- Pipe routing options
- Selection of the optimal heating scheme
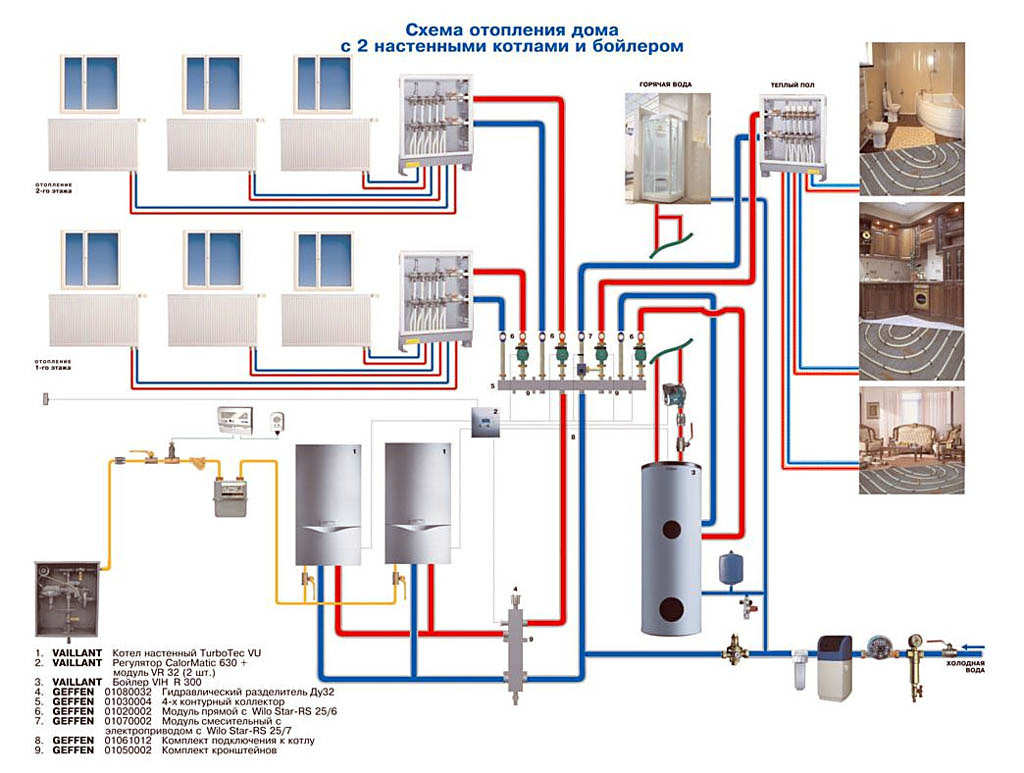
- Composition and principle of operation of the system
- The choice of heating in a two-story house
- Pipeline options
- Top and bottom wiring
- Counter and passing movement of the coolant
- Fan connection diagram
- Systems with natural and forced circulation - which is better?
- Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
- How coolant circulates
- Features of "natural" circulation
- Features of forced circulation
Pipe routing options
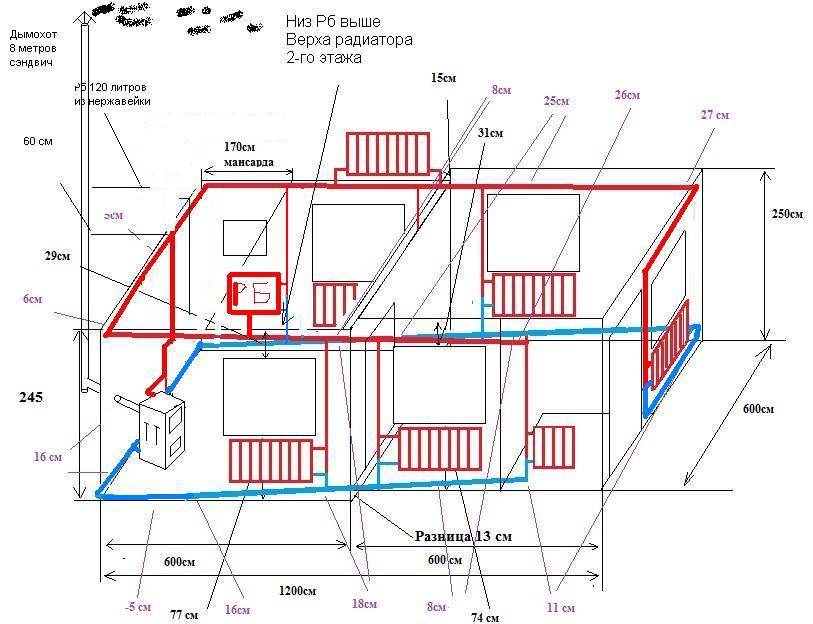
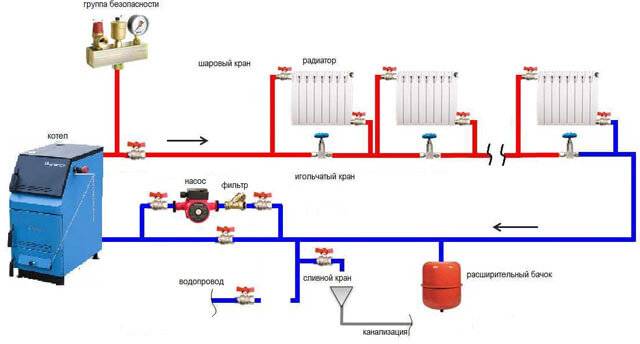
Heat supply schemes for a two-story house using heating batteries are distinguished not only by the type of connection of the pipeline and radiators, but also by the methods of laying other elements of the system. When choosing a specific option for arranging heating, the design and features of the property and the personal preferences of its owners are taken into account.
 Option one – implementation of piping by concealed installation. They are laid in such a way that they are located in the cavities of the ceiling and walls. This method is convenient because it allows you to create an original interior, in which there are no details that violate the integrity of the design solution.
Option one – implementation of piping by concealed installation. They are laid in such a way that they are located in the cavities of the ceiling and walls. This method is convenient because it allows you to create an original interior, in which there are no details that violate the integrity of the design solution.
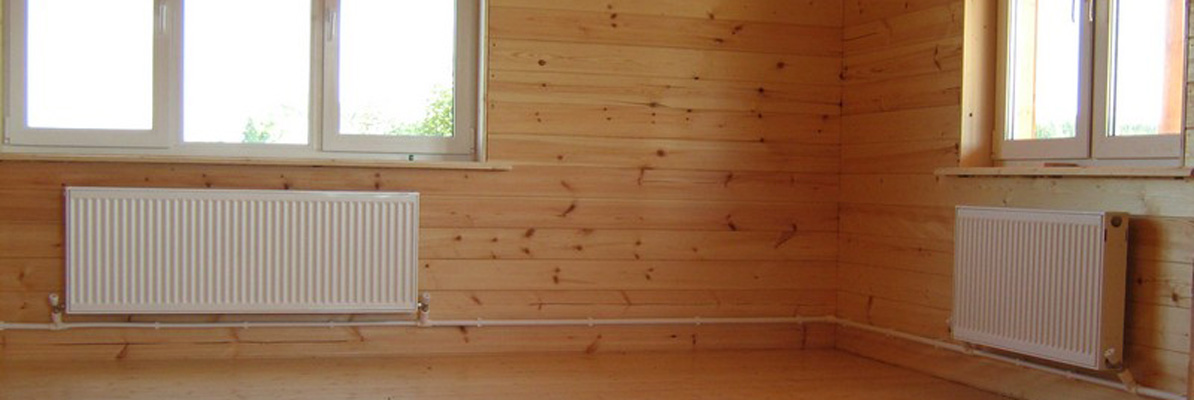
Option two - the location of pipes along the walls. This location is considered traditional, as it can be found in many houses, especially old buildings.In this case, pipes and radiators are mounted to the walls of the room using special fasteners.
