- What types of briquettes are offered to consumers
- Production technology
- Peat: consumption
- How to heat with briquettes
- sauna stove
- The nuances of the manufacture and use of briquettes
- The shape and subtleties of the manufacture of compressed fuel
- Features of the use of sawdust in heating
- biofuel
- Other sawdust-based insulation
- Pros and cons of a sawdust heating system
- Advantages
- Flaws
- Fuel briquettes or ordinary firewood: what to choose?
- Comparison with other similar fuels
- Making briquettes with your own hands
- Raw material selection and preparation
- Homemade pressing machines
- Stationary fuel press
- Briquette manufacturing technology
- What are fuel briquettes
- Differences in form
- Differences in material
- Table comments
- How to calculate the required amount?
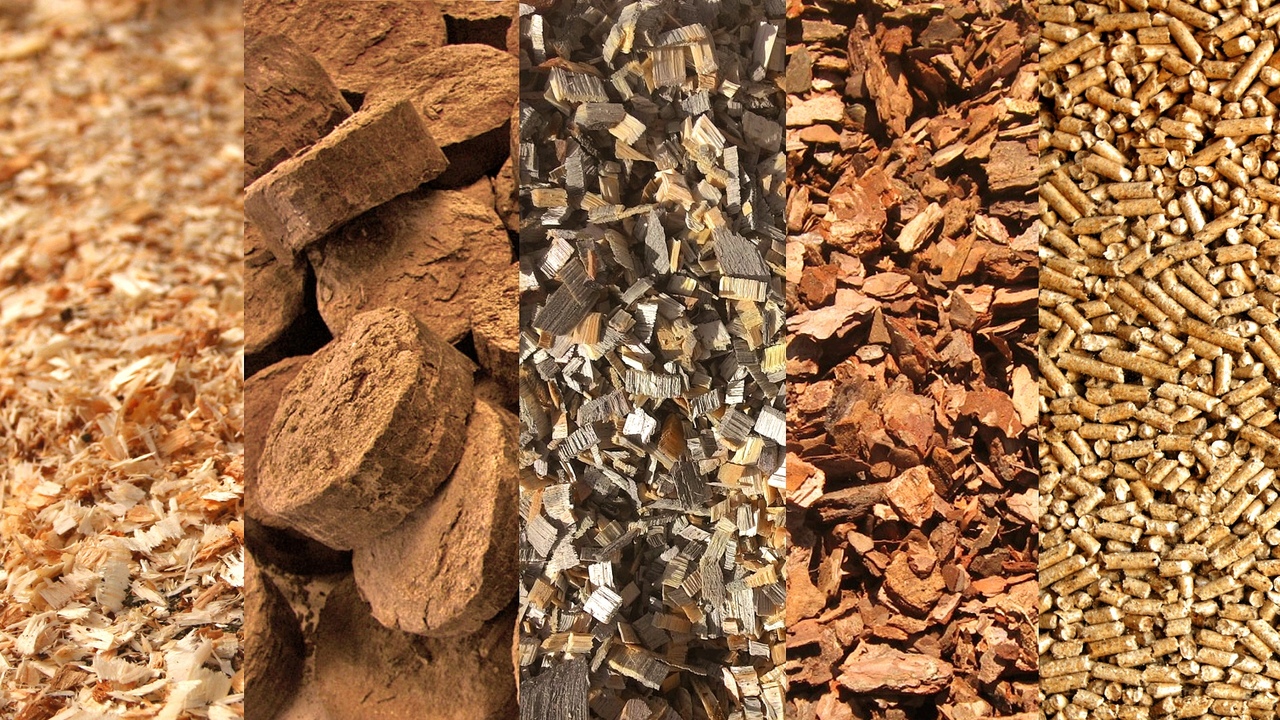
What types of briquettes are offered to consumers
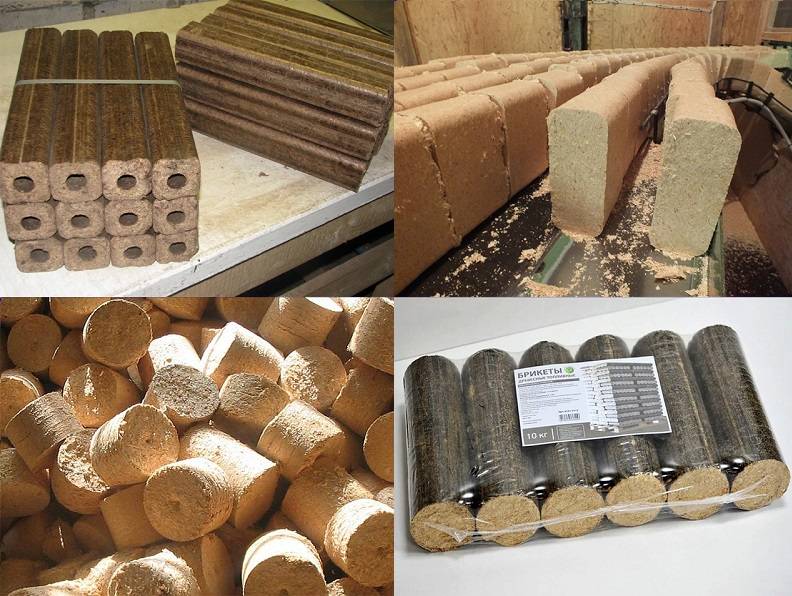
