- Application area
- Types of differential automata
- Device, principle of operation advantages and disadvantages
- The design of the differential machine
- Features and purpose of difavtomat
- Options
- Type of electromagnetic release
- Leakage current (residual breaking current) and its class
- Rated breaking capacity and current limiting class
- Electronic or electromechanical
- Working principle of selective type
- Selection of a differential automaton
- OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF THERMAL AND ELECTROMAGNETIC RELEASES
- HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT DIFFERENTIAL CIRCUIT BREAKER
- Space
- Marking and designations of the S200 series of ABB machines
- Features of the design of the difavtomat
- Pros and cons
- Photo of a differential machine
- How is the differential machine
- Why do you need a difavtomat in electrical wiring
- Purpose
Application area
Many people use this solution because of its small size and compactness. Regardless of the model, when installed, the device will take up a much smaller area compared to installing the RCD and the machine separately.

The tool perfectly copes with the protection of wiring, and therefore has found wide application both at home and in various enterprises.

The difference between the differential automaton lies in the fact that it is not inferior in performance to individual RCDs and auto switches, which allows it to be used without any restrictions.

Its installation is allowed both at the input and at the outgoing power lines, due to which it becomes possible to achieve an excellent level of fire safety and protect people from contact with high voltage.
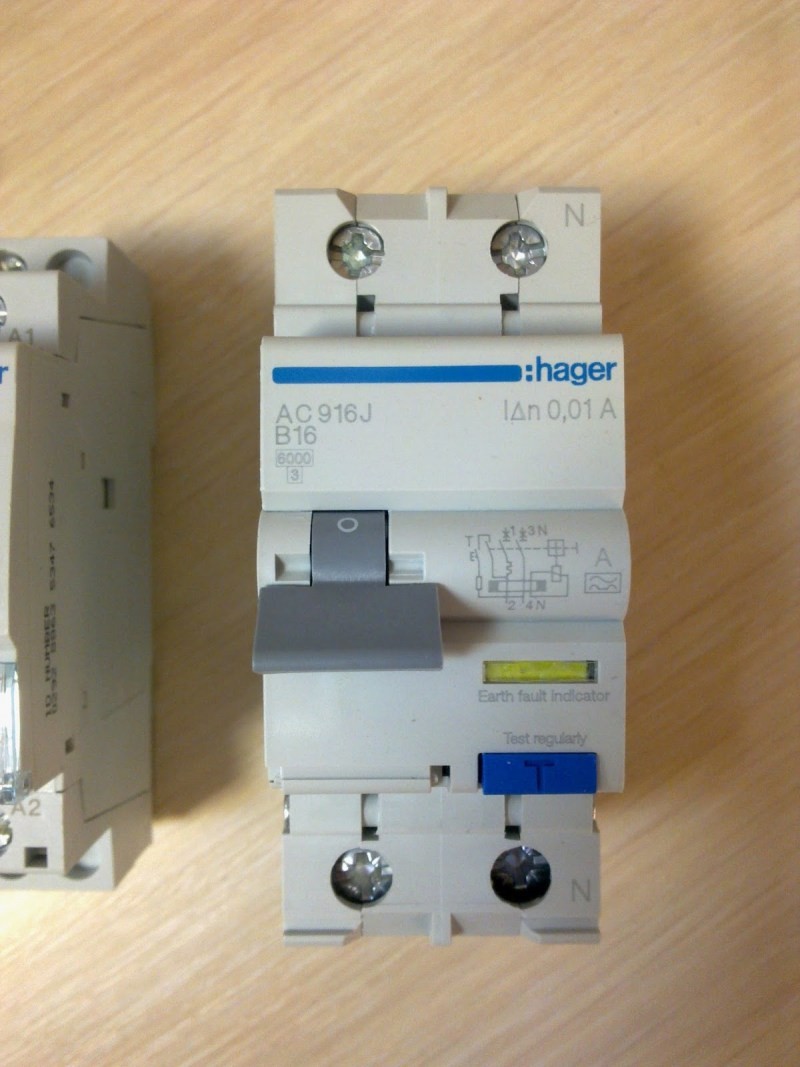

Installation of differential automata occurs, as well as the installation of RCDs. The network type determines the type of differential machine that will be installed. Two-pole diffusers are combined with a single-phase 220 volt network. The neutral and phase conductors of the active network are connected to the fastenings of the upper poles, similar load conductors to the lower poles.
Also, the manufacturer's brand and the features of the released series often predetermine the number of modules occupied when mounting on a DIN rail. Four-pole models are designed for three-phase networks with a voltage of 330 volts. Here, three phase cables are hung on the upper and lower terminals, only the lower ones are still zero from the loads.

After mounting on a DIN rail, they are located in a significantly larger number of modules, since a diffuse protection unit is also added.