Selection of the optimal heating scheme
To heat a home, the following schemes are most often used, how to install a heating boiler in a private house:
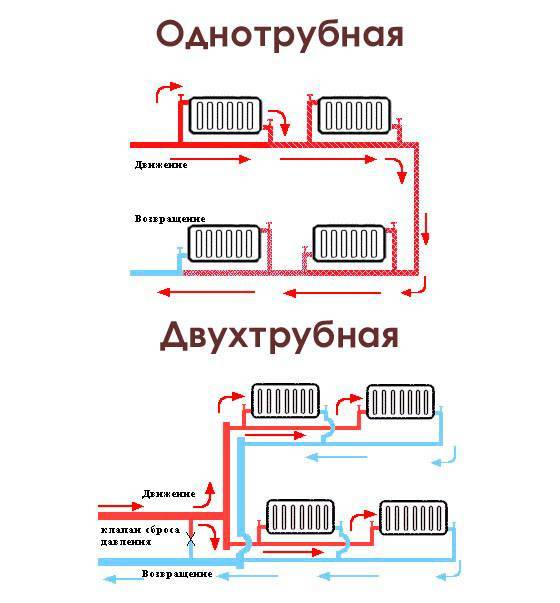
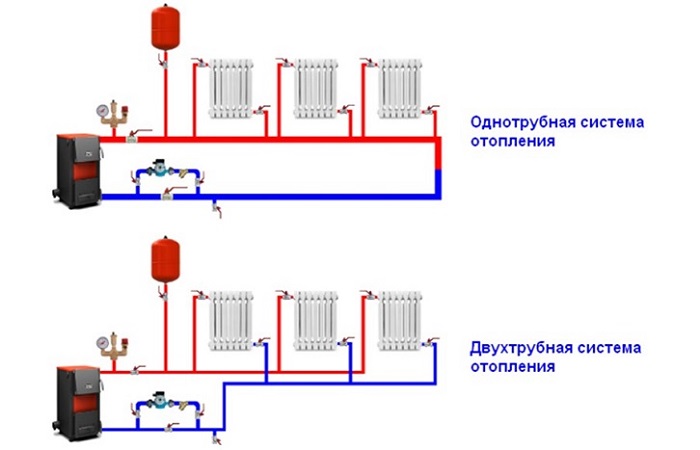
- Single-pipe. One manifold supplies all radiators. It plays the role of both supply and return, as it is laid in a closed loop next to all batteries.
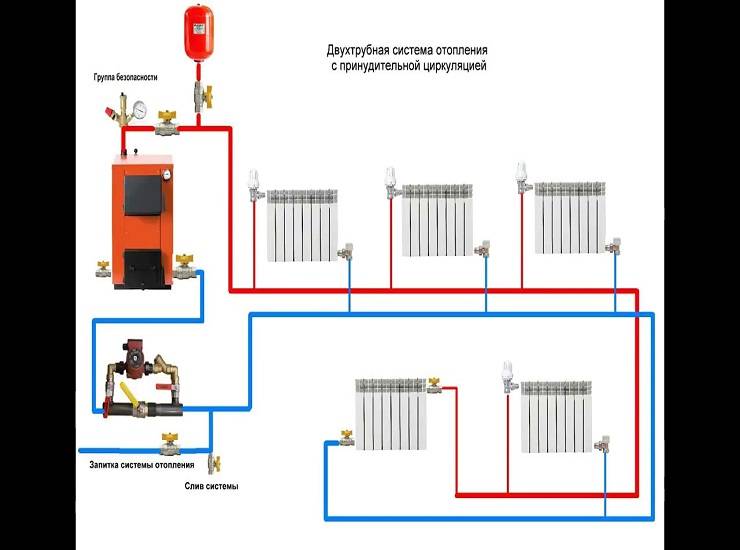
- Two-pipe. In this case, a separate return and supply is applied.
To choose the most optimal scheme for installing a heating boiler in a private house, it is recommended to consult with a specialist. However, in any case, a two-pipe system is a more progressive solution to the question of which heating scheme is best for a private house. Although at first glance it may seem that a single-pipe system saves on material, practice shows that such systems are both more expensive and more complicated.
It is important to understand that inside a single-pipe system, water cools much faster: as a result, more distant radiators have to be equipped with a large number of sections. Also, the distribution manifold must have a sufficient diameter that exceeds the two-pipe wiring lines.
In addition, in this scheme, there is a serious difficulty in organizing automatic control due to the influence of radiators on each other.
Small buildings such as summer cottages, where the number of radiators does not exceed 5, can be safely equipped with a single-pipe horizontal heating system for a private house with your own hands (it is also called "Leningradka"). If the number of batteries is increased, there will be failures in its functioning.Another application of such a decoupling is single-pipe vertical risers in two-story cottages. Such schemes are quite common and work without failures.
Two-pipe decoupling ensures delivery of coolant of the same temperature to all batteries. This allows you to refuse to build sections. The presence of a supply and return pipe creates optimal conditions for the introduction of automatic control of radiators, for which thermostatic valves are used. In this case, you can take pipes of smaller diameter and simpler schemes.
What are the heating schemes for a private house of a two-pipe type:
- dead end. In this case, the pipeline consists of separate branches, inside which the oncoming movement of the coolant is used.
- Associated two-pipe. Here, the return line acts as a continuation of the supply, which ensures the annular movement of the coolant inside the circuit.
- Radiation. The most expensive schemes, where each radiator has a separately laid hidden way (in the floor) line from the collector.
If, when laying horizontal lines of large diameter, a slope of 3-5 mm / m is used, then the gravitational mode of operation of the system will be achieved, and circulation pumps can be omitted. Thanks to this, complete energy independence of the system is achieved. This principle can be applied to both single-pipe and two-pipe schemes: the main thing is to create conditions for gravity-flow circulation of the coolant.
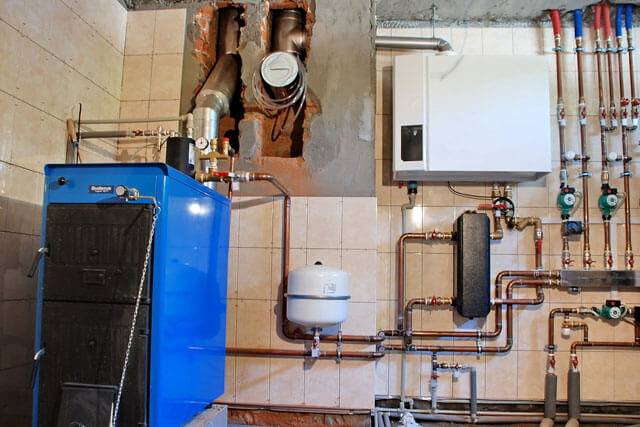

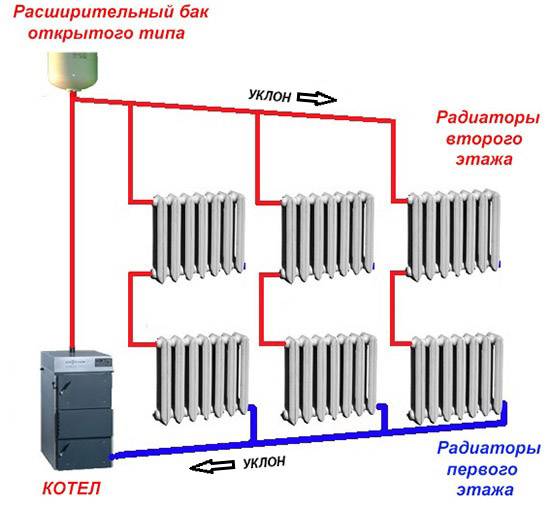
In open heating systems, an expansion tank will be required at the highest point: this approach is mandatory when arranging gravity circuits.However, the return pipe next to the boiler can be equipped with a diaphragm expander, which makes it possible to make the system closed, operating under overpressure conditions. This approach is considered more modern, and is most often used in forced-type systems.
