- Checking pressure gauges on gas cylinders
- Device and purpose of the flowmeter
- Frequency and verification procedure
- Laboratory for calibration of gas analyzers
- Fast, reliable, cheap...
- Accreditation certificate
- Features of gas analysis instruments
- What you need to know about calibration of gas analyzers
- Verification of gas analyzers. Process Features
- Calibration of pressure gauges - rules
- STAFF
- 3.1. Requirements for the organization of calibration work
- What is the essence of the method of verification work?
- Requirements for the design, installation (installation), adjustment of devices for monitoring the CO content in boiler rooms:
- Conditions for work
- Maintenance of the gas control system (gas alarms)
- Methods for verification (calibration) of pressure and vacuum measuring instruments
Checking pressure gauges on gas cylinders
When they talk about checking gearboxes, they actually mean checking pressure gauges on household gas cylinders. Let's open a secret: in the state register of the RF SI, the gearboxes are not indicated, but the pressure gauges are just there. And when specialists come, they check the operation of the flow meters - in the same way, how to make verification gas meters.
But it is also necessary to monitor the functioning of the gearbox, since these two devices work in the same bundle. Failure of one of the elements will immediately affect the operation of the entire system.
Device and purpose of the flowmeter
Pressure gauges are installed on household gearboxes that meet the requirements of GOST 2405-88. The main purpose of the devices is to control the pressure in the gas system. To accurately set the operating parameters, two devices are used - at the inlet and outlet.
The design of the flowmeters consists of the following elements:
- durable metal case, closed with glass on one side;
- scale with units of measurement - Pa, MPa, kgf / cm²;
- arrow painted in bright color;
- a sensitive element located inside the case and setting the arrow in motion.
The element responsible for the rotation of the arrow may differ. Membrane devices are used for low-pressure environments, but spring models are more often used for gas networks - the arrow moves by shortening or straightening the spring.
To make it easier for the user to navigate and adjust the parameters as necessary, a red line is applied to the scale - just opposite the working pressure marks.
Some rules for installation and operation:
By color marking, household pressure gauges for gas reducers differ from similar equipment for other types of gas. If oxygen valves are painted blue, ammonia valves are yellow, acetylene valves are white, then devices for propane-butane cylinders are only red.
Frequency and verification procedure
Any gas equipment is subject to regular verification, even if it is not used or is used seasonally, in the summer.
According to the norms, there is an initial verification - before commissioning or after repair. Other activities are carried out periodically, as planned or after an accident.
Only accredited or licensed organizations can perform verification.In our country, these are most often companies connected in one way or another with Gazprom, the main gas supplier. It is the duty of the owner of the housing in which gas cylinders are installed to issue a call in time and control the visit of a specialist.
Based on the results of verification, a sign is put on or a certificate is issued, which must be kept until the next procedure. A special sign is usually applied to the body of the device, and if it is not possible, then they are put directly on the certificate.
The requirements for a sign or documentation, as well as the verification procedure, are determined by the federal executive body.
It is very important not to violate the deadlines: the pressure gauges are checked and the seal (brand) is installed once every 12 months. If there is no stamp or seal on the pressure gauge, they forgot to call a representative of the service organization in time, the “behavior” of the arrow does not correspond to the real situation, or obvious mechanical damage is visible - the gas stove cannot be operated!
If there is no stamp or seal on the pressure gauge, they forgot to call a representative of the service organization in time, the “behavior” of the arrow does not correspond to the real situation, or obvious mechanical damage is visible - the gas stove cannot be operated!
At industrial facilities, every six months they make an additional check of the health of the equipment with a control pressure gauge, after which they make an entry in the journal. The procedure, frequency, terms are indicated in the instructions for the safe maintenance of cylinders
The requirements for equipment used for hot work are much stricter. For example, gas regulators for propane tanks are checked quarterly, and hoses every 3 months.
