- Greenhouse heating options
- Criterias of choice
- Biological heating of the greenhouse with biofuel
- The main design features of the thermos greenhouse
- How does it work
- 2.3 Air heating of greenhouses
- Polyethylene sleeve and heat generator
- Trumpet and fire (open fire)
- Heat fan (fixed or portable)
- Option # 4 - furnace heating
- Electric heating
- Mixed planting of vegetables in the garden, in the greenhouse, schemes, videos
- Check Also
- Electric heating
- Pit construction and site selection
- Design features
- Heating systems for greenhouses in different climates
- Winter greenhouses in warm climates
- Winter greenhouses in temperate climates
- Winter greenhouses in cold climates
Greenhouse heating options
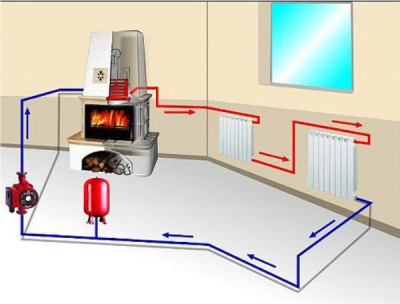
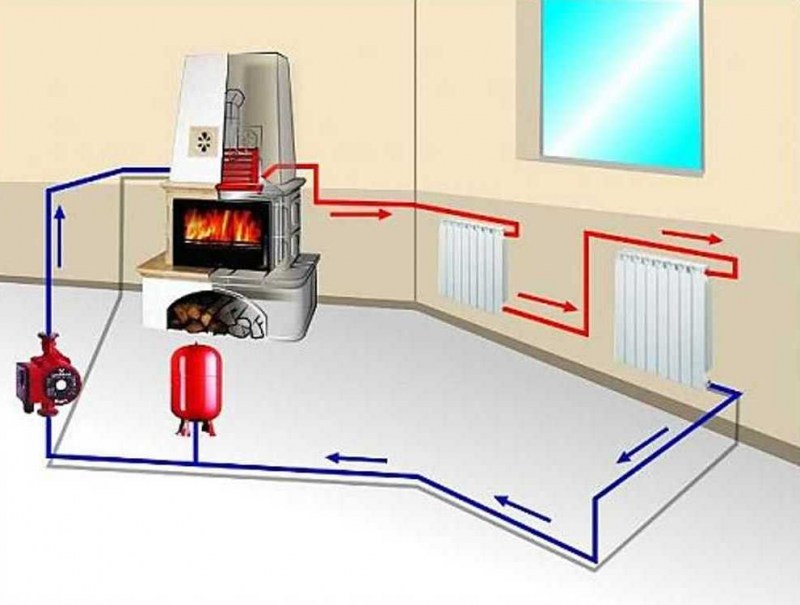
There are various ways of heating a winter greenhouse: gas, air, water, stove, electric.
All of these methods have certain advantages and disadvantages, so you need to consider all systems.
For example, there is no need to install complex expensive heating systems suitable for industrial premises in small greenhouses.
Video:
Only the correct calculation will allow to obtain the correct distribution of heat.
As already mentioned, only the correct calculation will ensure high-quality heating of the winter greenhouse.The calculation is necessary to determine the volume of the heating system, the power of the boilers and the number of radiators.
Heating a polycarbonate greenhouse requires making calculations in advance and carefully.
The calculation is made on the basis of indicators such as design parameters, ambient temperature. Having made the calculation, you can choose the desired method of heating.
The result is a heated greenhouse even in winter, when the earth and plants need warmth.
Heating is provided by hot water flowing through a pipeline located in the ground.
This heating system is a closed arrangement of pipes in which water circulates until it cools, and then enters the boilers for heating.
The cycle with the boiler is repeated until the system is turned off.
The water method has its drawbacks: slow heating of pipes, expensive boilers, constant monitoring.
The main component of the water system is the boiler, in which water is heated and then fed into the pipes using a pump. Pipes are installed plastic, copper and steel.
Plastic pipes are ideal for ground heating.
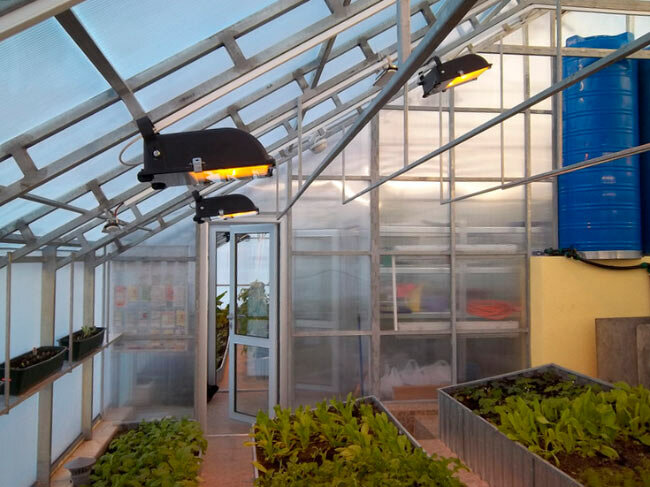
With infrared heating winter greenhouse heating can be carried out by an infrared lamp and an infrared heater.
Heating a greenhouse with an infrared heater has the following advantages:
- High intensity of heat transfer;
- Only the soil and plants are heated, while the air is not heated;
- Profitability, since the heater does not work constantly - it turns on at the moment when it is necessary to maintain a certain temperature. To do this, you can install a thermostat that will control the desired temperature.
An additional plus is the safety of infrared rays for people and plants, as natural climatic conditions are created for growing plants.
In this case, an important point is the competent calculation of the required heating power.