Underfloor heating deserves special mention when researching which heating scheme to choose for a private house. Such a system is quite expensive, since it requires several hundred meters of pipeline to be laid in a screed: this allows each room to be provided with a separate heating water circuit. The pipes are switched on the distribution manifold, which has a mixing unit and its own circulation pump. As a result, rooms are heated very evenly and economically, in a form that is comfortable for people. This type of heating can be used in various residential premises.
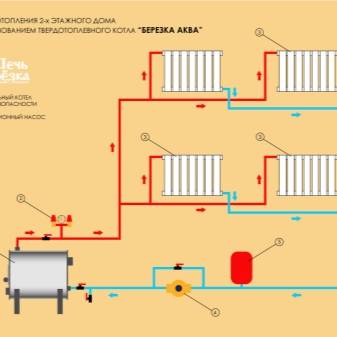
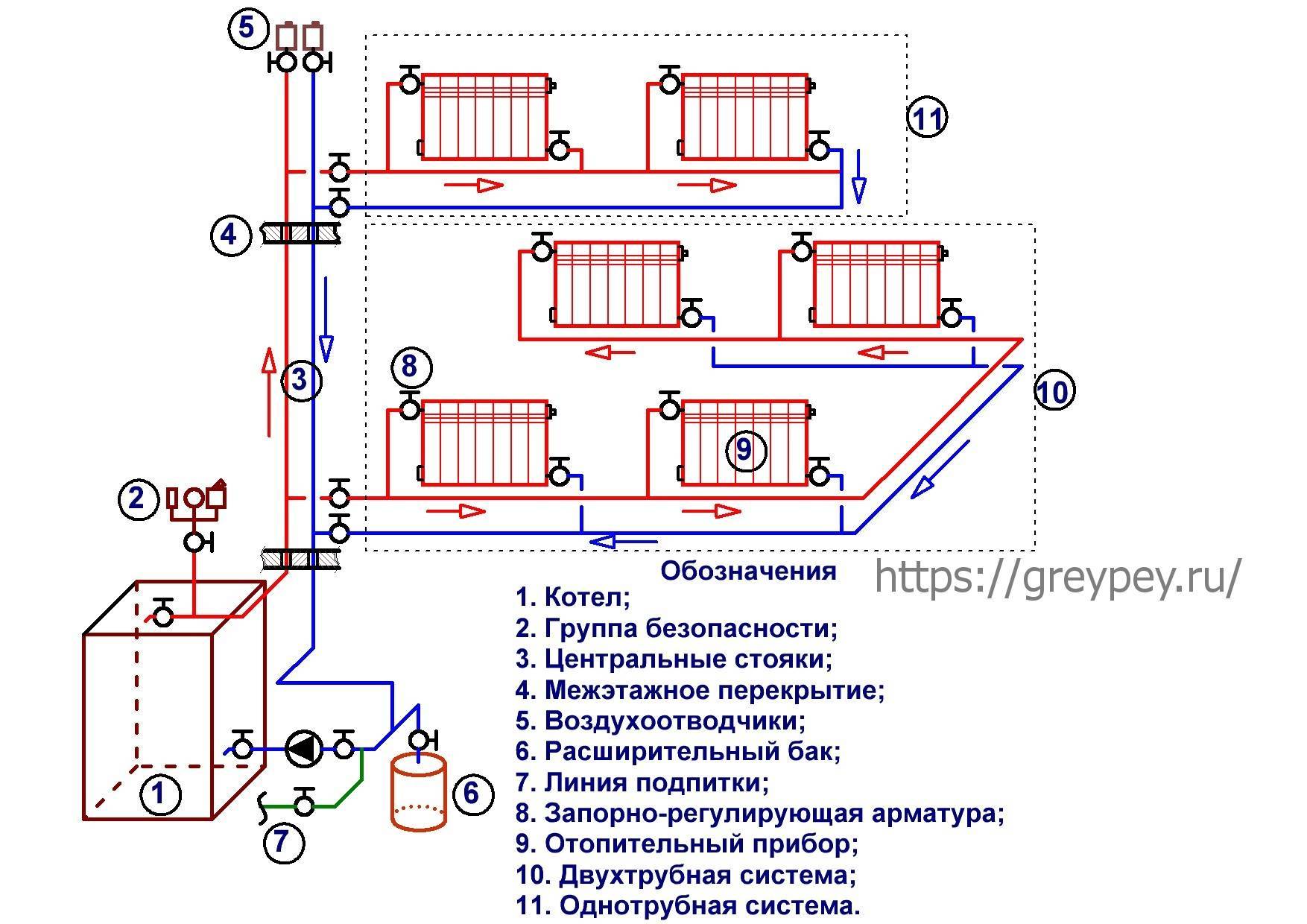
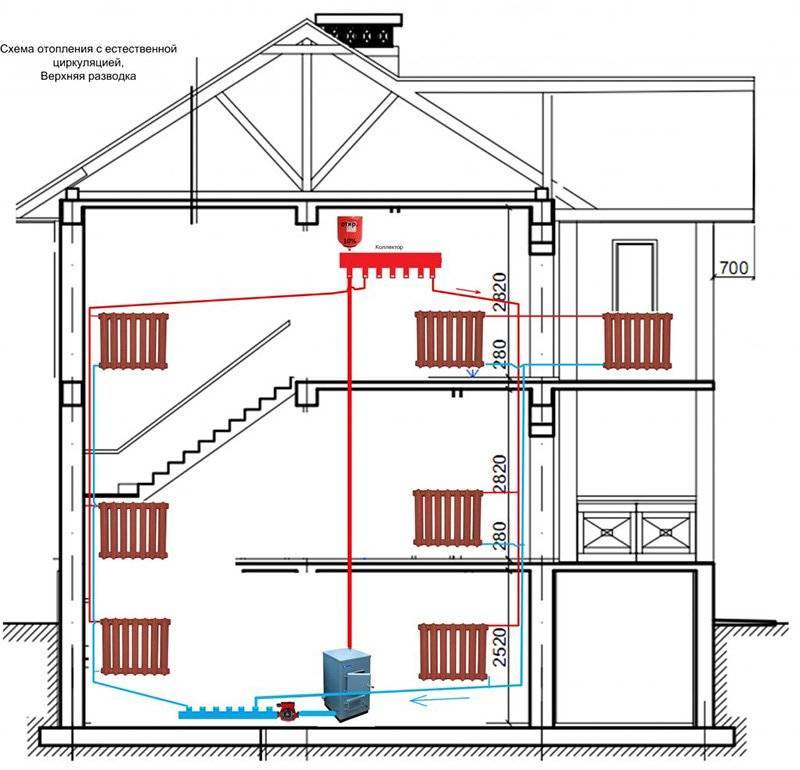
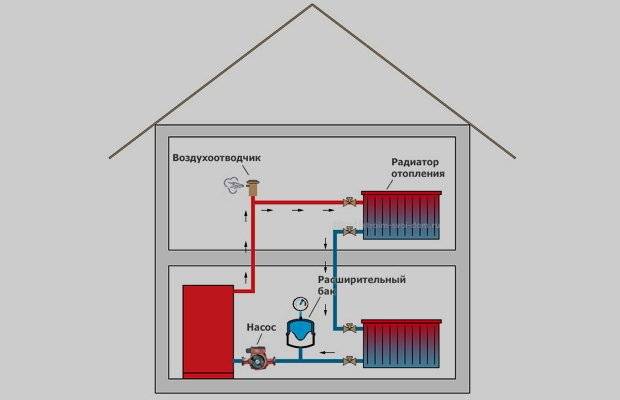
Composition and principle of operation of the system
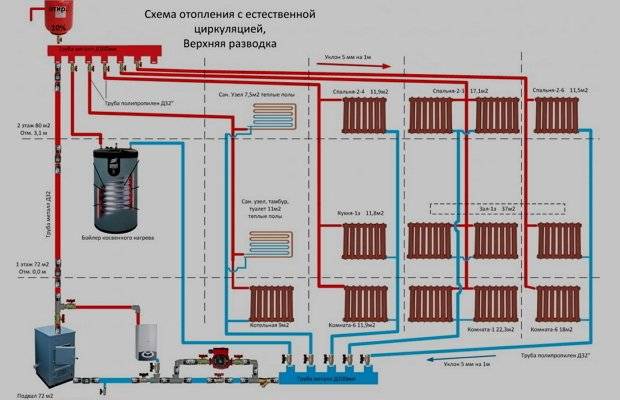
All heating systems of a private house with natural circulation of the coolant are designed for small lengths of pipelines - no more than 25-35 m in one direction.