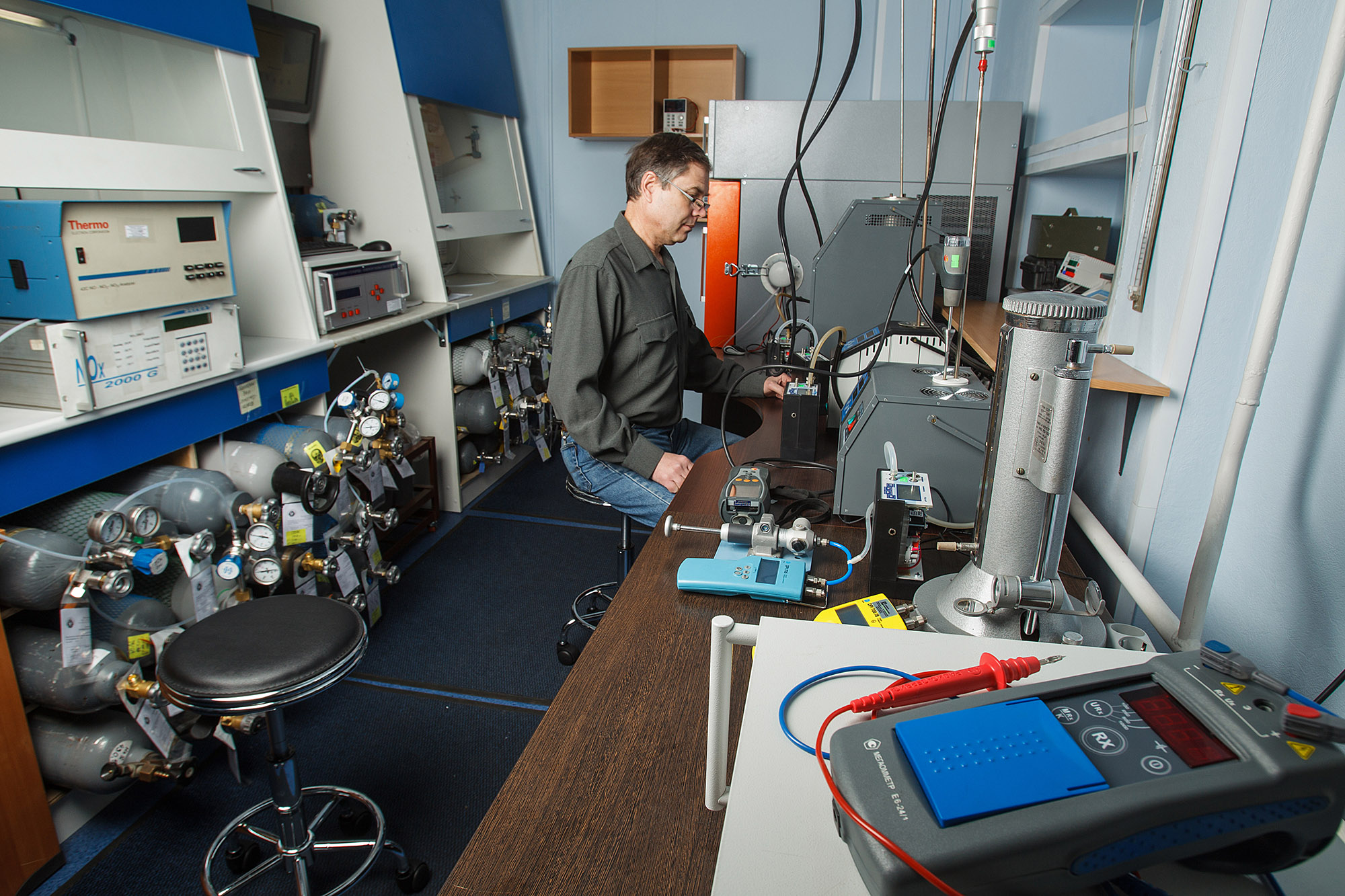
Laboratory for calibration of gas analyzers
For many years, the KPO-Electro metrological service has been providing services for primary and periodic verification of gas analytical equipment and calibration of all types of instruments, including stationary, portable and portable gas analytical measuring instruments (gas analyzers, gas detectors, detectors and sensors) to control the concentration of one or several substances in air or gaseous media.
The company has its own laboratory equipped with the latest equipment, which employs specialists with many years of experience working with gas analysis instruments of any complexity.
The metrological service of KPO-Electro provides a full range of services for users of domestic and foreign manufacturers, such as:
- Draeger / Draeger (various models of the Pac, X-am, Polytron, PIR, PEX series, etc.)
- Honeywell Analytics (BW GasAlert, ToxiRAE Pro, MultiRAE, MultiRAE Pro, MultiRAE Lite, QRAE 3, Searchpoint Optima Plus, XNX, Apex, Satellite XT, etc.)
- Elektronstandart-Pribor (SGOES, SSS-903, etc.)
