- How to count?
- How to correctly calculate the fee for cold and hot water without a meter, formula and example
- Guaranteed water supply method calculation
- I. General provisions
- Table of contents
- Sample Fill
- Collecting the necessary data
- Populating a PivotTable
- Sending documents
- Organization of the check
- Video about calculation methods and effective savings
- Composition of the water balance
- What problems can be solved by calculation?
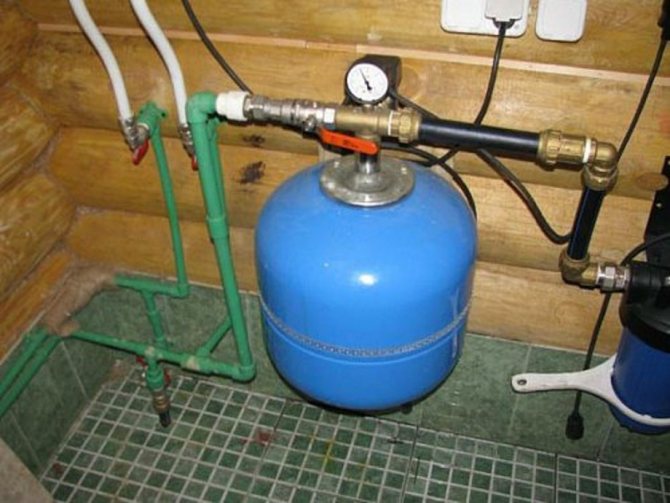
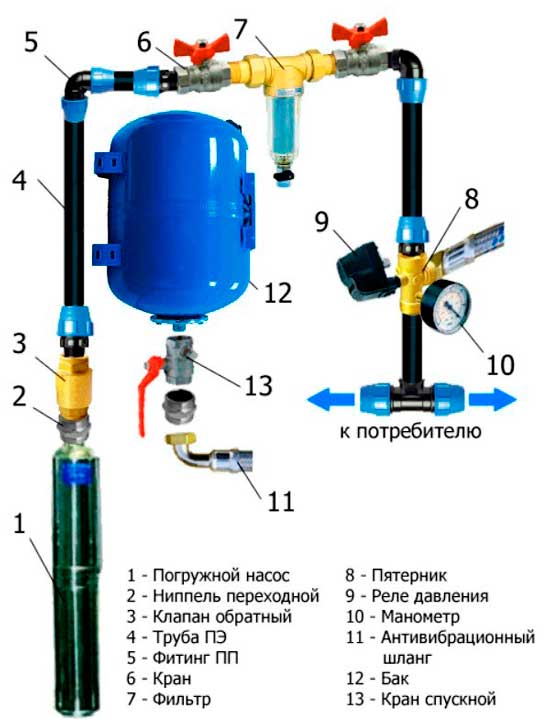
- 1. Well flow rate
- 2. The volume of household waste
- 3. Water consumption rate
- 4. Calculation of the WSS of the water supply source (well)
- Scope of influence of the normative document
- Flow meters and their principle of operation
- Relationship between water consumers and service provider
How to count?
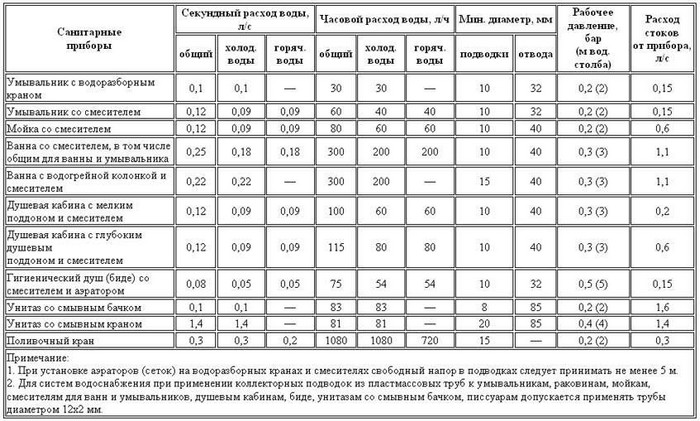
You will have to take into account each node, all plumbing fixtures. As a standard, each person uses up to 300 liters of water per day, this figure should be taken as a starting point if meters have not yet been installed. This number is multiplied by each person living in the house. The formula is simple: Q daily = 300 * N, where N is the number of people living, 300 is the standard rate of water per person.
BC 1xBet has released an application, now you can officially download 1xBet for Android by clicking on the active link for free and without any registration.
