- Valve marking
- Conditions for the production of fittings
- Types of valves
- Gas shut-off valves
- Purpose and application of valves
- Types of fittings for pipelines
- Gas pipeline installation technique
- Related video: Installation of a gas pipeline on the facade
- Types of components and their purpose
- Placement of valves on the pipe
- Placement of valves on the pipe
- Do-it-yourself valve repair
- Materials and accessories
- Shut-off devices on gas pipelines: types of valves and features of its installation
- Types of fastening structures
- Requirements for supports and hangers
- Choice of fasteners
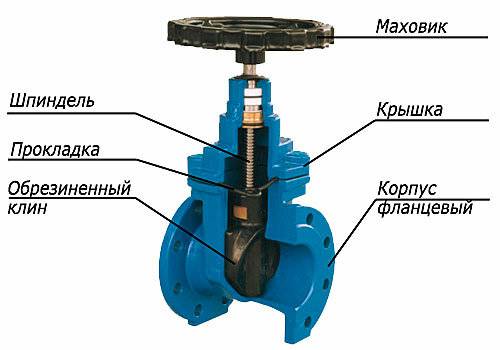
Valve marking
The key dimensions of all types of valves comply with GOST, so manufacturers must leave the appropriate marking on the product cases. It contains information about the manufacturer, material, remote control, working dimensions. Standardization of parameters simplifies the installation of fittings, and marking the choice.
Construction fittings.
In addition to shut-off and pipe fittings in construction, one often has to deal with fittings in the form of steel or plastic rods.
 Very often, such reinforcement is used to create a power frame inside concrete structures.
Very often, such reinforcement is used to create a power frame inside concrete structures.
You can learn more about this type of reinforcement in a separate article: building reinforcement, types of characteristics.
Conditions for the production of fittings
The material for the manufacture of pipeline fittings is determined by the future area of its application. If the system (or section of the system) will operate at pressures up to 1.6 MPa, ductile iron is used; if more - steel. For pipelines of small cross section, high-quality copper alloys are used, due to which corrosion of elements and sticking of fittings to pipes are not allowed.
It should be noted that the production of reinforcing elements is a complex and high-tech business, therefore, it must be carried out on special industrial equipment.
For the production of products you need:
- bake;
- special purpose press;
- machine for diagnostics;
- the table on which the assembly is carried out;
- lathe;
- drilling machine;
- conveyor;
- air compressor for painting products;
- auxiliary tools and devices.
Types of valves
There are different types of valves:
1. Stopcocks present in all pipelines. They are connected to the pipe with a flange or socket connection. Depending on the operating environment, valves are divided into ball and plug valves.
Gland coupling - plug valves with a rubber or hemp gland inside, cast iron for use in water and oil pipelines. The temperature of the transported substance should not exceed 100 degrees. The crane can be installed in any position.
Cork couplings - cast iron for gas pipelines. The maximum temperature threshold is 50 degrees. Also unpretentious to install.
Flanged ball valves - are produced in steel (temperature range 30-70 degrees) and cast iron, withstanding 100-degree load, version.
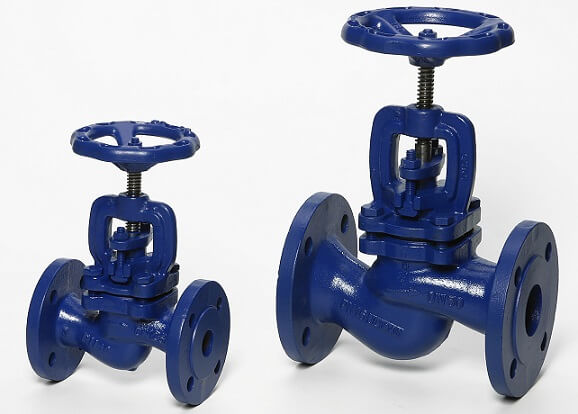
2. Gate valve made in the form of a disk rotating around its axis, located perpendicularly or at a certain angle in the direction of motion of the substance. They are mainly mounted on pipelines of large diameter with low pressure of the working medium. They are installed hydraulically or electrically, as well as manually cut into the pipeline by welding or flange connection. The body is made of cast iron and the disc is made of steel. Suitable for use in acidic and alkaline environments and maintenance free.
3. Pipeline valves periodically block the flow of the working medium. When equipped with an electric drive, it becomes possible to control remotely. They are made of cast iron, steel, stainless steel or non-ferrous metal alloys. The choice of material from which the stop valve device will be made depends on whether the alkaline or acidic medium will be transported through the pipeline.
4. Shut-off valve designed to completely shut off the flow. With it, it is impossible to regulate the working pressure. The valve must always be fully open or closed. The spool and spindle that make up the system block the flow parallel to its direction to prevent water hammer. Valves for high pressure systems are welded to thick-walled pipes. Connection by flange branch pipes and couplings is also possible.The latter is common in pipelines for transporting water, air or steam with a temperature not exceeding 50 degrees with the obligatory sealing of cast iron with a leather, rubber or paronite ring.
