- Natural exhaust ventilation
- The main characteristics of domestic air handling units
- PES performance by air
- Noise level generated by a working air handling unit
- Air heater power
- Natural ventilation in the house
- How can efficiency be improved?
- What are the regulations for ventilation systems
- Tips for arranging natural ventilation
- in the bathroom
- In the bath
- In the boiler room
- In living rooms
- In the kitchen
- Ventilation created artificially (mechanical) in production
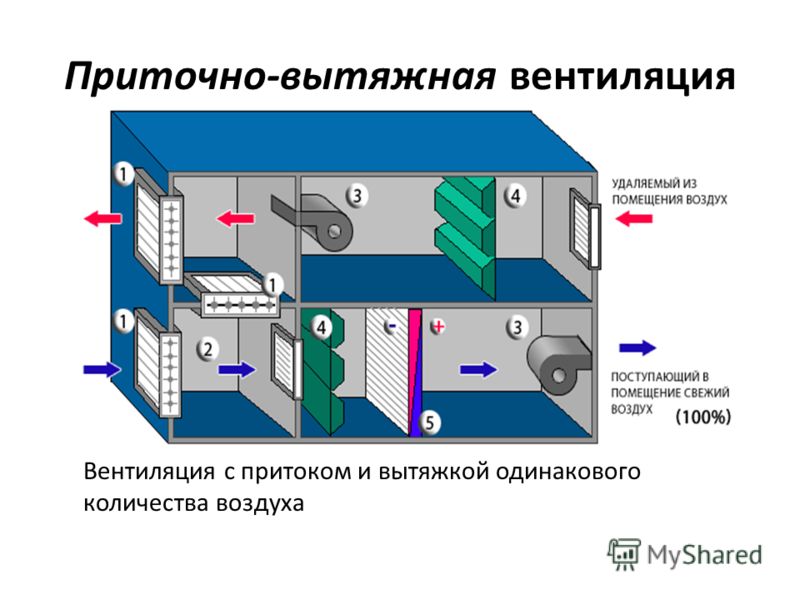
- Supply and exhaust natural ventilation in the room
- Types of systems
- Units for local exhaust system
- The physical basis of the ventilation system
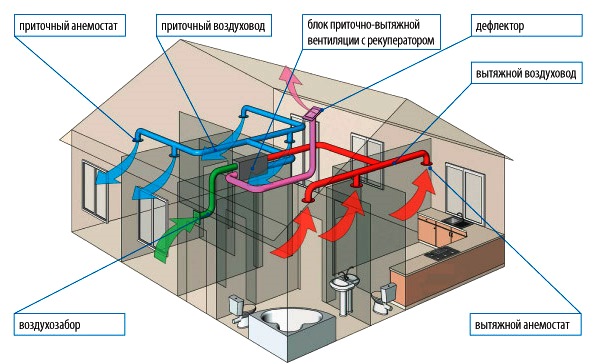
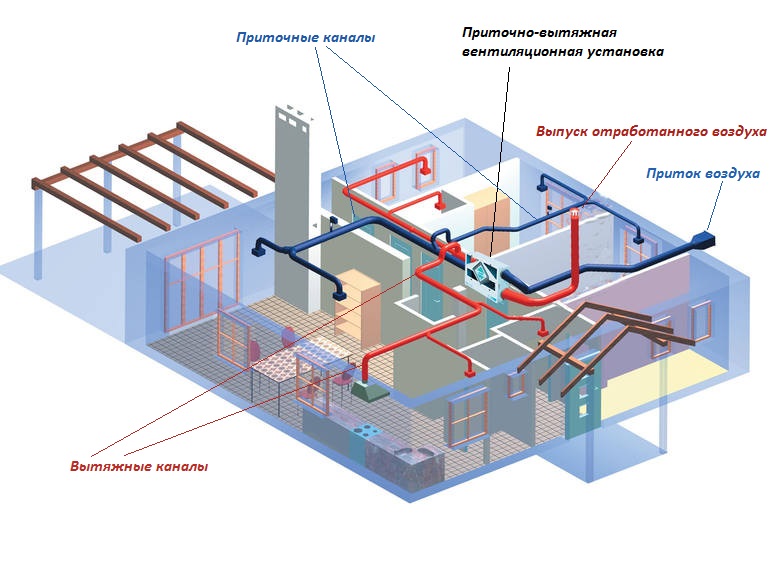
- Supply and exhaust system device
- Supply ventilation units: main components and principle of operation
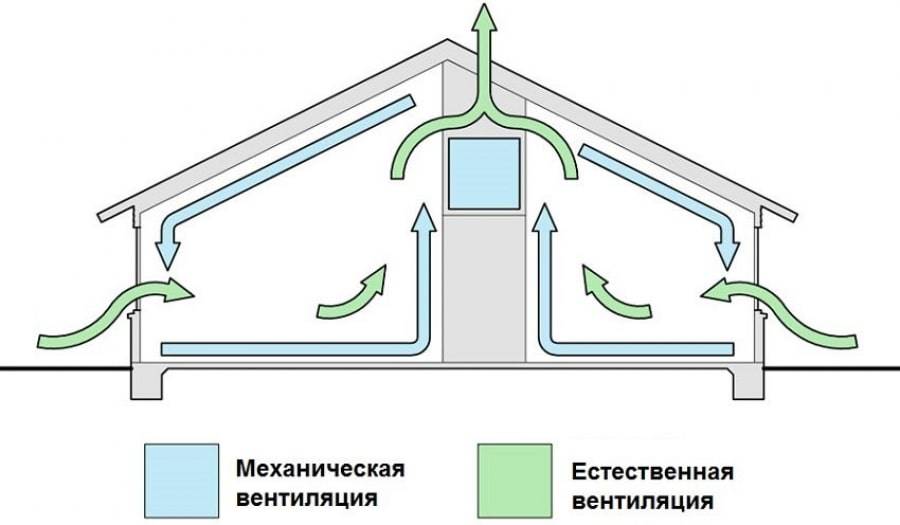
Natural exhaust ventilation
The exhaust system may be part of a complex responsible for the natural circulation of air. The process of mass exchange in it is based on the difference between external and internal parameters of temperature, pressure, it works from gusts of wind. All these physical phenomena are circulation engines. The influence of weather on the functioning is a disadvantage of such designs. So in summer there is no air exchange. After all, the temperature is the same indoors and outdoors.In winter, there is a big difference between these indicators. Cold air comes in from outside, the heating of which loads the heating at a high cost.
Efficiency can be increased by opening the windows, making gaps under the doors. In residential buildings, air ducts are located in kitchens and bathrooms. In general, natural exhaust ventilation is practically uncontrollable. It should be noted many "advantages" of such systems. But shortcomings can create difficulties for operation, during which nothing can be changed. However, natural ventilation can be optimized. With a lack of traction at a number of points, fans and valves are placed in the channels, preventing the masses from leaving not to the street, but to the neighbors.
The main characteristics of domestic air handling units
When choosing a supply and exhaust ventilation installation, experts first of all advise paying attention to the following characteristics
PES performance by air
Accurate calculations of the ventilation system for a particular house or apartment can only be done by a specialist. But at the preliminary stage, you can use the following hint:
| Air handling unit for an apartment | Air handling unit for home | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of rooms | Productivity (cubic m/h) | House area (sq. m) | Productivity (cubic m/h) |
| 1 | 150 — 200 | 100 | 800 — 1200 |
| 2 | 200 — 350 | 150 | 1000 — 1500 |
| 3 | 300 — 400 | 200 | 1500 — 2500 |
| 4 | 400 — 500 | 250 | 2500 — 3000 |
Attention! Manufacturers indicate in the documentation the maximum performance of the PES. The actual performance of the installed ventilation system will be lower than this value, due to the resistance that occurs in the air ducts.
