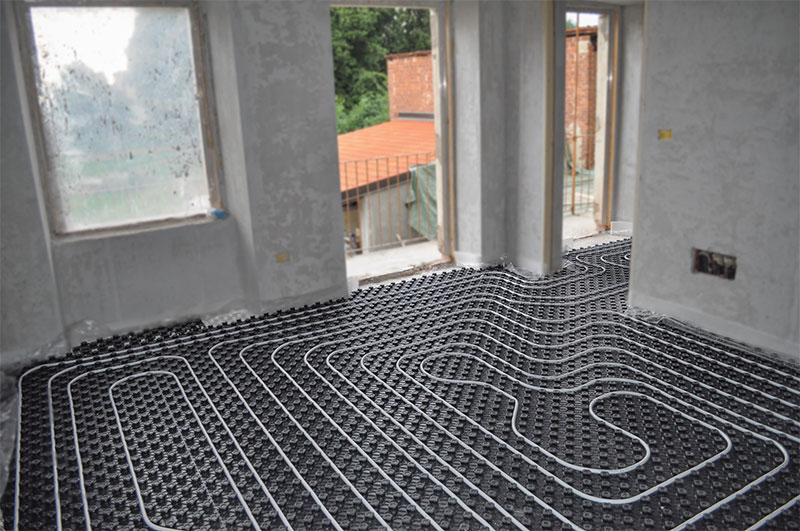
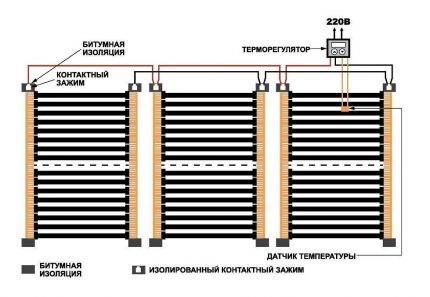
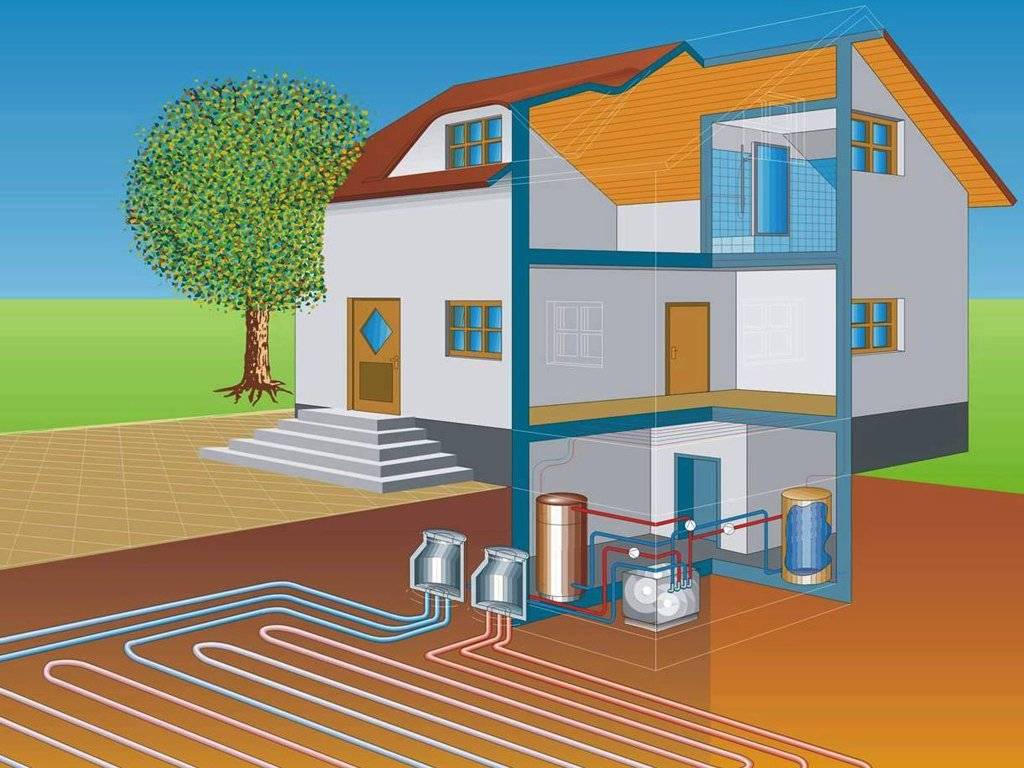
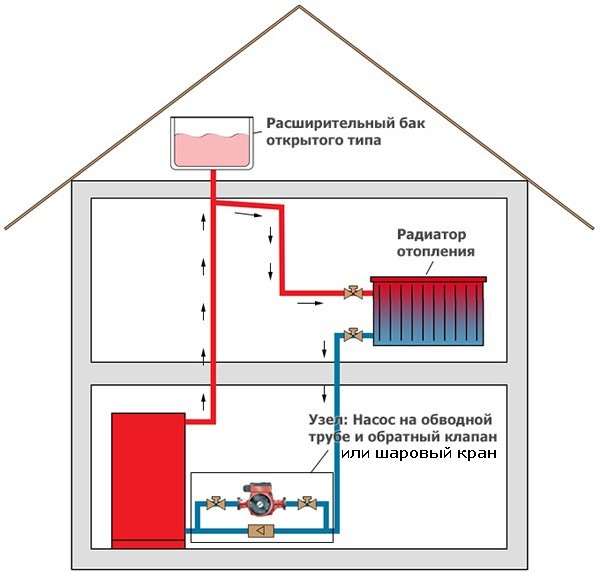
- Closed heating system - what is it
- Types of wiring
- Single pipe
- Two-pipe
- Two-pipe radial
- One-pipe heating scheme
- Radial piping layout: features
- Elements of the heating pipe wiring diagram
- Selection of inlet and outlet pipes
- Where is it applied?
- Single pipe main wiring
- Features of the difference between the operation of a closed circuit and an open circuit are as follows:
- How does it work
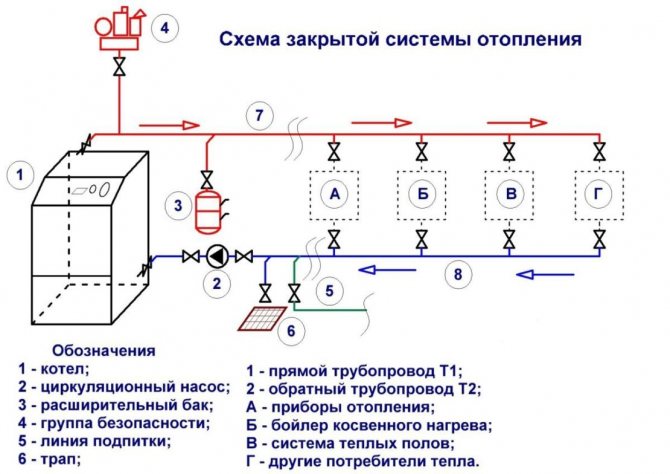
- The main elements of the water heating system
- Boiler selection by the number of circuits
- Boiler selection by type of fuel
- Boiler selection by power
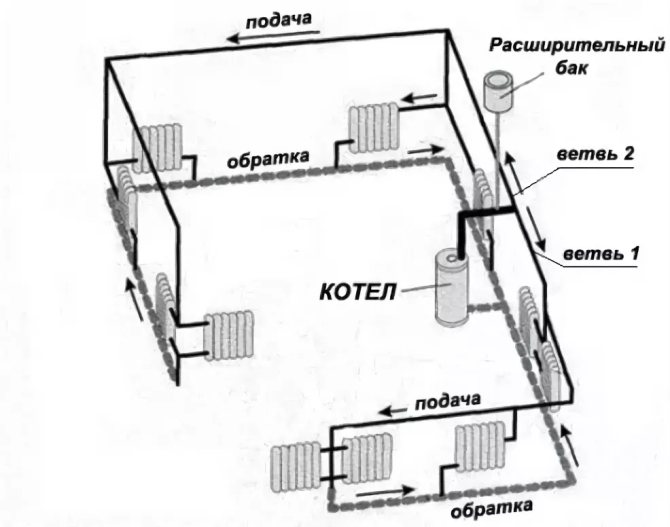
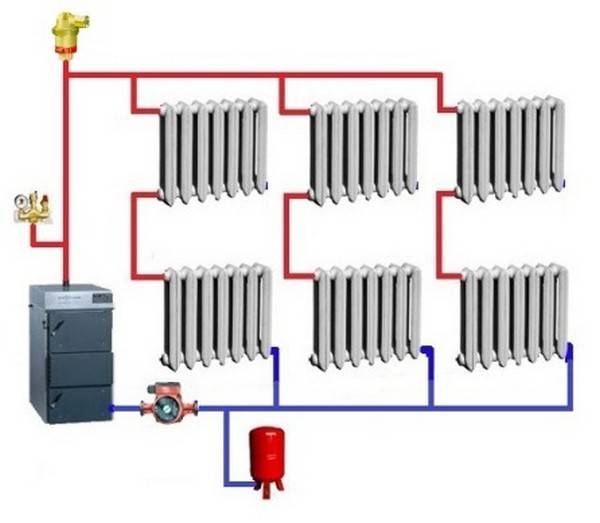
- Cottage heating schemes - piping
- One-pipe cottage system
- Two-pipe cottage heating scheme
- Collector heat supply of the cottage
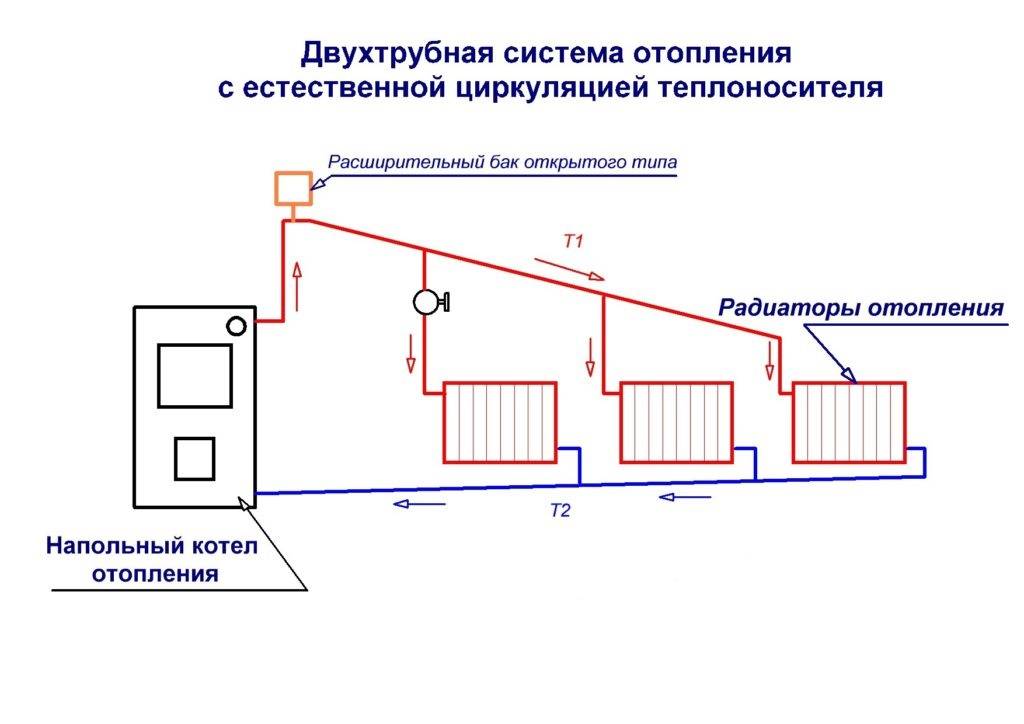
Closed heating system - what is it
The heating system of a private house has an expansion tank. This is a container that contains a certain amount of coolant. This tank compensates for thermal expansion under various operating conditions. By design, expansion tanks are open and closed, respectively, heating systems are called open and closed.
Two-pipe closed heating system
The closed heating circuit is automated, it works without human intervention for a long time.Any type of coolant is used, including antifreeze and antifreeze, the pressure is maintained constant. Let's talk about a few pluses that relate to wiring and operation:
- There is no direct contact of the coolant with air, therefore, there is no (or almost no) free oxygen, which is a powerful oxidizing agent. This means that the heating elements will not oxidize, which will increase their service life.
- An expansion tank of a closed type is placed anywhere, usually not far from the boiler (wall-mounted gas boilers come immediately with expansion tanks). An open tank should be in the attic, and these are additional pipes, as well as insulation measures so that heat does not “leak” through the roof.
- In a closed system, there are automatic air vents, so there is no airing.
All in all closed heating system considered more convenient. Its main drawback is energy dependence. The movement of the coolant is provided by a circulation pump (forced circulation), and it does not work without electricity. Natural circulation in closed systems can be organized, but it is difficult - flow control is required using the thickness of the pipes. This is a rather complicated calculation, because it is often believed that a closed heating system only works with a pump.
To reduce energy dependence and increase the reliability of heating, they install uninterruptible power supplies with batteries and / or small generators that will provide emergency power.
Types of wiring
Horizontal heating distribution, depending on its design, can be:
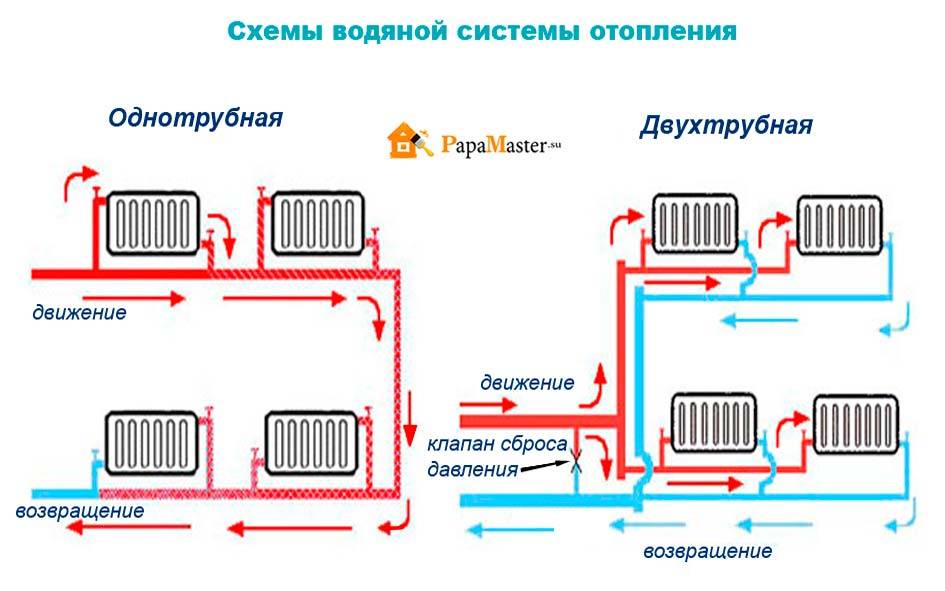
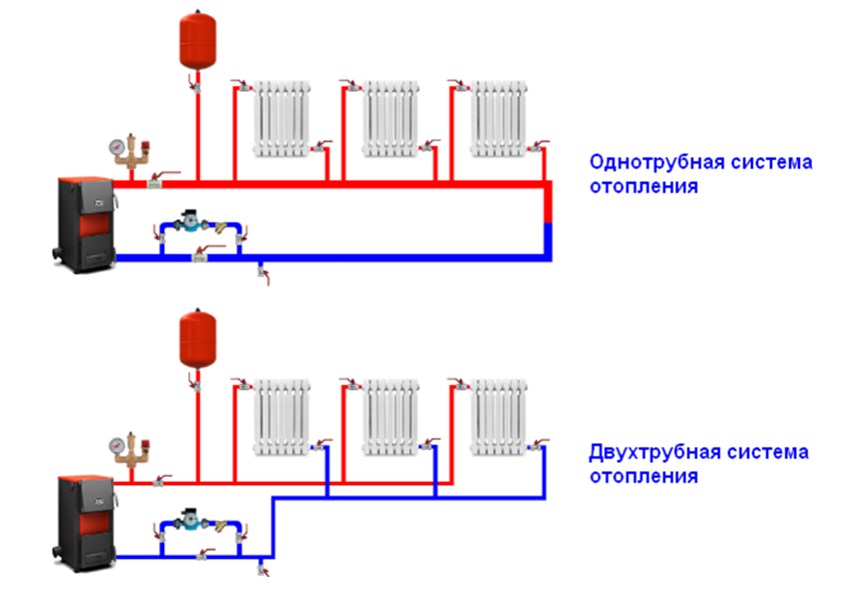
Single pipe
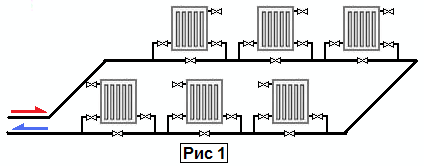
One-pipe connection diagram
As can be understood from the figure, in this embodiment, warm and cold liquid pass through the same pipe, and the radiators are connected in series with respect to each other.
