- What is a security connection device
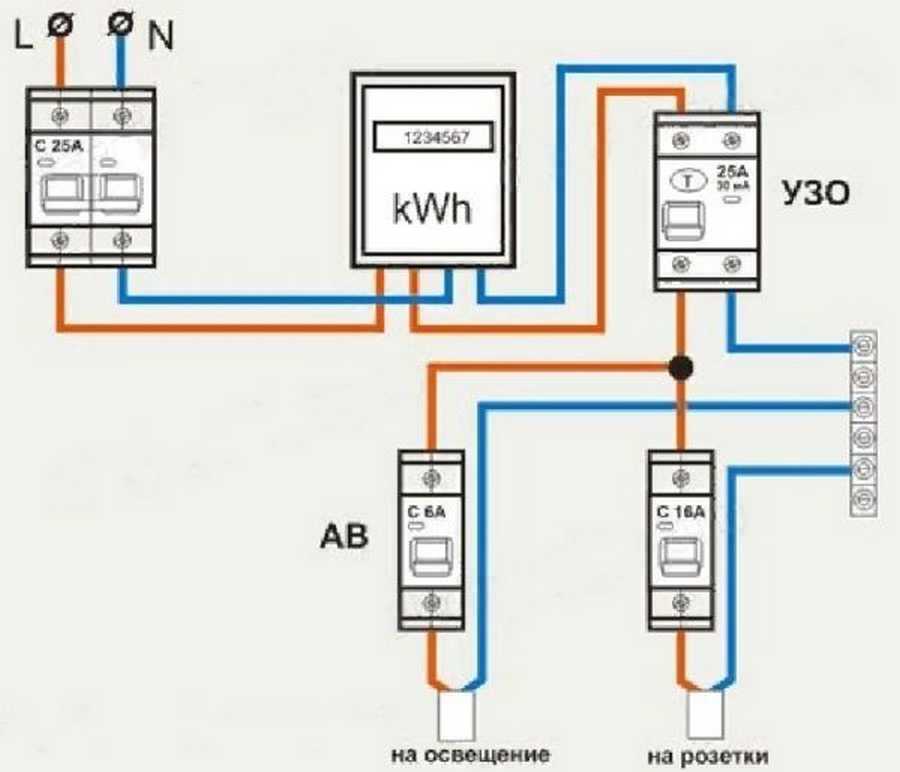
- Protection options for a single-phase network
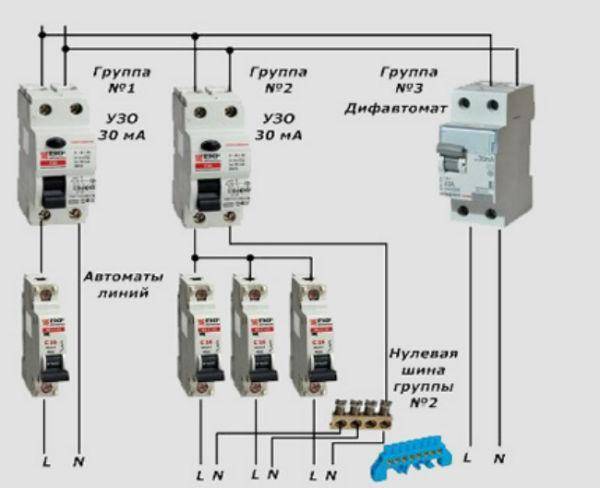
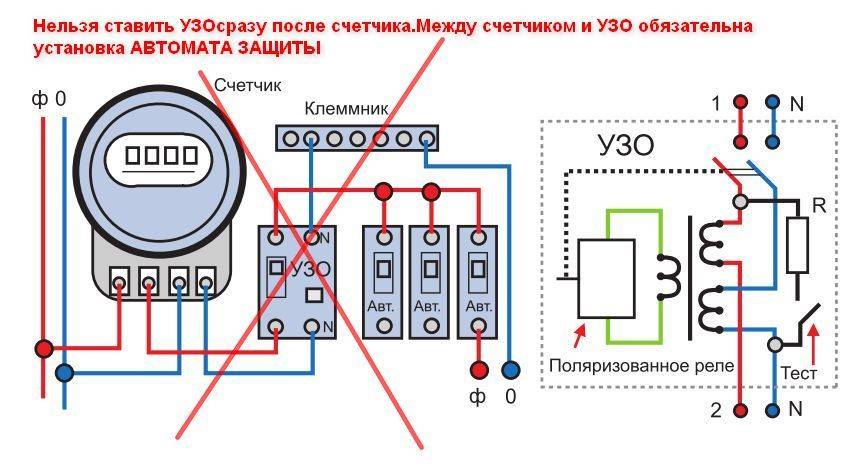
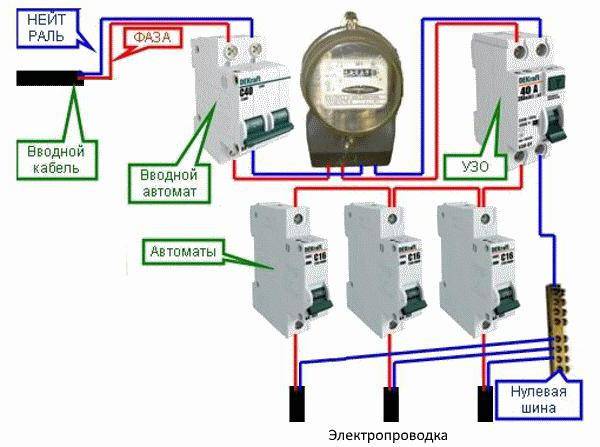
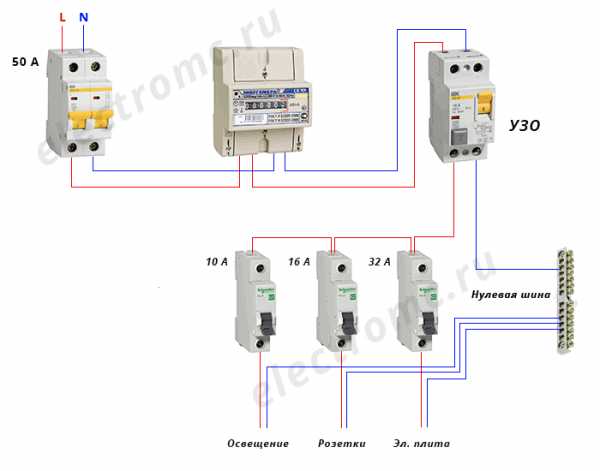
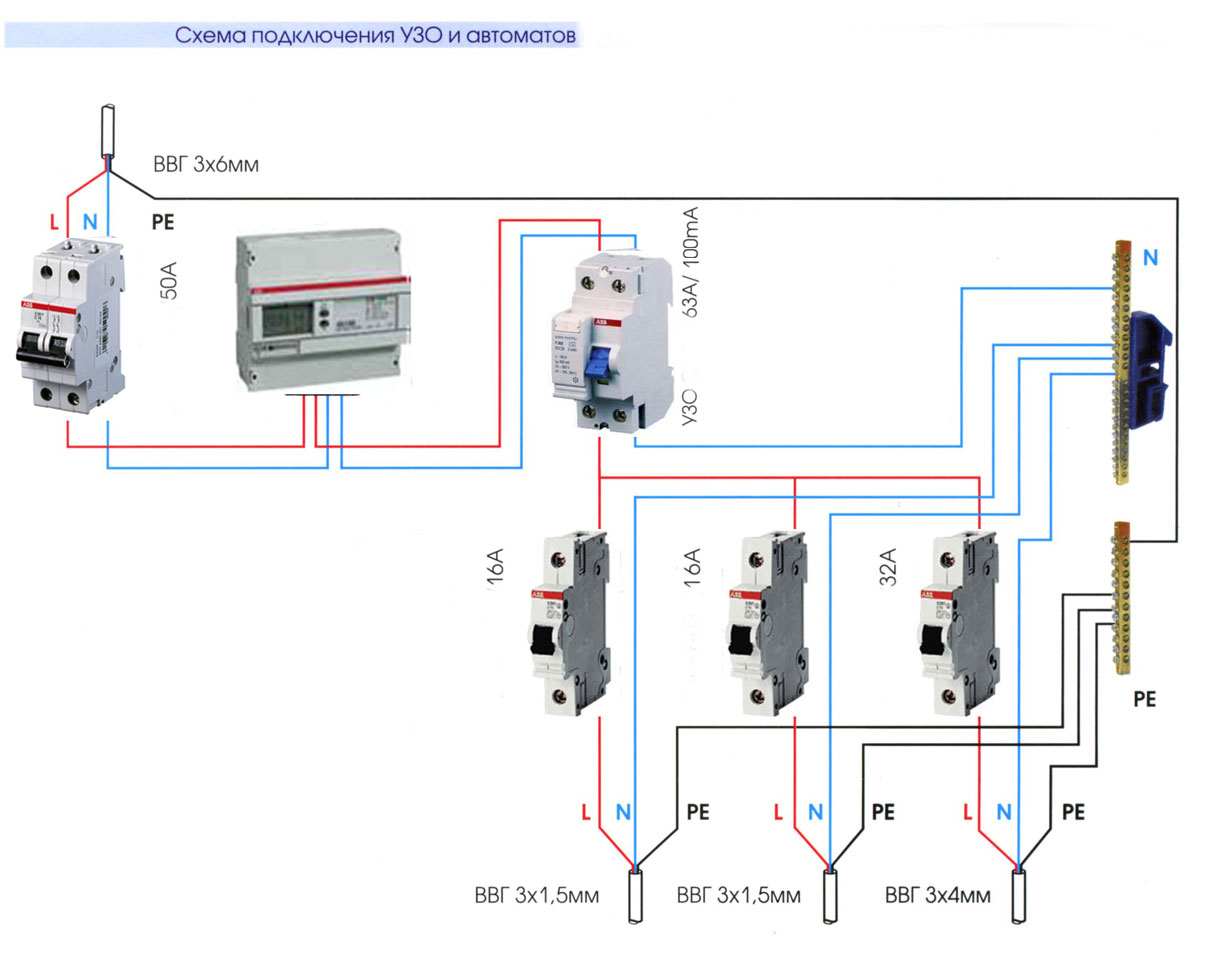
- Option #1 - common RCD for 1-phase network.