However, there are multiplying factors that are used in sewerage and water supply networks in private, public buildings and at an enterprise. The coefficient is 1.3. That is, the resulting Q daily indicator must be multiplied by another 1.3. But do not forget about the reduction factor, which is equal to 0.10. The figure includes the loss of the volume of the supplied flow to the filtration devices, even if they are not installed. So, the formula in the end looks like: Q total \u003d 1.3 * 300N + 0.1 * 1.3 * 300 * N.
When watering the garden, you need to multiply the amount by two, as well as if you have a pool and want to renew the water there a couple of times. Do not worry if the calculations of water consumption and sanitation are not entirely accurate, in case of an error, metering devices will show real data, and they are usually half as much. Not bad help in the issue of water consumption and wastewater ultrasonic flow meter. What is it, what measurement does the equipment carry out - it is worth talking in more detail.
How to correctly calculate the fee for cold and hot water without a meter, formula and example
To calculate how much water supply services will cost in an apartment that does not have metering devices (provided that it is possible to install them), use the formula:
P is the desired value;
N is the standard approved in the region;
K - increasing factor;
As a sample, let's take an average family of four, two adults, two children. They live in Samara. They do not have counters, although they could install them.
The standard for cold water is 7.9, for cold water - 3.6.
The multiplying factor is 1.5.
Let's take the minimum tariff for the region - 26.88 for cold water, 130.2 for hot water.
Using the calculator, we will perform simple calculations:
4 7.9 1.5 26.88 = 1274.112 (for cold water)
4 3.6 1.5 130.2 = 2812.32 (for hot)
If it is not possible to install meters in the apartment, then it is not necessary to multiply by the multiplying factor.
4 7.9 26.88 = 849.408 (for hvs)
4 3.6 130.2 = 1874.88 (for hot water)
The sum in the end is quite impressive. True, for some categories of the population, for example, disabled people, there are discounts.
Meanwhile, according to the counters, the fee comes out much less.
Guaranteed water supply method calculation
Part 2 of Article 13 of the Federal Law of November 23, 2009 No. 261-FZ provides for the calculation of the amount of energy resources in such a way as to encourage buyers to make payments based on data on their quantitative value determined using metering devices.
I. General provisions
1.
These Rules govern relations between federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local self-government bodies of settlements, urban districts (hereinafter referred to as local self-government bodies), organizations providing cold water supply and (or) water disposal (hereinafter referred to as water supply and sewerage organizations) , applicants, organizations engaged in the transportation of water, wastewater, other regulated activities in the field of water supply and (or) sanitation, subscribers in the field of cold water supply and sanitation for the provision of cold (drinking and (or) technical) water from centralized and non-centralized cold water systems water supply and wastewater disposal to the centralized water disposal system (hereinafter, respectively - subscribers, water disposal).
To the relations arising between water supply and sewerage organizations, owners and (or) users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings and (or) homeowners associations or housing construction, housing cooperatives and (or) other specialized consumer cooperatives, managing organizations, related to ensuring the provision of utilities for cold water supply and sanitation to owners and users of premises in an apartment building or residential building, the provisions of these Rules apply to the extent not regulated by housing legislation.
2. These Rules use the concepts defined in the Federal Law "On Water Supply and Sanitation", as well as the following concepts:
"accident" - a dangerous man-made incident that leads to the restriction or cessation of water supply and (or) sewerage, creating a threat to life on centralized water supply and (or) sewerage systems, individual objects of such systems, including water and (or) sewer networks and human health or causing damage to the environment;
"balance sheet ownership boundary" - a line for dividing objects of centralized cold water supply and (or) water disposal systems, including water supply and (or) sewer networks, between owners on the basis of ownership or possession on a different legal basis;
"limit of operational responsibility" - the dividing line of objects of centralized cold water supply and (or) sewerage systems, including water supply and (or) sewer networks, on the basis of duties (responsibility) for the operation of these systems or networks, established in the cold water supply agreement, agreement water disposal or a single contract for cold water supply and sanitation, an agreement for the transportation of cold water, an agreement for the transportation of wastewater;
"control sample" - a sample of wastewater received from subscribers (including wastewater from transit organizations) into the centralized sewerage system, taken from a control sewer well in order to determine the composition and properties of such wastewater;
"control sewer well" - a well intended for sampling the subscriber's wastewater, specified in the sewerage agreement or a single contract for cold water supply and sanitation, an agreement for the transportation of wastewater, or the last well on the subscriber's sewer network before it is connected to the centralized sewerage system;
"surface wastewater" - rainwater, melted water, infiltration, watering, drainage wastewater accepted into the centralized water disposal system;
"transit organization" - an organization, including an individual entrepreneur, operating water supply and (or) sewer networks and providing water and (or) wastewater transportation services.