- Analytpribor (ANKAT-7664Micro, STM-30M, DAH, DAK, etc.)
- Oldham (OLC/OLCT, CTX, MX 2100, BM 25 etc.)
- Net Safety Monitoring (Emerson) (Millennium II, Millennium II Basic)
- MSA (ULTIMA X, PrimaX, ALTAIR, etc.)
- Eris (PG ERIS-411, PG ERIS-414, DGS ERIS-210, DGS ERIS-230, etc.)
- Detcon (IR-700, TP-700, FP-700, etc.)
- Seitron (RGD, SGY, SGW, etc.)
- Bertoldo (Domino)
- NPP "Delta" (IGS-98, Sensis)
Verification of gas analyzers and calibration of stationary and portable gas analyzers is carried out exclusively using methods approved and permitted for use by specialized state control organizations.
The result of verification of the measuring instrument is the provision to the customer of a verified gas analyzer approved for use, with the issuance of a certificate of verification of the established sample. In case of detection of non-compliance with the approved technical characteristics, it is possible to carry out adjustment and / or repair of the product.
Fast, reliable, cheap...
KPO-Electro has developed the most convenient and well-thought-out scheme of work, which is absolutely understandable, convenient and beneficial for customers.
Working with us you always have the opportunity to:
- carrying out urgent verification of gas analyzers in your territory;
- choosing the method of delivery of devices for verification and their return to the place of operation;
- obtaining the services of a personal manager to agree on individual conditions - the cost and terms of verification of the device;
- use the unique software package of our organization, which allows us to reduce the time for generating an application for verification and receive prompt information to the customer about the progress of verification.
Accreditation certificate
Services are provided on the basis of an accreditation certificate in the field of ensuring the uniformity of measurements for the right to perform work (and provide services) for the verification of measuring instruments No. RA. RU. 311968 dated December 09, 2016, issued by the Federal Service for Accreditation (ROSAKKREDITATSIYA).
Features of gas analysis instruments
A gas analyzer is a device for determining the quantitative and qualitative composition of a gas mixture. That's what science says.Hand-held absorption analyzers are widely used, in which the reagents gradually absorb the constituents of the gas. Automatic devices continuously determine the physical and physico-chemical values of mixtures and their components.
Gas analyzers are divided into 3 groups. All devices operate on physical methods of analysis, and the difference is expressed in the ability to take into account chemical processes.
 Sigma-03 is a stationary multi-channel analyzer with separate blocks and modules, including the SIGMA-03.IPK infoblock, the set also includes up to 8 hardy sensors
Sigma-03 is a stationary multi-channel analyzer with separate blocks and modules, including the SIGMA-03.IPK infoblock, the set also includes up to 8 hardy sensors
Devices of the 1st type monitor, among other things, accompanying chemical reactions. The analyzers determine changes in the pressure of the fuel mixture and its volume after the chemical interaction between the components.
Gas analyzers of the 2nd type provide indicators of physical analysis, which extends to chromatographic, photoionization, electrochemical, thermochemical and other physical and physico-chemical processes.
Devices of the 3rd type work only on the principle of physical analysis. Their measurement methods are magnetic, densimetric, thermoconductometric and optical.
Instruments for the analysis of gas mixtures are also classified:
- by appointment;
- by the number of measuring channels;
- by the number of measured components;
- by design;
- by functionality.
It is worth knowing more about devices that differ in the latter feature. Gas analyzers perform the functions of conventional measuring instruments, as well as signaling devices, leak detectors, and indicators.
What you need to know about calibration of gas analyzers
Verification of gas analyzers (in some cases, calibration of gas analyzers) is a complex event, the purpose of which is to determine the technical, metrological and other characteristics of these devices and compare them with reference indicators. Verification of gas analyzers is carried out by the metrological center "Autoprogress-M" on a professional basis, in a short time and at favorable prices for customers. Ideally equipped laboratories are used as test rooms, which have all the equipment necessary for the correct implementation of the above procedure.
Verification of gas analyzers. Process Features
A modern gas analyzer is a measuring device, the main purpose of which is the most accurate and highly detailed determination of the composition of mixtures of various gases. To date, both manual gas analyzers and those of their variations that operate in automatic mode are actively used.
Verification of gas analyzers is carried out according to the methods approved by the State Metrological Service. In the vast majority of cases, the calibration of gas analyzers is carried out once a year, however, in some situations, the calibration interval can be reduced: both at the initiative of the owners of such equipment, and at the request of state regulatory authorities.