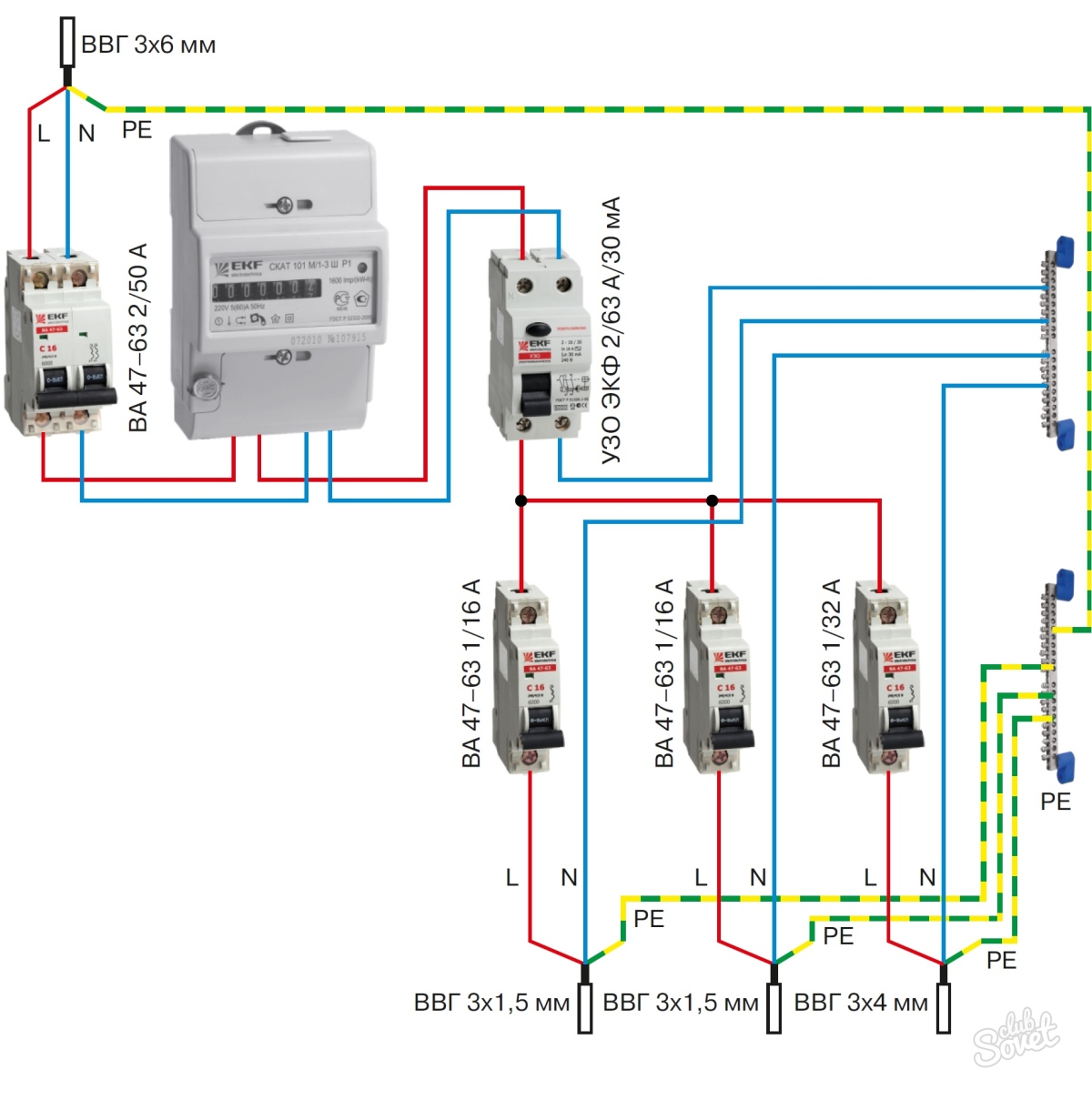
- Option #2 - common RCD for 1-phase network + meter.
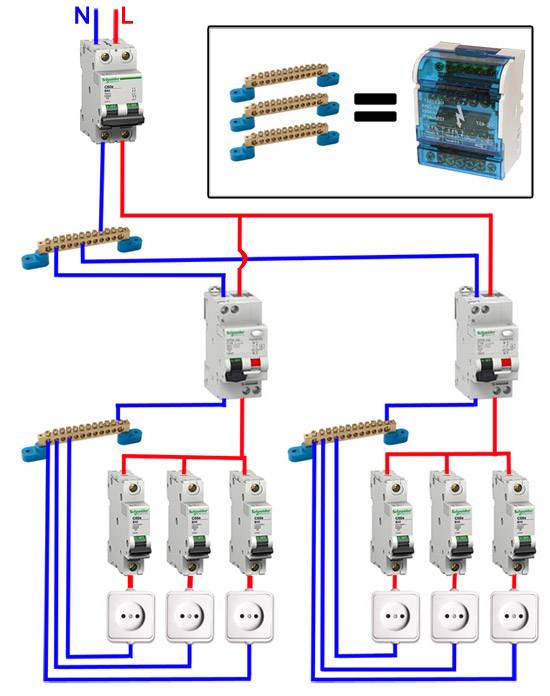
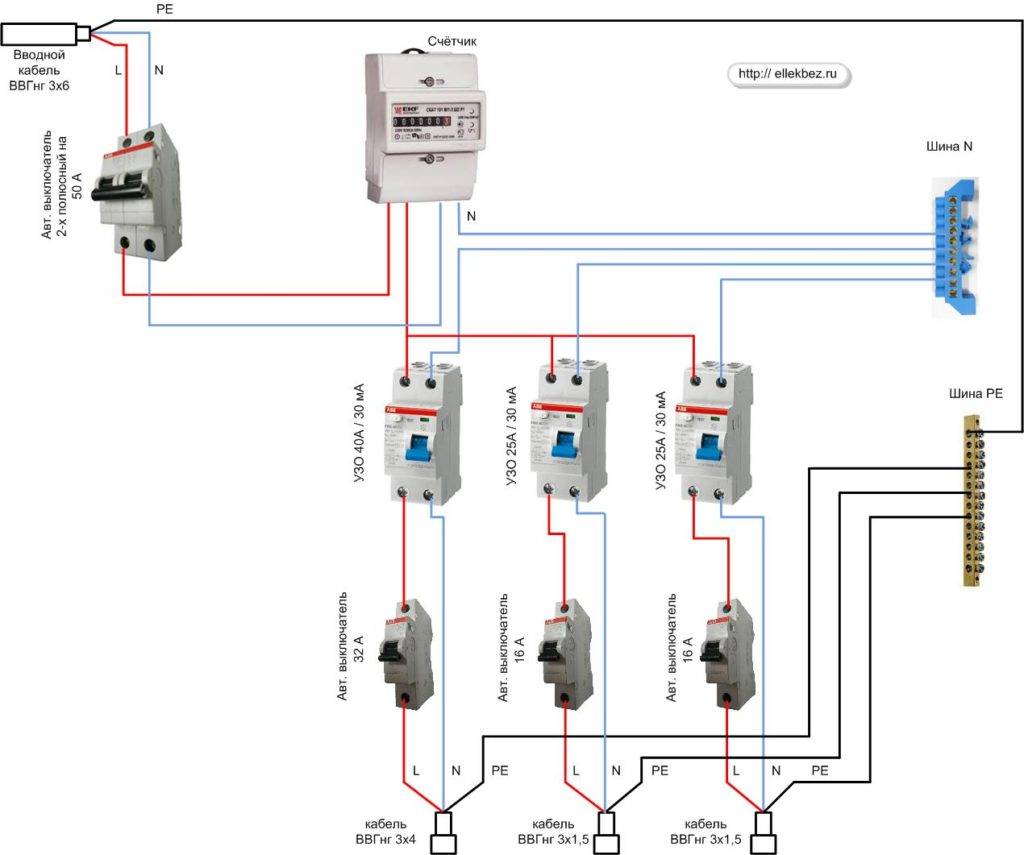
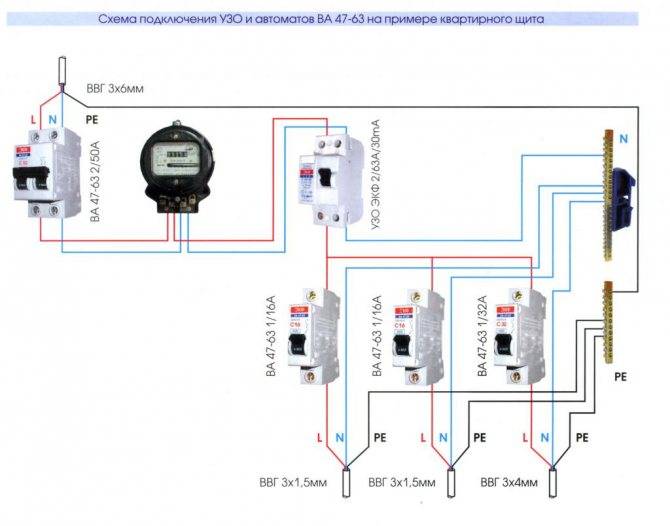
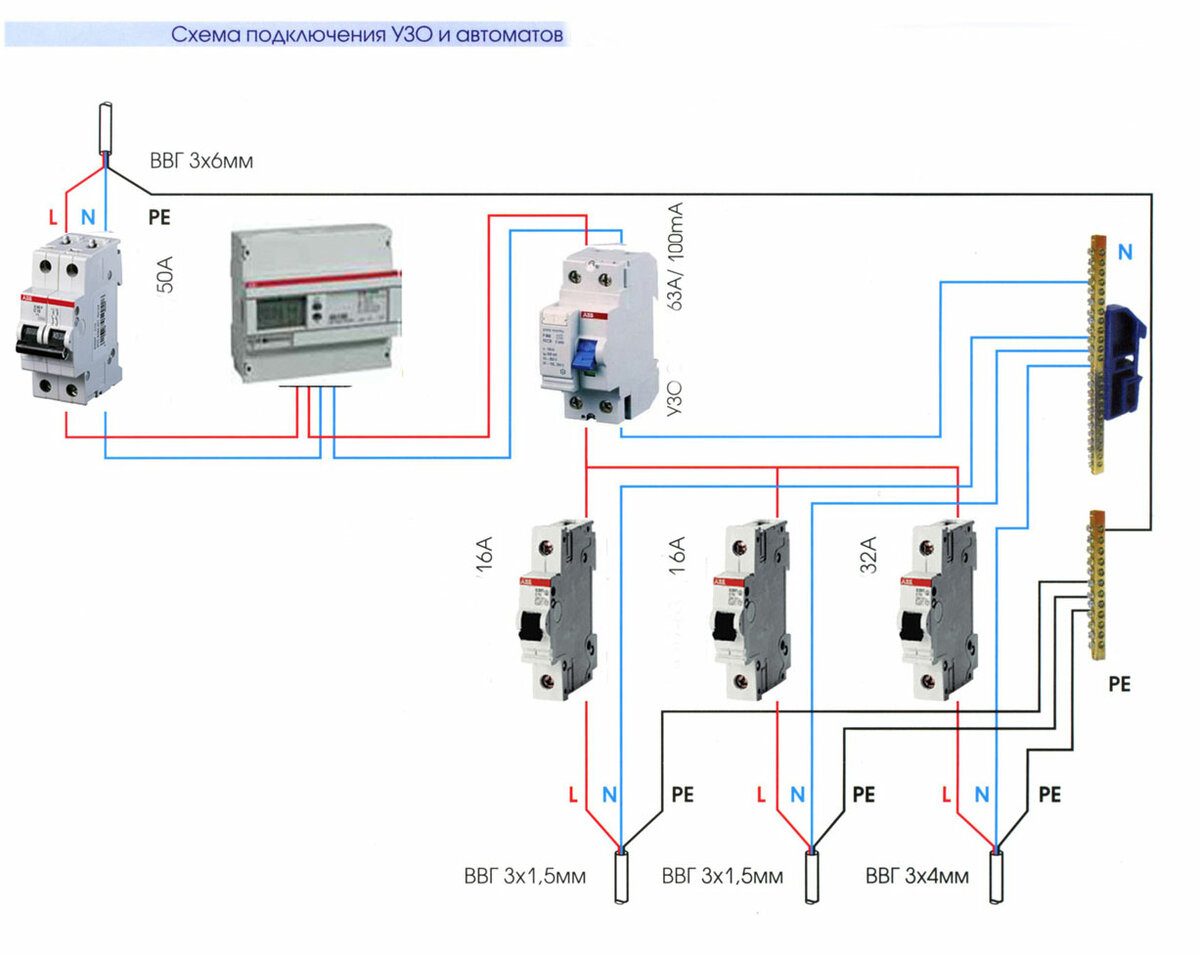
- Option #3 - common RCD for 1-phase network + group RCD.
- Option #4 - 1-phase network + group RCDs.
- Purpose of grounding
- Features of devices for disconnecting the load
- Circuit breakers - improved "plugs"
- Prices for protective automation
- RCD - automatic protection devices
- Features of devices for disconnecting the load