Of course, the price of such a design is much lower due to the savings in materials, but several tangible disadvantages also pop up:
Water cools down during the period until it passes through the entire circuit, which significantly reduces the efficiency and increases the cost of heating the room.
- A noticeable difference between the temperatures of the first and last radiators in the circuit. This negatively affects the uniformity of heat distribution.
- The difficulty of making adjustments with your own hands. Each change in the operation of one of the radiators will affect the functioning of all the others.

Adjusting the operation of the heating radiator
Inconvenience in carrying out repair work, since even the smallest restoration will require the shutdown of the entire system.
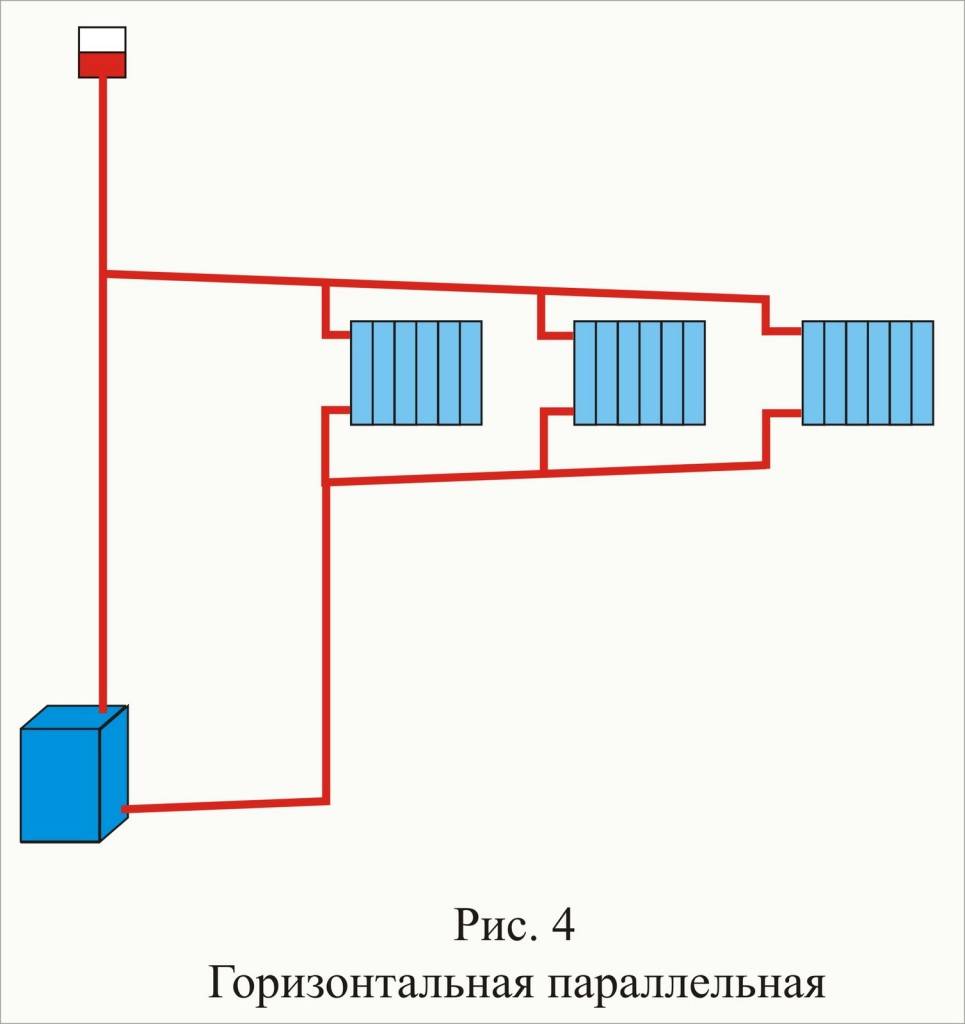
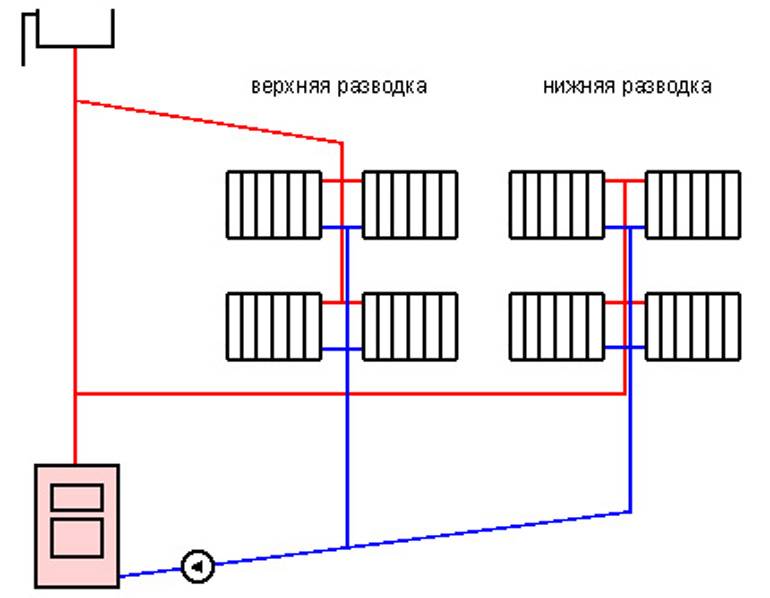
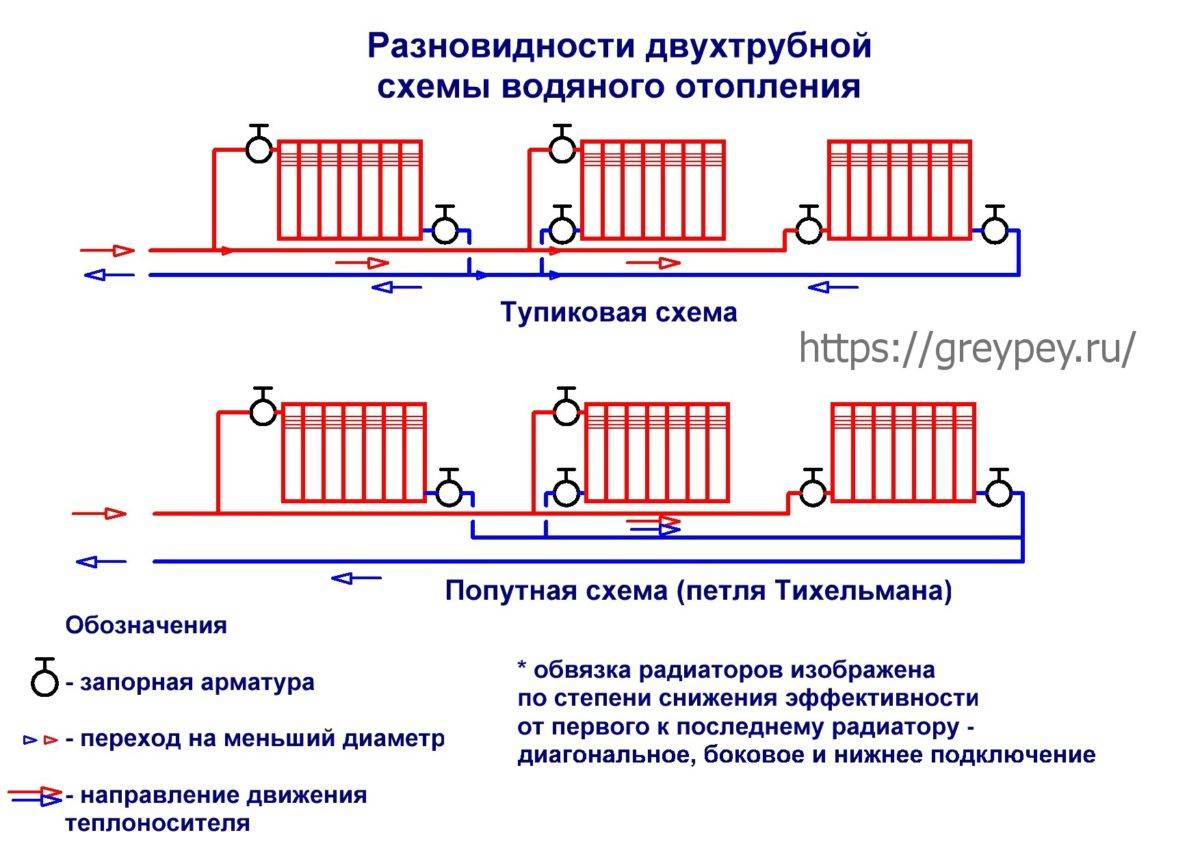
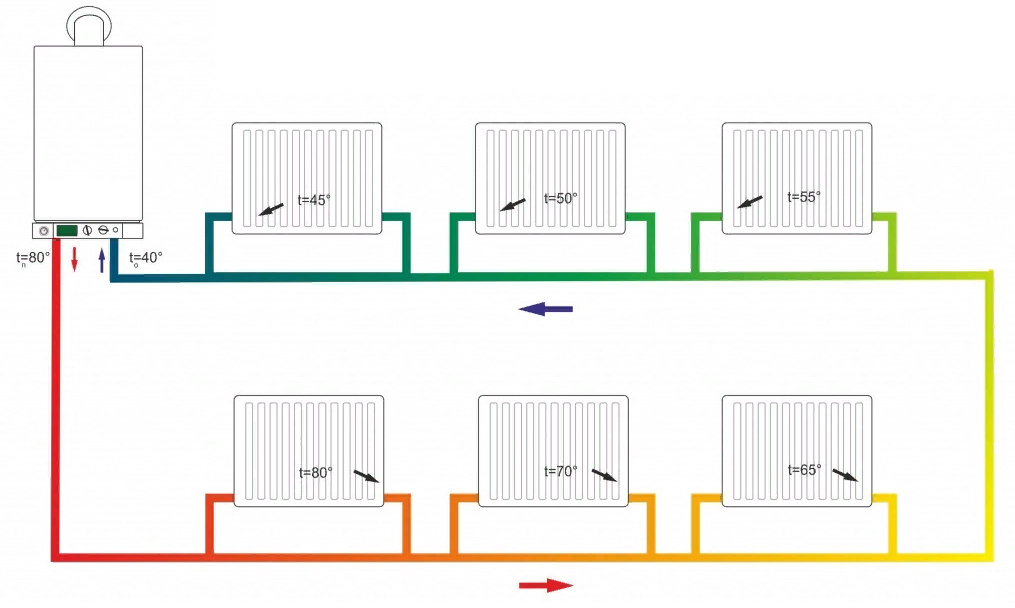
Two-pipe
Two-pipe connection diagram
There are already a lot of advantages over the previous option, and the potential of horizontal wiring is fully realized:
- The liquid flowing through the batteries does not have time to cool down, since the coolant is supplied through one pipe, and the cooled water is removed through the other.
- The radiators are heated in parallel, which makes it possible to achieve the same temperature on them, and, consequently, a better microclimate in the house.
- Possibility of temperature control. This allows you to use the heating system more economically, reducing its power during periods of warming outside.