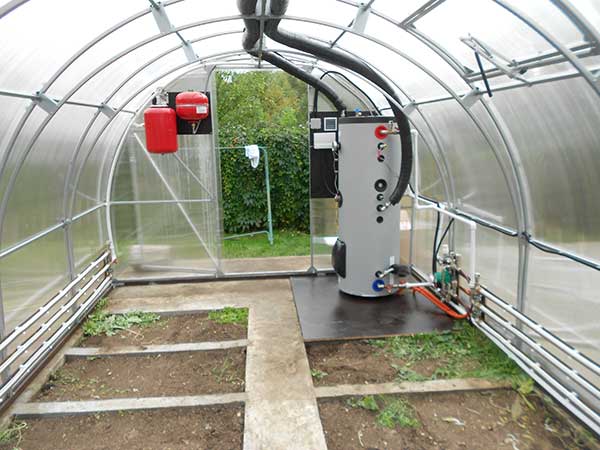
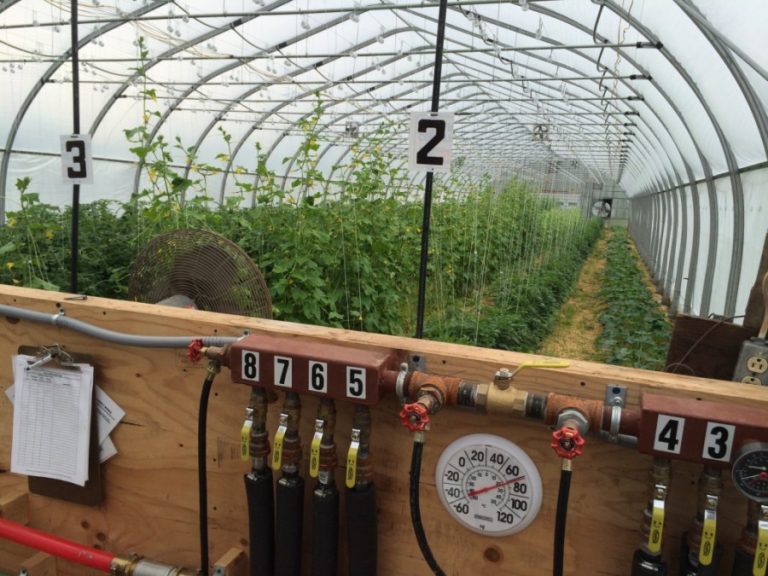
The next type of heating is air, which is based on boilers. The heat carrier here is air.
The work is carried out according to the following principle: the air is heated between the boiler and the furnace and then distributed through the air ducts. such heating is also suitable for industrial scale.
The heating of the soil is carried out by warm air, which comes from polyethylene sleeves laid out along the perimeter of the greenhouse structure.
This type of heating has a high heating rate, regardless of the area.
Heating with wood in a winter greenhouse is considered one of the inexpensive options.
Heating a greenhouse with wood has the following advantages: rapid heating of the room, maintaining the temperature at the required level for a long time, cost-effectiveness.
Solar heating is often used, in which the accumulation of solar energy that can maintain the required temperature occurs.
Video:
The gas heating system has a stable supply, but the disadvantage is the production of hydrocarbons, which harms plants, so it is recommended to ventilate the greenhouse.
The device of the gas heating system depends on the frequency of use.
So, for example, if the heating will be turned on for a short time, then cylinders can be used without pipelines.
To eliminate combustion waste, an exhaust hood is installed, which also prevents the release of gas into the air.
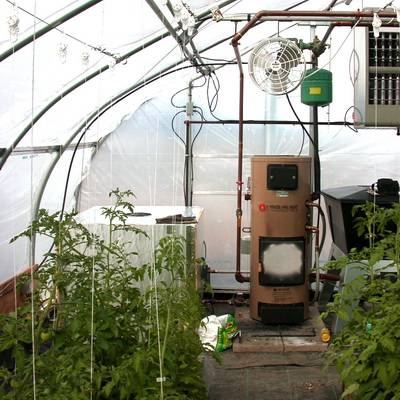
It is possible to organize furnace heating of a winter greenhouse, which is more economical than electric heating. Using a stove is great for heating a polycarbonate greenhouse.
The furnace can be fired with wood. The construction of the furnace can be done by hand without significant financial costs. The choice of furnace should be carried out based on the scale of the greenhouse.
with pyrolysis boiler heating system will be more perfect.
Criterias of choice
In principle, heating a greenhouse is possible using a variety of stoves and heaters, as long as the generated power allows you to create the desired temperature in a certain area. But if we are not talking about the “principle”, but about the practical use of certain solutions, we need to think about completely different things. Yes, the most the best projects of heating systems will be useless if their size does not allow the use of a particular device in a particular room. The power of devices varies not only according to the area, but also according to the material - it has long been known that heat loss through polyethylene is higher than through polycarbonate.


The next important criterion is the amount of costs, and one should take into account both the costs of the components, their installation, and subsequent use. Some types of heaters are completely impractical in small greenhouses, others are installed at a minimal price, but during operation they consume a large amount of fuel or energy.


Steam heating is justified if it is possible to connect the greenhouse to the heating system of the house. It is desirable to insulate the pipes properly, and it will be necessary to create a significant margin in boiler power. It is undesirable to use such a system when the distance from the dwelling to the greenhouse is more than 10 m.An autonomous steam heater can be installed in the greenhouse itself, water circulation is provided by special pumps.
In early spring, it is recommended to use solid fuel boilers and stoves, as they resist frost well. Boilers are better than stoves, because they do not require frequent addition of fuel, it is spent very efficiently. Solid fuel boilers should not be placed directly in the greenhouse, so as not to dry out the air, in extreme cases, humidifiers must be placed nearby.


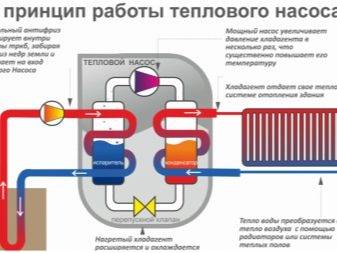
Geothermal heating of a greenhouse is practiced only occasionally, because heat pumps are expensive and very difficult to install. It is desirable to create an integrated heating system that simultaneously warms up not only the greenhouse, but also the house
Important: heat pumps are needed for liquid soil heating systems, they are not capable of supplying water to radiators
Water circulates through them, while it warms up quite strongly and enters a special line. Solar panels (or, in other words, photovoltaic panels) are not suitable for heating greenhouses, since they are designed to generate electricity. It is advisable to use, along with collectors, gas boilers, stoves, heat pumps and other means of heating in order to insure yourself at night.

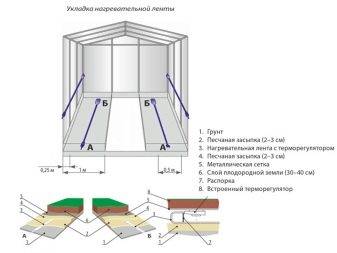
Thermal tape in the greenhouse is used quite often. In composition, it is a glass thread, supplemented by a thermostat. Inside there are eight nichrome strands surrounded by water-impervious rubber. The device works stably only in the temperature range from 15 to 20 degrees, which allows you to consume current only as needed.Each part of the plant is heated in the same way, the only alternative that can achieve the same effect is heating with manure. But the tape is better than it already because it helps to warm up the greenhouse in almost any weather, and not just in the warmer months.