- Circuit breakers - improved "plugs"
- Prices for protective automation
- RCD - automatic protection devices
- How many machines can be connected to one RCD?
- Installation of a differential machine in a network with one and three phases
- Video - Connecting a differential machine to a network with one phase
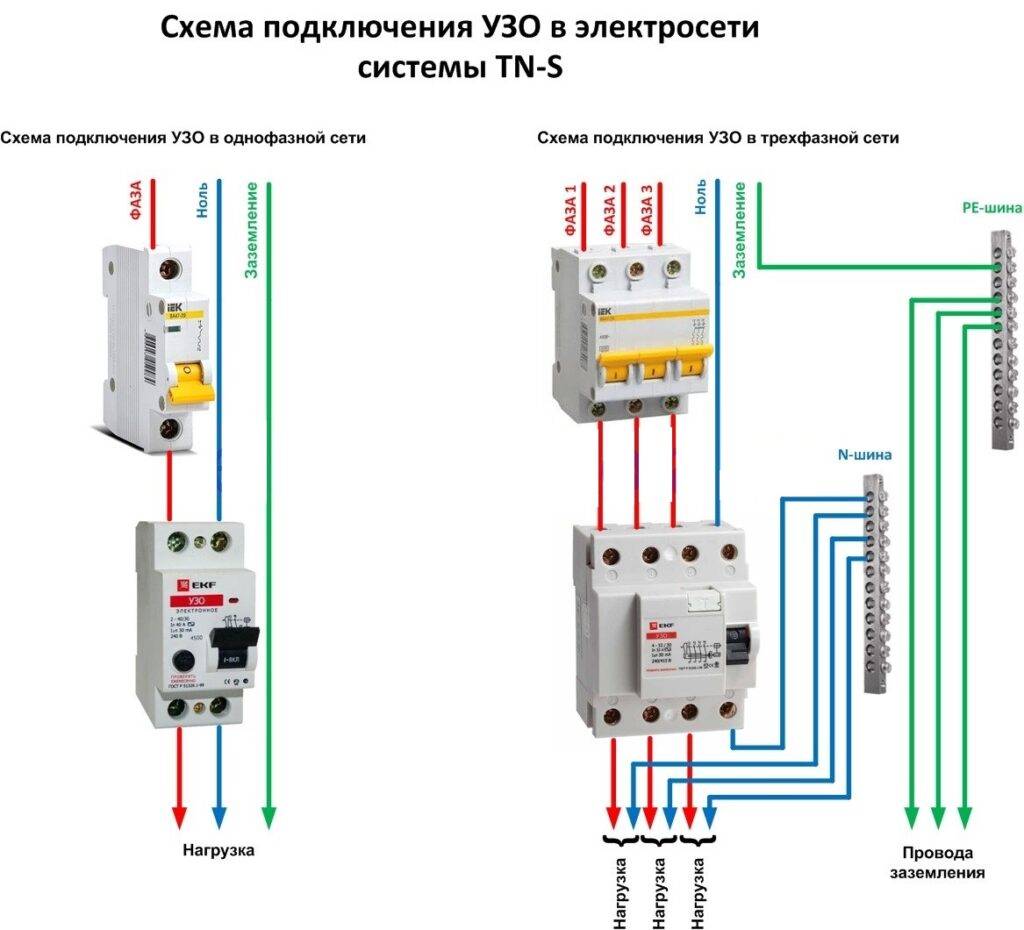
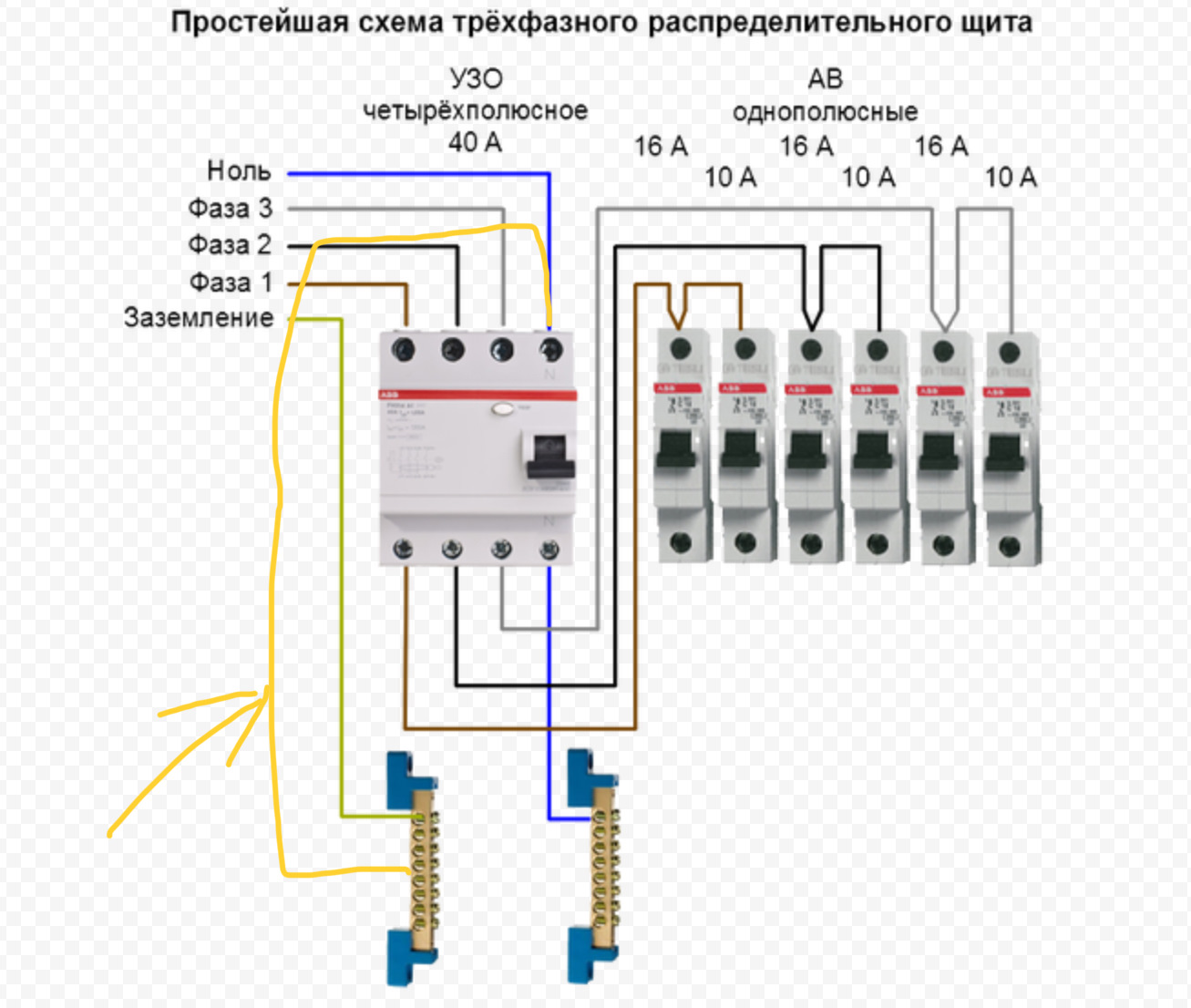
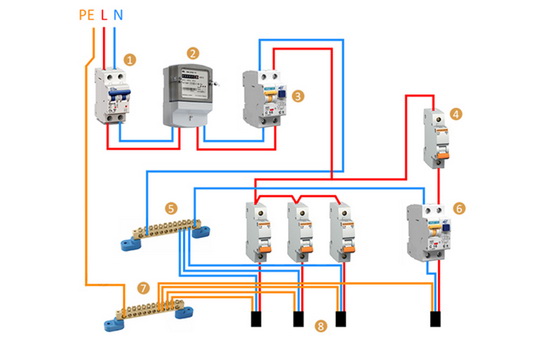
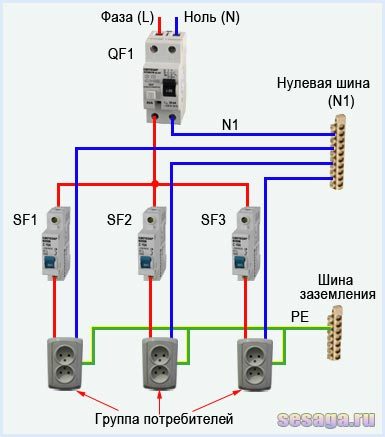
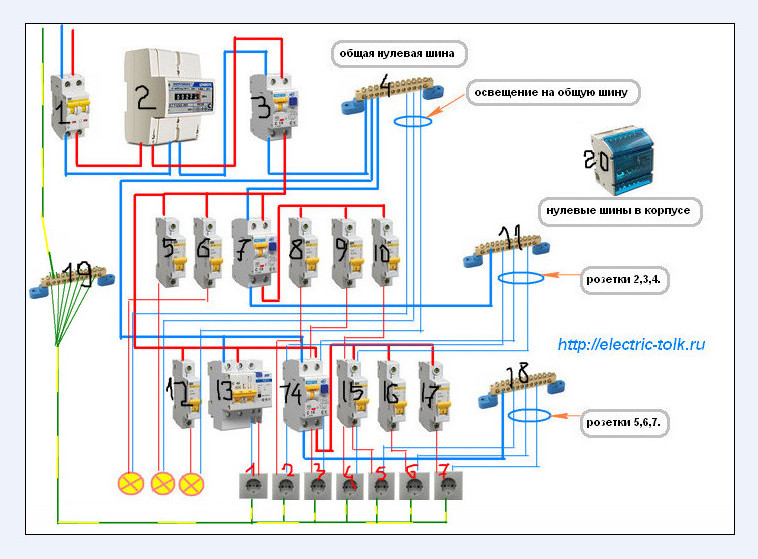
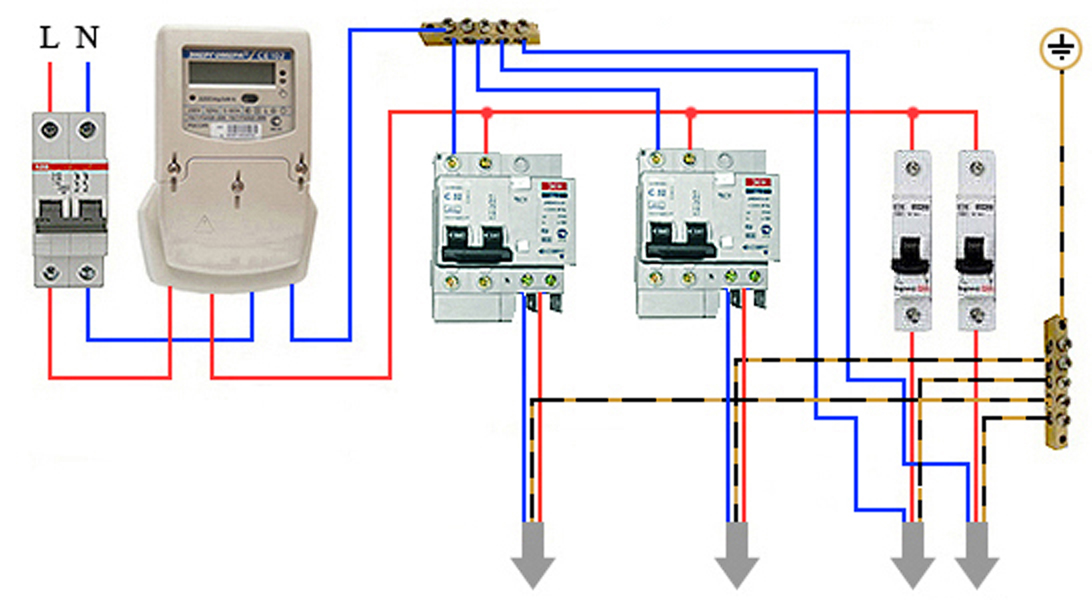
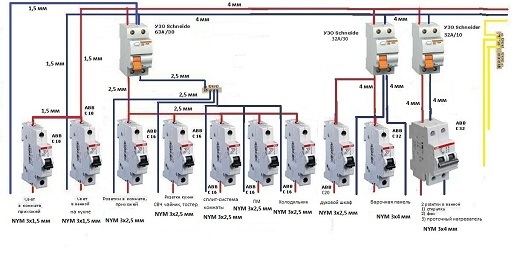
- Connection diagrams
- Introductory machine
- Expert advice
- Varieties of electrical networks
- RCD selection by parameters
- Rated current
- Breaking current
- Type of monitored leakage current and selectivity
What is a security connection device
Electric current is a directed movement of charged particles that does not appear visually, there are no signs of danger even in the presence of grounding.The consequences of the negative impact of the charge on the human body appear instantly, are of varying severity, up to death.