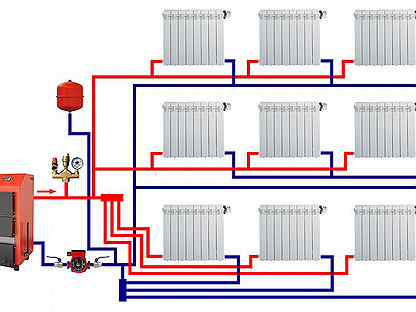
Two-pipe radial
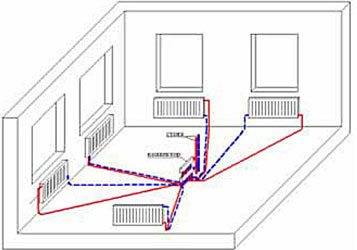
Diagram of a two-pipe beam connection
It is also a collector, as it provides for the installation of a collector in each apartment, which will distribute the coolant supply to each radiator individually.

Example of a collector for a horizontal heating system
Such a pipe layout, although it has several disadvantages:
- A large number of materials, which greatly increases the cost of the system.
- The need for circulation pumps.
But a large number of advantages still makes it the most progressive and in demand:
- The permissibility of adjusting the performance of each radiator individually. This provides unique opportunities to control the microclimate of your home.
- Each of the circuits is a closed self-sufficient system. They can be equipped with additional devices, and if repair work is necessary, it will not be necessary to turn off all heating, it will be enough to block the required battery.
- Air vents are not required on the radiators, they are already on the manifold.

Heat meter example
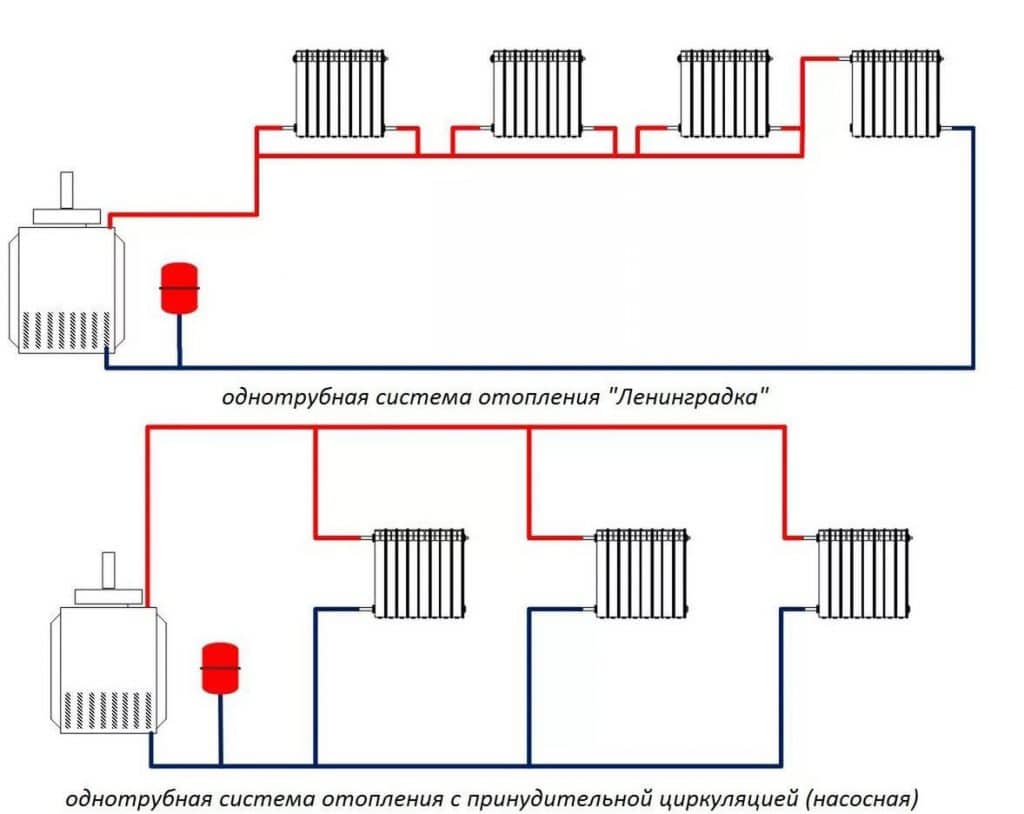
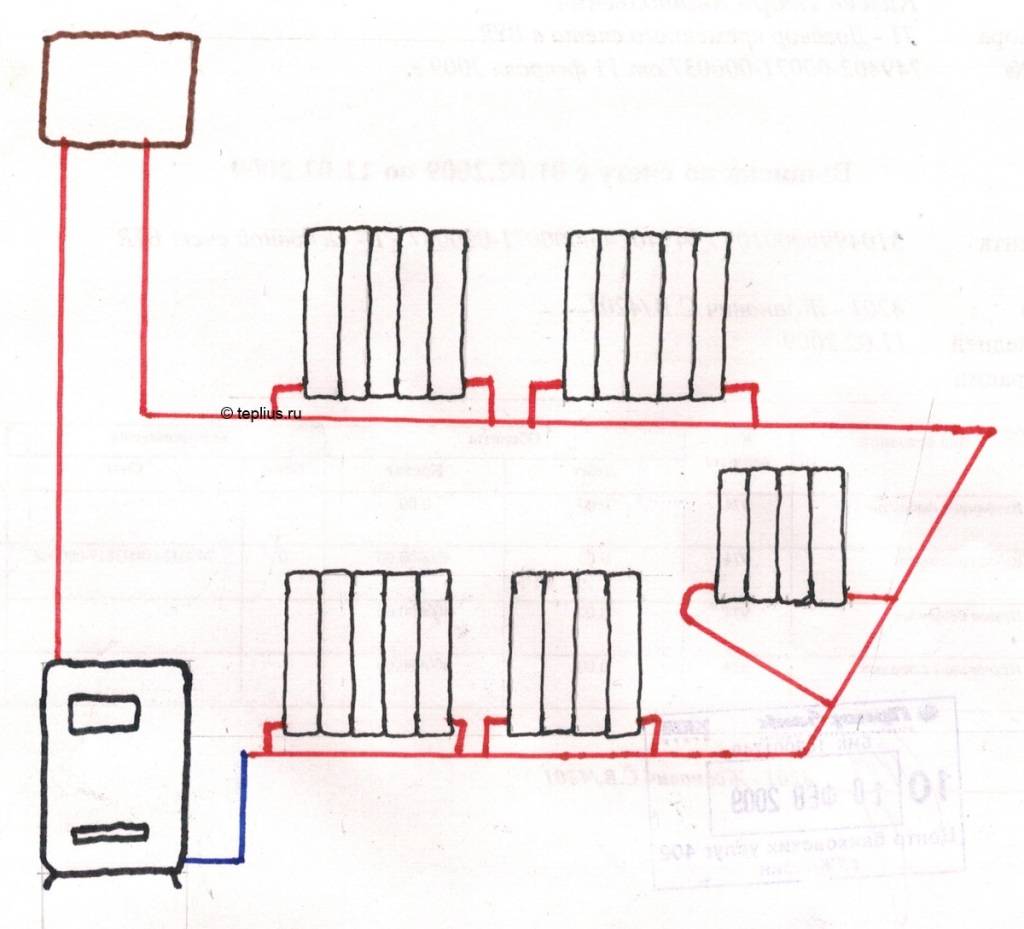
One-pipe heating scheme
From the heating boiler, you need to draw the main line representing the branching. After this action, it contains the required number of radiators or batteries. The line, drawn according to the design of the building, is connected to the boiler. The method forms the circulation of the coolant inside the pipe, heating the building completely. The circulation of warm water is adjusted individually.