Types of differential automata
For their designation, the letters of the Latin alphabet are used:
A. Automatic machines of this type are used in long-distance power networks and for the protection of semiconductor devices with a cut-off ratio of 2-4 In.
B. It is used in lighting networks of general purpose. Cut-off ratio - 3-6 In.
C. The overload capacity of such circuit breakers is 5-10 In. Used in installations with moderate starting electric currents.
D.Type D difautomats are designed for heavy starting electric motors. The frequency of operation of the electrodynamic release is 8-15 In.
K. Used for inductive loads only. Multiplicity of operation of the release - 8-15 In.
Z. Used in circuits with various electronic devices. Multiplicity of operation - 2-3 In.
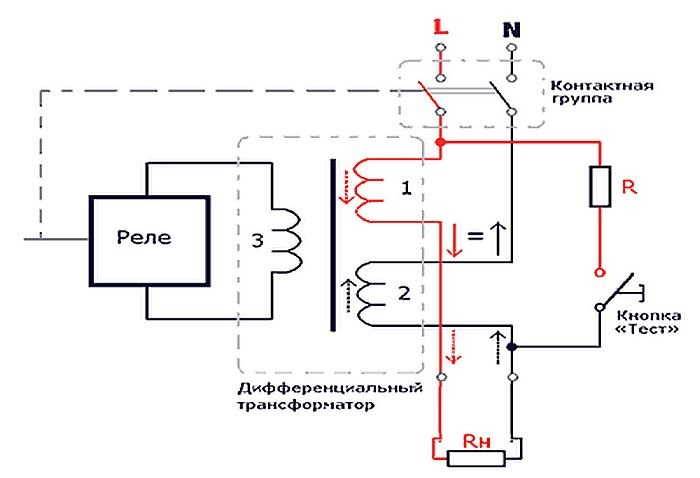
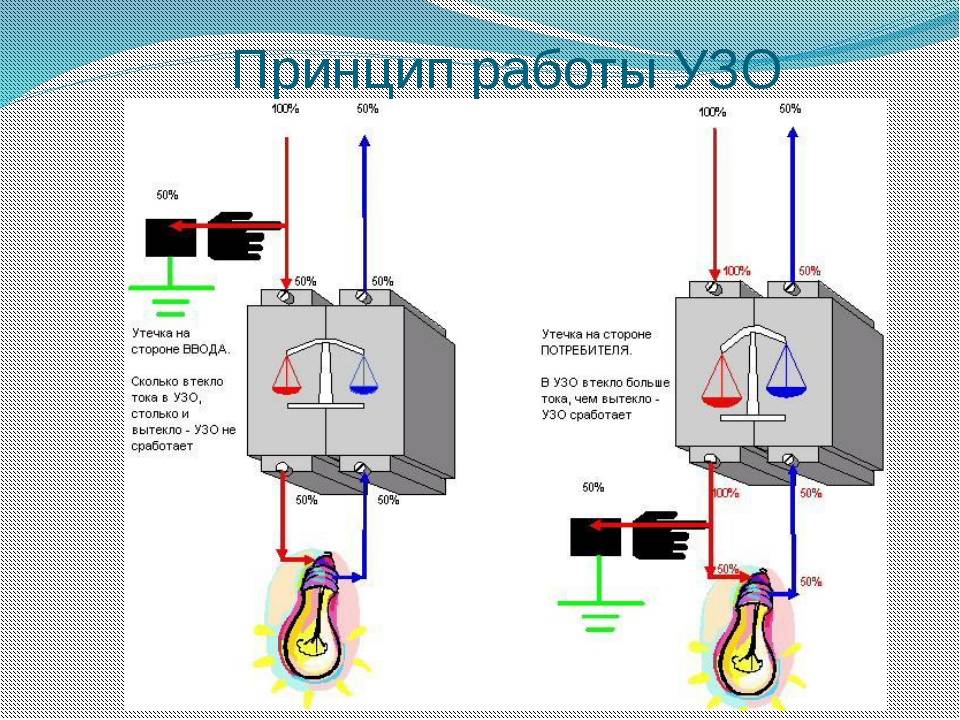
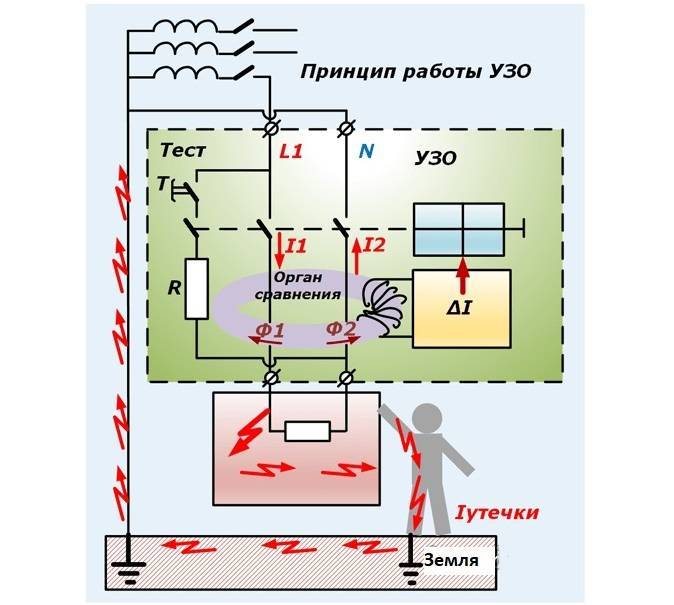
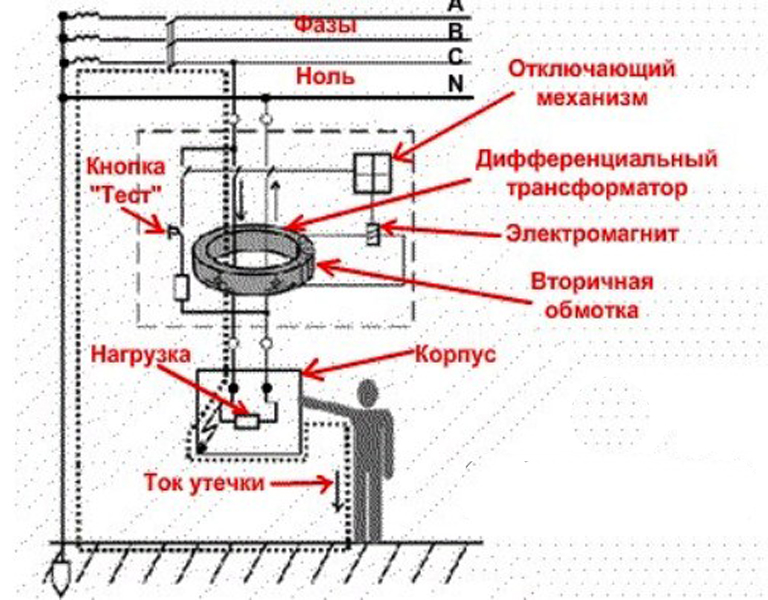
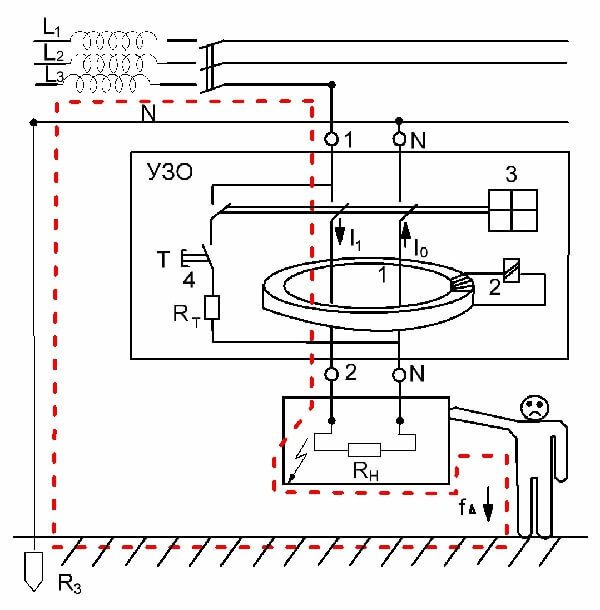
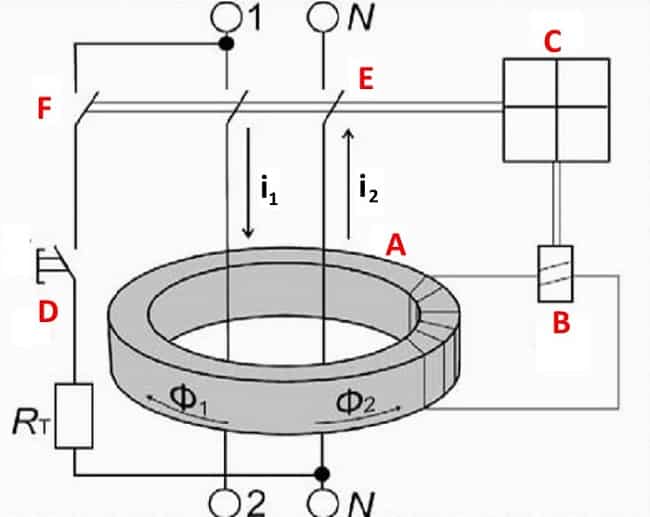
The principle of operation of differential protection is based on comparing the current in the neutral wire and the current directed to the load. Under normal operating conditions, these values are identical. The source of electromotive force in the home network is the neutral and phase wire. In a closed circuit, the electric current tends from a point of high potential, that is, from the phase wire, to the point with the lowest potential, the neutral wire. The values of the current flowing through the neutral and phase wires, as in the receiver circuit, are the same. This statement is true for a closed and well isolated circuit.
In a difavtomat, the phase and neutral wire circuit passes through the transformer core. When the electric currents in the wires are equal, the resulting flux in the core is zero. There is no current in the secondary circuits, therefore, the relay is inoperative.
In the event of insulation deterioration, due to the potential difference between the ground, neutral and phase wires, current leakage occurs. The appearance of a leak upsets the balance in the wires, as a result, a violation of the equality of electromagnetic fluxes is observed in the core.
A potential difference also appears on the secondary winding of the transformer, which is directly dependent on the imbalance on the wires.When a critical value is reached, the potential difference at the output of the transformer causes the relay to operate, which knocks out the latch and turns off the machine from the network.
An important condition for differential protection is the reliable and correct grounding of conductive parts, which, in case of leakage, may become energized. The speed of operation of the difavtomat depends on this nuance.
In accordance with the Electrical Installation Rules, the use of RCDs, including difavtomatov, is mandatory for TN-S and TN-C-S grounding systems.
At the same time, differential protection in networks with connected neutral and working wires, as well as in power networks without a neutral protective wire, is not possible. In the first case, the leakage current will always be present, and in the second case, there will be no leakage until the person closes the circuit for the leakage with his body.
Device, principle of operation advantages and disadvantages
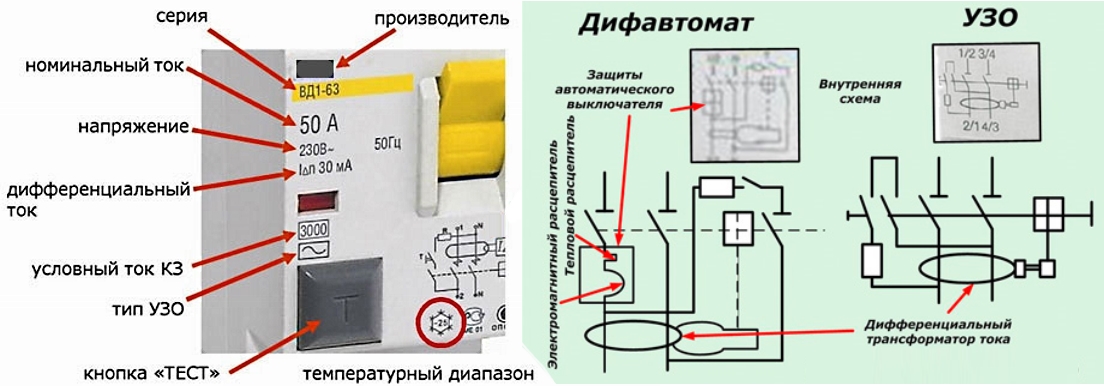
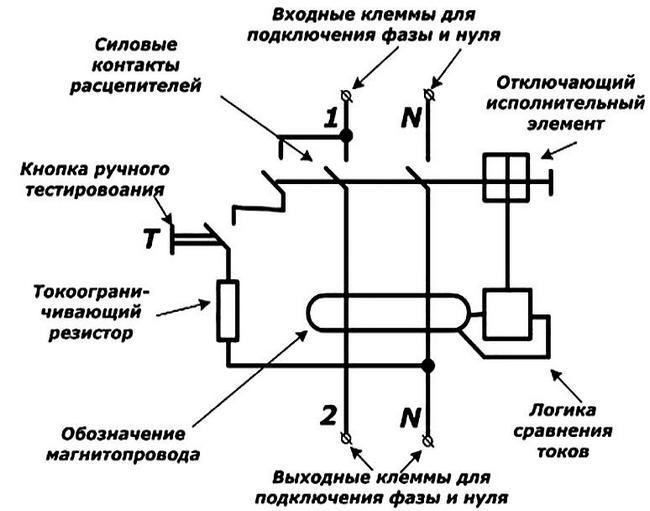