3.The procedure for using a centralized cold water supply system in emergency situations is determined by the requirements of technical regulations, state and national standards, as well as instructions for the preparation and operation of drinking water supply systems in emergency situations.
Table of contents
Introduction
1 area of use
2. Regulatory references
3. Conventions and abbreviations
4. General requirements
5. Examples of calculating the cost of water consumption for a residential building, a residential building with built-in premises, a business center, a shopping center, a sports complex, an industrial enterprise
5.1. An example of calculating the water consumption for a residential building
5.2. An example of calculating the water consumption of a residential building with built-in premises
5.3. An example of calculating the water consumption for a business center
5.3.1. An example of calculating the water consumption for a dining room
5.3.2. An example of calculating water costs for a business center as a whole
5.4. An example of performing a water consumption calculation for a shopping center
5.5. An example of calculating the water consumption for a sports complex
5.6. An example of calculating the water consumption for an industrial enterprise
6. An example of hydraulic calculation of internal water supply networks
6.1. Example of hydraulic calculation of internal water supply networks
6.2. An example of calculating pressure losses in fittings of a pipeline system
6.3. An example of calculating a heated towel rail
6.4. An example of hydraulic calculation of networks of domestic drinking water supply of cold water
6.5. An example of a hydraulic calculation of networks of an internal drinking water supply system for hot water
6.6.An example of a hydraulic calculation of networks of an internal unified utility and fire-fighting water supply
6.7. Throttle Bore Calculation Example
6.8. Example of determining the required head of a pumping station
7. An example of the selection of a water meter
7.1. Calculation of pressure losses in the meter by hydraulic resistance
7.2. Calculation of pressure losses in the meter in the absence of data on hydraulic resistance
7.3. Calculation of pressure losses in the filter of the water metering unit
8. An example of a thermal calculation, determining the circulation flow of a centralized hot water supply system
8.1. An example of calculating the heat loss of a pipeline section
8.2. Thermal calculation of the building's DHW system, determination of the circulation flow
8.3. Example of calculating the temperature of mixing flows
9. An example of a hydraulic calculation of a DHW system in circulation mode. Example of balancing valve selection
