- Features of household gas analyzers
- Principles of classification of gas analyzers
- Principle and advantages
- Installation of appliances
- Classification by form factor:
- What else to consider in the choice?
- Principles of classification of gas analyzers
- Operating principle
- Gas analyzers - principle of operation
- Types of gas analyzers according to the principle of operation
- Types of gas analyzers
- Thermal conductometric
- Pneumatic
- Magnetic
- ionization
- ultraviolet
- Luminescent
- X-ray analyzers
- The most common devices
- Main manufacturers
- Olympus Corporation
- FPI (Focused Photonics Inc)
- Bruker
Features of household gas analyzers
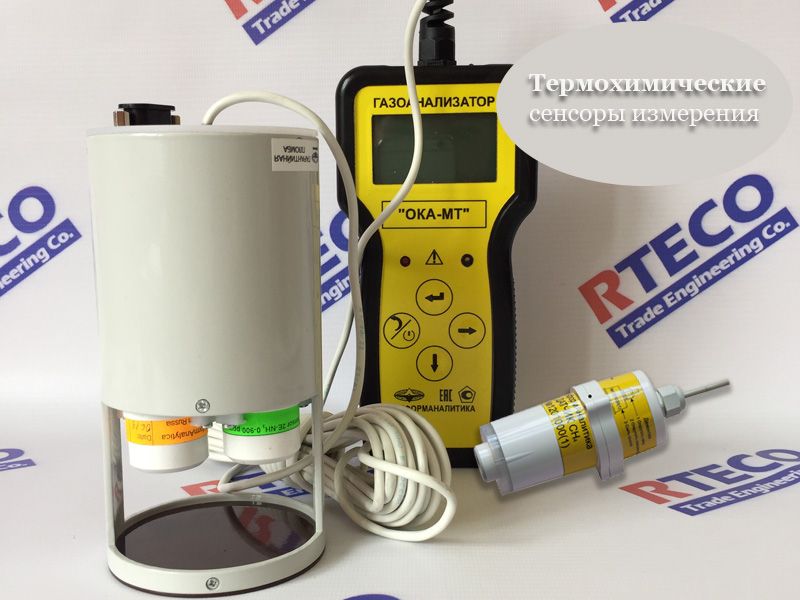
Devices for use at home are characterized by compactness, limited performance and ease of operation. If professional models involve stationary operation, then household natural gas analyzers can be moved from place to place, since most of them are portable devices.
The functionality of the home appliance is designed to detect gas leaks with the study of fumes at different points. At the same time, different levels of functional content are implemented in the segment of household appliances.
For example, a household gas analyzer from the budget category is equipped with the simplest warning system in the form of a light or sound indication.That is, if an excess of the concentration of gas vapors relative to the standard value is noticed in the room, the detector will give an appropriate signal, but without additional information.
More sophisticated household appliances are equipped with a display that reflects information with detailed air characteristics.
Household analyzers of gas mixtures are manufactured in manual and automatic versions. In the first case, this is a simple absorbent device with an average level of analysis accuracy. Automatic products are characterized by high accuracy and wide possibilities of various environmental studies. For example, in a continuous mode, check the set parameters of a mixture or its individual component.
It is worth noting that household appliances can be not only portable, but also stationary, requiring special installation. At the same time, home stationary gas analyzers also have compact dimensions, unpretentious maintenance and low performance.
Principles of classification of gas analyzers
All currently existing analyzing devices are classified based on structural and technological details. The classification characterizes the specific functionality of gas analysis instruments.
For example, an indicator and an alarm may be somewhat similar, but are classified as different meters. The same applies to leak detectors and gas analyzers.

A small-sized easy-to-use leak detector is a design that is directly related to gaseous medium analyzers. The use of such devices is relevant for various conditions of industrial production and the domestic sphere.
The design classification defines properties such as mobility and portability. The ability of instruments to measure a certain number of components is classified as a single-component or multi-component device.
Similarly with the number of measurement channels, where there is a classification for single-channel or multi-channel gas analyzers.
Finally, there is another criterion that shows the specific purpose of the devices. For example, there are gas analyzers for monitoring car exhaust gases, and there are devices that control technological processes.
Principle and advantages
The principle of operation of portable devices is the same as in stationary ones. Stationary ones take up a lot of space and require special handling skills. Learn to work with portable easier. Such devices weigh an average of 1.5-2 kg, the batteries last for several hours.
