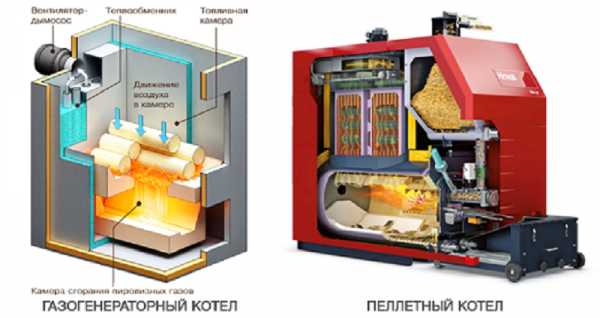
- Norms and methods of control
- Types of pressure and its norms in a gas boiler
- How is it measured
- The optimal value for a private house or cottage
- Optimal Performance
- In an open system
- Closed
- Reasons for increasing pressure in a gas boiler
- Leak test
- Training
- Stage 1 - cold test
- Stage 2 - hot check
- Plastic pipeline
- Air test
- Operating pressure in the heating system of an apartment building
- Types and their meanings
- Working pressure in the heating system of an apartment building: how to control?
- Pressure drops and its regulation
- Norm in an autonomous heating system
- The main reasons for the increase in pressure
- Consequences of instability in circuits
- Pressure surges
- How to control the pressure in the system?
- Determining factors: expansion tank capacity, system type and more
- Rationing of working pressure in apartment buildings
- What is the optimal pressure in a closed heating system
- Conclusion
Norms and methods of control
To begin with, we will briefly consider the types of pressure and how to measure it, which will help to better understand how it is formed in the heating circuit and the hot water circuit (DHW).
Types of pressure and its norms in a gas boiler
In both single-circuit and double-circuit heating systems, the pressure is:
- static - the natural pressure formed by gravity acting on the coolant (each meter of the height of the riser of the system creates approximately 0.1 bar);
- dynamic - artificial pressure created forcibly in a closed circuit (by a pump or expansion of a heated coolant) depends on the parameters of the pump, the temperature of the coolant and the tightness of the system.
- working - real pressure (static + dynamic), it is it that is measured by control and measuring instruments, values \u200b\u200bof 1.5 or 2 bar are considered normal;
- maximum - the maximum allowable for the operation of the system, even its short-term excess (water hammer) can most likely lead to emergency depressurization of the system (in other words, rupture of pipes, radiators or boiler heat exchanger).
How is it measured
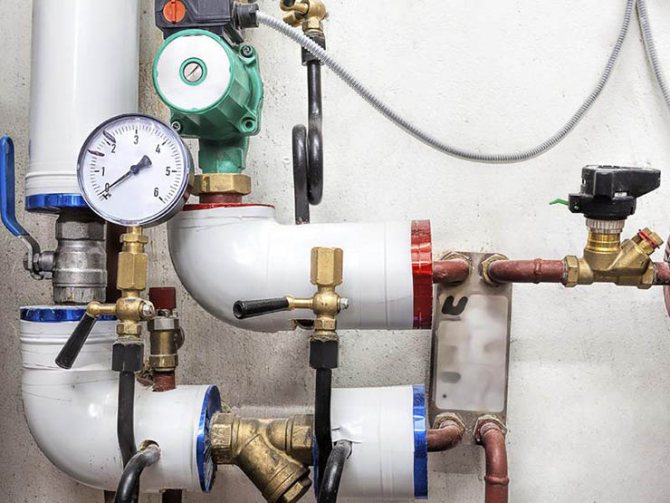
Most models of wall-mounted and floor-standing gas boilers have a built-in pressure gauge that measures the operating water pressure in the heating circuit. But even if it is available, it is recommended to install an additional one: as part of the safety group (pressure gauge / thermometer, safety valve, air bleed valve).
The optimal value for a private house or cottage
Any boiler operates under certain system settings, in particular, it is necessary to correctly calculate the water pressure. This value is affected by the number of storeys of the building, the type of system, the number of radiators and the total length of the pipes. Usually, for a private house, the pressure level is 1.5-2 atm, but for a multi-apartment five-story building, this value is 2-4 atm, and for a ten-story house, 5-7 atm. For higher buildings, the pressure level is 7-10 atm, the maximum value is reached in heating mains, here it is 12 atm.