9.1. An example of a hydraulic calculation of a DHW system in circulation mode
9.2. Example of balancing valve selection
9.2.1. Selection example for a manual balancing valve
9.2.2. An example of selecting an automatic balancing valve (flow temperature controller)
10. Examples of calculations for the disposal of wastewater from sanitary sewerage of buildings and structures
11. Examples of calculations for the removal of rain and melt water from the roof of buildings and structures
12. An example of hydraulic calculation of offtake gravity pipelines
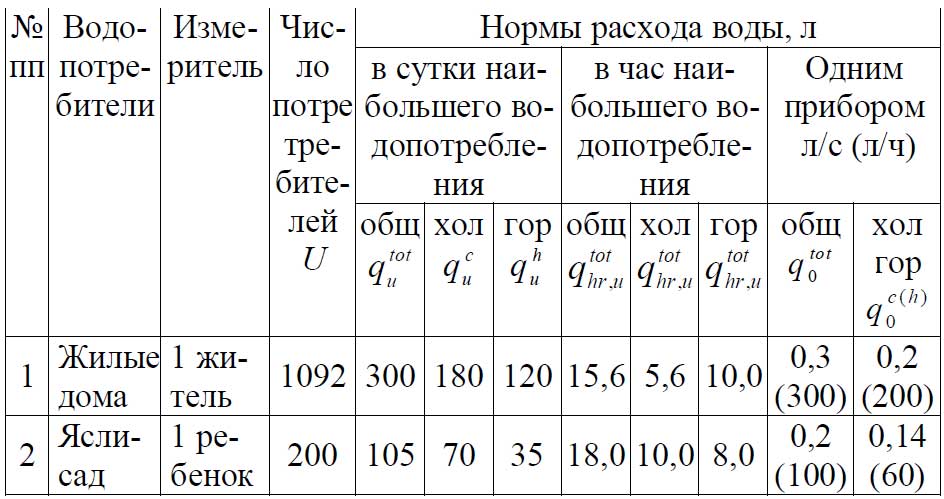
Appendix A. Estimated Water and Effluent Flows for Sanitary Appliances
Appendix B. Values of coefficients
Appendix C. Physical properties of water at different temperatures
Bibliography
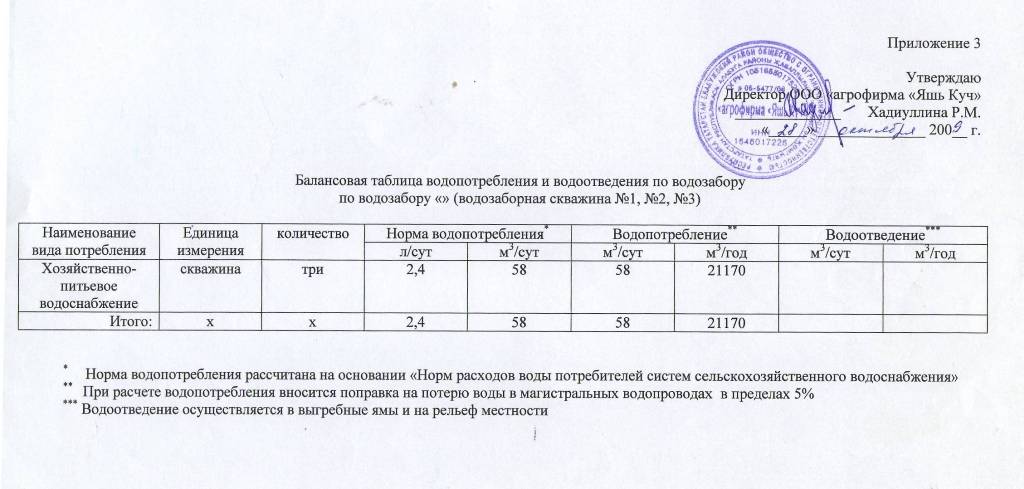
Sample Fill
The balance represents the ratio between the resources that were used and those that were originally provided. The purpose of its creation is to obtain water from networks. If you ignore the need to draw up this document, you will not be able to conclude an agreement with Vodokanal. The data presented in the table also saves a lot of money.
The procedure for issuing this document traditionally includes several steps.
Documents for download (free)
Sample calculation of the balance of water consumption and sanitation
Collecting the necessary data
This is the number of water consumers, as well as the volume of its daily use. The norms of fluid consumption, modes of operation of consumers of cold water and hot water are taken into account. The data is taken from the relevant regulatory documents, on the basis of which the calculation of standards is carried out.
Units of measurement are defined for all initial information. This is the number of liters per person, volume in cubic meters or square meters. Pieces, hours are also used in calculations.
Next, you need to enter data in the first three columns of the balance sheet - these are, respectively, “serial number”, “name of consumer”, “volume of water consumption in a daily period”.
There is no specific form of the document approved at the state legislative level. The main thing is that it contains a set of initial information.
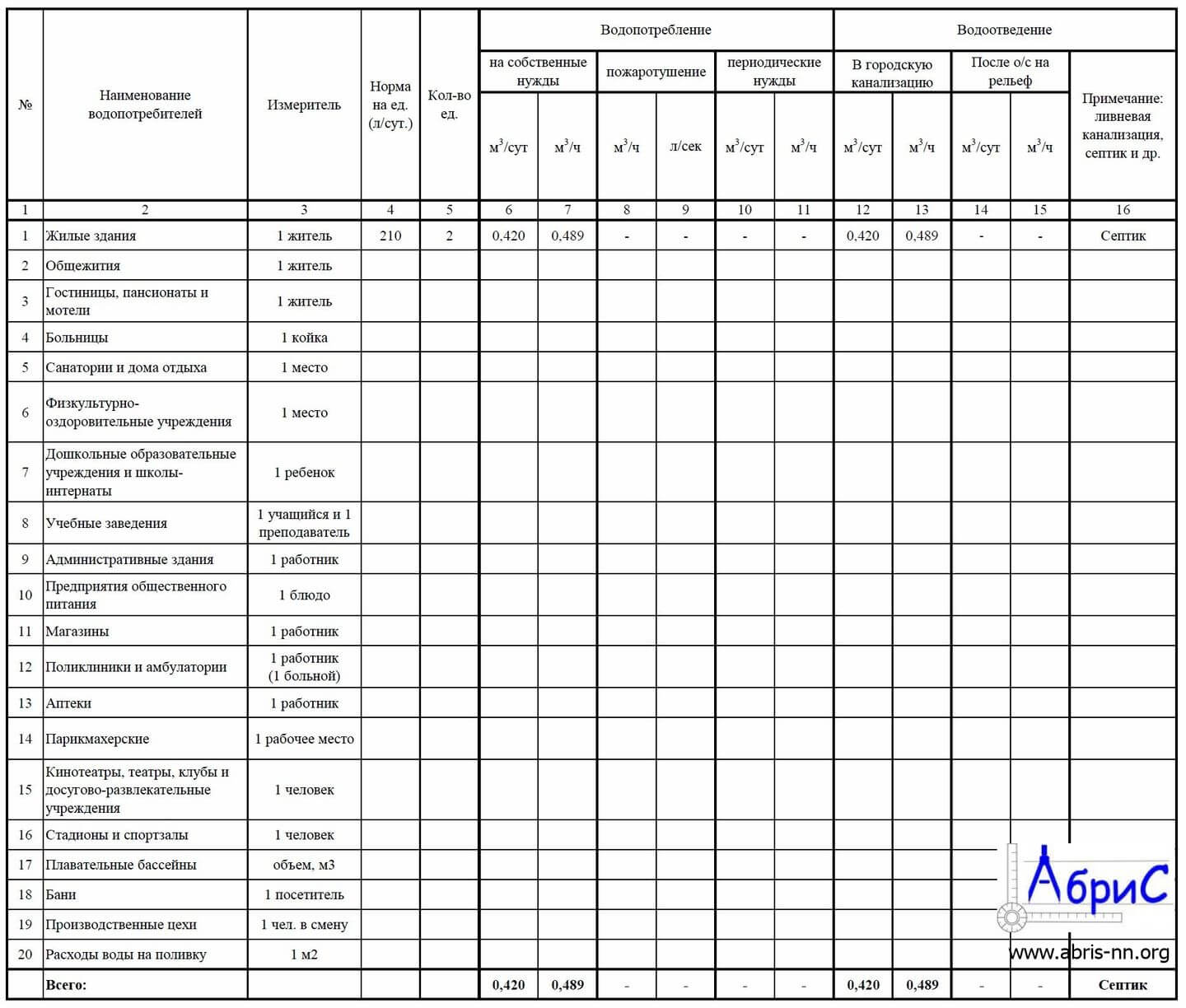
Populating a PivotTable

The second step after data collection is to fill in the "Standard" section. Accordingly, the following data is entered in the table - “Cold water standard”, “Hot water standard”, “Units of measurement”. Gradually, information on each consumer is entered into the lines.
