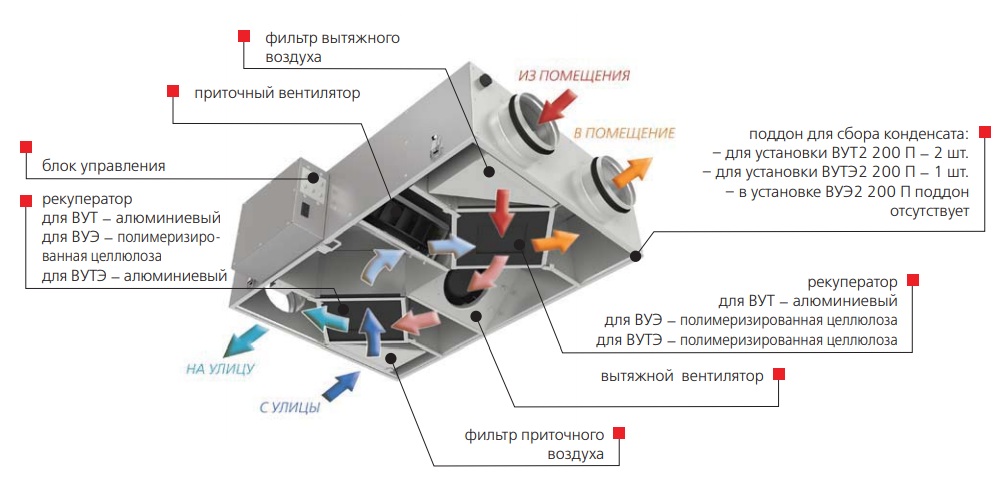
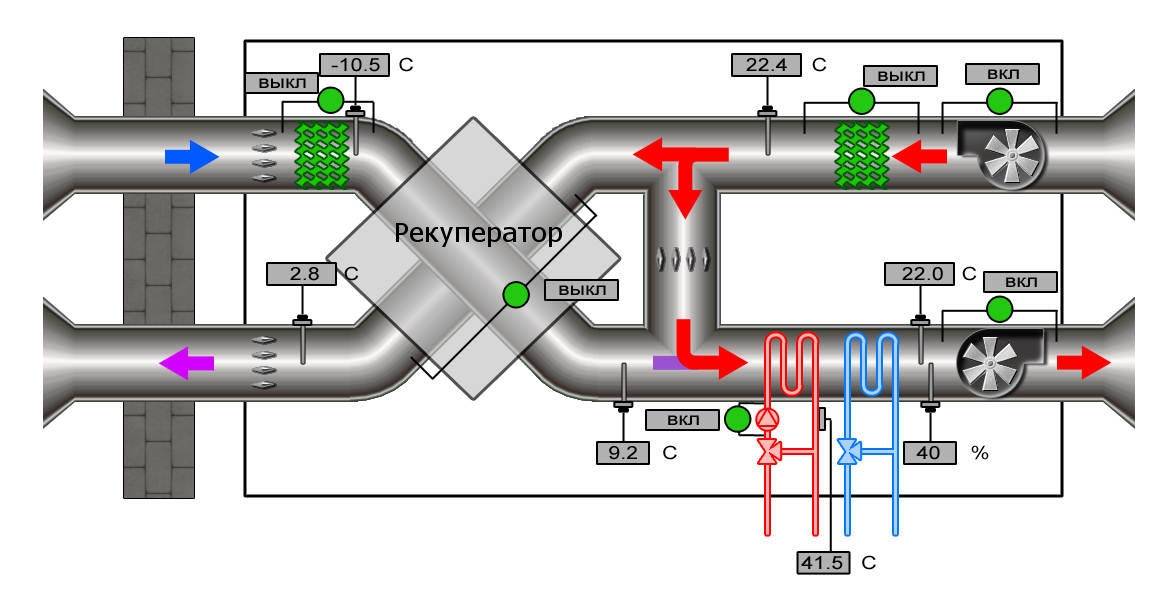
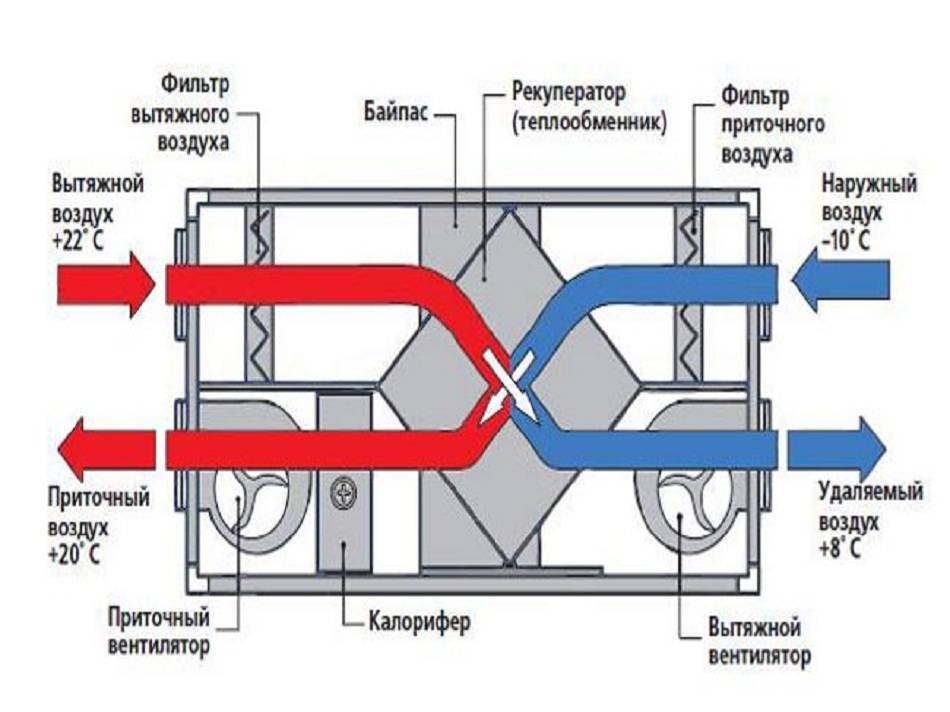
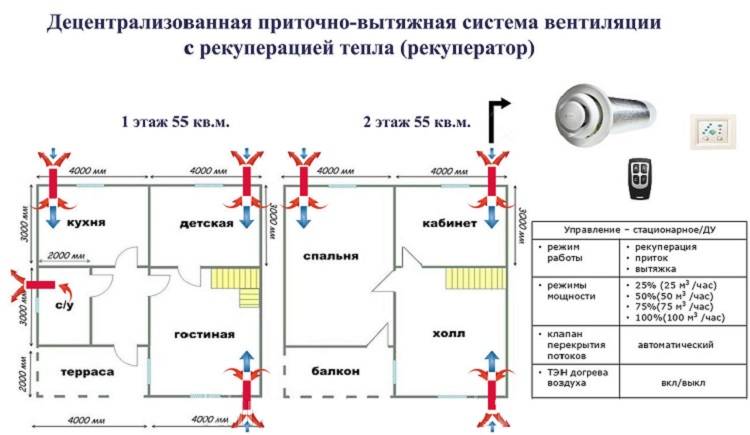
- Air ducts for ventilation
- Ventilation system
- Air mixing principle
- How to calculate ventilation in a private house
- The principle of operation of the supply and exhaust complex
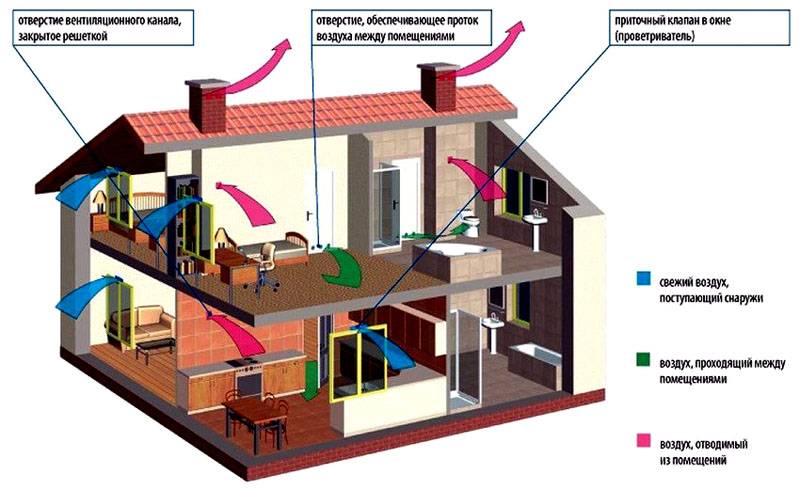
- Components of gravitational air exchange
- Window inlet valve
- Wall exhaust or supply device
- Interroom transfer grates
- What are there?