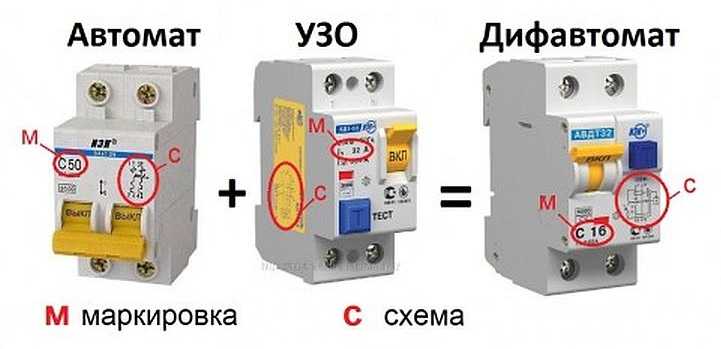
Difavtomat refers to modular electrical products. Compact and fast, it is mounted on a DIN rail and, depending on the network, it can have 4 (single-phase) or 8 (three-phase) terminals. It is made by manufacturers from different countries in a case made of non-combustible plastic with terminals for connecting outgoing and incoming conductors. It has a lever/levers for operating the voltage on and a "Test" button. It is necessary to check the operation of the electrical protective device. There is also a signal beacon in the design. It shows the type of operation (leakage current or overload current).
Difavtomat combines 2 functions - a residual current device (RCD) and a circuit breaker. Has a working and protective part. The working part is automatic switch two- or four-pole, which is equipped with an independent trip mechanism and a reset rail. The difavtomat is equipped with two types of releases - thermal, which cuts off power when the protected group is overloaded, and electromagnetic, the purpose of which is to turn off the line when a short circuit occurs.
The protection module may contain additional devices. These can be a differential transformer, which is installed to detect the leakage current, and an electronic type amplifier to detect its residual value.
The principle of operation of the difavtomat is based on a change in the magnitude of the differential current, which can occur when a person comes into contact with conductive elements. In the absence of damage to the electrical wiring, there is no leakage current, because in the neutral and phase wires they are equal. In the event of its occurrence, the balance of this value and the magnetic field is disturbed, and a current arises in the secondary winding, with the help of which the magnetoelectric latch is triggered. It will unhook the machine and the necessary contact system.
The main advantages of difavtomatov include the following factors:
- operate in a wide temperature range (from minus 25 to 50 0С);
- wear resistance;
- lightning-fast operation (speed);
- quick installation and dismantling (installed on a DIN rail);
- the effectiveness of protective properties.
They have one single drawback - they cannot be installed to a group of outlets where computer equipment is connected, because. false positives may occur, which adversely affects the operation of such equipment.
Difamats are classified according to the method of control. They are independent and dependent on the mains voltage.According to the installation method, they can be stationary or portable (with connection to a power source). By the nature of the setting differential automatic machines come with one or multi-position step. They can also be operated with and without delay. According to the degree of protection, they are produced in unprotected and protected versions, which allows them to be installed in rooms with different environmental conditions (dust and moisture saturated).
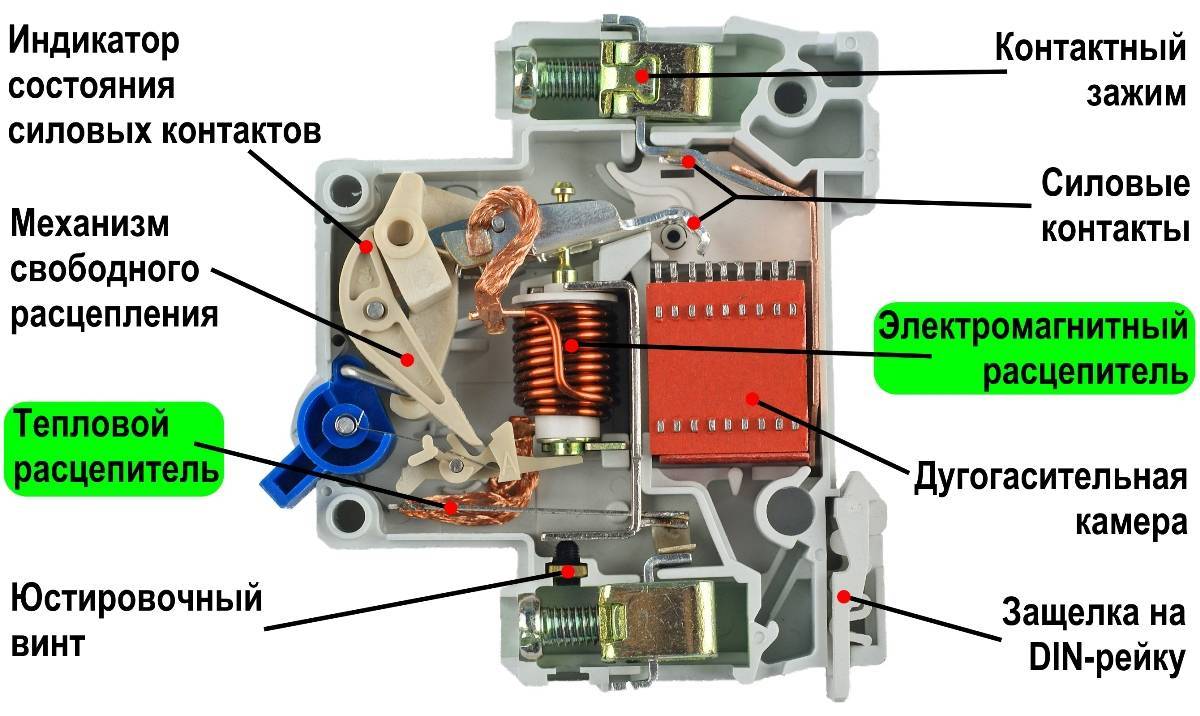
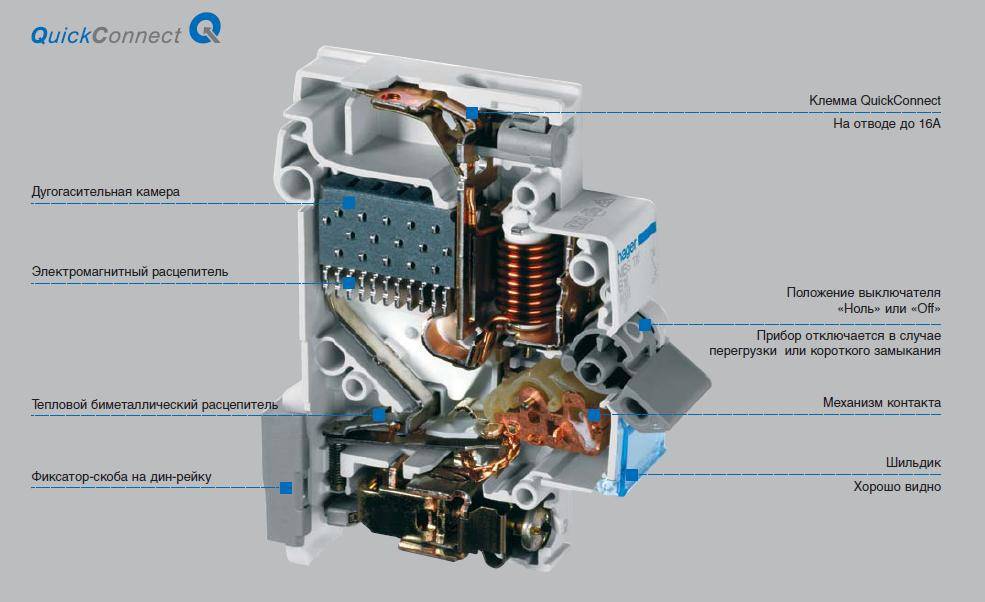
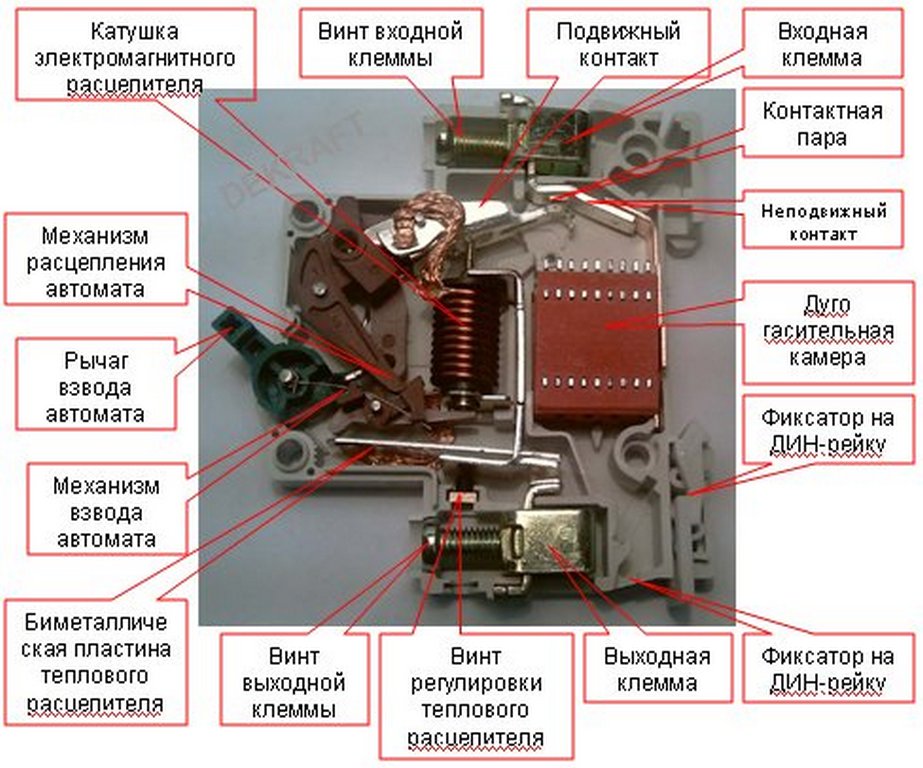
The design of the differential machine
- electrodynamic release;
- corps;
- releases: thermal and electrodynamic;
- control lever;
- relay;
- executive mechanism;
- transformer with a toroidal core;
- systems of springs and levers that hold the machine in working condition and turn it off when the relay is triggered.

