- Convert how many amperes kw online. Ampere to Watt Current Conversion Calculator
- How many watts in 1 ampere and amperes in watt?
- Power of household electrical appliances
- Convert Watts(W) to Amps(A).
- Converting amperes to kilowatts (single-phase network 220V)
- Converting kilowatts to amperes (single-phase network 220V)
- We translate amperes into kilowatts (three-phase network 380V)
- We translate kilowatts into amperes (three-phase network 380V)
- Volt ampere
- Translation rules
- Single phase electrical circuit
- Three-phase electrical circuit
- Basic rules for converting amperes to kilowatts in three-phase networks
- Connection of power and current in a three-phase network
- What is the difference between ampere and kilowatt
- History reference
- Frequently asked Questions
- 5 amps how many watts?
Convert how many amperes kw online. Ampere to Watt Current Conversion Calculator
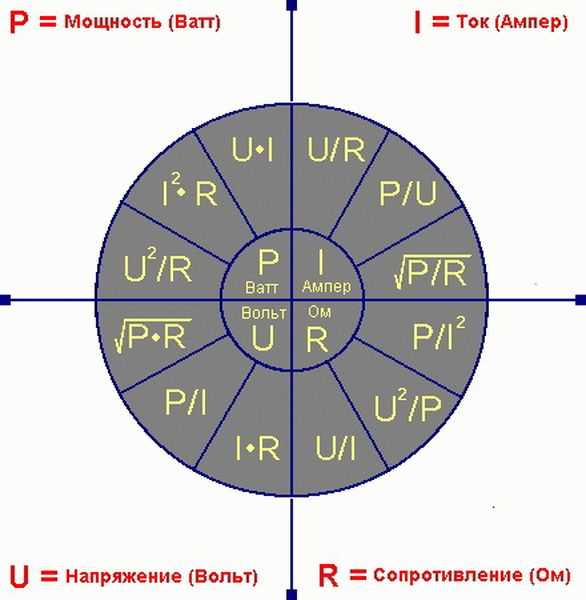
Power in an electrical circuit is the energy consumed by the load from the source per unit of time, showing the rate of its consumption. unit of measurement Watt . The current strength displays the amount of energy that has passed over the amount of time, that is, it indicates the speed of passage. measured in amperes . And the voltage of the flow of electric current (potential difference between two points) is measured in volts. The current strength is directly proportional to the voltage.
To independently calculate the Ampere / Watt or W / A ratio, you need to use the well-known Ohm's law. Power is numerically equal to the product of the current flowing through the load and the voltage applied to it. It is determined by one of three equalities: P \u003d I * U \u003d R * I² \u003d U² / R.
Therefore, in order to determine the power of the energy consumption source, when the current strength in the network is known, you need to use the formula: W (watts) \u003d A (amps) x I (volts).
And in order to make the reverse conversion, it is necessary to convert the power in watts to the power of current consumption in amperes: Watt / Volt.
When we are dealing with a 3-phase network, we will also have to take into account the coefficient 1.73 for the current strength in each phase.
How many watts in 1 ampere and amperes in watt?
- To convert Watts to Amps with AC or DC voltage, you need the formula:
- I = P / U, where
- I is the current strength in amperes; P - power in watts; U - voltage in volts, if the network is three-phase, then I \u003d P / (√3xU), since you need to take into account the voltage in each of the phases.
- The square root of three is approximately 1.73.
That is, in one watt 4.5 mAm (1A = 1000mAm) at a voltage of 220 volts and 0.083 Am at 12 volts.
When it is necessary to convert current into power (find out how many watts are in 1 ampere), then apply the formula:
P = I * U or P = √3 * I * U if calculations are carried out in a 3-phase 380 V network.
So, if we are dealing with a 12 volt car network, then 1 ampere is 12 watts, and in a 220 V household electrical network, such a current will be in an electrical appliance with a power of 220 W (0.22 kW). In industrial equipment powered by 380 volts, as many as 657 watts.
Power of household electrical appliances
Household electrical appliances usually have a power rating.Some lamps limit the power of the bulbs that can be used in them, for example, no more than 60 watts. This is because higher wattage bulbs generate a lot of heat and the bulb holder can be damaged. And the lamp itself at a high temperature in the lamp will not last long. This is mainly a problem with incandescent lamps. LED, fluorescent and other lamps generally operate at lower wattage at the same brightness and if used in luminaires designed for incandescent lamps there are no wattage problems.