- Spiral
- Rotary heat exchangers
- Plate heat exchanger
- Finned plate heat exchanger
- Industrial and domestic recuperators - what are the differences?
- Supply and exhaust ventilation of the apartment
- Compact ventilation system for an apartment
- Complete ventilation system
- Purpose of ventilation systems and their types
- Ventilation cleaning equipment
- Features of forced air exchange
- Description of mechanical ventilation option
- Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery
- System without heat recovery
- Fans for ventilation systems
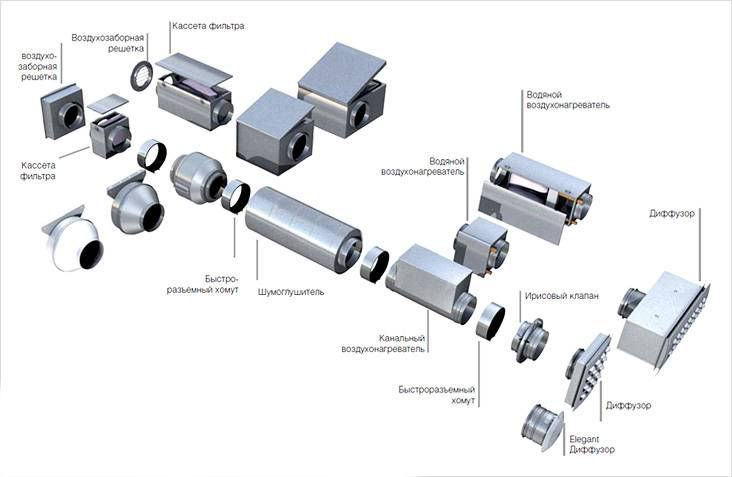
Air ducts for ventilation
Air ducts are transport arteries through which air masses move. The effectiveness of their work depends on three criteria:
- the form,
- section,
- the material from which they were made.
The shape of the section is round or rectangular. The first ones allow air to pass through them better, the second ones are easier to install. Material: metal or plastic.The former are most often used in industrial premises. They easily withstand different loads. The latter are more commonly used in everyday life. It should be noted that plastic air ducts for ventilation are a wide variety of types and sizes.
Plastic pipes are made from PVC, PTFE, polypropylene and low-pressure polyethylene. The last position is flexible, so such ducts are more often used for complex wiring.
 Plastic air ducts in the ventilation system of a private house
Plastic air ducts in the ventilation system of a private house
We add that ventilation in a private house made of plastic pipes is a list of the following advantages.
- Standard dimensions: diameter - 100 ÷ 200 mm, for rectangular ones the width is 100 to 200 mm, the height is from 50 to 200 mm. All parameters comply with the regulations.
- Low specific weight, which allows the production of simple fasteners.
- Ease of installation.
- Smooth inner surface, which reduces the possibility of build-up of debris.
- Long term operation.
Ventilation system
Ventilation and air conditioning in an apartment or house is carried out using various devices and structures. These include systems that provide:
- air inflow - ventilation valves for windows, walls and doors;
- the removal of polluted air - hoods in the kitchen, channels in the bathroom;
- cooling of air masses - air conditioners, fans;
- heating - thermal curtains.
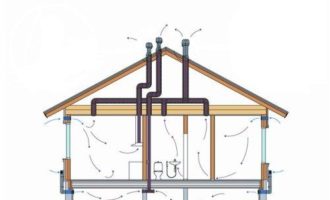
According to building codes, normal air exchange in residential buildings should be ensured by general ventilation systems. They are a long channel running from the basement of the house to the attic, which has numerous exits in each apartment.
Industrial ventilation and air conditioning is widespread, which is installed at enterprises and in other non-residential buildings:
- in industrial premises;
- in warehouses and workshops;
- in office centers;
- in markets and shopping malls.
Such systems differ significantly from those used in residential apartment buildings. As a rule, more powerful and overall equipment is used here: advanced air conditioning and heating systems, large-scale hoods and fans.
Air mixing principle

When mixing, clean air enters the room in several ways, and the exhaust exits through one stream. One of the key parameters is ejection (this is when one medium affects another). To avoid drafts, if there is a significant temperature difference, diffusers should have a significant value. The importance of the speed of air masses also plays an important role. In order to properly design the ventilation system, it is necessary to take into account the presence of obstacles on the ceiling in the form of chandeliers, lamps, ceilings, columns and other things.
There are types of non-standard rooms where a special approach to the design of ventilation is required. So many students are concentrated in classrooms, so fresh air should flow under the seats of students. But it is impossible to determine with certain accuracy the direction of the flow of polluted air in the audience, so the best option would be to have special air vents behind the back desks. But if these air outlets are placed in other parts of the audience, then there will be no optimal air purity.
How to calculate ventilation in a private house
In the calculation of ventilation, an indicator such as the frequency of air exchange is used. It was already mentioned at the beginning of the article. This parameter was fixed by SNiP under the number 2.08.01-89 * under the name "Residential buildings". So, in Appendix No. 4, a table is given in which the air exchange rate is shown depending on the purpose of the room. We will not rewrite the entire table, we will indicate the main premises:
| room | Air exchange rate |
| Residential | 3 m³/h for each square meter of area with a ceiling height of 3 m |
| Kitchen with electric stove | 60 m³/hour |
Kitchen with gas stove:
|
|
| Bathroom | 25 |
| Toilet | 25 |
| Combined bathroom | 50 |
Now, as for the calculation. For this, the formula is used:
N = V x L, where
- N - ventilation performance,
- V is the volume of the room,
- L is the air exchange rate.
Pay attention to the multiplicity in living quarters. Basically, it turns out that it is equal to "1"
That is, in one hour the volume of air in them should change completely. From this it turns out that the ventilation performance should be equal to the volume of the room.
But this is just a calculation, which is based on standards. The ventilation system itself is air ducts, which should provide the necessary permeability of air masses. Therefore, there are rules here as well. For example, a round pipe with a diameter of 150 mm, and this section, equal to 0.016 m³, provides a throughput of 30 m³ / h. The same parameter supports 100×100 mm rectangular duct. At the same time, such a volume maintains a riser height of 3 m. That is, if this value is less, the performance will decrease accordingly.
