- No. 7. What diameter/size of pipe do you need?
- Characteristics of corrugated pipes
- Kinds
- Areas of use
- How to hide the kitchen hood air duct: decor methods
- Little tricks: masking the duct
- Analysis of rumors and speculation
- Brief overview of materials
- Disassembly of PVC pipes
- Polypropylene ventilation pipes
- Polyurethane ventilation pipes
- Characteristics of PTFE pipes
- Features of air ducts
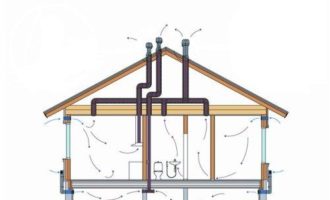
No. 7. What diameter/size of pipe do you need?
Calculating ventilation is not an easy task. There are programs where you can upload all the initial data, and then get the recommended values \u200b\u200bof air exchange and duct size. There are specialists who will perform the calculation, taking into account all the features of the premises of the house. The general principle of calculation is as follows.
First you need to find the amount of air that should enter the house and be removed from it per unit hour. In theory, the volume of incoming air = the volume of air removed. How much air must go in and out for us to be comfortable? Everything has already been taken into account in the regulations.
According to SNiP 31-02-2001, air exchange for residential premises is equal to the volume of the room, i.e. in 1 hour, the air should be completely renewed 1 time.For the kitchen, this figure is at least 60 m3 / h, for the bathroom - 25 m3 / h. The volume of a room is easy to calculate.
Design standards "ABOK" 2.1-2008 speak of the following air exchange standards.
Sometimes, according to these standards, slightly different values \u200b\u200bare obtained, it is better to take into account what is larger. For a correct calculation, it is necessary to arm yourself with a house plan, which indicates the parameters of each room. It is convenient to do everything in the form of a table.
From each pair of numbers, choose the larger one and sum them up. In the example, the total air exchange is 430 m3/h. In living rooms, it will be necessary to organize an inflow and exhaust, and in the kitchen and in the bathroom - only an extract. Fresh air will come from neighboring rooms.
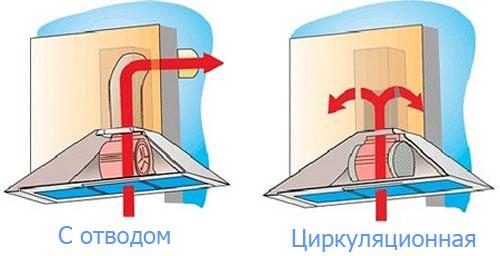
Further, when calculating, it is necessary to take into account how the air will be discharged, naturally or forcibly. With the natural method, the speed of the air flow inside the duct will be no more than 1 m / s, with forced - up to 5 m / s, in the branches - up to 3 m / s.
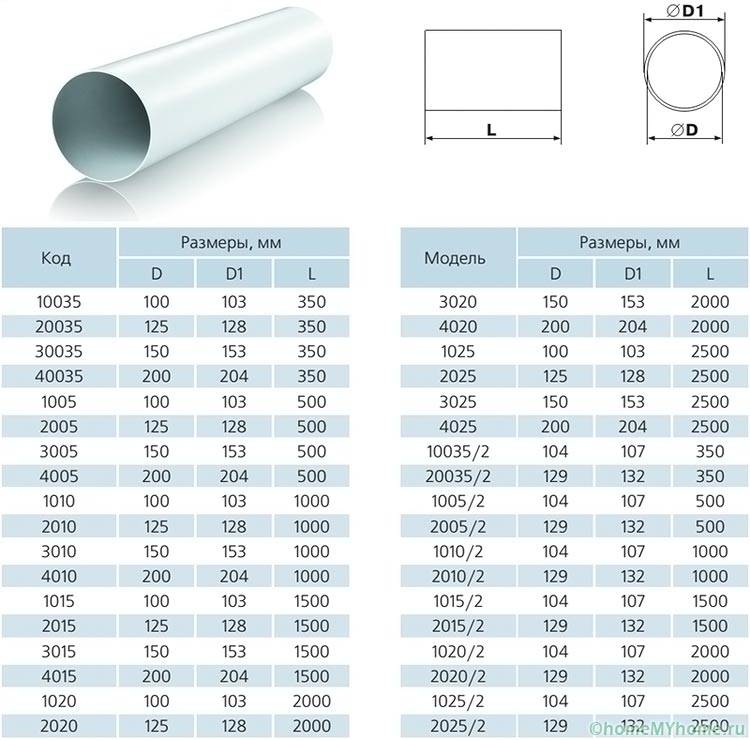
The cross section of the channel is calculated according to the formula S=L/(V 3600) m2, where L is the air exchange and V is the flow rate. You can also use a special chart. In this case, fans are indispensable. If we take the flow velocity as 3 m/s, then we get S = 0.0398 m2, or 398 cm2. It is possible to organize ventilation with one air duct 200*200 mm, two 170*170, or three 150*150. This is all just so that you understand the general calculation scheme. It is safer, of course, to turn to specialists.