The method of using ouzo is still interpreted in two ways: the installation of switching equipment is not provided for in the protection circuit of the conductor of electricity. The wording changed periodically, but the meaning remained unchanged: it is forbidden to install, but they are switching devices. By opening the electrical circuit with grounding, the ouzo simultaneously prevents damage to the protective device when the power is turned off.
The first application of ouzo is a relay protection circuit for power lines by cutting off electricity in the event of an accident when a leakage current is triggered. Then the connection area expanded to protect the safety of individual electrical equipment objects. According to the working diagram, two contacts are provided for the ouzo, the method of operation of this device does not provide for the mandatory connection of grounding.
Protection options for a single-phase network
Manufacturers of powerful household appliances mention the need to install a set of protective devices. Often, the accompanying documentation for a washing machine, electric stove, dishwasher or boiler indicates which devices need to be additionally installed in the network.
However, more and more often several devices are used - for separate circuits or groups. In this case, the device in conjunction with the machine (s) is mounted in a panel and connected to a certain line
Considering the number of different circuits serving sockets, switches, equipment that loads the network to the maximum, we can say that there are an infinite number of RCD connection schemes. In domestic conditions, you can even install a socket with a built-in RCD.
Next, consider the popular connection options, which are the main ones.
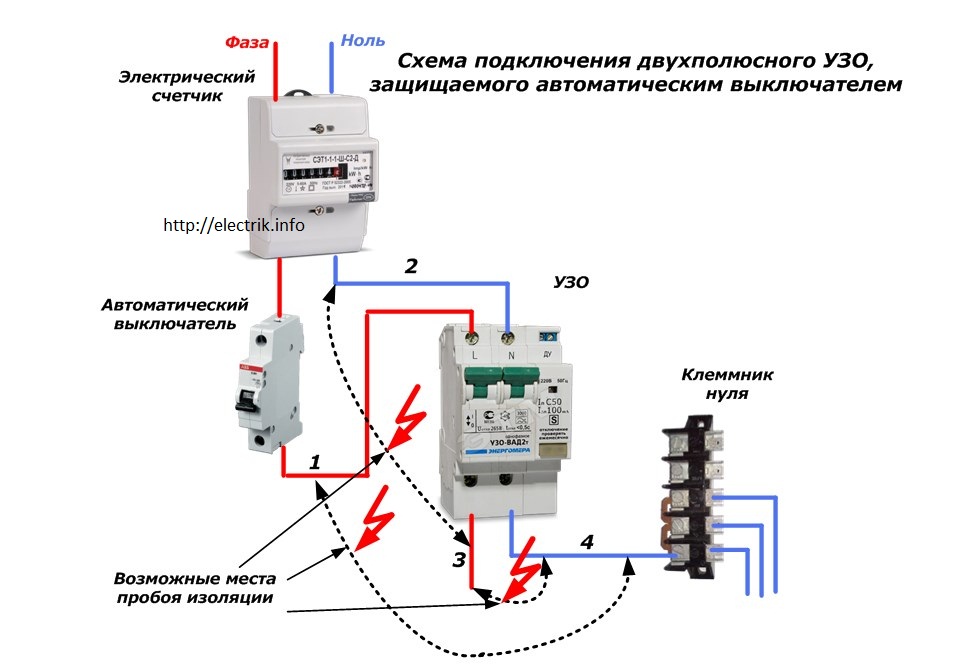
Option #1 - common RCD for 1-phase network.
The place of the RCD is at the entrance of the power line to the apartment (house). It is installed between a common 2-pole machine and a set of machines for servicing various power lines - lighting and socket circuits, separate branches for household appliances, etc.
If a leakage current occurs on any of the outgoing electrical circuits, the protective device will immediately turn off all lines. This, of course, is its minus, since it will not be possible to determine exactly where the malfunction is.
Suppose that a current leakage has occurred due to the contact of a phase wire with a metal device connected to the network. The RCD trips, the voltage in the system disappears, and it will be quite difficult to find the cause of the shutdown.
The positive side concerns savings: one device costs less, and it takes up less space in the electrical panel.
Option #2 - common RCD for 1-phase network + meter.
A distinctive feature of the scheme is the presence of an electricity meter, the installation of which is mandatory.
Current leakage protection is also connected to the machines, but a meter is connected to it on the incoming line.
If it is necessary to cut off the power supply to an apartment or house, they turn off the general machine, and not the RCD, although they are installed side by side and serve the same network
The advantages of this arrangement are the same as those of the previous solution - saving space on the electrical panel and money. The disadvantage is the difficulty of detecting the place of current leakage.
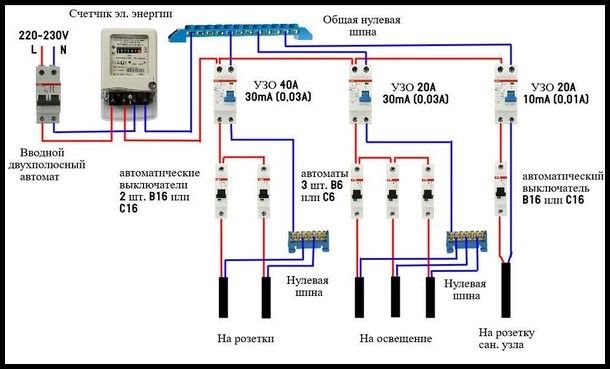
Option #3 - common RCD for 1-phase network + group RCD.
The scheme is one of the more complicated varieties of the previous version.
Thanks to the installation of additional devices for each working circuit, protection against leakage currents becomes double. From a security point of view, this is a great option.
Suppose an emergency current leakage occurred, and the connected RCD of the lighting circuit for some reason did not work. Then the common device reacts and disconnects all lines
So that both devices (private and common) do not immediately work, it is necessary to observe selectivity, that is, when installing, take into account both the response time and the current characteristics of the devices.
The positive side of the scheme is that in an emergency one circuit will turn off. It is extremely rare that the entire network goes down.
This can happen if the RCD installed on a particular line:
- defective;
- out of order;
- does not match the load.
To avoid such situations, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the methods for checking the RCD for performance.
Cons - the workload of the electrical panel with a lot of the same type of devices and additional expenses.
Option #4 - 1-phase network + group RCDs.
Practice has shown that the circuit without installing a common RCD also functions well.
Of course, there is no insurance against the failure of one protection, but this can be easily fixed by purchasing a more expensive device from a manufacturer you can trust.
The scheme resembles a variant with general protection, but without installing an RCD for each individual group. It has an important positive point - it is easier to determine the source of the leak here
From the point of view of economy, the wiring of several devices loses - one common one would cost much less.
If the electrical network in your apartment is not grounded, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the RCD connection diagrams without grounding.
Purpose of grounding
An electrical line using grounding is laid using a three-wire cable. Each cable wire connects the elements of its circuit and is: phase (L), zero (PE) and earth (PN). The value that occurs between the phase wire and zero is called the phase voltage. It is equal to 220 volts or 380 volts, depending on the type of system.
These parts may become live if there is a malfunction in the equipment itself or in the insulation of the wiring. If there is a PN connection, there will actually be a short circuit between the phase conductor and earth. The current, choosing the path with the least resistance, will flow to the ground. This current is called leakage current. During contact with metal parts, the voltage on them will be less, and, accordingly, the value of the damaging current will be less.
Grounding is also necessary for the operation of devices such as RCDs. If the conductive places of the devices are not connected to the ground, then the leakage current will not occur and the RCD will not work. There are several types of grounding, but only two are common for domestic use:
- TN-C. The type in which the neutral and ground conductors are combined with each other, in other words, zeroing. This system was developed in 1913 by the German company AEG. A significant drawback is that when zero is opened, a voltage appears on the device cases that exceeds the phase voltage by 1.7 times.
- TN-S. Type developed by French engineers introduced in 1930. The neutral and earth wires are independent of each other and are separated from each other at the substation.This approach to the organization of the grounding contact made it possible to create differential current (leakage) metering devices that work on the principle of comparing the magnitude of the current in different wires.
As often happens, in high-rise buildings only a two-wire line is used, consisting of a phase and zero. Therefore, to create optimal protection, it is better to additionally perform grounding. For self-execution of the ground line, a triangle is welded from metal corners. Its recommended side length is 1.2 meters. Vertical posts with a length of at least 1.5 meters are welded to the vertices of the triangle.
Thus, a structure is obtained, consisting of a vertical and horizontal ground strip. Further, the structure itself is buried in the ground with columns down to a depth of at least half a meter from the surface to the base of the triangle. A conductive bus is screwed to this base with a bolt or welded, serving as the third wire connecting the instrument cases to the ground.