 Scheme for calculation example
Scheme for calculation example
Calculation example. Input data:
- total area of residential premises - 60 m²;
- the kitchen has a 4-burner gas stove;
- toilet and bathroom are separate;
- ceiling height - 3 m;
- inflow from the living quarters, extract from the kitchen, bathroom and toilet.
First of all, the volume of supply air is calculated. It is equal to the volume of residential premises: 60 × 3 = 180 m³ / h. Now we need to calculate the volume of air removed. Here you have to refer to the table:
- in the kitchen, this figure is 90 m³ / h,
- in the toilet and bathroom for 25.
In general, it turns out: 90 + 25 + 25 = 140 m³ / h. Now the two values obtained must be compared. It is clear that 180 is greater than 140. This means that the performance of the ventilation system in this particular case will be 180 m³ / h.
This calculation is valid for both natural ventilation and mechanical ventilation.
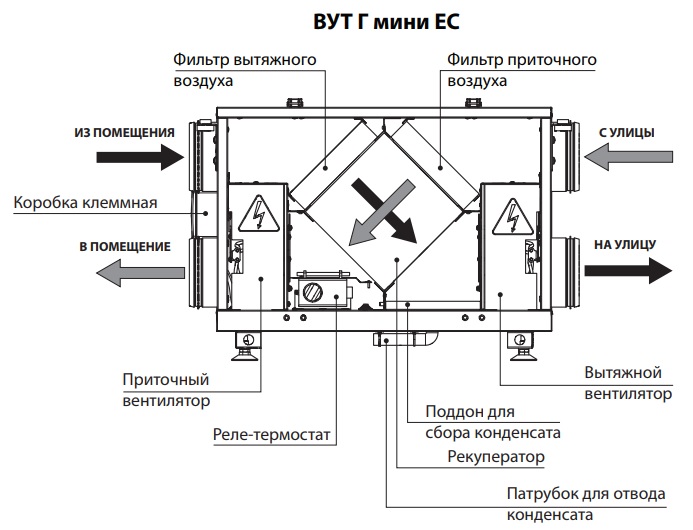
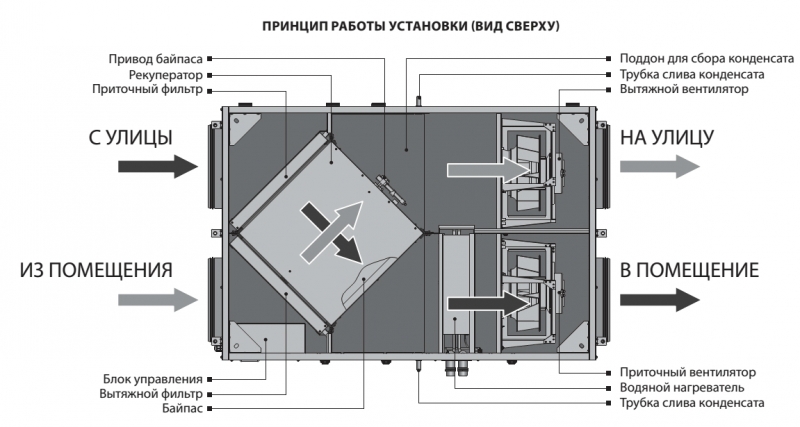
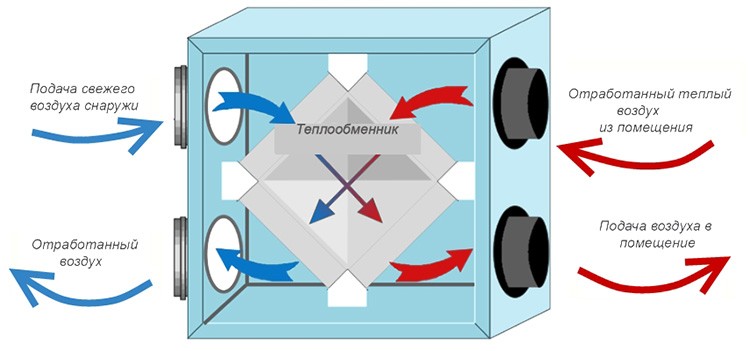
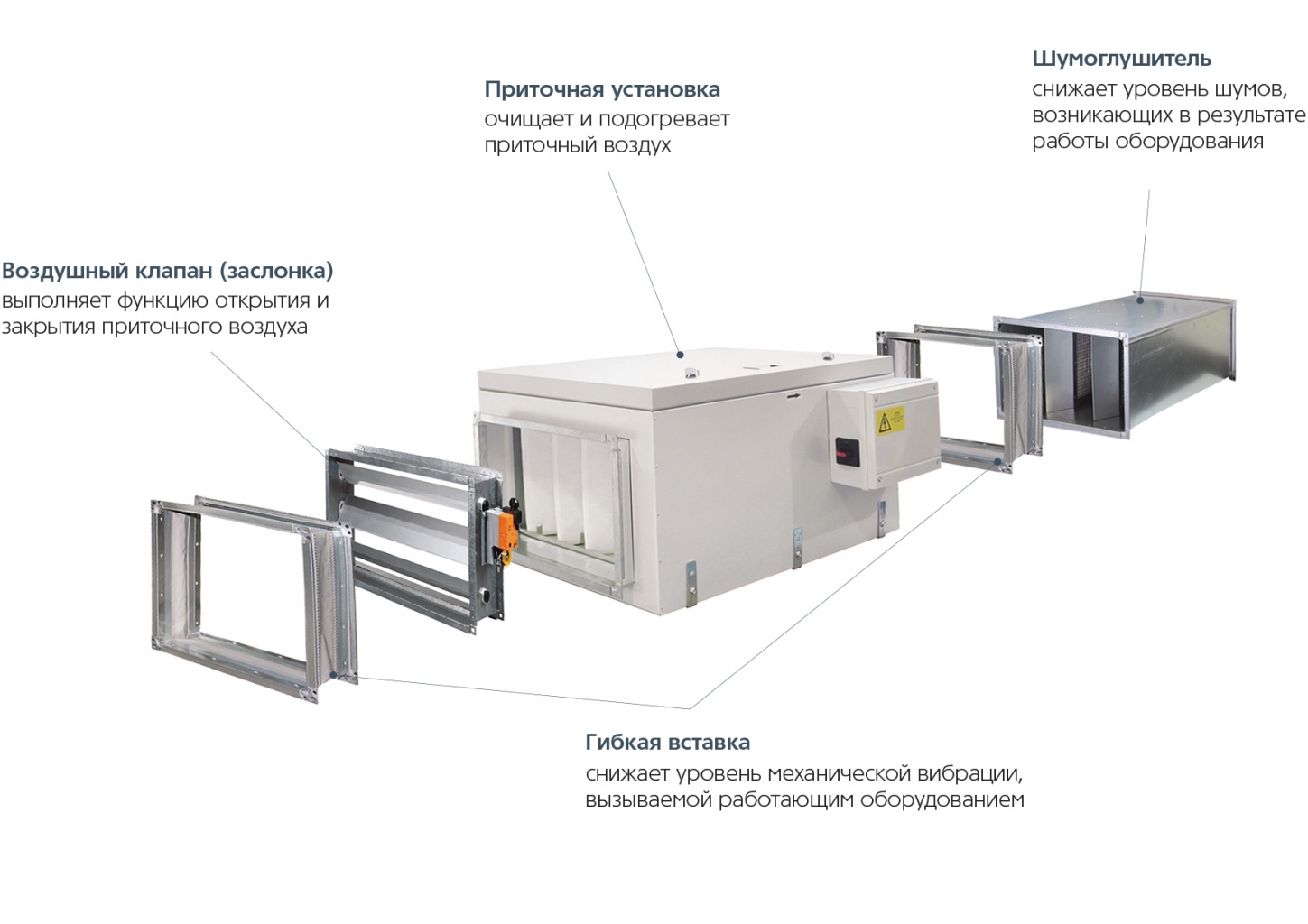
The principle of operation of the supply and exhaust complex
The operating cycle of the PES is based on a two-loop transport scheme.