Several types of briquetted fuel can be purchased on the domestic market. They differ from each other not only in shape, but also in density, and, accordingly, the level of heat transfer. Consumers choose according to characteristics such as price, quality and practicality.
Varieties of fuel briquettes:
- fuel briquettes RUF;
- eurobriquettes PINI KAY;
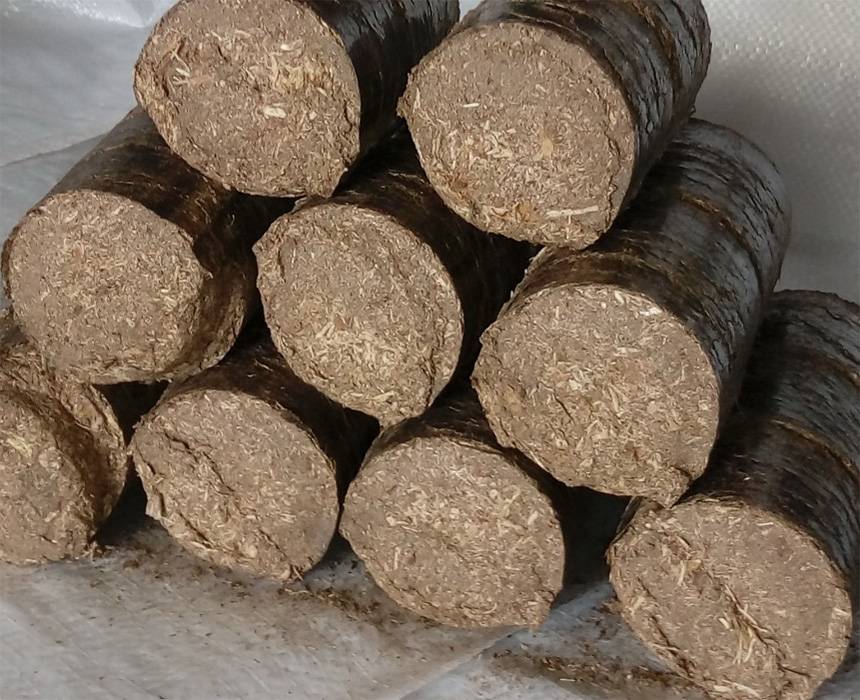
- ordinary cylindrical briquettes;
- fuel briquettes from coal, peat.

Each type of briquetted fuel has its pros and cons, so you can choose which one is more convenient to use in this case. Compressed sawdust for stoves, which go through a longer manufacturing process, will be stronger, more calorific, but also more expensive. Quality naturally adds up to the price of the product.
Production technology
The material for the manufacture of this type of fuel is wood processing and processing waste, such as:
- croaker;
- trimmings;
- non-commercial wood;
- branches and branches.
Substandard wood is loaded into chippers and grinders of various types, which we talked about in these articles:
- Equipment for wood processing.
- Business on a chip.