Parts made from brass are lightweight and operate at high compression rates, providing 100% coverage.
Sealing in such systems can be provided:
- bellows;
- diaphragm;
- stuffing box.
The types of valves also include those special valves, gate valves and dampers that are operated on pipelines through which aggressive substances move. For such products, brass is most often used resistant to acid and alkali.
Bellows parts are used when it is necessary to ensure the tightness of the connection, withstand high temperatures and prevent possible leakage.
Anti-corrosion properties are also very important for valves used in aggressive environments, so the use of rubber-coated flanged, porcelain and orifice valves is often acceptable.
Gas shut-off valves
Gas shut-off valves are an integral part in the gas transmission system, the function of which is to turn on or off the gas, change the direction of its flow, control the pressure or the amount of the passing product.
Valves that will be used in gas pipelines are required to hermetically shut off existing sections in gas pipelines. Therefore, taps, gate valves, check valves and valves must be certified and made of high quality materials, because their reliability depends on whether a malfunction occurs, which will lead to atmospheric pollution or a gas explosion.
Purpose and application of valves
Components for heating networks provide control of heat supply systems during their operation. For heating network systems, they are necessary to block heat flows, to drain water and release air.
The classification of devices for heating networks is carried out according to the following types:
- Locking;
- Regulatory;
- Safety;
- Protective.
Shut-off valves are used in industry to shut off the flow of steam, liquid and gas in pipelines and provide the necessary degree of tightness.
Stainless steel valves for steam are designed to shut off steam flows in steam pipelines, they are used at high temperatures.
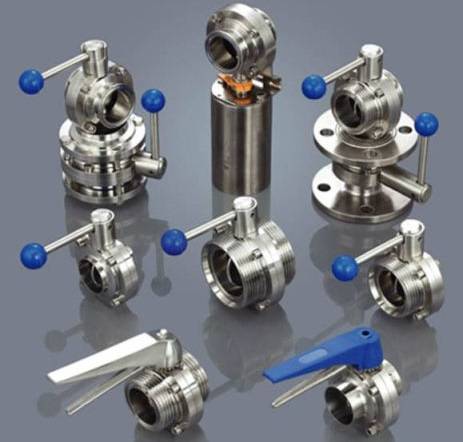

Stop valves made of stainless steel
Shut-off and control valves are an integral part of heating systems. Components are designed for heating networks, so that it is possible to turn off the mains and branches between them, section off distribution heating networks during repairs and flushing of heating mains.
Control valves are designed to control flow, pressure, temperature. The safety valve, in turn, protects the heating main from high pressure. Protective fittings are used to protect heating networks with an increase in the parameters of the coolant. According to regulatory documents, steel reinforcement is used for heating networks.
Sanitary stainless steel valves are used for:
- heating radiators;
- Towel dryer;
- wash basins;
- Dishwashers and washing machines.
It controls the parameters of the circulating fluid and is designed for the efficient functioning of heating (radiators, convectors), heated towel rails, etc.
The comfort of each house depends on the quality of heating in the winter season. Therefore, before the start of the heating season, the shut-off valves are pressure tested in order to identify defects and carry out repair work. With the help of locking devices for heating radiators, the temperature of the heat supply is regulated. To date, there are many varieties of heating radiators, which differ in appearance and technical characteristics.

Shut-off valves for heating systems
Depending on the type of heating radiators, components are selected. When choosing heating radiators, the heat transfer capacity, service life and internal pressure should be taken into account. The radiators are connected according to the diagrams, where there is a designation of the piping system.
Types of fittings for pipelines
There are the following types of pipe fittings:
- regulatory;
- shut-off and regulating;
- non-return-locking;
- shut-off;
- safety;
- reverse;
- irrevocably controlled;
- mixing and distribution;
- drainage (drainage);
- branch;
- disconnecting (protective);
- reduction (throttle);
- phase separation;
- control.
As you might guess, each type of product is designed for specific purposes, which also correspond to the installation of pipeline valves.
For example, shut-off pipeline valves are used to block the movement of the working medium (or a combination of media) in order to carry out preventive maintenance in the network.
The fuses serve to protect the pipeline from exceeding the working pressure, as a result of which the system may fail, by dumping excess conveyed medium.
Control valves are designed to maintain the required amount of carrier by changing its flow rate.

The occurrence of a return flow, which reduces the performance of the system, is prevented by reverse elements (in particular, non-return-shut-off and non-return-controlled).
Discharge from the pipeline system of the working medium is carried out by using trigger, or drainage, devices.
Phase separation (provided that several phase states of the medium move in the pipes) is carried out using phase separation elements.