The composition of the heating system of a private house with natural circulation of the coolant includes the following elements:
- the boiler is usually solid fuel;
- pipelines: depending on there may be one or two pipelines - supply and return;
- heating radiators;
- expansion tank.
The first figure shows the relationship of all the above components.
Image 2. Scheme of the occurrence of circulation pressure.
The boiler burns fuel (wood, briquettes, and so on). The heated coolant is delivered to the radiators through the supply pipeline. Here, the coolant gives off part of its heat to the environment.Through the return pipeline, the cooled coolant enters the boiler back. The expansion tank is needed for continuous supply of coolant to the heating system.
This cycle is constantly repeated. The coolant moves due to the generated pressure. It creates an expansion tank. Water pressure is created due to atmospheric pressure, since the expansion tank is located above all other elements of the heating system of a private house. It is for this reason that such systems are called natural circulation systems.
work on the same principle, only they also have vertical pipelines, which are called risers.
Water flows through them due to pressure, in the formation of which three factors take part at once:
- pressure due to the expansion tank;
- pressure due to the expansion of the coolant due to its heating;
- pressure due to the action of a cold, heavier coolant.
Water, strongly heated from the boiler, rises up the riser, and then is forced out by heavier cold water. Further, the water spreads along a horizontal pipeline. These movements occur only due to the above components of the total pressure, that is, by gravity. In the same way, water flows back.
Scheme of the distributing pipeline for hot and cold water.
In addition, the slope of the pipelines facilitates the removal of air cushions through the expansion tank. This is due to the fact that air is lighter than water, so it tends to get to the highest point - the expansion tank.
The expansion tank also has another purpose - to take in heated water, the volume of which increases when heated, and when cooled, the water returns.
In short, the principle of the movement of water is as follows: water rises up the riser due to heating, and also under the influence of pressure. The circulation of the coolant is determined by the difference between two densities - heated and cooled water.
Despite the presence of pressure, albeit small, the movement of water does not have a high speed. This is due to the fact that it is spent on overcoming the resistance that occurs as a result of water friction against the inner walls of the pipes. The coolant experiences especially great resistance at the places where the pipe turns, at the places where it passes through the water fittings, and so on.
In a general sense, the speed of the coolant, that is, its pressure, depends on many factors:
- from the difference of two heights - the height of the center of the boiler and the height of the center of the heating radiator. The greater this difference, the faster the water moves in the heating system of a two-story private house with natural circulation;
- on the difference between the densities of cold and hot water - the higher the temperature, the lower its density, and, accordingly, the difference is greater.
The choice of heating in a two-story house
To choose the right scheme, you need to consider many factors:
- preferred type of fuel or energy carrier;
- the size of the heated area;
- reliability of power supply in your area;
- the budget allocated for the purchase of equipment and installation;
- the material from which the building is built;
- the complexity of laying pipes;
- other conditions.
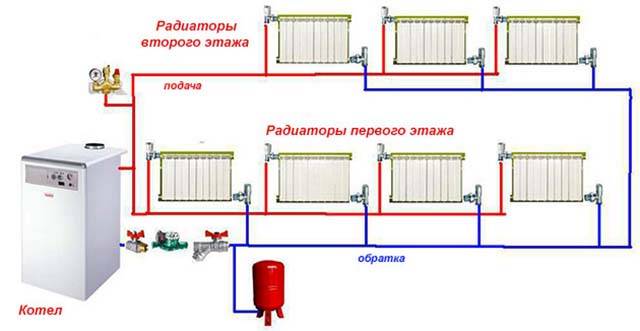
As already mentioned, the first place in all respects is occupied by a two-pipe closed-type system with a membrane expansion tank. In a two-story cottage of medium size (up to 300 m²), a pipe diameter of 20-25 mm is enough for you, which, if desired, can be easily carried out in a hidden way. Unless at the beginning of the scheme you will have to put a pipeline Ø32 mm.

We offer a few more recommendations for choosing a heating scheme for a house on 2 floors:
- With frequent and prolonged power outages, you need to think about installing an open gravity system and installing a floor-standing boiler that can work autonomously. Buying uninterruptible power supplies or generators is not always justified.
- Under the same conditions, it is impossible to mount floor networks connected to the comb. They won't work without a pump.
- In a building with stove heating, it is better to use wiring with natural circulation and an open expansion tank. How to independently make a water circuit in the stove is described in this instruction.
- To organize heating with underfloor heating without radiators from a solid fuel boiler, you will have to install a buffer tank and a mixing unit, which is not available to everyone. It is cheaper to make a high-temperature radiator network and connect it in a two-pipe scheme. A backup power supply for the pump is required in this case.
- Use Leningradka in houses of small area (up to 150 m²), and do it with forced circulation. If the size of the building is larger, and you need a gravity system, then feel free to mount vertical risers with an upper coolant supply and an open tank installed in the attic.
