- Features of the heating system
- Two-pipe circuit in a private house
- Ways of distributing heating
- Features of organizing a heating system with your own hands
- The device and elements of a single-pipe heating system
- Single pipe solution
- System Components
- 1. Heat generator
- 2. Pipes
- 3. Expansion tank
- 4. Radiators
- 5. Devices and accessories
- Alternative heating methods
- Solar collectors
- Wind turbines
- Heat pump
- Calculation of the heating system at home
- How to calculate the heating of a private house?
- Heating system piping
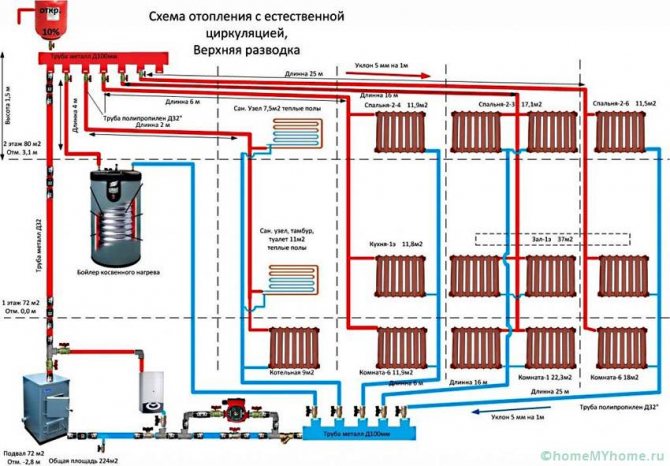
- Scheme with natural circulation
- Scope and disadvantages of gravity
- Design Tips
Features of the heating system
When designing a heating system in a private house, all its features are preliminarily calculated, all, even the most insignificant, nuances are taken into account. A preliminary assessment of the effectiveness of the work is also carried out.
If a professional acts as a designer, he will definitely get acquainted with all your requirements for the finished result and take into account all the wishes in the work
Of course, requirements that are contrary to generally accepted technical standards and norms will not be taken into account for design
What features of gas heating of country houses should be taken into account?
- The total operating power of the boiler (or boilers if your heating system requires several heating boilers).
- Pump power (if we are talking about a gas heating system, then the presence of a pump, in principle, can be considered a mandatory factor).
- Features and basic parameters of radiators (the heating of your home will directly depend on this).
- The possibility of implementing a “warm floor” system (a fairly popular and, perhaps, one of the most effective systems today function: the heating area increases several times).
- The presence of pools, jacuzzis, additional taps.
By carefully considering all these factors, you can get the most efficient and high-quality heating system that fully meets all the needs of the owner of the house (apartment).
By the way, gas heating in the country is also calculated according to the above parameters.
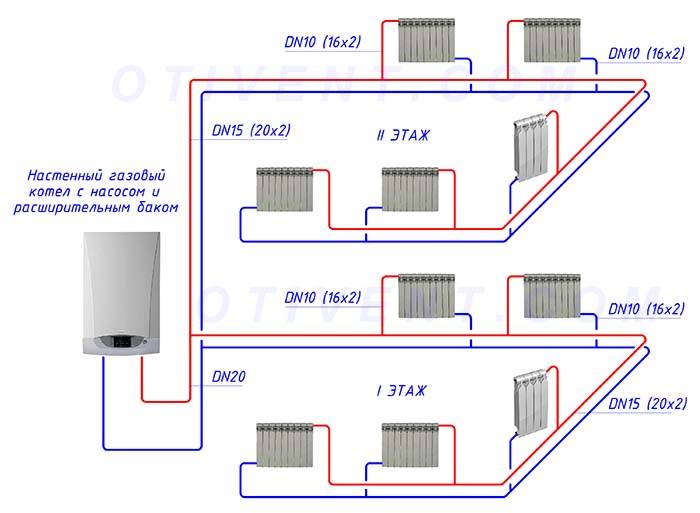
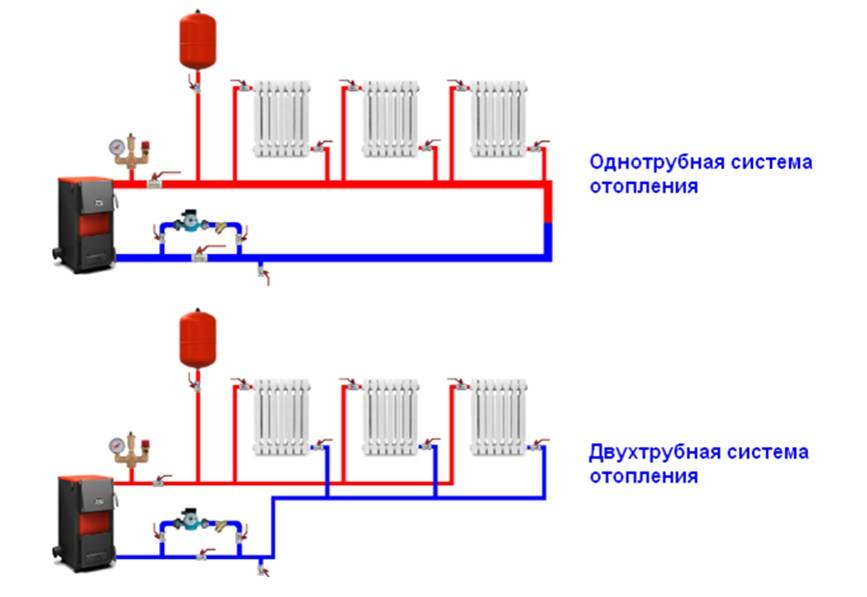
Two-pipe circuit in a private house
First, let's generalize a bit. Take for example the calculation of the diameter of pipes made of polypropylene for heating in a private house. Basically, products with a cross section of 25 mm are used for the circuit, and 20 mm are placed to the radiators. Due to the fact that the size of pipes for heating in a private house used as branch pipes to batteries is smaller, the following processes occur:
coolant speed increases;
improves circulation in the radiator;
the battery warms up evenly, which is important when connecting at the bottom.
Combinations of 20 mm main loop diameter and 16 mm elbows are also possible.
To verify the above data, you can calculate the diameter of the pipes for heating a private house on your own. This will require the following values:
square footage of the room.
Knowing the number of heated square meters, we can calculate the power of the boiler and what pipe diameter to choose for heating. The more powerful the heater, the larger the section of the product can be used in tandem with it. To heat one square meter of a room, 0.1 kW of boiler power is required. The data is valid if the ceilings are standard 2.5 m;
heat loss.
The indicator depends on the region and wall insulation. The bottom line is that the greater the heat loss, the more powerful the heater should be. To get around complicated calculations that are inappropriate in the approximate calculation, you just need to add 20% to the boiler power calculated above;
the speed of the water in the circuit.
The coolant velocity is allowed in the range from 0.2 to 1.5 m/s. At the same time, in most calculations of the diameter of pipes for heating with forced circulation, it is customary to take an average value of 0.6 m / s. At this speed, the appearance of noise from the friction of the coolant against the walls is excluded;
how cool the coolant is.
To do this, the return temperature is subtracted from the supply temperature. Naturally, you cannot know the exact data, especially since you are at the design stage. Therefore, operate with average data, which are 80 and 60 degrees, respectively. Based on this, heat loss is 20 degrees.
Now the calculation itself is how to choose the diameter of the pipe for heating. To do this, take a formula in which initially there are two constants, the sum of which is 304.44.
The last action is the extraction of the square root of the result. For clarity, let's calculate what pipe diameter to use for heating a private house with one floor with an area of 120 m2:
304.44 x (120 x 0.1 + 20%) / 20 / 0.6 = 368.328
Now we calculate the square root of 368.328, which is equal to 19.11 mm. Before choosing the diameter of the pipe for heating, we once again emphasize that this is the so-called conditional passage. Products made of different materials have different wall thicknesses. So, for example, polypropylene has thicker walls than metal-plastic. Since we have slugged a polypropylene contour as a sample, we will continue to consider this material. The marking of these products indicates the outer section and wall thickness. Using the subtraction method, we find out the value we need and select it in the store.
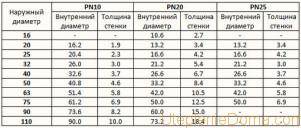
The ratio of the outer and inner diameters of polypropylene pipes
For convenience, we use a table.
Based on the results of the table, we can conclude:
- if a nominal pressure of 10 atmospheres is sufficient, then the outer section of the pipe for heating is 25 mm;
- if a nominal pressure of 20 or 25 atmospheres is required, then 32 mm.