The process of verification of gas analyzers is regulated by the existing regulatory documentation of the Russian Federation. The main provisions regarding the above process are specified in the Law of the Russian Federation "On Ensuring the Uniformity of Measurements".
Calibration of gas analyzers is traditionally carried out in several stages, including: inspection of equipment, testing of equipment in general and its constituent elements in particular, instrument adjustment. In case of successful completion of the calibration procedure for gas analyzers, information about this is entered into the official database, and the devices can be used for a year, until their next calibration.
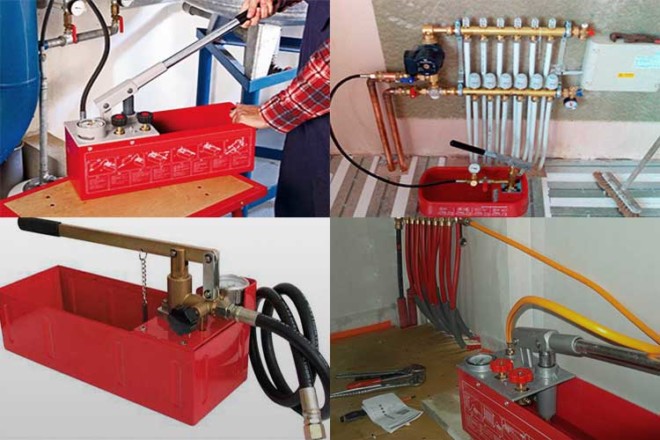
Calibration of pressure gauges - rules
In order to accurately examine the measuring device, it is necessary to follow some rules for checking pressure gauges:
- inspect for external defects (for example, broken glass);
- it is necessary to create conditions close to normal during verification (atmospheric pressure 760 mm Hg, air humidity up to 65%, room temperature 20 ◦ C);
- set the dial hand to zero;
- compare the readings of the reference instrument and the test instrument.
The last two points, if it is impossible to set the arrow to zero and differences appear between the reference and the device under test, should be adjusted using bolts. If the setting of the nominal parameters does not occur, it may be easier to replace the pressure gauge with a new one, given the low cost of the device.
STAFF
4.1. The personnel composition of the MS is presented in
MS passport.
4.2. The organizational structure of the MS is given
in the regulation on the metrological service.
4.3. Personnel responsibility for
Quality assurance of calibration is set out in job descriptions.
4.4. MS employees are certified in
in the manner established in RD 34.11.112-96.
4.5. The head of the MS organizes the study and
the use of foreign and domestic experience by MS employees in providing
calibration quality, establishes deadlines and procedures for internal control
efficiency of the calibration quality system.
3.1. Requirements for the organization of calibration work
3.1.1. Metrological service for organizing and conducting calibration
works should have:
means
calibration;
documentation
for calibration;
personnel;
premises.
3.1.2. The means of calibration are presented
the following requirements.
Metrological
the service must have means of calibration that meet the requirements of regulatory
calibration documents and relevant scopes of accreditation.
Funds
calibrations must be kept under conditions that ensure their safety and
damage protection.
Need
metrological services (calibration laboratories) in calibration tools
determined according to MI 2314-94.
3.1.3. To the calibration documentation
the following requirements apply.
Metrological
The service must have up-to-date documentation including:
position
about the metrological service (calibration laboratory);
certificate
accreditation for the right to carry out calibration work;
official
instructions;
charts
verification of calibration means;
charts
calibration of measuring instruments;
regulatory and technical
documents for calibration (verification, methods, instructions, guidelines and
etc.);
technical
description and operating instructions for calibration tools and measuring instruments;
the passport
on measuring instruments and means of calibration;
the documents,
determining the procedure for recording and storing information and calibration results
(protocols, work logs, reports, etc.);
the documents
on the education and certification of specialists performing the calibration of means
measurements (diplomas, certificates, certificates, certificates);
acts
on the condition of the production facilities.
Metrological
the service must have a quality assurance system appropriate to its
activities in the field of calibration and the scope of work performed. The form
"Quality Guide" is given in the appendix.
3.1.4. To the staff of calibration laboratories
the following requirements apply.
Specialists
metrological service must have professional training and experience
calibration of measuring instruments in the declared scope of accreditation.
For
each specialist should establish the functions, duties, rights and
responsibility, requirements for education, technical knowledge and work experience,
which should be included in the job description.