The whole ventilation process can be divided into several stages:
- Air flow intake from the street, its cleaning and supply to the distributors through the air duct.
- The intake of contaminated masses into the exhaust channel and their subsequent transportation to the outlet grate.
- Ejection of waste streams to the outside.
The circulation scheme can be supplemented by stages of transfer of thermal energy between two flows, additional heating of the incoming air, etc.
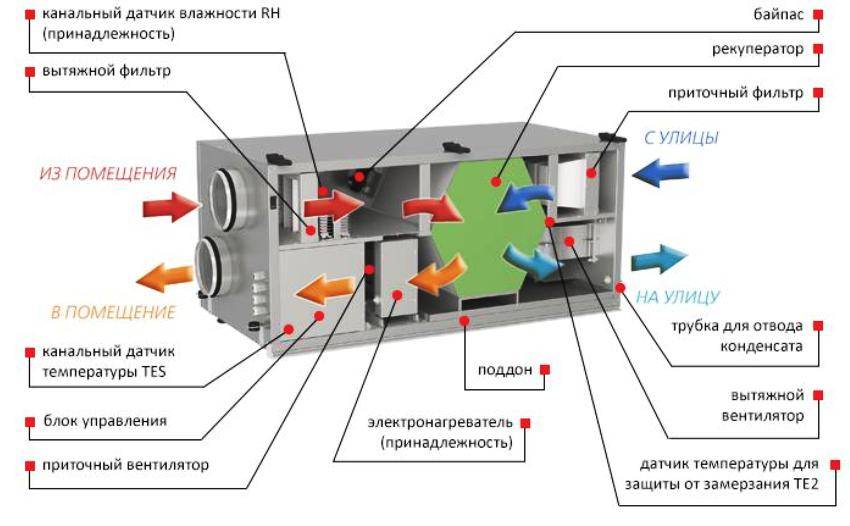
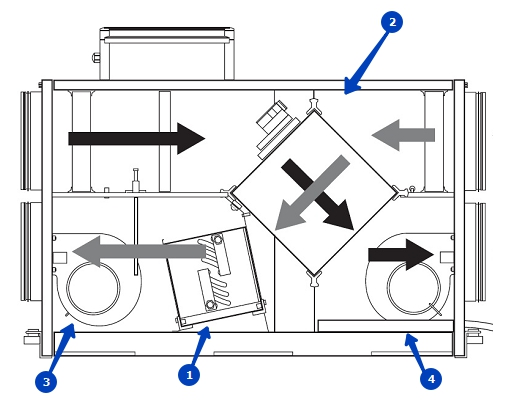
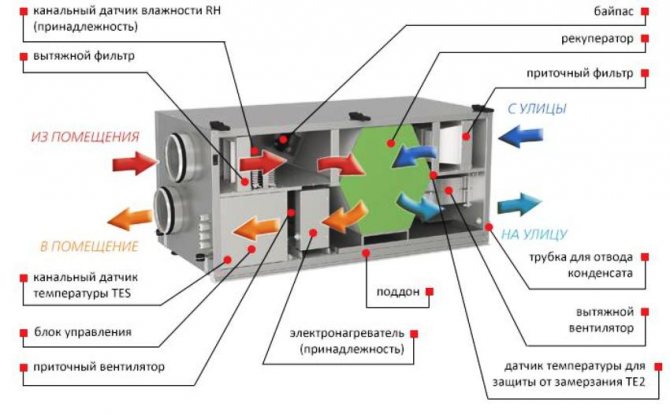
 PVU work. Designations in the figure: 1 - supply and exhaust module, 2 - supply of fresh air, 3 - intake of "exhaust", 4 - exhaust of used air masses to the outside (+)
PVU work. Designations in the figure: 1 - supply and exhaust module, 2 - supply of fresh air, 3 - intake of "exhaust", 4 - exhaust of used air masses to the outside (+)
The operation of the forced system provides a set of advantages compared to natural air exchange:
- maintaining the set indicators - the sensors respond to changes in the atmosphere and adjust the mode of operation of the PES;
- filtration of the incoming flow and the possibility of its processing - heating, cooling, humidification;
- saving heating costs - relevant for devices with recuperation.
The disadvantages of using PES include: the high cost of the ventilation complex, the complexity of installation after the completion of repair and construction work, and the noise effect. In monoblock installations, the last disadvantage is eliminated due to the use of a soundproof housing.
Components of gravitational air exchange
One of the common problems with natural ventilation in a private house is the lack of fresh air entering the room. Gravitational ventilation works flawlessly only when the density of the air mass outside the window is much higher than inside the premises. In the summer, when their density equalizes, the air from the street does not flow by itself.
In addition, serious obstacles are now being placed in the way of naturally moving air currents. Window and door seals, offered to the consumer today, perfectly resist heat leakage, but they also do not let air in from the outside.
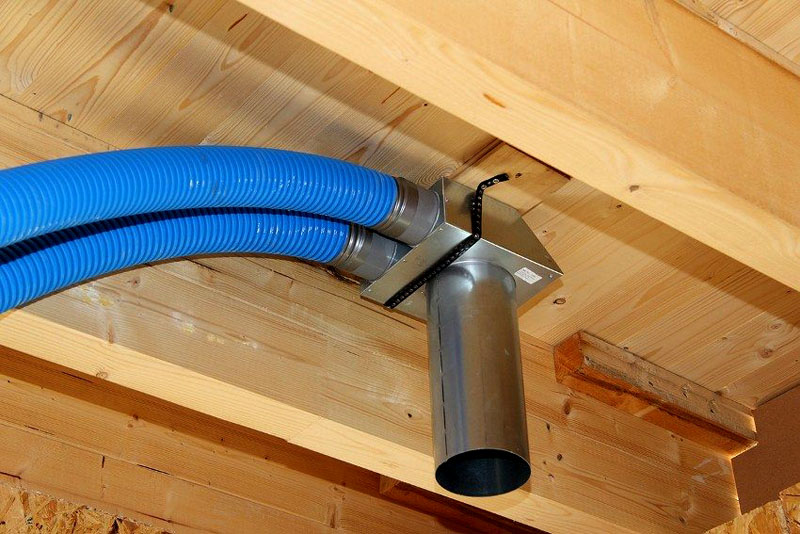
 In order to ensure natural inflow in houses with sealed windows, it is worth putting inlet valves into the wall, and supplying exhaust ventilation pipes with deflectors
In order to ensure natural inflow in houses with sealed windows, it is worth putting inlet valves into the wall, and supplying exhaust ventilation pipes with deflectors
The issue of fresh air entering rooms with practically hermetic windows and doors is solved by installing ventilation inlet valves.If you don’t want to install valves, you will have to purchase air inlets for plastic windows or buy window packages with air inlets built into them initially.
Window inlet valve
This device is also called a window ventilator. Refers to the most common options for solving the problem of air exchange. The design of such a valve is mounted directly in the window profile.