Many people treat ventilation too neglectfully. If you don’t want to face microclimate problems later, break walls and ceilings or install pipes for a fine finish, it’s better to think everything through in advance.
Characteristics of corrugated pipes
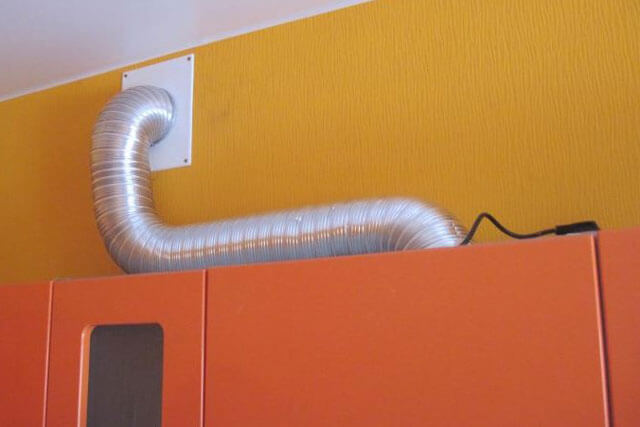
Such pipes are made of thin aluminum. In this case, there is a significant minus - the appearance of the air path. It is unlikely that there will be many who want to see a metal pipe in their kitchen. Therefore, the use of this material implies the obligatory masking of the pipe. But there are obvious benefits too:
- ease of installation work - the corrugated pipe is easily cut, can be bent at any angle, easily fastened with special clamps;
- lack of resonant hum;
- low cost compared to plastic air ducts;
- sharp pipe bends are excluded, which increases the efficiency of the ventilation system.
Such pipes are produced in the form of small pieces, which are stretched to a significant length.
Kinds
Air ducts designed for proper operation of the hood are different. They are made from various materials, which always affects their performance and final cost. Let us consider in detail what varieties of such aggregates exist, and according to what parameters they are divided.
All types of air ducts are mainly divided into rigid and flexible types.
Flexible type air ducts can be placed at a variety of angles. If required, they can be stretched or compressed (of course, within the limits of the possible). However, it must be taken into account that a slightly elongated air outlet is characterized by a stronger resistance to air flow. This is not the best way to affect the overall efficiency of the system as a whole. In most cases, these models are made of aluminum.The main disadvantage of such systems is that it is not recommended to make a corrugated box for them longer than 3 m, since any extra centimeter in this situation will reduce productivity by about 5-10%.
And also all air ducts are divided according to their immediate form. There are several variants of such systems.
Let us consider in detail what air ducts for hoods are.
Rectangular and square. These types of air ducts are recognized as one of the most popular and are found with enviable regularity. Many owners choose them precisely because of their shape, which allows them to be placed right behind the kitchen cabinets. Thanks to this feature, it is possible to lay almost any trajectory from the exhaust equipment to the ventilation shaft. Rectangular pieces will be an excellent solution for kitchens with any ceilings (meaning any height setting). In addition, these models can boast of a good appearance.
- Flat. These duct options are one of the varieties of rectangular models. They are very modest in size and seem completely invisible.
- Rounded. Such varieties are more demanding - they can only be installed in rooms with high ceilings. This requirement is due to the large dimensions of the equipment. If the outlet has a rectangular structure, then it will be necessary to additionally use rectangular adapters with the appropriate section for rounded models.
- Oval. These specimens have the same strengths and weaknesses as rounded specimens.
Of the listed options for air ducts, flat rectangular models should be distinguished.
