- Connection in the apartment
- RCD connection without grounding
- Features of wiring for connecting RCD
- Preparing to connect
- Connection diagrams for a three-phase network
- The need for grounding
- 5 frequently asked questions
- Differences between old and new networks
- Why do you need
- Purpose of grounding
- How to choose
- Marking
- Installation of RCD without grounding
- Why is RCD needed?
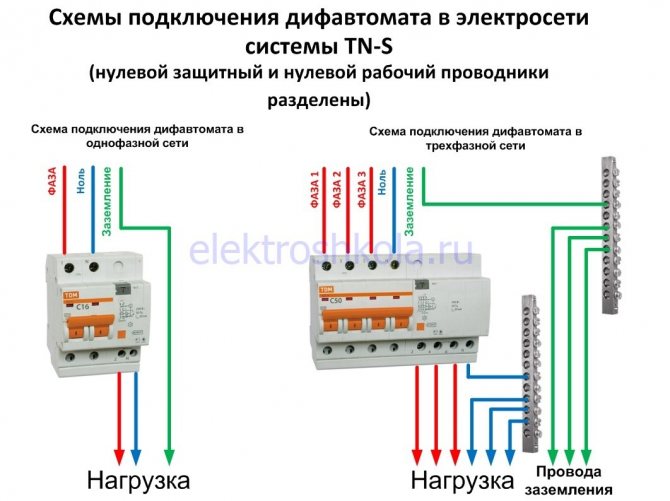
- Connecting an RCD and a difavtomat - a circuit with grounding
- Installing the device in a single-phase network with grounding: possible options
- What is the best way to connect a differential machine?
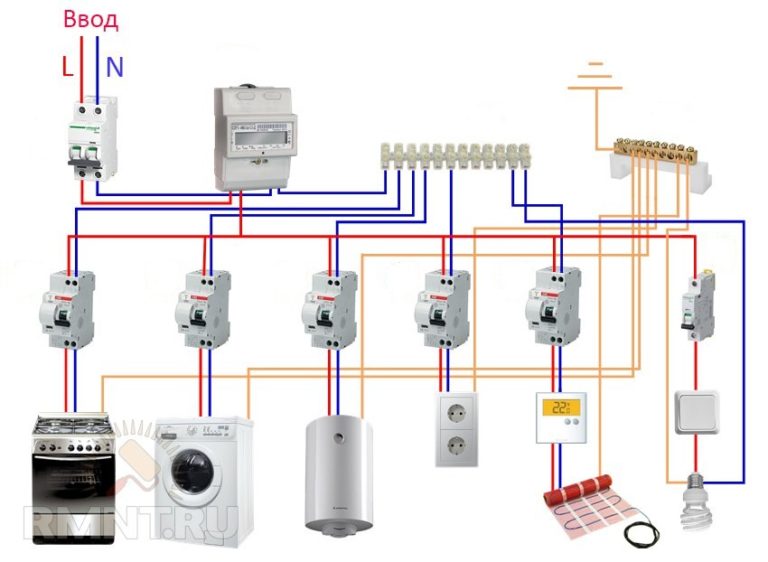
Connection in the apartment
The owner of the apartment does not have the opportunity to choose the dimensions of the switchboard, so he may face a lack of space to install all the necessary protection devices. It will be useful for such persons to know that there are compact devices that simultaneously perform the functions of an RCD and a circuit breaker. They are called differential automata.
Choose a difavtomat with special flags that allow you to understand which part worked: VA or RCD. Without such an indicator, it will be more difficult to recognize the reason for the operation of the device and identify the problem.
In the apartment, as in the house, all sockets should be connected through the RCD, as well as separately powered devices that the user can touch.
Air conditioning, for example, is not one of them.
But devices that work with water - a boiler, a washing machine and a dishwasher - must be connected through an RCD, and with a leakage current setting of 10 mA.
It is important to know that household RCDs are divided into two types:
- Recording only alternating current leakage.
- Recording AC and DC leakage.
Since today many electrical appliances are equipped with switching power supplies, the second type RCD is more suitable.
RCD connection without grounding
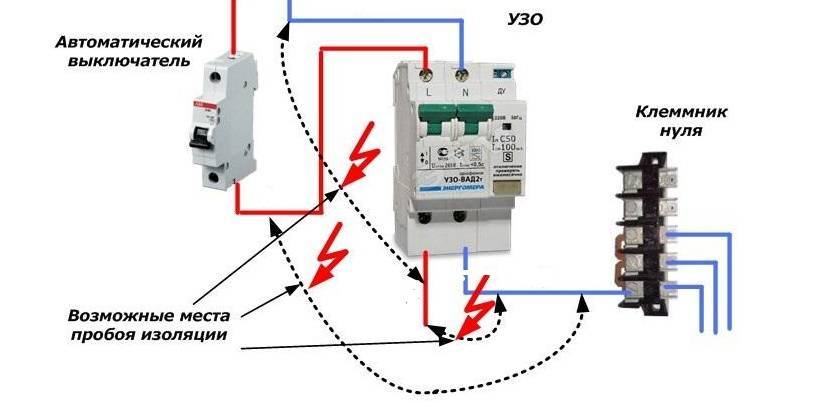
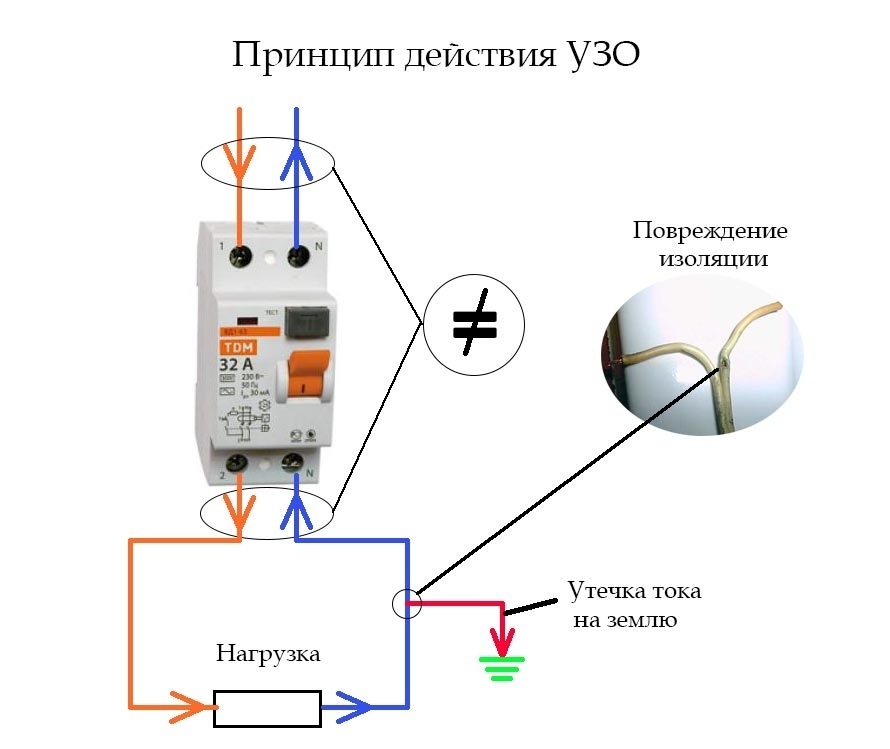
The construction of new houses is provided with protective grounding. When the RCD is connected to a single-phase network with grounding, if the insulation is broken and the mains wire is shorted to the body of the electrical appliance, a leakage current will occur, which will close to the conductive case of the electrical appliance and the RCD protection will work.
Let's imagine that there is no protective earth. The RCD will not work until a leakage current appears, and it will appear if a person accidentally touches the conductive body of the electrical appliance. The leakage current will pass along the path of the mains wire, the body of the electrical appliance and the person standing on the floor, as a result, the RCD protection mechanism will work.