After that, the columns "Operating mode per day" and "Operating mode per year" are filled in. You can take this data from the internal documentation of the enterprise in accordance with the classic work schedule. At the next step, information on days and years is entered into the water consumption of cold and hot water. To fill in these columns, it is necessary to take into account the readings of meters and measuring instruments.
The next step is to enter information into the "Water Disposal" section. Data is displayed per day and per year. The numbers are taken from the counters and measuring instruments used in the organization. The sixth column contains information about the regulatory documents that act as a base.
No more data is entered, the table is considered complete. The preparation of this document allows you to determine the amount of water consumed, as well as make a calculation, take measures to reduce the level of consumption. A set of such measures will contribute to a significant reduction in cash costs, which will affect the cost of production and the final profit of the enterprise.
Sending documents
First, the subscriber of the organization provides the contractor with a list of initial data. It consists of technical regulations, passports, certificates. Further, as already noted, a table is developed.
After that, the balance document, along with other papers, is sent to Vodokanal in order to conduct an audit and draw up a connection agreement. In order not to have to fill out the papers again, you should draw them up correctly and avoid entering erroneous information.
Organization of the check
After receiving a set of required documents, representatives of the responsible organization will carry out an inspection visit. As part of this event, they will be able to make sure that all the data provided is 100% correct and is reliable and valid. Based on the results of the audit, it will become clear whether the balance sheet is approved or not.
The procedure for connecting a production facility to water supply and sanitation networks is presented below.
Video about calculation methods and effective savings
How to properly calculate water consumption:
Water saver. Water consumption is reduced by 70:
In order to perfectly understand the intricacies of water supply and drainage from the point of view of the rules, one must be a specialist with a specialized education. But everyone needs general information to understand how much water we get and how much we pay for it. Economical water consumption and bringing the specific consumption to the level of true needs are not mutually exclusive concepts, and this is worth striving for.
Well, tomorrow or the day after tomorrow, are you going to submit an application in order to get the coveted technical specifications for water in a couple of weeks? Well, fine! In the meantime, you have a free evening, take care of the calculation of water consumption and sanitation.