 They have a liquid crystal display, which displays information about the composition in the form of symbols used in chemistry.
They have a liquid crystal display, which displays information about the composition in the form of symbols used in chemistry.
The device has the ability to accumulate and store information, including test results and photographs.
Accuracy - 0.1%, which is enough to work in the field of recycling.
Here's what you can check with a portable analyzer:
- Large structures.
- Complex structures.
- Ingots.
- Small parts.
- Pipes.
- Rods.
- Blanks.
- Electrodes.
- Chips and metal dust.
Installation of appliances
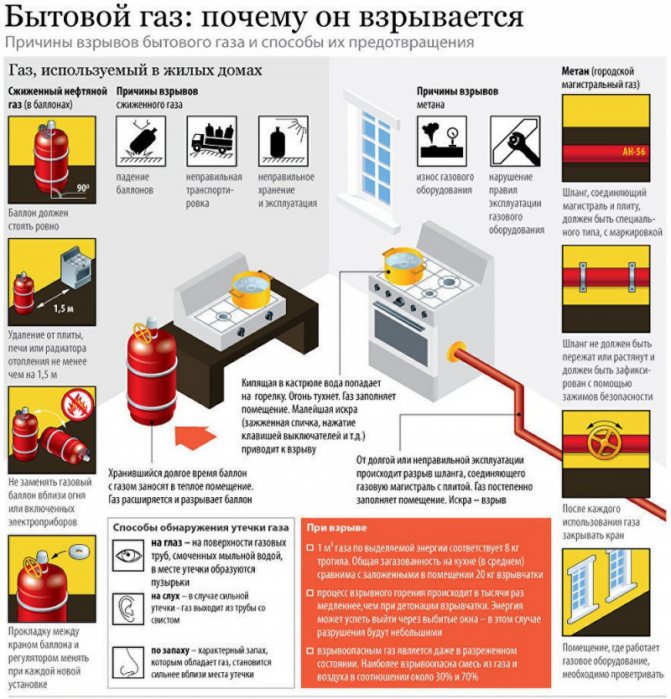
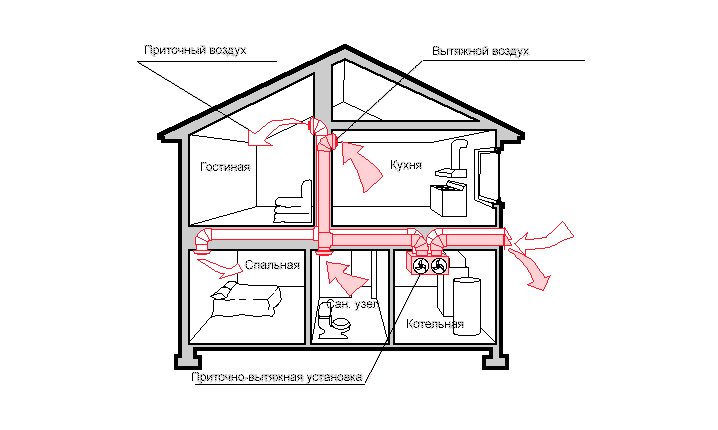
For the installation of gas analyzers, vertical surfaces are best suited - places of possible gas leakage (near meters, columns, boilers, stoves).
The device cannot be mounted:
- At a distance of less than 1 m from the burners.
- In dirty and dusty areas.
- Close to ventilation tunnels.
- In areas where combustible and toxic materials are stored.
During installation, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the gas and the height of its concentration. So the positions of the gases from the floor are as follows:
- methane - 50 cm,
- carbon monoxide - 180 cm (to the ceiling - 30 cm)
- propane - 50 cm.
It is better to mount the combined model in the range of 50-30 cm to the ceiling.
To make the valves work stably, put batteries in the device that can automatically switch to emergency power.
Installing the device is not difficult. It can be fixed with dowels or screws.
His passport details the connection of electricity to it and its contact with other equipment.
At least once a year, the gas analyzer must be subject to an inspection procedure.