For radiators that operate at different heights and at a fairly decent distance from the boiler, constant pressure adjustment is required. At the same time, special regulators are used to reduce, and pumps are used to increase. But the regulator must always be in good condition, otherwise sharp fluctuations and drops in the temperature of the coolant will be observed in some areas. Correction of the system must be carried out so that the shut-off valves are never completely closed.
Optimal Performance
There are generally accepted averages:
- For a small private house or apartment with individual heating, pressure ranging from 0.7 to 1.5 atmospheres is sufficient.
- For private households in 2-3 floors - from 1.5 to 2 atmospheres.
- For a building of 4 floors and above, from 2.5 to 4 atmospheres are recommended with the installation of additional pressure gauges on the floors for control.
Attention! To carry out calculations, it is important to understand which of the two types of systems is being installed. Open - heating system in which the expansion tank for excess fluid interacts with the atmosphere
Open - a heating system in which the expansion tank for excess fluid interacts with the atmosphere.
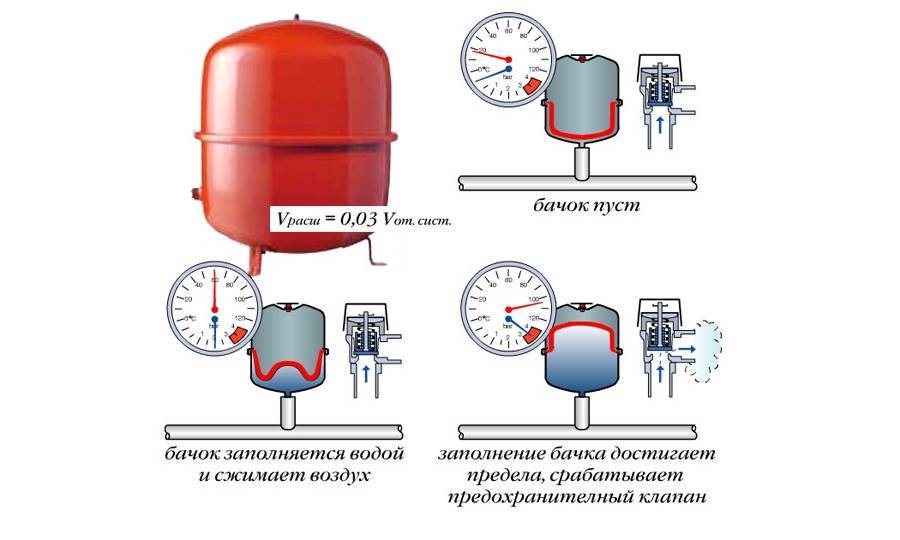
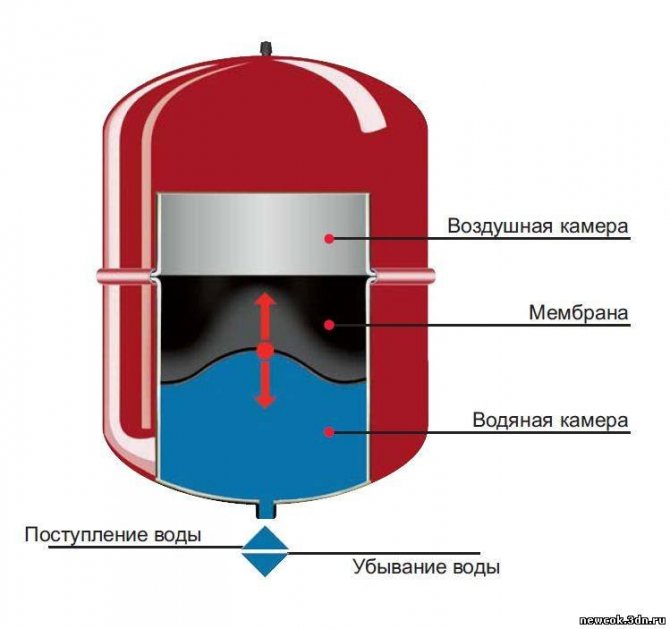
Closed - hermetic heating system. It contains a closed expansion vessel of a special shape with a membrane inside, which divides it into 2 parts. One of them is filled with air, and the second is connected to the circuit.
Photo 1. Scheme of a closed heating system with a membrane expansion tank and a circulation pump.
The expansion vessel takes in excess water as it expands when heated.When the water cools and decreases in volume, the vessel makes up for the deficiency in the system, preventing it from breaking when the energy carrier is heated.
In an open system, the expansion tank must be installed in the highest part of the circuit and connected, on the one hand, to the riser pipe, and on the other, to the drain pipe. The drain pipe insures the expansion tank from overfilling.