The fuel fraction depends on the machine settings, and the calorific value depends on the type of wood and the percentage of bark. Therefore, the best chips are obtained from debarked wood of any type, and the worst - from unbarked branches and branches.

Peat: consumption
The traditional fuel in some regions of Russia - peat - is gradually being replaced by a more efficient product for use in furnaces and solid fuel boilers. Peat briquettes for heating produced on the basis of new technologies, including grinding, dispersion, drying and pressing. The resulting biofuel is distinguished by the duration of smoldering (4-10 hours) with the release of a large amount of heat (up to 4500 kcal / kg) and can be used for night heating in houses.
Peat-based fuel is a fairly strong pieces of the same shape
The production of peat briquettes does not require high costs - inexpensive equipment for their production, including drying units and presses, pays for itself quite quickly. Pressed peat fuel is subject to long-term storage, it is convenient to transport, and its high calorific value makes pressed peat indispensable when used in centralized boilers for heating residential, construction and household facilities.
How to heat with briquettes
sauna stove
Eurobriquettes are a universal tool suitable for kindling a steel stove in a bathhouse. Here, not only the amount of heat released is important, but also the duration of the combustion of the fuel.
After ignition, the pressed product smolders for approximately 2 hours. Regular wood burns much faster. Eurobriquettes have a high density and low humidity, which explains their long-term combustion.
Based on observations, the complete filling of the furnace is undesirable. This will help to avoid the rapid achievement of maximum heat transfer.
Since the density of fuel briquettes is high, the product is almost completely burned, and the remaining ash can be used as fertilizer.
When using eurobriquettes, smoke emission is minimal, so you have to clean the heaters less often. It is believed that linden fuel bars contain less resin, so chimneys are almost not polluted.
Eurowood can be used to heat a black sauna. Since the fuel is environmentally friendly, and there is almost no smoke, heated air does not have a harmful effect on the human body.
The nuances of the manufacture and use of briquettes
The idea of using sawdust and wood shavings for heating is not new.This type of fuel, along with wood and coal, is often used for burning in stoves.
The shape and subtleties of the manufacture of compressed fuel
The chemical structure of sawdust and shavings is identical to the wood species from which they were obtained. Commonly used in woodworking are birch and softwoods such as pine, spruce, larch, fir and cedar. Less often you can find waste from ash, oak and other “expensive” species.
Loose combustible material has a number of disadvantages:
- Dirt. Scattered sawdust and small wood debris quickly litter the area. Therefore, the scope of their use as fuel is often limited to non-residential facilities for which cleanliness is not important: stokers, greenhouses and various household premises.
- Weigh. When sawdust is stored, the smallest particles rise into the air. The dust they create is harmful to health, as it provokes the development of pulmonary diseases. In addition, a high concentration of a combustible substance is explosive and therefore the use of small wood waste without proper ventilation (which leads to additional costs) is prohibited in industrial facilities.
- Rapid and uneven combustion. When burning sawdust or shavings, it is quite difficult to achieve the planned heat transfer, since it depends on the size of the material, as well as on its moisture content and tree species.
All these problems can be solved by compressing wood waste into briquettes.
The shape and size of pressed waste may vary depending on the manufacturer. Therefore, it is easy to choose convenient briquettes for a specific firebox.
Wood is 20-30% lignin, which holds the fiber together. When high pressure is created using a press, this natural polymer is released, which quite firmly binds those placed in the form of sawdust.
When using industrial equipment for the production of briquettes from sawdust or shavings, the creation of high pressure in the mold provides the necessary density and hardness of the structure. When using less powerful home-made devices, binders, such as clay or cheap wallpaper paste, are added to wood waste to give strength to wood waste.
Features of the use of sawdust in heating
The chemical composition of firewood and pressed wood waste is the same, but the physical structure is different. This largely determines the specifics in their combustion.
The porosity of the briquettes contributes to their easy ignition. This allows you to control the intensity of heat transfer. Pressed, like dried rotten wood (dust), is able to slowly smolder without the risk of complete attenuation.
 The pressed structure facilitates the ignition process. Sometimes for this, a small amount of fuel briquettes from sawdust and shavings is specially purchased.
The pressed structure facilitates the ignition process. Sometimes for this, a small amount of fuel briquettes from sawdust and shavings is specially purchased.