Classification by form factor:
By form factor, devices can be divided into:
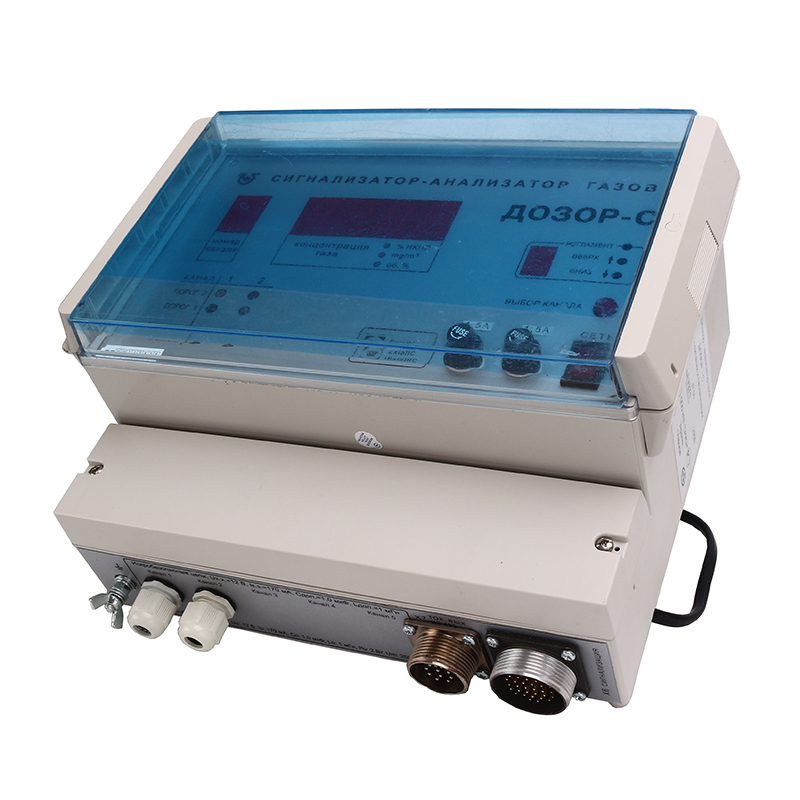
- Stationary gas analyzers are devices designed for stationary installation in the working area of industrial plants and combines, chemical laboratories, oil refineries and gas production enterprises and other industries
- Portable gas analyzers are devices for individual use that serve as additional protection for stationary gas analyzers
- Portable gas analyzers are devices that occupy an intermediate niche between stationary and portable ones. Larger than portable devices, but with more features. Suitable for small businesses.
Gas analyzers are indispensable devices that are used both in production and at home and allow you to determine the qualitative and quantitative composition of pollutants in the work area or any other room where there are dangerous factors for the leakage of harmful substances and gases.
What else to consider in the choice?
In addition to the basic possibilities of analyzing the gaseous environment, the switching capabilities and the degree of protection of the housing should be taken into account. Stationary and independent alarm sensors do not have to communicate with electronic controllers and computers. But if you need a household gas analyzer with a gas shut-off device, then it is desirable to provide for the presence of interfaces such as RS-232 (for connecting to a computer) and a control relay for integrating the device into complex security tools. This will allow you to connect the device to the hood, gas equipment valve regulators and the siren.
The degree of protection of the device itself is determined by the IP marking. Room household models, as a rule, are provided with an IP20 dust and moisture protection class. The most durable and reliable gas analyzers have an IP67 multi-layered shell that protects against shock, aggressive chemical environments and water flooding.
Principles of classification of gas analyzers
All currently existing analyzing devices are classified based on structural and technological details. The classification characterizes the specific functionality of gas analysis instruments: for example, an indicator and a signaling device may be somewhat similar, but are classified as different meters. The same applies to leak detectors and gas analyzers.
A small-sized easy-to-use leak detector is a design that is directly related to gaseous medium analyzers. The use of such devices is relevant for various conditions of industrial production and the domestic sphere.
The design classification defines properties such as mobility and portability. The ability of instruments to measure a certain number of components is classified as a single-component or multi-component device. Similarly with the number of measurement channels, where there is a classification for single-channel or multi-channel gas analyzers.
Finally, there is another criterion that shows the specific purpose of the devices. For example, there are gas analyzers for monitoring car exhaust gases, and there are devices that control technological processes.
Operating principle
In the catalogs, gas analyzers are represented by models of several types.