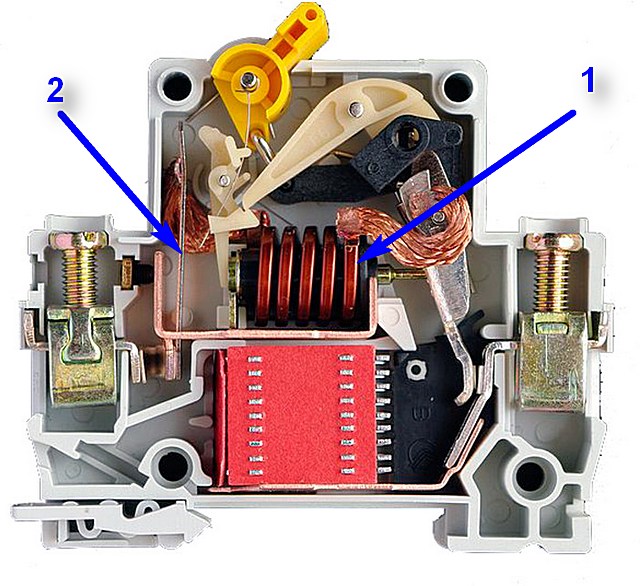
The body of the machine is made of non-flammable polymer. The electrodynamic release consists of a coil with a dynamic core, which is connected to the main contacts of the difavtomat.
When short-circuit electric currents with high parameters pass through the coil, the core with considerable force and speed knocks out the latch that keeps the machine in working condition. The tripping time of the release is minimal, and the magnitude of the tripping current is expressed by the value of In and depends on its design.
The electrodynamic release belongs to an independent type of device, since the magnitude of the current has no effect on the speed of its operation. The thermal release is made of plates made of an alloy of two metals with a different coefficient of thermal expansion.