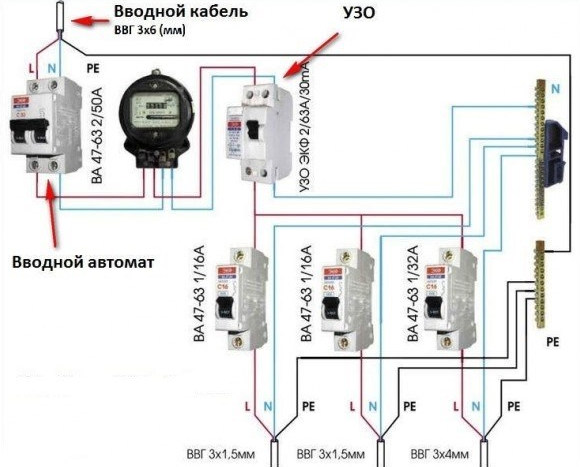
RCD connection diagram with protective earth
What happens? In the presence of grounding of the electrical appliance case, in an emergency, the RCD will operate without a person touching the appliance case, since a leakage current occurs through the grounding conductor. In the absence of protective grounding, the RCD leakage current will appear only when a person touches the energized housing.In the second option, a person becomes a "guinea pig".
However, the response time of the RCD protection is milliseconds, and a person will not feel the effect of an electric current. Even with the full presence of the phase on the housing of the household device, at best, you will feel a slight tingling. Which RCD connection scheme to choose is up to you.
However, I advise you to choose an RCD installation with earthing, and safer protection. It is not difficult to make a protective ground loop in the house, and in an apartment, protective ground can be taken from the electrical panel in the entrance and the ground wire can be routed along the plinth to the sockets of powerful current consumers - this is a washing machine, boiler, electric stove, sockets in the bathroom.
Features of wiring for connecting RCD
When an RCD is connected in a single-phase network without grounding, the wiring is done with a three-wire cable, but the third conductor is not connected to the zero terminals of the sockets and instrument cases until the system is upgraded to TN-C-S or TN-S. With the PE wire connected, all conductive cases of the devices will be energized if the phase falls on one of them, and there is no grounding. In addition, the capacitive and static currents of electrical appliances are summed up, creating a danger of human injury.
Having no experience in wiring and electrical equipment, the easiest way is to purchase an adapter with an RCD for 30 mA and use it when connecting to electrical outlets. This connection method significantly increases electrical safety.
For electrical appliances and sockets in the bathroom and other rooms with high humidity, it is necessary to install an RCD of 10 mA.
Preparing to connect
Properly performed preparatory and installation work will ensure the stable operation of the RCD.
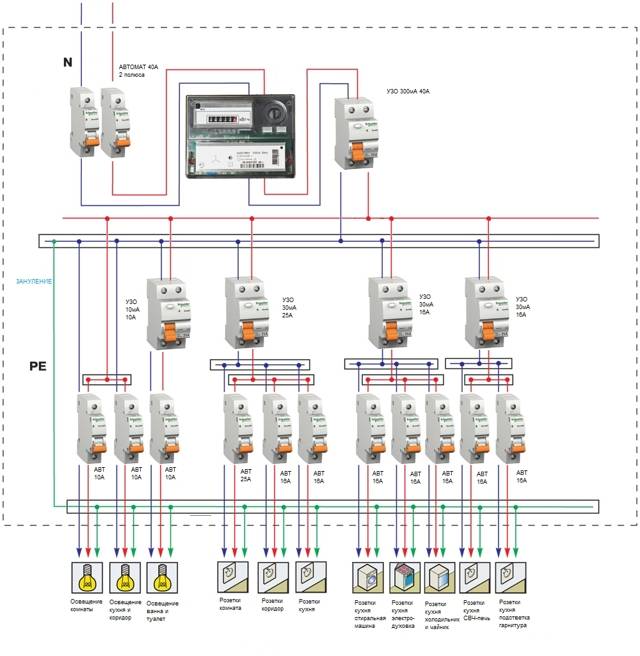
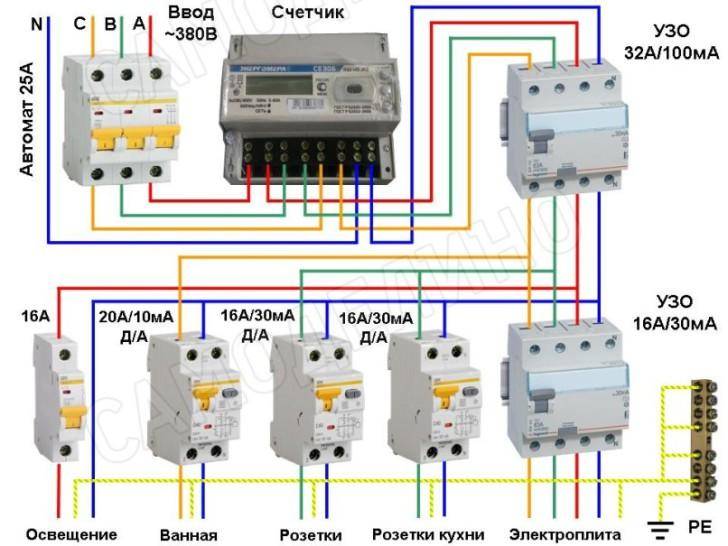
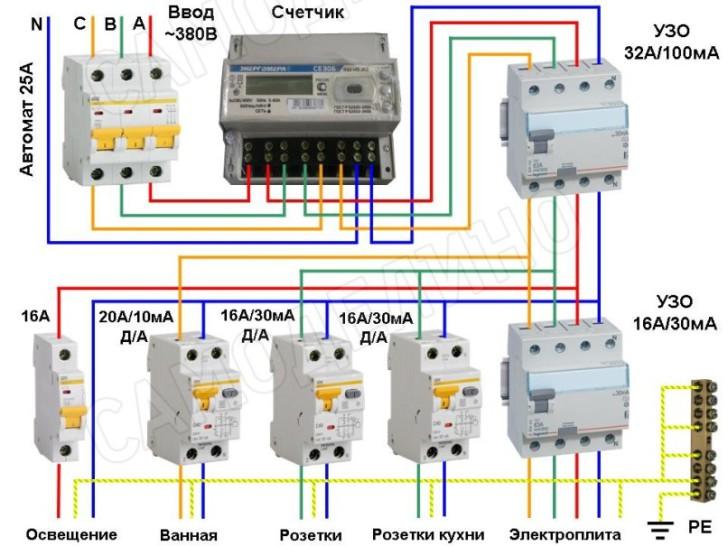
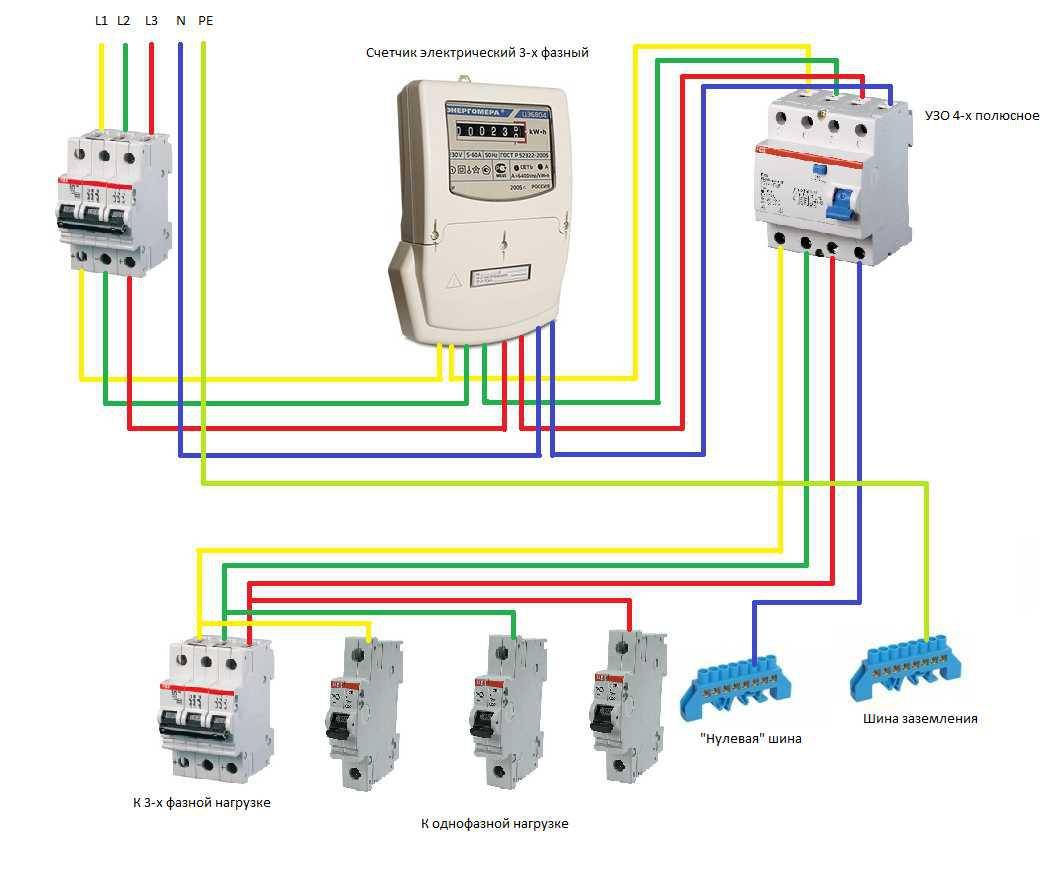
Connection diagrams for a three-phase network
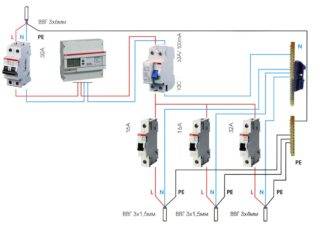
When installing an RCD, the following operating schemes are used:
- Complete electrical shutdown. One unit has the ability to de-energize all consumers of electricity in the event of an emergency.