 The flow of incoming air through the window ventilator is directed upwards, so that the cold supply air is more efficiently mixed with the already heated indoor air and does not cause discomfort to residents
The flow of incoming air through the window ventilator is directed upwards, so that the cold supply air is more efficiently mixed with the already heated indoor air and does not cause discomfort to residents
Some valves are equipped with automatic air flow control. It is worth noting that manufacturers do not equip all models of ventilators with mechanical adjustment. This can create certain problems with sudden temperature changes.
The main disadvantage of the window inlet valve is the relatively low performance. Its bandwidth is limited by the size of the profile.
Wall exhaust or supply device
To install a wall ventilator, you need to make a through hole in the wall. The performance of such a valve is usually higher than that of a window valve. As in the case of a window air inlet, the incoming volume of fresh air is controlled both manually and automatically.
Wall exhaust valves are usually located at the top of the wall, where the exhaust air naturally rises. Inlet valves to the wall are most often mounted between the window and the radiator. They do this so that the incoming cold air at the same time also heats up.
 If the wall vent valve is installed directly above the radiator, the fresh air flow will spontaneously heat up before being delivered to the room.
If the wall vent valve is installed directly above the radiator, the fresh air flow will spontaneously heat up before being delivered to the room.
Advantages of installing a supply valve over conventional ventilation:
- The ability to regulate the flow of fresh air;
- The ability to pass significantly less street noise;
- The presence of filters of varying degrees of air purification.
The design of the wall supply and exhaust valve does not allow moisture to penetrate into the room. Many models of these local ventilation devices often include filters to purify the air.
Interroom transfer grates
In order for fresh air to freely penetrate into all parts of the house, overflow components are needed. They allow air flows to flow freely from the inlet to the exhaust, taking with them dust suspended in the air mass, animal hair, carbon dioxide, unpleasant odors, household fumes and similar inclusions.
The flow is carried out through open doorways. However, it should not stop even if the interior doors are closed. To do this, a gap of 1.5-2.0 cm is left between the floor and the canvas of interior doors.
 In order for fresh air to move freely to the hood and wash all the rooms, overflow grilles are installed in the door leafs. If they are not there, then a gap of up to 2 cm is left between the floor plane and the canvas.
In order for fresh air to move freely to the hood and wash all the rooms, overflow grilles are installed in the door leafs. If they are not there, then a gap of up to 2 cm is left between the floor plane and the canvas.
Also for these purposes, overflow gratings are used, mounted in a door or wall. The design of such gratings consists of two frames with blinds. They are made from plastic, metal or wood.
What are there?
Units are divided into the following types:
- By type of construction - shell-and-tube, spiral, rotary, lamellar, lamellar finned.
- By appointment - air, gas, liquid. The air unit is understood as a ventilation unit, the task of which is ventilation with heat recovery. In gas-type appliances, smoke is used as a heat carrier. Liquid recuperators - spiral and coil - are often installed in swimming pools.
- According to the temperature of the coolant - high-temperature, medium-temperature, low-temperature. Heat exchangers are called high-temperature heat exchangers, the heat carriers of which reach 600C and above. Medium temperature - these are devices with coolant characteristics in the region of 300-600C. The temperature of the coolant of the low-temperature unit is below 300C.
- According to the method of media movement - direct-flow, counter-flow, cross-flow. They differ depending on the direction of air flow. In cross-flow units, the flows are perpendicular to each other, in counter-flow units, the inflow and exhaust are opposite to each other, and in direct-flow units, the flows are unidirectional and parallel.
Spiral
In spiral models, heat exchangers look like two spiral channels through which media move. Made from rolled material, they are wound around a dividing wall located in the center.
Rotary heat exchangers
Are established in forced-air and exhaust ventilating systems. The way they operate is based on the passage of supply and exhaust flows through a special rotary heat exchanger of a rotating type.
Plate heat exchanger
It is a heat exchanger where heat is transferred from a hot medium to a cold one by passing through steel, graphite, titanium and copper plates.
Finned plate heat exchanger
Its design is based on thin-walled panels with a ribbed surface, produced using high-frequency welding and connected to each other in turn with a turn of 90. Such a design, as well as a variety of materials used, allows achieving a high temperature of the heating medium, minimum resistance, long service life, high indicators of heat transfer area in relation to the total mass of the heat exchanger. In addition, such devices are inexpensive and are most often used for processing heat from exhaust gas media.
The popularity of ribbed models is based on the following advantages (in comparison with analogues of the rotary and traditional plastic type):
- high operating temperatures (up to 1250C);
- small weight and size;
- more budgetary;
- quick payback;
- low resistance along gas-air paths;
- resistance to slagging;
- ease of cleaning channels from pollution;
- long service life;
- simplified installation and transportation;
- high rates of thermoplasticity.
Industrial and domestic recuperators - what are the differences?
Industrial units are used in industries where there are thermal technological processes. Most often, industrial means precisely traditional plate heat exchangers.
Domestic devices include devices characterized by small dimensions and low productivity. These can be supply and exhaust models, the main task of which is ventilation with heat recovery. Such systems can be implemented in different ways - both in the form of a rotary and in the form of a plate heat exchanger. And each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Next, consider the main selection criteria in order to understand which recuperator is better to buy.
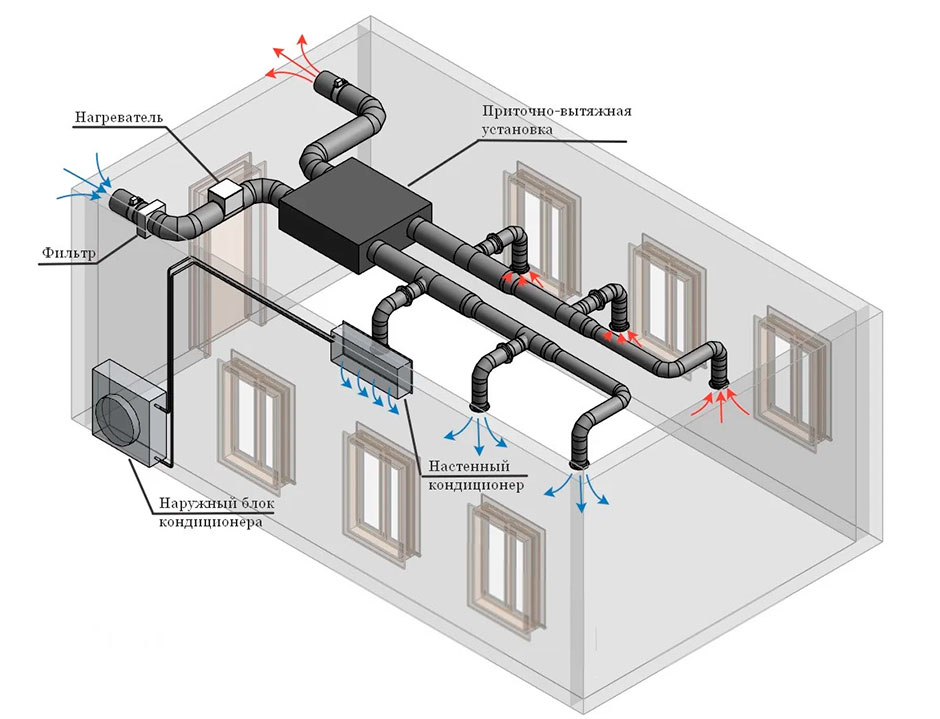
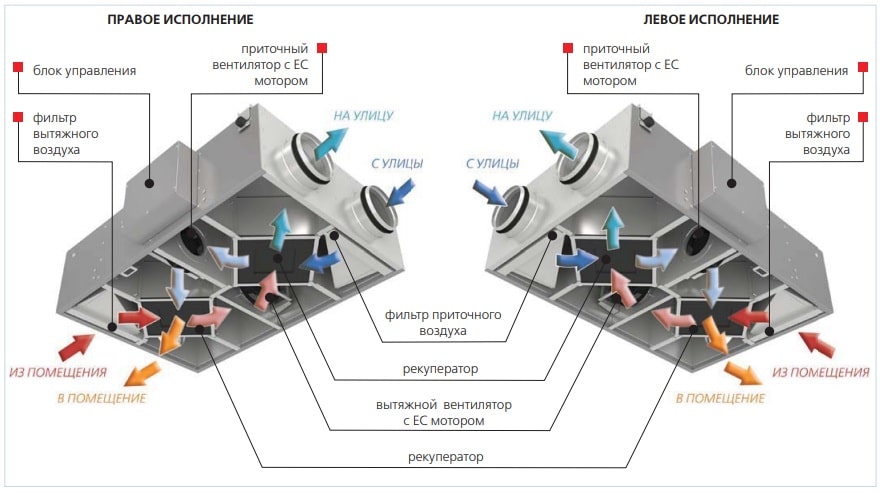
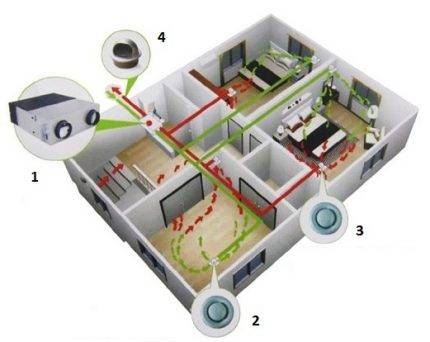
Supply and exhaust ventilation of the apartment
Forced ventilation in the apartment has a structure different from domestic natural ventilation, consists of the following elements:
- Protective grilles for the inlet, which prevent the entry of debris from the ventilation into the apartment.