They differ from each other by the principle of action:
thermal conductometric - work on the basis of the dependence of the thermal conductivity of a gas or air mixture on its composition. Devices selective, highly sensitive;
thermochemical - a catalyst is installed in the body of the device, on which the component to be determined is oxidized or another reaction occurs with its participation. The concentration is determined by the thermal effect of the process;
magnetic - designed to determine the oxygen content. The principle of operation of the devices is based on the dependence of the magnetic susceptibility of the mixture on the concentration of O2;
pneumatic - determine the density and viscosity of the gas mixture, which depends on the qualitative and quantitative composition;
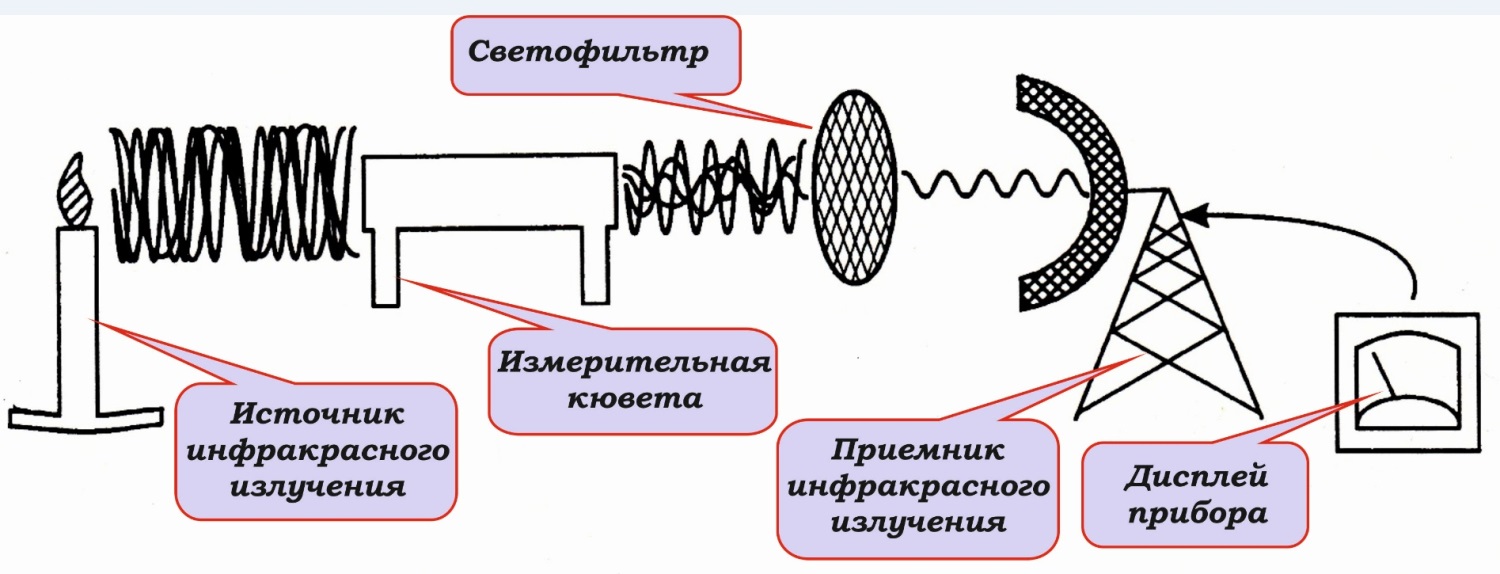
infrared - analyze the degree of absorption of infrared rays by various components of the gas mixture. The equipment is highly selective in relation to compounds whose molecules consist of two or more atoms, therefore it is widely used in laboratory conditions;
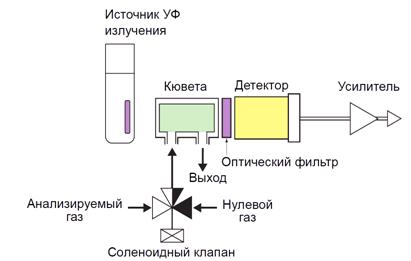
ultraviolet - generate radiation in the range of 200-450 nm. Instruments are effective for determining the concentration of monatomic gases;
luminescent - work on the basis of the phenomenon of luminescence, which occurs as a result of the chemical reaction of the component being determined with the reagent;
photocolorimetric - measure the intensity of staining of substances obtained as a result of the reaction between a specific reagent and the component being determined. The peculiarity of this type of gas analyzers lies in the different aggregate states of the reagent. The process can take place in the liquid phase or on a solid carrier: tablet, tape, etc.;
electrochemical - measure the electrochemical characteristics of the analyzed mixture. Devices have low selectivity;
ionization - determine the electrical conductivity of the medium, which depends on the type, quantity, mobility of ions of different components.