- Partial shutdown of devices. When emergencies occur, only some consumers are de-energized.
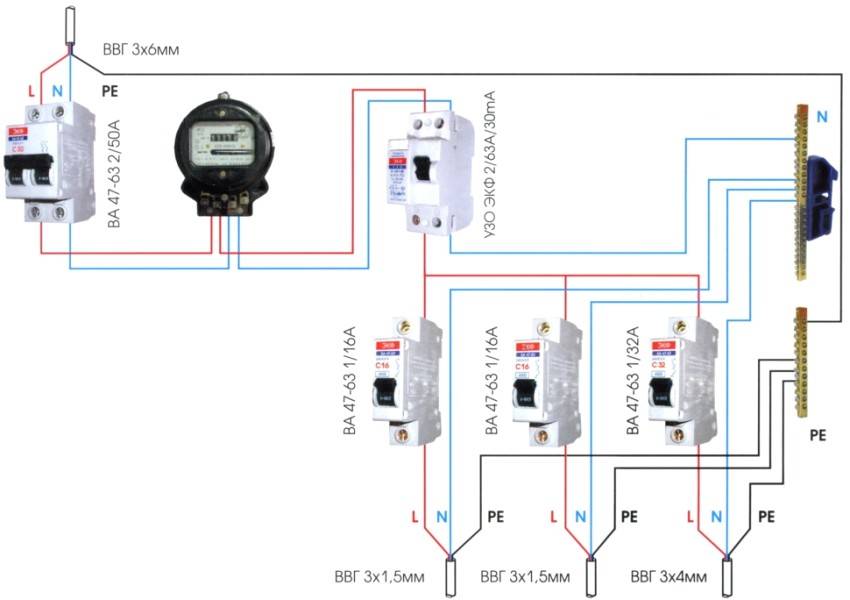
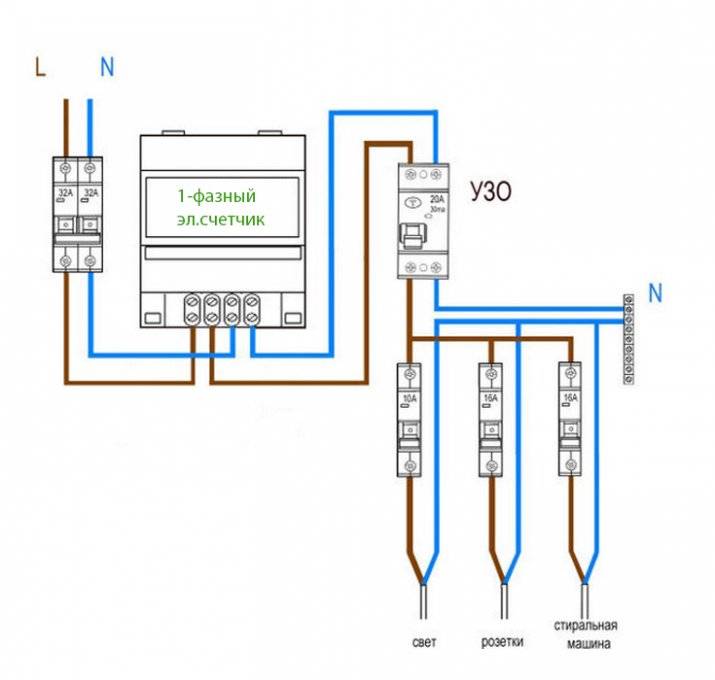
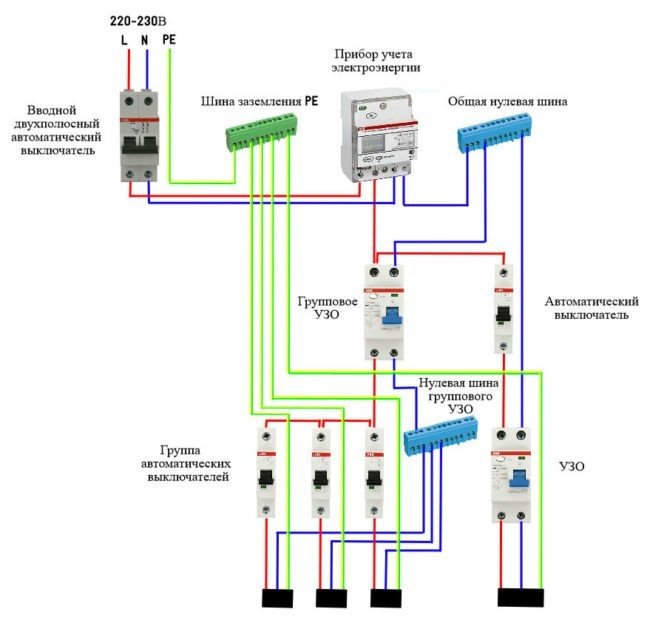
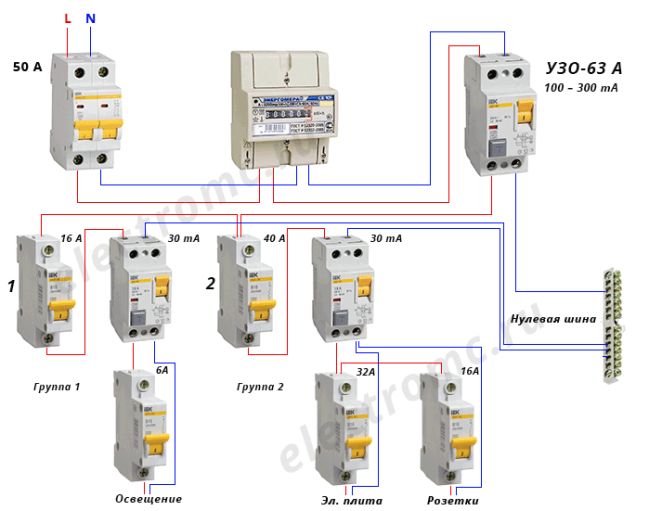
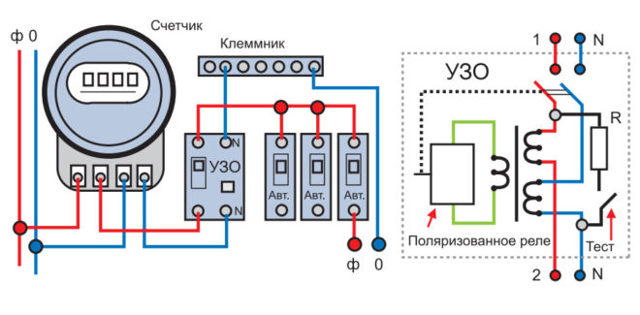
The first connection scheme is used in apartment buildings. Installation of the device is carried out near the electricity meter. If the RCD works, the whole house is de-energized.
