reduce losses and efficient heat recovery, recuperators are used. Climatic equipment allows you to use the energy of the waste masses to heat the incoming air.
Do you have something to add, or do you have questions about the operation of various ventilation recuperators? Please leave comments on the publication, share your experience in operating such installations. The contact form is in the bottom block.