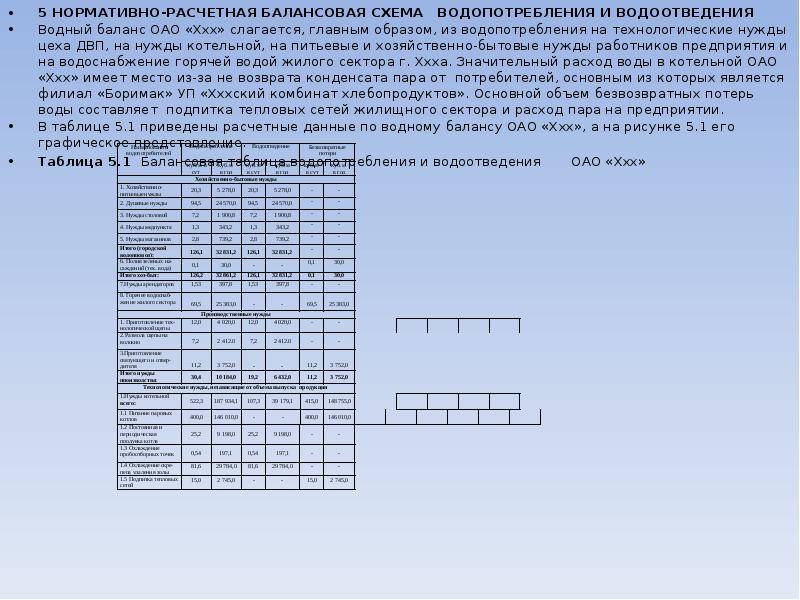
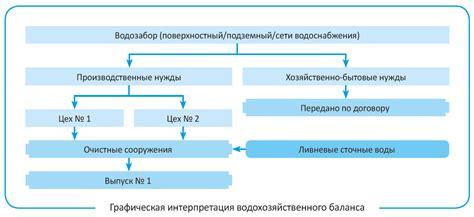
Composition of the water balance
The water management balance is a correlation of the estimated volume of water consumption from all sources and the estimated volume of wastewater discharged. Relatively speaking, the water management balance, like any other, consists of two parts - "incoming" and "expenditure" (water consumption and sanitation).
Water consumption includes all sources of water supply for all needs:
• surface water intake (from water bodies);
• underground water intake (from wells);
• water intake from centralized water supply systems (under the contract);
• water intake from the networks of other enterprises (under the contract).
In terms of wastewater disposal, it is necessary to indicate everything related to the discharge of wastewater and their transfer:
• discharges of wastewater into water bodies;
• transfer of wastewater under the contract to other enterprises for treatment or production needs;
• transfer of wastewater for treatment to the centralized networks of water and communal services (under the contract).
Losses and irretrievable water consumption can stand as separate positions.
In addition, many enterprises use water reuse and recycling systems.
Reuse of water - the use of wastewater discharged by the facility for water supply. The transfer of water from one workshop to another after use for a further production cycle can also be attributed to the reuse of water.
Recycled water supply - re-supply of waste water for production needs after cleaning, cooling and processing. The circulating water supply is a closed system and fresh water is only used for make-up.
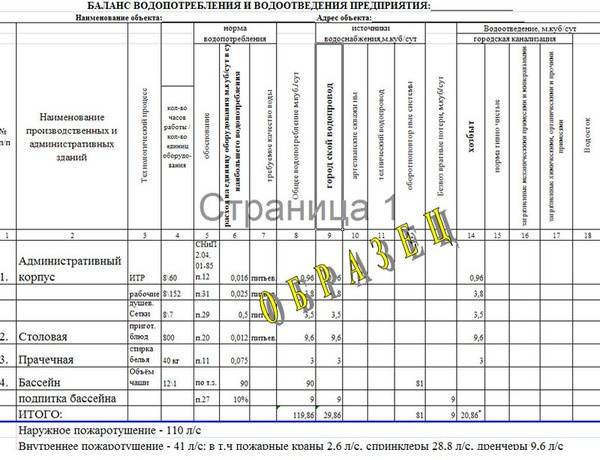
The estimated volumes of water consumption and wastewater disposal can be presented in the form of a table. one.

Please note: if the enterprise has several types of water intake at once, they can be placed in separate columns of the table. The format of the table may vary depending on the production
What problems can be solved by calculation?