- Air filters that purify the outdoor air.
- Specialized valves that help control the level of thrust and the volume of incoming air.
- Noise insulating pad. The operation of ventilation delivers a lot of noise, and in order to prevent a violation of the noise level in the apartment, ventilation shafts are laid with soundproofing materials.
- Elements of automatic control over the operation of ventilation.
- Air outlets and monoblocks, which connect all parts into a single system.
Artificial ventilation for apartment buildings can be divided into two types:
- Compact.
- Complete.
Scheme of supply and exhaust ventilation in the apartment
Compact ventilation system for an apartment
Compact supply ventilation is a small-sized system, which, in addition to dimensions, has several more positive aspects.Compact supply ventilation systems are easy to install, they can be installed even by a person without specialized education. For installation, you only need the system itself and a device capable of making holes in the walls. Such systems are low cost. The supply ventilation device can be installed directly under the window in any room or on the balcony. Thanks to filtration and ionization, the air in the room will become cleaner. Filters do not require regular replacement and are economical to use.
Compact ventilation systems are much quieter than large ones, so they can even be installed in the bedroom. And thanks to their modern design, they will perfectly complement any interior. Compact ventilation units are best suited for installation on the upper floors of apartment buildings, as on the top floor, it is most difficult to establish proper air exchange.
Another disadvantage of compact systems is a small coverage. They can only be installed in small rooms up to 45 square meters, otherwise they simply do not make sense.
Some systems are equipped with heaters for heating outdoor air in winter. In some, recuperators are installed, this additionally helps to save electricity when heating a living space.
Complete ventilation system
Supply ventilation in the apartment can be implemented with the help of a full-fledged automatic ventilation system. Such a system has a number of negative aspects: large size, difficult to install, and expensive.
Such a ventilation system in an apartment can provide sufficient air inflow and outflow and partially save on space heating, since systems are often equipped with a heat exchanger.The use of a full-fledged supply system in a small apartment is impractical; the system is more suitable for normalizing air exchange in large rooms.
Full supply and exhaust ventilation in the apartment has a number of advantages:
- Provides inflow and outflow of air in large volumes, fully regulates air exchange in the apartment.
- Helps to distribute air throughout the apartment.
- Thanks to the installed filters, the air in the apartment becomes clean, does not contain dust and allergens.
- Such a ventilation device in an apartment can humidify the air, cool or additionally warm it up.
- Some systems are equipped with automatic climate control, which allows you to fully automate the process of air exchange in the house.
Such devices can be located both on the floor and be hinged, it all depends on the size of the system. But most often, full-fledged supply and exhaust systems are located near the central heating battery at about the same height.
2 id="naznachenie-ventilyatsionnyh-sistem-i-ih"> Purpose of ventilation systems and their types

Ventilation systems are emergency and working type. If the working systems maintain sanitary conditions for people in the premises, then the emergency ones are switched on only when an emergency situation arises that threatens the life and health of the people present there. It can be fire, toxic fumes, explosive gases, toxic substances. In an emergency, there is no air supply from the outside, it only prevents the contaminated air from reaching other rooms.
They are:
- local type;
- general type.
The general exchange system contributes to the presence of a sufficient amount of air exchange in the premises. It also helps to remove excess moisture, pollution, high temperature. When used for air exchange channel and non-channel systems. Local ventilation supplies air to a specific room and removes pollution in the resulting place. It is installed where the number of employees is small, and the room is large, so air exchange is carried out only at the places of work of people.
The design of ventilation systems is:
- channel type;
- channelless type.
The duct view is an air vent system that transports air. This system is installed in rooms with a large area. If channels are not provided, then such a system is called channelless. Channelless systems are laid under the ceiling or floor. These systems are among the simplest and least energy-intensive options.
Ventilation cleaning equipment
When professionals get down to business, ventilation cleaning begins with “reconnaissance”. For this, modern means are used - video cameras placed inside the air ducts.

Since initially the channels do not abound with inspection hatches, they have to be cut out in the places previously indicated on the diagram. A video camera is inserted into these openings, and the most advanced option is a mobile radio-controlled camera, shown in the photo:

When the images of the channels of supply and exhaust forced ventilation are obtained, a mechanical cleaning plan is developed.

In general, the process technology is unchanged; the following equipment is used for its implementation:
- brush installation;
- a compressor that drives the brushes;
- vacuum machine with powerful high pressure fan;
- filter block.

The brush unit is a long hose (up to 30 m) with a brush of a certain configuration installed at the end, matched to the shape of the section and the material from which the pipe is made. The brush is inserted through a cut-out hatch into the air duct on one side, and on the other, a hose of a vacuum machine is connected to it. To capture all the dirt, the machine is attached to the filter unit, as shown in the general diagram:
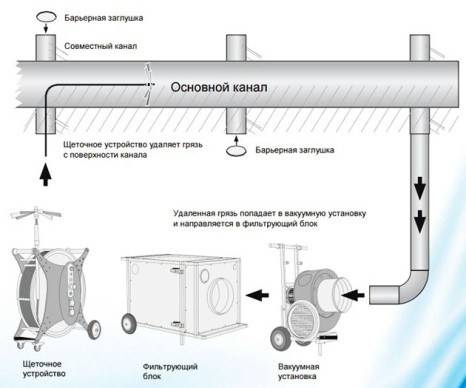
To start cleaning, all units are turned on at the same time, while the rotating brush is already in the ventilation channel. The compressor not only drives the brushing apparatus, but also constantly blows dirt out from under the hard bristles, helping the vacuum machine to draw it in. How this happens is shown in detail in the video:
When the exhaust ventilation is clogged with fatty deposits, the process becomes more complicated. A tool with very hard bristles, a power scraper, or a chemical cleaner is being used. The solution is fed into the pipe during cleaning, and flows out along with grease and dirt through a hole made in the lower part of the channel. The procedure is very laborious and time consuming.