Gas analyzers - principle of operation
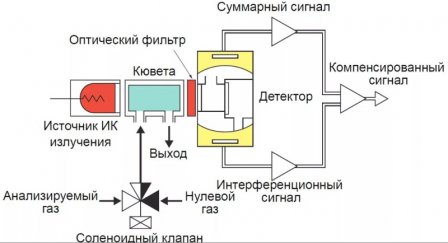
Gas analyzers are measuring instruments designed to obtain measurement information about the amount of a substance or its concentration in the analyzed gaseous medium.
In the food industry, gas analyzers are widely used to analyze flue gases during the combustion of various types of fuel, to control the composition of gaseous media in baking and drying chambers, to control the concentration of limit values in fire and explosion hazardous industries and premises where the accumulation of gases harmful to the health of the attendant is possible. personnel.
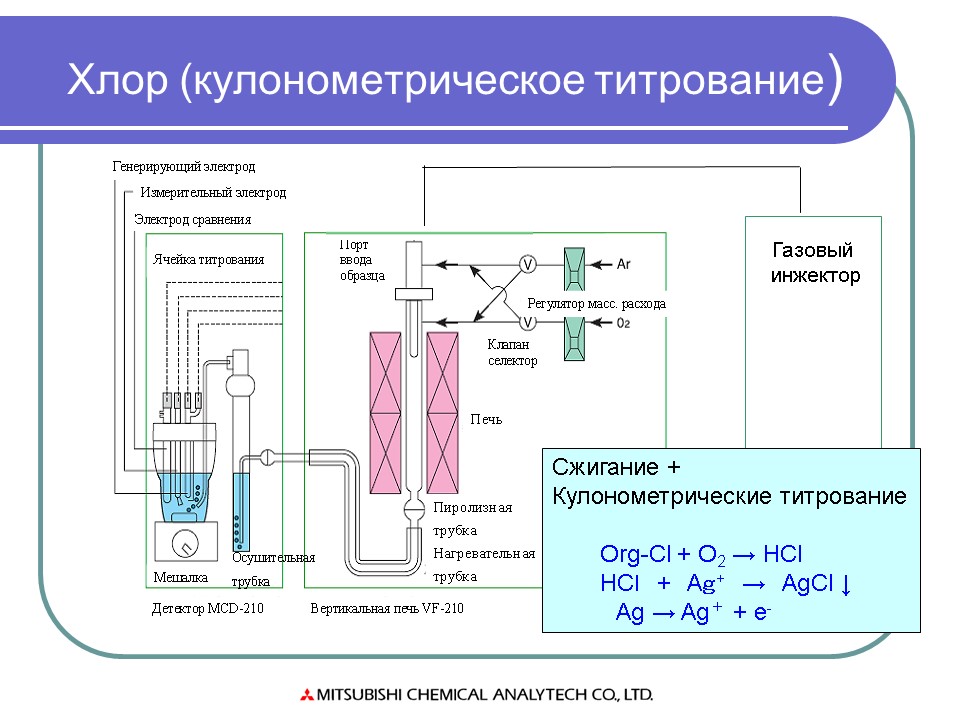
The principle of operation of the device is based on the dependence of the thermal conductivity of the analyzed mixture on the concentration of CO2 in it, the thermal conductivity of which is lower than other components.
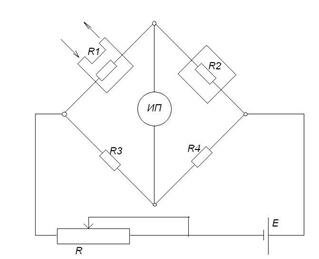
The basis of the device is a compensation comparative bridge circuit of alternating current from 3 bridges: working, comparative and compensation. The working bridge is built according to the differential scheme. Its sensitive elements are placed in closed ampoules. Two elements are washed by the analyzed gas, the other two - by the control.
Determination of oxygen concentration by magnetic gas analyzers is based on a physical property - paramagnetism.
Paramagnetic materials are drawn into the magnetic field, while diamagnetic materials are pushed out of it.
Oxygen (+1) and nitric oxide (+0.36) have the highest positive susceptibility.