They are represented by products with the following parameters:
- 110x55 mm - such options are required for hoods with a capacity of not more than 300 m3 / h;
- 120x60 mm - suitable for equipping hoods, the performance level of which does not go beyond 350 m3 / h;
- 204x60 mm - perfectly suited for operation in conjunction with high-performance units - up to 1000 m3 / h.
Areas of use
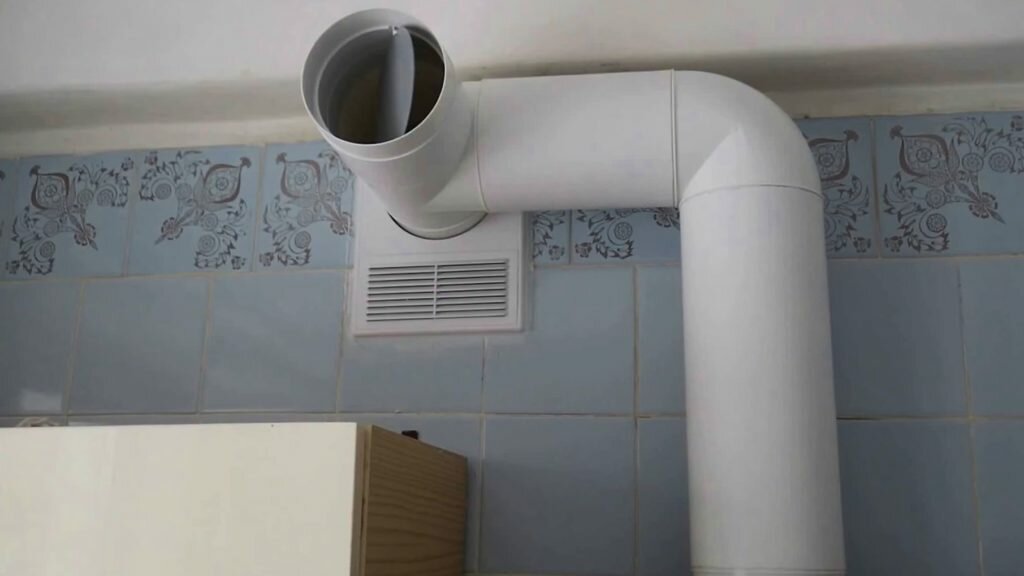
Plastic pipes for ventilation meet all sanitary standards and look quite presentable, so they are installed in public places such as fitness clubs and gyms, bars, cafes and restaurants.
The obsolete galvanized air ducts used in residential construction until recently are being replaced by analogues made of polymers.
On the market you can find polymer products from such materials:
- polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
- polyurethane;
- polypropylene.

Due to their low weight, PVC pipes are in the greatest demand.
The advantages of such products include the following properties:
- complete tightness of the connection;
- high resistance to ultraviolet;
- ease of maintenance (cleaning);
- ease of installation structures.
And PVC products do not pose a threat to the human body.
The technology for the production of ventilation pipes from polymers makes it possible to make their inner surface solid and absolutely smooth. Additionally, such products are antistatic treated, so that any static electricity is extinguished, and dust does not stick to the surface of the pipe. Therefore, regular cleaning of such pipes is not necessary.
As for industrial enterprises, air ducts made of polymeric materials are very often used in them. The selection of a specific type of pipe is made at the design stage of the ventilation system, based on the conditions of the technological process.
How to hide the kitchen hood air duct: decor methods
An air duct that runs from the hood to the vent is unlikely to look beautiful in the interior (especially if it is corrugated). Therefore, they often decide to hide it.
The ways to do it are:
-
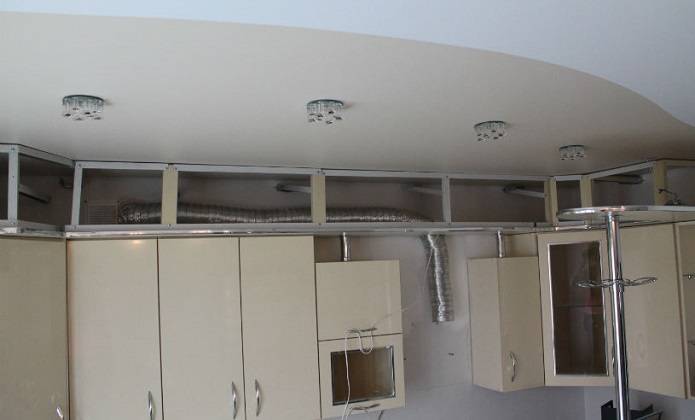
Plasterboard lining. In this case, a crate is mounted around the duct, on which drywall is then attached, and then finished, like the rest of the room. This option can be beautifully implemented, but it will be difficult to get to the duct if necessary.