The greater the power of the electrical appliance, the higher the energy consumption and the cost of using the appliance. Therefore, manufacturers are constantly improving electrical appliances and lamps. The luminous flux of lamps, measured in lumens, depends on the power, but also on the type of lamps. The greater the luminous flux of the lamp, the brighter its light looks. For people, it is high brightness that is important, and not the power consumed by the llama, so recently alternatives to incandescent lamps have become increasingly popular. Below are examples of types of lamps, their power and the luminous flux they create.
Convert Watts(W) to Amps(A).
Converting amperes to kilowatts (single-phase network 220V)
For example, take a single-pole circuit breaker, the rated current of which is 16A. Those. no more than 16A current should flow through the machine. In order to determine the maximum possible power that the machine can withstand, you must use the formula:
P = U*I
where: P - power, W (watt);
U - voltage, V (volt);
I - current strength, A (ampere).
Substitute the known values into the formula and get the following:
P = 220V * 16A = 3520W
The power turned out in watts. We translate the value into kilowatts, divide 3520W by 1000 and get 3.52kW (kilowatts). Those. the total power of all consumers that will be powered by a machine with a rating of 16A should not exceed 3.52 kW.
Converting kilowatts to amperes (single-phase network 220V)
The power of all consumers must be known:
Washing machine 2400 W, Split system 2.3 kW, microwave oven 750 W. Now we need to convert all values into one indicator, i.e. convert kW to watts. 1 kW = 1000 W, respectively, Split system 2.3 kW * 1000 = 2300 W. Let's sum up all the values:
2400W+2300W+750W=5450W
To find the current strength, power 5450W at a mains voltage of 220V, we use the power formula P \u003d U * I. Let's transform the formula and get:
I \u003d P / U \u003d 5450W / 220V ≈ 24.77A
We see that the rated current of the selected machine must be at least this value.
We translate amperes into kilowatts (three-phase network 380V)
To determine the power consumption in a three-phase network, the following formula is used:
P = √3*U*I
where: P - power, W (watt);
U - voltage, V (volt);
I - current strength, A (ampere);
It is necessary to determine the power that a three-phase circuit breaker with a rated current of 32A can withstand. Substitute the known values into the formula and get:
P = √3*380V*32A ≈ 21061W
We convert watts to kilowatts by dividing 21061W by 1000 and we get that the power is approximately 21kW. Those. a three-phase machine for 32A is able to withstand a load with a power of 21kW
We translate kilowatts into amperes (three-phase network 380V)
The current of the machine is determined by the following expression:
I = P/(√3*U)
The power of a three-phase consumer is known, which is 5 kW. The power in watts will be 5kW * 1000 = 5000W.Determine the current strength:
I \u003d 5000W / (√3 * 380) ≈ 7.6 A.
We see that for a consumer with a power of 5 kW, a 10A circuit breaker is suitable.
Volt ampere
Home > Theory > Volt Amp
Many have seen the designation in the form of V * A or volt amperes on electrical appliances. What it is, and how to correctly convert volt amperes to watts, we will find out below.
The simplest translation example
Based on the designation, we can distinguish:
On VA devices, as power, it can also be expressed in Russian letters, for example, 100 V * A.
note
So what is a volt ampere? This is voltage multiplied by current, indicating power.
Many are accustomed to noticing that VA power is usually considered to be watts, kilowatts, and so on, and in this formula, it is voltamperes that are visible. This is explained by the fact that this force has several concepts. She happens:
- Active (P);
- Reactive (Q);
- Full (S).
Watts are used to express active power, vars are used to express reactive power. Volt amperes are relevant to denote the total force. As a rule, such measurements are found in AC circuits, respectively, they always exceed the readings of active and reactive. In a word, full power will always be higher than active power. Let's analyze the concept of VA power with an example.
Power is when a certain active (useful) work is performed, for example, the fan blades rotate due to an electric motor.
If we take household appliances as an example, it will consume about 90 watts.
However, for the operation of the electric motor itself, auxiliary energy is required - reactive, due to which a magnetic flux is created, and all electronic components work.
To understand how to convert VA to VT, consider an example of the technical characteristics of such a device as an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). For this, the instruction manual for the device is useful. It should be understood that power supplies have losses, and quite significant ones, reaching 30%.
Let's look at the translation using the UPS as an example
The order looks like this:
- In the instructions, where the technical characteristics of the UPS are noted, we find indications of how much power it consumes. As a rule, the manufacturer indicates this data in voltamperes. The number indicates how much the device can consume from the mains (full power). Let's take 1500 VA as an example;
- Now the efficiency of the device is determined. Here, in order to competently make a translation, you need to know the quality of the UPS and how much equipment is connected to it. The level of efficiency can vary between 60-90%. For example, if the UPS works together with a printer, monitor and other equipment, then transfer it and get 65% (0.65). In the case of a PC and office equipment, a value within 0.6-0.7 is considered normal;
- To convert amps to watts, you need to find out the power of the UPS, for which there is the following formula:
B \u003d VA * efficiency.