In a closed system, the expansion vessel can be installed in any part of the circuit. When heated, water enters the vessel, and the air in its second half is compressed. In the process of cooling the water, the pressure decreases, and the water, under the pressure of compressed air or other gas, returns back to the network.
In an open system
In order for the excess pressure on the open system to be only 1 atmosphere, it is necessary to install the tank at a height of 10 meters from the lowest point of the circuit.
And in order to destroy a boiler that can withstand a power of 3 atmospheres (the power of an average boiler), you need to install an open tank at a height of more than 30 meters.
Therefore, an open system is more often used in one-story houses.
And the pressure in it rarely exceeds the usual hydrostatic, even when the water is heated.
Therefore, additional safety devices, in addition to the described drain pipe, are not needed.
Important! For normal operation of an open system, the boiler is installed at the lowest point, and the expansion tank is at the highest point. The diameter of the pipe at the inlet to the boiler must be narrower, and at the outlet - wider
Closed
Since the pressure is much higher and changes when heated, it must be equipped with a safety valve, which is usually set to 2.5 atmospheres for a 2-story building. In small houses, the pressure can remain in the range of 1.5-2 atmospheres.If the number of storeys is from 3 and above, the boundary indicators are up to 4-5 atmospheres, but then the installation of an appropriate boiler, additional pumps and pressure gauges is required.
The presence of a pump provides the following advantages:
- The length of the pipeline can be arbitrarily large.
- Connection of any number of radiators.
- Use both serial and parallel circuits for connecting radiators.
- The system operates at minimum temperatures, which is economical in the off-season.
- The boiler operates in a sparing mode, since the forced circulation quickly moves the water through the pipes, and it does not have time to cool down, reaching the extreme points.
Photo 2. Measurement of pressure in a closed-type heating system using a pressure gauge. The device is installed next to the pump.
Reasons for increasing pressure in a gas boiler
In addition to the pressure gauge indicators, frequent discharge of water through the safety valve and blocking the operation of the device help to detect an increase in pressure in a gas boiler. Having determined the high pressure, first of all, they dump excess air through the Mayevsky taps and turn off the boiler. There may be several reasons for failures.
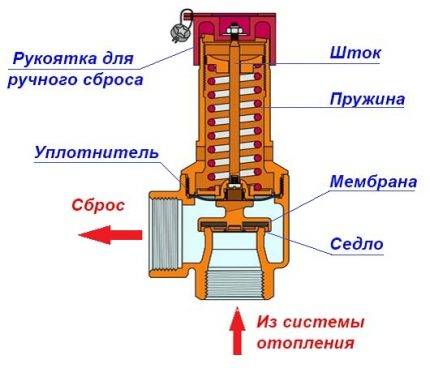 The normal upper pressure value is provided by the system by discharging excess coolant through the safety valve into the drain
The normal upper pressure value is provided by the system by discharging excess coolant through the safety valve into the drain
An increase in pressure in a gas boiler can be caused by damage to the partition of the secondary heat exchanger, which simultaneously serves to isolate and increase the area of \u200b\u200bcontact between the two circuits - heating and hot water supply.
The secondary heat exchanger draws water from the heating circuit for the preparation and supply of hot water in a double-circuit boiler.Damage to the partition leads to forcing water from the DHW circuit into the heating system, increasing the pressure in it.
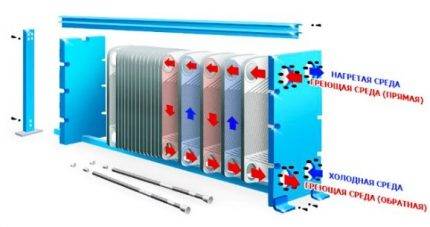 The secondary heat exchanger serves to service the hot water supply system. Water for domestic hot water is heated as a result of contact with the heat carrier of the heating circuit. A metal partition protects the system from mixing the two circuits, damage to which leads to the exchange of fluids and a violation of normal pressure
The secondary heat exchanger serves to service the hot water supply system. Water for domestic hot water is heated as a result of contact with the heat carrier of the heating circuit. A metal partition protects the system from mixing the two circuits, damage to which leads to the exchange of fluids and a violation of normal pressure
Replacing the heat exchanger will solve the problem. It is possible to carry out repairs on your own, but it is undesirable to do this, since intervention in the operation of gas equipment requires knowledge and experience in this area. In addition, self-repair of the boiler will deprive you of the right to warranty service.