Noise level generated by a working air handling unit
The comfort of those who live in a house or apartment directly depends on this indicator.Agree, to live among the eternal noise is very tiring. Therefore, a very noisy supply ventilation system negates all its advantages.
When choosing the model of air handling unit you need, please note that there are quite a lot of indicators by which noise from a working PES is measured. First, this noise is non-uniform and varies by location.
Therefore, manufacturers usually indicate 3 "noise" indicators:
- at the system inlet (where air is taken in);
- at the exits or outlets - where ventilation grilles or diffusers are installed;
- on the body of the monoblock air handling unit.
Attention! The latter indicator is especially important if your PES will not be located in a special non-residential premises - a ventilation chamber, but directly where people will constantly be. In this case, it is better to choose the option with the minimum value of this indicator.
Natalia Sokolova, Product Manager, Systemair
“European manufacturers are required to apply special stickers to the equipment, which indicate the energy efficiency class of the model, the air flow and the noise level of the installation at 100 Pa. These characteristics allow the end user to shorten the selection process from the variety of ventilation units on the market.
Additional difficulties are created by the fact that in order to assess the noise level, manufacturers often indicate in the documentation not only the noise level or acoustic power (denoted by LwA), but also another indicator: Sound pressure level (denoted by LpA). Remember that it is incorrect to compare different indicators with each other. And LpA is always slightly less than LwA.
But even a comparison of the same indicators is not always objective, because. different manufacturers may measure the noise level of their products in different ways.
Air heater power
Another important factor when choosing a supply and exhaust ventilation installation is the power of the heater, which serves to heat the cold air “from the street”. If your ventilation system will supply air at a negative temperature to the house in winter, it is unlikely that anyone will like it. Therefore, an air heater is necessary, but here a new problem arises: in order to heat a large amount of intake air, the power of the heater must be quite large. This guarantees not only serious costs for electricity. Worse than the other - many old houses have a power supply system that is not designed for such power.
In this case, you will have to purchase a PES with a heater of lower power, and in order for the air to still be heated, artificially reduce the number of revolutions of the air handling unit fan in cold weather. A number of PES models already have a built-in function to automatically reduce the fan speed at low air temperatures.
As a rule, the power of an air heater in the range of 3–5 kW is sufficient for an apartment.
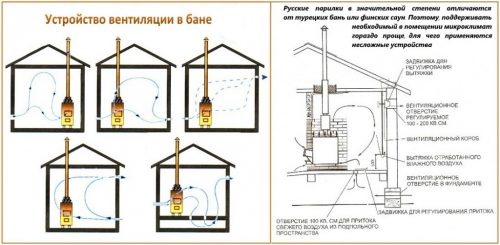
Natural ventilation in the house
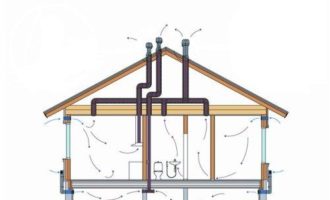
To organize natural air exchange, the concept of vertical ventilation ducts is used. One end is mounted indoors, and the other is brought out slightly above the roof of the building.
Since the air temperature in the house usually differs from the street temperature, warm streams gradually rise through the exhaust duct. A fresh portion enters the rooms from the outside through window and door blocks.
 The performance of the natural ventilation scheme depends on factors beyond human control - wind and ambient temperature
The performance of the natural ventilation scheme depends on factors beyond human control - wind and ambient temperature
Among the main advantages of such a system are simplicity and minimal costs for arrangement, saturation of rooms with natural air, and independence from electricity.
But there are also significant downsides. So, natural ventilation in a private building will work only until the air temperature in the street exceeds 12 degrees Celsius. At high rates, the hood will not be able to fully work.
At first glance, this situation seems ideal for winter, but there is also a drawback that simply cannot be ignored. With a significant temperature difference between outdoor and indoor air, the system will start to work faster. All the heat will literally fly out freely into the chimney.
Therefore, residents of cottages and private houses spend more energy resources on heating than normal climatic conditions require.
 Unstable work in the summer is the main disadvantage of the natural ventilation scheme
Unstable work in the summer is the main disadvantage of the natural ventilation scheme
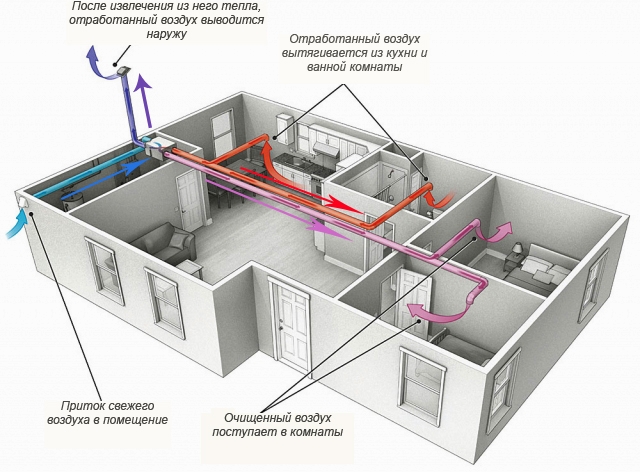
To organize a ventilation system of this type, separate ducts are laid from each utility room to a common shaft. From the kitchen, you need to lay two channels - one from the exhaust grille under the ceiling, and the other from the kitchen hood.
And it is also necessary to pay special attention to all rooms that are completely / partially located below ground level in the house. They accumulate toxic radon
To reduce the amount of dangerous gas, a powerful exhaust duct should be equipped.
In addition, you need to take care of reliable waterproofing of the basement.After all, even the most efficient supply and exhaust system will not cope with its tasks if it is always damp in the basement of a private house or cottage.
How can efficiency be improved?
There are several ways to help improve the performance of a naturally aspirated air exchange system:
- install a special valve at the inlet to the channel;
- install grilles with valves on the inflow and outflow channels;
- use deflector.
Equipped with automation, the valve reacts even to a slight change in air humidity. It is mounted at the entrance to the duct inside the building. When the humidity rises in the room, the automatic relay is activated and the internal valve opens the channel more.
In the event of a decrease in performance, the device closes the entrance. The sensing element is a sensor that picks up signals from the environment. It is installed outside the house.
In winter, the valve must be additionally covered. This will minimize the ingress of cold air into the residential building. However, the installation of such a device will not cover all the shortcomings of natural ventilation.
 Exhaust ventilation ducts are equipped in the main internal walls of the building. It is advisable to combine air ducts into small groups so that the passage through the roof is organized in one pipe
Exhaust ventilation ducts are equipped in the main internal walls of the building. It is advisable to combine air ducts into small groups so that the passage through the roof is organized in one pipe
Another effective method is the installation of grilles with valves on the channels for the inflow and removal of air masses. They can only be controlled manually. The position of the valve must be adjusted at least once a season, when the outside temperature changes.
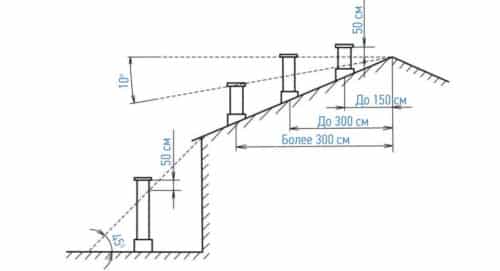
The wind can also increase the draft in the vertical exhaust ducts.To use natural force, a deflector is put on the upper part of the pipe - a special device that protects the air duct from debris and precipitation, and also increases traction.

The use of a deflector allows you to increase the performance of the chimney / ventilation duct by 20%
The deflector cuts one air stream into two or even more at different speeds. It creates a vacuum, which in turn increases the pressure drop in the pipe. As a result, the air duct draws out the exhaust air better.