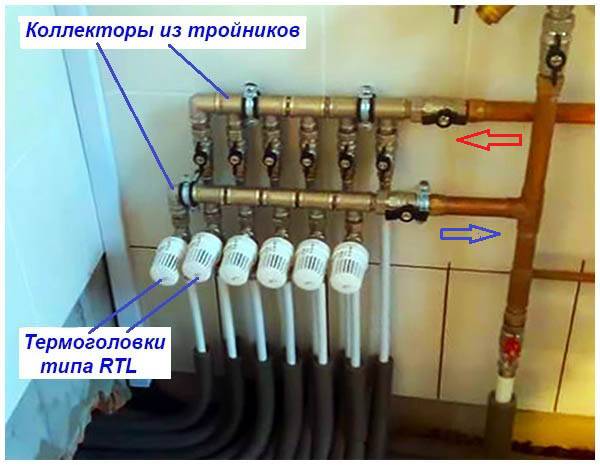
There are 2 ways to reduce the cost of purchasing equipment for warm floors.The first is the installation of the RTL thermal heads shown in the photo instead of the mixing unit. They are put to the return manifold water and regulate the flow in each circuit according to the temperature of the coolant.

The second option is to use a wall-mounted gas boiler capable of maintaining an outlet temperature of up to 50 ° C. True, in this mode of operation, it will consume more gas and become clogged with soot faster.
For a detailed analysis of various heating systems for two-story private houses, see the last video:
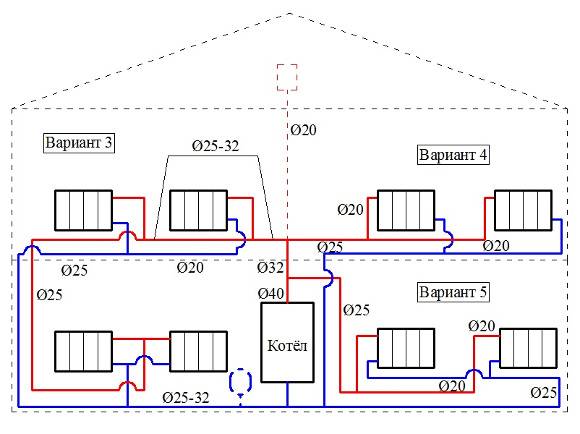
Pipeline options
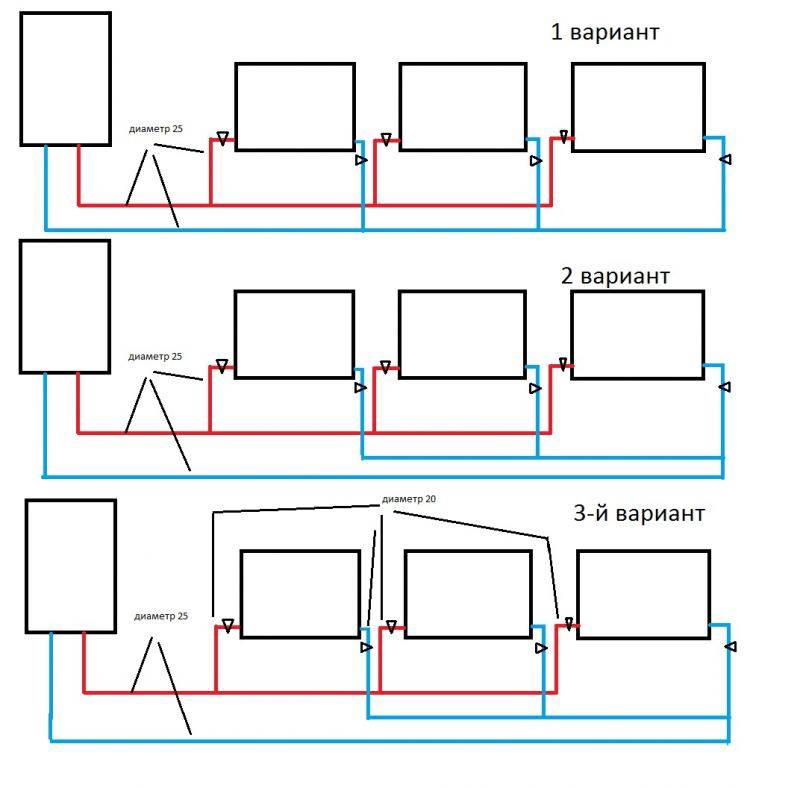
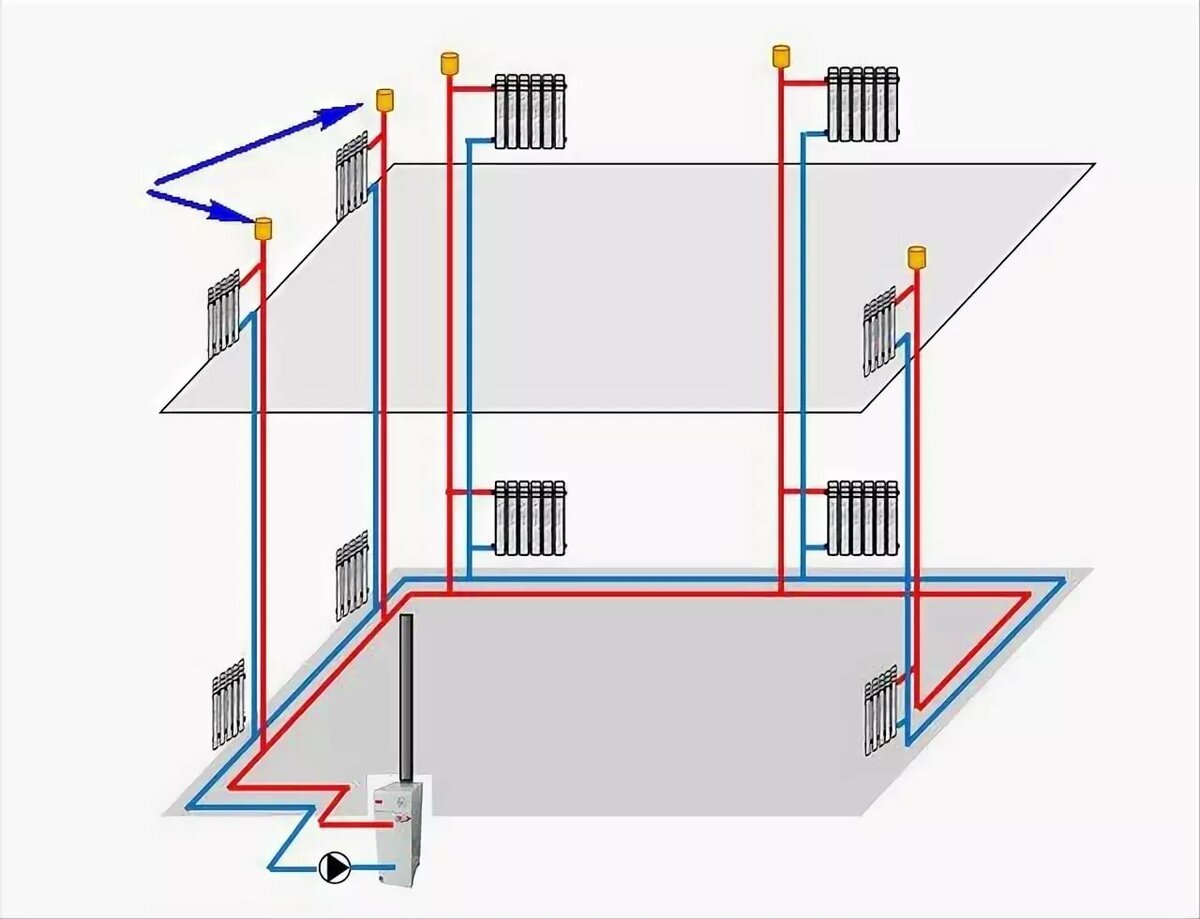
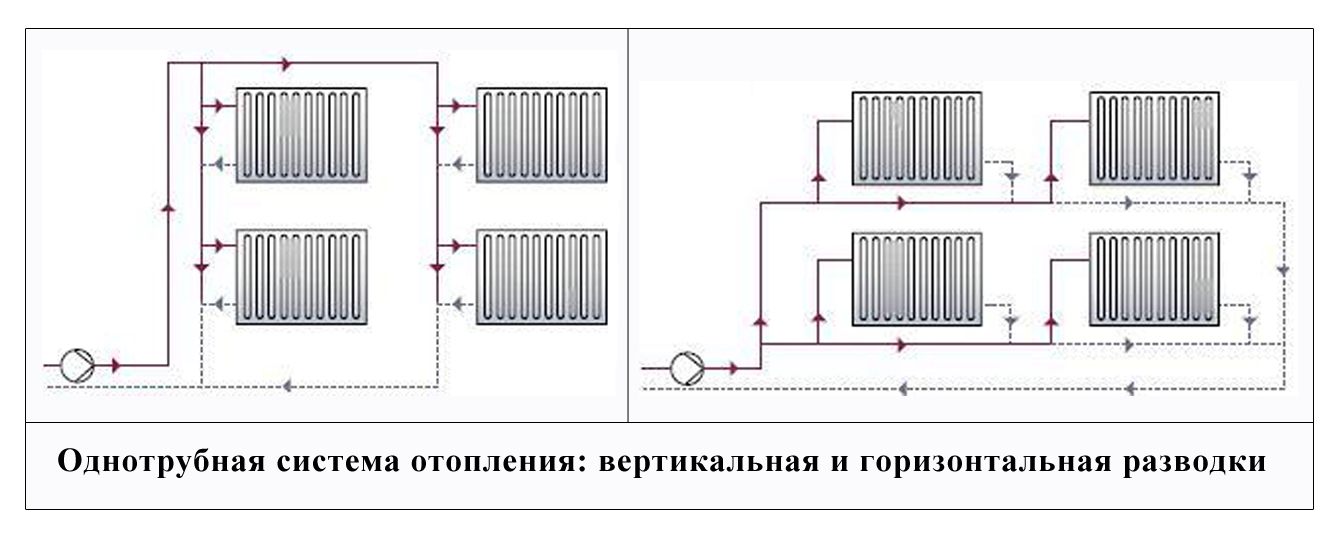
There are two types of two-pipe wiring: vertical and horizontal. Vertical pipelines are usually located in multi-storey buildings. This scheme allows you to provide heating for each apartment, but at the same time there is a large consumption of materials.
Top and bottom wiring
The distribution of the coolant is carried out according to the upper or lower principle. With the upper wiring, the supply pipe runs under the ceiling and goes down to the radiator. The return pipe runs along the floor.