A closed heating scheme is planned for Leningradka. In this process, a single-pipe complex is mounted according to the current design of private houses. At the request of the owner, elements are added to:
- Radiator controllers.
- Temperature controllers.
- balancing valves.
- Ball valves.
Leningradka regulates the heating of certain radiators.
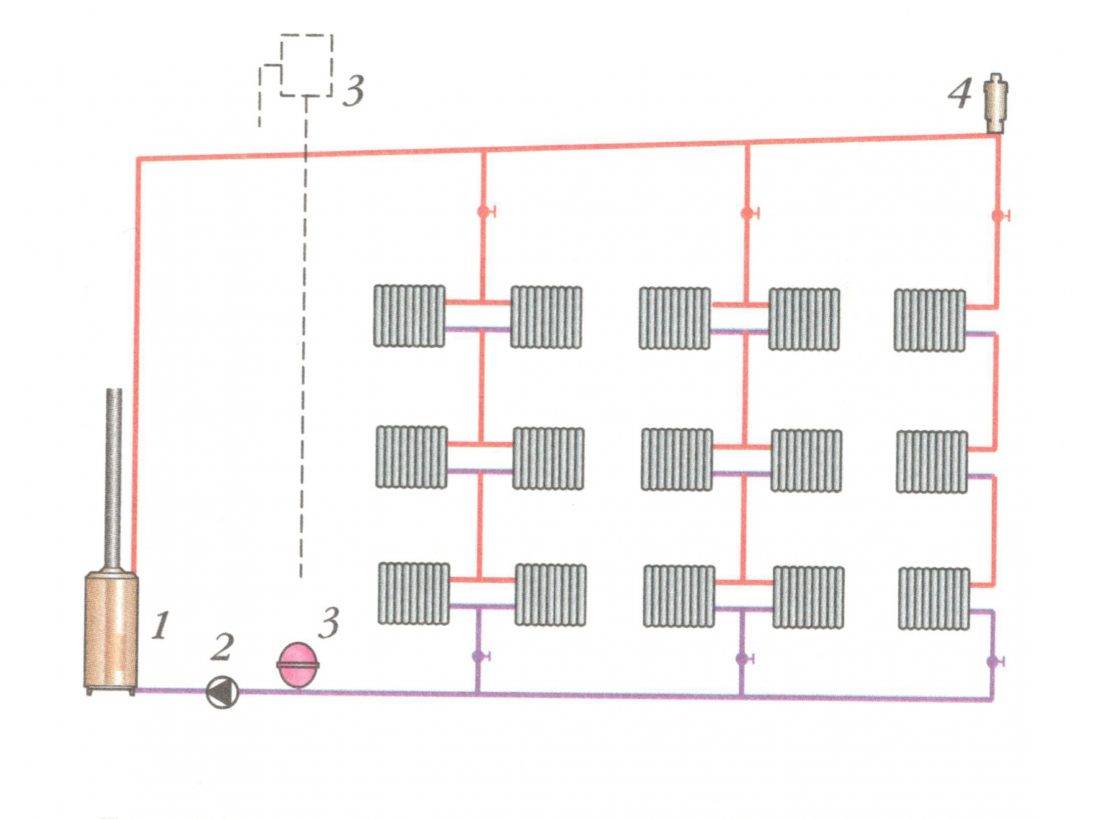
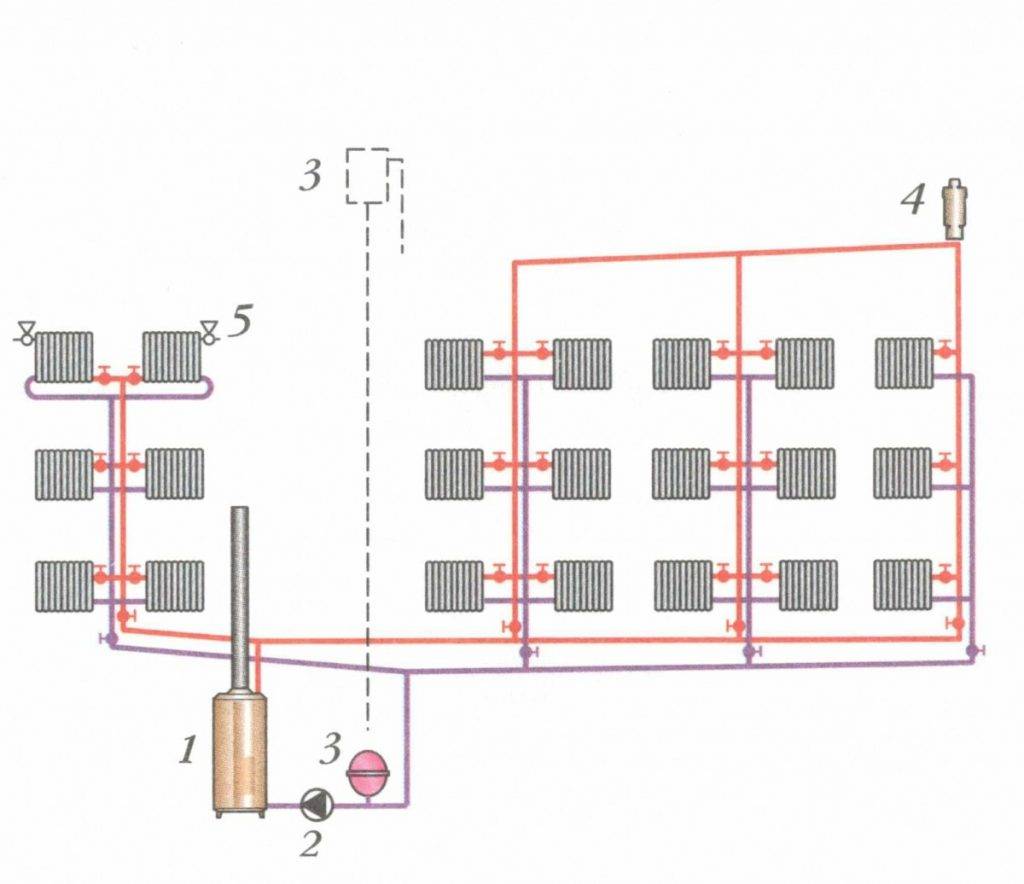
Radial piping layout: features
The most optimal beam distribution of the heating system is suitable for those cases where the house has several floors or there are a large number of rooms. Thus, it is possible to significantly increase the efficiency of all equipment, guarantee high-quality heat transfer, and eliminate unnecessary heat losses.