What are the regulations for ventilation systems
The recommended air exchange parameters depend on various conditions and are prescribed in the relevant regulations, which must be taken into account when designing. In general terms, for domestic premises, when rooms for different purposes are concentrated on the same floor, the following amount of air should change in an hour:
-
office - 60 cubic meters;
-
common living rooms or halls - 40 cubes;
-
corridors - 10 cubes;
-
bathrooms and showers - 70 cubic meters;
-
smoking rooms - over 100 cubic meters.
In living rooms, the air mass exchange is calculated per person. It should be more than 30 cubes per hour. If the calculation is based on living space, then the standard is 3 cubic meters per 1 meter.
For non-residential premises, the average standard is 20 cubic meters per square meter. If the area is large, then the ventilation systems include a multi-component system of paired fans.
Tips for arranging natural ventilation
Each room in country buildings or a country house has features that must be taken into account when installing ventilation devices.
in the bathroom
For a toilet and a bathroom in a suburban building, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of micro-ventilation through windows or doors.
In the bath
When equipping ventilation in the bath, it is necessary to place the supply channel at the installation site of the furnace. Outdoor air penetrates from below, gradually displacing warm air to the ceiling, heating itself. The exhaust valve in the steam room is installed under the ceiling.
I open the valves if necessary to quickly dry the steam room or washing room.
In the boiler room
If a country house is heated by gas, it must provide a separate room for placing equipment. A gas boiler is an object of increased danger, therefore, the requirements for equipping a boiler hood are quite serious.
The ventilation of the boiler room is mounted separately and does not cut into a common exhaust pipe; most often, an external pipe is used to get rid of smoke and gas.
Supply air devices are used to deliver outside air to boiler rooms. The weak point of the natural type supply and exhaust system in boiler rooms is the dependence on wind power. In quiet, calm weather, it is impossible to provide good traction.
 Turning the ventilation ducts reduces efficiency by 10%.
Turning the ventilation ducts reduces efficiency by 10%.
In living rooms
To ensure efficient air circulation between individual rooms in the house, it is necessary to arrange small holes or gaps between the door leaf and the floor in the lower part of the door panels.
In the kitchen
When installing an exhaust ventilation grille above the stove, it is necessary to place this device at a distance of 2 meters from the floor. This position of the hood allows you to effectively remove excess heat, soot and odors, preventing them from spreading around the room.
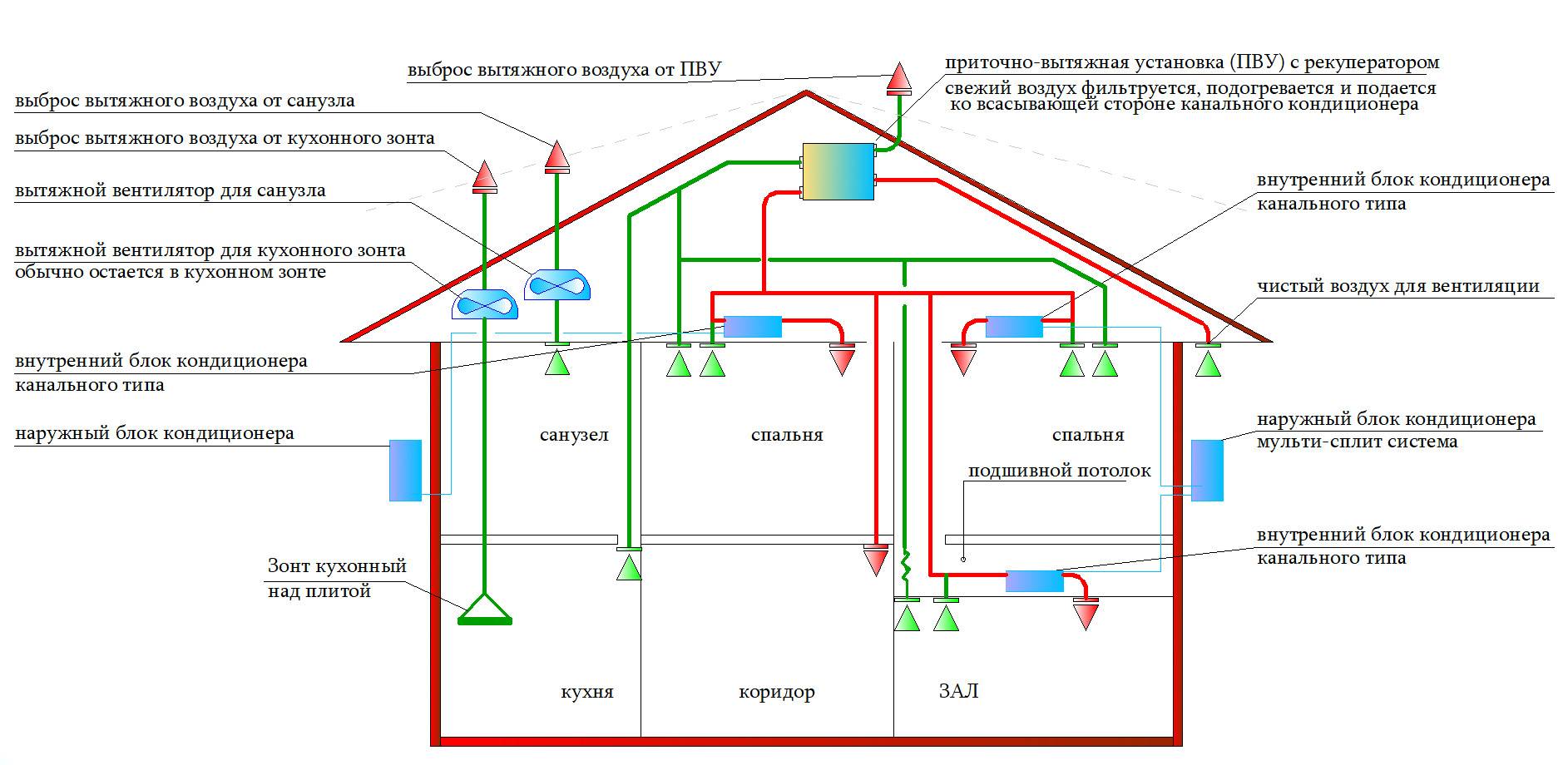
Ventilation created artificially (mechanical) in production
This type provides the intake and removal of air flows with the help of fans. The organization of a mechanical system requires the investment of large energy resources and economic costs. Despite this, it has several advantages:
- Allows air to be taken from the desired location
- It is possible to influence the physical properties: cool or heat the air flow, increase or decrease the humidity level
- It is possible to supply air directly to the workplace or exhaust with subsequent filtration
Purification of polluted air from the premises, a prerequisite for production. This factor is under strict control of environmental organizations.
The mechanical system, depending on the design, goals, and tasks assigned to it, differs:
- Supply
- exhaust
- Supply and exhaust
In production places, the air system is selected based on the needs and specifics of the place of operation.
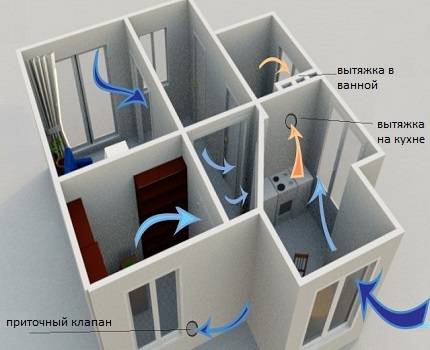
Supply and exhaust natural ventilation in the room
Myth number 2 - a natural hood functions under any environmental conditions.
Reality - a natural hood functions with a difference in air temperatures inside and outside the room. In other situations, it becomes an influx or does not work at all.
So, exhaust ventilation is well carried out in winter, when the air temperature outside is several times lower than in the apartment. As a result, warm air masses rise through the exhaust ducts and are thrown out.
At the same time, in hot weather, the flow, on the contrary, from the street enters the house with a cooler temperature.That is why the room becomes stuffy, and the constant operation of air conditioners does not eliminate the lack of oxygen.
The same applies to situations where the external and internal temperatures in the house are the same - the room is not ventilated, the microclimate stagnates.