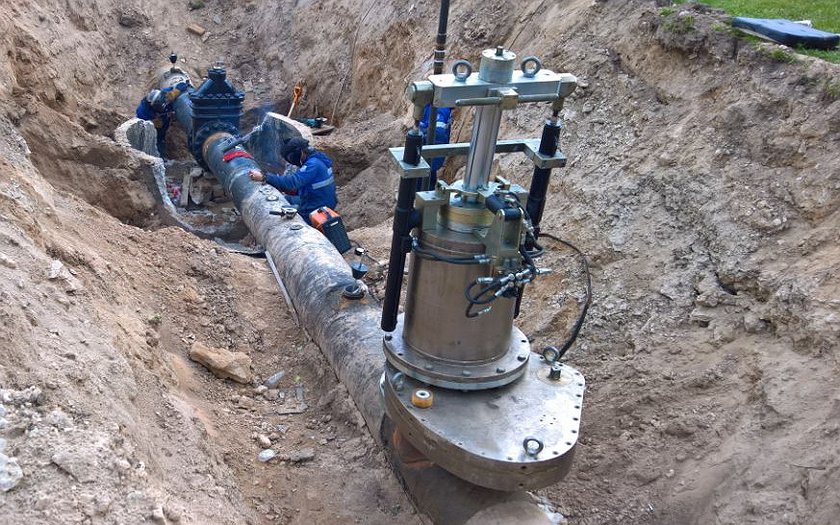
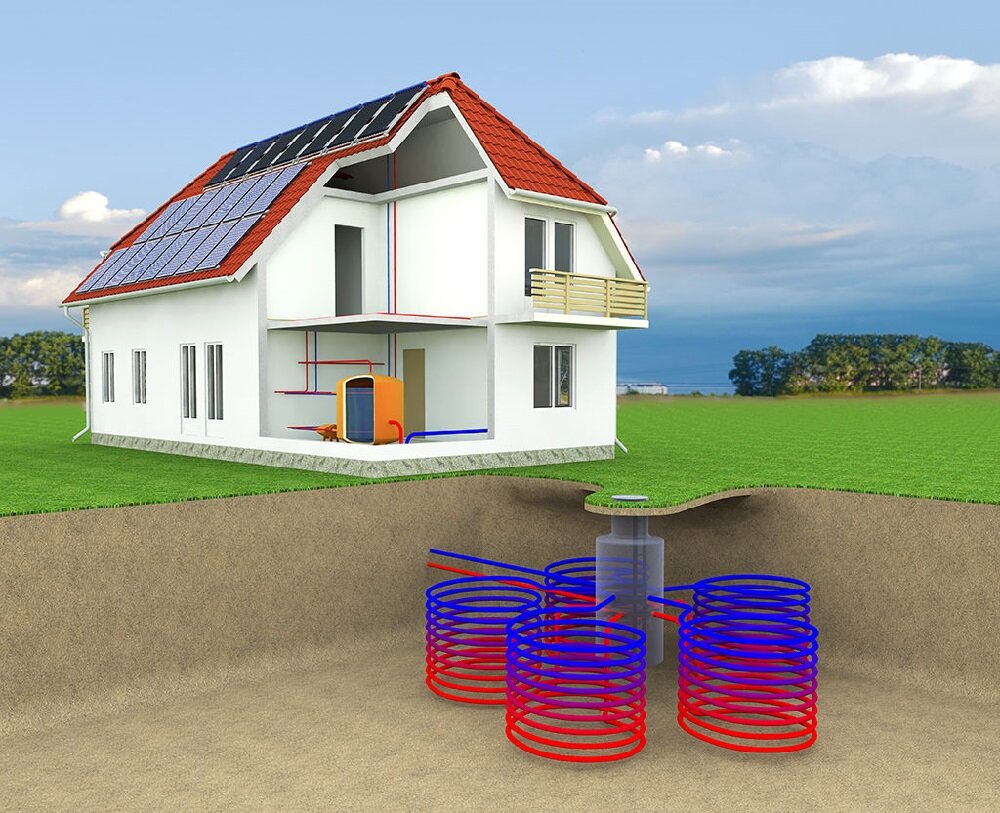
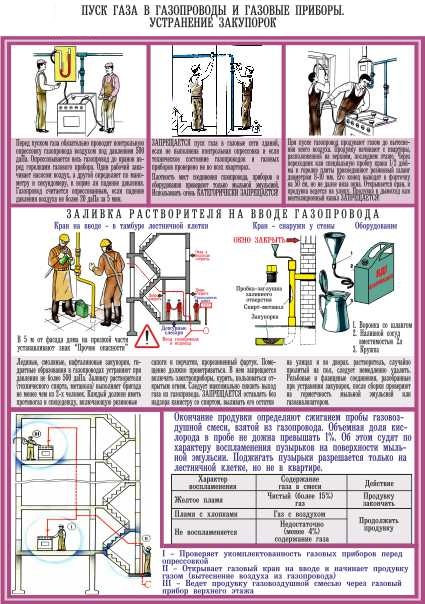
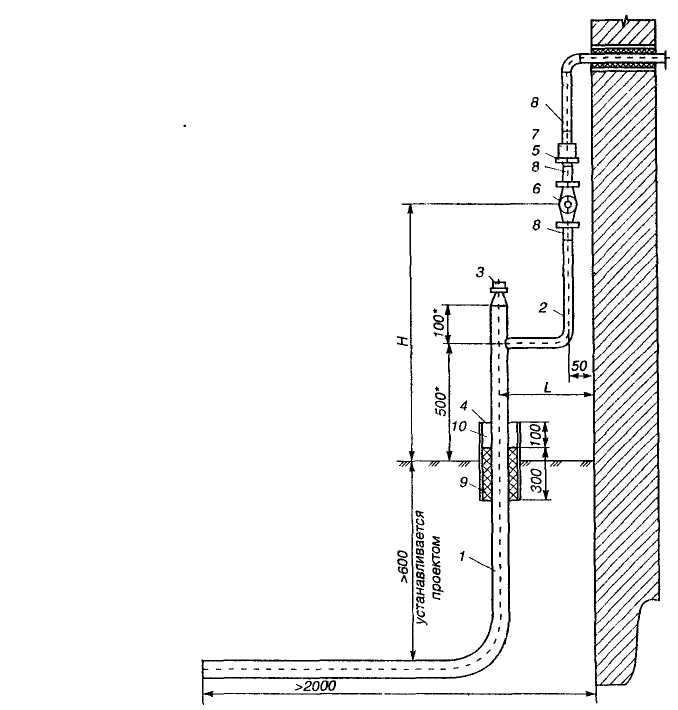
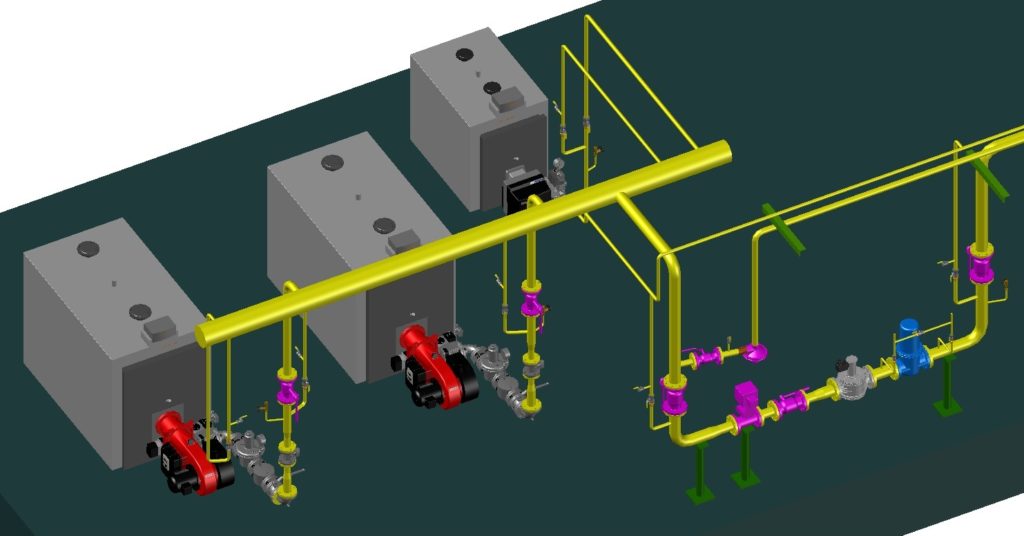
Gas pipeline installation technique

Work begins with the introduction of pipes into the building. To do this, a case is placed in the outer wall and an input is made through it. Already inside, a riser is fixed, located 20 mm from the walls in a vertical position. Connections at this stage are made using a welding machine.
Cases should be located at all intersections of the pipe with interfloor ceilings, walls and stairwells.
Gas pipe fittings must be installed at least 2 m apart. These rules apply to pipes with a diameter of 25 mm. They should allow for the repair and diagnosis of possible damage during operation. The end of each of the fasteners is hammered into a special wooden plug located in the wall. After that, the attachment point is poured with cement mortar to give additional strength.
There are a number of rules for performing welding work:
- Welding can be performed on pipes with a diameter not exceeding 150 mm and with a wall thickness of up to 5 mm.
- Arc welding is used when the pipe thickness exceeds 150 mm or the wall thickness exceeds 5 mm.
- Before installation, it is necessary to prepare pipes for welding. To do this, they are cleaned of contaminants.
- Each welded joint must be easily accessible. Hiding seams in the wall or case is not allowed.