With this design, the natural circulation of the coolant occurs well, thanks to the height difference, it has time to pick up speed. But such wiring has not been widely used due to external unattractiveness.
The scheme of a two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring is much more common. In it, the pipes are located at the bottom, but the supply, as a rule, passes slightly above the return. Moreover, pipelines are sometimes carried out under the floor or in the basement, which is a great advantage of such a system.
This arrangement is suitable for schemes with forced movement of the coolant, since during natural circulation the boiler must be at least 0.5 m lower than the radiators. Therefore, it is very difficult to install it.
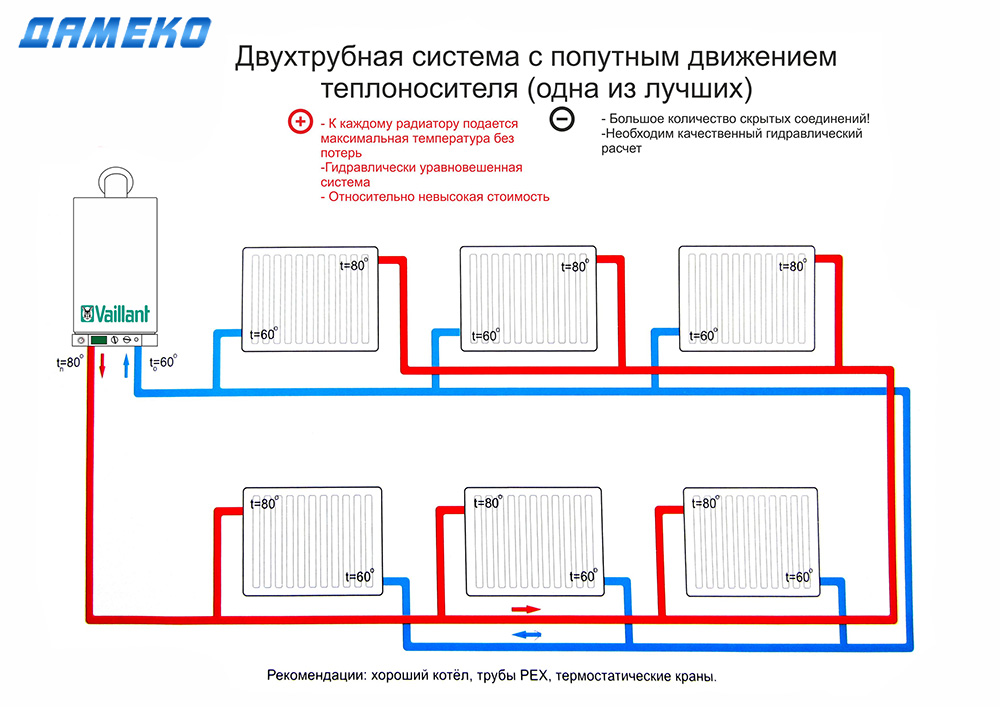
Counter and passing movement of the coolant
The scheme of two-pipe heating, in which hot water moves in different directions, is called oncoming or dead-end. When the movement of the coolant is carried out through both pipelines in the same direction, it is called an associated system.
In such heating, when installing pipes, they often resort to the principle of a telescope, which facilitates adjustment. That is, when assembling the pipeline, sections of pipes are laid in series, gradually reducing their diameter. With the oncoming movement of the coolant, thermal valves and needle valves for adjustment are always present.