When using the second scheme, the protective mechanism is installed on a piece of electrical wiring going to a particular room. Since all devices are connected in series to the circuit, when the RCD is triggered, only the “problem” consumer will turn off, while others will continue to function.
The second version of the scheme can be implemented in a different way. The point of installation of the RCD is the beginning of the serial connection to the wiring, which allows for the selective operation of the unit for certain groups of consumers. Also, a protective mechanism can be installed directly in front of the exit device.
The need for grounding

Old electrical networks belong to the tn-c system, where there is no neutral conductor to turn on the ground. In this case, protection must be provided separately for the house or equipment, which ensures the safe discharge of currents. In the absence of grounding, it is forbidden to install a 4-pole RCD.
The correct scheme for connecting to the electrical network provides for compliance with the following rules:
- The ground conductor is connected only to the output cable.Connection directly to the RCD is unacceptable.
- In the presence of a single-phase network, a four-pole device cannot be used.
- Connection to the B3 type network is prohibited.
5 frequently asked questions
The main question that arises when studying the topic is whether the operation of the RCD is possible in a two-phase network? Answer: yes, you can operate the device without grounding. The details are discussed above. Modernization of the power grid in large volumes is not required.
The second question is, what is protection for? The residual current device ensures the safety of the consumer by disconnecting a section of the electrical network. It is necessary, moreover, protection must be installed in a dangerous area.
Do you connect the RCD with your own hands or do you need the help of a professional electrician? Yes, you can install electrical equipment with your own hands. But, if you are not confident in your abilities in the calculation of characteristics or installation, it is worth inviting electricians.
Are electrical wiring errors dangerous? Yes, at best they will lead to false network outages, at worst, to a malfunction of electricity consumers or to injury to the user.
How to choose an RCD? To do this, you need to understand the principle of its operation, and the parameters of your electrical network. Based on these parameters, the type of product and its connection scheme are selected.
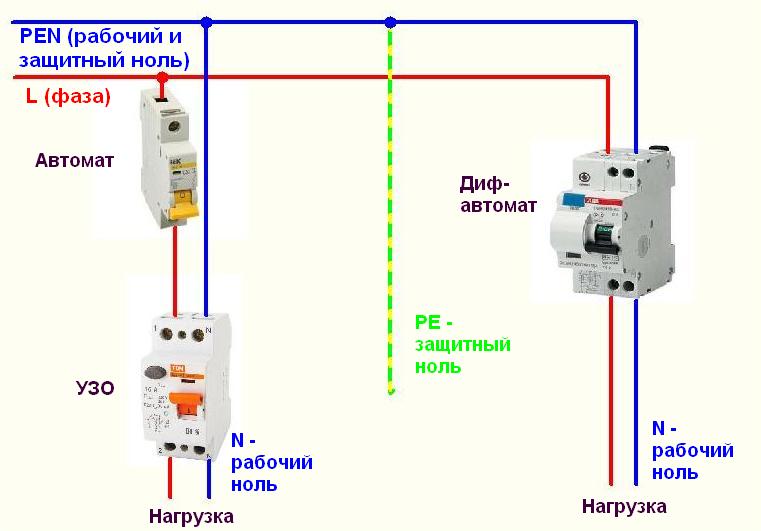
Differences between old and new networks
In modern homes, there is a separate PE protective conductor in the electrical wiring. Thus, in a single-phase network there are three wires: phase, zero and ground (PE). In old houses, all lines consist of two wires, since a single PEN - a conductor, performs the functions of two wires at once - zero and protection (PE + N).This system with a combined conductor was named TN-C. In this case, there is no separate ground conductor.
How will the residual current device work in such wiring? The scheme of operation of the RCD will be different, since the instrument cases are not grounded. If the insulation is damaged and there is a breakdown on the case, the current has no path for further escape to the ground. At the same time, the body of the device will have a potential that is dangerous to human health and life.
If a person touches the body, a circuit is formed, through which the current from the device through the body will flow into the ground. When the leakage current reaches the operating threshold in accordance with the RCD setting, the device circuit will be disconnected from the mains supply. A person will be under the influence of electricity, depending on the time of operation of the RCD. Despite the fact that the protection works quickly enough, during the action of the current it is quite possible to get a serious injury.
As a result, a certain period of time is formed, during which the body of the device will have a potential that is dangerous to humans. This period begins with insulation damage and ends with protection operation and disconnection from the network. In the presence of grounding on the body of the device, a protective shutdown would occur immediately after the breakdown of the insulation.
Why do you need
Installation of such devices is necessary for several reasons. Mainly, it was designed for protection. From what? Firstly, the RCD protects people from electric shock, especially in cases where there are malfunctions in the electrical installation.Secondly, the device trips and turns off the current due to accidental or erroneous contact with the current-carrying parts of the electrical installation, in case a current leak occurs. And, thirdly, ignition of the electrical wiring is prevented in the event of a short circuit. As can be seen from the above, this machine actually performs the most important function.

RCD Today you can find differential automata, the peculiarity of which is to combine a circuit breaker and an RCD. Their advantage is that they take up less space in the shield. In all cases, when connecting, all contact connections should be brought to it not from below, but only from above. One of the reasons is a more aesthetic appearance. But there is a much more significant reason. The fact is that the RCD is able to reduce the efficiency of the work of all household items. Moreover, during repair work, the electrician will not get confused, and he will not have to study complex, intricate circuits. So, now it's time to consider connectivity options.
Purpose of grounding
An electrical line using grounding is laid using a three-wire cable. Each cable wire connects the elements of its circuit and is: phase (L), zero (PE) and earth (PN). The value that occurs between the phase wire and zero is called the phase voltage. It is equal to 220 volts or 380 volts, depending on the type of system.
These parts may become live if there is a malfunction in the equipment itself or in the insulation of the wiring. If there is a PN connection, there will actually be a short circuit between the phase conductor and earth. The current, choosing the path with the least resistance, will flow to the ground.This current is called leakage current. During contact with metal parts, the voltage on them will be less, and, accordingly, the value of the damaging current will be less.
Grounding is also necessary for the operation of devices such as RCDs. If the conductive places of the devices are not connected to the ground, then the leakage current will not occur and the RCD will not work. There are several types of grounding, but only two are common for domestic use:
- TN-C. The type in which the neutral and ground conductors are combined with each other, in other words, zeroing. This system was developed in 1913 by the German company AEG. A significant drawback is that when zero is opened, a voltage appears on the device cases that exceeds the phase voltage by 1.7 times.
- TN-S. Type developed by French engineers introduced in 1930. The neutral and earth wires are independent of each other and are separated from each other at the substation. This approach to the organization of the grounding contact made it possible to create differential current (leakage) metering devices that work on the principle of comparing the magnitude of the current in different wires.
As often happens, in high-rise buildings only a two-wire line is used, consisting of a phase and zero. Therefore, to create optimal protection, it is better to additionally perform grounding. For self-execution of the ground line, a triangle is welded from metal corners. Its recommended side length is 1.2 meters. Vertical posts with a length of at least 1.5 meters are welded to the vertices of the triangle.
Thus, a structure is obtained, consisting of a vertical and horizontal ground strip.Further, the structure itself is buried in the ground with columns down to a depth of at least half a meter from the surface to the base of the triangle. A conductive bus is screwed to this base with a bolt or welded, serving as the third wire connecting the instrument cases to the ground.