The passage of electric current through the plates leads to their heating - the difference in the linear expansion of the metals leads to their bending. If the current reaches the limit value, then the plates bend in such a way that they knock out the latch that holds the machine in the on state.
The thermal release is dependent - the speed of its operation depends on the magnitude of the electric current and the heating rate.
The combination of thermal and electrodynamic releases characterizes the protective property of the circuit breaker, which is displayed as a graph with the coordinates of time and current. This graph is the combined curves of the operation of the electrodynamic and thermal releases.
Features and purpose of difavtomat
If almost everyone knows about ordinary electric machines, then, having heard the word “difavtomat”, many will ask: “What is this?” In simple terms, a differential circuit breaker is a circuit protection device that cuts off power in case of any malfunction that could damage the line or cause electric shock to people.

The device consists of several main parts:
- Plastic case resistant to melting and fire.
- One or two feed and power off levers.
- Marked terminals to which incoming and outgoing cables are connected.
- The "Test" button, designed to check the health of the device.
In the latest models of these machines, a signal indicator is also installed, which makes it possible to differentiate the causes of operation. Thanks to him, you can determine why the device turned off - due to current leakage or due to line overload. This feature makes troubleshooting easier.
Clearly about the device difavtomat on video:
Automatic residual current circuit breakers can be installed in both single-phase and three-phase lines. They are designed for:
- Protection of the electrical network from overcurrent short circuit and excessive voltage.
- Prevent electrical leakage that could cause fire or electric shock to people and pets.
The residual current switch for domestic lines with one phase and operating voltage 220V has two poles. In industrial networks at 380V, a three-phase four-pole differential machine is installed. Quadripoles take up more space in the switchboard, since a differential protection unit is installed with them.

Options
 When installing a difavtomat, three main parameters should be considered:
When installing a difavtomat, three main parameters should be considered:
- Supply voltage and number of phases - 220V or 380V, 1 phase or 3.
- Operation current. This parameter is similar to that of the circuit breaker.
- leakage current. Here everything is similar to RCD.
There are a few more options that not everyone is familiar with:
- Rated breaking capacity. The short-circuit current that the device can withstand without disrupting its operation.
- Operate time of differential protection.
- Current limiting class. Indicates the time for extinguishing the electric arc in case of a short circuit.
- The type of electromagnetic release, on which the excess of the operating current in comparison with the nominal one depends.
Type of electromagnetic release
The electromagnetic release in the difavtomat is designed to instantly open the circuit when the rated current is exceeded by a specified number of times. The following types are common:
- B - the operating current exceeds the rated current by 3-5 times.
- C - the operation current exceeds the rated current by 5-10 times.
- D - operation current exceeds the rated current by 10-20 times.
Leakage current (residual breaking current) and its class
The sensitivity threshold of the differential transformer determines the leakage current that causes the protection to trip. The most widespread are differential transformers with a sensitivity of 10 and 30 mA.
In addition to the numerical value of the leakage current, the form is important. In accordance with this, the following classes of protection devices are distinguished:
AC - sinusoidal leakage current is controlled.
A - in addition to sinusoidal, a pulsating constant is taken into account, which is important when protecting digital electronic equipment.
B - a smoothed direct current is added to the listed currents.
S - time delay for shutdown - 200-300 ms.
G - time delay - 60-80 ms.
Rated breaking capacity and current limiting class
This parameter characterizes the short-circuit current that the contact group of the circuit breaker is able to withstand without damage during the trip time. The higher the value of the parameter, the more likely it is that after the damage in the network is eliminated, the difavtomat will remain operational. A typical range of values is as follows:
- 3000 A;
- 4500 A - together with the first value, it is practically not used today;
- 6000 A is a commonly used value;
- 10000 A - suitable for places close to the supply substation, but has a high cost.
The current limiting class characterizes the shutdown speed when a critical current flows. The break time (speed) includes the arc quenching time between break contacts.A shorter time, i.e. a higher shutdown speed, guarantees greater safety. There are three classes: from the first to the third.
Electronic or electromechanical
According to the internal equipment, electromechanical and electronic devices are distinguished. Electromechanical difavtomatov are considered more reliable and do not require external power for operation.
Electronic devices have more stable parameters, but for normal operation, a stable power supply is required at the input.
Working principle of selective type
 In branched electrical networks, a two-level protection system is used.
In branched electrical networks, a two-level protection system is used.
At the first level, a differential machine is installed, which controls the load line completely. On the second, difavtomats control each selected circuit separately.
To prevent the simultaneous operation of protection devices of both levels, the first difavtomat must have selectivity, which is determined by the time delay to turn off. For these purposes, automata of classes S or G are used.
Selection of a differential automaton
A large number of manufacturers of electrical equipment, as well as a wide range of difautomats on the market, make it difficult to choose these devices.
In order to choose the right high-quality leakage current switch for a particular power supply system, it is necessary to pay attention to its following characteristics: Number of poles
Each pole provides an independent current path and can be disconnected by a common disconnect mechanism.Thus, to protect a single-phase network, two-pole differential circuit breakers should be used, and for installation in a three-phase network, four-pole ones.
Number of poles. Each pole provides an independent current path and can be disconnected by a common disconnect mechanism. Thus, to protect a single-phase network, two-pole differential automata should be used, and for installation in a three-phase network, four-pole ones.