-
Plastic box. On sale there are special plastic boxes designed specifically for decorating corrugations in the interior. A simpler and cheaper analogue of drywall sheathing.
-
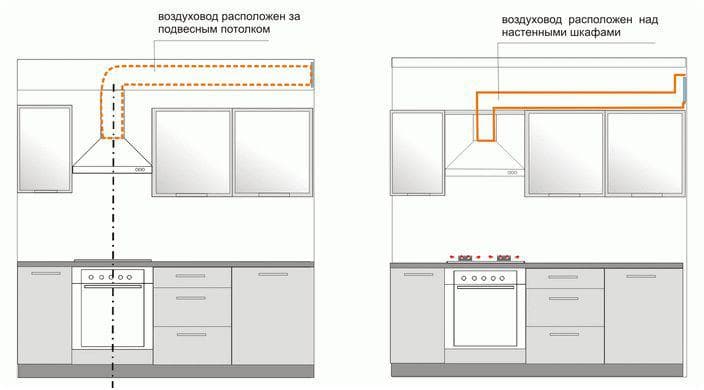
Installation above a false/stretch ceiling. In this case, the air duct rises from the hood up and hides under the ceiling structure. The segment going from the hood to the ceiling is either covered or left without decor. Of the minuses - the option is suitable only at the stage of repairing the premises (that is, if you buy a hood after the completion of the decoration, this will no longer work). And if you need to get to the air duct, you can do it only by dismantling the ceiling.

-
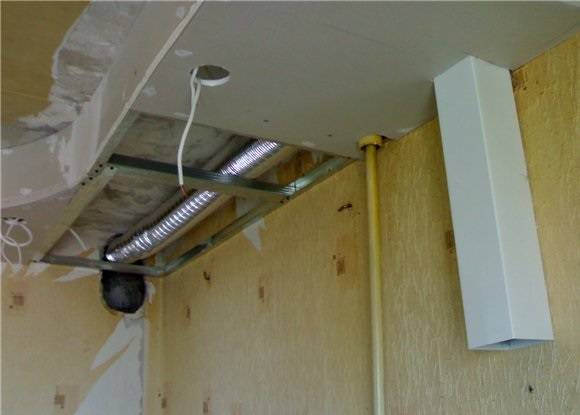
Embedding the hood and air duct in furniture (wall cabinets). In this case, a cabinet is hung on the wall (under the ceiling), and the air duct passes inside it. Of the minuses - the free space for various kitchen utensils is reduced.

-
Hinged "visor" on the locker.Budget version of the previous method. The cabinet is not made to the ceiling, the air duct is brought up from it and led to the ventilation shaft. A visor is installed on the cabinet, protruding upward - which will hide the air duct.

-
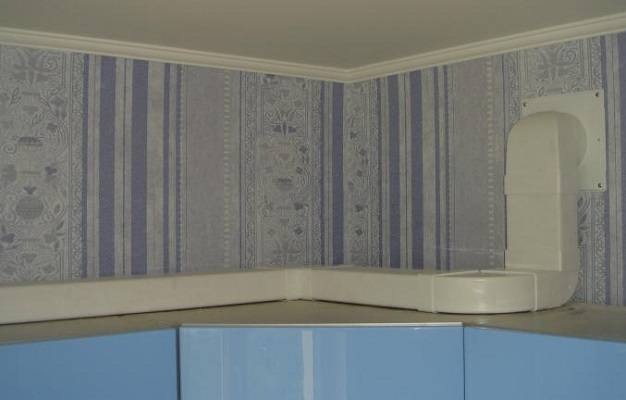
Laying the air duct above the kitchen cabinets close to the wall. If the cabinets are high and deep (protrude far), then the air duct will either not be visible at all, or it will not be so conspicuous.

-
Painting. The cheapest and easiest way is to paint the pipe to match the interior so that it does not catch the eye.