How to choose
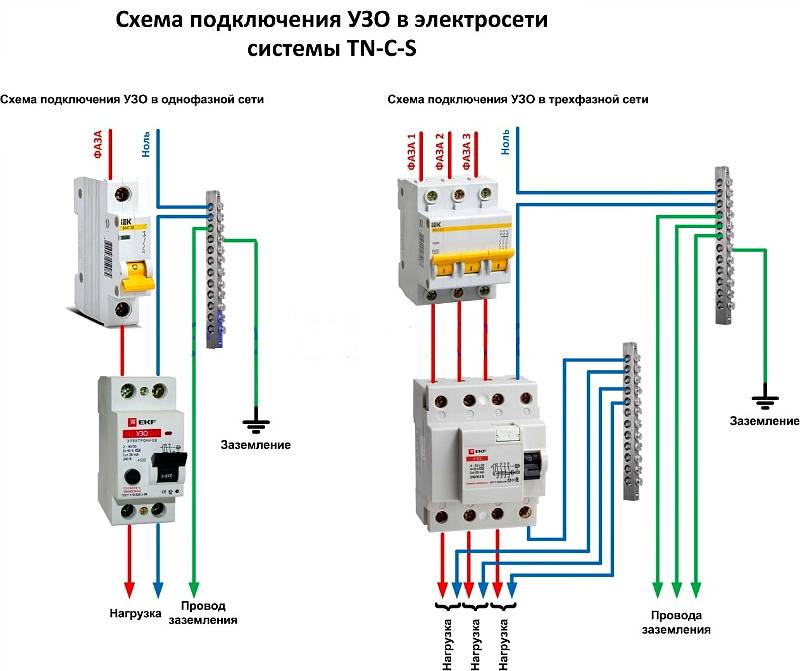
The first parameter by which the RCD is selected is the type of wiring in the room where the device will be installed. For rooms with two-phase electrical wiring with a voltage of 220 V, an RCD with two poles is suitable. In the case of a three-phase wiring (apartments of a modern layout, semi-industrial and industrial premises), a four-pole device should be installed.
To mount the correct protective device circuitry, you will need several protective devices of different ratings. The difference will be in the place of their installation and the type of protected section of the circuit.
The selection of RCDs must be made taking into account certain electrical parameters in the home electrical network, namely:
- The cut-off current of the RCD must be greater than the highest current consumed in the room (apartment) by 25%. The value of the maximum current can be found in the communal structures serving the premises (housing office, energy service).
- The rated current of the RCD, it should be chosen with a margin in relation to the rated current of the circuit breaker that protects the circuit section. For example, if the circuit breaker is designed for a current of 10 A, then the RCD should be selected with a current of 16A. It should be borne in mind that the RCD only protects against leakage, and not against overload and short circuit. Based on this, a mandatory requirement is the installation of a circuit breaker in a circuit section together with an RCD.
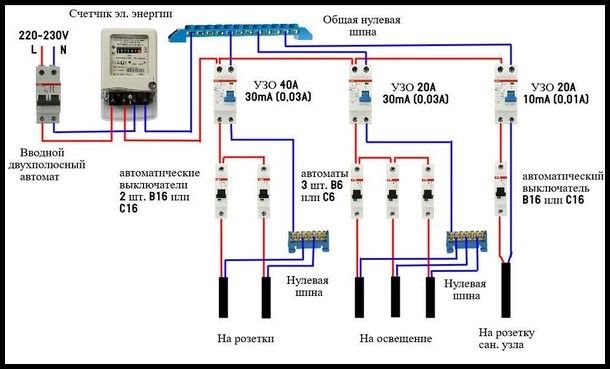
- RCD differential current.The value of the leakage current, at the moment of which the device will perform an emergency power off of the network. In domestic premises, to ensure the protection of several consumers (a group of sockets, a group of lamps), an RCD with a differential current setting of 30 mA is selected. Choosing a device with a lower setting is fraught with frequent false RCD trips (there are always current leaks in the network of any room, even during minimal load). For groups or single consumers in high humidity conditions (shower, dishwasher, washing machine), an RCD with a differential current value of 10 mA should be installed. Working conditions in a wet room are considered especially dangerous from the point of view of electrical safety. It is not necessary to install a single RCD for many consumer groups. For small rooms, it is permissible to install one RCD with a setting current of 30 mA on the incoming electrical panel. But with such an installation, during an emergency operation, the RCD will turn off the electricity in the entire apartment. It will be correct to install an RCD for each consumer group and an input device with the highest setting current. (More details on the arrangement of protective devices are discussed below).
- And also the RCD is selected according to the type of differential current. For AC networks, devices with marking (AC) are produced.
Marking
The marking is applied to the front panel of the device, we will tell you what it means using the example of a two-pole device.
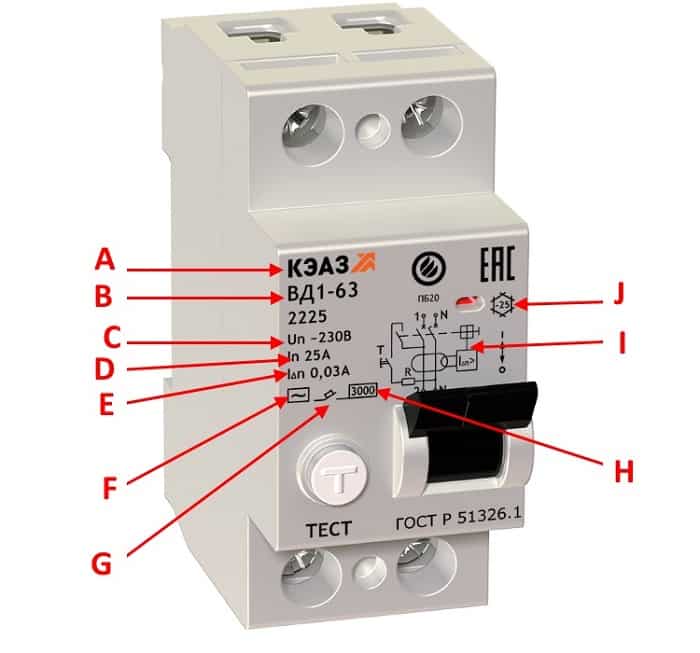
RCD marking
Designations:
- A - Abbreviation or logo of the manufacturer.
- B is the designation of the series.
- C - The value of the rated voltage.
- D - Rated current parameter.
- E - The value of the breaking current.
- F - Graphic designation of the type of breaking current, can be duplicated by letters (in our case, a sinusoid is shown, which indicates the type of AC).
- G - Graphic designation of the device on circuit diagrams.
- H - The value of the conditional short circuit current.
- I - Device diagram.
- J - The minimum value of the operating temperature (in our case: - 25 ° C).
We have given a typical marking, which is used in most devices of this class.