Features of devices for disconnecting the load
If the electrical system is divided into circuits, then a separate circuit breaker is installed for each line in the chain, and a protection device is mounted at the output. However, there are many connection options. Therefore, first you need to understand the differences between RCDs and other automation.
Circuit breakers - improved "plugs"
Years earlier, when there were no modern network protection devices, with an increase in the load on the common line, “plugs” were triggered - the simplest devices for emergency power outages.
Over time, they were significantly improved, which made it possible to obtain machines that work in the following situations - with a short circuit and excessive load on the line. In a common electrical panel, from one to several circuit breakers can be located. The exact number will differ depending on the number of lines that are available in a particular apartment.
It is worth noting that the more separately running electrical lines, the easier it is to carry out repairs. Indeed, in order to make the installation of one device, it is not necessary to turn off the entire electrical network.
Instead of obsolete "traffic jams" use circuit breakers
Installation of automation is a mandatory stage in the assembly of an electrical panel for home use. After all, the switches instantly respond to network overload when a short circuit occurs. However, they do not protect the system from leakage current.
Prices for protective automation
Protective automation
RCD - automatic protection devices
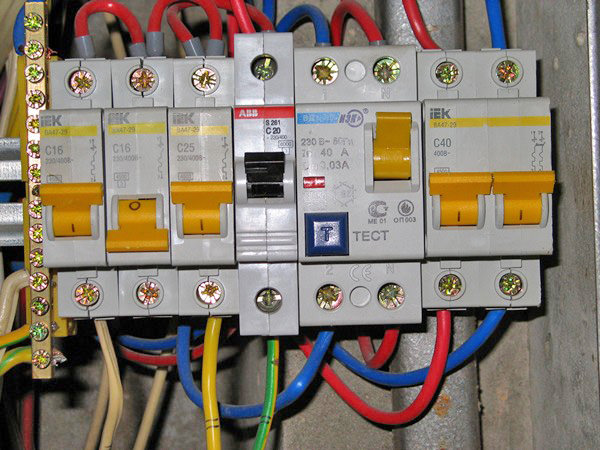
RCD is a device that is responsible for controlling the current strength and preventing its loss. In appearance, the protective device has no fundamental differences from the circuit breaker, but functions differently.
RCD in electrical panel
It is worth noting that this is a multi-phase device that operates at a voltage of 230/400 V and currents up to 32 A. However, the device operates at lower values.
Sometimes devices with the designation 10 mA are used to bring a line into a room with a high level of humidity. There are two main types of RCDs. In order to choose the appropriate option, you need to consider them in more detail.
Table number 1. Types of RCDs.
| View | Description |
|---|---|
| Electromechanical | Here, the main functioning device is a magnetic circuit with windings. His job is to compare the level of current that goes into the network, and then returns. |
| Electronic | This device allows you to compare current values, but only here the board is responsible for this process. However, it only functions when voltage is present. |
It should be noted that the electromechanical device is more popular. After all, if the consumer accidentally touches the phase conductor in the presence of a de-energized board, he will receive an electric shock. While the electromechanical RCD will remain operational.
It turns out that the RCD only protects the system from current leakage, but it is considered useless with increased voltage on the line. It is for this reason that it is mounted only in combination with a circuit breaker. Only two of these devices will provide full protection of the electrical network.
Features of devices for disconnecting the load
If the electrical system is divided into circuits, then a separate circuit breaker is installed for each line in the circuit, and a protective device is installed at the output. However, there are many connection options. Therefore, first you need to understand the differences between RCDs and other automation.
Circuit breakers - improved "plugs"
Years earlier, when there were no modern network protection devices, when the load on the common line increased, the simplest devices for emergency power outages worked.
Over time, they were significantly improved, which made it possible to obtain machines that work in the following situations - with a short circuit and excessive load on the line.A typical electrical panel may contain from one to several circuit breakers. The exact number will vary depending on the number of lines available in a particular apartment.
It is worth noting that the more individual wiring lines, the easier it is to make repairs. Indeed, in order to install one device, it is not necessary to turn off the entire electrical network.
Instead of obsolete "traffic jams" use circuit breakers
Installation of automation is a mandatory stage in the assembly of an electrical panel for home use. After all, the switches instantly respond to network overload in the event of a short circuit. However, they do not protect the system from leakage current.
Prices for protective automation
RCD - automatic protection devices
RCD is a device responsible for controlling the current strength and preventing its loss. In appearance, the protective device does not fundamentally differ from the circuit breaker, but its functionality is different.
RCD in electrical panel
It is worth noting that this is a multi-phase device that operates at a voltage of 230/400 V and currents up to 32 A. However, the device also works at lower values.
Sometimes devices with the designation 10 mA are used to connect the line to a room with a high level of humidity. There are two main types of RCDs. In order to choose the appropriate option, you need to consider them in more detail.
Table - types of RCDs.
| View | Description |
|---|---|
| Electromechanical | Here, the main functioning device is a magnetic circuit with windings.His job is to compare the level of current that goes into the network, and then returns. |
| Electronic | This device allows you to compare current values, but only here the board is responsible for this process. However, it only functions when voltage is present. |
It should be noted that the electromechanical device is more popular. After all, if the consumer accidentally touches the phase conductor in the presence of a de-energized board, he will receive an electric shock. While the electromechanical RCD will remain in working condition.
It turns out that the RCD protects the system only from current leakage, but is considered useless when the voltage in the network rises. It is for this reason that it is only mounted in combination with a circuit breaker. Only two of these devices will provide complete protection for the electrical network.
How many machines can be connected to one RCD?
It is optimal to connect no more than 3 socket groups, respectively, 3 VA, to one device, the reasons are as follows:
- with a larger number, after the protection has tripped, it is difficult to find the place of current leakage;
- if the circuit to be protected contains many wires and contacts, the amount of normal leakage current always present in the wiring can cause false trips of the differential switch.
Normal leaks are calculated using the formula Iу = 0.4 In + 0.01 L, where:
- Iy is the normal current leakage, mA;
- In - rated current in the circuit, A;
- L is the length of the wires in the circuit, m.
For example, in a circuit that consumes a current of 40 A with a wire length of 300 m, normal leakage will be Iy \u003d 0.4 * 40 + 0.01 * 300 \u003d 19 mA. At the same time, according to the rules (SP 31-110-2003, Appendix A 1.2), this value cannot exceed 1/3 of the RCD leakage current setting, otherwise false alarms are possible.
Therefore, it is impossible to install a 30 mA device that protects against electric shock on such a circuit, but only a 100 mA device that provides only fire protection.
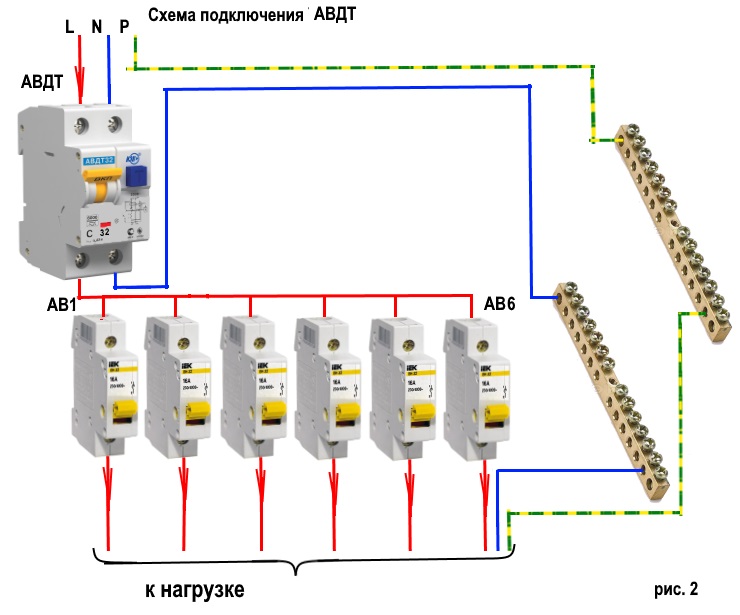
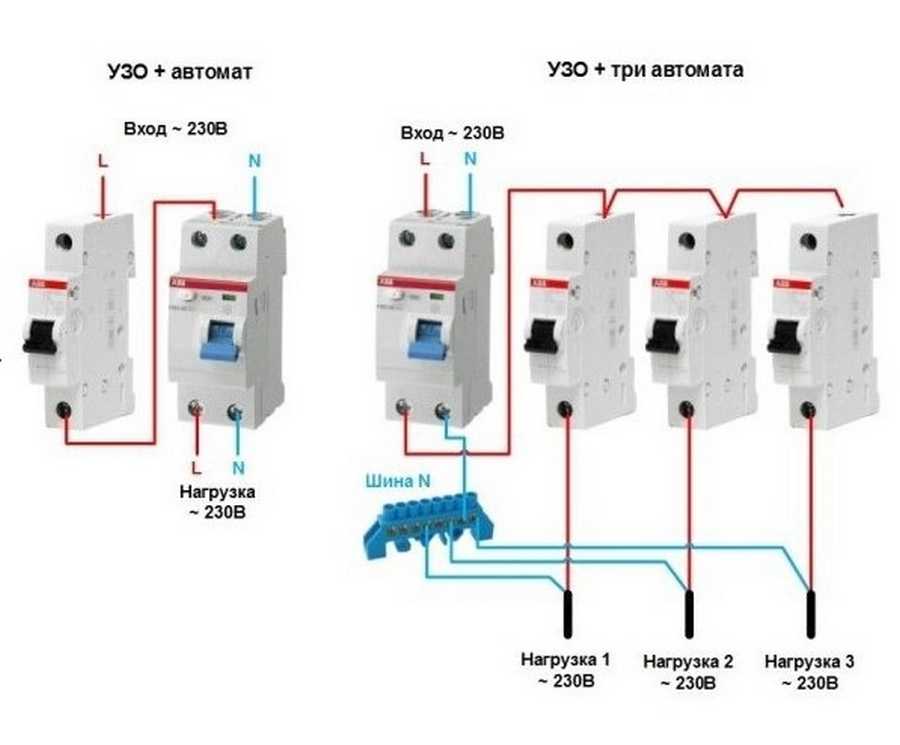
Installation of a differential machine in a network with one and three phases
Before proceeding with the installation of equipment, you need to find the "Test" button on its body and hold it down. This allows you to create an artificial current leakage, to which the device reacts by switching off. This feature checks the functionality of the protective device. If during the test the network was not disconnected, then the installation of this device should be abandoned.