All connections are made by welding. Threaded connections are allowed only at the installation sites of shutoff valves, metering devices (gas meters), pipe connections with a hose leading directly to gas equipment.
Related video: Installation of a gas pipeline on the facade
A selection of questions
- Mikhail, Lipetsk — What discs for metal cutting should be used?
- Ivan, Moscow — What is the GOST of metal-rolled sheet steel?
- Maksim, Tver — What are the best racks for storing rolled metal products?
- Vladimir, Novosibirsk — What does ultrasonic processing of metals mean without the use of abrasive substances?
- Valery, Moscow — How to forge a knife from a bearing with your own hands?
- Stanislav, Voronezh — What equipment is used for the production of galvanized steel air ducts?
Types of components and their purpose
The classification of all pipeline fittings is carried out according to the following criteria:
- The method of overlapping the working environment;
- Areas of use;
- management method;
- The amount of pressure;
- type of material;
- Attachment method.
The use of each subspecies is possible only with strict adherence to standards. According to the method of overlapping, the classification of components is carried out according to the following varieties:

At the valve, the locking or regulating element moves perpendicular to the axis of the flow of the working medium. They are used on those pipelines through which they are pumped:
To transfer steam to industrial enterprises, such as thermal, nuclear power plants, steam heating systems, a steam pipeline is used. At the moment, electric shut-off valves are very popular in use. The electric actuator drives the valve to the open or closed position remotely, using the remote control.
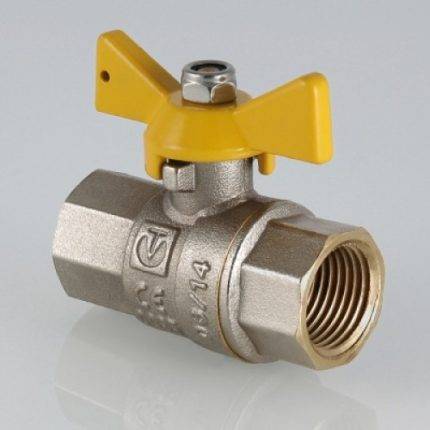
All valves are installed on water, oil or gas pipelines. Cranes come in two subspecies - ball and cork.
Ball valves are one of the most modern, high quality and progressive types of fittings with a high degree of tightness.

The advantages of ball valves are:
- High degree of tightness;
- Simple construction;
- Small size;
- Safety and reliability of work;
- Optimal price.
A shut-off valve is necessary to completely shut off the working medium, because it cannot regulate the working pressure of the line. Shut-off valves are used on highways where water, steam or air is supplied.