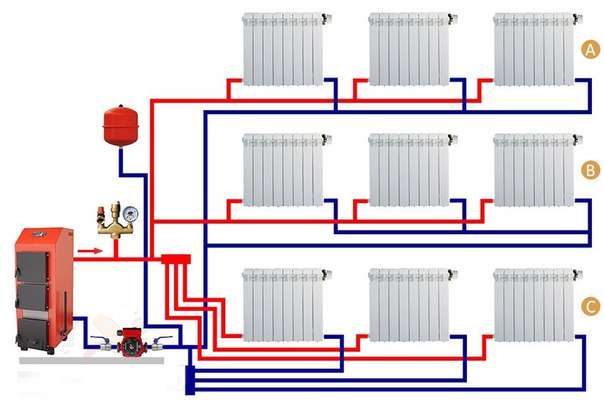
Ways of distributing heating
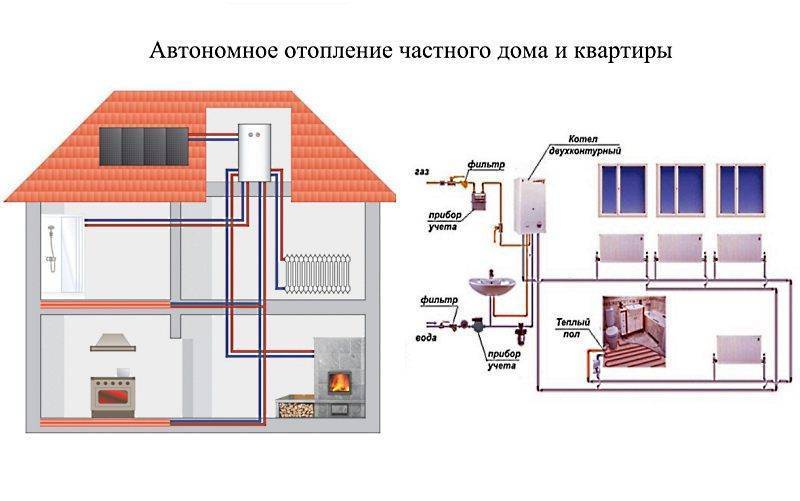
In the interior of a modern private house, you can often see a fireplace or a stove, but most often they are elements of the general style of the room. In this case, a single-circuit or double-circuit boiler is responsible for the heat in the house. Moreover, the first option is used only for heating rooms, the second type boiler simultaneously serves to supply heat and heat water.
The arrangement of the heating system in a private house can be carried out using a single-pipe and two-pipe wiring diagram from a heating boiler. Before choosing one of the options, you should study in more detail the features and characteristics of each type, as well as identify their advantages and disadvantages.
Features of organizing a heating system with your own hands
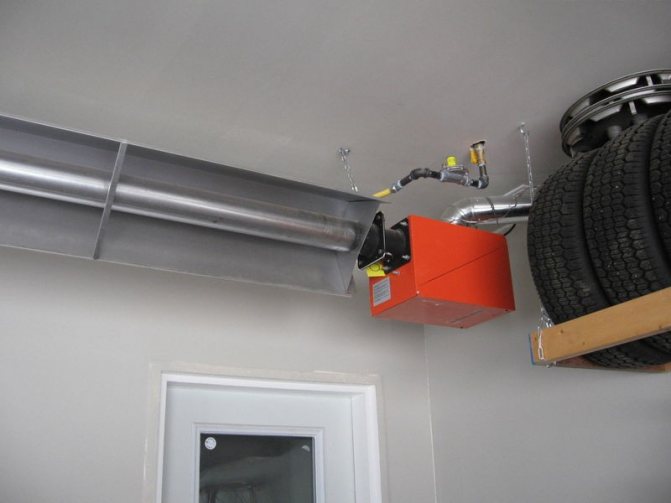
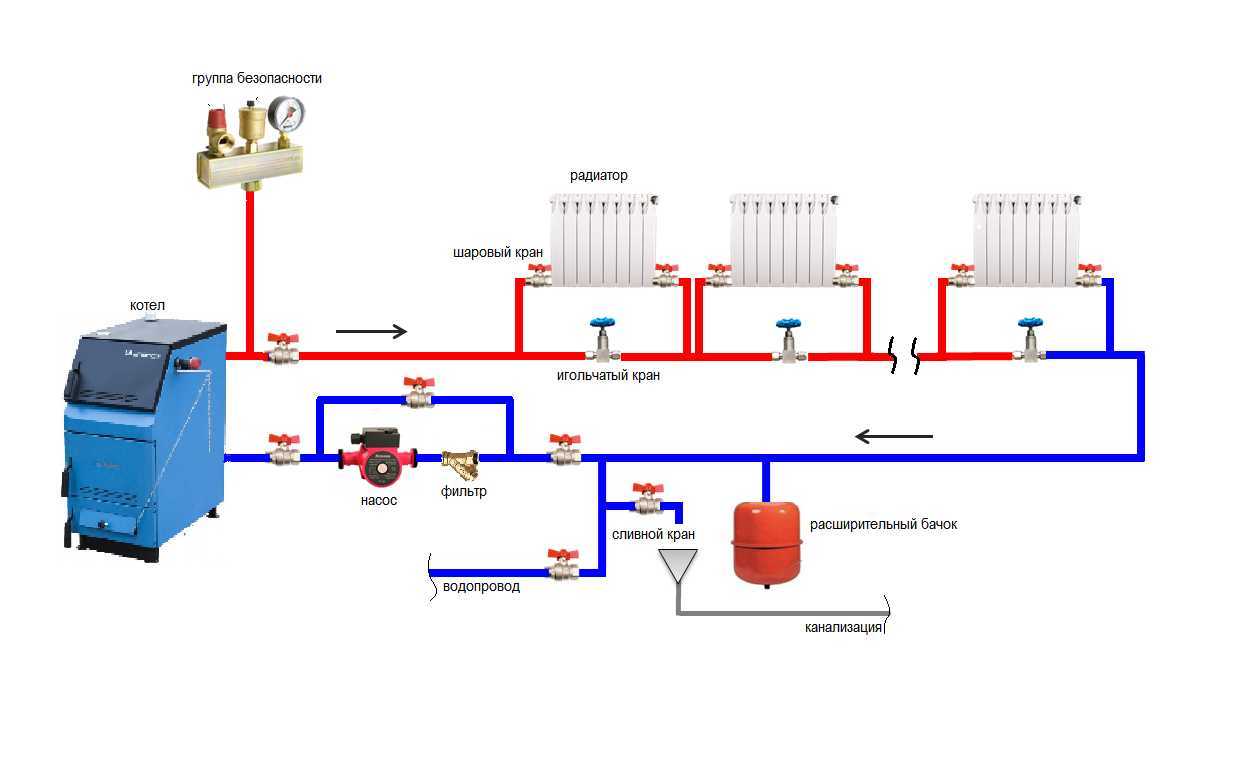
Do-it-yourself heating connection in a private house begins with installation work on the installation and piping of the boiler. If the power of the device does not exceed 60 kW, it is allowed to mount it in the kitchen room. For more powerful heat generators, a special boiler room will be required. Heating appliances with an open combustion chamber, designed to burn different types of fuel, need a good air supply. In addition, a chimney is required to remove combustion products. In order for the water to move naturally, the boiler return pipe must be lower than the level of the batteries on the ground floor.
When installing the heat generator, the minimum permissible distances to walls and other appliances must be taken into account. Most often, these instructions are found in the instructions attached to the product.

In the absence of special instructions, the following rules apply when installing the boiler:
- The width of the passage on the front side of the boiler must be at least 1m.
- If there is no need to maintain the device from the side and back, then a gap of 70 to 150 cm is left there.
- Neighboring devices should be located no closer than 70 cm.
- If two boilers are mounted side by side, then there should be a passage of 1 m between them. If the installation is carried out opposite, the distance increases to 2 meters.
- Hanging installation makes it possible to do without side passages: the main thing is that there is a gap in front for ease of maintenance.