Connection rules
With a standard single-phase electrical network (at a voltage of 220 V), a device with two poles is installed. Installation of a differential machine in a single-phase network requires the correct connection of the neutral conductors: from the load, zero is connected from the bottom of the case, respectively, from the top from the power supply.
Video - Connecting a differential machine to a network with one phase
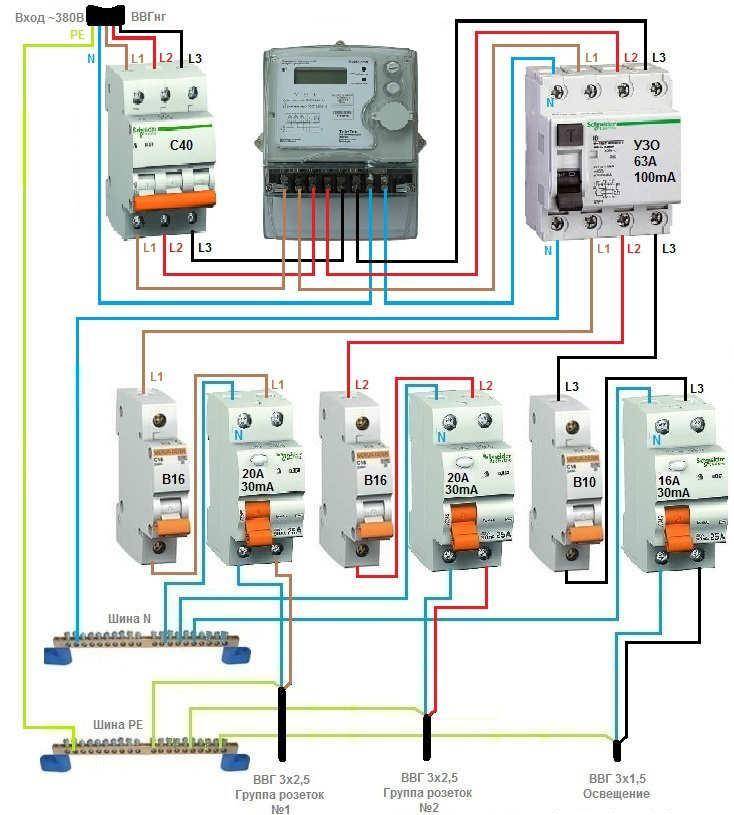
The installation of a difavtomat with four poles is necessary if there is a three-phase electrical network, where the voltage will be 380 V. Otherwise, the connection method has no fundamental differences. The difference is that the three-phase apparatus has an impressive size, which means it requires more space. This is due to the need to install an auxiliary differential protection unit.
There are certain types of protective devices marked 230/400 V. Their peculiarity is that they are intended for networks with both one and three phases.
Connection diagrams
According to the rules, when drawing up an automation connection diagram, it should be borne in mind that the difavtomat must be connected to the neutral and phase wires only on the branch for which it is intended.
Wiring diagram of a differential machineWiring diagram of a differential machine
Introductory machine
The difavtomat with such a connection must be fixed at the input of the wiring. The connection scheme received a characteristic name because it involves the protection of different groups of consumers and branches.
When choosing a device for this scheme, all line criteria must be taken into account, especially the degree of power consumption. This method of connecting the protection device has many advantages:
- saving money on the purchase of equipment, because only one RCD is installed on the whole electrical network;
- no need to purchase an overall shield (the device has a minimum size).
Connection of an introductory machine for several energy consumers
However, such an electrical circuit has some disadvantages:
- in the presence of interruptions in the operation of the protection system, the power supply to the apartment or private house is turned off, and not to individual lines;
- again, in the event of malfunctions, a lot of time and effort will have to be spent in order to find an inoperative branch. In addition, you will have to look for the cause of the failure.
Expert advice
In conclusion, some tips from experts in this field are given that can help with the installation of RCDs:
- For the installation of this equipment in a residential area, it is best to abandon modern electronic models, since their operation depends on the built-in circuit.
- If a wiring diagram is used that does not provide for grounding, it is imperative to add a circuit breaker to it. It will provide protection against voltage overloads and short circuits, while the RCD will monitor the absence of current leakage, thus obtaining a combined protection.
- After the implementation of any circuit or the replacement of one of its elements, it is always necessary to run the protective device to test its performance in order to ensure the correct functioning of the entire system.
- Connecting such a protective device is often a rather difficult task, while this device performs important functions, therefore, if there is the slightest uncertainty in one's own abilities and knowledge, it is recommended to seek help from a professional electrician.
Varieties of electrical networks
The power supply to our apartments and houses comes from a single-phase or three-phase network.
Single-phase electrical power is one phase and zero. To power household appliances and lighting fixtures, you need a phase voltage, which is obtained at the output after a step-down transformer. Such a single-phase power supply assumes power supply from one phase of the line.
An electric current moves along the phase conductor, and it returns to the ground along the zero conductor. Most often, this type of wiring is applicable in an apartment, and it has two varieties:
- Single-phase network of two-wire execution (without earth). This type of electrical network can most often be found in old houses; it does not provide for grounding electrical appliances.The circuit includes only a neutral wire, which is marked with the letter N, and one phase conductor, it is respectively denoted by the letter L.
- Single-phase network of three-wire execution. In addition to the zero and phase, it also has a protective grounding conductor, designated PE. The cases of electrical appliances must be connected to grounding conductors, this will protect the equipment itself from burnout, and the person from the action of electric current.
The house often has equipment that needs three-phase voltage (pumps, motors, if there are machines in a barn or garage). In this case, the network will consist of zero and three phase wires (L1, L2, L3).
Similarly, a three-phase network can be four-wire and five-wire (when there is still protective earth conductor).
We have decided on the types of networks, and now we will directly proceed to the question, is it possible to connect an RCD without grounding and how to install this device correctly?