Myth No. 3 - the fan is capable of forced movement of exhaust air.
Reality - in the absence of inflow in the room, the exhaust fan works in vain, “idle”. This means that the forced air movement device in the bathroom will not be able to provide an extract if a sealed door is installed in the room.
Therefore, when installing a fan in a bathroom for natural supply and exhaust ventilation, it is necessary to have a small gap under the door up to 5 mm high. Then the hood will begin to function, and the air flow will come from neighboring rooms.
Myth #4 - supply air heating carried out independently.
Reality - additional energy is needed to heat the air inflow that enters the room during natural ventilation. Cold air is heated by household items, people and heating radiators, as if “taking away” thermal energy from them.
Types of systems
These designs exist in several forms.
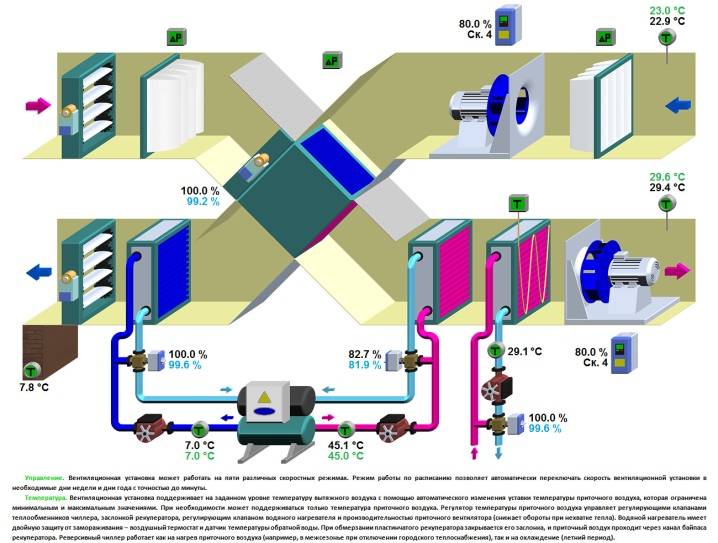
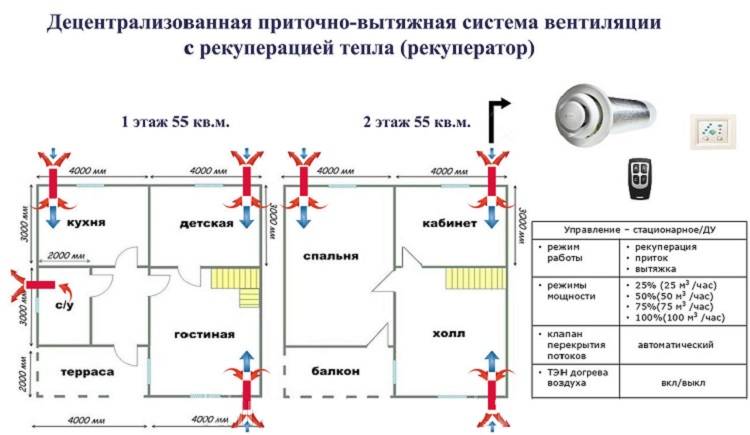
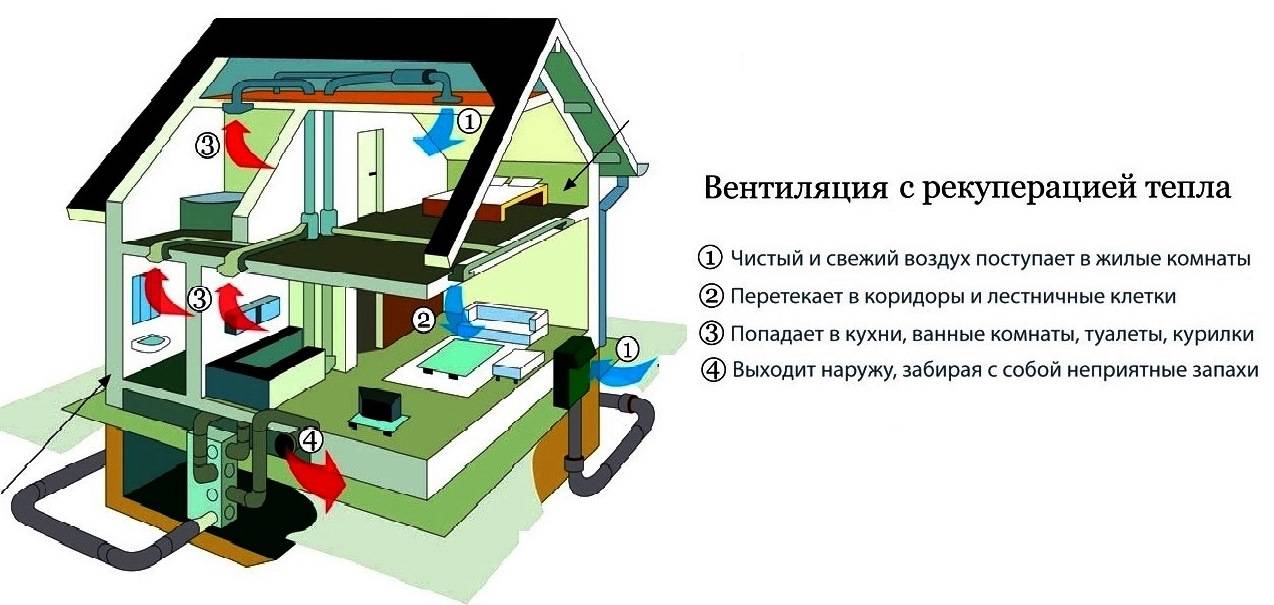
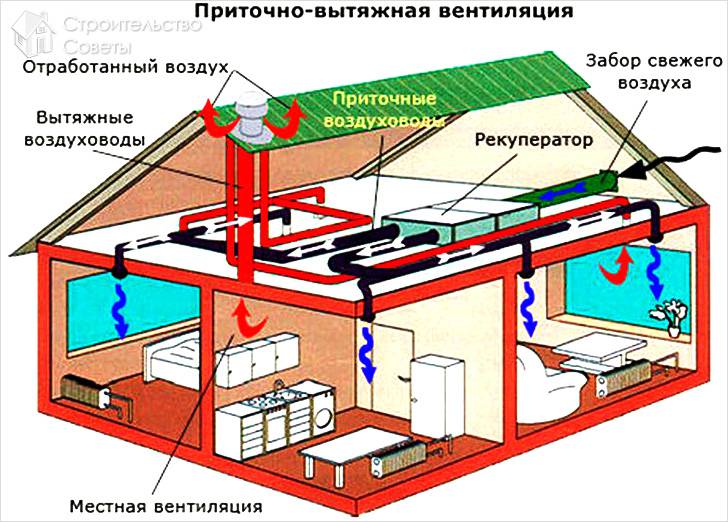
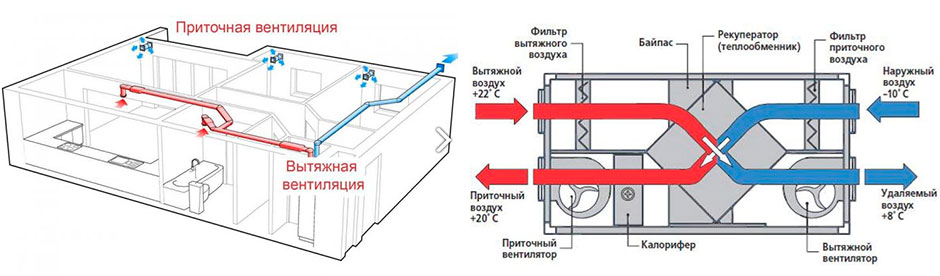
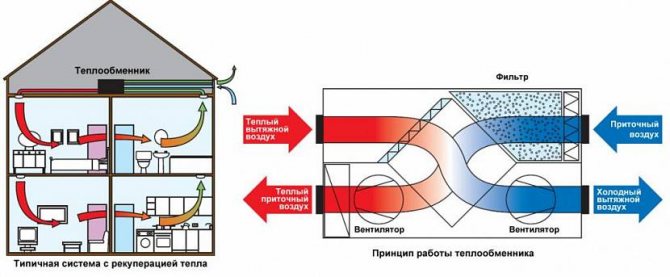
- With heat recovery. Installations of this type are designed to purify and change the temperature regime of air masses, they also save resources. Due to the presence of a heat exchanger, in the cold season, the air that comes in from outside is heated by the heat of what is thrown out. In the hot season, the opposite happens.