With the help of the tape, the death of plants is prevented during sudden frosts.
Quite often, a lamp or even a row of lamps is used for the purpose of heating. Infrared heating of this type is directed from top to bottom and effectively affects the entire plant, and also warms up the soil layer. According to studies, such systems increase germination by 30-40%.

Biological heating of the greenhouse with biofuel
The essence of the biological heating of the greenhouse is that aerobic bacteria that decompose organic materials (manure, sawdust, garbage) with air access release heat in an amount sufficient for heating.
Biofuel refers to any organic material that can be consumed by microorganisms, releasing thermal energy. The temperature of biofuel can reach +72°C, so the process of decomposition of biofuel with the release of heat is called combustion. Hot biofuels are used in greenhouses to maintain temperature at the optimal level for plants.
The following are used as biofuels:
- animal manure mixed with loosening materials (straw, sawdust, horse peat, leaves), see table 2
- waste from woodworking enterprises (bark, shavings, sawdust, chips), see table 3,
- urban waste, consisting of organic waste, see Table 3.
| Characteristics of biofuel | Manure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse | Bovine | Pork | Sheep | |
| Weight 1m3, kg | 350-450 | 400-500 | 400-500 | 550-700 |
| Acidity, pH | 8-9 | 6-7 | 7-8 | 6-7 |
| Humidity, % | 65-70 | 75-80 | 65-67 | 73-77 |
| Max. stack temperature, °C | 60-72 | 40-52 | 55-60 | 20-30 |
| Interruption period, days | 7-9 | 18-20 | 9-10 | 20-30 |
| Avg. temperature, °C | 33-38 | 12-20 | 30-35 | 14-16 |
| Duration of burning, days | 70-90 | 75-100 | 90-120 | 60-70 |
| Characteristics of biofuel | Household waste | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sawdust | Bark | household waste | Garbage compost | |
| Weight 1m3, kg | 150-200 | 400-500 | 700-750 | 650-750 |
| Acidity, pH | 5-6 | 5-7 | 7-9 | 7-8 |
| Humidity, % | 30-40 | 60-75 | 35-60 | up to 50 |
| Max. stack temperature, °C | 30-40 | 40-50 | 60-65 | 50-60 |
| Interruption period, days | 20-25 | 10-15 | 10-12 | 5-7 |
| Avg. temperature, °C | 15-20 | 20-25 | 36-48 | 30-35 |
| Duration of burning, days | 40-60 | 100-120 | 80-100 | 120-180 |
Read more about the characteristics of biofuels in the article: Manure and straw; wonderful greenhouse! Biofuel for greenhouse heating
If necessary, to protect the biofuel from combustion, it is stacked and compacted. In the compacted state, biofuel will not burn or will burn weakly.
To warm up the biofuel, it is interrupted and placed loosely in a stack, hot stones or burning coal are placed inside the stack. After 3-5 days, the biofuel starts to burn and can be used to heat the greenhouse.
Biofuels heat up well in the presence of nitrogenous nutrients. Therefore, sawdust is watered with slurry or animal urine. Mixing manure with wood waste has a good effect. Active activity of microorganisms is possible with sufficient moisture content. Therefore, biofuels are moistened if necessary.
The temperature of the biofuel reaches a maximum a week after heating, and then begins to decrease. The release of heat continues for 2-3 months, gradually fading.
Heating the greenhouse with biological waste helps to dispose of it, rationally using the energy stored in biofuels, and also improves the air-gas environment in the greenhouse by releasing a large amount of carbon dioxide, which plants need for photosynthesis.
The spent biofuel is suitable as an organic fertilizer both in the greenhouse and in the open field.
Biofuel stacking. Hot biofuel is laid in the greenhouse loose, evenly distributed over the area and slightly compacted with a pitchfork. Fertile soil is poured onto biofuel with a layer of 15–18 cm for growing seedlings; if seedlings are grown in pots, then the layer of earth is reduced to 7–8 cm. When growing vegetable plants, the thickness of the earth layer should be increased to 20 cm.
Sowing and planting of plants begin after the soil warms up to the optimum temperature.
The disadvantage of biological heating is that it is impossible to control the thermal regime if it is necessary to raise the temperature to the required level.
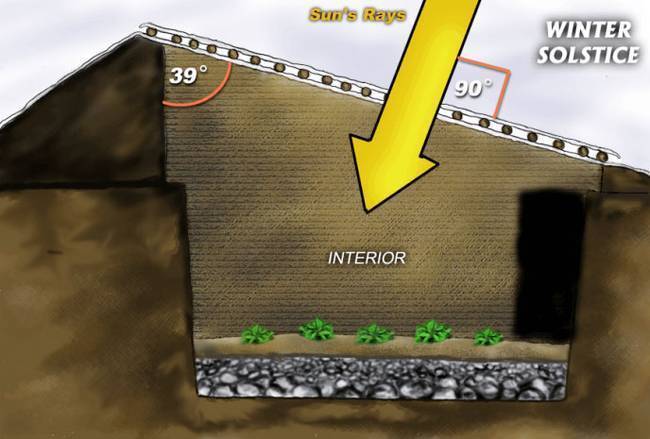
The main design features of the thermos greenhouse
This is a rather expensive capital structure that requires a significant investment, but with a good payback and simple operation. Its uniqueness lies in the following:
- The greenhouse is designed in such a way that the possibility of heat escaping through the floor and walls is reduced to a minimum, and the interior space is heated as much as possible thanks to the sun's rays penetrating through the roof.
- All such structures are buried in the ground, since the soil does not freeze below the level of 2 m, and the ground maintains a positive temperature all year round without much fluctuation.
- A special feature is the frequent arrangement of a shed roof, due to the slope of which the sun's rays fall on the light-absorbing surface at an angle closest to a straight one. In the greenhouse, one wall (northern) is specially made opaque and covered with a black film inside, arranging a kind of heat accumulator (solar collector).
- The inner space of the walls is covered with reflective and heat-insulating material, so there is very little shadow and bright natural light in the room.
- With proper construction and the use of high-quality materials, the service life and reliability of work is much longer than that of ordinary structures.