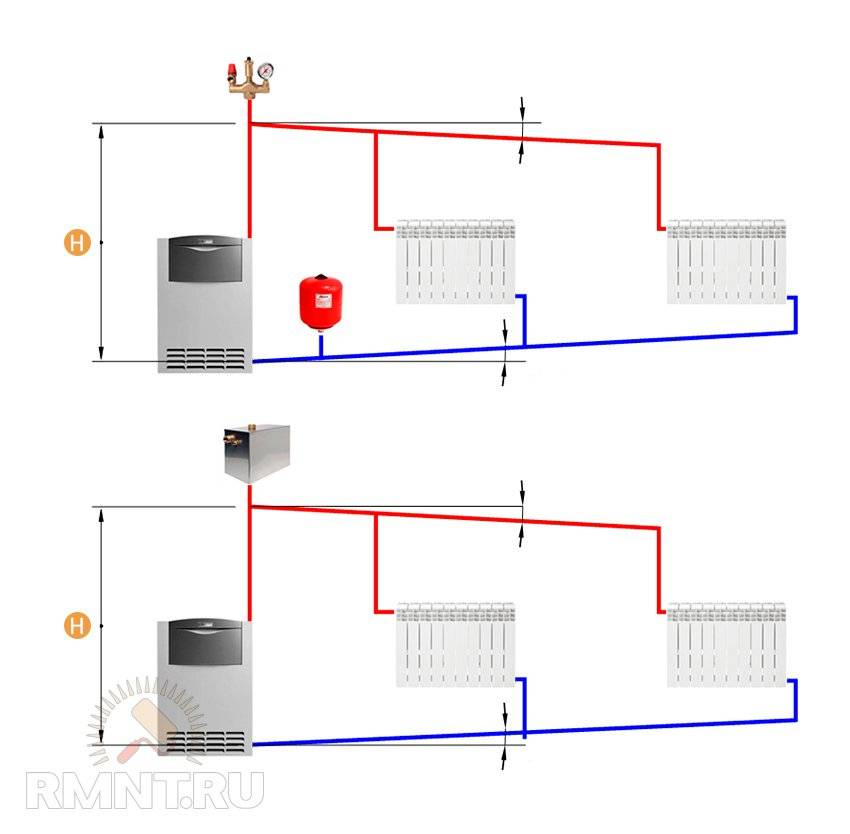
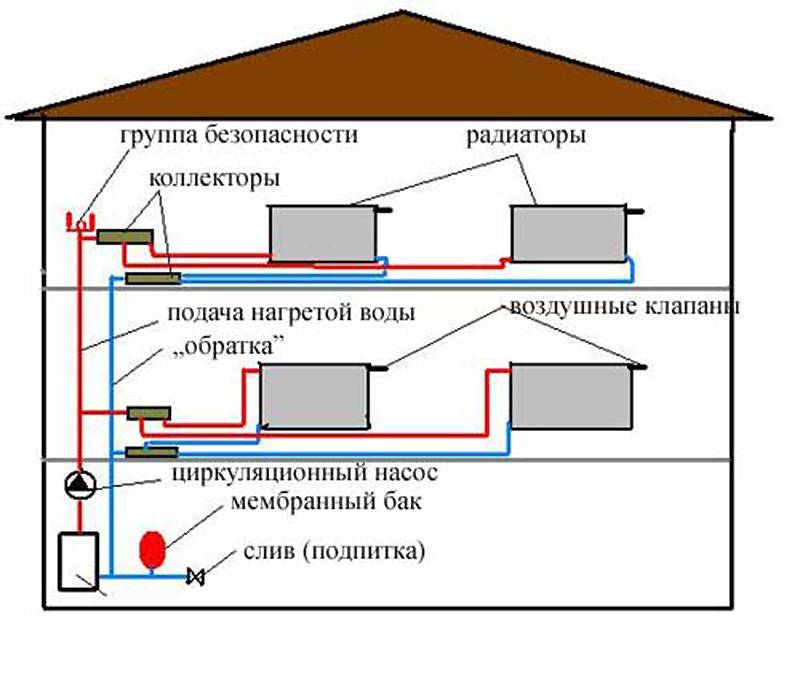
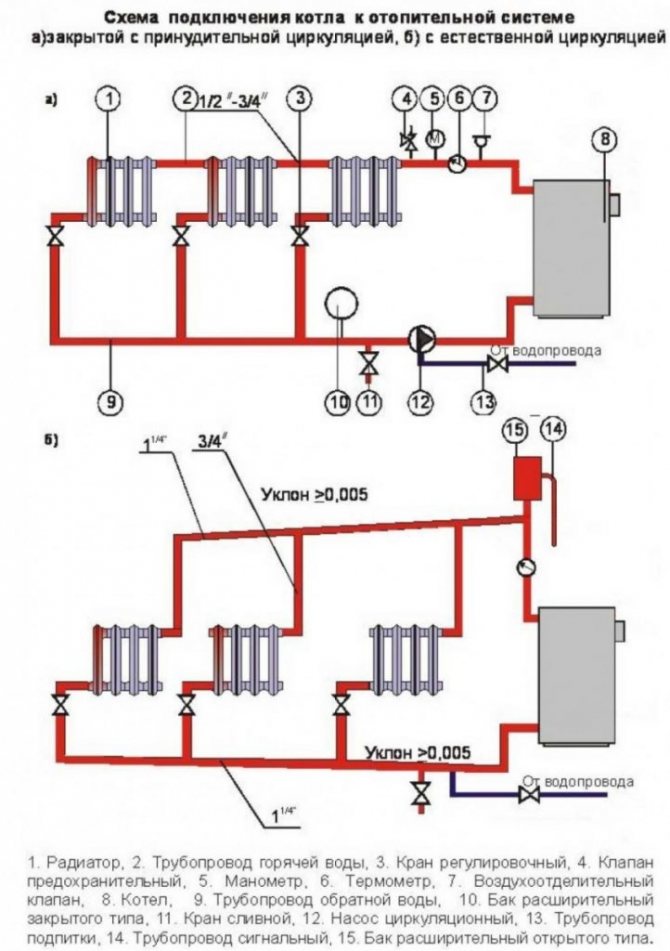
The device and elements of a single-pipe heating system
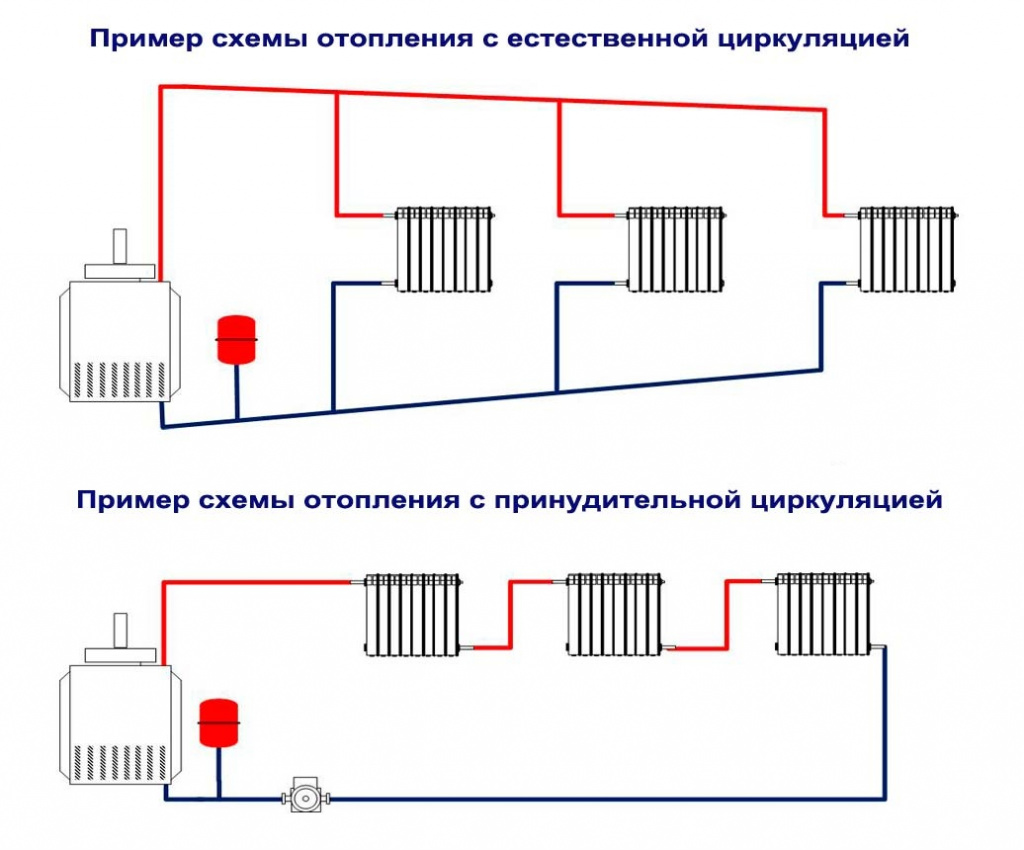
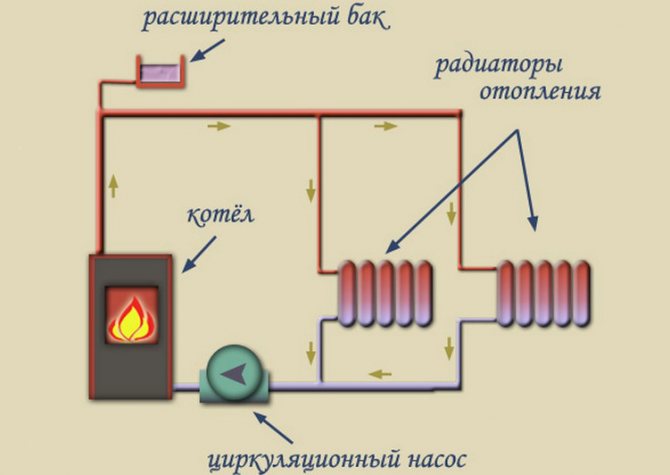
A single-pipe system, as already mentioned, is a closed circuit that includes a boiler, a main pipeline, radiators, an expansion tank, as well as elements that circulate the coolant. Circulation can be natural or forced.
With natural circulation, the movement of the coolant is ensured by different water densities: less dense hot water, under the pressure of cooled water coming from the return circuit, is forced into the system, rises up the riser to the upper point, from where it moves along the main pipe and is disassembled through radiators and other elements of the system. The slope of the pipe must be at least 3-5 degrees. This condition cannot always be met, especially in large one-story houses with an extended heating system, because the height difference with such a slope is from 5 to 7 cm per meter of pipe length.
Forced circulation is carried out by a circulation pump, which is installed in the reverse part of the circuit right in front of the boiler inlet. With the help of a pump, pressure is created sufficient to maintain the temperature of the heating water within the established limits. The slope of the main pipe in a system with forced circulation can be much less - usually it is enough to provide a difference of 0.5 cm per 1 meter of pipe length.