Little tricks: masking the duct
Whatever air duct you choose, it will not decorate the interior of your kitchen: there is something state-of-the-art in this detail. Therefore, it is better to hide the mounted structure:
- for a false ceiling, if any, in the kitchen. The vertical section of the duct can be sheathed with the same material from which the ceiling is made. To do this, you just need to build a frame from a metal profile around the pipe and attach sheathing sheets to it using self-tapping screws (with decorative heads). The frame itself is attached to the wall;
- in a decorative box. Many modifications of such boxes are produced. They differ in shape, material, color. You can purchase a box with spotlights built into it;
- you can immediately buy a built-in hood, then the air duct will be placed inside the cabinet or laid along its “roof”;
- you can make a decorative drywall box of any configuration yourself and insert lamps into it. Thus, you can create an exclusive element of the interior.
Correct and incorrect duct placement
The issue of disguise can be solved more simply: paint the pipe in accordance with the interior of the kitchen or paste over it with wallpaper.
Analysis of rumors and speculation
Rumor: Plastic sewer pipes, when used in a supply ventilation system, will emit harmful, and possibly toxic, substances, poisoning the air. They have a different purpose and harmful chemicals can be used in the production. Therefore, when arranging a ventilation system, it is better not to risk it.
All, without exception, manufacturers of sewer pipes have documentation confirming environmental safety. It is impossible to refute or confirm this, since the production technology is kept secret. The manufacturer can acquaint you with the quality certificate for their product.
Rumor: Polymer air duct sellers spread the word that sewer pipes quickly become electrified, which leads to dirt and dust sticking to the inner surface of the pipes.
The movement of air can indeed provoke the formation of an electrical static charge inside the pipe. It is strange why everyone is talking about fan products, because tin pipes are also electrified. It's all about processing.
Manufacturers of plastic air ducts must perform antistatic treatment. If you treat sewer plastic pipes with antistatic before installation, then the electrification property will disappear.
Brief overview of materials
The range of pipes, both flexible and rigid, is very large, it is not difficult to work with them, so they are appreciated by consumers. They are confidently replacing steel counterparts from the sphere of private construction.
Polymers such as polypropylene (PN), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyurethane (PPU), fluoroplastic (PVDF) are used for their production. PVC pipes are in the greatest demand.
Disassembly of PVC pipes
This inert polymer has sufficient rigidity. Its elasticity is increased by introducing plasticizers into the composition. Its glass transition temperature is quite high - 75⁰С.
Under normal conditions, the decomposition of the material takes decades, but at temperatures from 160 to 180⁰ C, it begins to break down very quickly. Because of this, it cannot be used for ventilation in rooms such as saunas, where the steam temperature sometimes reaches 200⁰.
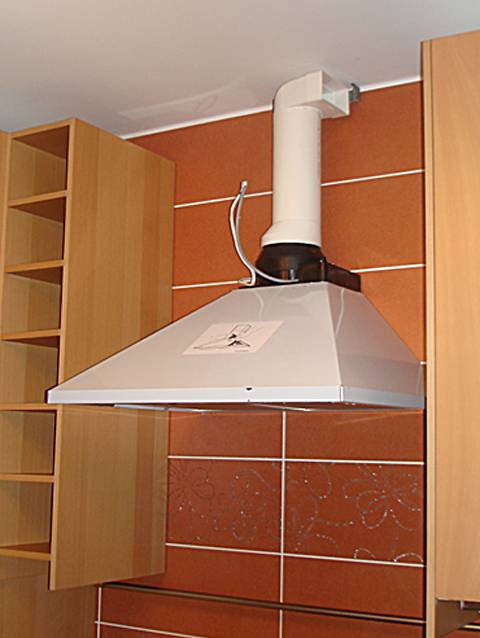

A rectangular PVC pipe is connected through adapters. When air passes through it, it remains motionless, so the hood almost does not make noise
When the material decomposes, carbon monoxide (CO) is released, the inhalation of which is accompanied by asphyxiation, hydrogen chloride (HCl), which forms hydrochloric acid in an environment with high humidity - an invisible liquid that announces itself with a pungent odor.
The compound has a very negative effect on health, in particular, on the condition of the respiratory tract. In severe cases, vision may deteriorate sharply.
From this we can conclude: PVC pipe is great for a kitchen hood, but only in those places if the temperature threshold does not exceed +120⁰С. Negative temperatures are also contraindicated for these pipes.