- It becomes possible to breed heat-loving crops from the tropics and subtropics in regions with a temperate climate and in the north.
How does it work
The operation of the greenhouse is based on the principle of light transmission. For the arrangement of the structure, a technology is used that allows you to maintain the optimal temperature not only during the day, but also at night. Temperature changes during the night hours are insignificant. The difference with daily indicators is only 5-7 degrees.
At the same time, in the heat, the temperature in the greenhouse does not change. So, if on the street the indicator is + 45С, then inside the building it is + 25-30С.
The recessed greenhouse is characterized by good illumination. This indicator is several times better than that of a conventional above-ground greenhouse.

The recessed greenhouse is characterized by good illumination
Thanks to this, the microclimate necessary for the growth and development of plants is created in the building. It is underground greenhouses that help to get a rich harvest.
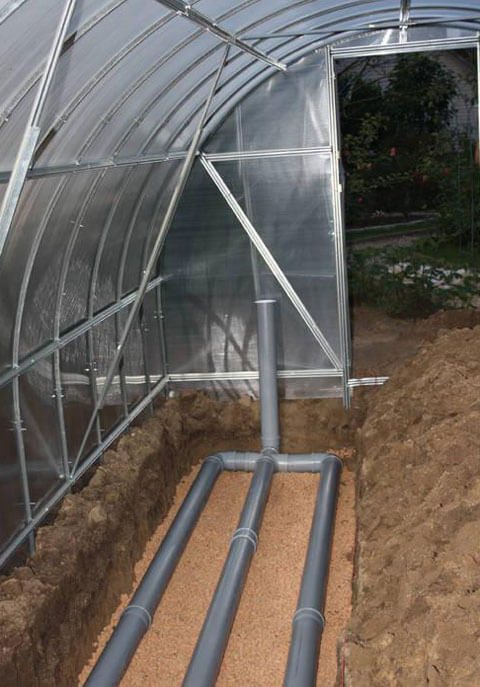
2.3 Air heating of greenhouses
Polyethylene sleeve and heat generator
The system consists of a polyethylene sleeve and a thermal
generator. The sleeves are filled with air and thanks to the perforation arranged in it
give it over the entire area of the greenhouse. Although the initial cost
for the arrangement of the system are small, it is not widely used in
for reasons such as:
no ground heating. Polyethylene sleeves are usually
located on top so that warm air does not burn the foliage. Thus, to
very little heat reaches the soil, and the root system develops poorly.
Advice. It is not necessary to improve this system by
laying sleeves around the perimeter of the greenhouse. The distance between them and the nearest
plant is up to half a meter, and this leads to irrational
use of the greenhouse area.
the need for constant monitoring of humidity levels. Steam,
coming from the sleeve, strongly dries the air, which negatively affects growth
plants.
fast cooling. The air that has ceased to be heated,
cools instantly, unlike water, which gives off heat for a long time.
Trumpet and fire (open fire)
A primitive version of this system is the installation
pipes with a diameter of 50-60 cm. One of its ends is brought out into the greenhouse, and the other into the street.
A fire is built under the street tip. And if you constantly keep the fire
in it, then theoretically it will be warm in the greenhouse. However, this heating scheme
greenhouses, is more suitable for emergency heating of plants than for
permanent. Because the smokeiness of the greenhouse does not contribute to the increase
cult productivity.
Heat fan (fixed or portable)
The fan allows you to heat the air in the greenhouse without creating
additional pipe system or polyethylene sleeves.
The advantage of the system in the rapid heating of the air, 100% efficiency,
mobility, low weight, the ability to control the air temperature, which
served. When there is no need for heating, the fan can simply
promote the movement of air masses. After all, the ventilation of the greenhouse is the same