Circulation pump for one-pipe heating system
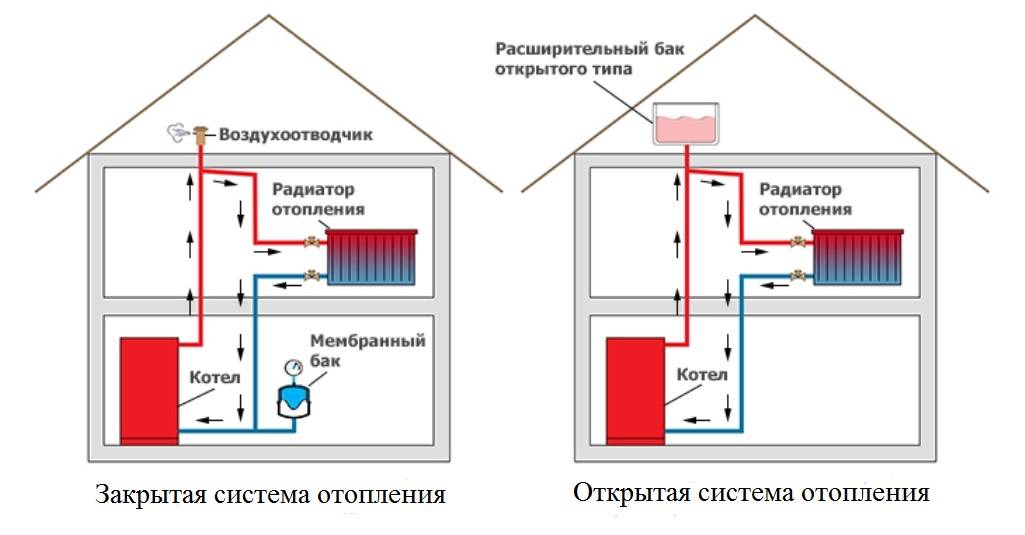
To avoid stagnation of the coolant in the event of a power outage, in systems with forced circulation, an accelerating collector is installed - a pipe that raises the coolant to a height of at least one and a half meters.At the upper point of the accelerating manifold, a pipe is drained into an expansion tank, the purpose of which is to regulate the pressure in the system and exclude its emergency increase.
In modern systems, expansion tanks of a closed type are installed, excluding the contact of the coolant with air. A flexible membrane is installed inside such a tank, on one side of which air is pumped with excess pressure, on the other side, the coolant exit is provided. They can be installed anywhere in the system.
An example of connecting an expansion tank to a single-pipe heating system
Open-type expansion tanks are simpler in design, but require mandatory installation at the top of the system, in addition, the coolant in them is actively saturated with oxygen, which can lead to premature failure of steel pipes and radiators due to active corrosion.
The sequence of installation of elements is as follows:
- Heating boiler heating (gas, diesel, solid fuel, electric or combined);
- Accelerating manifold with access to the expansion tank;
- The main pipeline that bypasses all the premises of the house along a given route. First of all, it is necessary to draw a circuit to the rooms that need heating the most: a children's room, a bedroom, a bathroom, since the water temperature at the beginning of the circuit is always higher;
- Radiators installed in selected locations;
- Circulation pump immediately before the inlet of the return part of the circuit into the boiler.
Single pipe solution

heats up and rushes into the supply risers
There are two installation options. In the first case, part of the coolant passes into the radiators, while the other part fills the heat transfer devices below.The water flow is adjusted as needed.
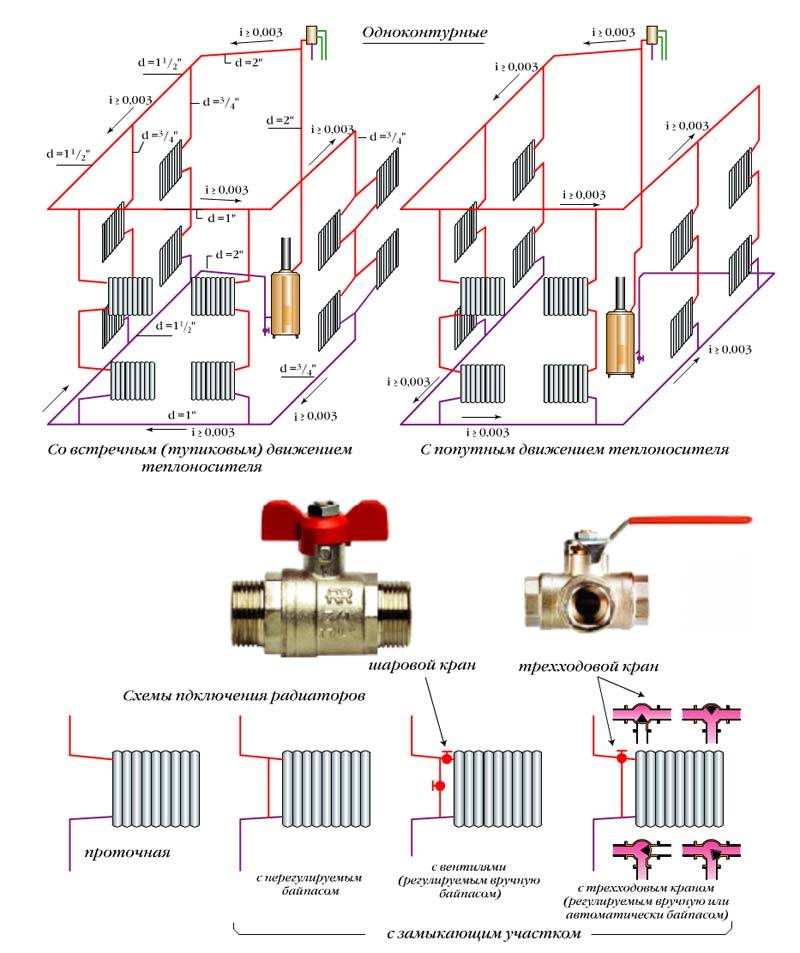
The flow option provides for the sequential movement of the coolant through all radiators installed along the line of the main pipe. Returns, unlike the first scheme, only cold water. The flow system does not allow you to regulate the heating process.
The efficiency of an autonomous system is affected by the pressure difference at the inlet and outlet. It is responsible for the speed of the coolant. Regarding the single-pipe connection scheme, it should be noted that the pressure is provided by the diameter of the pipes and the height of the collector at the starting point and its decrease at the end.
Solar energy is the most economical. The resource can be obtained free of charge by installing the appropriate equipment - a battery, and the degrees are not important at all for its heating, but only sunlight is required. Another alternative form of energy is wind turbines. They are used in countries where there is little sun. It is possible that the benefits of natural energy will encourage you to experiment when the issue of energy availability becomes acute.
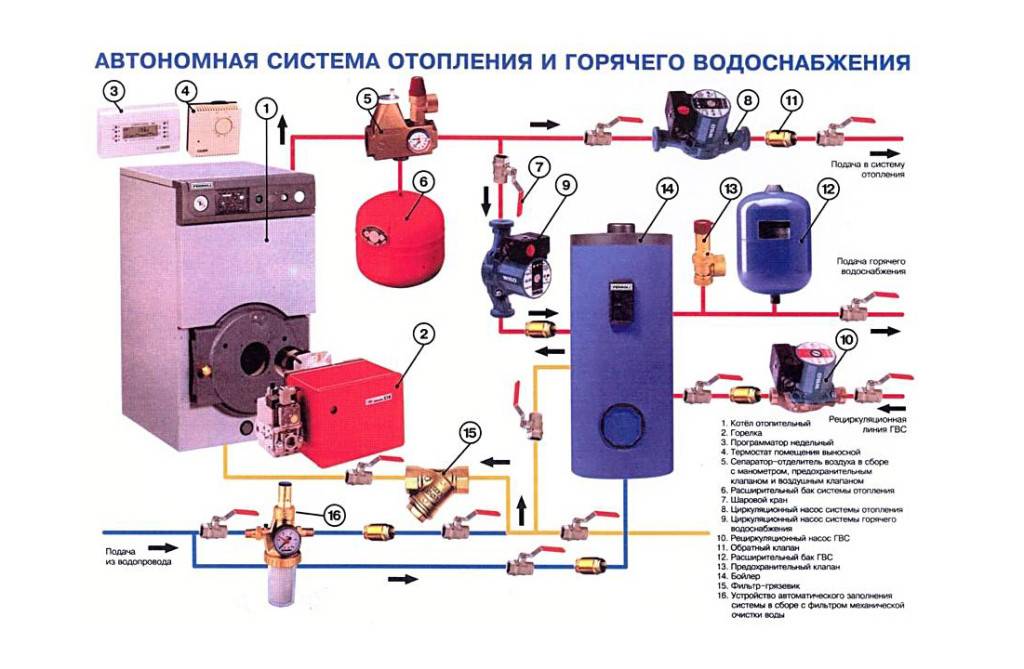
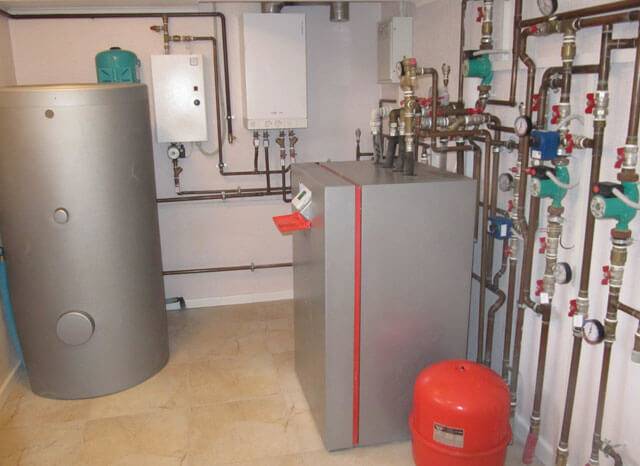
System Components
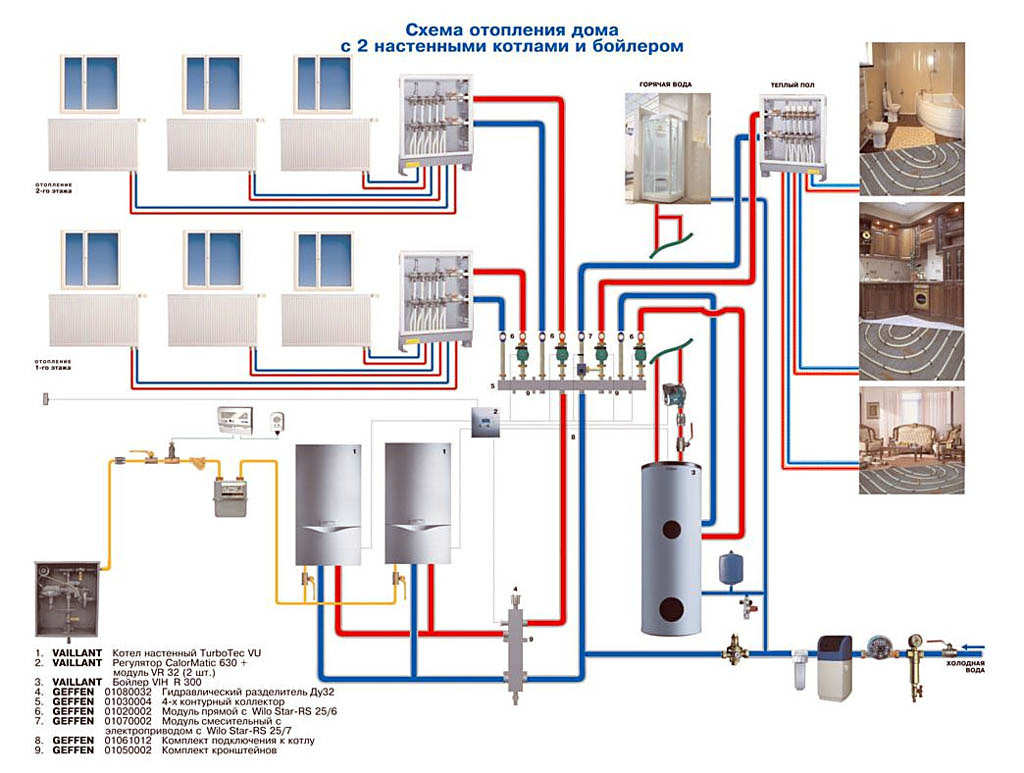
Before the start of work, a draft of the future heating system is drawn up. The heating scheme of a private house with a gas boiler takes into account the size and location of the building, on the basis of which the components are selected:
1. Heat generator
The type of heating system is determined by the selected fuel. Depending on the fuel used, there are:
- Gas boilers. Gas can be obtained centrally or create your own storage.
- Diesel.

Economical and reliable way of heating - gas boiler
- On solid fuel. The raw material is coal, firewood, peat, fuel briquettes or pellets (wood fuel pellets).
- Electrical.Electrolysis (electrode), induction devices, as well as boilers on heating elements are used.
- Combined. Popular options are combinations of gas with solid or liquid fuels.
- Universal. The design has several fireboxes for different types of fuel.
2. Pipes
Installation of gas heating in a private house involves the use of several types of pipes:
- Steel. There are ordinary and galvanized products that are connected both by welding and mechanical (threaded) method. Can cause an accident (rupture) if water is allowed to freeze.
- Polymer (plastic). They are not subject to corrosion, are silent, tolerate frost without problems. The pipes have a significant coefficient of thermal expansion and do not cope well with high temperatures (only metal pipes are suitable for arranging the chimney and piping the boiler).