Polypropylene ventilation pipes
Polypropylene is a durable polymer, the hardest of the plastics and easy to transform. Its softening occurs at 140⁰С. Polypropylene does not withstand negative temperatures well - it immediately becomes brittle, brittle, therefore it is suitable only for internal use.
For the exhaust device, polypropylene pipes with the designation PN10 are taken. This type is characterized by such dimensions as outer diameter - 2-11 cm, wall thickness - 0.19-1 cm.

Polypropylene is a safe, reliable and simply ideal material for molding. In the photo, ventilation pipes and elements of plastic ventilation
Pipes made of polypropylene are single-layer and multi-layer.
The first includes products labeled:
- РРН - made of homopropylene;
- PPB - the material for the manufacture is a block copolymer of polypropylene;
- PRR - made from polypropylene random copolymer;
- РРs - flame-retardant material is used in the manufacture.
Multilayer pipes are reinforced with foil and fiberglass. They have increased rigidity and a small coefficient of thermal expansion. Products made of polypropylene are less strong than those of PVC, so they have thicker walls and their cost is higher.
Polyurethane ventilation pipes
The characteristics of polyurethane pipes are in many ways similar to PVC pipes. They are plastic and wear-resistant, they can be given any shape.
The main difference is the ability to remain unchanged until the temperature reaches 280⁰С. Above this threshold, polyurethane becomes very hazardous to health, as it releases nitrogen compounds.

On a pipe made of polyurethane, even under the influence of high stresses, cracks will not appear. It can be bent as you like, but as soon as the load disappears, the original shape of the product returns.
They are used in areas with complex trajectories, many turns and shifts.The presence of roughness on their inner surface somewhat reduces the aerodynamic characteristics of these pipes. The cost of such pipes is quite high.
Characteristics of PTFE pipes
Pipes made of this material have high strength characteristics. They have proven themselves in the temperature range from -40 to +140⁰С. Fluoroplast is recognized as the most slippery polymer, this fact is even recorded in the Guinness book.

Fluoroplastic pipes are exceptionally resistant even compared to precious metals. This material does not lose its characteristics in extreme conditions
They are resistant to aggressive alkaline and acid vapors, therefore they are indispensable for exhaust systems at chemical industrial enterprises. The diameter of the products ranges from 15 to 60 cm.
Due to their high cost, it is irrational to use them in the private sector. Also a limitation for their use is their increased gas permeability.
Features of air ducts
Each implementation has its own advantages and disadvantages. It all depends on the space that you can allocate for the placement of the duct.
- Rectangular sections are conveniently hidden behind kitchen cabinets. In addition, ducts of this configuration are available in separate sections, so you can assemble them into a duct of any length you need.
- Flexible ducts for exhaust can be placed at any angle, if necessary, stretch or compress (within the allowable range). True, it should be borne in mind that an insufficiently stretched duct has a higher resistance to air flow. This negatively affects the performance of the exhaust system.But, nevertheless, the user has a field for maneuver.
- Round air ducts are appropriate in a kitchen with a high ceiling: they are large-sized products.
- A variety of rectangular structures are flat ducts for exhaust. They take up little space and are not conspicuous. Manufacturers offer three sizes of flat systems:
- 110x55 mm (used for hoods with a capacity of not more than 300 m3 / h);
- 120x60 mm (used for equipment of hoods, the productivity of which does not exceed 350 m3 / h);
- 204x60 mm (suitable for pairing with high-performance hoods - up to 1000 m3 / h).
- Plastic exhaust ducts are the most popular: they are easier to maintain, and they are less noisy. Their inner surface is devoid of roughness, which has a very positive effect on reducing resistance to a minimum. But they have one significant drawback: when heated strongly, they can become a source of harmful substances released into the kitchen space.