an important part of life, like heating.
Among the disadvantages: a small area heated by one
fan, the likelihood of burning the leaves with a direct stream of heated air,
significant electricity bills.
Option # 4 - furnace heating
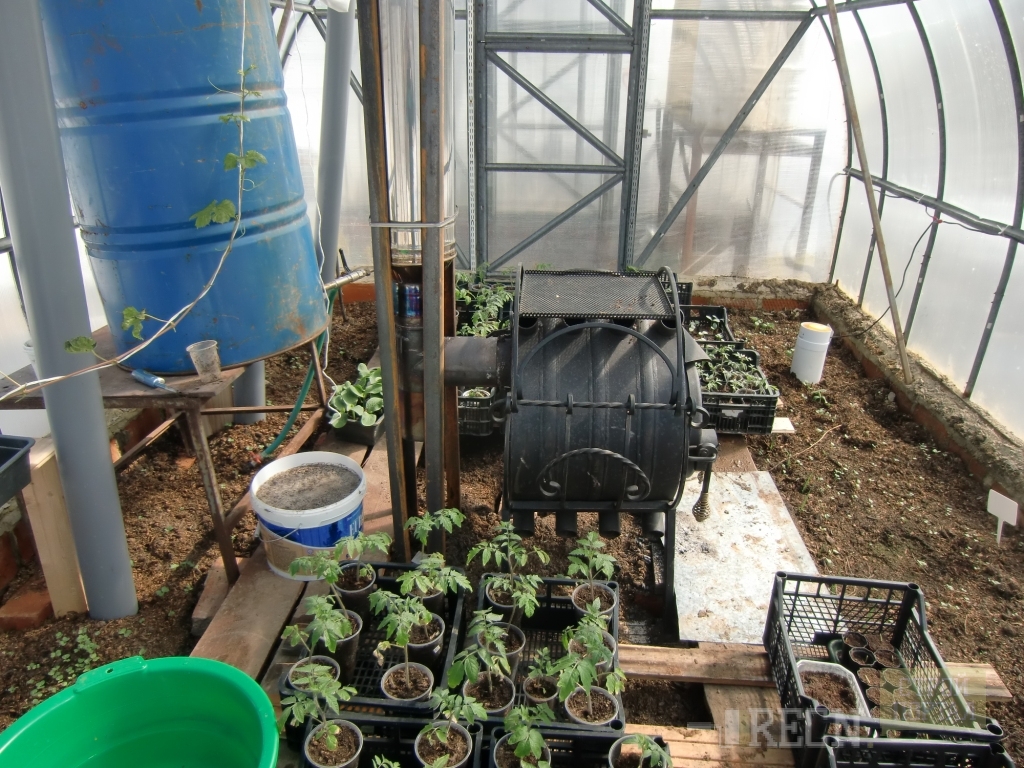
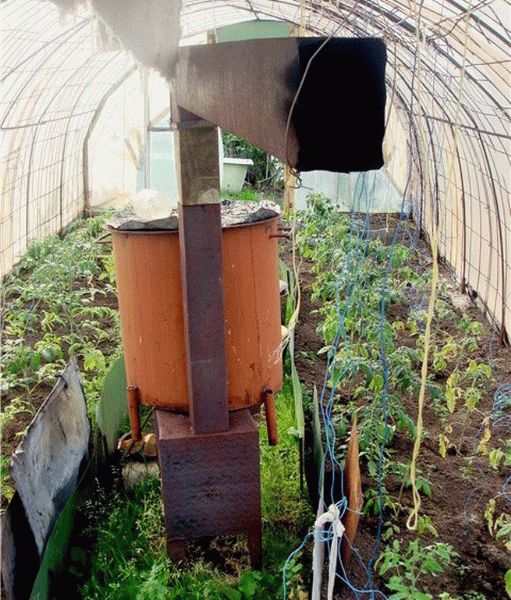
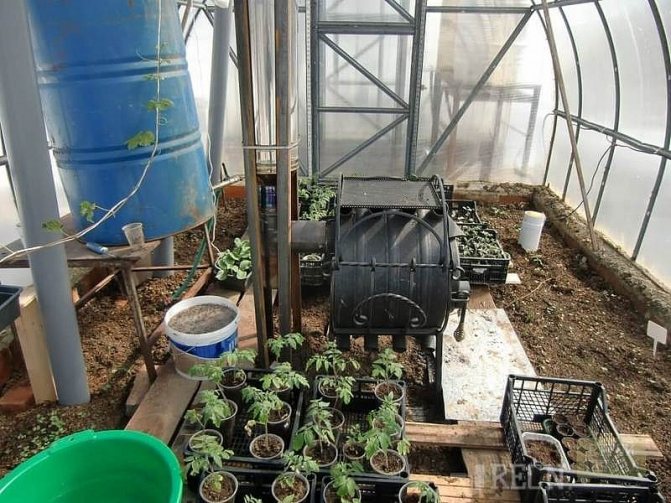
Unlike electric heating, classic stove heating is not so financially burdensome. So, you can build a simple greenhouse stove with a hog or a horizontal chimney with your own hands and at no special cost. Its device principle is quite simple:
- Step 1. A brick firebox is laid out in the vestibule of the greenhouse.
- Step 2. A chimney is laid out along the entire length of the greenhouse, either under the beds or under the racks.
- Step 3. This chimney is removed from the greenhouse on the other side so that carbon monoxide leaves, and all the heat remains inside the building. As a result, the distance between the end wall of the greenhouse and the firebox itself should be at least 25 cm, but from the garden bed or rack with plants to the top of the hog - from 15 cm.
Or in this way:
- Step 1. You need to take a large barrel, with a capacity of about 3 cubes, and paint it from the inside in 2 layers so that it does not rust.
- Step 2. Holes are made inside the barrel for a chimney, a stove, an expansion barrel on top and a drain valve on the bottom.
- Step 3. The stove is boiled and inserted into the barrel.
- Step 4A chimney is removed from the barrel, and a pipe 5 meters high is placed on the street.
- Step 5. A home-made expansion tank of 20 liters is installed on top of the barrel, which is pre-cooked from simple sheet iron.
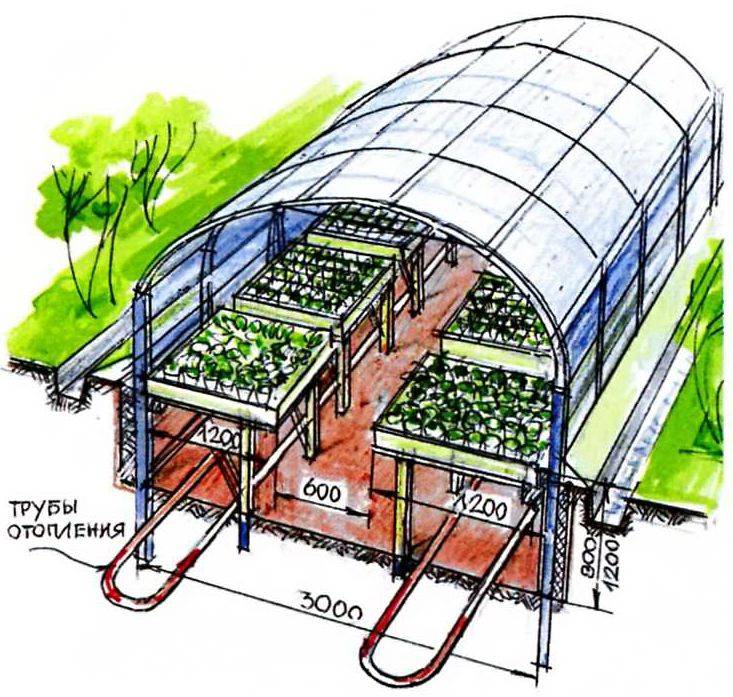
- Step 6. Heating is cooked from a profile pipe 40x20x1.5, and the pipes are laid out on the ground at a distance of 1.2 m. So they must be laid out so that the soil near the roots of the plants warms up well.
- Step 7. To circulate water in such a home-made heating system, a special, but inexpensive pump is purchased.
You can heat such a stove with any wood, and the drain tap at the bottom of the barrel can be used not only to drain water, but also for drip irrigation when the water itself has cooled. To control the temperature in such a greenhouse, inside it can be installed electronic temperature sensor, and the digital display itself is right in the house.
Electric heating
If we consider options for heating a greenhouse in winter, we can note the predominance of electrical systems. Among the many methods, gardeners usually choose one of the following:
- Electrical cable
- Heating mats
- Convection units
- Heat pumps
- Infrared heaters
One of the simplest and most popular methods is heating greenhouses with a convector. It is an installation with spirals inside, through which the air is heated. Air currents are distributed evenly throughout the greenhouse, however, the warmest masses accumulate at the top. It is recommended to use the convection method in conjunction with the biological methods considered later, since it is not able to warm the soil on its own.