A malfunction of the gas boiler automation or a loose pump impeller that sucks in air also increases the pressure in the gas boiler. Equipment malfunctions that lead to violations of the normal pressure may be as a result of a factory defect, a breakdown of the control board, or an incorrectly configured system. Only a qualified technician can fix this kind of problem.
Leak test
In order for the heating to be reliable, after installation it is checked for leaks (pressure tested).
This can be done immediately on the entire structure or its individual elements. If a partial pressure test is carried out, then after it is completed, the entire system as a whole must be checked for leaks.
Regardless of which heating system is installed (open or closed), the sequence of work will be almost the same.
Training
The test pressure is 1.5 times the working pressure.But this is not enough to completely detect a coolant leak. Pipes and couplings can withstand up to 25 atmospheres, so it is better to check the heating system under such pressure.
Corresponding indicators are created by a hand pump. There should be no air in the pipes: even a small amount of it will distort the tightness of the pipeline.
The highest pressure will be at the lowest point in the system, a monometer is installed there (reading accuracy 0.01 MPa).
Stage 1 - cold test
In the course of half an hour in the system filled with water, the pressure is increased to the initial values. Do this twice, every 10-15 minutes. For another half an hour, the fall will continue, but without exceeding the mark of 0.06 MPa, and after two hours - 0.02 MPa.
At the end of the inspection, the pipeline is inspected for leaks.
Stage 2 - hot check
The first stage has been successfully completed, you can proceed to the hot leak test. To do this, connect a heating device, most often it is a boiler. Set the maximum performance, they should not be more than the calculated values.
Houses are preheated for at least 72 hours. Test passed if no water leak is detected.
Plastic pipeline
The plastic heating system is checked at the same temperature of the coolant in the pipeline and the environment. Changing these values will increase the pressure, but in fact there is a water leak in the system.
For half an hour, the pressure is maintained at a value one and a half times higher than the normative one. If necessary, it is slightly pumped up.
After 30 minutes, the pressure is sharply lowered to readings equal to half the working one, and they are held for an hour and a half.If the indicators began to grow, it means that the pipes are expanding, the structure is tight.
Often, craftsmen, when checking the system, make a pressure drop several times, then raising it, then lowering it, so that it resembles normal, everyday working conditions. This method will help to identify leaky connections.
Air test
Multi-storey buildings are tested for tightness in autumn. Instead of liquid in such cases, air can be used. The test results are slightly inaccurate due to the fact that the air is first heated during compression, then it is cooled, which contributes to a pressure drop. Compressors will help increase this parameter.
The sequence of checking the heating system is carried out as follows:
- The structure is filled with air (trial values - 1.5 atmospheres).
- If a hiss is heard, it means that there are defects, the pressure is reduced to atmospheric pressure and the defects are eliminated (for this, a foaming substance is used, it is applied to the joints).
- The pipeline is again filled with air (pressure - 1 atmosphere), hold for 5 minutes.
Operating pressure in the heating system of an apartment building
The page contains information about the operating pressure in the heating system of an apartment building: how to control the drop in pipes and batteries, as well as the maximum rate in an autonomous heating system.
For efficient operation of the heating system of a high-rise building, several parameters must comply with the norm at the same time.
The water pressure in the heating system of an apartment building is the main criterion by which they are equal, and on which all other nodes of this rather complex mechanism depend.
Types and their meanings
The working pressure in the heating system of an apartment building combines 3 types:
- Static pressure in the heating of apartment buildings shows how strongly or weakly the coolant presses from the inside on pipes and radiators. It depends on how high the equipment is.
- Dynamic is the pressure with which water moves through the system.
- The maximum pressure in the heating system of an apartment building (also called “permissible”) indicates what pressure is considered safe for the structure.
Since almost all multi-storey buildings use closed-type heating systems, there are not so many indicators.
- for buildings up to 5 floors - 3-5 atmospheres;
- in nine-story houses - this is 5-7 atm;
- in skyscrapers from 10 floors - 7-10 atm;
For the heating main, which stretches from the boiler house to the heat consumption systems, the normal pressure is 12 atm.
To equalize the pressure and ensure stable operation of the entire mechanism, a pressure regulator is used in the heating system of an apartment building. This balancing manual valve regulates the amount of heating medium with simple turns of the handle, each of which corresponds to a certain water flow. These data are indicated in the instructions attached to the regulator.
Working pressure in the heating system of an apartment building: how to control?