To reduce heat release when using briquettes, it is necessary to reduce the supply of oxygen - close the supply.
If necessary, increase the intensity of combustion - open access to the firebox to fresh air. Pressed waste responds to such changes much faster than firewood.
biofuel
 Methyl alcohol is obtained from sawdust, which can be used for heating and any engines configured to run on gasoline or gas.
Methyl alcohol is obtained from sawdust, which can be used for heating and any engines configured to run on gasoline or gas.
Methyl alcohol is very poisonous, so you can not drink it.
There are industrial and home methods for obtaining alcohol from this product, the difference between them is in the method of obtaining glucose from sawdust.
For both methods, it is necessary to grind sawdust as much as possible - the smaller their size, the higher the yield of the finished product.
For more information about shredding devices, see the article “Equipment for processing wood waste”.
Having turned the sawdust into glucose, they are fermented with yeast, and after fermentation is completed, they are heated to a temperature of 60-70 degrees so that the alcohols evaporate. Then this steam is cooled and a mixture of various alcohols is obtained, which, after purification, becomes biofuel.
Any gasoline engine can run on such fuel, although the engine needs to be slightly modified for maximum efficiency.
Read more about obtaining and using biofuels here.
Other sawdust-based insulation
Sawdust as a heater is used not only in its pure loose form, it is used, for example, to make “warm” plaster for interior work, for this clay, cement, water and newspapers are added to them. The resulting mixture is compacted into special blanks-capacities, and after drying, heat-insulating sheets are obtained.
On the basis of sawdust, other building materials used for heat saving are also made, for example:
- Arbolit - a mixture of concrete and sawdust, it is made in the form of blocks that cannot be exposed to moisture.
- Sawdust concrete - a material consisting of sawdust, concrete, sand and cement, has high quality indicators and fire resistance.
- Sawdust granules - a heater consisting of compressed sawdust with the addition of carboxymethyl cellulose glue, flame retardant and antisepic.
- Sawdust blocks are non-moisture resistant heat-insulating blocks made on the basis of sawdust, cement and copper sulphate.
Pros and cons of a sawdust heating system
To get the most complete picture of the chips that can act as fuel for modern heating systems, it is very useful to consider the advantages and disadvantages inherent in the method under consideration.
Advantages
- Among all the advantages that heating with wood waste has, the main one should be called low heating costs. Consumers will be able to achieve maximum savings, provided that woodworking enterprises operate in their area of residence. Indeed, in this case, they will be able to buy sawdust at very low prices.
- When using wood as fuel, heating water will take a minimum of time. In addition, these wastes allow you to get the maximum amount of thermal energy. The choice in favor of briquetted chips is even more preferable, since in this case you can provide the house with even more heat.
- When operating a boiler that uses natural raw materials for operation, the environment is not harmed, since a very small amount of toxins enters the atmosphere during the combustion of wood waste.
- An additional advantage is that the sawdust boiler is available to everyone. In addition to this, in order to install this device, there is no need to issue the same large number of permits that is required when connecting the boiler to the gas main.
Flaws
With all their advantages, installations using sawdust also have a number of disadvantages.These include the difficulties that arise with the storage of fuel. Although pressed chips and shavings are compact in size, care must still be taken to have a room large enough to store a supply of this fuel.
It should be borne in mind that in the process of burning wood, a lot of ash and soot is produced. Many people know that ash can serve as fertilizer. However, it is impossible to benefit from soot. For this reason, an operation such as cleaning chimneys should be carried out on a regular basis.
Fuel briquettes or ordinary firewood: what to choose?
What to give preference to: ordinary firewood or fuel briquettes? To answer this question, it is necessary to study the advantages and disadvantages of both.
We list the most important advantages of fuel briquettes:
- A fuel briquette, when compared with ordinary firewood, burns 4 times longer than the latter, which contributes to the economical consumption of such fuel.
- After the combustion of pellets, very little ash remains - about 1% of the total mass of used fuel. When using conventional firewood, this figure can reach up to 20% of the total mass of fuel used. The ash left after the combustion of wood briquettes or any other type can be used as a fertilizer containing a large amount of potassium.