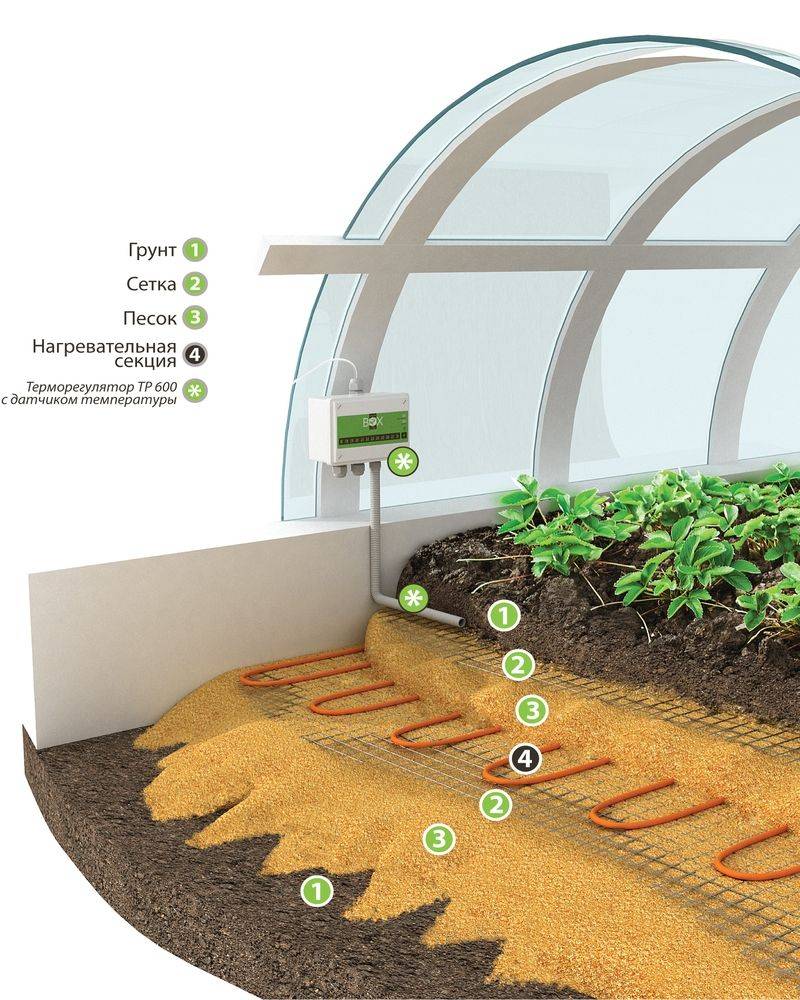
The use of heating mats or electric cable is a very effective and inexpensive method of heating a greenhouse in winter. Their main advantage is the possibility of laying in those areas that the summer resident needs (outside the greenhouse, between rows, etc.). The option when the heating elements are located directly in the ground is popular. However, if you make a mistake with the temperature, you can overheat the root system of plants.
Despite their effectiveness, heat pumps for heating greenhouses have not received wide distribution. The reason for this is the high cost of installing the necessary equipment. If the greenhouse is small and is being built for personal purposes, you should not expect a return on investment.
A very interesting and popular option for heating greenhouses - installation of infrared heaters. If you correctly design the system, it will be possible to warm up individual parts of the greenhouse in which plants germinate. Having tried, the entire area can be divided into zones, setting in each of them the temperature suitable for a particular crop being grown.

Of course, heating a greenhouse in winter has one significant advantage - the possibility of their joint use with temperature sensors. Having made the correct setting, a constant desired air temperature will be maintained inside the greenhouse. The market offers numerous additional equipment designed to normalize the climate inside.
Mixed planting of vegetables in the garden, in the greenhouse, schemes, videos

Check Also
Spring and autumn planting of irises in open ground It is irises that look incredibly beautiful in a garden or in a flower bed from perennial flowers, planting and leaving in ...
Autumn is the time when many trees shed their leaves. Some earlier, others later. The apple tree is no exception. However, both our columns and the neighboring full-fledged apple tree ...
Spathiphyllum - home care. How to care for spathiphyllum (“female happiness”) Flower growers often breed spathiphyllum or “female happiness” - an unpretentious indoor plant, with an interesting ...
Created on 03/12/2013 11:20 am Spider mites on plants. Control measures. A photo. If indoor plants live in your house, then get ready for a long fight with spider mites. …
How to grow a lemon at home from a seed so that it bears fruit? Fans of exotic plants are always wondering how to grow a lemon at home so that the tree is healthy, beautiful and ...
Snapdragon needs no introduction as it is one of the most famous ornamental plants. Moreover, it has such pronounced decorative properties that any ...
from diseases, pests Fruit rot of an apple tree. Affected fruits with conidiospore pads and a mummified fetus. For the control of weeds, diseases and pests of cultivated plants, ...
Natalia Kombarova • 03/02/2018 Rhododendrons are beautiful ornamental plants of the heather family. They are difficult to grow in our climate. Homeland - subtropics, so they love warmth and ...
Money tree (fat woman): home care. The desire of people to enrich themselves is boundless. To do this, they resort to the most unexpected actions, which sometimes plunge others into shock. One…
The term floribunda means gratefully blooming or blooming profusely. This is a variety obtained by crossing hybrid tea and polyanthus. This was first done by the breeder Poulsen in 1924.Then it started...
TO EVERYONE WHO CARES FOR THE FATE OF RUSSIAN AGRICULTURE AND FOOD SECURITY OF RUSSIA. TO EVERYONE WHO WANTS TO WORK ON FERTILITY LANDS WITHOUT NEEDING LOANS. Nikolai Ivanovich Kurdyumov, FERTILITY ...
Fittonia (Fittonia) is a herbaceous plant of the acanthus family. It is native to the tropical forests of Peru. Phytonia has about 10 species. Perennial creeping plant with pubescent shoots, which serves ...
Ficuses are the most popular indoor decorative leafy plants. Their large shiny leaves attract both experienced flower growers and beginners in this exciting, but sometimes difficult business. …
Let's continue our conversation about gooseberries. In a previous article, we learned about what a useful gooseberry is, as well as how to choose seedlings and ...
What useful, healing properties does cypress have? Energy of cypress. What is the use of cypress? Healing properties of cypress. Cypress belongs to the cypress family, which has significant differences from other representatives ...
How to care for indoor jasmine at home? + PHOTO Introducing indoor jasmine (sambac, polyanthus) and home care: watering, top dressing, pruning, reproduction, ...
If there is gloxinia in the grower's home collection, planting a tuber is a mandatory step in growing this amazingly beautiful houseplant. When, after mass flowering, decorative ...