- Depending on the rated voltage, there are machines for 220 and 400 V.
- Since the difavtomat performs the functions of protection against short-circuit currents and overloads, when choosing it, one should be guided by the same rules as for a circuit breaker. The most important parameters of these devices are the rated current, the value of which is determined based on the rated power of the connected load, as well as the type of time-current characteristic. This parameter shows the dependence of the current flowing through the circuit breaker on the tripping time of the release. For installation in domestic electrical networks, it is recommended to use automatic machines with a time-current characteristic of type C.
- Rated leakage current. Shows the maximum value of the current difference (to determine this parameter there is a special symbol Δ printed on the body of the device), at which the difavtomat does not open the electrical circuit. As a rule, for household electrical networks, the nominal value of the leakage current is 30 mA.

- There are automatic differential current switches designed to operate in direct (A or DC) or alternating (AC) current networks.
- Device reliability. This parameter largely depends on the manufacturer.When choosing and purchasing a differential machine, you need to be wary of fakes by purchasing electrical equipment in specialized stores that have all the necessary documents and permits.
If the grounding conductor breaks, a situation may arise in which the difavtomat will not react to the appearance of an increased potential relative to the ground on the electrical installation case. However, in this case, the device will operate if a person touches such an electrical installation and thus creates a leakage current path.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF THERMAL AND ELECTROMAGNETIC RELEASES
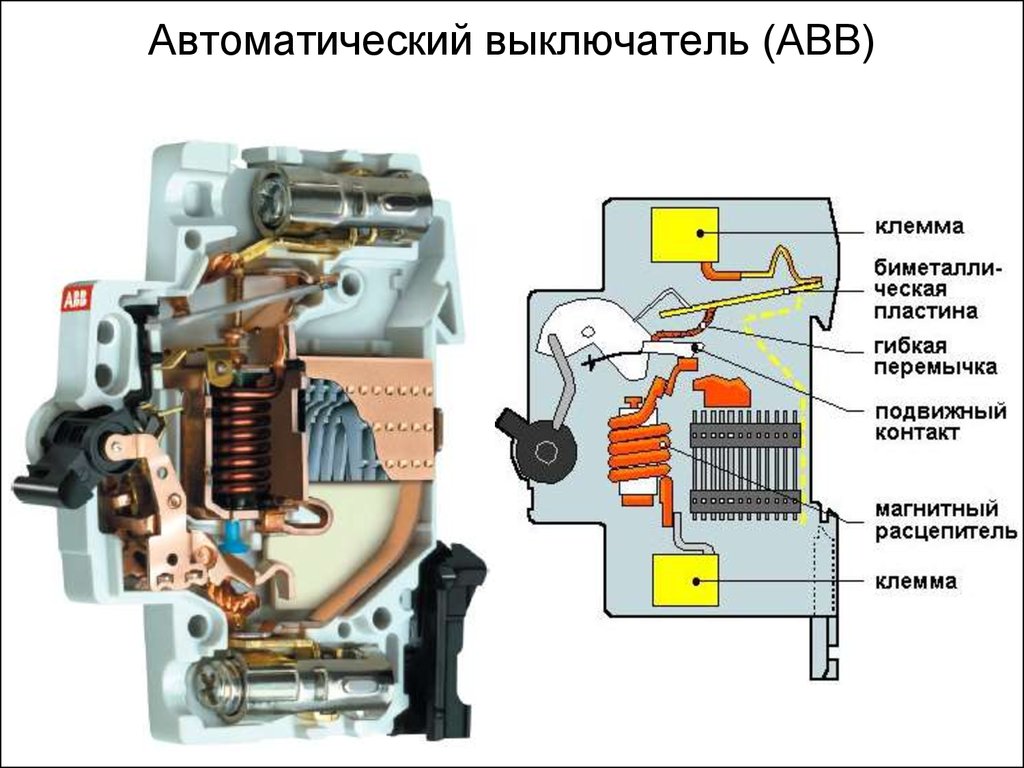
Electromagnetic release difavtomat consists of a current coil, inside which is a movable magnetic core (strike). The electromagnetic system of the release is configured in such a way that when the current in the coil reaches a certain value, the magnetic core is drawn in.
Retracting, the core-striker acts on the latch drive that holds the machine in the on position. The disengaged latch releases the circuit breaker drive, which, under the influence of springs, moves to the off position, breaking the current poles of the difavtomat.
The electromagnetic release of the machine plays the role of protection against overcurrents that occur during short circuits.
Thermal release mechanism difavtomat contains a bimetallic element that changes its shape when heated. A bimetallic element is a combination of two plates of dissimilar metal alloys with different coefficients of thermal expansion.
Heating of such a structure causes its bending due to the difference in the linear expansion of dissimilar materials.The heating of the bimetal is carried out under the action of an electric current flowing directly through the plates, or along a spiral wound around them.
The bimetal deformed due to heating acts on the latch of the drive of the machine, which causes it to turn off.
The characteristic of the thermal release of the machine has an integral dependence. The value of the linear displacement of the bimetal, proportional to the amount of heat released by the conductor, is determined by two factors:
- the magnitude of the flowing electric current;
the duration of its action.
Thus, the time of automatic operation of the thermal release of the difavtomat depends on the current value.
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT DIFFERENTIAL CIRCUIT BREAKER
The installation of difavtomatov is expedient wherever it is planned to place residual current devices. Since the difavtomat combines the functions of two devices, its choice includes two tasks:
- selection of circuit breaker parameters;
- RCD characteristic selection.
The machine is selected primarily at face value, which should, with some margin, cover the current load of all electrical appliances in the protected area of \u200b\u200bthe wiring. If possible, the selectivity of the protections should be ensured.
This means that if an overload occurs on an electrical appliance, the circuit breaker that directly supplies this electrical appliance must open.
To select circuit breakers according to the conditions of selectivity, the time-current characteristics of the devices are compared. It is relatively easy to achieve selective operation of thermal protections. As for electromagnetic releases, it is most often not possible to coordinate their work.
For example, in the event of a short circuit in the outlet, not only the switch that feeds this outlet group is turned off, but also the input automat. However, in domestic conditions, this does not create any special problems.
When choosing a differential protection module, the main reference point is the leakage current setting. To protect against indirect contact, difavtomatov with a rating of 10-30 mA are used.
When installing a differential machine at the input of an apartment or house, a model with a rating of 100-300 mA is selected. Such ratings provide fire protection in case of damage to the insulation of the electrical wiring.
* * *
2014-2020 All rights reserved. The site materials are for informational purposes only and cannot be used as guidelines or normative documents.
Space
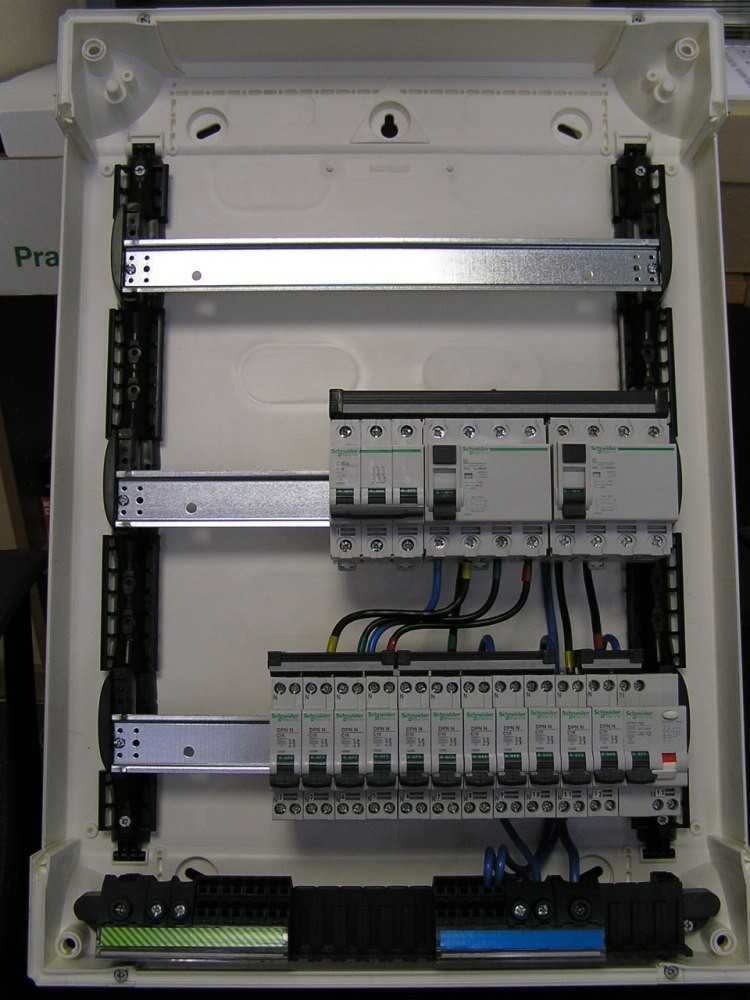