Specialist,
who performs the calibration of measuring instruments must be certified in the manner
installed in the power industry.
Training
and certification of personnel should be carried out in accordance with the requirements of the RD
34.11.112-96.
3.1.5. To the premises of calibration laboratories
the following requirements apply.
Premises
must correspond to the production area, condition and provided
in them, the requirements of the applicable regulatory and technical documents on
calibration, sanitary norms and rules, labor safety requirements and
environmental protection.
Need
metrological services (calibration laboratories) in production areas
determined according to MI 670-84.
At
When placing calibration equipment, it is recommended to comply with the following standards:
passage width - not less than 1.5 m; width of unoccupied space around individual
calibration installations (sets of verification tools) or their stationary
elements - at least 1 m; distance from cabinets and tables with measuring instruments
or calibration to heating systems - not less than 0.2 m; the distance between
working tables, if one calibrator works at the table - not less than 0.8 m, and
if two - at least 1.5 m.
Coefficient
natural light on the surface of the table of the calibrator is allowed in
within 1.00 - 1.50. Illumination at workplace level should not be
less than 300 lux.
Operations
associated with the use of aggressive, toxic or explosive substances or with
preparation of measuring instruments for calibration (re-preservation, cleaning, etc.) and
accompanied by air pollution or flammable fumes, it is recommended
produced in separate isolated rooms.
What is the essence of the method of verification work?
The verification procedure is a document with detailed operations to confirm the suitability of the gas analyzer. For different brands and models, the approach is different.
Excerpt from the methodology for gas analyzers models 1800, 1900, 2200, 5100, 5200 of Servomex Group Limited: the first point is verification operations
The document usually includes 7 points:
- verification operations. We are talking about the main indicators, including errors.
- Funds. These include instruments and gas mixtures for testing and determining metrological characteristics.
- Safety requirements.
- Conditions for holding.
- Training.
- Holding.
- Formulation of test results. At this stage, the verifier draws up a protocol and issues a document-certificate.
The verification itself begins with the fact that a cylinder with a calibration gas is connected to the control valve. Then a rotameter is brought to the exit.The latter is attached with an adapter for verification work. The mixture is then allowed to enter the gas analyzer, and when the device gives readings, they are fixed.
The specialist will calculate the error and determine the time it took to establish the readings. The verifier will compare the indicators with the standards and issue the results.
Requirements for the design, installation (installation), adjustment of devices for monitoring the CO content in boiler rooms:
• In boiler rooms with constant attendance of service personnel, sensors of control devices are installed at a distance of 150-180 cm above the floor or work platform, where the operator's stay is likely and long during the work shift. This is a seat at the work table in the breathing zone at the front of the boiler.
• In fully automated boiler rooms, which are serviced periodically, sensors of control devices are installed at the entrance to the room, and the alarm from the control device is displayed on the operator's desk.
• When installing devices (signaling devices/gas analyzers) in boiler rooms with non-continuous floors, each floor should be considered as an independent room.
• For every 200 m2 of the boiler room, 1 sensor should be installed to the control device, but not less than 1 sensor for each room.
• Sensors of control devices (alarms/gas analyzers) must be installed no closer than 2 m from supply air supply points and open vents. When installing sensors, the requirements of the manufacturer's installation instructions should be taken into account, which should maximally exclude a negative effect on the accuracy of measuring the CO concentration from moving air flows, relative humidity in the boiler room and thermal radiation.
• Sensors of control devices (signaling devices/gas analyzers) must be protected from moisture ingress by installing a protective visor.
• In dusty rooms it is necessary to provide for the installation of sensors with dust filters. Periodic cleaning of contaminated filters should be carried out in the manner prescribed by the production instructions.
• Projects of newly built boiler houses should provide for the installation of CO control devices in the boiler rooms.
• Installation of control devices (alarms/gas analyzers) in operating and reconstructed boiler houses must be carried out by the owner of this boiler house within the time limits agreed with the territorial authority of the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia.
On the Russian market there are a number of domestic and foreign devices for monitoring CO and CH4, which meet the above requirements to varying degrees.
Conditions for work
First of all, provide security. For verification, only those rooms where there is supply and exhaust ventilation are suitable. After fulfilling this requirement, the content of harmful substances in the working area of the enterprise is checked, and the norm was indicated in GOST 12.1.005.