To know if the pressure in the heating pipes in an apartment building is normal, there are special pressure gauges that can not only indicate deviations, even the smallest ones, but also block the operation of the system.
Since the pressure is different in different sections of the heating main, several such devices need to be installed.
Usually they are mounted:
- at the outlet and at the inlet of the heating boiler;
- on both sides of the circulation pump;
- on both sides of the filters;
- at points of the system located at different heights (maximum and minimum);
- close to collectors and system branches.
Pressure drops and its regulation
Jumps in the pressure of the coolant in the system are most often indicated with an increase in:
- for severe overheating of water;
- the cross section of the pipes does not correspond to the norm (less than required);
- clogging of pipes and deposits in heating appliances;
- presence of air pockets;
- pump performance is higher than required;
- any of its nodes are blocked in the system.
On downgrade:
- about the violation of the integrity of the system and the leakage of the coolant;
- breakdown or malfunction of the pump;
- may be caused by malfunctions in the operation of the safety unit or a rupture of the membrane in the expansion tank;
- coolant outflow from the heating medium to the carrier circuit;
- clogging of filters and pipes of the system.
Norm in an autonomous heating system
In the case when autonomous heating is installed in the apartment, the coolant is heated using a boiler, usually of low power. Since the pipeline in a separate apartment is small, it does not require numerous measuring instruments, and 1.5-2 atmospheres is considered normal pressure.
During start-up and testing of an autonomous system, it is filled with cold water, which, at a minimum pressure, gradually warms up, expands and reaches the norm. If suddenly in such a design the pressure in the batteries drops, then there is no need to panic, since the reason for this is most often their airiness.It is enough to free the circuit from excess air, fill it with coolant and the pressure itself will reach the norm.
To avoid emergency situations when the pressure in the heating batteries of an apartment building rises sharply by at least 3 atmospheres, you need to install either an expansion tank or a safety valve. If this is not done, the system may be depressurized and then it will have to be changed.
- carry out diagnostics;
- clean its elements;
- check the performance of measuring instruments.
2 thousand
1.4 thousand
6 min.
The main reasons for the increase in pressure
Most often, the reason why the pressure in the heating circuit in a closed heating system rises is equipment failure, due to which the indicators either jump up or drop sharply down. But other than that, the reasons also include the following:
- A sharp increase in coolant pressure due to closed shutoff valves. An increase in pressure is observed in the system, after which the boiler is blocked and the system stops. To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to check the fittings for leaks, open valves and taps to relieve pressure.
- The reason for the rise in pressure in the heating system may be contamination of the mud filter. Rust particles, debris, sand and slag accumulate on the surface of such a filter. As a result, pressure rises strongly in the area between the boiler and the filter. To eliminate the cause, it is necessary to clean the filters regularly, at least 3-4 times a year. It is also a good solution to replace conventional mud collectors with magnetic or flush filters. They cost more, but their maintenance is much easier.
- The working pressure of the system may increase due to a malfunction of the boiler automation.This is a factory defect, incorrectly configured system settings, a breakdown of the control board. All these problems require repair of the boiler, which can only be carried out by a master.
- There are leaks in the make-up tap, that is, water will constantly penetrate into the common circuit, which causes a pressure surge. Repair is usually quite simple, you just need to replace the rubber gaskets. But if there is a marriage, the crane or equipment should be completely replaced.
Why does pressure drop in a double-circuit or conventional boiler? This situation most often occurs when the expansion tank breaks down or the air valve passes. To fix the problem, it may be necessary to repair or completely replace the tank.
Consequences of instability in circuits
Too little or too much pressure in the heating circuit is equally bad. In the first case, part of the radiators will not effectively heat the premises, in the second case, the integrity of the heating system will be violated, its individual elements will fail.
Proper piping will allow you to connect the boiler to the heating circuit as necessary for the high-quality operation of the heating system
An increase in dynamic pressure in the heating pipeline occurs if:
- the coolant is too hot;
- the cross section of the pipes is insufficient;
- the boiler and pipeline are overgrown with scale;
- air jams in the system;
- too powerful booster pump installed;
- water supply occurs.
Also, increased pressure in a closed circuit causes incorrect balancing by valves (the system is overregulated) or a malfunction of individual valve regulators.