Copper pipes in the distribution of heating a private house with a gas boiler
- Metal-plastic. Composite (multilayer) products, reliable and durable. Installation is carried out using fittings.
- Copper. They are not afraid of freezing because of their plasticity, they have high thermal conductivity (higher than that of steel products). Copper pipes are subject to electrochemical corrosion and are also expensive.
3. Expansion tank
Water has a significant thermal expansion (when heated to 90°C, its volume increases by 4%). If in an open (not sealed) system this is not critical, then in a closed (with forced circulation) it is fraught with equipment damage.In order not to spoil the system and compensate for the pressure in the pipes, an expansion tank (hydraulic accumulator) is built into it.
The expansion tank is a sealed steel (sometimes stainless) cylinder, consisting of two compartments. A flexible membrane is built between the compartments, separating the hot coolant and the pressurized gas.
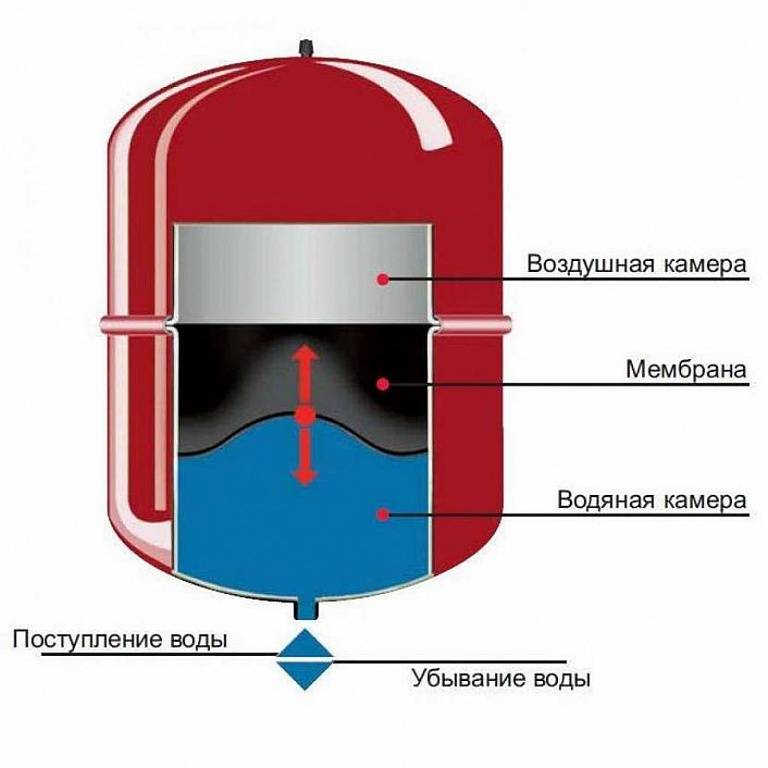
Expansion tank action algorithm
4. Radiators
Manufacturers produce batteries for different heating systems; they differ in the material of manufacture (cast iron, steel, aluminum, bimetallic radiators) and in the number of sections. There are several types of heating radiators:
- Sectional. Old cast iron radiators and modern tubular steel varieties.
- Panel. All-forged steel, with heating and convection plates, on which the heat output of the radiator depends.
- Vertical (towel dryer).
- Convectors.
- Underfloor heating systems.
5. Devices and accessories
The water heating system needs to be controlled. For this are intended:
- manometers;
- control and safety valves (shut-off valves and thermostatic valves).

The pressure gauge on the expansion tank monitors the pressure in the heating system
Alternative heating methods
 Non-traditional energy sources still cannot completely replace traditional ones, but their use will positively affect the cost of basic heating.
Non-traditional energy sources still cannot completely replace traditional ones, but their use will positively affect the cost of basic heating.
Mankind uses the energy gifts of nature:
- sun;
- wind;
- heat of the ground or water.
Solar collectors
The easiest way to get free heat, which also does not require energy costs.The collector is a radiator exposed to the sun, which is connected by pipes to a heat accumulator (a large barrel of water).
The coolant circulates in the system, which heats up in the radiator, and then gives off the received heat to the heat accumulator. The latter, by means of a heat exchanger, heats the working medium for the heating system.
The most efficient are vacuum collectors, in which the radiator tubes are placed in flasks with evacuated air (the coolant is, as it were, in a thermos).
Wind turbines
- wind generator (to produce 4 kW of energy, you need a 10-meter impeller);
- battery;
- inverter to convert DC to AC.
The weak point of the system is the battery: it is expensive, you have to change it often.
Heat pump
The device, completely similar to those that work in refrigerators and air conditioners, allows you to "pump out" thermal energy from low-grade sources - soil or water with a temperature of +5 - +7 degrees.
The system requires electricity, but for every kW of electricity consumed, it is possible to obtain from 3 to 5 kW of heat.

How a heat pump works
Calculation of the heating system at home
| The calculation of heating systems for a private house is the very first thing that begins with the design of such a system. We will talk with you about the air heating system - these are the systems that our company designs and installs both in private homes and in commercial buildings and industrial premises. Air heating has many advantages over traditional water heating systems – you can read more about it here. |
System calculation - online calculator
Why is a preliminary calculation of heating in a private house necessary? This is required to select the correct power of the necessary heating equipment, which allows you to implement a heating system that provides heat in a balanced way to the corresponding rooms of a private house. A competent choice of equipment and the correct calculation of the power of the heating system of a private house will rationally compensate for heat loss from building envelopes and the flow of street air for ventilation needs. The formulas themselves for such a calculation are quite complex - therefore, we suggest you use the online calculation (above), or by filling out the questionnaire (below) - in this case, our chief engineer will calculate, and this service is completely free.