One of the options for arranging the collector scheme of the pipeline
The principle of operation of the heating circuit, made according to the collector circuit, is quite simple, but at the same time, there are some features in it. So, for example, a radiant heating scheme involves the installation of several collectors on each floor of a building, and from them the organization of piping, direct and reverse supply of coolant. As a rule, the instruction for such a wiring diagram implies the installation of all elements in a cement screed.
Elements of the heating pipe wiring diagram
Modern radiant heating is a whole structure, which consists of several main elements:
Boiler. Starting point, the unit from which the coolant is supplied to pipelines and radiators. The power of the equipment must necessarily correspond to the amount of heat consumed by heating;
Collector for the heating circuit
When choosing a circulation pump for a collector piping scheme (this is also required by the instructions), it is imperative to take into account a lot of parameters, ranging from the height and length of the pipelines (these elements create hydraulic resistance) to the materials of the radiators.
The power of the pump is not the main parameters (it only determines the amount of energy consumed) - attention should be paid to the speed of pumping the liquid. This parameter shows how much coolant the circulation pump can transfer in a certain unit of time;
Installation of plastic pipes in the heating collector circuit
Collectors for such systems can additionally be equipped with a variety of thermostatic or shut-off and control elements, thanks to which it is possible to provide a certain coolant flow in each of the branches (beams) of the system. In addition, the additional installation of automatic air purifiers and thermometers allows you to set up a more efficient operation of the system at no extra cost.
One of the options for distributing plastic pipes in a collector circuit
The selection of one or another type of collectors (and they are presented on the domestic market in a large assortment) is made according to the number of connected radiators or heating circuits. In addition, all combs also differ in the materials from which they are made - these can be polymeric materials, steel or brass;
Cabinets. Beam wiring of the heating system requires the hiding of all elements (distribution manifold, pipelines, valves) in special collector cabinets. Such designs are quite simple, but at the same time functional and practical. They can be both external and built into the walls.
Selection of inlet and outlet pipes
Before starting any work on the arrangement of the heating system, it is important to determine the main parameters of the pipes.To begin with, it should be noted that the outlets at the boiler, the supply line, as well as the entrance at the collector must have the same dimensions
Based on these properties, pipe diameters are also selected, and, if necessary, special adapters are used.
Selection of coolant from the tank and its distribution through the pipeline
The materials of the pipes for supplying and discharging the coolant can be very different, but it is best to use plastic products. It's all about their practicality, ease of installation work and accessibility.
Where is it applied?
It is logical to assume that the horizontal distribution of heat circuits is more suitable for private houses with individual heating. But in practice, such wiring is successfully used for apartment services in apartment buildings. Each apartment receives its own branch of the distributing thermal circuit with its own account, however, no methods of regulation without a special jumper are expected.
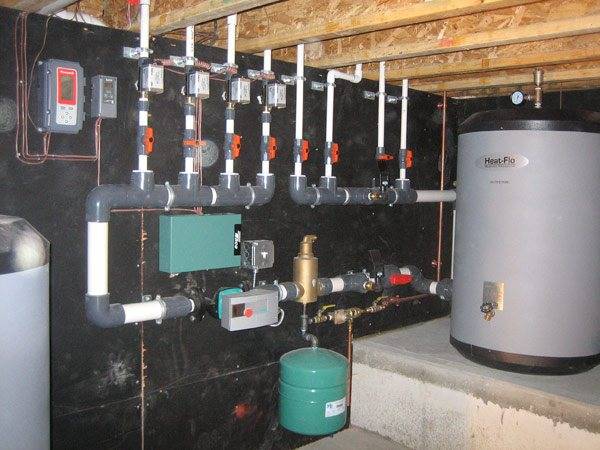

But there is another argument in favor of using such systems exclusively in private engineering - premium materials. Indeed, if vertical systems are usually based on metal pipes, then horizontal ones are mounted from polymeric materials with a heat-resistant coating. Obviously, cross-linked polyethylene PEX significantly increases the cost of the technical implementation of such a scheme. But it is the durability and reliability of this material that allows the use of horizontal heating systems in low-class apartment buildings. The cost of both installation and maintenance of the system is reduced.For example, if for welding with metal pipes in vertical risers it is necessary to connect a highly qualified welder, then the technology for assembling circuits from plastic pipes is within the power of a home master. With the help of permanent connections, it is easy to assemble the structure, and only in extreme cases, cross-linked propylene is welded with special soldering stations at the junctions.
Single pipe main wiring
In such a system, there are several heat sources through which the heating pipes pass. The coolant moves through such a system and gives off heat to devices located in certain sections of the circuit. Single-pipe horizontal heating in an apartment building has good efficiency and is relatively low cost.
The advantages of such a system are as follows:
- Minimum cost;
- Ease of installation;
- Wear resistance and long service life;
- Possibility of full heating of the building of any area.
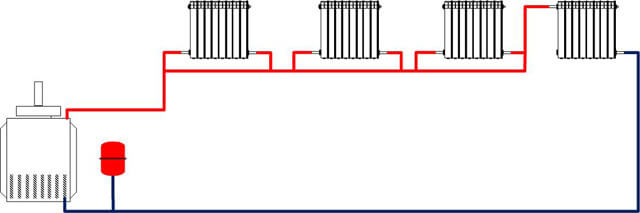
There are also disadvantages:
- The ability to adjust the temperature on each individual device is limited;
- Weak resistance to mechanical damage.
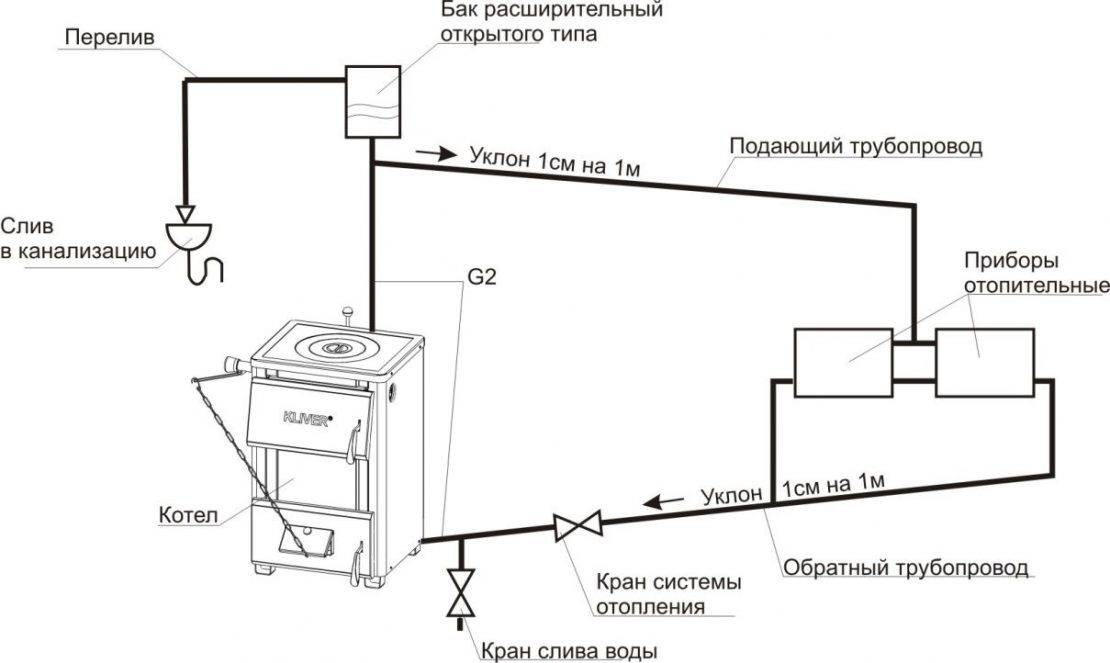
Features of the difference between the operation of a closed circuit and an open circuit are as follows:
- The expansion of the liquid, which occurs as a result of its heating in the boiler, is compensated in a membrane expansion tank. After the coolant entering the tank has cooled, it returns to the system again. Thus, a constant pressure is maintained in it.
- The creation of the necessary pressure occurs even at the stage of installation of the heating circuit.