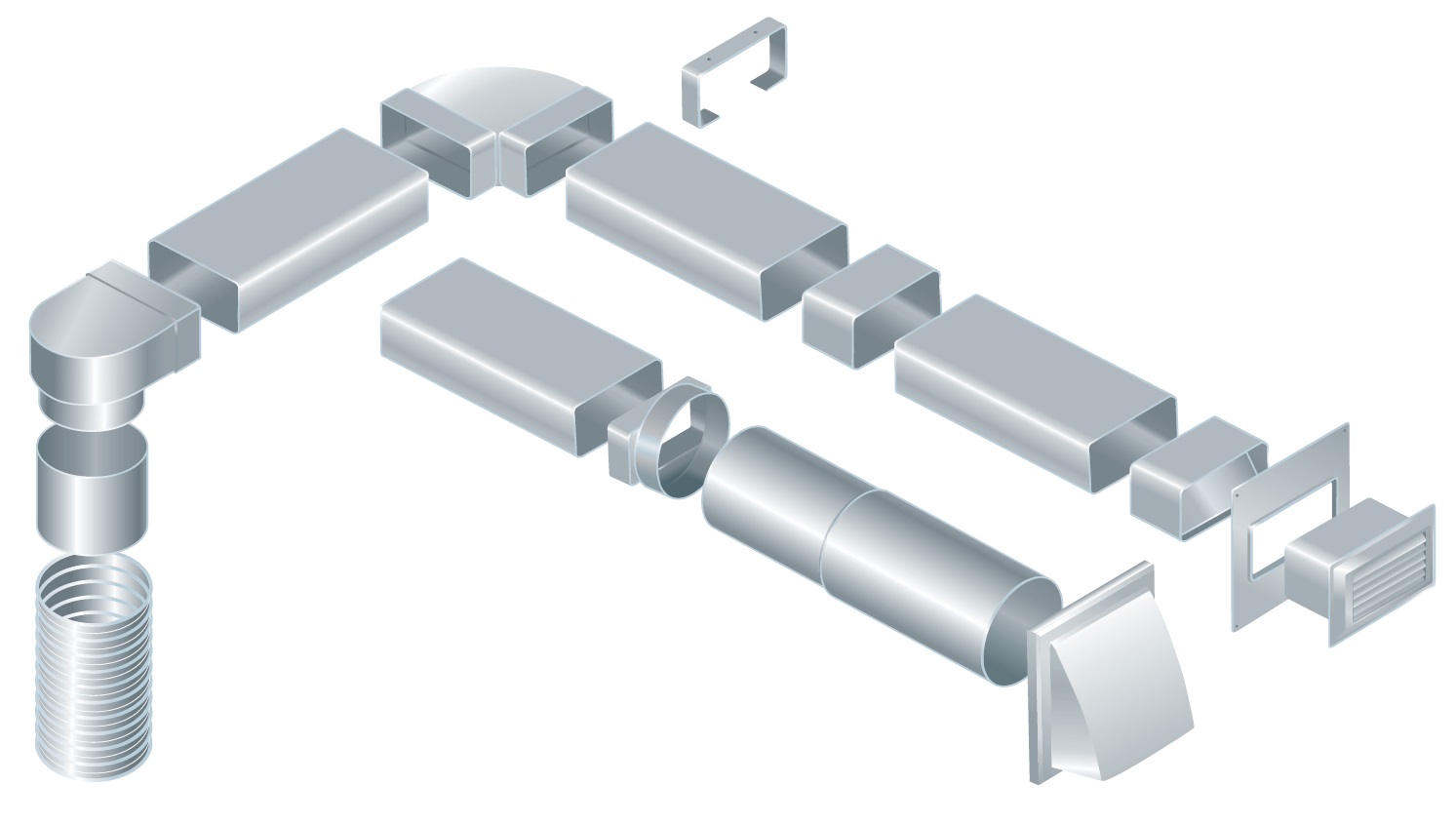
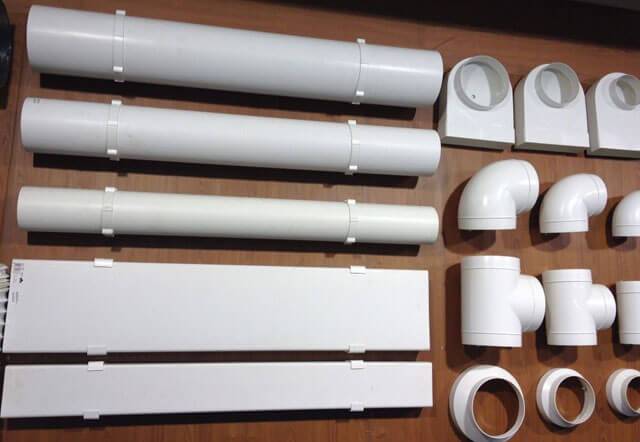
Flat duct and accessories
IMPORTANT! One more nuance: the maximum length of the corrugated duct should not exceed three meters. Each extra meter will "eat" from 5 to 10% of productivity