How to calculate the heating of a private house?
Where does such a calculation begin? Firstly, it is required to determine the maximum heat loss of the object (in our case, this is a private country house) under the worst weather conditions (such a calculation is carried out taking into account the coldest five-day period for this region). It will not work to calculate the heating system of a private house on the knee - for this they use specialized calculation formulas and programs that allow you to build a calculation based on the initial data on the construction of the house (walls, windows, roofs, etc.). As a result of the data obtained, equipment is selected whose net power must be greater than or equal to the calculated value. During the calculation of the heating system, the desired model of the duct air heater is selected (usually it is a gas air heater, although we can use other types of heaters - water, electric).Then the maximum air performance of the heater is calculated - in other words, how much air is pumped by the fan of this equipment per unit of time. It should be remembered that the performance of the equipment differs depending on the intended mode of use: for example, when air conditioning, the performance is greater than when heating. Therefore, if in the future it is planned to use an air conditioner, then it is necessary to take the air flow in this mode as the initial value of the desired performance - if not, then only the value in the heating mode is sufficient.
At the next stage, the calculation of air heating systems for a private house is reduced to the correct determination of the configuration of the air distribution system and the calculation of the cross sections of the air ducts. For our systems, we use flangeless rectangular air ducts with a rectangular section - they are easy to assemble, reliable and conveniently located in the space between the structural elements of the house. Since air heating is a low-pressure system, certain requirements must be taken into account when building it, for example, to minimize the number of turns of the air duct - both the main and the terminal branches leading to the grates. The static resistance of the route should not exceed 100 Pa. Based on the performance of the equipment and the configuration of the air distribution system, the required section of the main air duct is calculated. The number of terminal branches is determined based on the number of feed grates required for each specific room of the house.In the air heating system of a house, standard supply grilles with a size of 250x100 mm with a fixed throughput are usually used - it is calculated taking into account the minimum air velocity at the outlet. Thanks to this speed, air movement is not felt in the premises of the house, there are no drafts and extraneous noise.
| The final cost of heating a private house is calculated after the end of the design stage based on the specification with a list of installed equipment and elements of the air distribution system, as well as additional control and automation devices. To make an initial calculation of the cost of heating, you can use the questionnaire for calculating the cost of the heating system below: |