Gate valves are used on large diameter lines at low pressure working environment. They have much less requirements for tightness.
According to the pressure value, the devices are vacuum, low, medium and high pressure. High-pressure shut-off valves are widely in demand in the oil refining, gas production, and chemical industries.
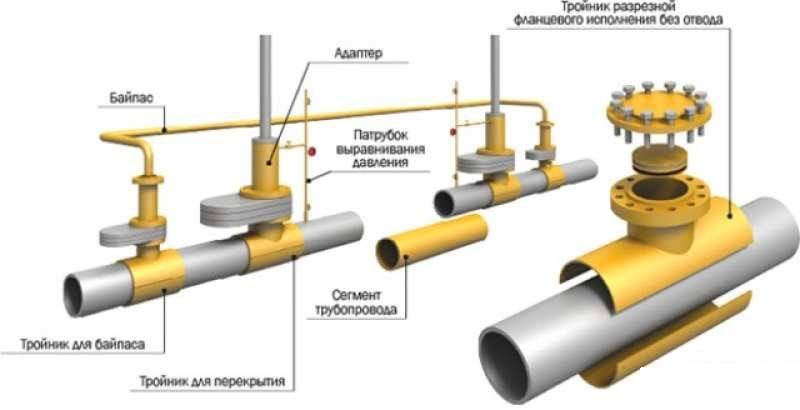
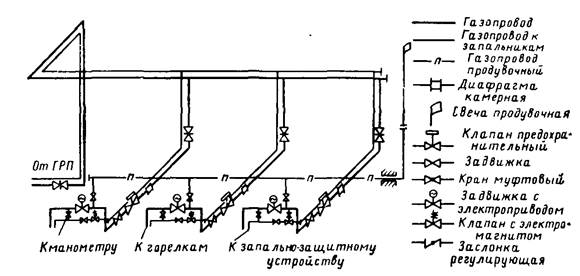
Placement of valves on the pipe
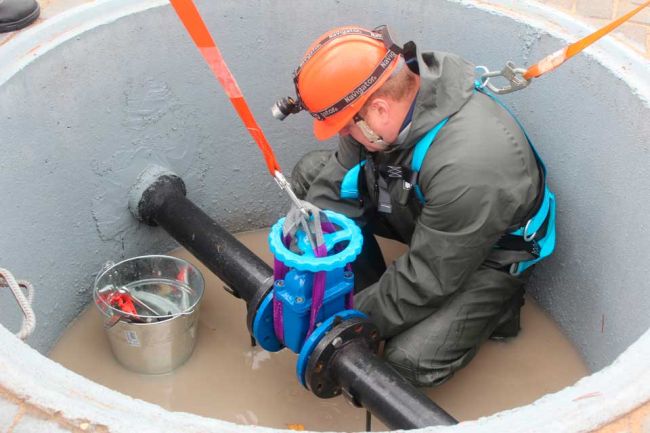
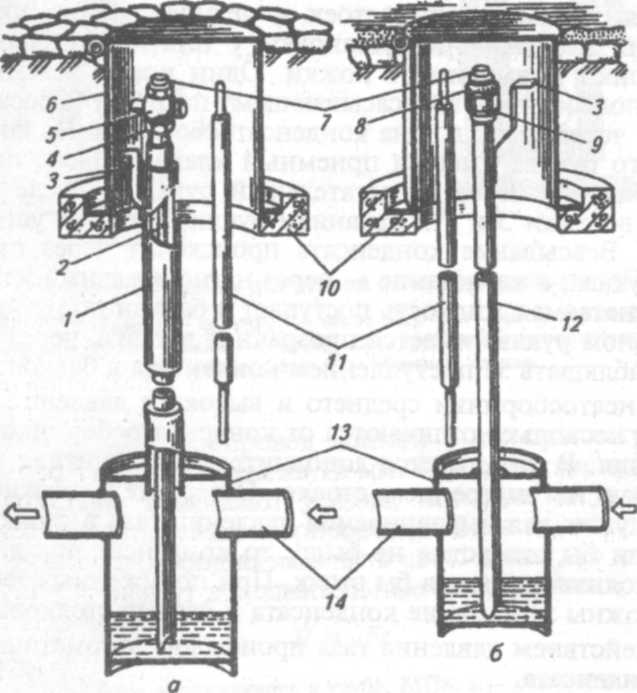
Before installation in the gas pipeline system, valves and gate valves are subjected to an external audit, lubrication, gasket check and leak test. At the same time, the place for installing a disconnecting device on the gas pipeline is selected in accordance with the recommendations of SP 42-101-2003.
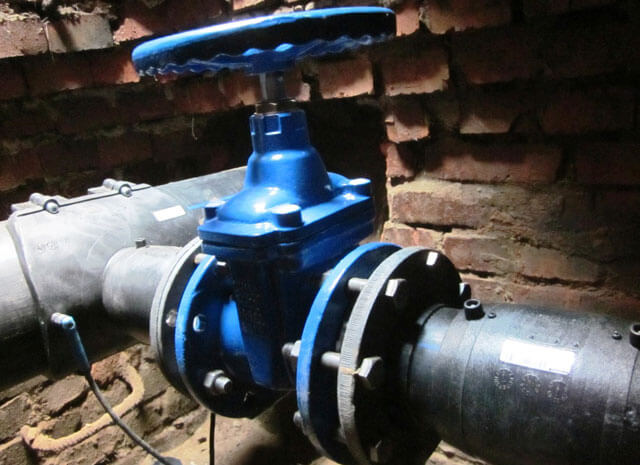
The installation of disconnecting devices on the gas pipeline is carried out underground - in a well or directly in the ground or above ground - in fireproof cabinets, on walls or pipes.
The installation of shut-off valves is carried out so that it can be inspected, serviced and, if necessary, dismantled.
The place for inserting the disconnecting device into the gas pipeline is selected:
- on branches from the main - outside the territory of the consumer and no further than 100 m from the distribution pipeline;
- in the presence of parallel pipes - at a distance convenient for servicing both devices;
- at the outputs and inputs of hydraulic fracturing - at a distance of 5-100 meters from the point;
- when the gas pipeline crosses an overhead power transmission line - outside its security zone;
- on the walls of private houses - at least half a meter from door and window openings;
- near the gas stove - on the side of the pipe at the level of the connecting fitting at a distance of 20 cm or more from the stove;
- at a gas stove or column with an upper wiring - at a height of 1.5 above the floor.
If the fittings are mounted at a height of more than 2.2 m, then a metal ladder and / or platform should be provided at this level.
If wells are being installed, then they should be made from fireproof building materials. Suitable stone, brick, concrete, etc. But no wood or plastic.