The letter B denotes the active power (W), VA is the consumption in voltamperes (indicated in the operating instructions). Based on the example under consideration, the calculation will be as follows:
1500*0.65 = 975 (W).
This figure will be the active power consumption of the UPS. You may need a calculator to make counting easier.
Important! The active force cannot be higher than the total one.However, in the case of an incandescent lamp, the power readings will be identical. So, it is not difficult to correctly convert VA to W - for it is enough to know the technical characteristics of the device and a simple formula
How many volts the device consumes, as a rule, is indicated in the instructions for it.
So, correctly converting VA to W is not difficult - for it is enough to know the technical characteristics of the device and a simple formula. How many volts the device consumes, as a rule, is indicated in the instructions for it.
Translation rules
Often studying the instructions attached to some devices, you can see the designation of power in volt-amperes. Experts know the difference between watts (W) and volt-amperes (VA), but in practice these quantities mean the same thing, so nothing needs to be converted here. But kW / h and kilowatts are different concepts and should not be confused in any case.
To demonstrate how to express electrical power in terms of current, you need to use the following tools:
tester;
clamp meters;
electrical reference book;
calculator.
When converting amperes to kW, the following algorithm is used:
- Take a voltage tester and measure the voltage in the electrical circuit.
- Using current measuring keys, measure the current strength.
- Recalculate using the formula for DC or AC voltage.
As a result, power is obtained in watts. To convert them to kilowatts, divide the result by 1000.
Single phase electrical circuit
Most household appliances are designed for a single-phase circuit (220 V). The load here is measured in kilowatts, and the AB marking contains amperes.
In order not to engage in calculations, when choosing a machine, you can use the ampere-watt table.There are already ready-made parameters obtained by performing a translation in compliance with all the rules
The key to the translation in this case is Ohm's law, which states that P, i.e. power, equal to I (current) times U (voltage). Learn more about power, current, and voltage calculations, and the relationship of these quantities we talked about in this article.
It follows from this:
kW = (1A x 1 V) / 1 0ᶾ
But what does it look like in practice? To understand, consider a specific example.
Let's say the automatic fuse on the old type meter is rated at 16 A. In order to determine the power of devices that can be safely connected to the network at the same time, you need to carry out convert amps to kilowatts using the above formula.
We get:
220 x 16 x 1 = 3520 W = 3.5 kW
The same conversion formula applies for both direct and alternating current, but it is valid only for active consumers, such as incandescent lamp heaters. With a capacitive load, a phase shift necessarily occurs between current and voltage.
This is the power factor or cos φ
Whereas in the presence of only an active load, this parameter is taken as a unit, then with a reactive load it must be taken into account
If the load is mixed, the parameter value fluctuates in the range of 0.85. The smaller the reactive power component, the smaller the losses and the higher the power factor. For this reason, the last parameter is sought to be increased. Manufacturers usually indicate the value of the power factor on the label.
Three-phase electrical circuit
In the case of alternating current in a three-phase network, the value of the electric current of one phase is taken, then multiplied by the voltage of the same phase. What you get is multiplied by cosine phi.
The connection of consumers can be made in one of two options - a star and a triangle. In the first case, these are 4 wires, of which 3 are phase, and one is zero. In the second, three wires are used
After calculating the voltage in all phases, the data obtained are added up. The amount received as a result of these actions is the power of the electrical installation connected to the three-phase network.
The main formulas are as follows:
Watt = √3 Amp x Volt or P = √3 x U x I
Amp \u003d √3 x Volt or I \u003d P / √3 x U
You should have an idea about the difference between phase and linear voltage, as well as between linear and phase currents. In any case, the conversion of amperes to kilowatts is carried out according to the same formula. An exception is the delta connection when calculating loads connected individually.
On the cases or packaging of the latest models of electrical appliances, both the current and power are indicated. With these data, we can consider the question of how to quickly convert amperes to kilowatts resolved.
Specialists use a confidential rule for alternating current circuits: the current strength is divided by two, if you need to roughly calculate the power in the process of selecting ballasts. They also act when calculating the diameter of conductors for such circuits.
Basic rules for converting amperes to kilowatts in three-phase networks
In this case, the basic formulas will be:
- To begin with, to calculate Watt, you need to know that Watt \u003d √3 * Ampere * Volt. This results in the following formula: P = √3*U*I.