Fan connection diagram
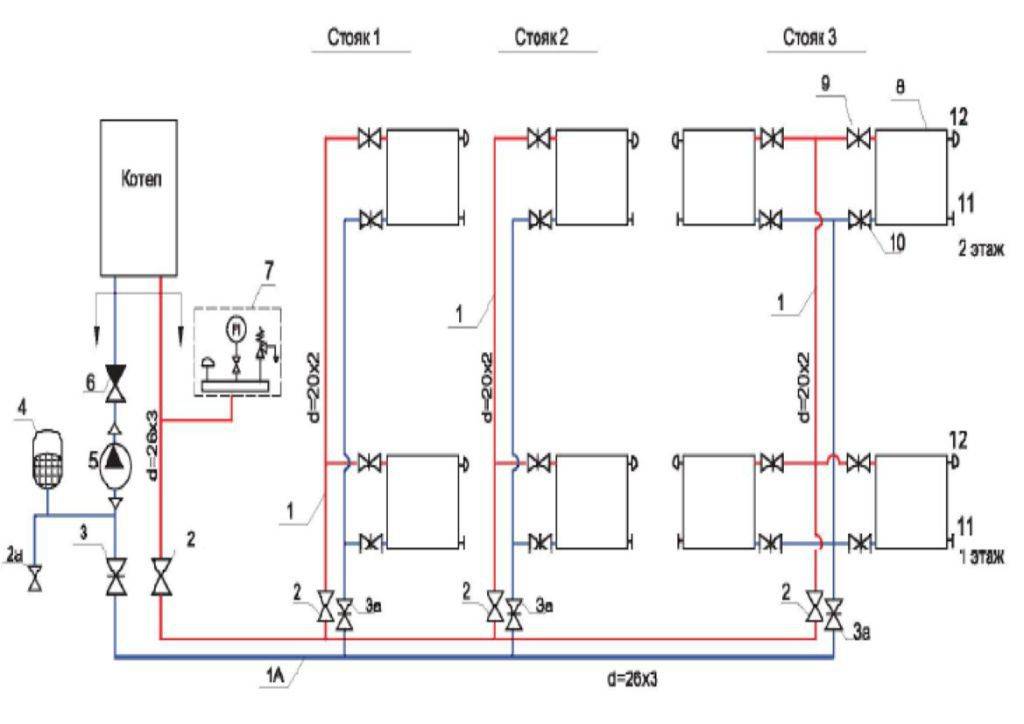
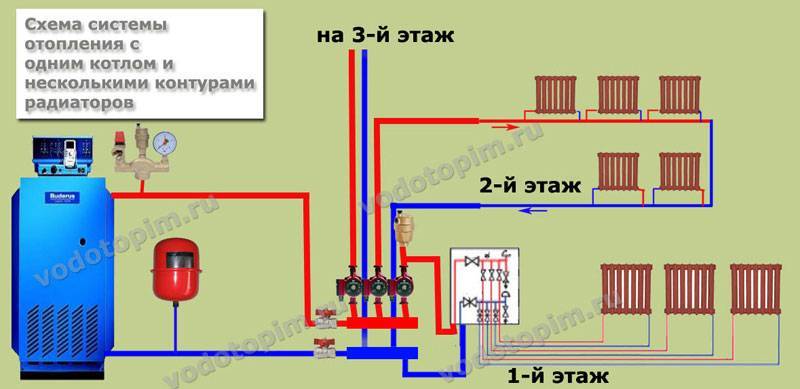
The fan or beam scheme is used in multi-storey buildings to connect each apartment with the possibility of installing meters. To do this, a collector is installed on each floor with a pipe outlet for each apartment.
Moreover, only whole sections of pipes are used for wiring, that is, they do not have joints. Thermal metering devices are installed on pipelines. This allows each owner to control their heat consumption. During the construction of a private house, such a scheme is used for floor-by-floor piping.
To do this, a comb is installed in the boiler piping, from which each radiator is connected separately. This allows you to evenly distribute the coolant between the devices and reduce its loss from the heating system.
Systems with natural and forced circulation - which is better?
The difference between these two types of circulation lies in the way water moves through the CO. To implement a forced circuit, it is necessary to install special equipment, in particular a circulation pump, there is no such need for a natural one.
EC is characterized by a number of advantages:
- absence of noise and vibration during operation of the system;
- elementary installation and maintenance;
- long service life.
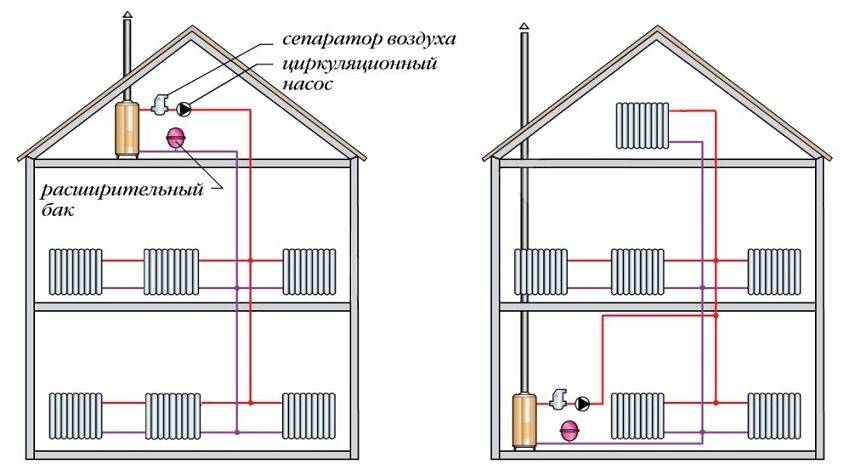
Installation of a natural circulation system
At the same time, COs with natural circulation start up rather slowly, the water in the pipes of such systems can freeze at sub-zero temperatures outside. Another disadvantage is the need to install large pipes (they are more expensive and more difficult to install).
Now such systems are rarely used. Users prefer a more modern and efficient heating scheme. It is a forced circulation CO with the following important advantages:
- the possibility of building a wiring of any length in a private house;
- independence of the quality of heating from the indicators of the temperature of the coolant;
- simple adjustment of operating modes.
CO with forced circulation
In versions with forced circulation, hot water flows through the pipes due to the operation of pumping equipment. Water comes from the boiler, in which it is heated, under the action of a special pump (it is called a circulation pump).
On each radiator with such a heating scheme, Mayevsky valves and taps are installed. The first ones make it possible to choose the heating temperature of a particular battery. Valves can be automatic or manual. And the Mayevsky crane allows you to remove unnecessary air from the system.
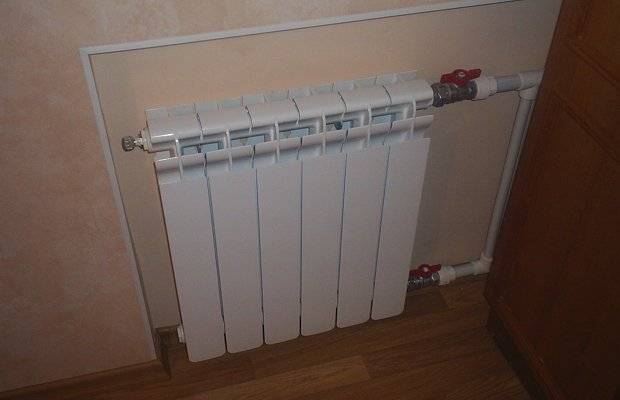

Maevsky valves and taps
Experts advise to install CO in two-story cottages with a double-circuit boiler and forced circulation. Then it will be very easy for you to make a “warm floor” in the house, install heated towel rails and always control the operation of the CO, setting the most comfortable temperature for yourself.
Types of forced circulation of heat carrier in heating
The use of forced circulation heating schemes in two-story houses is used due to the length of the system lines (more than 30 m). This method is carried out using a circulation pump that pumps the liquid of the circuit. It is mounted at the inlet to the heater, where the coolant temperature is the lowest.
With a closed circuit, the degree of pressure that the pump develops does not depend on the number of storeys and the area of \u200b\u200bthe building. The speed of the water flow becomes greater, therefore, when passing through the pipeline lines, the coolant does not cool down much. This contributes to a more even distribution of heat throughout the system and the use of the heat generator in a sparing mode.
The expansion tank can be located not only at the highest point of the system, but also near the boiler. To perfect the scheme, the designers introduced an accelerating collector into it. Now, if there is a power outage and the subsequent stop of the pump, the system will continue to work in convection mode.
- with one pipe
- two;
- collector.
Each can be mounted by yourself or invite specialists.
Variant of the scheme with one pipe
Shutoff valves are also mounted at the battery inlet, which serves to regulate the temperature in the room, as well as necessary when replacing equipment. An air bleed valve is installed on top of the radiator.