1. Well flow rate
Allows you to select a borehole (submersible) pump (otherwise called: a deep pump) by the volume of pumped water (water consumption, water intake, water withdrawal, flow rate) from the principle: a larger flow rate - a larger pump diameter.The selection is also necessary to determine the cost of drilling a well, i.e. according to the maximum diameter of the pump, the diameter of the casing strings in the well is selected and, together with the cut (the predicted list of passable rocks), the well design is obtained.
2. The volume of household waste
Based on the principle (for residential development): how much water is consumed, how much domestic wastewater is diverted (therefore, the calculation is also called balance), you can determine the amount of wastewater, which will allow you to determine the volumes (dimensions) of local treatment facilities (VOCs) for the facility or the amount of waste that the company operating the sewer networks must accept.
For industrial enterprises, the volume of effluents (wastewater) is reduced by the volume of gratuitous losses in the production of a unit of output, for example, when:
bottling, bottling of various drinks (water is a filler);
air humidification (significant gratuitous losses);
draining water from tanks into storm sewers;
supply of heating (other) systems;
other cases.
It should be noted that recycled water is not taken into account in the balance (calculation) of water consumption.
3. Water consumption rate
In the calculation, each type of consumer is singled out separately, which is very convenient for subsequent rationing in production when producing finished products, calculating technical and economic indicators.
4. Calculation of the WSS of the water supply source (well)
The calculation of water consumption is also necessary for the subsequent calculation of sanitary protection zones (ZSO) of the source of water supply, that is, in this case, an artesian well.
Fill out an online application for the calculation of water consumption and sanitation
Scope of influence of the normative document
“Rules for cold water supply and sanitation” - this is the full name of the document approved on July 29, 2013 for N 644. The last edition is April 2018, changes and additions are valid from April 12, 2018.
The rules determine the relationship between subscribers (consumers of services) and organizations that supply them, based on the conclusion of binding contracts.
The conclusion of a contract for the supply of water and sanitation will not take much time if you collect a full package of necessary papers in advance (+)
The document also covers:
- consumers of services - individuals, budgetary organizations, enterprises, etc.;
- algorithm for connecting objects to the CA (central systems);
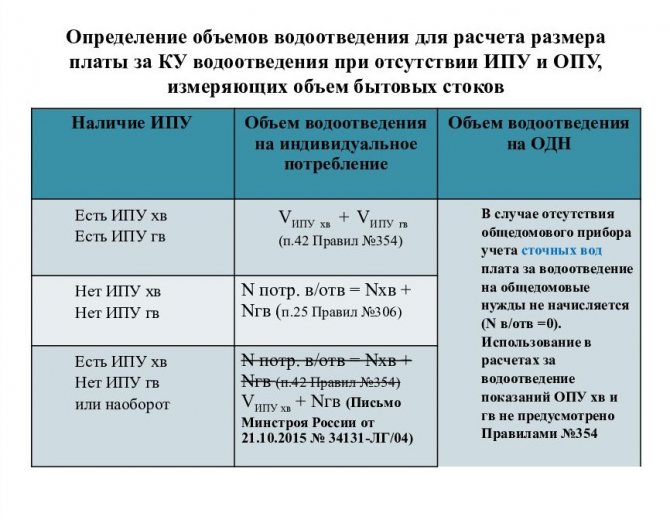
- accounting for released water, accounting for diverted effluents, quality control;
- consumers who are required to take into account the discharge of effluents into the CA by measuring instruments;
- calculation of compensation for the discharge of excessively polluted effluents, the procedure for informing about changes in their composition and properties (submission of declarations);
- standards, a mechanism for monitoring their use in practice, determining the amount of excess fees;
It should be thought out and provided, and, if necessary, created access to the subscriber's water and sewer communications, to points for sampling water and wastewater for testing.
Image gallery
Photo from
Determining the balance and calculations for water supply and sanitation systems are carried out separately for each residential, industrial, public facility
The calculation will reveal the volume of technical and domestic drinking water required to cover real needs
Sewer and plumbing systems are calculated and constructed only in pairs. Water supply cannot be provided to an object that is not equipped with a drainage system.
The drainage system is calculated so that it is able to transport not only water supply, but also storm, drainage and technical water, if any.
Water supply and sanitation systems
Ensuring adequate water supply
The relationship between water supply and sewerage
The device of the drainage system in the industrial version
Flow meters and their principle of operation
Traditional effluent metering methods involve determining the volume by meters on the pipe. However, it is not always possible to correctly calculate the indicators, especially if part of the flow is spent on irrigation, without discharge into the sewer. This is where flow meters come in handy.