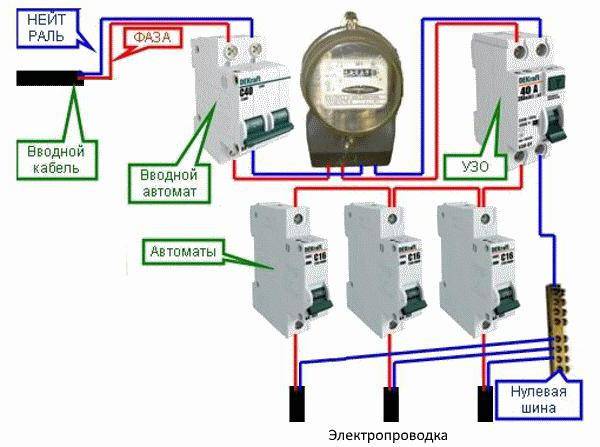
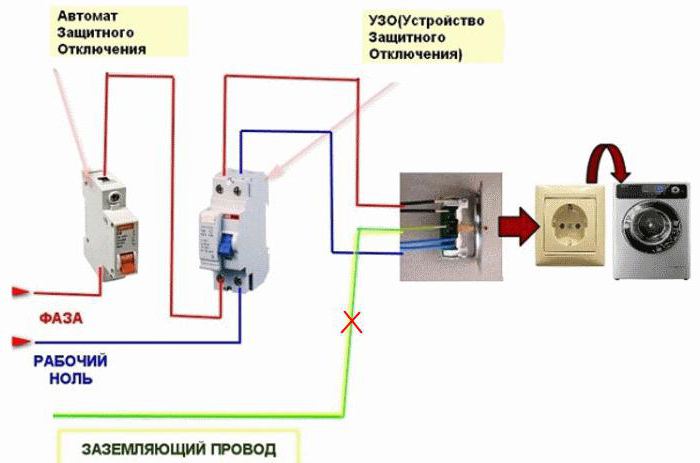
Installation of RCD without grounding
Before starting to deal with the topic of connecting an RCD without grounding, I would like to dwell on one very important point. The residual current device only absorbs leakage currents, but in no way restrains high loads in the network and high currents that arise due to short circuits
The circuit breaker should be responsible for this, therefore both devices: the automatic machine and the RCD are installed in the networks at the same time. But it should be noted that the connection diagram of two protective devices can have two options:
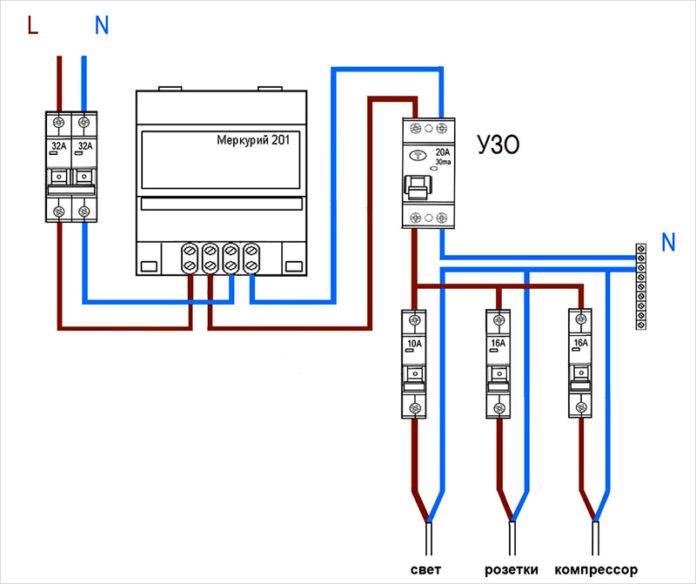
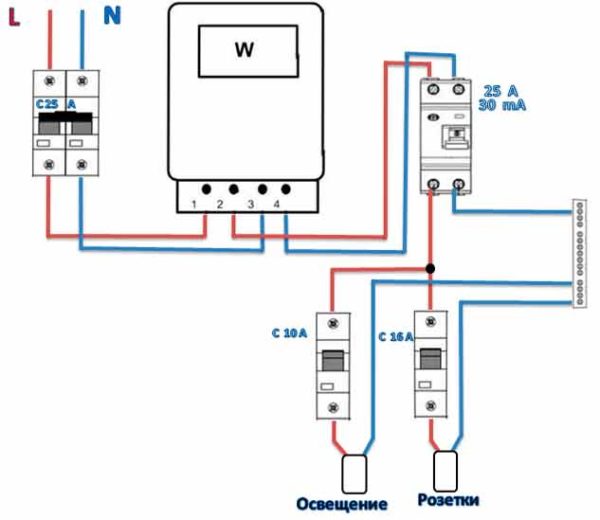
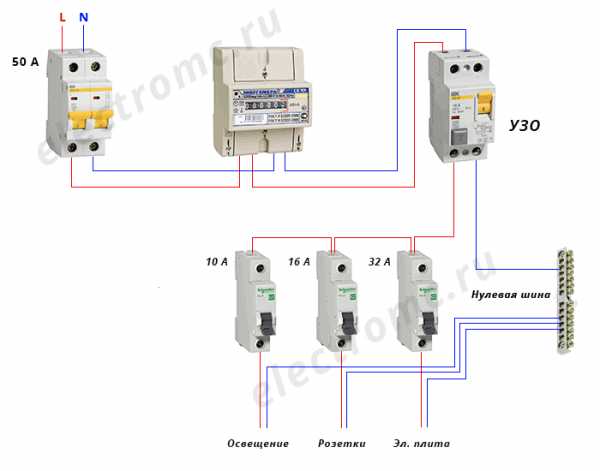
- When the device is installed on the whole apartment or on the whole house in a single copy. The installation location of the introductory switchboard after the electricity meter and control. By the way, the connection diagram of an RCD without grounding of this type is in the figure below.
- When one low-power trip protection device is installed for each electrical distribution loop (group of consumers). How many groups, so many devices in the shield. True, to assemble such a circuit, a more capacious switchboard is required.
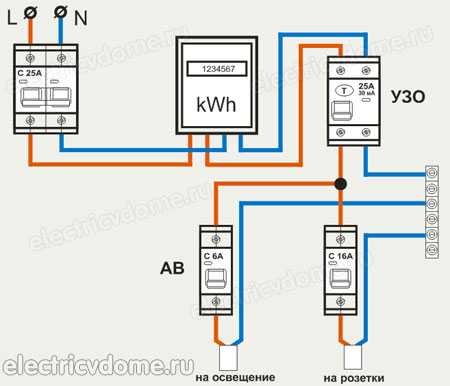
What are the pros and cons of each scheme:
- The first option has one even very big minus.For example, if in a house in some household appliance there was a violation of the insulation, which led to the appearance of a leakage current, then the RCD will immediately work. The device will simply de-energize the entire house, and it will not be clear in which section (loop) the violation occurred. Finding this place will be difficult.
- In this regard, the second option is more effective. The RCD worked on one of the groups, which means that the problems must be looked for precisely in this area, in addition, the remaining groups will work, as they say, in the operating mode. But the cost indicator can be much higher than in the first scheme, of course, everything will depend on the number of consumer groups. It is clear that even three low-power devices will cost more than one low-power one.
By the way, about the power of the device. The advice is this - its power should be slightly more than the power of the machine or group of machines, which is installed after the protective device itself. Why exactly? The thing is that the circuit breaker does not work immediately during overloads or short circuits. Some can withstand a few seconds of rising current. At the same time, the RCD itself cannot withstand such loads for a long time if their nominal parameter is equal to the nominal value of the machine. It will simply fail.
It should be noted that today the grounding scheme is not present in all apartments and houses. The old housing stock still lives according to the old laws, where ground loops have not yet been installed. And the requirements of the PUE are becoming tougher and tougher. For example, regardless of whether the issue of installing an RCD in an apartment is being resolved, this device must be installed in consumer groups that are located in wet rooms.
And one more thing, which became the reason that automata and RCDs become unnecessary when assembling switchboards. They were replaced by difavtomatami. What is a difautomatic? This is a kind of symbiosis of an RCD and a traditional circuit breaker, so to speak, two in one. This device performs the same functions, that is, it protects the network from overloads, short circuits and current leaks. Convenient, economical and efficient. And yet we are interested in how the RCD works and is installed in a single-phase network.
Why is RCD needed?
For understanding operating principle of RCD and the features of its installation, a number of key points should be considered.
First of all, you need to understand that the use of a large number of electrical appliances in everyday life increases the risk of a person falling under the influence of electricity. Therefore, the formation of protective nodes that protect against this dangerous factor is a necessity in modern residential premises. The Residual Current Device itself is an element of the protection system, and functionally has several purposes:
- In the event of a short circuit in the wiring, the RCD protects the room from fire.
- At the moment the human body gets under the influence of electric current, the RCD turns off the power to the entire network or a specific electrical appliance to perform protection (local or general shutdown depends on the position of the RCD in the power system).
- And also the RCD turns off the supply circuit when the current in this circuit rises by a certain amount, which is also a protection function.
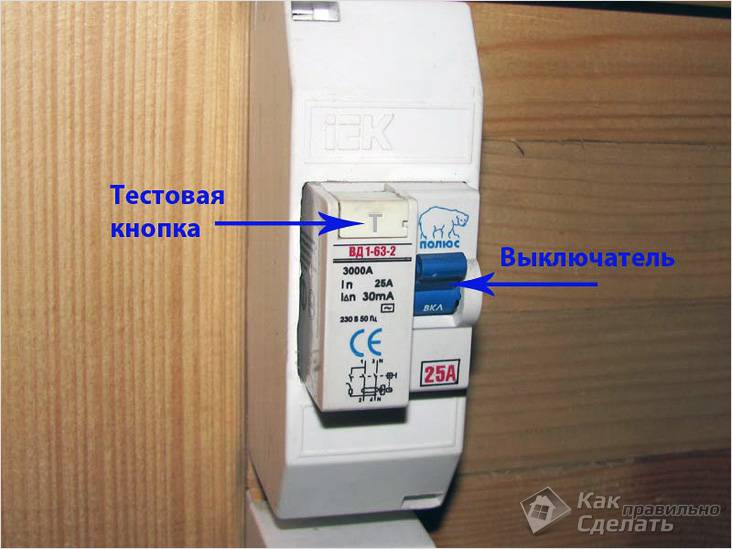
Structurally, an RCD is a device that has a protective shutdown function, outwardly similar to a circuit breaker, but has a different purpose and test switching function. The RCD is mounted using a standard din-rail connector.