Flower POTS for indoor plants: types + TIPS! Introducing pots for indoor flowers. Consider the types of flower pots for indoor plants, their advantages and disadvantages. Let's share…
Electric heating
Heating a greenhouse using electricity is available to every gardener.
 infrared lamps
infrared lamps
Electric heating can be implemented in several ways:
- using a heating cable laid in the ground;
- using electric heaters or convectors;
- infrared heaters or lamps;
- using an electric boiler.
Advantages of electric heating:
- availability of electricity;
- ease of installation and operation;
- low price of heating devices;
- rapid heating of air and soil;
- high level of automation.
Flaws:
- high price of electricity;
- it is not always possible to connect devices of the required power.
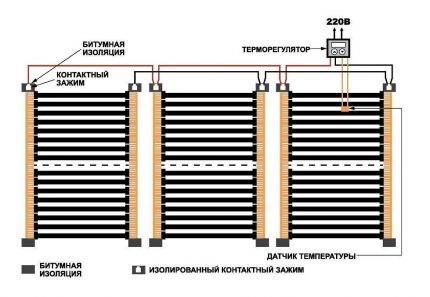
A special heating cable is laid inside heated ridges and used to heat the soil and protect it from freezing in the northern regions. The cable laying scheme is shown in the figure.
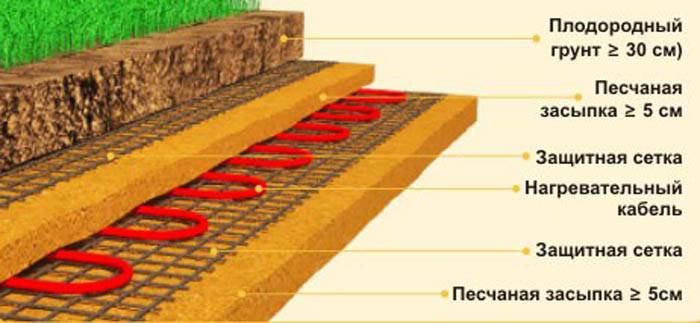 Soil heating with a heating cable
Soil heating with a heating cable
Convectors or radiators located along the main walls - the devices create protection from cold air currents. It is better not to install them in the immediate vicinity of polycarbonate - during operation, the body of the convectors heats up, so the material may melt.
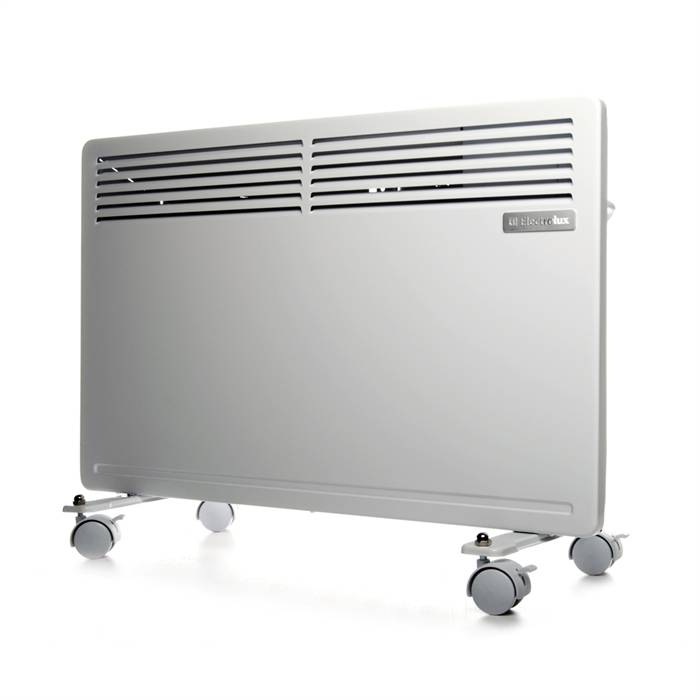 Electric convector
Electric convector
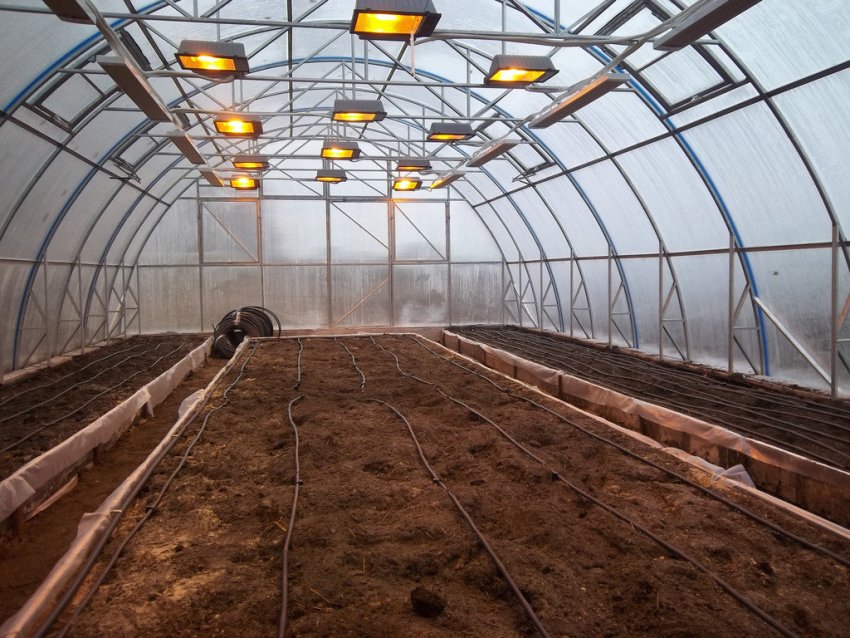
Infrared heaters do not heat the air, but the surfaces on which the rays fall. As a result, the soil and the plants themselves, paths, ridge fences, inventory and irrigation systems are heated. The heaters are mounted on brackets or hangers to the frame of the greenhouse. The radiation spectrum of infrared heaters is close to that of the sun and is beneficial for plants.
 Infrared heater
Infrared heater
Electric boilers for heating greenhouses are quite convenient, but require the installation of a water circuit, which increases the cost of installation.At the same time, their efficiency does not exceed that of other types of electric heating.
 Another option is a film heater.
Another option is a film heater.