- The amount of thermal energy released during the combustion of eurofirewood is almost twice as much as when using ordinary firewood.
- During combustion, fuel briquettes emit heat almost all the time, which cannot be said about ordinary firewood, the heat output of which decreases rapidly as it burns.
- During combustion, fuel briquettes practically do not spark, emit a minimum amount of smoke and smell. Thus, this type of fuel does not create discomfort and does not harm the environment. In addition, when burning firewood infected with mold or fungus, toxic smoke is formed, which is excluded when using eurofirewood, for the production of which carefully dried sawdust or shavings are used.
- When using wood briquettes as fuel, much less soot is deposited on the walls of chimneys than when using conventional firewood.
- The compact dimensions that distinguish eurofirewood allow more economical use of the area for storing such fuel. Moreover, when storing fuel briquettes, usually placed in a neat package, there is no garbage and wood dust, which are necessarily present in places where ordinary firewood is stored.
Compact storage is an indisputable advantage of fuel briquettes
Naturally, this type of fuel has certain disadvantages:
- Due to the high density of the internal structure, fuel briquettes flare up for a long time, it will not be possible to quickly warm up the room with the help of such fuel.
- The low moisture resistance of eurofirewood can cause them to simply deteriorate if the required storage conditions are not provided.
- Fuel briquettes, which are compressed sawdust, are characterized by a rather low resistance to mechanical damage.
- When burning fuel briquettes, there is no such beautiful flame as when using ordinary firewood, which somewhat limits the use of pellets as fuel for fireplaces, where the aesthetic component of the combustion process is also very important.
Comparison of the main parameters of various types of solid fuels
To make a choice between fuel briquettes and ordinary firewood, the advantages of the latter should also be taken into account.
- When burning ordinary firewood, as mentioned above, more heat is generated, respectively, with the help of such fuel it is possible to quickly warm up the heated room.
- The cost of ordinary firewood in comparison with fuel briquettes is much lower.
- Firewood is more resistant to mechanical damage.
- When burning firewood, a beautiful flame is formed, which is an especially important quality for fireplace fuel. In addition, when burning firewood, essential oils contained in wood are released into the surrounding air, which has a beneficial effect on the nervous and respiratory systems of a person who is in a heated room.
- The characteristic crackle that firewood emits during combustion also has a beneficial effect on the nervous system.
- The ash left after burning ordinary firewood does not have such a tart smell as the product of burning pellets.
Comparison with other similar fuels

The main competitors of wood chips are:
- sawdust;
- shavings;
- pellets.
Due to its structure, sawdust is poorly suited for automatic fuel supply systems, as well as for heating appliances in which the fire does not move down, but up.
Chips are in many ways similar to wood chips, but it is difficult to obtain it in the required volumes on your own, so you won’t be able to save on it.
Pellets, not only are they noticeably more expensive than wood chips, but their independent production also requires much more serious equipment costs.
Although, in terms of calorific value at the same humidity, they are noticeably superior to wood chips, but saving on them will not work.
Making briquettes with your own hands
In the manufacture of sawdust briquettes on an industrial scale, a natural adhesive material lignin is released from them, which acts as a glue and makes the product a monolith. At home, with improvised means, it is impossible to achieve such a density with home-made devices, and therefore additional components must be added when pressing. Some of the more popular binders include:
- wallpaper glue;
- manure;
- clay.
The moisture content of the original wood should be below 12%, and the amount of damaged and unusable sawdust should be 5%.
Raw material selection and preparation
To create such pressed fuel with your own hands, you should choose a quality material. The base ones are:
- sawdust;
- shavings after processing crops;
- waste paper;
- straw;
- secondary raw materials from coal and peat.
The total share of wood chips when choosing a combined composition of raw materials should not be lower than 60%. In this case, the high quality of combustion of the briquette is ensured.
Homemade pressing machines
Machine tools for the manufacture of sawdust created in a handicraft way can be divided into the following types:
- manual;
- based on jacks;
- hydraulic.
To achieve the production of lignin, devices based on a lifting mechanism (hydraulic type or screw type) can be used. Their main disadvantage is low performance.