online calculator
Heating system piping
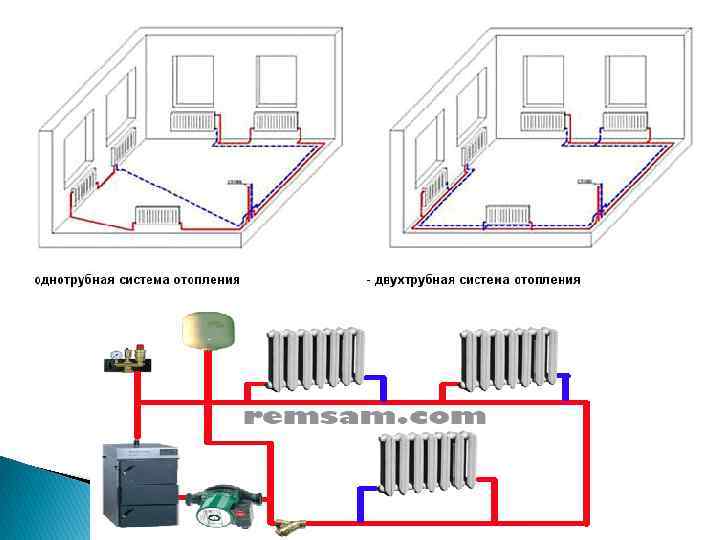
The most popular are 2 schemes: one-pipe and two-pipe. Let's take a look at what they are.
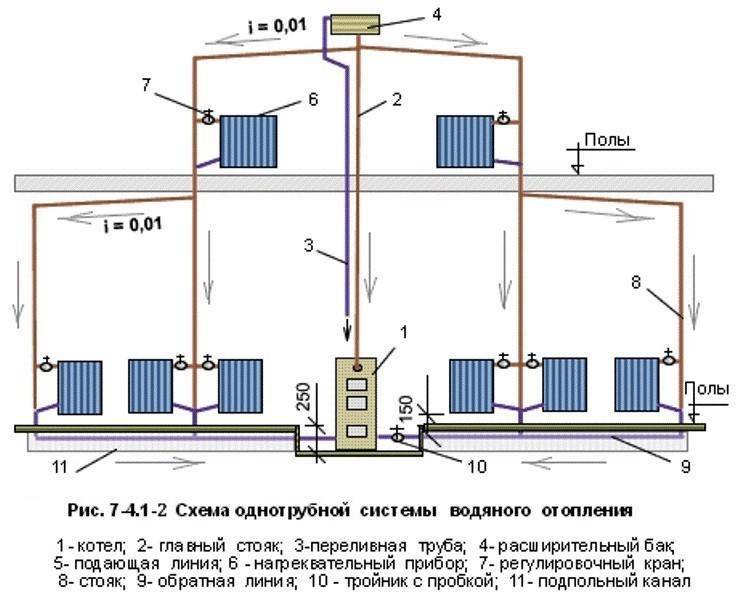
A single-pipe system is the most elementary option, however, not the most effective. It is a vicious circle of pipes, valves, automation, the center of which is the boiler. A pipe runs from it along the lower plinth to all rooms, connecting to all batteries and other heating devices.
Plus diagrams. ease of installation, a small amount of material for the construction of the circuit.
Minus. uneven distribution of coolant over radiators. Batteries in the outermost rooms will warm up worse, as the last ones in the way of water movement. However, this problem is solved by installing a pump or increasing the number of sections in the last radiators.
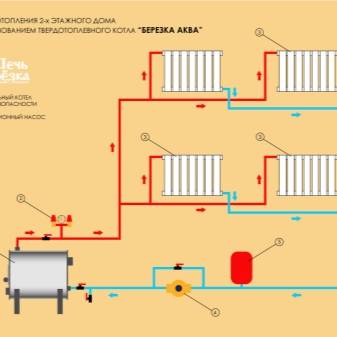
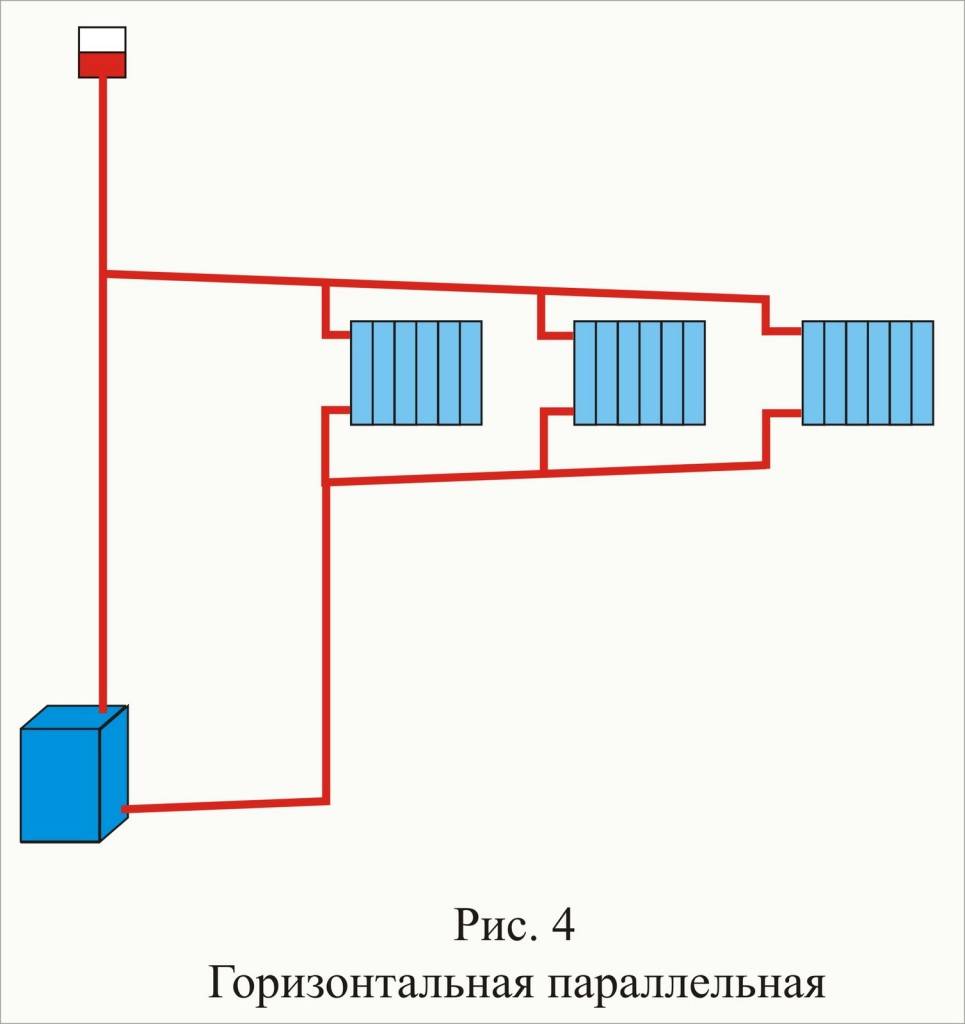
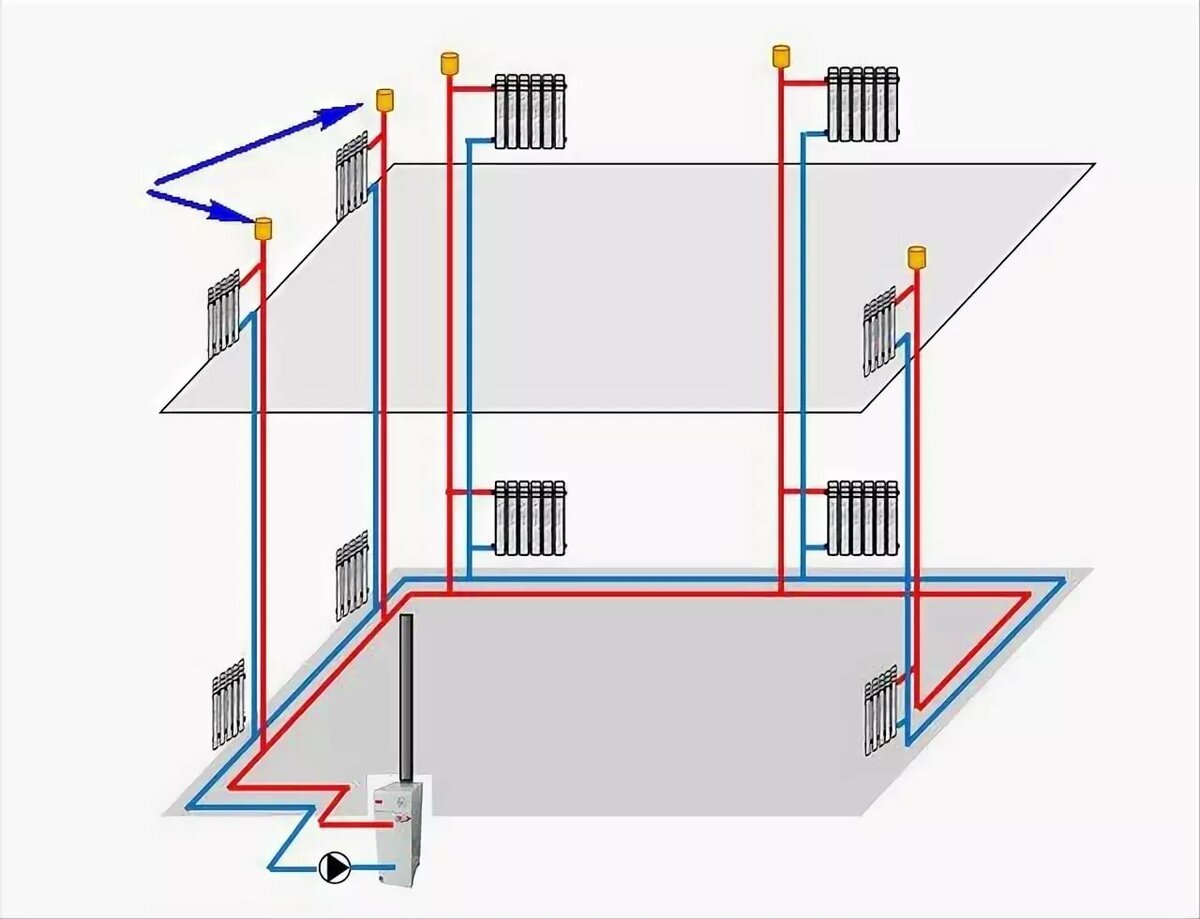
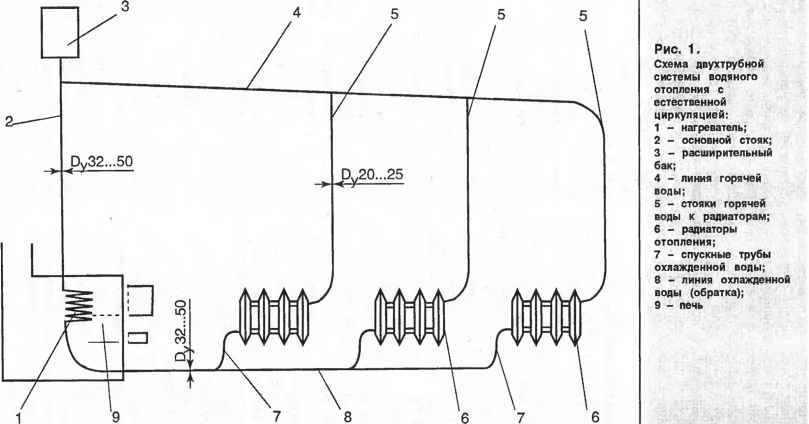
A two-pipe system is a more efficient way, since it solves the problem of uniform distribution of water across all heating devices. Pipes can be located at the top (this option is preferable, because then the water can circulate for natural reasons) or at the bottom (then a pump is required).
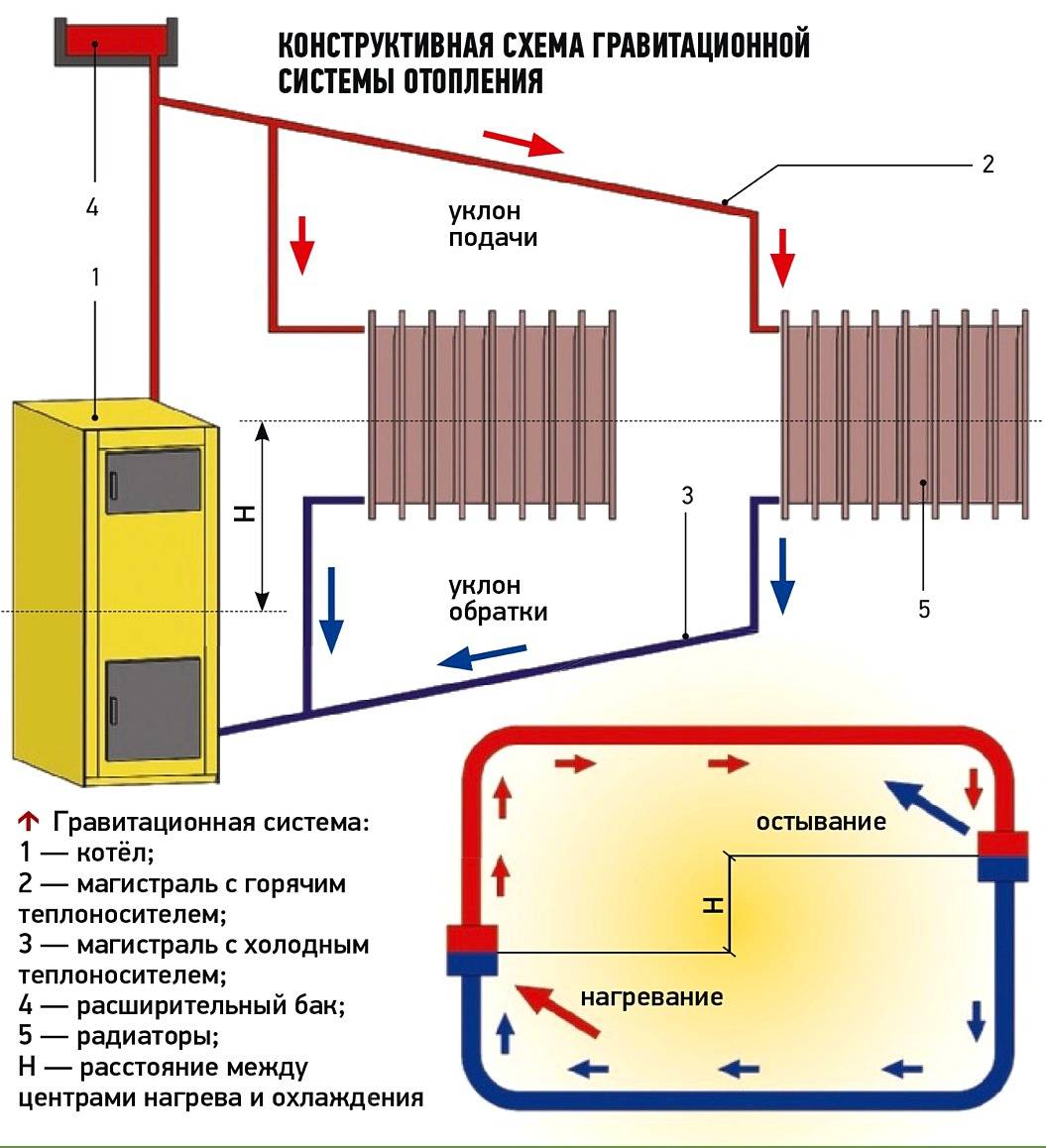
Scheme with natural circulation
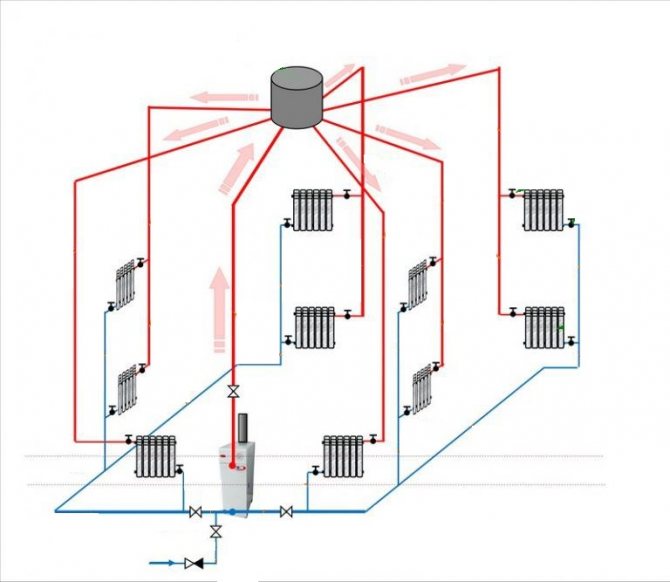
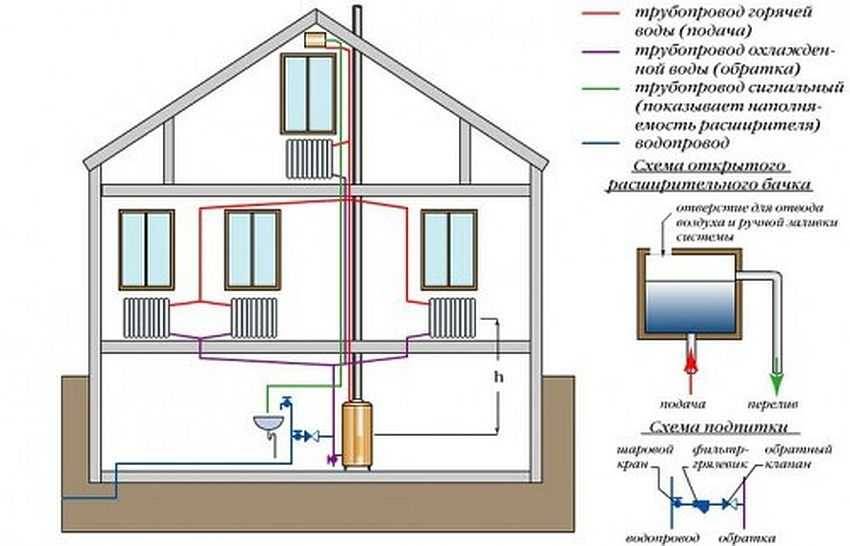
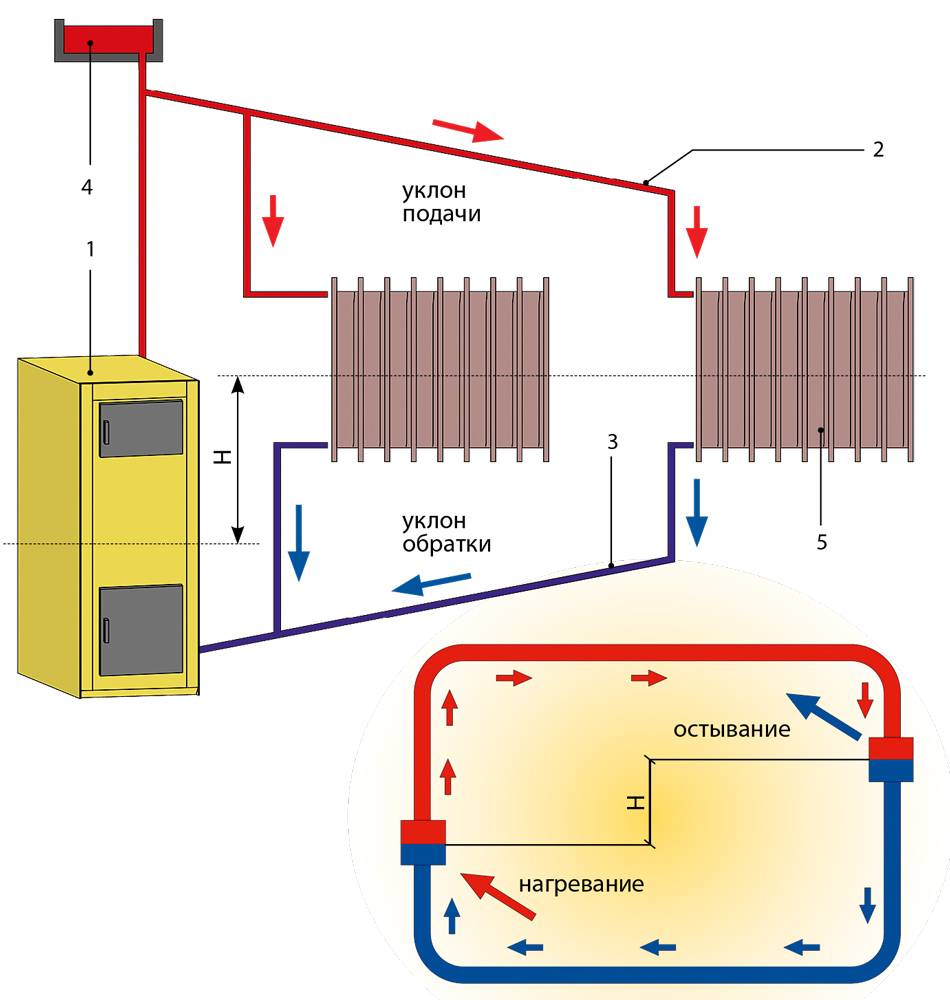
To understand the principle of operation of the gravity system, study the typical scheme used in two-story private houses. Combined wiring is implemented here: the supply and return of the coolant occurs through two horizontal lines, united by single-pipe vertical risers with radiators.
How gravity heating of a two-story house works:
- The specific gravity of the water heated by the boiler becomes smaller. A colder and heavier coolant begins to displace hot water up and take its place in the heat exchanger.
- The heated coolant moves along a vertical collector and is distributed along horizontal lines laid with a slope towards the radiators. The flow velocity is low, about 0.1–0.2 m/s.
- Diverging along the risers, the water enters the batteries, where it successfully gives off heat and cools. Under the influence of gravity, it returns to the boiler through the return collector, which collects the coolant from the remaining risers.
- The increase in water volume is compensated by an expansion tank installed at the highest point. Typically, the insulated container is located in the attic of the building.
Schematic diagram of gravity distribution with a circulation pump
In the modern design, gravity systems are equipped with pumps that accelerate the circulation and heating of the premises.The pumping unit is placed on the bypass parallel to the supply line and operates in the presence of electricity. When the light is turned off, the pump is idle, and the coolant circulates due to gravity.
Scope and disadvantages of gravity