Magnetic gas analyzers are divided into thermomagnetic and magnetomechanical.
The thermomagnetic method has received wider application.
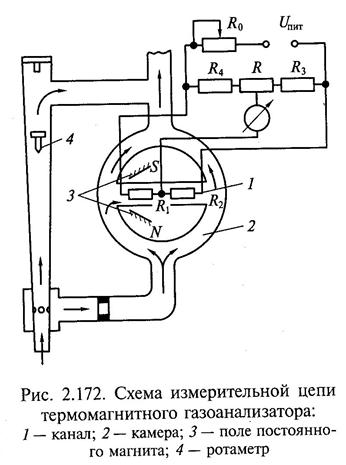
It is based on the change in volumetric magnetic susceptibility with temperature (Fig. 2.62).
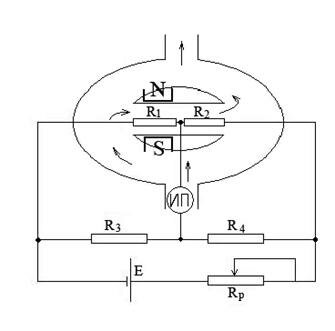 |
Rice. 2.62. Schematic diagram of the measuring transducer of a thermomagnetic gas analyzer
The presence of oxygen in the analyzed gas leads to its movement along the heating elements, which simultaneously cools the resistor R1 and heats the resistor R2, i.e. changes their resistance. The difference in resistance, functionally related to the oxygen concentration, leads to an unbalance of the bridge, which leads to a change in the output voltage, measured by a secondary device calibrated in percent concentration.
To measure the volume concentration of oxygen in the flue gases of boiler plants, a gas analyzer of the MN 5110T type is used. The gas circuit of the device includes two gas intake devices with ceramic filters for cleaning, auxiliary devices for bringing the parameters of gas and air to the required values, working and comparative chambers of two receivers and two flow drivers that ensure the pumping of gas and air through the system.
Gas for analysis is taken from the boiler through a ceramic filter, from where it enters the moisture equalization unit, where it is either dried (with condensate removal) or humidified. A manometer is used to control the vacuum in the system.
Types of gas analyzers according to the principle of operation
1. Devices, the action of which is based on physical methods of analysis, including auxiliary chemical reactions. With the help of such gas analyzers, a change in the volume or pressure of a gas mixture is determined as a result of chemical reactions of its individual components.
2. Devices, the action of which is based on physical methods of analysis, including auxiliary physical and chemical processes (thermochemical, electrochemical, photocolorimetric, etc.). Thermochemical methods are based on measuring the thermal effect of the reaction of catalytic oxidation (combustion) of a gas. Electrochemical methods make it possible to determine the concentration of a gas in a mixture by the value of the electrical conductivity of the electrolyte that has absorbed this gas. Photocolorimetric methods are based on the change in color of certain substances when they react with the analyzed component of the gas mixture.
3. Devices, the operation of which is based on purely physical methods of analysis (thermoconductometric, thermomagnetic, optical, etc.).Thermoconductometric are based on measuring the thermal conductivity of gases. Thermomagnetic gas analyzers are mainly used to determine the concentration of oxygen, which has a high magnetic susceptibility. Optical gas analyzers are based on the measurement of optical density, absorption spectra or emission spectra of a gas mixture.
Gas analyzers can be divided into several types depending on the tasks performed - these are combustion gas analyzers, gas analyzers for determining the parameters of the working area, gas analyzers for monitoring technological processes and emissions, gas analyzers for water purification and analysis, etc., they are also divided according to the constructive execution for portable, portable and stationary, by the number of measured components (there may be a measurement of one substance or several), by the number of measurement channels (single-channel and multi-channel), by functionality (indicators, signaling devices, gas analyzers).
Combustion gas analyzers are designed for setting up and monitoring boilers, furnaces, gas turbines, burners and other fuel-burning installations. They also allow monitoring emissions of hydrocarbons, carbon oxides, nitrogen, and sulfur.
Gas analyzers (gas detectors, gas detectors) for monitoring the parameters of the air in the working area. Monitor the presence of hazardous gases and vapors in the working area, indoors, mines, wells, collectors.
Stationary gas analyzers are designed to control the composition of gas during technological measurements and control emissions in metallurgy, energy, petrochemistry, and the cement industry. Gas analyzers measure the content of oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur oxides, freon, hydrogen, methane and other substances.