If you still want to connect electrical appliances there, then this will not be easy, especially if all the repair work has already been completed. Not the most pleasant stage begins, when it is necessary to swap all the modules so that new devices finally enter there.

Everyone knows perfectly well that the RCD does not protect the wiring from overcurrents. It is additionally defended by machine guns. Each accessory has its own on/off switch. As a result, a lot of extra space is occupied in the brush, because of which nothing will fit in it soon.

That is why any type of difavtomatov take up much less space, which leads to more flexible operation and the ability to add new electrical appliances.

A new topic has also appeared on the market - these are single-module difautomatic machines. They are very similar in all functions to AVDTs, that is, there is both an RCD and an automatic device, but all this is located in one housing, which noticeably frees up space.

Marking and designations of the S200 series of ABB machines
STO S 201 C1 S20 - series of S200 circuit breakers, Additional letter indicates breaking capacity:
- • no letter - 6kA,
- • letter M - 10 kA,
- • letter R — 15-25 kA.
1 at the end of the series (S201) - number of poles:
- • S201 one pole,
- • S202 two poles,
- • S203 three poles,
- • S204 four poles.
The letter after the designation of the series and the number of poles is the characteristic of the operation during short circuit (the type of purpose of the machine):
- • B - for protection under active loads (lighting lines with grounding),
- • C - for protection against active and inductive loads (low power motors, fans, compressors),
- • D - for protection at high starting currents and high switching current (transformers, arresters, pumps, etc.),
- • K - for protection of lines with connection of active-inductive loads (electric motors, transformers, etc.),
- • Z - to protect electronic systems with semiconductor elements.
The last digits in the designation are the ratings (settings) of the currents.
Features of the design of the difavtomat
Since the difavtomat is designed to perform several different functions, its design includes relatively separate elements, the principle of operation and the purpose of which are somewhat different. All component parts of the device are assembled in a compact dielectric housing, which has fasteners for mounting on a DIN rail in an electrical panel.
The working part of the differential machine includes:
- Independent release mechanism.
- Electromagnetic release. This device consists of an inductor equipped with a movable metal core.The core is connected to a spring-loaded return mechanism, which ensures reliable closing of the circuit breaker contacts in normal operation of the electrical circuit. The electromagnetic release is activated in cases where a short-circuit current flows in the circuit.
- Thermal release. This device opens the electrical circuit when a current flows through it that slightly exceeds the nominal value.
- Reset rail.
The protective part of the device includes a differential protection module that operates in cases where there is current in the ground wires of the electrical installation. If this current exceeds a certain value, the device gives a command to open the main contacts, and also signals the reasons for the operation of the protection of the differential machine.

The components of the protection module design are:
- Differential transformer.
- Electronic amplifier.
- Electromagnetic reset coil.
- The device for monitoring the health of the protective part of the difavtomat.
There is a special button on the front of the product case, which is designed to checking the operability of the protective part of the device. To provoke the control operation of the difavtomat, you just need to press the button, and the circuit closes, causing a leakage current, to which the protection responds.
Pros and cons
The advantage of the difavtomat in the first place is the small size of the device. It takes up little space in the electrical panel. With such dimensions, it becomes possible to install a smaller electrical panel.
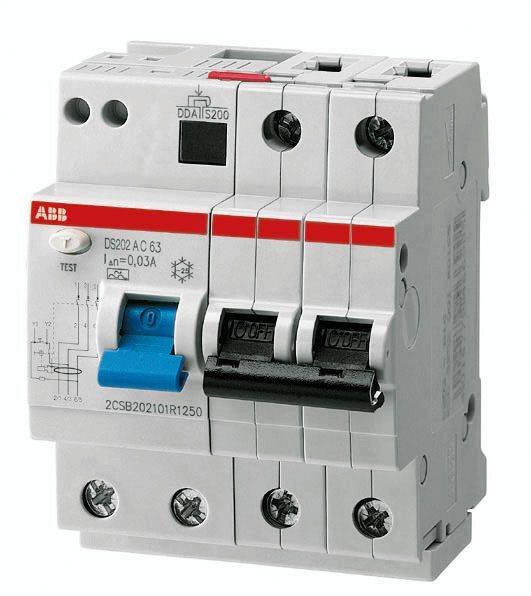 Modern difavtomat
Modern difavtomat
The process of connecting a difavtomat is less costly and time-consuming. Installing the device will not take much time.In addition, this device does not require additional devices for its use, therefore, when replacing, only one difavtomat is needed.
Until recently, the minus of the difavtomat was the difficulty in detecting a malfunction when triggered. Modern manufacturers have equipped the device with signal flags. In this case, it is possible to determine the section of the circuit where the malfunction occurred.
When the device is triggered, it is very difficult to understand the cause of the trigger, since there may be several of them. Either it worked on current leakage, or from overvoltage, or maybe from a short circuit in the network. This is also a disadvantage of this device.
An electronic-type difavtomat has a flaw: if the neutral conductor breaks, the phase wire is energized, which can lead to electric shock to a person. An electromechanical type device does not have such a negative moment, and its performance remains at the same level. However, these types of devices are expensive, unlike electronic ones.
Photo of a differential machine