After all the pipes are cleaned, the supply and exhaust units are serviced. Depending on the type of units, SKD is performed with the cleaning of all parts and elements that come into contact with the transported air.All filters must be changed without fail, otherwise, after the fans are started, the dust from them will again be inside the air ducts. Then the effectiveness of the entire procedure will be minimized.
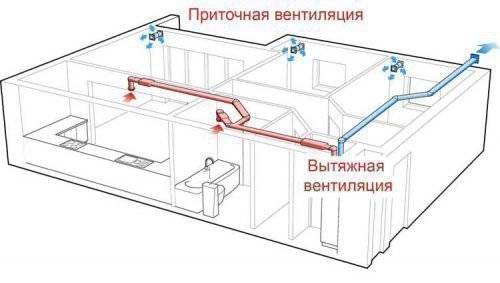
Features of forced air exchange
If natural ventilation does not provide full air renewal, a powerful supply and exhaust system is installed in a private house.
It helps to balance the air currents that circulate between rooms and the outside environment continuously. Such ventilation guarantees a stable supply of purified fresh air and the removal of polluted air to the outside.
Description of mechanical ventilation option
Modern multifunctional supply and exhaust ventilation units make the most of the energy of the supplied air flows and convert it into heat.
Such systems produce deep cleaning of the supply air, completely filtering from dust, various allergens, bacteria and other harmful microorganisms.
Additional processing is created using filtration equipment, highly efficient noise absorbers, ionization and humidification devices, and sometimes flavoring devices are used.
The air flows that have been processed are distributed throughout the house through special ventilation ducts. Prepared clean air enters the bedroom and children's room, study, living room, kitchen and bathrooms, auxiliary rooms, and is removed from there by the exhaust system
The functional elements of a system with forced air exchange are filters and recuperators, fans, hoods, control devices and, directly, the ventilation unit.
The built-in electronics makes it possible to selectively set the optimal user operating modes of the system in terms of temperature and humidity, and in time. Remote controls and smart controllers greatly simplify operation.
Mechanical ventilation helps prevent the formation of unpleasant odors in the kitchen, prevents the appearance of dampness and the spread of multi-colored mold, solves the problem of constant humidity in the bathroom and condensation on the surface of the heated floor, double-glazed windows, door blocks.
Powerful units with integrated filters, special noise absorbers and heaters take up a lot of space. To arrange them, you need to free up space in the attic or in the basement of a private house
Modern multifunctional forced ventilation systems are often combined with intelligent control and monitoring systems. Such measures optimize the operation of the equipment of all installed engineering systems in the house, allow you to organize user-friendly remote control of equipment via the Internet.
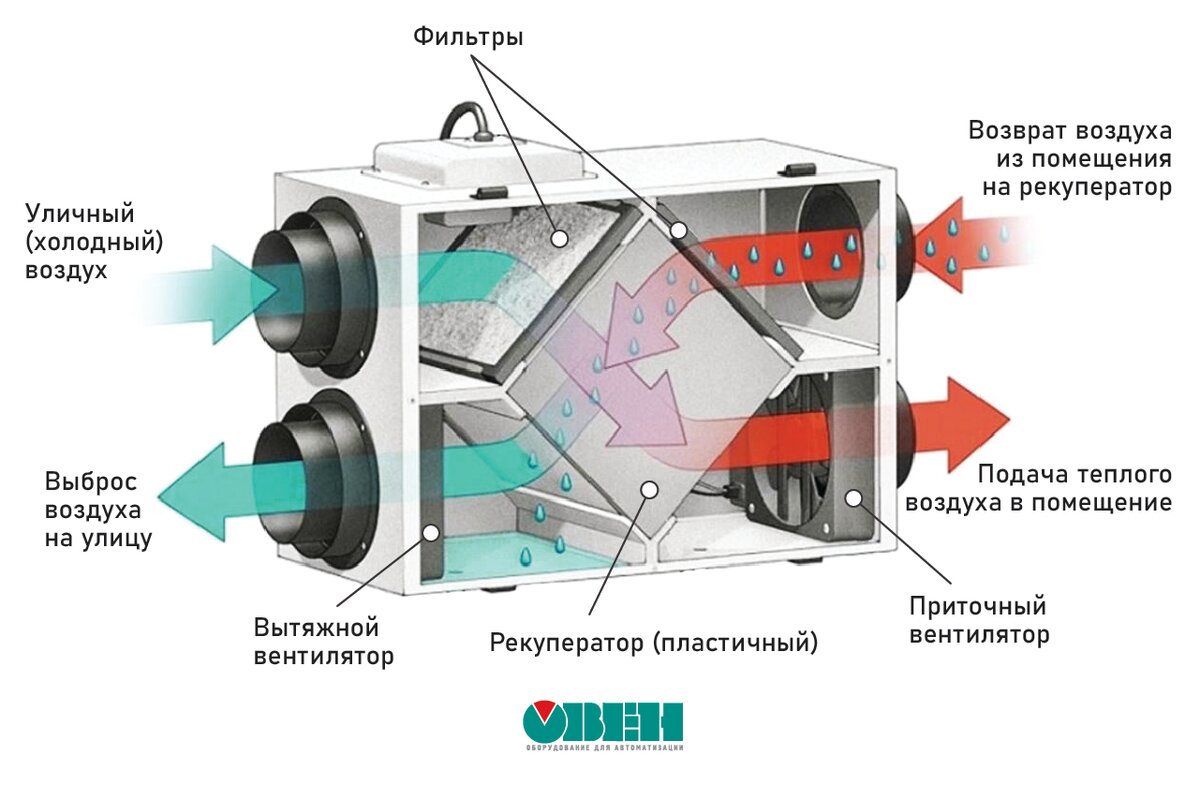
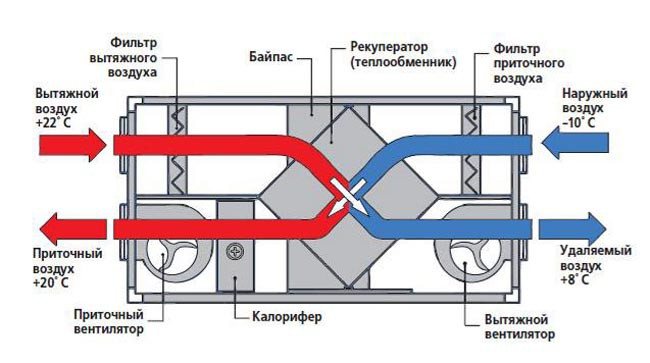
Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery
AT heat recovery schemes The supply and exhaust fixed installation is responsible for the air exchange in the building. The air from the environment enters the system, after which it is cleaned from dust and contaminants by the filter and is sent to the heat exchanger for the main heating.
The air masses are heated to the required temperature in an electric / water heater and are distributed throughout the house through durable galvanized steel ventilation ducts.
A heat recovery system will ensure high air quality in a residential building all year round.At low speeds of working fans, stationary air handling units operate almost silently.
Automation makes it possible to flexibly control the operation of the equipment: regulate the air supply, set a comfortable temperature, change the speed of air flows.
Recuperation is the rational use of the thermal energy of the exhaust air for the subsequent heating of the supply air. This allows you to reduce up to 85% of heat costs for heating the air flow from the external environment in winter
Maintenance of such an installation consists of regular filter changes. It is recommended to replace new elements for air purification from dust once a quarter.