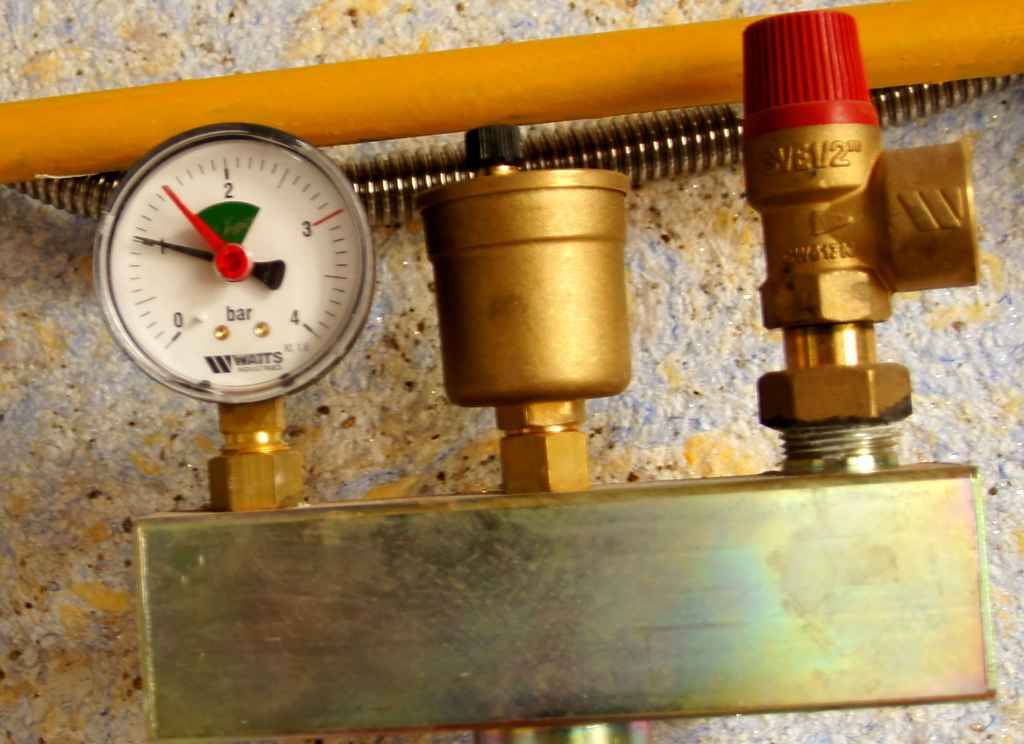
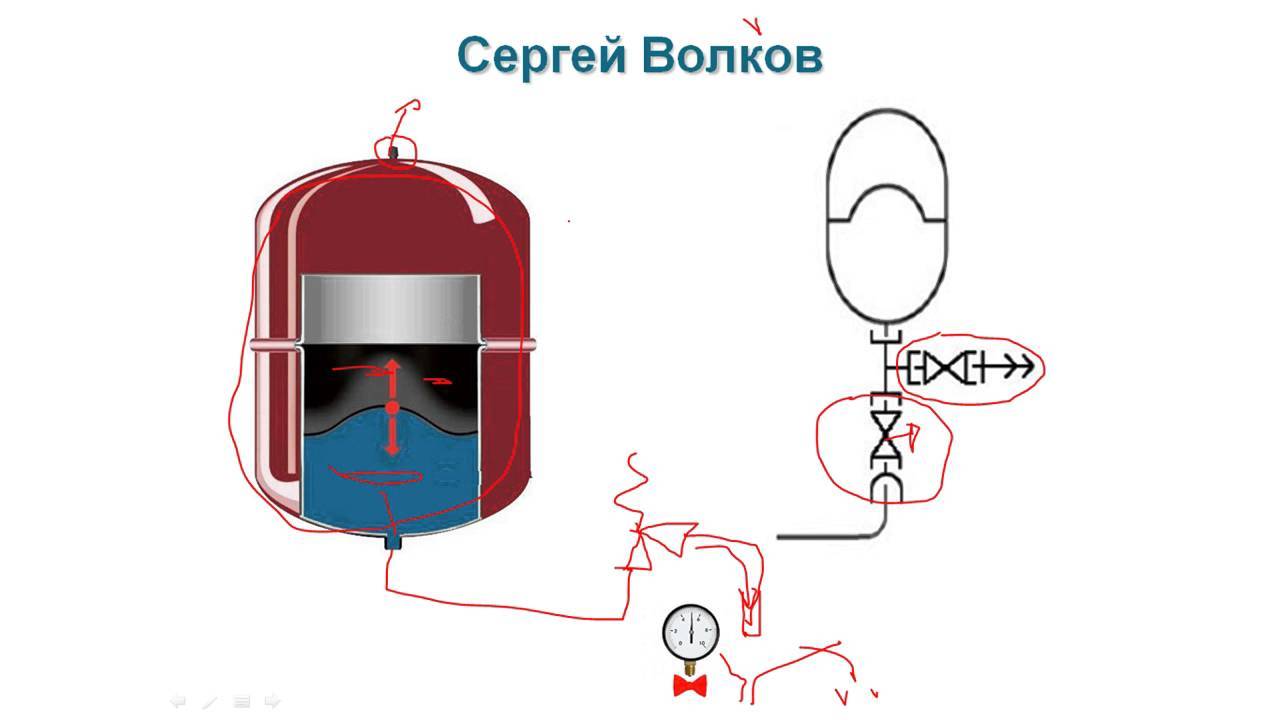
To control the operating parameters in closed heating circuits and to automatically adjust them, a safety group is set:
The pressure in the heating pipeline drops for the following reasons:
- coolant leakage;
- pump malfunction;
- breakthrough of the expansion tank membrane, cracks in the walls of a conventional expansion tank;
- malfunctions of the security unit;
- water leakage from the heating system into the feed circuit.