- For the correct calculation of Ampere, you need to lean towards the following calculations:
Amp \u003d Wat / (√3 * Volt), we get I \u003d P / √3 * U

You can consider an example with a kettle, it consists in this: there is a certain current, it passes through the wiring, then when the kettle starts its work with a power of two kilowatts, and also has a variable electric power of 220 volts. For this case, you need to use the following formula:
I \u003d P / U \u003d 2000/220 \u003d 9 Amps.
If we consider this answer, we can say about it that this is a small tension. When selecting the cord to be used, it is necessary to correctly and intelligently select its section. For example, an aluminum cord can withstand much lower loads, but a copper wire with the same cross section can withstand a load twice as powerful.
Therefore, in order to correctly calculate and convert amperes to kilowatts, it is necessary to adhere to the above induced formulas. You should also be extremely careful when working with electrical appliances so as not to harm your health and not spoil this unit, which will be used in the future.
From the school physics course, we all know that the strength of the electric current is measured in amperes, and the mechanical, thermal and electrical power is measured in watts. These physical quantities are interconnected by certain formulas, but since they are different indicators, it is impossible to simply take and translate them into each other. To do this, one unit must be expressed in terms of others.
Electric current power (MET) is the amount of work done in one second. The amount of electricity that passes through the cross section of the cable in one second is called the strength of the electric current. MET in this case is a directly proportional dependence of the potential difference, in other words, voltage, and current strength in the electrical circuit.
Now let's figure out how the strength of the electric current and power are related in various electrical circuits.
We need the following set of tools:
- calculator
- electrotechnical reference book
- clamp meter
- multimeter or similar device.
The algorithm for converting A to kW in practice is as follows:
1. We measure with a voltage tester in an electrical circuit.
2. We measure the current strength with the help of current-measuring keys.
3. With a constant voltage in the circuit, the current value is multiplied by the network voltage parameters. As a result, we get the power in watts. To convert it to kilowatts, divide the product by 1000.
4. With an alternating voltage of a single-phase power supply, the current value is multiplied by the mains voltage and by the power factor (cosine of the angle phi). As a result, we will get the active consumed MET in watts. Similarly, we translate the value into kW.
5. The cosine of the angle between the active and full MET in the power triangle is equal to the ratio of the first to the second. The angle phi is the phase shift between current and voltage. It occurs as a result of inductance. With a purely resistive load, for example, in incandescent lamps or electric heaters, the cosine phi is equal to one. With a mixed load, its values vary within 0.85. The power factor always strives to increase, since the smaller the reactive component of the MET, the lower the losses.
6. With an alternating voltage in a three-phase network, the parameters of the electric current of one phase are multiplied by the voltage of this phase. The calculated product is then multiplied by the power factor. Similarly, the MET of other phases is calculated. Then all values are summed up.With a symmetrical load, the total active MET of the phases is equal to three times the product of the cosine of the angle phi by the phase electric current and the phase voltage.
Note that on most modern electrical appliances, the current strength and the consumed MET are already indicated. You can find these parameters on the packaging, case or in the instructions. Knowing the initial data, converting amperes to kilowatts or amperes to kilowatts is a matter of a few seconds.
For electrical circuits with alternating current, there is an unspoken rule: in order to get an approximate power value when calculating the cross-sections of conductors and when choosing starting and control equipment, you need to divide the current strength by two.
Connection of power and current in a three-phase network
The principle of calculating power and current for three-phase networks remains the same. The main difference lies in a slight modernization of the calculation formulas, which allows you to fully take into account the features of the construction of this type of wiring.
The expression is traditionally taken as the basic ratio:
W \u003d 1.73 * U * I, (4)
where U in this case is the line voltage, i.e. is U = 380 V.
From expression (4) follows the profitability of using three-phase networks in justified cases: with such a wiring diagram, the current load on individual wires drops to the root of three times with a simultaneous threefold increase in the power delivered to the load.
To prove the last fact, it suffices to note that 380/220 = 1.73, and taking into account the first numerical coefficient, we get 1.73 * 1.73 = 3.
The above rules for the connection of currents and power for a three-phase network are formulated in the following form:
- one kW corresponds to 1.5 A of current consumption;
- one ampere corresponds to a power of 0.66 kW.
We point out that all of the above is true in relation to the case of connecting the load by the so-called star, which is most often encountered in practice.

It is also possible to connect with a triangle, which changes the rules of calculation, but it is quite rare and in this situation it is advisable to contact a specialist.
What is the difference between ampere and kilowatt
The fundamental difference between the units of measurement of the parameters of the electrical network, which are placed in the title of this section, is that they represent a numerical measure of various physical quantities.