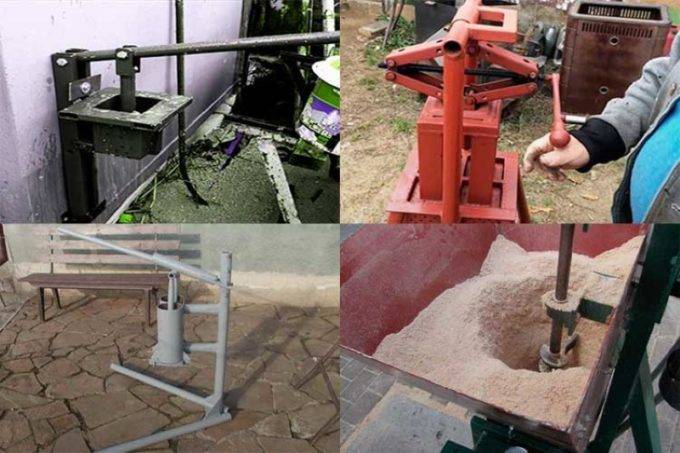

In addition to the jack, which performs the function of a press, a matrix and a punch are used in the machine. They give the finished firewood a certain shape. A do-it-yourself screw extruder simplifies the task of producing compressed fuel, but it is also much more difficult to make it.
Stationary fuel press
You can make a briquette press with the following spare parts available:
- motor;
- bearings;
- reducer;
- shaft;
- screw;
- heating elements;
- relay for temperature control.
If the voltage consists of three phases, then a 9 kW motor is used, and if work is to be done from a standard 220 V network, then a 2.5 kW motor will be needed. It, together with the gearbox and other components, is fixed on a welded frame.
In this installation, the screw is a special design of two components, one of which acts as a punch, and the other delivers sawdust to a specialized container for loading. The matrix is replaced by a profile pipe.

Before starting a home-made machine, the pipe should be heated to 260 ° C, and the heating process of the heating elements is regulated by a relay. The disadvantage of this design is the high coefficient of heat loss to the air.
Briquette manufacturing technology
Manufacturing procedure briquettes with their own hands is divided into several successive processes:
- Preparatory processes for raw materials and their purification.
- Grinding sawdust to a caliber of less than 0.6 cm.
- Pressing.
- Drying.
- Warehousing.
After the chips have gone through all the preparatory processes, they are mixed with clay powder in a ratio of 10:1. Then the mass is stirred by adding a small amount of water. The mixture should be of medium thickness to keep its shape.
It is unloaded into the bunker for further formation of briquettes. After all, it remains only to dry the finished firewood.
It is possible to artificially increase the flammability of pressed fuel by adding a little cardboard soaked in liquid to the clay.
What are fuel briquettes
Briquettes differ in shape and material of manufacture.
Differences in form
There are three main forms of fuel briquettes: pini-cay, ruf and nestro. Their difference is only in the maximum density that can be achieved in each of the forms. In terms of chemical composition or mass calorific value, there are no differences between European firewood.