Types of gas analyzers
A variety of gas analyzers according to the physical signs of work. To date, there are more than 10 varieties of gas analyzers, which are divided according to the physical characteristics of the analysis of the gaseous environment.
But, as such, a universal design does not exist, according to which the composition of impurities is measured. For some, a certain physical principle is suitable, while for others it will be unacceptable.
By the way, read this article too: Equipment Corrosion
Thermal conductometric
Can respond to the thermal conductivity of mixtures. It analyzes how efficiently the temperature is transferred in the gaseous medium. This device is suitable only if the thermal conductivity of impurities and gases differs significantly from each other.
Pneumatic
Designed to determine the viscosity of the mixture, which is inherent in this room. They are also used in explosive sites, as they do not have an electrical component. There is no spark, therefore, the gas will not ignite.
Magnetic
It is suitable for oxygen analysis. These devices are used in those mechanisms where the gas mixture is to be burned. Indicator example: lambdazont. It is found in the exhaust system of cars, which are now relevant in the modern car market. Designed to determine the concentration of oxygen in the ratio of the output of exhaust gases. It also serves to determine how well the automotive fuel has warmed up. Infrared
They are needed in order to irradiate the gaseous medium with infrared rays. They have a built-in explosion-proof housing, as they are used where there are explosive substances.It is used for laboratories and industry.
ionization
Checks for electrical conductivity. If there is an impurity in the composition, then the electrical conductivity is different. This is fixed and reflected as a percentage on the scoreboard. It is designed for gases that are not flammable.
ultraviolet
They have the same principle as the infrared ones. But there is a difference in the fact that they are irradiated with ultraviolet rays. These devices can analyze the intensity of the absorption of the medium, using the rays that are directed at them.
Luminescent
It is necessary in order to determine which gases have luminescent properties. They depend on the concentration of these impurities. This is a rare type of device because it is the most complex type. In practice, as a rule, simpler technologies are used. There are other equipment that have other physical principles. It is the most expensive and requires complex maintenance. Equipment based on chemical principles is filled with certain chemicals. They are used when there are specific gases for which other methods are not suitable.
By the way, read this article too: Oil classification
X-ray analyzers
Each device has:
- an x-ray tube that fluoresces;
- detector;
- registration device;
- control module.
An important feature that is necessary for large acceptance points is the adaptation of the device to the solid-state mode of operation. This type of device analyzes several dozen elements in alloys at once.
Sample size can be negligible, e.g. chips
This type of device analyzes several dozen elements in alloys at once.Sample size can be negligible, for example chips.
In general, even slag-like and dust-like elements up to 50 microns are suitable. They work quickly, since they do not need to be calibrated each time for a new analysis. A separate setting is carried out only for certain complex tasks.
The most common devices
Optical and electrochemical models stand out as the most common devices that are part of the three noted groups. Their attractiveness is due to the possibility of making measurements in a real-time state.
At the same time, technologically, the devices support multicomponent analysis with the ability to save the results in a memory chip.

An example from the group of optical gas analyzers - devices that are most widely used in various fields. Optical gas analyzers have high measurement accuracy
For the industrial sector, such devices are indispensable equipment. Especially where constant monitoring of emissions or process analysis is required.
Main manufacturers
- Olympus Corporation.
- FPI (Focused Photonics Inc).
- Bruker.
Olympus Corporation
A Japanese company known for its products in the field of optics and photographic equipment. Its metal analyzers are popular as they are considered Japanese-style reliable and are in the middle price segment.
The company invests in R&D and software development. For portable analyzers, Delta X-act Count technology has been created, due to which the speed and detection limits have been reduced.
FPI (Focused Photonics Inc)
A Chinese company founded by graduates of prestigious American universities.It is considered one of the leaders in the production of all kinds of systems for monitoring the ecology of the environment. Their metal analyzers are also in demand.
The portable FPI metal analyzer is slightly cheaper than the main competitors.
Bruker
German company founded over 50 years ago. Production, laboratories and representative offices are located in 90 countries. It consists of four departments that deal with different areas. Bruker AXS and Bruker Daltonics are developing and manufacturing metal analysis systems.
They are considered of high quality and are quite common in the Russian market due to the good work of representative offices.
You need to look for them depending on your location.