The design of the RCD is two-pole - a standard two-phase electrical network of alternating current 220V.
Such a device is suitable for installation in standard buildings (with electrical wiring made with a two-wire wire). If an apartment or house is equipped with three-phase wiring (modern new buildings, industrial and semi-industrial premises), then in this case an RCD with four poles is used.
Two-pole and four-pole version
The device itself has a diagram of its connection and the basic characteristics of the device.
- Serial serial number of the device, manufacturer.
- The maximum value of the current at which the RCD operates for a long time and performs its functions. This value is called the rated current of the device, it is measured in amperes. It usually corresponds to the standardized current values of electrical appliances. Designated on the instrument panel as In. This value is set by taking into account the cross section of the wire and the design of the RCD contact terminals.
- RCD cutoff current. The correct name is rated residual current. It is measured in milliamps. On the body of the device is marked - I∆n. The specified value of the leakage current indicator causes the protective mechanism of the RCD to operate. Operation occurs if all other parameters do not reach emergency values and the installation is performed correctly. The leakage current parameter is determined by standard values.
- The value of the rated differential current that does not lead to an emergency shutdown of the RCD operating under normal conditions. Correctly called the rated non-switching differential current. Marked on the case - In0 and corresponds to half the value of the RCD cutoff current. This indicator covers the range of leakage current values, during the appearance of which an emergency operation of the device occurs. For example, for an RCD with a cutoff current of 30 mA, the value of the non-tripping differential current will be 15 mA, and the emergency shutdown of the RCD will occur during the formation of a leakage current in the network with a value corresponding to the range from 15 to 30 mA.
- The voltage value of the operating RCD is 220 or 380 V.
- The case also indicates the highest value of the short-circuit current, at the time of the formation of which the RCD will continue to operate in good condition. This parameter is called the rated conditional short-circuit current, denoted as Inc. This current value has standardized values.
- The indicator of the nominal trip time of the device. This indicator is referred to as Tn. The time it describes is the interval from the moment the differential breaking current is formed in the circuit to the time at which the electric arc was completely extinguished at the power contacts of the RCD.
Example notation:
An example of the designation of the main characteristics of the device
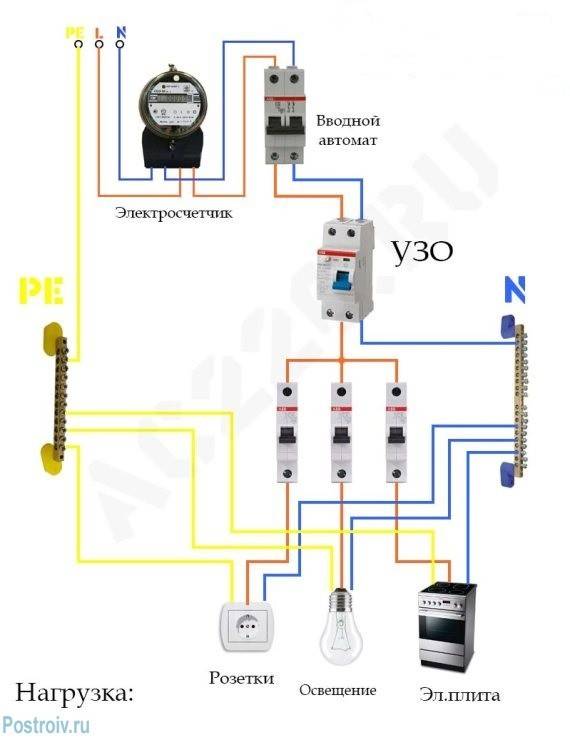
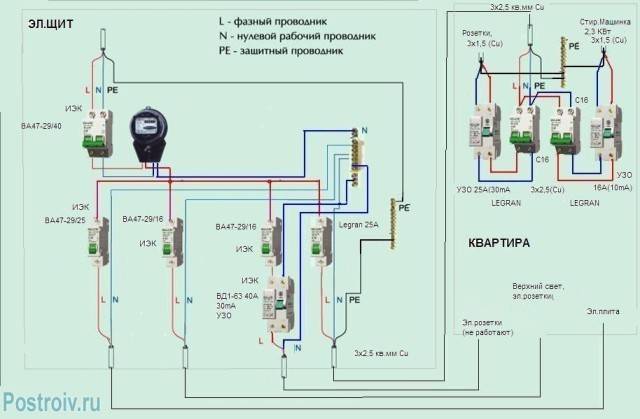
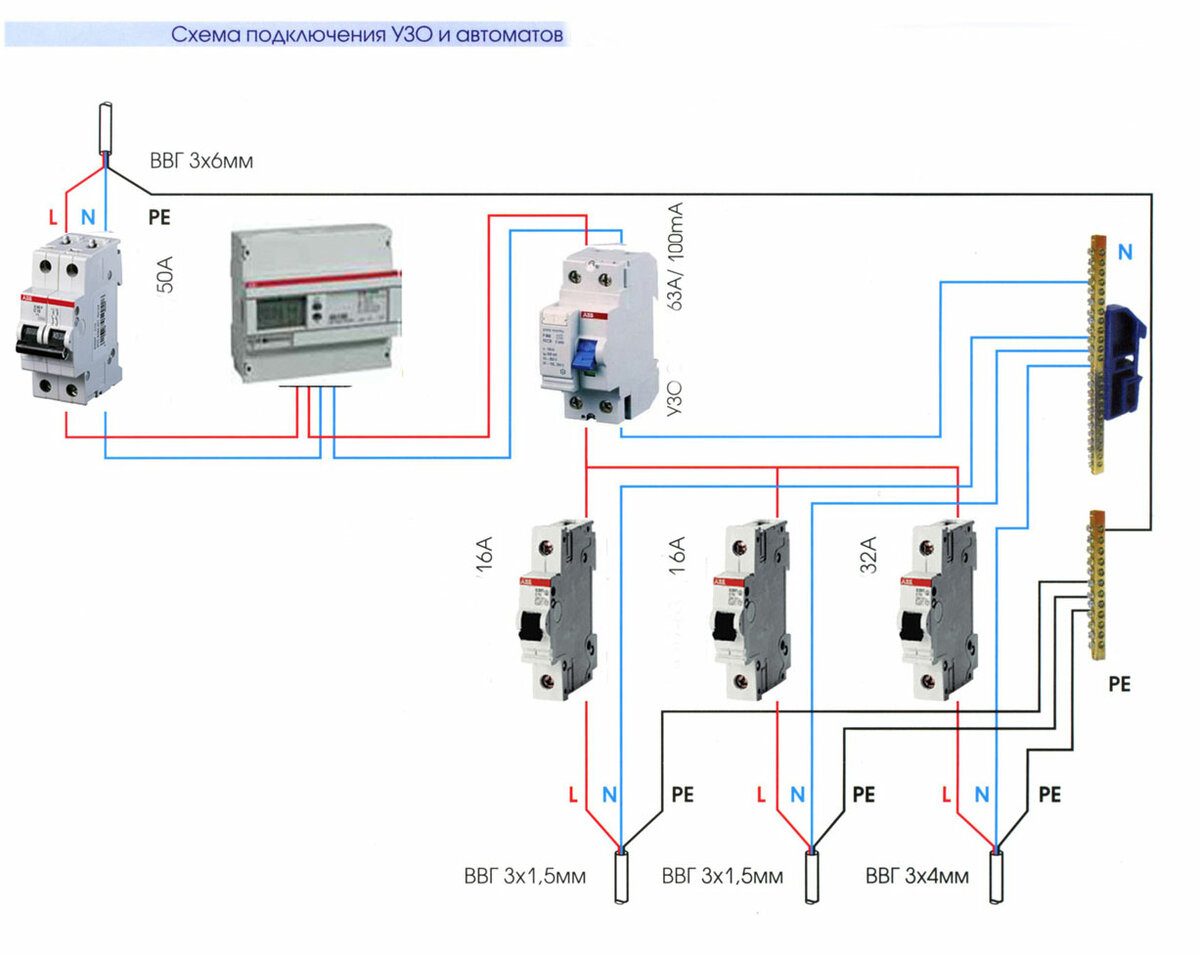
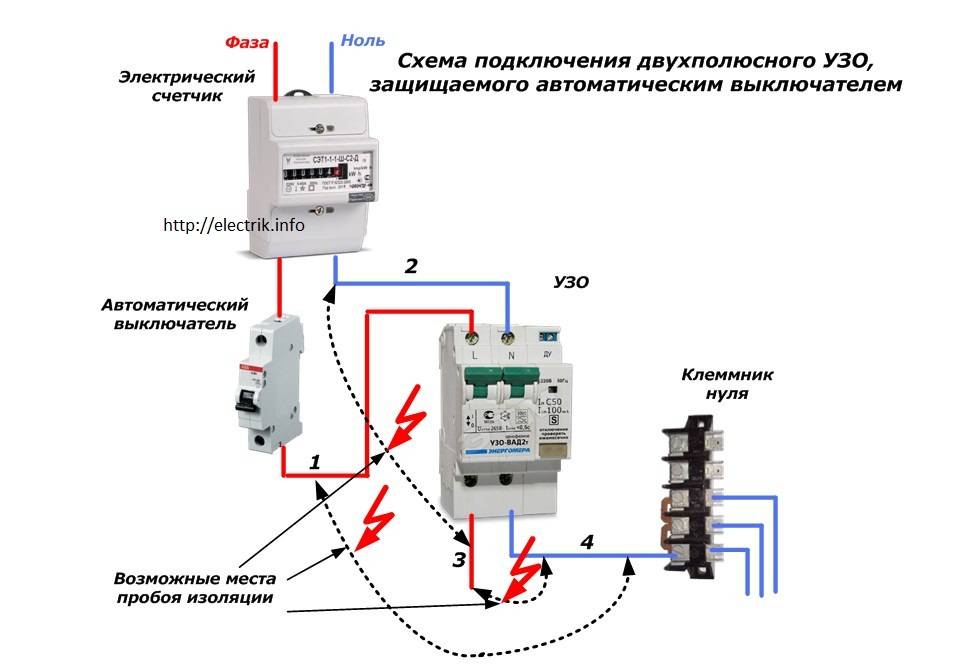
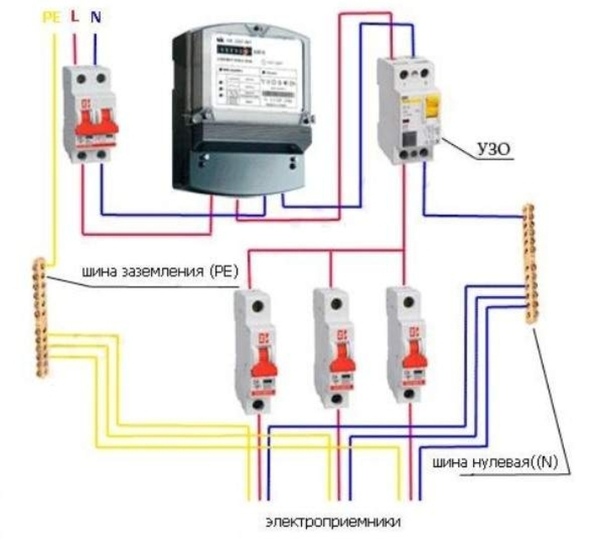
Connecting an RCD and a difavtomat - a circuit with grounding