 The owner of the enterprise is responsible for the safety in the verification room, for each type of explosive gas there is a permissible concentration in the air
The owner of the enterprise is responsible for the safety in the verification room, for each type of explosive gas there is a permissible concentration in the air
Employees are protected from electric shocks - based on GOST 12.2.007.0 and other requirements from safety regulations. The use of gas mixtures in cylinders is regulated by PB 03-576-03, they are also the Rules for the Design and Safe Operation of Pressure Vessels.
To carry out verification, the following requirements and restrictions will have to be met:
- voltage 220 V;
- consumption of ASG at the level of 0.18-0.35 dm³/min;
- atmospheric pressure not lower than 84 kPa and not higher than 106;
- relative air humidity within 30-80%;
- ambient temperature from +15 to +25 °C.
Verification is carried out only by certified employees in terms of measuring instruments according to PR 50.2.012-94. Before doing their job, they must read the manual for the gas analyzer and also work with the instruments.
During the process, the specialist will keep a record and enter the following data:
- Document Number;
- date;
- the name of the owner of the gas analyzer;
- number of the verified device;
- instrument readings and error parameters.
As a result, the owner of the meter will receive a signed certificate marked “Good”, but if the quality of the device is not lucky, then a notice with the entry “Not good”.
Representatives of the Center for Standardization and Metrology will immediately stop verification if they receive an unsatisfactory result in terms of indication variation, basic or absolute error, or alarm response time.
The verification certificate must confirm the suitability of the product, as well as certify compliance with the methodology for a particular gas analyzer, indicating its name and serial number
Equipment for fuel accounting before verification must have an information block, a charger and a passport. The same applies to the act of the last verification, if it was carried out, as well as replaceable cassettes and remote probes, if any.
Maintenance of the gas control system (gas alarms)
Maintenance of the gas pollution control system at the LLC Tekhnologii Kontrolya company will ensure reliable and safe operation of your boiler house.Personnel servicing the gas pollution control system must be certified in accordance with the requirements of Federal Law No. 116 dated 06/22/2007 and PB 12-529-03 p. 5.7.10, p. 5.7.11, copies of the certification protocols are attached to the maintenance contract. The scope of work on maintenance of the gas control system:
- checking the operation of sensors of the gas pollution control system using control gas mixtures with the preparation of acts
Methods for verification (calibration) of pressure and vacuum measuring instruments
41. GOST 8.053-73
GSI. Pressure gauges, pressure and vacuum gauges, vacuum gauges, pressure gauges, thrust gauges and
draft gauges with pneumatic output signals. verification method.
42. GOST 8.092-73
GSI. Pressure gauges, vacuum gauges, pressure and vacuum gauges, draft gauges, pressure gauges and
thrust gauges with unified electrical (current) output
signals. Methods and means of verification.
43. GOST 8.146-75
GSI. Differential indicating and self-recording pressure gauges with GSP integrators.
verification method.
44. GOST 8.240-77
GSI. Pressure difference measuring transducers GSP with unified
current output signals. Methods and means of verification.
45. GOST 8.243-77
GSI. Pressure difference measuring transducers GSP with unified
output parameters of mutual inductance. Methods and means of verification.
46. RD 50-213-80. Flow Measurement Rules
gas and liquid by standard narrowing devices.
47. RD 50-411-83. Methodical instructions.
Consumption of liquids and gases. Measurement technique using special
narrowing devices.
48. MI 333-83. Converters
measuring instruments "Sapphire-22". Methodical instructions for verification.
49. MI 1348-86 GSI. Pressure gauges
deformation indicating and measuring pressure transducers GSP.
verification method.
50. MI 1997-89 GSI. Converters
measuring pressures. verification method.
51. MI 2102-90 GSI. Manometers and vacuum gauges
deformation exemplary with conditional scales. Graduation technique.
52. MI 2145-91 GSI. Manometers and vacuum gauges
deformation exemplary with conditional scales. verification method.
53. MI 2124-90 GSI. Pressure gauges, vacuum gauges,
pressure and vacuum gauges, pressure gauges, draft gauges, thrust gauges showing and
self-recording. verification method.
54. MI 2189-92 GSI. Difference converters
pressure. verification method.
55. MI 2203-92 GSI. Verification methods
means of measuring pressure.
56 MI 2204-92 GSI. Consumption, mass and volume
natural gas. Measurement technique with narrowing devices.
57. Instruction 7-63. Instructions for checking draft meters,
micromanometers and differential pressure gauges.