Is it possible to connect an RCD without grounding - on the video:
RCD selection by parameters
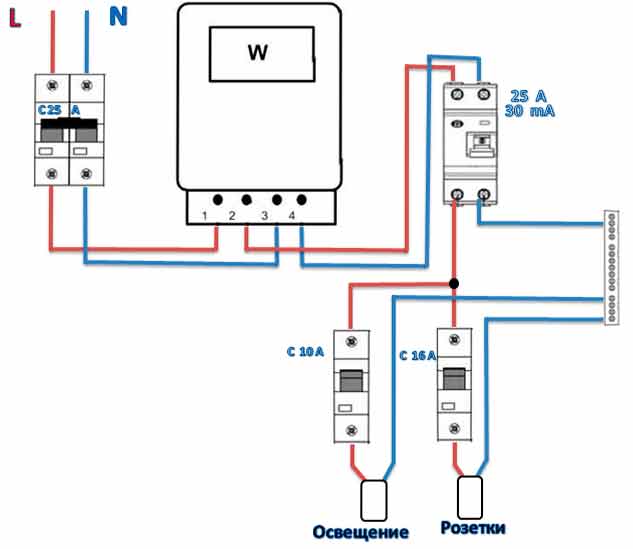
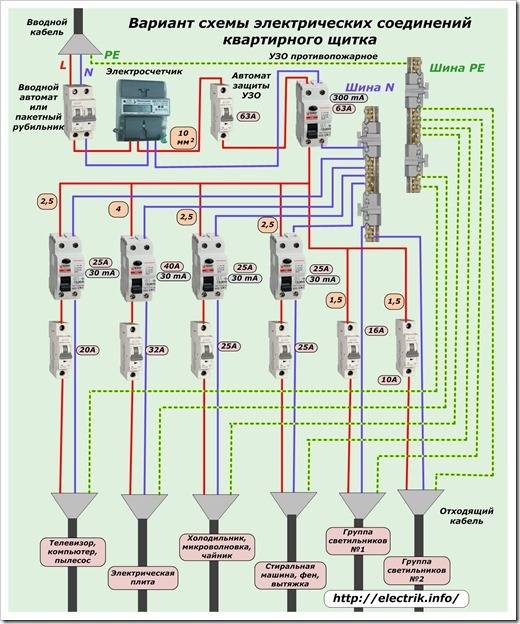
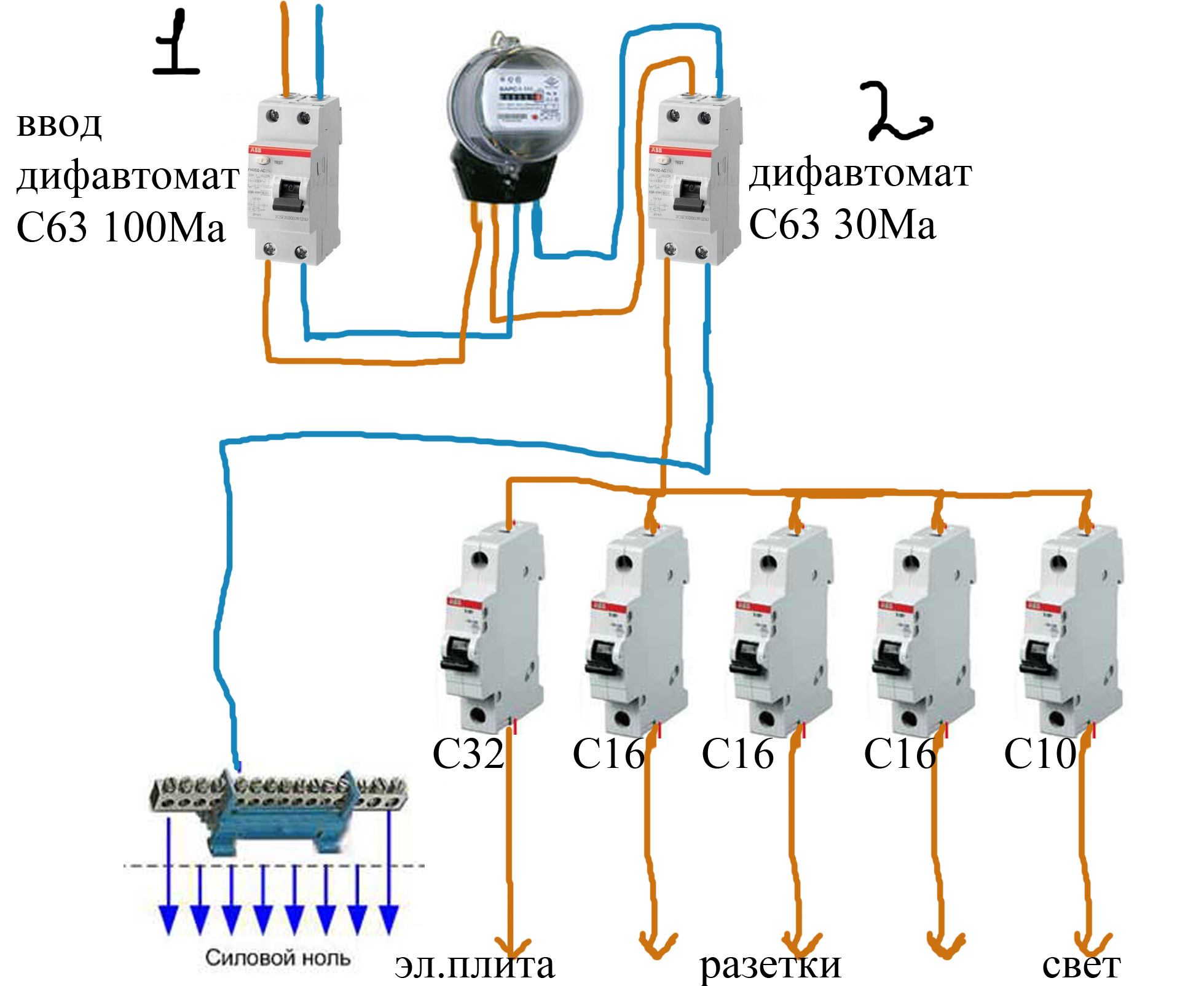
After the RCD connection diagram is ready, it is necessary to determine the parameters of the RCD. As you know, it will not save the network from congestion. And short circuit too. These parameters are monitored by the automaton. To ensure the safety of all wiring, an introductory machine is placed at the entrance. After it there is a counter, and then they usually put a fire protection RCD. It is chosen specifically. The leakage current is 100 mA or 300 mA, and the rating is the same as that of the introductory machine or one step higher. That is, if the input machine is at 50 A, the RCD after the counter is set to either 50 A or 63 A.
Fire protection RCD is selected according to the nominal value of the introductory machine
Why a step up? Because the automatic safety switches are triggered with a delay. The current exceeding the nominal by no more than 25%, they can pass at least an hour. The RCD is not designed for long-term exposure to increased currents, and with a high probability it will burn out. The house will be left without electricity. But this concerns the determination of the value of the fire RCD. Others are chosen differently.
Rated current
How to choose the value of the RCD? It is selected according to the method for determining the nominal value of the machine - depending on the cross-section of the wire on which the device is installed. The rated current of the protective device cannot be greater than the maximum allowable current for a given wire. For ease of selection, there are special tables, one of them is below.
Table for selecting the rating of the circuit breaker and RCD
In the leftmost column we find the cross section of the wire, to the right there is the recommended rating of the circuit breaker. The same should be with the RCD. So it is not difficult to choose the value of the protective device against leakage current.
Breaking current
When determining this parameter, you will also need an RCD connection diagram. The rated breaking current of the RCD is the value of the leakage current at which the power is turned off on the protected line. This setting can be 6mA, 10mA, 30mA, 100mA, 500mA. The smallest current - 6 mA - is used in the USA, in European countries, and we don’t have them on sale either. Devices with a maximum leakage current of 100 mA or more are used as fire protection. They stand in front of the entrance machine.
For all other RCDs, this parameter is selected according to simple rules:
- Protection devices with a rated tripping current of 10 mA are installed on lines that go to rooms with high humidity.In a house and apartment, this is a bathroom; there may also be lighting or sockets in a bathhouse, pool, etc. The same tripping current is set if the line feeds one electrical appliance. For example, a washing machine, electric stove, etc. But if there are sockets in the same line, more leakage current is needed.
- An RCD with a leakage current of 30 mA is placed on group power lines. When more than one device is connected.
This is a simple algorithm based on experience. There is another method that takes into account not only the number of consumers, but also the rated current in the protection zone, or rather, the cross section of the wire, since the rated current of the power line depends on this parameter. This is more correct, as it explains how to choose the amount of leakage current for general RCD, for example, and not just for devices that put on consumers.
Table for selection of rated tripping current for RCD
It is also necessary to take into account the individual leakage currents of each of the devices. The fact is that on every more or less complex device, some small current “leaks”. Responsible manufacturers indicate it in the specifications. Suppose there is only one device on the line, but its own leakage current is more than 10 mA, an RCD with a leakage current of 30 mA is installed.
Type of monitored leakage current and selectivity
Different devices and devices use different forms of current, respectively, the RCD must control leakage currents of a different nature.
- AC - alternating current is monitored (sinusoidal form);
- A - variable + pulsating (pulses);
- B - constant, impulse, smoothed variable, variable;
- Selectivity. S and G - with a shutdown time delay (to exclude accidental trips), the G-type has a shorter shutter speed.
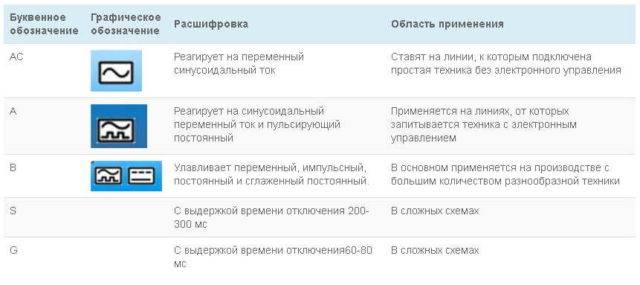
Selecting the type of leakage current to be monitored
RCD is selected depending on the type of protected load. If digital equipment is to be connected to the line, either type A is required. Lighting on the line is AC. Type B, of course, is good, but too expensive. It is usually placed in rooms with increased danger in production, and very rarely in the private sector or in apartments.
RCDs of class G and S are installed in complex circuits if there are RCDs of several levels. This class is chosen for the "highest" level, then when one of the "lower" ones is triggered, the input protective device will not turn off the power.