 Film infrared heaters in the greenhouse
Film infrared heaters in the greenhouse
 Infrared film can be used for “lower” heating of the greenhouse soil or cover plants with it from above during very cold periods
Infrared film can be used for “lower” heating of the greenhouse soil or cover plants with it from above during very cold periods
Pit construction and site selection
Before you start building a thermos greenhouse, first choose a place where it will be located. Consider the following points.
- The greenhouse should not be in the shade of other structures or plantings, otherwise the plants living in it will lack light.
- The plot for the greenhouse should be oriented and have a length from east to west. Then the illumination will be maximum in intensity and duration.
- On the site, groundwater should not come close to the surface, otherwise the water will flood the structure. In the case of a close occurrence of groundwater, it is better to place the structure somewhere on a hill.
- Remember that you cannot move the greenhouse to another place - the structure can only be completely disassembled, in other words, destroyed.
 Pit under the greenhouse
Pit under the greenhouse
Since the thermos greenhouse in our case will be partially (or rather, almost completely) below the soil level, it is necessary to dig a huge pit for it. Its dimensions, as a rule, vary from 10 to 50 m2 (it all depends on what size greenhouse you plan to build). A shovel, even the most convenient one, cannot handle such volumes manually, and therefore immediately think about whether large-sized equipment can drive to the right place (this aspect should also be taken into account when choosing a place for a greenhouse).Try to find a professional excavator, such delicate work should not be trusted to inexperienced workers.
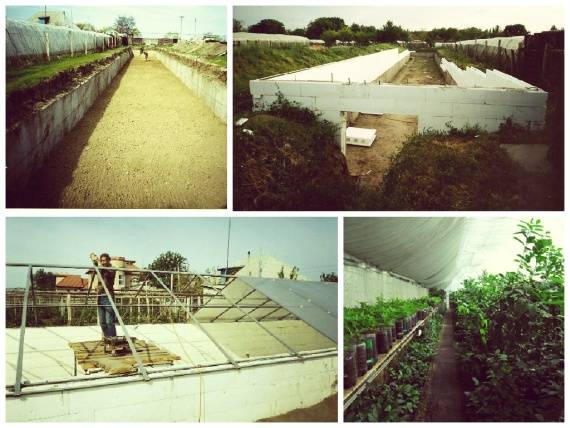


Design features
All types of greenhouses function in the same way, but winter structures must meet the following requirements:
- provide heating of air and soil;
- withstand high humidity;
- open as much as possible, which is necessary in the warm season;
- well pass the sun's rays;
- have exhaust ventilation;
- have a drain to drain excess water;
- be mechanically strong to withstand snow and wind.
When designing a structure, you should pay attention to the following features of greenhouses for growing vegetables and herbs in winter:
- Foundation. The structure must be built on a solid foundation of brick, concrete or gas blocks.
- Coating material. It is not advisable to use a film for this. Glass or polycarbonate is best.
- Roof. The roof structure should be gable or arched so that snow can easily roll off it.
- frame material. The base of the building must withstand glazing and snow loads, so you can use a wooden beam or a steel profile. An aluminum pipe will not withstand such loads.
- Lighting system. Since it gets dark early in winter, the greenhouse is equipped with lighting that artificially prolongs the day, which is necessary for growing vegetables.
- Heating system. The building can be equipped with electrical heating devices, the best of which are considered to be a heat pump, cable heating, infrared radiation, heaters, convectors, water heating. For large structures, gas heating is recommended.In this case, good ventilation is necessary, since carbon dioxide can be burned. Some experienced gardeners on large areas use ordinary stoves and combustible materials.
Heating systems for greenhouses in different climates
The region in which it is installed has a great influence on the choice of heating in the greenhouse. So, in the south, it makes no sense to install an expensive heating system with a boiler - it will be used for several weeks a year, and the costs of its installation will not pay off soon. In the northern regions, constant heating is indispensable.
Winter greenhouses in warm climates
For the southern regions, it is enough to build warm beds with bioheating and install a backup source of heating in case of frost - for example, electric convectors.
How to make biological heating
The main source of heat in such a greenhouse will be solar energy. Warming up during the day, the air and soil in the greenhouse gradually cool down during the night. When the minimum allowable temperature is reached, convectors are turned on, supplying warm air to the plants. The soil is additionally warmed up due to the processes taking place in a warm bed: it is filled with organic residues, which, when decomposed, actively release heat.
Warm climate
The cost of installing such a greenhouse is not too high
It is important to perform the correct installation of polycarbonate and insulate the north side, especially in regions with strong winds. The greenhouse must be equipped with a ventilation system, since in the bright sun, even in winter, the temperature in it can rise greatly
Winter greenhouses in temperate climates
In regions with a temperate climate, solar energy in winter is not enough to warm up the greenhouse, so you have to resort to warming the blind area and installing heating appliances. A budget option is a wood-burning stove or other fuel. It is installed on the north side of the greenhouse or in the vestibule, the entire area is heated by natural convection or air ducts laid along the ridges. They heat the stove in the evening and when the outside temperature drops.
Warm beds with manure or compost as biofuel are also effective for ground heating. A properly laid warm bed warms the soil for 5-8 years, and heating costs are significantly reduced. The roots of plants remain warm, while most crops tolerate even significant fluctuations in air temperature.
Temperate climate
In case of peak temperature drops, additional heating can be installed. Infrared lamps or heaters are perfect for heating the soil: directed radiation warms the surface of the soil and the plants themselves, while the objective temperature in the greenhouse may be low. The air is heated with convectors or fan heaters.
Winter greenhouses in cold climates
In cold climates in winter, the daylight hours are short and the sun does not significantly affect the temperature in the greenhouse. Heating it must be continuous. This task is best done water heating circuitlaid along the perimeter of the greenhouse. It may consist of registers or radiators connected by pipes. At the same time, a curtain of warm air is created along the walls, the plants do not experience the effects of cold from the walls of the greenhouse.
How to do technical heating
Soil heating with biofuels in cold climates can be inefficient: with a single freezing of the beds, the activity of soil organisms stops, and the release of heat stops. Therefore, the beds in the winter greenhouses of the northern regions are insulated and equipped with artificial heating using an electric cable or heating pipes, which are placed at the bottom of the ridges and covered with soil.
cold climate
In addition to the region, the choice of heating system also depends on the crops you are going to grow. If the winter greenhouse is designed for cold-resistant herbs and greenery, you can get by with ground heating and backup electric heaters. Heat-loving tomatoes, peppers and cucumbers require a stable microclimate, constant heating and additional lighting.