- The circulation of the liquid is carried out only with the help of a pump.As a result, the closed circuit is entirely dependent on the availability of electricity (in addition to the cases of connecting an autonomous generator).
- The presence of a circulation pump does not impose strict limits on the diameter of the pipes used. In addition, the pipeline does not have to be located with a slope. The main condition is the location of the pump on the "return" in order for the cooled coolant to enter it.
- The lack of pipe slope can play a negative role. After all, even with a slight slope, the system will function without electricity. And with a horizontal arrangement of pipes, this system does not work. This disadvantage of a closed circuit covers its high efficiency and other advantages.
- The installation of this network is simple and can be applied to any premises, regardless of their area. In addition, insulation of the line is not required, since the pipes heat up very quickly.
- In the closed type, it is possible to use antifreeze as a coolant, instead of water. Also, this circuit is less exposed to corrosion, due to its tightness.
-
Despite the closeness of the system from the environment, its tightness can be broken. This can happen at the joints of the circuit, or at the stage of filling it with a coolant. Pipe bends and high points are also particularly critical. In order to get rid of air congestion, the network is equipped with a special. valves and cocks Mayevsky. If there are aluminum heating devices in the circuit, air vents are required (oxygen is released when aluminum and the coolant come into contact).
- The coolant must move in the same direction as the air. That is from bottom to top.
- After switching on the system, open the air outlet valves and close the water outlet valves.
- As soon as water comes out of the air faucet, close it.
- Only after all of the above, start the circulation pump.
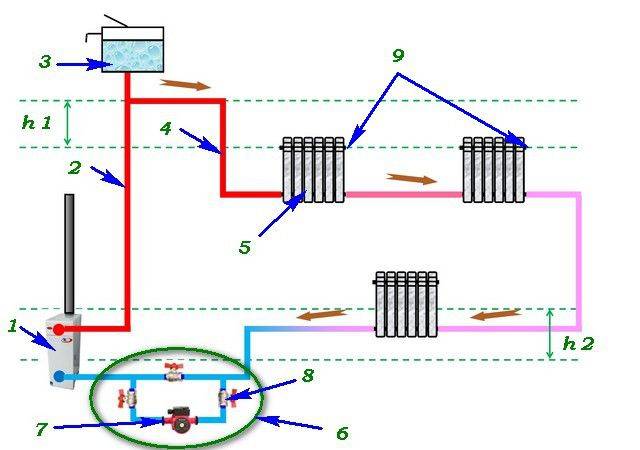
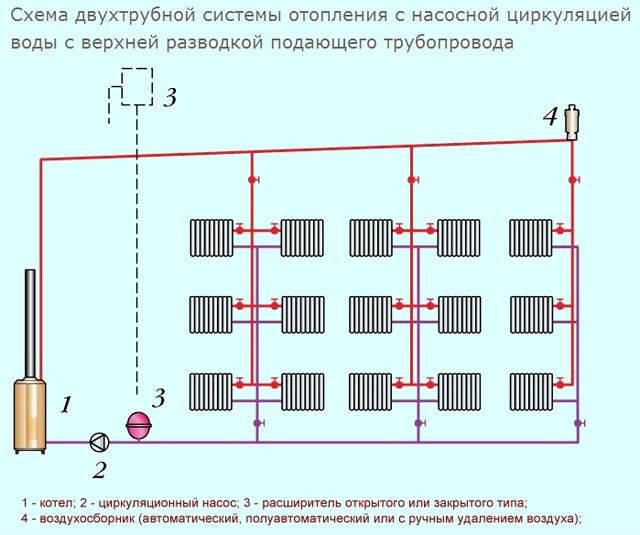
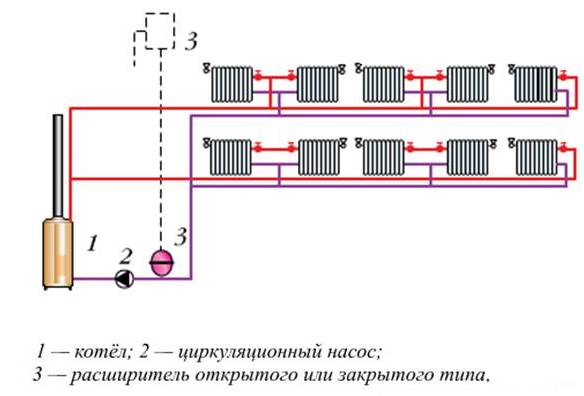
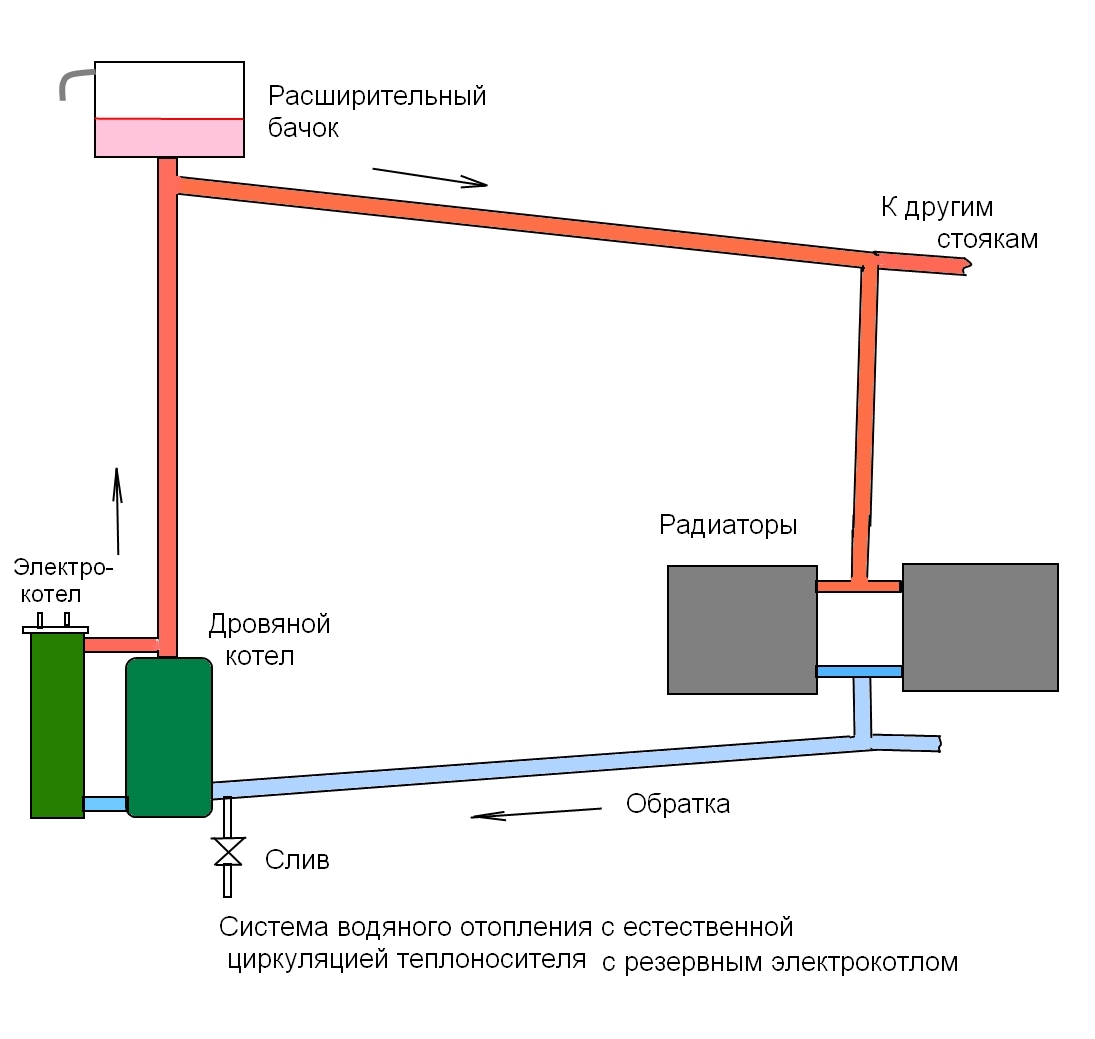
How does it work
Principle of operation
The scheme of such a heating system is quite simple. At the heart of everything is any boiler. It heats the coolant supplied through the pipe coming from the boiler. Why is such a scheme called one-pipe? Because one pipe is laid along the entire perimeter, which comes from the boiler and enters it. In the right places, radiators are installed on the brackets and connected to the pipe. The coolant (most often water) moves from the boiler, filling the first radiator in the node, then the second one, and so on. At the end, the water returns to the starting point and the cycle repeats. There is a continuous circulation process.