System without heat recovery
To organize functional supply and exhaust ventilation without an air heat exchanger, several exhaust systems and a central supply unit are used at once. Outdoor air is heated or cooled, then it is cleaned in a filter, after which it is distributed through a network of channels to living rooms.
Removal of spent heavy air masses is carried out by hoods in the premises for economic and technical purposes. Such systems are made partly natural and partly forced. They function due to natural draft and due to duct fans.
Supply and exhaust circuits without heat recovery provide heating and purification of the air entering the house, but consume a large amount of energy for the constant processing of air flows.
Fans for ventilation systems
For mechanical air supply in ventilation systems, blowing mechanisms are used. One of the most common is fans.Classification of these devices according to various criteria:
| sign | Subspecies |
| Design | Axial or axial views |
| Diagonal fans | |
| Centrifugal devices | |
| Diameter devices | |
| Bladeless direct-flow | |
| Application conditions | Devices for air with a temperature regime of not more than + 80 ° С |
| Devices for rooms with high humidity | |
| Heat resistant fans | |
| Mechanisms with increased explosion resistance | |
| Devices capable of working in rooms with a lot of dust and other impurities | |
| Drive features | Directly connected to the electric motor |
| Devices on socket connections | |
| V-belt drives | |
| Infinitely Variable Drives | |
| Installation location | Frame - mounted on special supports |
| Duct - installed in the duct cavity | |
| Roofing - mounted on the roofs of buildings |
In addition to the listed signs, fans can differ in power and speed of rotation, noise level.
Axial fans are the most common type devices used in ventilation systems of residential buildings. Such devices are characterized by high efficiency and simple design.
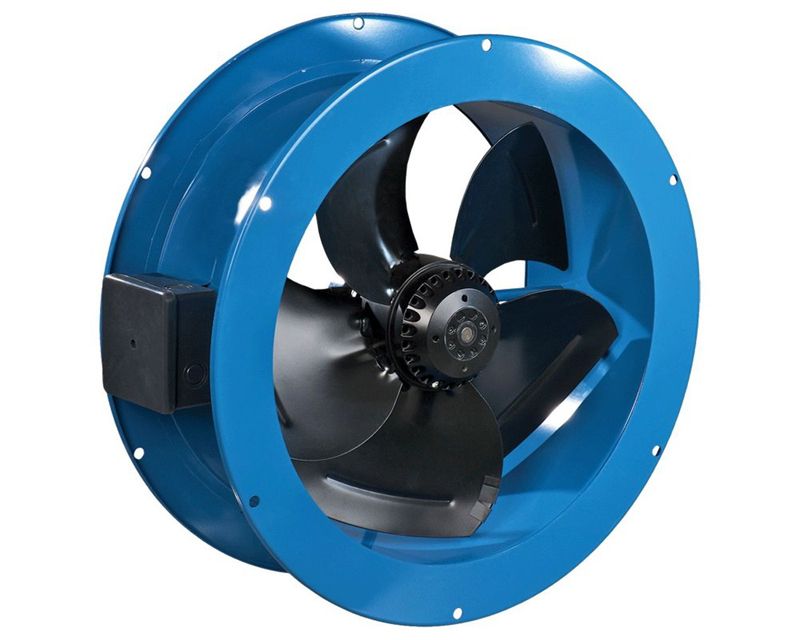 Axial fan
Axial fan
Radial devices are distinguished by a special spiral shape of the blades. The blades are rigidly fixed in the cylinder. The main feature of the operation of such a device is that the flow of outgoing air is always directed perpendicular to the incoming one.
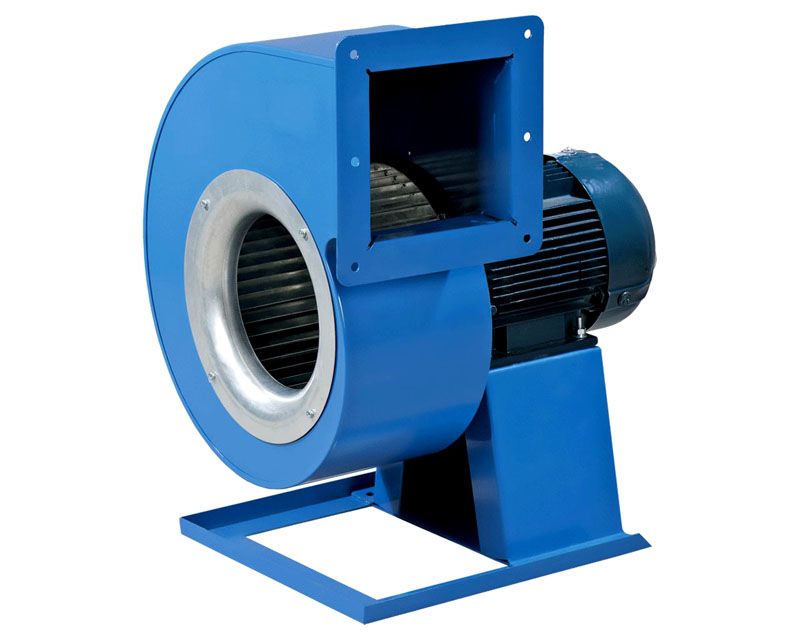 Radial fan
Radial fan
Diagonal structures are outwardly similar to axial ones, but they direct the air flow in a diagonal direction. This effect is achieved due to the specific design of the case. Such devices produce much less noise.
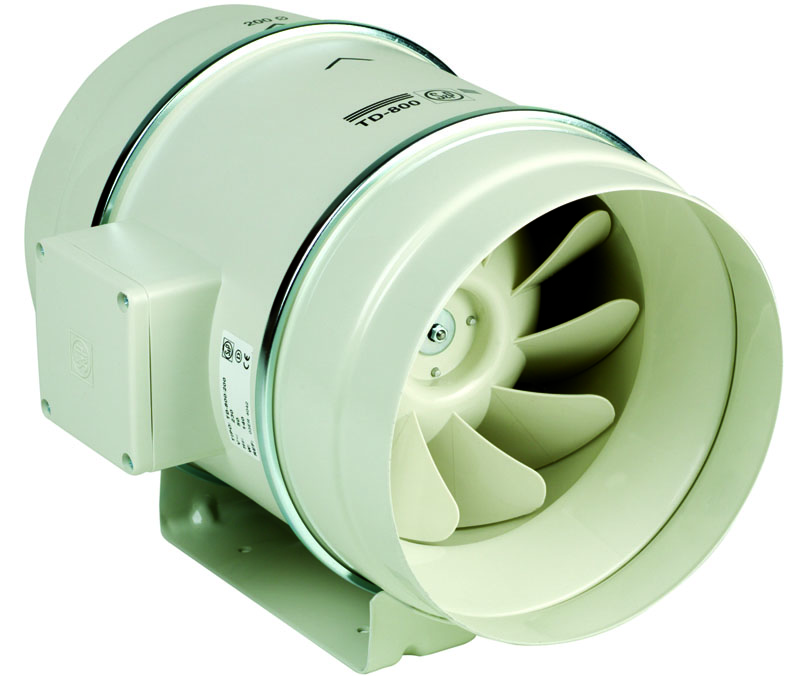 Diagonal device
Diagonal device
Diametric products are similar to drums with blades that have an upward bend.They are highly aerodynamic and can serve large ducts.
 Product with a diametrical design
Product with a diametrical design
Direct-flow turbines force air through frames of a special design. Such devices pump large volumes of oxygen and allow you to direct the flows in the right direction.
 Direct flow device
Direct flow device