For internal and aboveground external gas pipelines with steel and polyethylene pipes used for natural gas and LPG in the vapor phase with a pressure of up to 0.005 MPa, conventional ball valves are recommended
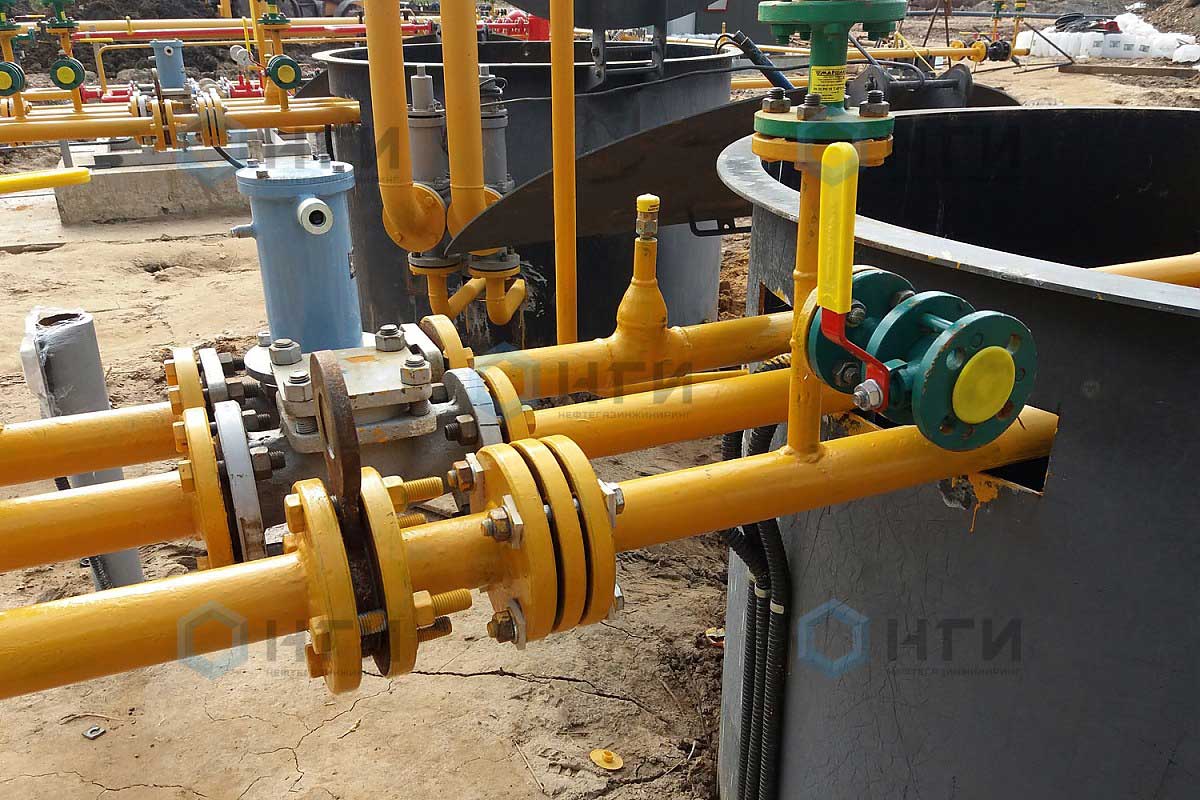
Flange connections should be sealed with the following gaskets from:
- paronite - at a pressure of up to 1.6 MPa;
- oil and petrol resistant rubber - at a pressure of up to 0.6 MPa;
- aluminum - at any pressure;
- copper - at any pressure (except for gas pipelines with sulfur dioxide);
- polyethylene of high and low density, fluoroplast - at a pressure of up to 0.6 MPa.
It is worth noting that rectangular and square type flange connections are quite difficult to process and it is difficult to ensure reliable tightness of the connection, so it is better to give preference to round flange connections.
Disconnect devices must be installed:
- at the entrance to the building;
- in front of an outdoor installation that consumes gas;
- at the input and output of hydraulic fracturing;
- on long dead ends;
- on branches from a common highway to a village, quarter or enterprise;
- when the pipeline crosses railways and roads, as well as water barriers.
All rotary valves to be installed must have a handle rotation limiter of 90, and gate valves - an opening degree indicator.
And all devices with a diameter of up to 80 mm must have a risk on the case indicating the direction of the gas flow.
Placement of valves on the pipe
Before installation in the gas pipeline system, valves and gate valves are subjected to an external audit, lubrication, gasket check and leak test. At the same time, the place for installing a disconnecting device on the gas pipeline is selected in accordance with the recommendations of SP 42-101-2003.
The installation of disconnecting devices on the gas pipeline is carried out underground - in a well or directly in the ground or above ground - in fireproof cabinets, on walls or pipes.
The installation of shut-off valves is carried out so that it can be inspected, serviced and, if necessary, dismantled.
The place for inserting the disconnecting device into the gas pipeline is selected:
- on branches from the main - outside the territory of the consumer and no further than 100 m from the distribution pipeline;
- in the presence of parallel pipes - at a distance convenient for servicing both devices;
- at the outputs and inputs of hydraulic fracturing - at a distance of 5-100 meters from the point;
- when the gas pipeline crosses an overhead power transmission line - outside its security zone;
- on the walls of private houses - at least half a meter from door and window openings;
- near the gas stove - on the side of the pipe at the level of the connecting fitting at a distance of 20 cm or more from the stove;
- at a gas stove or column with an upper wiring - at a height of 1.5 above the floor.