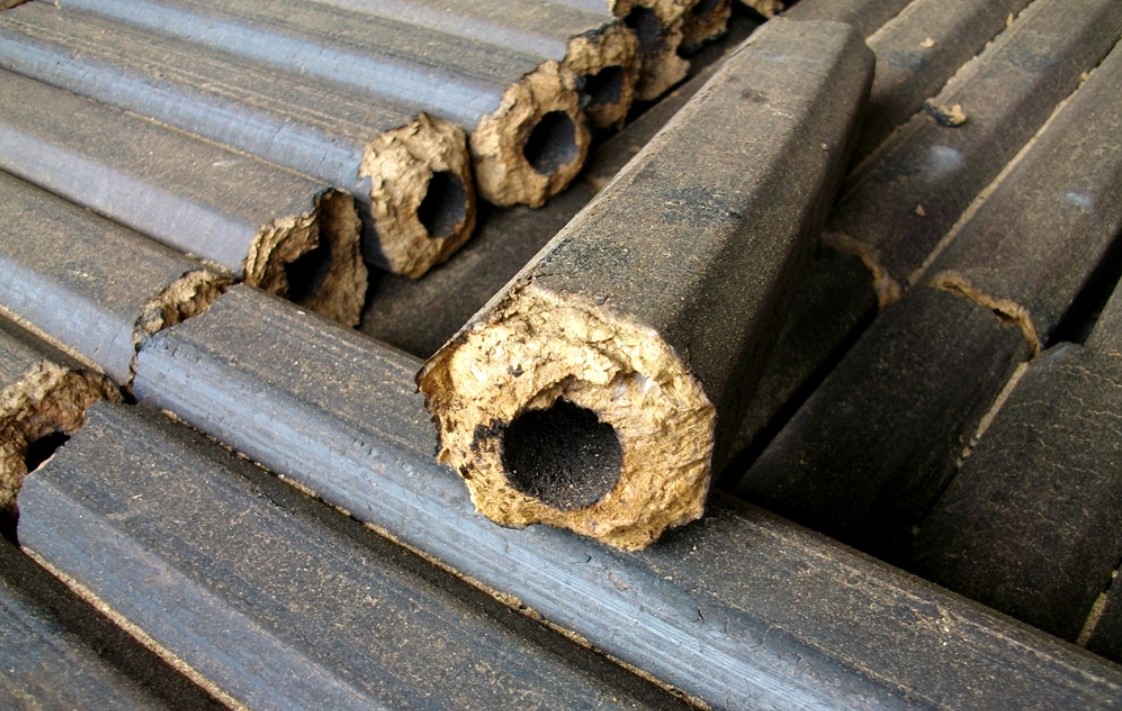
Fuel briquettes pini-kay
The highest density is from 1.08 to 1.40g/cm3. Section shape - square or hexagon. There is a through hole in the center, which provides better air movement and combustion of the briquette.
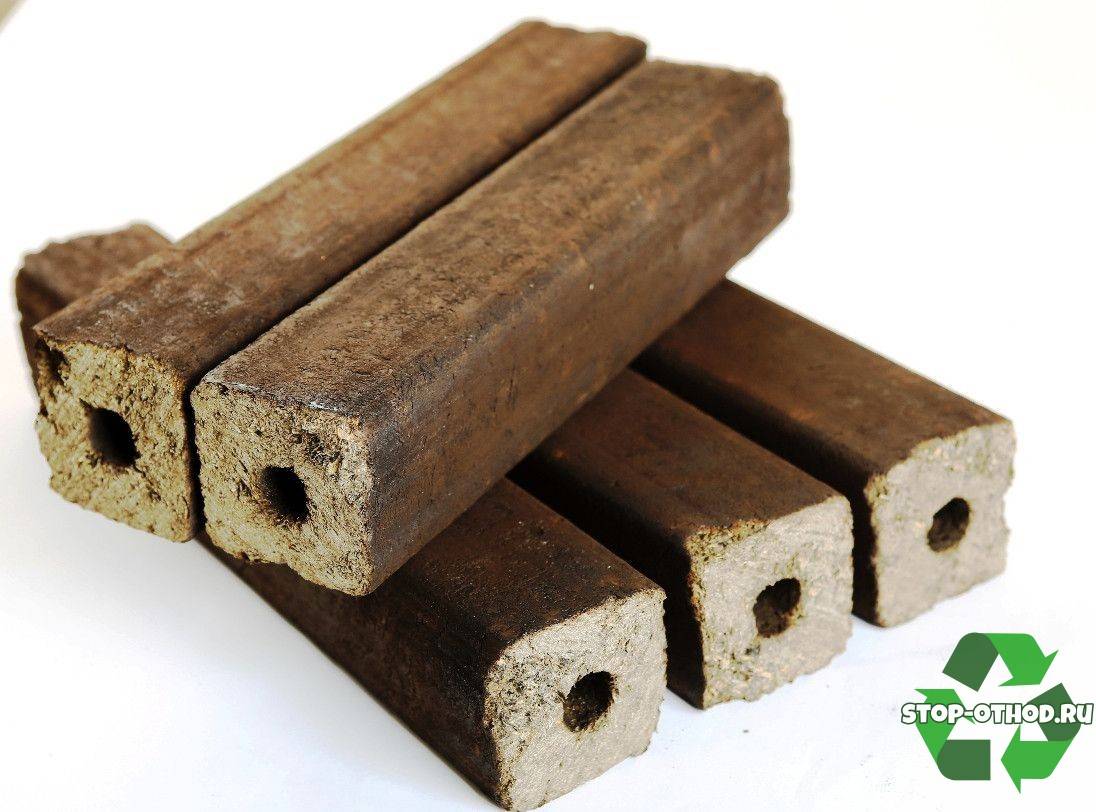
Fuel briquettes from sawdust ruf, in the form of a brick. They have a small size and the lowest density - 0.75-0.8 g / cm3.