Dynamic pressure will be increased if the cavities of the pipes and radiators are clogged, if the trapping filters are dirty. In such situations, the pump works with an increased load, and the efficiency of the heating circuit is reduced. Leaks in connections and even rupture of pipes become a standard result of exceeding pressure values.
The pressure parameters will be lower than expected for normal functionality if an insufficiently powerful pump is installed in the line. He will not be able to move the coolant at the required speed, which means that a somewhat cooled working medium will be supplied to the device.
The second striking example of a pressure drop is when the duct is blocked by a tap. A symptom of these problems is the loss of pressure in a separate pipeline segment located after the coolant obstruction.
Since all heating circuits have devices that protect against overpressure (at least a safety valve), the problem of low pressure occurs much more often. Consider the causes of the fall and ways to increase pressure, and therefore improve water circulation, in open and closed heating systems.
Pressure surges
The decrease in pressure may be due to the following reasons:

- a large amount of scale has formed in the pipelines (relevant for regions where water is hard - the Moscow region, by the way, also applies to them);
- small cracks in the heat pipes, which could have formed due to wear or even a factory defect;
- destruction of the heat exchanger itself, which failed due to water hammer;
- the expansion chamber is damaged or deformed.
As a matter of fact, such problems, with the exception of problems with the heat exchanger, are quite easy to fix even with your own hands.
You can, for example, install an expansion regulator, do not forget about such an important detail as crimping: it must be done before starting the entire system! There are many cases when, in the same Moscow, management companies did not go through this procedure before putting the house into operation, and then the tenants literally froze from the cold, having paid tens of millions of rubles for housing. True, this applies mainly to high-rise buildings, and not to private houses.
True, this applies mainly to high-rise buildings, and not to private houses.
There are many cases when, in the same Moscow, management companies did not go through this procedure before putting the house into operation, and then the tenants literally froze from the cold, having paid tens of millions of rubles for housing. True, this applies mainly to high-rise buildings, and not to private houses.
Increased pressure may be due to the following reasons:
- the movement of water or antifreeze is stopped (here it is imperative to check the regulator, as well as the expansion tank and tank);
- a constant replenishment of the coolant is carried out, which can be caused both by a failure of the automation and by the wrong actions of the owner of the house;
- along the perimeter of the movement of the heat carrier, the valve or safety valve was closed;
- a plug of air has formed (very often this happens when the water circulation system is natural, it is just a scourge of such systems);
-
the sump or filter element is very dirty.
In general, problems with excess pressure are much more difficult to solve.
How to control the pressure in the system?
To control at various points in the heating system, pressure gauges are inserted, and (as mentioned above) they record excess pressure. As a rule, these are deformation devices with a Bredan tube. In the event that it is necessary to take into account that the pressure gauge must work not only for visual control, but also in the automation system, electrocontact or other types of sensors are used.
The tie-in points are defined by regulatory documents, but even if you have installed a small boiler for heating a private house that is not controlled by GosTekhnadzor, it is still advisable to use these rules, since they highlight the most important heating system points for pressure control.
It is imperative to embed pressure gauges through three-way valves, which ensure their purge, reset to zero and replacement without stopping all heating.