Battery valve
To increase the uniformity of heat distribution, radiators are installed along the bypass line. If you do not use this scheme, then you will need to select batteries of different capacities, taking into account the loss of heat carrier, that is, the farther from the boiler, the more sections.
The use of shut-off valves is optional, but without it, the maneuverability of the entire heating system is reduced. If necessary, you will not be able to disconnect the second or first floor from the network to save fuel.
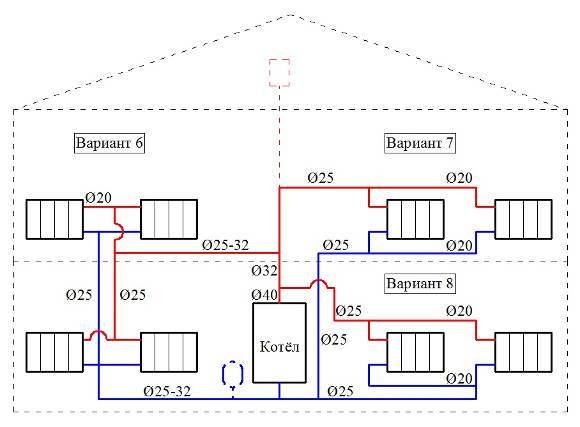
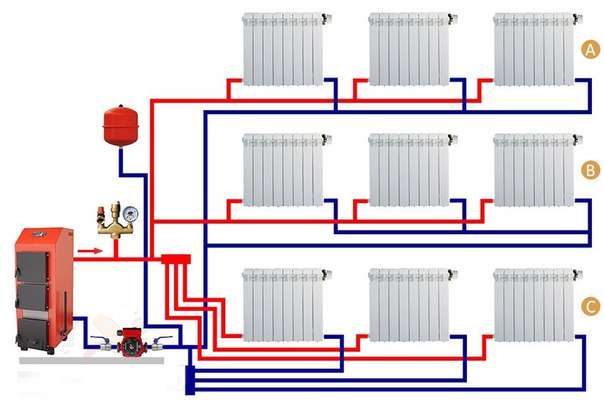
To get away from the uneven distribution of the heat carrier, schemes with two pipes are used.
- dead end;
- passing;
- collector.
Options for dead-end and passing schemes
The associated option makes it easy to control the level of heat, but it is necessary to increase the length of the pipeline.
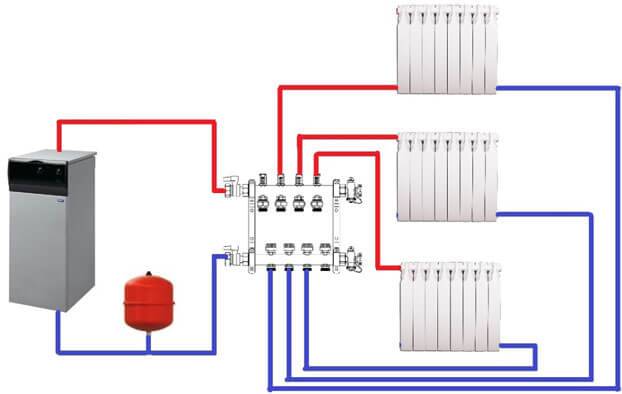
The collector circuit is recognized as the most effective, which allows you to bring a separate pipe to each radiator. Heat is distributed evenly. There is one minus - the high cost of equipment, as the amount of consumables increases.
Scheme of collector horizontal heating
There are also vertical options for supplying heat carrier, which are found with the lower and upper wiring. In the first case, the drain with the supply of a heat carrier passes through the floors, in the second, the riser goes up from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to the heating elements.
Vertical layout
Two-story houses can have a very different area, ranging from a few tens to hundreds of square meters. They also differ in the location of the rooms, the presence of outbuildings and heated verandas, the position to the cardinal points.Focusing on these and many other factors, you should decide on the natural or forced circulation of the coolant.
A simple scheme of coolant circulation in a private house with a natural circulation heating system.
Heating schemes with natural circulation of the coolant are distinguished by their simplicity. Here, the coolant moves through the pipes on its own, without the help of a circulation pump - under the influence of heat, it rises up, enters the pipes, is distributed over the radiators, cools down and enters the return pipe to go back to the boiler. That is, the coolant moves by gravity, obeying the laws of physics.
Scheme of a closed two-pipe heating system of a two-story house with forced circulation
- More uniform heating of the entire household;
- Significantly longer horizontal sections (depending on the power of the pump used, it can reach several hundred meters);
- Possibility of more efficient connection of radiators (for example, diagonally);
- Possibility of mounting additional fittings and bends without the risk of pressure drop below the minimum limit.
Thus, in modern two-story houses, it is best to use heating systems with forced circulation. It is also possible to install a bypass, which will help you choose between forced or natural circulation in order to select the most optimal option. We make a choice towards coercive systems, as more effective.
Forced circulation has a couple of disadvantages - this is the need to purchase a circulation pump and the increased noise level associated with its operation.
How coolant circulates
The heat carrier can be:
- antifreeze;
- alcohol solution;
- water.
Circulation can be both "natural" and forced. There may be several pumps. Also only one pump is used.
Features of "natural" circulation
Due to the special properties of the fluid, gravity expands as the temperature rises.
As water cools, the density increases. Then the water rushes to the point of departure. This closes the loop.
Recommended material is high quality polypropylene
Pressure can be provided:
installation difference (the heating installation is mounted below. This usually happens in the basement area, or in the basement)
The lower the elevation difference, the lower the speed at which the coolant moves;
temperature difference (taking into account the difference in the room and within the system itself). The warmer the house, the slower the movement of heated water.
In order to reduce the resistance of pipes, it is recommended to have horizontal sections slightly sloped. You should focus on the movement of water.
The circulation rate depends on the following indicators:
| Index | Description |
| Circuit Features | One of the important criteria is the number of connections. The best effect can be achieved against the background of the linear placement of heating units. |
| Pipe diameter (routing) | It is recommended to choose models with a large internal section. This will help to reduce the resistance when moving the fluid. |
| Material used | The recommended material is polypropylene. It has higher throughput. Also, the material is resistant to corrosion and lime deposits. The most undesirable material is metal-plastic. |
If the installation was done correctly, it can last several decades.
One of the main disadvantages is the limitation of the length of the circuit, up to 30 meters. The fluid moves very slowly along the line. Against this background, the liquid in the radiators also heats up slowly.
Features of forced circulation
The slow speed of the heating medium can be increased by means of a pump. Due to this, even with a small diameter of the line, sufficiently fast heating is ensured.
The type of system for forced movement is closed. Air access is not provided. The expansion tank is the only area where important processes take place. The best choice is sealing.
Pressure gauges help regulate pressure
To ensure the stability of pressure and the safety of the entire system, the following are used:
- air venting device. You can find it in the expansion tank. Its main purpose is to extract the air formed in the process of boiling water;
- fuse. If the pressure is very high, it contributes to the fact that the excess water is removed "automatically";
- pressure gauges. Designed to regulate and control the pressure in the inner part of the circuit.
Next to the boiler, on the return circuit, it is recommended to install a pump. This helps to reduce the adverse effect of the heated liquid on the installation gaskets made of rubber. This increases its lifespan. Repair is not required for a very long time.
If the system is equipped with a circulation pump, its functioning is affected by alternating current. To ensure proper operation, a bypass is recommended. This will help ensure that the system transitions to another mode.