To understand how the RCD and the machine are connected, the diagram of which is presented on our website, you first need to figure out what the functional purpose of both of these devices is.
Despite their external similarity, they perform different functions.So, a residual current device is installed to prevent damage to electrical wiring, as well as to provide protection against electric shock.
As for the differential machine, it perfectly copes with the above tasks, and can also prevent overloads and short circuits in the wiring.
The residual current device is just an indicator with which to monitor leaks.
The device is not capable of providing network protection, and therefore it is recommended to install both of these devices.
Connecting the RCD and the machine (the diagram implies their sequential placement) will provide maximum protection, as it will turn off the system when the normal level of energy consumption is exceeded.
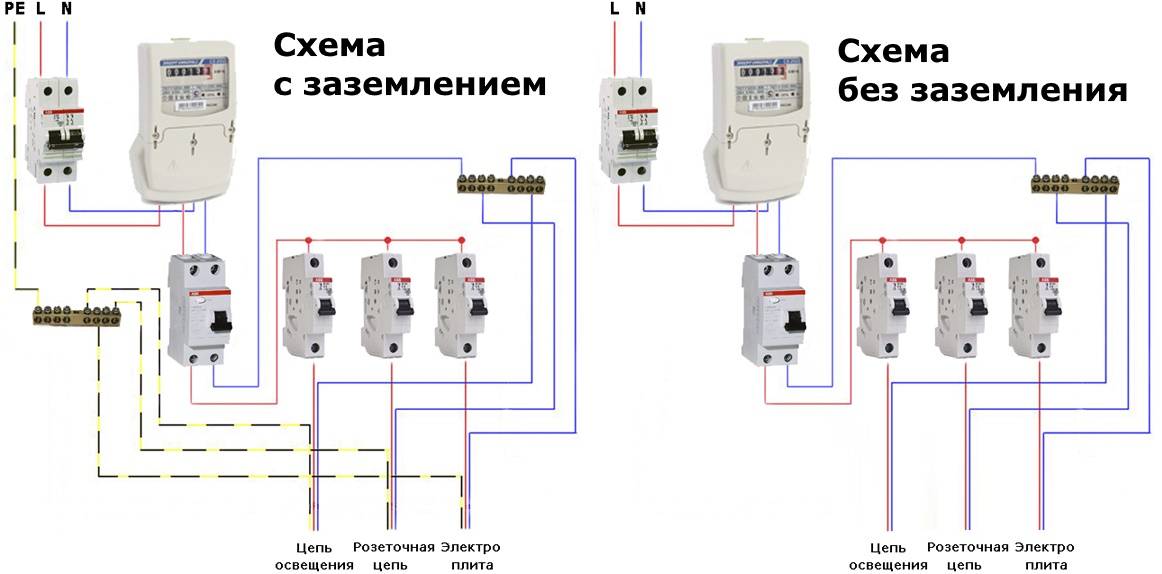
Installing the device in a single-phase network with grounding: possible options
Connecting an RCD with grounding provides reliable protection for humans, household appliances and wiring. The type of grounding used also plays an important role here. It is possible to increase the reliability of the electrical safety system by using all the components separately, however, connecting an RCD with grounding is more preferable.
Often, in private houses and apartments, a single-phase version of electrical wiring with a rated voltage of 220 V is used. The circuit for switching on an RCD in a single-phase network is quite simple. There are several options for connecting this device, but the general principle, in general, remains unchanged.
Advice
The most common is the option in which the device is at the entrance to the house / apartment. Such a scheme, in itself, is budgetary, which contributes to its widespread use.It is worth noting that when the device is triggered, it will be difficult to determine the cause of the ongoing processes.
It is also possible to connect with the installation of several devices - in this case, a separate RCD is responsible for each group of sockets or lighting, therefore, when one of the devices is triggered, it will be easier to determine the cause, since it will not be necessary to de-energize the entire apartment. The switching circuit of the RCD in a single-phase network is indicated, as a rule, on the body of the product and in its passport.
What is the best way to connect a differential machine?
The difavtomat, the connection scheme of which, in a sense, is similar to the principles for installing an automaton or an RCD, is sometimes able to replace both of these devices and provide several degrees of protection at once.
If a problem occurs in one of the connected networks, then its automation will work in emergency mode, and all groups will be disabled. The scheme for connecting a difavtomat in a single-phase network may also imply its inclusion in a circuit to control the operation of a certain electrical group - this option is effective, useful and reliable.