The control points are:
- Before and after the heating boiler;
- Before and after the circulation pumps;
- Output of heat networks from a heat generating plant (boiler house);
- Entering heating into the building;
- If a heating regulator is used, then the pressure gauges cut in before and after it;
- In the presence of mud collectors or filters, it is advisable to insert pressure gauges before and after them.Thus, it is easy to control their clogging, taking into account the fact that a serviceable element almost does not create a drop.
System with installed pressure gauges
A symptom of malfunctions or improper operation of the heating system is pressure surges. What do they stand for?
Determining factors: expansion tank capacity, system type and more
The pressure in the heating system depends on several factors:
- Equipment power. Static is set by the height of a multi-storey building or by the rise of an expansion tank. The dynamic component is largely determined by the power of the circulation pump and, to a lesser extent, by the power of the heating boiler.
When providing the required pressure in the system, the appearance of obstacles to the movement of the coolant in pipes and radiators is taken into account. With prolonged use, scale, oxides and sediment accumulate in them. This leads to a decrease in diameter, and hence to an increase in resistance to fluid movement. Especially noticeable with increased hardness (mineralization) of water. To eliminate the problem, a thorough flushing of the entire heating structure is periodically carried out. In regions where the water is hard, clean filters for hot water are installed.
Rationing of working pressure in apartment buildings
Multi-storey buildings are connected to central heating, where the coolant comes from the CHP, or to domestic boilers. In modern heating systems, indicators are maintained in accordance with GOST and SNiP 41-01-2003. Normal pressure provides room temperature of 20-22 ° C at a humidity of 30-45%.
Depending on the height of the building, the following standards are established:
- in houses up to 5 floors high 2-4 atm;
- in buildings up to 10 floors 4-7 atm;
- in buildings above 10 floors 8-12 atm.
It is important to ensure uniform heating of apartments located on different floors. The condition is considered normal when the difference between the operating pressures on the first and last floor of a multi-storey building is no more than 8-10%
The condition is considered normal when the difference between the operating pressures on the first and last floor of a multi-storey building is no more than 8-10%.
During periods when heating is not needed, the minimum indicators are maintained in the system. It is determined by the formula 0.1(Нх3+5+3), where Н is the number of floors.
In addition to the number of storeys of the building, the value depends on the temperature of the incoming coolant. Minimum values have been established: at 130°C - 1.7-1.9 atm., at 140°C - 2.6-2.8 atm. and at 150 °C - 3.8 atm.
Attention! Periodic performance checks play an important role in heating efficiency. Control them during the heating season and in the off-season
During operation, control is carried out by pressure gauges installed at the inlet and outlet of the heating circuit. At the inlet, the value of the incoming coolant must comply with the established standards.
Check the pressure difference between inlet and outlet. Normally, the difference is 0.1-0.2 atm. The absence of a drop indicates that there is no movement of water to the upper floors. An increase in the difference indicates the presence of coolant leaks.
In the warm season, the heating system is checked using pressure tests. Typically, testing is provided by cold water pumped through. The depressurization of the system is fixed when the indicators fall within 25-30 minutes by more than 0.07 MPa. The norm is considered to be a drop of 0.02 MPa within 1.5-2 hours.
Photo 1. The process of pressure testing the heating system.An electric pump is used, which is connected to a radiator.
What is the optimal pressure in a closed heating system
Above, the heating of "high-rise buildings" is considered, which is provided according to a closed scheme. When arranging a closed system in private homes, there are nuances. Typically, circulation pumps are used that maintain the desired performance. The main condition for their installation is that the pressure created should not exceed the indicators for which the heating boiler is designed (indicated in the instructions for the equipment).
At the same time, it must ensure the movement of the coolant throughout the system, while the difference in water temperature at the outlet of the boiler and at the return point should not exceed 25–30 °C.
For private, one-story buildings, the pressure in a closed heating system in the range of 1.5–3 atm is considered the norm. The length of the pipeline with gravity is limited to 30 m, and when using a pump, the restriction is removed.
Conclusion
To eliminate the causes of an increase or decrease in pressure in a home heating system, it is necessary to initially correctly design the system and, when installing it, strictly follow the sequence of actions without deviating from what was planned. If you notice that the pressure in the heating system is growing, you should immediately contact the specialists in order to prevent damage to the equipment.
Read more:
How does the airing of the heating system occur, and how to deal with it
We understand why the gas boiler blows out, and eliminate the causes
What does the pressure in the expansion tank of the heating mean?
Types, functions and design features of expansion tanks
We solve the problem of how to expel air from the heating system