These are modern wastewater metering devices equipped with electronic components and ensuring the accuracy of measurements. Calculations are carried out both in open channels and pipelines, so the equipment is initially adapted to perform functions in heavily polluted aggressive environments.
According to their principle of operation, flowmeters are divided into two types:
- Only the flow level is taken into account, where the volume of effluents is determined by the flow rate of the channel.
- Taking into account not only the volume of the flow, but also the speed characteristics, which makes it possible to guarantee the best measurement accuracy.
The range of flowmeters includes the following models:
- An ultrasonic device that has sensors for measuring the level of the flow depth. Can be installed without prior construction work. Data is transmitted via cable, modem connection.
- Electromagnetic flowmeters are meters that operate when a fluid flow interacts with a magnetic field, but in this case, sewage drains must be conductive.
- Pendulum-lever flowmeters measure effluents in open or closed channels by means of a float with a rotary blade, which calculates the speed of the entire flow.
The assortment list includes mobile or temporary metering devices that take measurements during the replacement and inspection of removed permanent flow meters. An ultrasonic flow meter is ideal for private household equipment, which measures wastewater with maximum accuracy.
Drainage standards make it obvious the feasibility of installing equipment. At the same time, there are mandatory rules, which indicate that if it is technically impossible to install a flowmeter, a special permit document must be issued. Otherwise, drain counters must be.
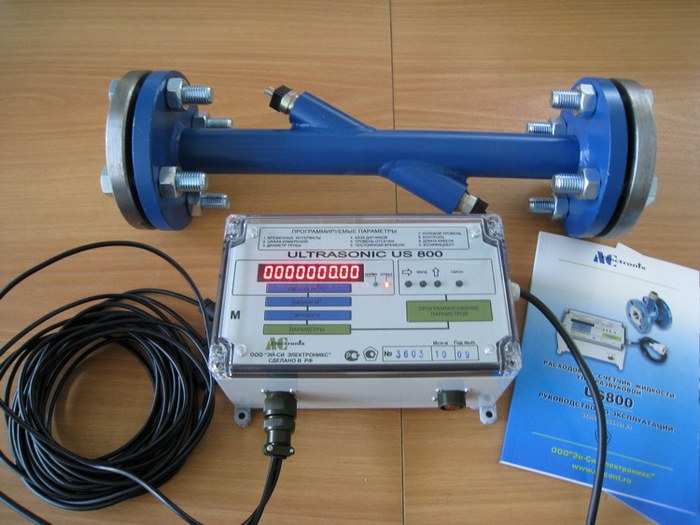

When choosing an ultrasonic flow meter or meters of another type, it is necessary to take into account the features of the object, the place where the measurement of water consumption and wastewater will be carried out. As a rule, the flowmeter is mounted on operating networks in specially equipped wells. It is impossible to measure the flow and account for wastewater in manholes, since the mines are located in places where the level of water supply networks changes or the pipeline turns, and the rules state that an ultrasonic, electromagnetic or pendulum-lever flow meter must be installed on a straight-line section.
The water discharge rate is a value that is important for every consumer to know.Having understood what water consumption is, as well as water disposal, it would be useful to check the amount billed for payment by the service provider
And additional metering devices will only help reduce costs. And remember that flow meters can be installed on non-pressure pipelines, so the equipment deserves the closest attention and selection.
Relationship between water consumers and service provider
By entering into a contractual relationship with the water supply and sewerage organization, you become a consumer of the water supply / sanitation service.
Your rights as a user of the provided service:
- require the supplier to continuously provide the proper service (normative water pressure, its chemical composition that is safe for life and health);
- apply for the installation of water meters;
- demand recalculation and payment of penalties in case of provision of services in an incomplete volume (the act must be drawn up within 24 hours after the application is submitted);
- terminate the contract unilaterally, but subject to a 15-day notice and full payment for the services received;
The subscriber has the right to receive information about payment (status of the personal account) free of charge.

No water or barely flowing? Call the dispatch service and demand the arrival of a representative of the water utility to draw up an act
List of rights of the second party:
- stop (with a few days' notice) in full or in part the supply of water and the reception of wastewater in case of unsatisfactory technical condition of water supply networks and sewerage;
- require admission to the territory of the client to take readings of water meters, check seals, inspect the water supply and sewer systems;
- carry out preventive maintenance according to the schedule;
- turn off water to debtors;
- stop water supply without warning in case of accidents, natural disasters, power outages.
Disputes and disagreements are resolved through negotiations or in court.