Briquettes Nestro
Nestro fuel briquettes have a cylinder shape and an average density of 1-1.15 g/cm3.
Peat briquettes
Peat fuel briquettes have a special shape, unlike the others. And because of the high ash content and the presence of other harmful impurities in the composition, they are not recommended for use at home. Such briquettes are suitable for industrial furnaces or boilers that can run on low-quality fuel.
Fuel briquette from peat
Differences in material
Eurowood is made from sawdust, seed husks, rice and buckwheat, straw, tyrsa, peat and other materials. The material affects the calorie content of the fuel briquette, ash content, the amount of soot emitted, the quality and completeness of combustion.
Below in the table is a comparison of the characteristics of briquettes from different materials - seed husks, rice, straw, tyrsa and sawdust. Such an analysis shows not only that briquettes made of different materials differ from each other. But also the fact that even briquettes from the same material differ in quality and properties.
All data are taken from real test reports of fuel briquettes.
Calorie content, humidity, ash content and density of fuel briquettes from different materials.
Table comments
Seed. The highest calorific value of seed husk briquettes is 5151kcal/kg. This is due to their low ash content (2.9-3.6%) and the presence of oil in the briquette, which burns and is of energy value. On the other hand, due to oil, such briquettes more intensively pollute the chimney with soot, and it has to be cleaned more often.
Wood. Wood sawdust briquettes are in second place in terms of calorific value - 5043kcal/kg at 4% humidity and 4341kcal/kg at 10.3% humidity. The ash content of wood briquettes is the same as that of a whole tree - 0.5-2.5%.
Straw. Straw briquettes are not much inferior to seed husks or sawdust and have a good potential for use. They have a slightly lower calorie content - 4740 kcal / kg and 4097 kcal / kg, and a relatively high ash content - 4.8-7.3%.
Tyrsa. Tyrsa is a perennial herb. Such briquettes have a fairly low ash content - 0.7% and good heat transfer of 4400 kcal / kg.
Rice. Rice husk briquettes have the highest ash content - 20% and low calorific value - 3458 kcal / kg. This is even less than that of wood, at 20% humidity.
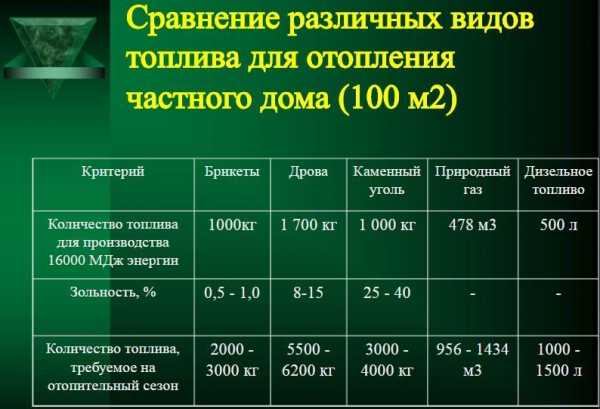
How to calculate the required amount?
Knowing exactly the parameters of the calorific value, as well as the coefficient efficiency of the furnace or boiler, it will be possible to correctly calculate the required mass of wood fuel for a specific period without any problems. Wood briquettes pressed using a special technology, as a rule, are sold either by weight or by volume. If we are talking about the second case, then here you need to take into account some important nuances that are directly related to the structure of products.


For such purposes, you can use one simple calculation formula. It provides for the following sequence of actions:
- first you need to know exactly the level of density of pressed eco-friendly raw materials (q);
- then you need to calculate the fill factor (k) of the volume of the cube with sawdust;
- after that, the mass (m) of one cubic meter is easily calculated using the following formula: m = k * q * 103.