- with recycling.Such ventilation systems can save energy consumption by mixing part of the incoming and outgoing air. The disadvantage of ventilation with recirculation is their inability to use in rooms where explosive substances are present. Such devices are unable to optimally mix air of different temperatures in cold weather.

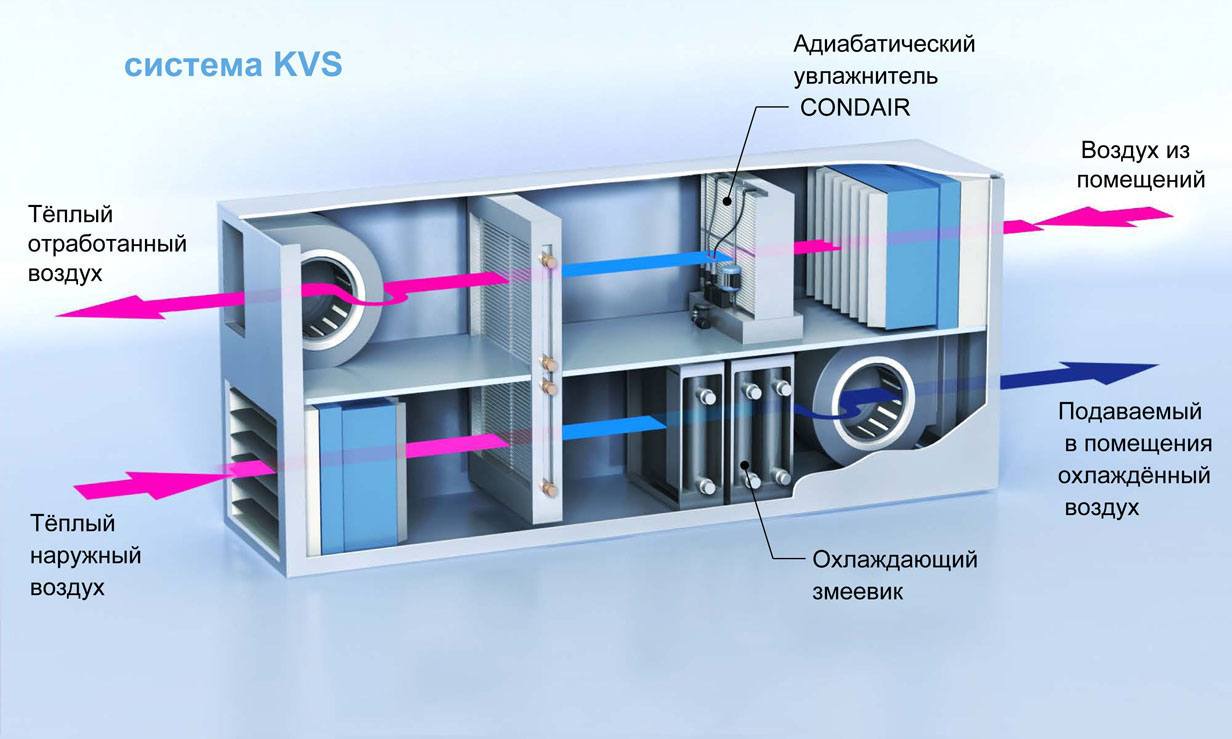
- With cooling. This type of ventilation system is relevant for rooms where products and materials that require cold are stored. They are usually used in rooms where technological processes need low temperatures and a public place in the summer season.
- With air conditioning. This is a device with a heat pump, air conditioning and filters that are in a heat-insulated housing. This type of ventilation with a water heater is considered relevant for rooms with high humidity, such as swimming pools.
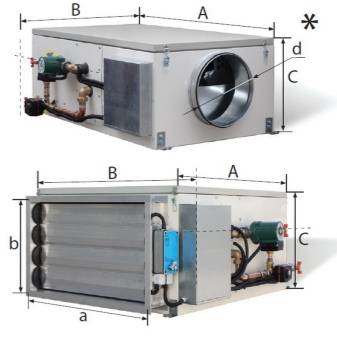

The compact air handling unit VUT 100 P mini is very popular these days. It is used to organize energy-saving ventilation of a separate room in buildings that have a variety of purposes. The SkyStar-2 and SkyStar-4 wall suspended installations deserve due attention. These systems are considered ideal for commercial, administrative and restaurant buildings, they are inexpensive and quite easy to install.


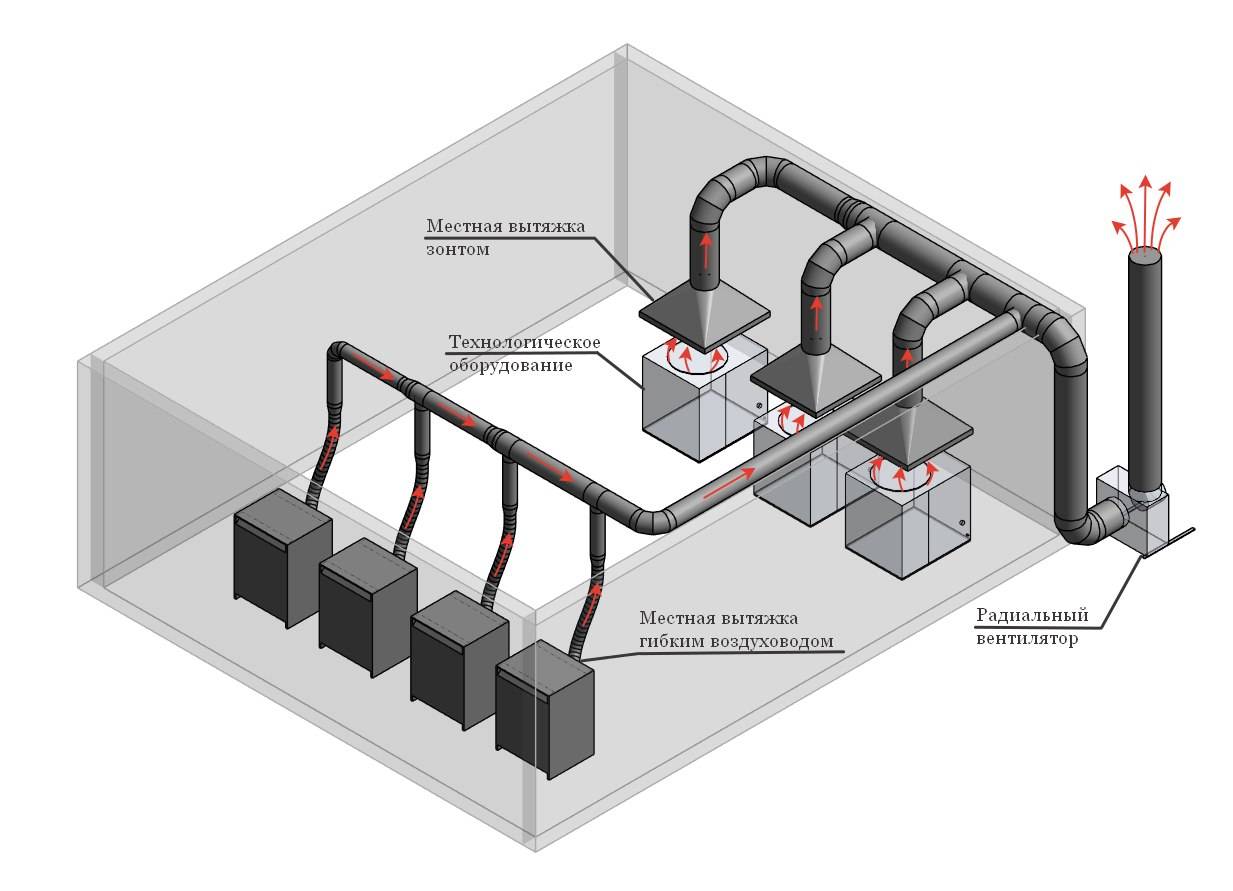
Units for local exhaust system
Existing shelters, which are equipped with exhaust ventilation systems, are divided into several specialized categories:
- units installed at the source of pollution;
- solutions that block the source of pollution;
- reblowing products.