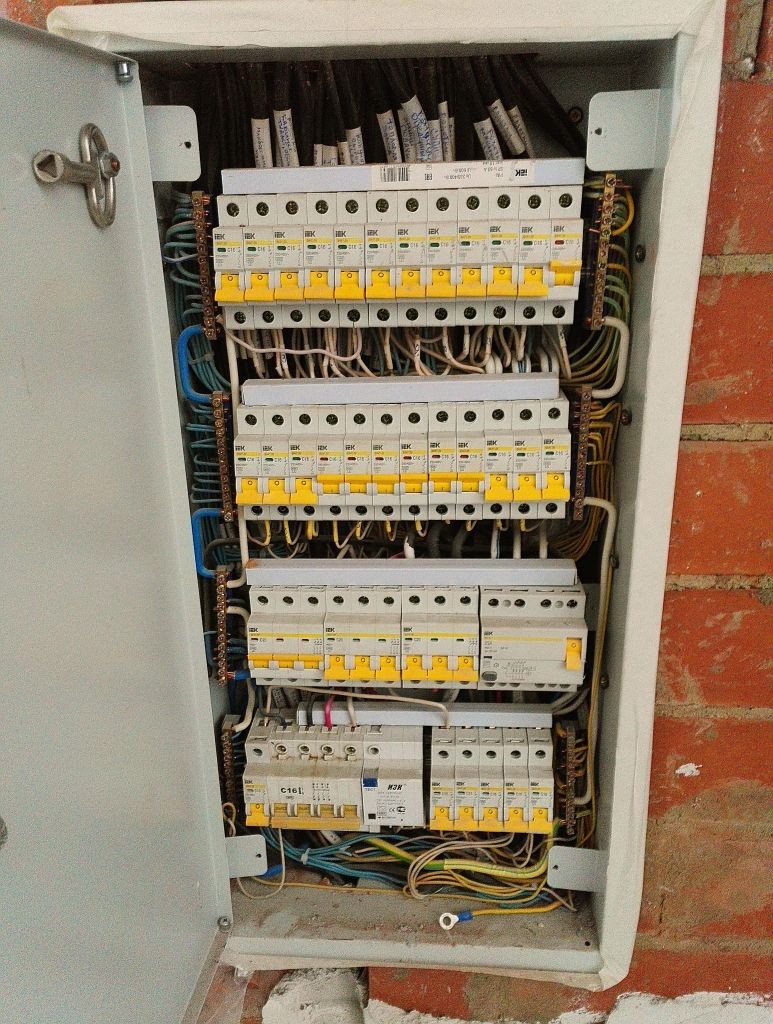





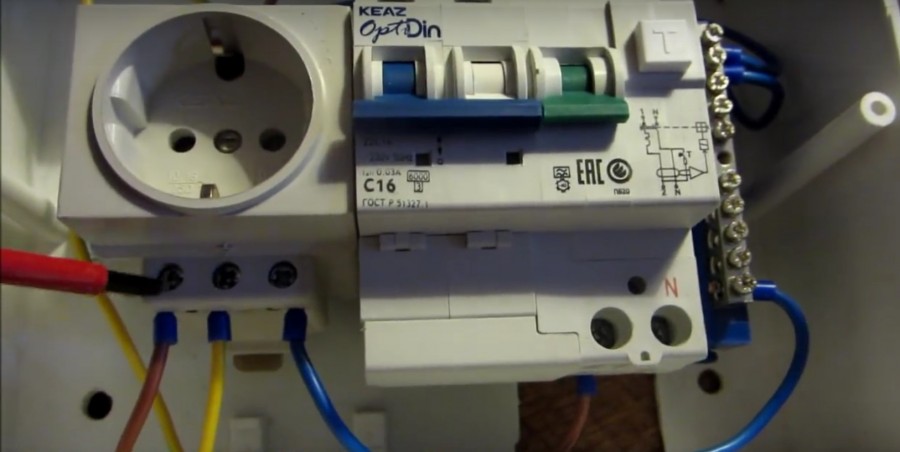



We also recommend viewing:
- Scheme of connecting the pass-through switch
- How to choose and install an electrical switchboard
- Types of junction boxes for electrical wiring
- Which cable ties to choose
- How to choose the best doorbell
- Which power cable is better to choose
- Varieties and schemes for connecting a TV outlet
- What is heat shrink tubing for?
- Which thermostat for underfloor heating is better to choose
- How to choose and connect a double socket
- Instructions on how to connect the outlet with your own hands
- Switch wiring diagram
- How to connect a double switch
- The best motion sensor light for home
- Which electricity meter is better to choose
- How to choose and install a socket
- RJ45 computer sockets
- What should be the height of the sockets
- How to connect a ground outlet
- The best voltage stabilizers for the home
- How to choose and configure an outlet with a timer
- How to connect a telephone socket yourself
- How to choose a fluorescent lamp
- Retractable and built-in sockets
- How to choose the best halogen spotlight
- Which LED spotlight to choose
- The best plastic boxes for electrical wiring
- What is a smart socket
- What is RCD and how does it work
- Overview of modern touch switches
- Selection and installation of a single-gang switch
- Choosing the right circuit breaker
- Choosing the best wire fasteners
- Types of corrugations for electrical cables
- How to choose a spotlight for stretch ceilings
How is the differential machine
Difaavtomat consists of working and protective parts. The first includes the machine. It contains: a trip system and a rail that resets the circuit breaker. Depending on the type of device, there are two-pole and four-pole RCDs. The release system has two releases:
- electromagnetic - turns off the power line when a short circuit appears in the network;
- thermal - turns off the power line in the event of a high load.
The second part of the difavtomat includes a differential protection module. It is able to detect the leakage current. In addition, this element converts current into mechanical action. In this case, the reset rail trips the circuit breaker.
The basis of the difavtomat design is a transformer that detects residual current.
Why do you need a difavtomat in electrical wiring
First of all, difavtomat is a protective device. Like a conventional circuit breaker, the difavtomat protects the circuit section on which it is installed from overload and short circuit. If such phenomena occur in the circuit, the difavtomat will turn off the area under its protection, similar to a conventional circuit breaker.
Additionally, the difavtomat is equipped with a function to protect a person from electric shock if a person accidentally touches live parts. In this sense, the difavtomat performs the function of an RCD.
This combination of the necessary types of protection makes the difavtomat in demand in the process of installation and operation of electrical networks for various purposes.
The versatility of this device is confirmed by its size, which has not increased much when combining the functions of the other two devices. Difavtomat is installed on a din-rail similarly to other devices.
Combining the functions of an RCD and a circuit breaker
The safety and performance of the electrical network largely depends on the protection devices used. But the greatest value at all times remains human life. The protection of people maintaining and operating electrical networks must always remain a priority. In this sense, the difavtomat is the optimal solution in the equipment of a protected electrical network.
With undoubted practical advantages, difautomats are also somewhat more economical than a separate installation of an RCD and a circuit breaker.
Purpose
Consider briefly what is it needed for difavtomat. Its appearance is shown in the photo:

Firstly, this electrical device serves to protect a section of the electrical network from damage due to the flow of overcurrents through it, which occur during overload or short circuit (circuit breaker function). Secondly, the differential circuit breaker prevents fire and electric shock to people as a result of electricity leakage through the damaged insulation of the cable of the electrical wiring line or a faulty household appliance (residual current device function).