It should be noted that by assembling such a scheme, one may encounter one difficulty. Since the rate of advance of the coolant can be small, temperature losses are possible. Why? If we talk about a two-pipe system, then the principle of its operation is as follows: water enters the battery through one pipe, and leaves it through the other. In this case, its movement passes immediately through all the radiators, and there is no heat loss.
In a single-pipe system, the coolant enters all batteries gradually and, passing through them, loses temperature. So, if the temperature of the carrier was 60˚C when leaving the boiler, after passing through all pipes and radiators, it can drop to 50˚C.What to do in this case? To overcome such fluctuations, it is possible to increase the heat capacity of the batteries at the end of the chain, increasing their heat transfer, or to increase the temperature in the boiler itself. But all this will lead to additional costs that are unprofitable and make the cost of heating more expensive.
To get rid of such a problem without high costs, you need to increase the speed of the coolant through the pipes. There are 2 ways to do this:
Pump installation technology in the heating system
Install a circulation pump. So you can significantly increase the speed of movement of water in the system. In this case, the heat loss at the outlet will be significantly reduced. The maximum loss can be several degrees. These pumps are powered by electricity. It should be noted that for country houses where electricity is often cut off, this option will not be ideal.
Installing a collector directly behind the boiler
Install the booster manifold. This is a high straight pipe, thanks to which the water, passing through it, gains high speed. Then the coolant in the natural circulation system makes a full circle faster, which also solves the problem of heat loss. It is especially good to use this method in a multi-storey building, since work will be inefficient in a one-story building with low ceilings. For normal functioning of the collector, its height must be more than 2.2 m. You should know that the higher the accelerating collector is, the faster, more efficient and quieter the movement in the pipeline will be.
In such a system, there must be an expansion tank, which is best installed at the top point. It acts as a stabilizer, controlling the increase in the volume of the coolant. How does he work? When heated, the volume of water increases.These excesses enter the tank, preventing overpressure from occurring. When the temperature drops, the volume decreases and from the expansion tank goes back to the heating network.
That's the whole principle of operation of a single-pipe heating system. This is a closed circuit, which includes a boiler, main pipes, radiators, an expansion tank and elements that provide water circulation. Distinguish forced circulation, when all the work is done by the pump, and natural, in which the accelerating manifold is mounted. The difference of this design is that it does not provide a reverse-action pipe through which the coolant returns to the boiler. The second half of this wiring is called the return line.
The main elements of the water heating system
The main elements of the water heating system include:
- boiler;
- a device that supplies air to the combustion chamber;
- equipment responsible for the removal of combustion products;
- pumping units that ensure the circulation of the coolant through the heating circuit;
- pipelines and fittings (fittings, shut-off valves, etc.);
- radiators (cast iron, steel, aluminum, etc.).
Boiler selection by the number of circuits
For heating the cottage, you can choose a single-circuit or double-circuit boiler. What is the difference between these models of boiler equipment? A single-circuit boiler is designed only for heating the coolant intended for circulation through the heating system. Indirect heating boilers are connected to single-circuit models, which supply the facility with hot water for technical purposes. In dual-circuit models, the operation of the unit is provided in two directions that do not intersect with each other.One circuit is responsible only for heating, the other for hot water supply.
Boiler selection by type of fuel
The most economical and convenient type of fuel for modern boilers has always been and remains main gas. The efficiency of gas boilers is not disputed, since their efficiency is 95%, and in some models this figure goes off scale for 100%. We are talking about condensing units capable of "pulling" heat from the products of combustion, flying away in other models simply "into the pipe".
Heating a country cottage with a wall-mounted gas boiler is one of the most popular ways to heat living space in gasified regions.
However, not all territories are gasified, therefore, boiler equipment operating on solid and liquid fuels, as well as on electricity, is very popular. It is even more convenient and safer to use electric boilers for heating a cottage than gas, provided that the stable operation of the power grid is established in the region. Many owners are stopped by the cost of electricity, as well as the limitation of the rate of its release for one object. The requirement to connect an electric boiler to a three-phase network with a voltage of 380 V is also not to everyone's liking and affordability. It is possible to make electric heating of cottages more economical by using alternative sources of electricity (windmills, solar panels, etc.).
In cottages built in remote regions, cut off from gas and electric mains, liquid fuel boilers are installed.As fuel in these units, diesel fuel (diesel oil) or used oil is used, if there is a source of its constant replenishment. Solid fuel units operating on coal, wood, peat briquettes, pellets, etc. are very common.
Heating a country cottage with a solid fuel boiler that runs on pellets - granulated wood pellets that have a cylindrical shape and a certain size
Boiler selection by power
Having decided on the type of boiler equipment according to the fuel criterion, they begin to select a boiler of the required power. The higher this indicator, the more expensive the model, so you should not miscalculate when determining the power of the unit purchased for a particular cottage. You can't follow the path: the less, the better. Since in this case the equipment cannot fully cope with the task of heating the entire area of a country house to a comfortable temperature.
Cottage heating schemes - piping
Heating scheme for a cottage with a geothermal system
Any cottage heating project begins with the selection of a piping layout. The rate of heating of radiators, the maintainability of the system and the possibility of expansion for heating additional premises or household buildings will depend on it.
One-pipe cottage system
Single pipe scheme
Installation of a single-pipe circuit is one of the easiest ways to make turnkey cottage heating. Its design principle is to install only one line, to which radiators are connected in series.
It requires powerful gas boilers for heating the cottage, since as hot water passes through the radiators, a significant decrease in its temperature will be observed. The single-pipe scheme is distinguished by ease of installation and low costs for the purchase of materials. However, at present, this cottage heating system scheme is practically not used for the following reasons:
- Problems when performing hydraulic and thermal calculations. It is difficult to predict the possible pressure in the cottage heating system, since the characteristics of the coolant change as it cools;
- The difficulty of adjusting the degree of heating of the batteries. Limiting the inflow of coolant into one of them will change the thermal mode of operation of the entire system;
- Limited number of connected batteries.
Two-pipe cottage heating scheme
Two-pipe heating system
To improve operational parameters, it is recommended to install a two-pipe heating system for the cottage. It differs from the above by the presence of an additional line - a return pipe. In this case, the radiators are connected in parallel.
If you plan to heat the cottage with gas, you need to take care of reducing its consumption. This can be done in several ways. But the most optimal is the installation of a two-pipe heating system for the cottage. For independent design and selection of materials For installation according to this scheme, it is necessary to take into account the following points:
- Mandatory calculation of the diameter of the pipes to minimize hydraulic losses and prevent a decrease in pressure in the heating system of the cottage;
- The consumption of material compared to a single-pipe will increase at least twice.This will affect the overall budget for creating a cottage heating project;
- Mandatory installation of thermostats on radiators. With their help, you can change the heating of devices without affecting the overall parameters of the system.
Design flexibility is inherent in this scheme of the cottage heating system. If necessary, additional risers (horizontal or vertical) can be installed to connect new radiators or conduct heat supply to another room or building.
Collector heat supply of the cottage
Collector heating of the cottage
How to properly make heating in a cottage if its area is equal to or exceeds 200 m². Even the installation of a two-pipe system in this case would be impractical. To solve this issue, it is best to use collector piping.
Currently, this is one of the most difficult ways to organize the heating of a cottage with your own hands. To evenly distribute the coolant over a large area of the building, a multipath piping layout is used. Immediately after the boiler, the main and return collectors are installed, to which several independent lines are connected. Unlike the two-pipe heating system of the cottage, the collector provides for the possibility of regulating the operation of heat supply for each individual circuit. To do this, control devices are installed - temperature controllers and flow meters.
The features of the collector heating of a cottage made by one's own hands include:
- Uniform distribution of heat over all circuits, regardless of their distance;
- The possibility of using pipes of small diameter - up to 20 mm. This is due to the small length of each node of the system;
- Increased pipe consumption. In order to properly make collector heating in a cottage, it is necessary to draw up a scheme for installing pipelines in advance. They can be wall or floor mounted;
- Mandatory installation of a pump for each circuit. This is due to the large hydraulic resistance that occurs in the collector. It can interfere with the circulation of the coolant.
When choosing a ready-made heat supply project for a cottage or when compiling it yourself, you need to take into account the heat losses of the building. The estimated power of the entire system will depend on them.