In this case:
- amperes (abbreviation A) show the strength of the current;
- watts and kilowatts (abbreviations W and kW, respectively) characterize active (actually useful) power.
In practice, an extended description of power is also used with its measurement in volt-amperes and, accordingly, kilovolt-amperes, which are briefly referred to as VA and kVA.
They, unlike W and kW, which describe active power, indicate apparent power.
In DC circuits, the total and active powers are the same. Similarly, in an AC network with a low power load, at the engineering level of rigor, the difference between W (kW) and VA (kVA) can be ignored, i.e. work only with the first two units.
For such circuits, the following simple relation applies:
W = U*I, (1)
where W is the (active) power in watts, U is the voltage in volts, and I is the current in amps.
With an increase in load power to a level of a thousand watts and above for direct current, relation (1) does not change, and for alternating current it is advisable to write it as:
W = U*I*cosφ, (2)
where cosφ is the so-called power factor or simply “cosine phi”, showing the efficiency of converting electric current into active power.
Physically, φ is the angle between the AC and voltage vectors or the angle of the phase shift between voltage and current.
A good criterion for the need to take this feature into account are those cases when VA or kVA are indicated instead of kW in the passport data and / or on the body nameplates of electrical appliances, mostly powerful, with a consumption of more than 1 kW.
Usually for household electrical devices with powerful electric motors (washing machines and dishwashers, pumps and the like), cosφ = 0.85 can be set.
This means that 85% of the consumed energy is useful, and 15% forms the so-called reactive power, which continuously transfers from the network to the load and back until it is dissipated in the form of heat during these transitions.
At the same time, the network itself should be designed specifically for full power, and not for useful power. To indicate this fact, it is indicated not in watts, but in volt-amperes.
As a unit of measurement, watts (volt-amperes) are sometimes too small, which leads to numbers that are difficult to visually perceive with a large number of characters. Given this feature, in some cases, power is indicated in kilowatts and kilovolt-amperes.
For these units, the following is true:
1000W = 1kW and 1000VA = 1kVA. (3).
History reference
The symbol L, used for inductance, was adopted in honor of Emil Khristianovich Lenz (Heinrich Friedrich Emil Lenz), who is known for his contribution to the study of electromagnetism, and who derived Lenz's rule about the properties of induced current.The unit of inductance is named after Joseph Henry, who discovered self-induction. The term inductance itself was coined by Oliver Heaviside in February 1886.
Among the scientists who took part in researching the properties of inductance and developing its various applications, it is necessary to mention Sir Henry Cavendish, who conducted experiments with electricity; Michael Faraday, who discovered electromagnetic induction; Nikola Tesla, who is known for his work on electrical transmission systems; André-Marie Ampere, who is considered the discoverer of the theory of electromagnetism; Gustav Robert Kirchhoff, who researched electrical circuits; James Clark Maxwell, who studied electromagnetic fields and their particular examples: electricity, magnetism and optics; Henry Rudolph Hertz, who proved that electromagnetic waves do exist; Albert Abraham Michelson and Robert Andrews Milliken. Of course, all these scientists have also explored other problems that are not mentioned here.
Frequently asked Questions
-
If we are talking about the car network, then in one ampere 12 watts at a voltage of 12V. In household power supply 220 volt, the current strength of 1 ampere will be equal to the power of the consumer at 220 watts, but if we are talking about an industrial network 380 Volt, then 657 watts per amp.
-
How many watts of power at 12 amperes of current consumption will depend on the voltage the consumer works with in the network. So 12A it can be: 144 watts in a 12V car network; 2640 watts in a 220V network; 7889 watts in the mains 380 volts.
-
The current strength of a consumer with a power of 220 watts will differ depending on the network in which it operates.It can be: 18A at a voltage of 12 Volts, 1A if the voltage is 220 Volts, or 6A when current consumption occurs in a 380 Volt network.
-
5 amps how many watts?
To find out how many watts a source consumes for 5 amperes, it is enough to use the formula P \u003d I * U. That is, if the consumer is connected to a car network where there are only 12 volts, then 5A will be 60W. When consuming 5 amperes in a 220V network, it means that the consumer's power is 1100W. When the consumption of five amperes occurs in a two-phase 380V network, the source power is 3290 watts.










![Unit Converter Convert millijoule/second [mJ/s] to volt-ampere [va] • Power Converter • Common Unit Converters • Compact Calculator • Online Unit Converters](https://fix.housecope.com/wp-content/uploads/0/6/a/06a2fc3fb793cbfcd590ea0a0796039a.jpeg)