The purpose of the gravity scheme is to supply heat to dwellings without being tied to electricity, which is important in remote regions with frequent power outages. A network of gravity pipelines and batteries is able to work together with any non-volatile boiler or from furnace (formerly called steam) heating.
Let's analyze the negative aspects of using gravity:
- due to the low flow rate, it is necessary to increase the coolant flow rate through the use of large diameter pipes, otherwise the radiators will not warm up;
- in order to “spur” natural circulation, horizontal sections are laid with a slope of 2-3 mm per 1 m of the main;
- healthy pipes running under the ceiling of the second floor and above the floor of the first floor spoil the appearance of the rooms, which is noticeable in the photo;
- automatic regulation of air temperature is difficult - only full-bore thermostatic valves should be purchased for batteries that do not interfere with the convective circulation of the coolant;
- the scheme is unable to work with underfloor heating in a 3-storey building;
- an increased volume of water in the heating network implies a long warm-up and high fuel costs.
In order to fulfill requirement No. 1 (see the first section) in conditions of unreliable power supply, the owner of a two-story private house will have to bear the cost of materials - pipes of increased diameter and lining for the manufacture of decorative boxes.The remaining disadvantages are not critical - slow heating is eliminated by installing a circulation pump, lack of efficiency - by installing special thermal heads on radiators and pipe insulation.
Design Tips
If you took the development of a gravity heating scheme into your own hands, be sure to consider the following recommendations:
- The minimum diameter of the vertical section coming from the boiler is 50 mm (meaning the internal size of the nominal bore of the pipe).
- The horizontal distributing and collecting manifold can be reduced to 40 mm, in front of the last batteries - up to 32 mm.
- A slope of 2-3 mm per 1 meter of pipeline is made towards the radiators on the supply and the boiler on the return.
- The inlet pipe of the heat generator must be located below the batteries of the first floor, taking into account the slope of the return line. You may have to make a small pit in the boiler room for installing a heat source.
- On the connections to the heating appliances of the second floor, it is better to install a direct bypass of small diameter (15 mm).
- Try to lay the upper distribution manifold in the attic so as not to lead under the ceilings of the rooms.
- Use an open-type expansion tank with an overflow pipe leading to the street, and not to the sewer. So it is more convenient to monitor the overflow of the container. The system will not work with a membrane tank.
The calculation and design of gravity heating in a complex-planned cottage should be entrusted to specialists. And the last thing: lines Ø50 mm and more will have to be made with steel pipes, copper or cross-linked polyethylene. The maximum size of metal-plastic is 40 mm, and the diameter of polypropylene will come out simply menacing due to the wall thickness.