In practice, units with the help of which the source of the spread of hazardous substances is localized in a certain area are very popular. However, such solutions are not always convenient and appropriate to apply. They were replaced by more modern hoods with a vent to the ventilation:
- metal and polycarbonate umbrellas with hood function;
- local suction units;
- powerful fume hoods;
- encapsulated solutions;
- removal of secretions from the body of machine tools and working units;
- showcase, shaped and board solutions.
Local ventilation systems are very common in places where it is necessary to ensure the required standards for air exchange in a specific, local area.
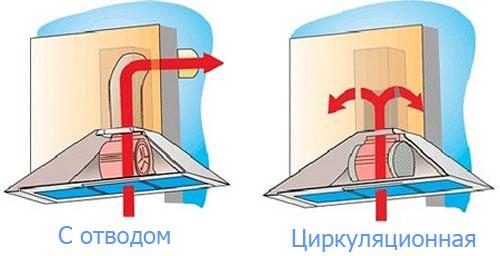
Exhaust hoods are the most popular and common suction designs. They equip small working areas (tables for soldering, cooking). Dangerous impurities are quickly collected and redirected upwards, after which they are discharged. Ventilation for the hood functions both through natural draft and forced draft.
Specialized suction - draw out unwanted and potentially dangerous substances with a minimum consumption of oxygen. Industrial exhaust ventilation is often represented by several local units. Their main feature is that they do not interfere with work.
Fume hoods are one of the most effective solutions for the forced removal of harmful fumes, substances, while forming a minimum level of air exchange. There are several types of such cabinets on sale:
- with an upper outlet device, through which hot and humid air is removed;
- with the removal of contaminated streams of the side structure - we are talking about some analogue of a "snail", for collecting residual products;
- with diverting solutions of the combined type located at the bottom of the unit.
Local hoods: a - fume hood; b - display case; c - shelter-casing for a grinding machine; g - exhaust hood; e - umbrella-visor over the open opening of the furnace; e - exhaust funnel when welding large-sized products; g - lower suction; h - lateral suction; and - inclined exhaust panel; j - double-sided suction from the galvanic bath; l - single-side suction with blowing; m - annular suction for a manual welding gun
The fan, located in the air exchange system, creates a swirl in the flow so that the dust is localized in a small area, and does not spread throughout the room. An example of such an installation is a welding post, where forced exhaust ventilation is represented by a small cabinet. The suction in them is located at the top of the structure.
If we are talking about the removal of non-hazardous substances, then the speed of movement is allowed within the following limits:
- 0.5 – 0.7 m/s;
- 1.1 - 1.6 m / s - for those cases when toxic impurities, metal fumes are removed from the room.
Fume hoods are installed in chemical laboratories
As for the suction panels, they are used in cases where the air in a confined space is saturated with toxic gases, dust and heat. The panel is positioned so that the toxic compounds are at the maximum distance from the worker. Exhaust pipes for ventilation complement the built-in motor and quickly remove dangerous suspensions.The installations under consideration are used at welding posts, when processing large products. From welding, they are located at a distance of up to 3.5 m, equipped with fans with one or two motors.
The speed of movement of air masses must meet the following criteria:
- from 3.5 to 5 m / s, when it comes to the release of hot dust;
- from 2 to 3.5 m / s, if toxic or non-dusty suspensions are released during operation.
Experts focus on one important point - the installation of exhaust ventilation is carried out on the condition that 1 m2 of the panel removes 3.3 thousand m3 of air hourly
Onboard suctions are relevant for cases when the source of pollution is held in a vertical position using special lifts. Such installations are widely used in the shops where the galvanic processing of metals is carried out, in which hazardous substances are poured into a special container and then sucked in through a small hole.
From a constructive point of view, the exhaust ventilation of industrial premises consists of several air ducts, the inlets of which have a narrow shape (up to 10 cm), they are located at the edges of the bath.
The physical basis of the ventilation system
The supply and exhaust ventilation system is a multifunctional complex for ultra-fast processing of the gas-air mixture. Although this is a system of forced transportation of gas, it is based on quite understandable physical processes.
To create the effect of natural convection of air flows, heat sources are placed as low as possible, and supply elements in the ceiling or under it
The very word "ventilation" is closely related to the concept of convection.It is one of the key elements in the movement of air masses.
Convection is the phenomenon of circulation of thermal energy between cold and warm gas flows. There is natural and forced convection.
A bit of school physics to understand the essence of what is happening. The temperature in the room is determined by the air temperature. Molecules are carriers of thermal energy.
Air is a multimolecular gas mixture that consists of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%) and other impurities (1%).
Being in a closed space (room), we have a temperature inhomogeneity relative to height. This is due to the heterogeneity of the concentration of molecules.
Given the uniformity of gas pressure in a closed space (room), according to the basic equation of molecular kinetic theory: the pressure is proportional to the product of the concentration of molecules and their average temperature.
If the pressure is the same everywhere, then the product of the concentration of molecules and the temperature in the upper part of the room will be equivalent to the same product of concentration and temperature:
p=nkT, nup*Tup=ndown*Tdown, nup/ndown=Tdown/Tup
The lower the temperature, the greater the concentration of molecules, and hence the greater the total mass of the gas. Therefore, they say that warm air is “lighter” and cold air is “heavier”.
Proper ventilation combined with the effect of convection are able to maintain the set temperature and humidity in the room during periods of automatic shutdown of the main heating
In connection with the foregoing, the basic principle of arranging ventilation becomes clear: the air supply (inflow) is usually equipped from the bottom of the room, and the outlet (exhaust) is from above.This is an axiom that must be taken into account when designing a ventilation system.
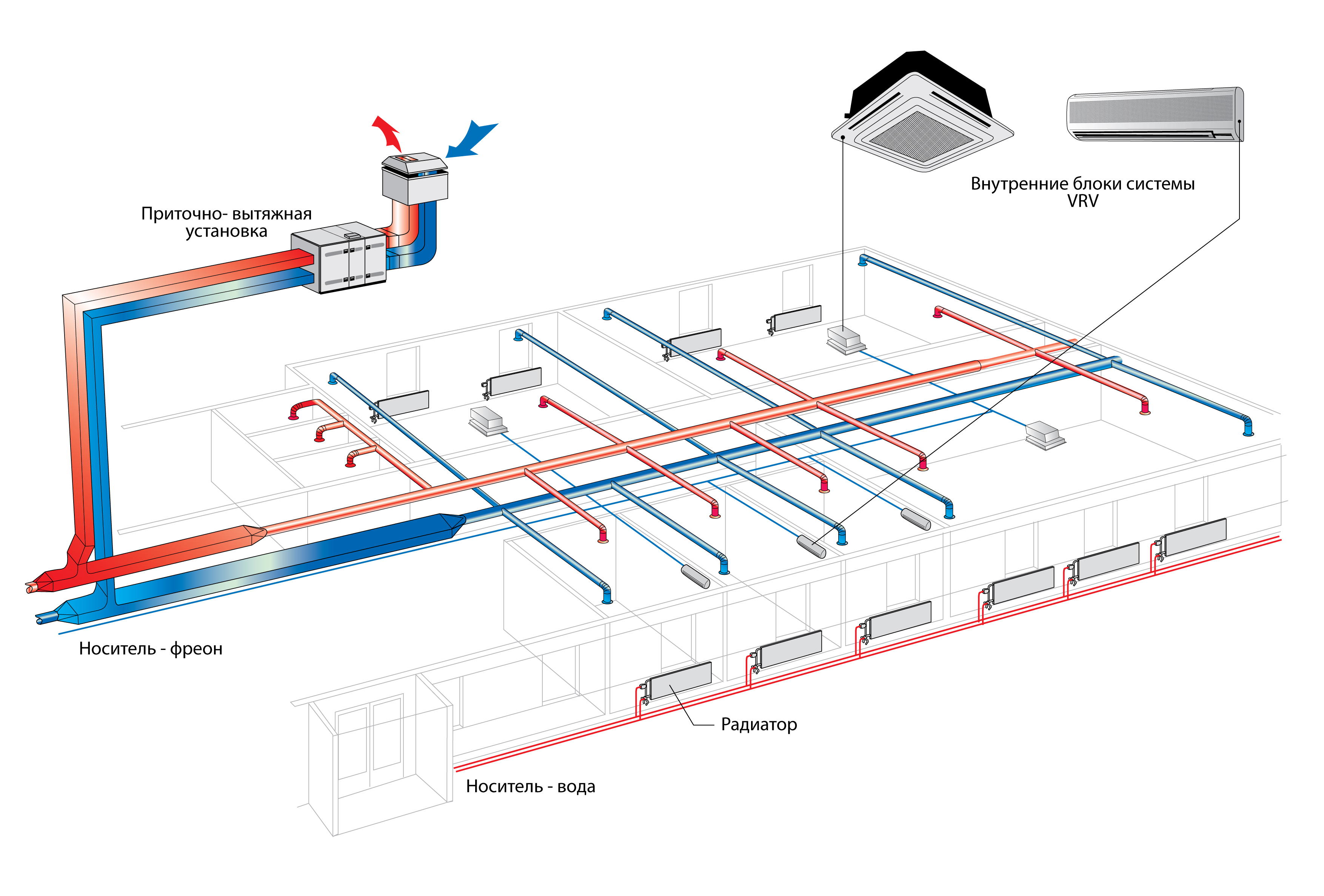
Supply and exhaust system device
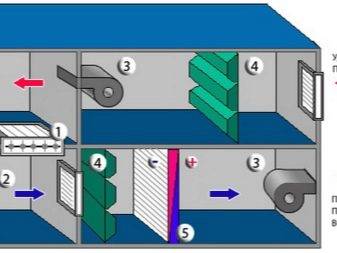
According to the name, the supply and exhaust system consists of two independent parts that ensure the normal functioning of the entire system. So the supply part of the system ensures the forced flow of air into the room, heating it, cleaning it, if necessary, can also cool it. The purpose of the second part also becomes clear from its name, namely, it ensures the outflow of air from the room. Very often, in this case, just an air duct is used, however, sometimes special exhaust systems can be installed.
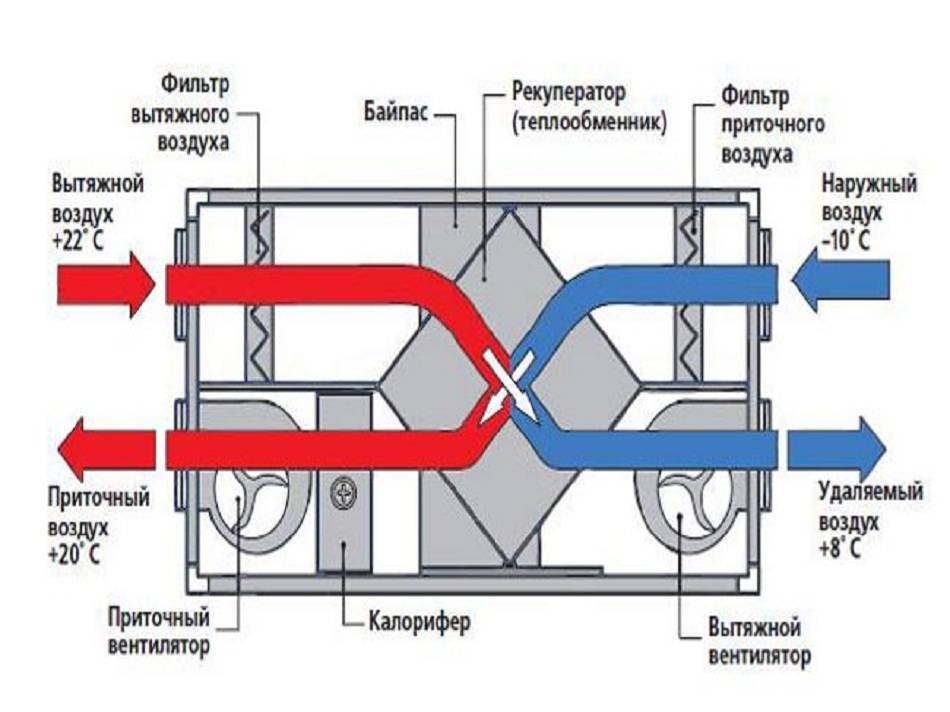
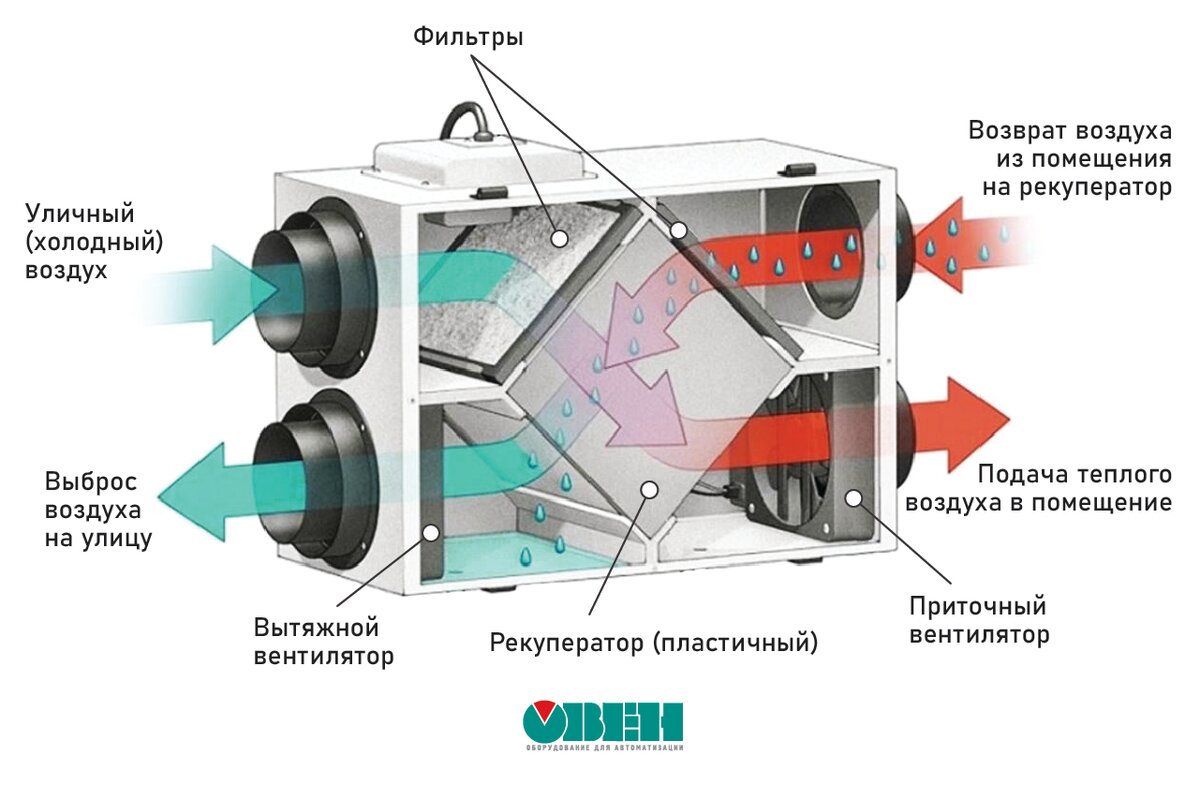
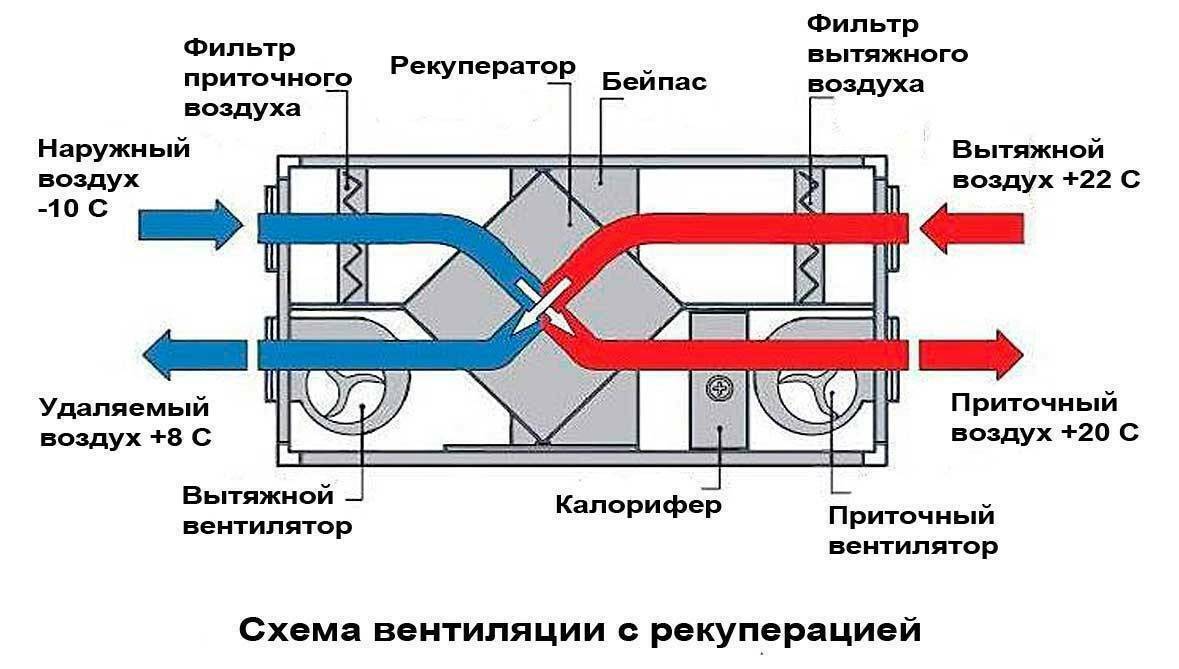
Since it is necessary to heat the incoming air in winter, a complex solution is often used for this, in which a kind of heat exchanger is used. It's called a recuperator. This unit works on the principle where the outgoing air from the room heats the incoming air, while mixing of two streams not happening.
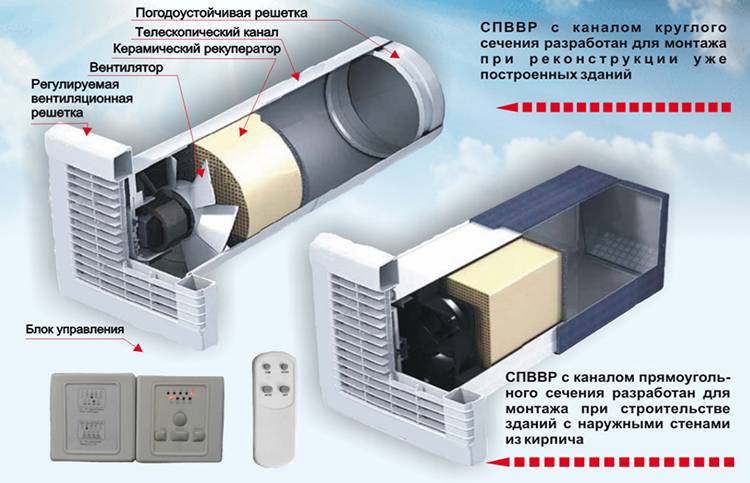
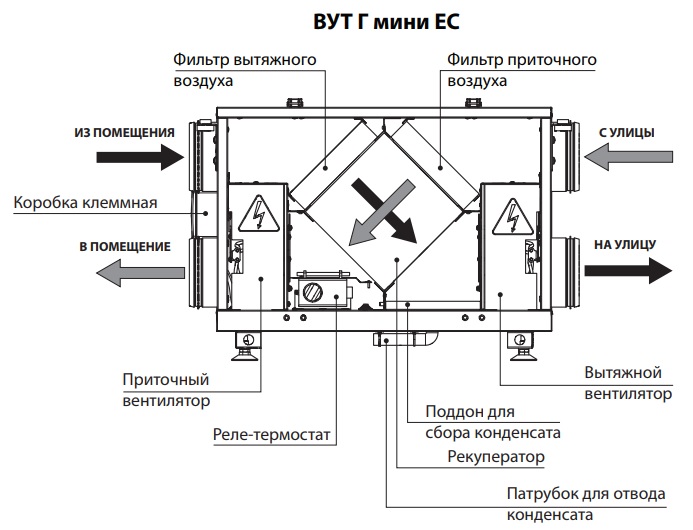
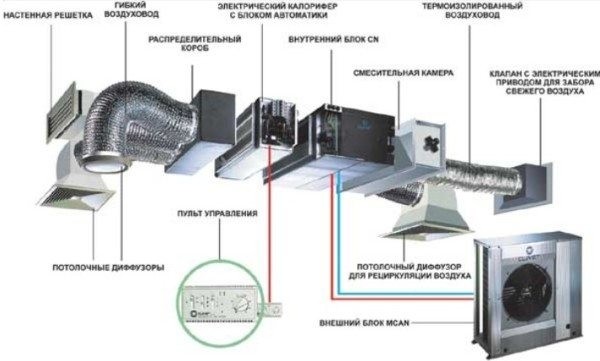
Supply ventilation units: main components and principle of operation
Supply ventilation units are used for a constant supply of fresh air in the room, while it is pre-filtered, heated, cooled and, in some models, dehumidified / humidified. Almost all models have the ability to regulate the set supply air temperature by heating or cooling (if there is a cooling unit).
To understand the principle of operation of supply ventilation units, you should first familiarize yourself with their main elements.
Fan
The main element of the system, which ensures the supply of fresh air, thanks to the generated forced pressure.
Filter
It is installed at the inlet of the supply unit and is needed to clean the supply air masses from foreign odors, protect them from small insects, dust and other mechanical contaminants. Depending on the set of filters installed (coarse / fine / ultrafine), the level and quality of the filtered air depends.
Air valve
It is necessary to control the air flow of incoming air and to block it in case the ventilation system is turned off.
Heater (heater)
It is used to heat the supply air to the required temperature. Heaters can be water or electric. The former are connected to the heat supply system (technical water or heating) of the building, while the latter are powered by the electrical network.
Silencer
Designed minimize noise levels, which occurs during the movement of air through the ducts and from the vibrations of the fan.
Thus, the principle of operation of air handling units is to supply fresh air, previously cleaned of dust, heated / cooled to the desired temperature, by means of its forced injection by means of a fan.