If the fittings are mounted at a height of more than 2.2 m, then a metal ladder and / or platform should be provided at this level.
If wells are being installed, then they should be made from fireproof building materials. Suitable stone, brick, concrete, etc. But no wood or plastic.
Flange connections should be sealed with the following gaskets from:
- paronite - at a pressure of up to 1.6 MPa;
- oil and petrol resistant rubber - at a pressure of up to 0.6 MPa;
- aluminum - at any pressure;
- copper - at any pressure (except for gas pipelines with sulfur dioxide);
- polyethylene of high and low density, fluoroplast - at a pressure of up to 0.6 MPa.
It is worth noting that rectangular and square type flange connections are quite difficult to process and it is difficult to ensure reliable tightness of the connection, so it is better to give preference to round flange connections.
Disconnect devices must be installed:
- at the entrance to the building;
- in front of an outdoor installation that consumes gas;
- at the input and output of hydraulic fracturing;
- on long dead ends;
- on branches from a common highway to a village, quarter or enterprise;
- when the pipeline crosses railways and roads, as well as water barriers.
All installed rotary valves must have a handle rotation limiter of 90 0, and gate valves - an opening degree indicator.
And all devices with a diameter of up to 80 mm must have a risk on the case indicating the direction of the gas flow.
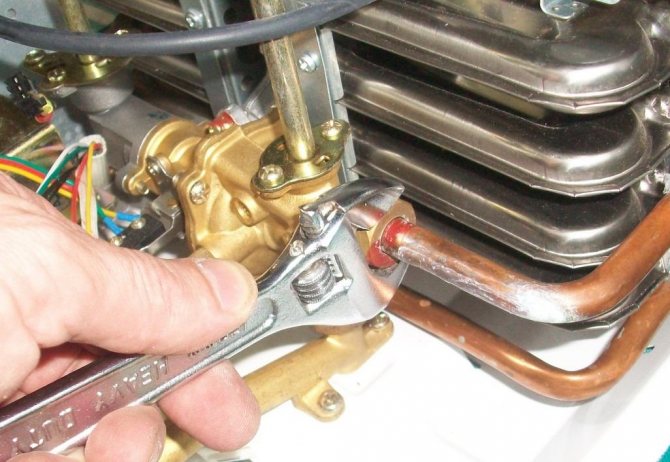
Do-it-yourself valve repair
In order for the devices to serve for a longer period of time, it is necessary to periodically service and repair valves.
The most common causes of leakage are:
- wear of sealing gaskets;
- insufficient gland packing.
To replace gaskets, follow these steps:
- partial disassembly of the device. With an adjustable wrench, the crane box is removed, which fixes the spindle;
- remove worn gasket. In some devices, the gasket is attached with a bolt, while in others it is simply superimposed on the rod;
- install a new gasket and assemble the crane;
- check the tightness of the device.

Elimination of leaking valves
Repair of shut-off valves, if it is necessary to seal the gland packing, is carried out in the following way:
- the flow in the pipeline is blocked;
- the cap nut is loosened.In order to perform the operations correctly and loosen exactly the desired nut, it is necessary to fix the stem in one position;
- to remove the flywheel and stuffing box bushing, loosen the fixing screw;
- the gland packing is removed (if a complete replacement of the material is required) or the required amount of packing is added (with little wear);
- the fittings are assembled in the reverse order and the elimination of leakage is checked.
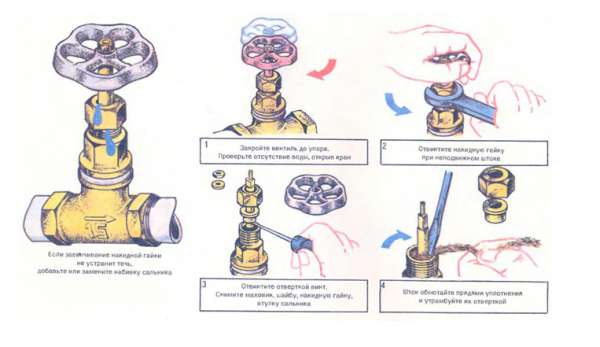
Elimination of leakage caused by insufficient stuffing box packing
All types of valves are interchangeable. For example, a threaded valve can be installed in place of a welded tap, and so on. The process of installing a new locking device is carried out according to the schemes presented in the article.
Materials and accessories
The materials used for the manufacture of valves and components must comply with the general specifications in accordance with the standards of the Central Design Bureau of Valve Engineering (TsKBA) “Pipeline valves. General technical conditions”, which came into force in January 2006, as well as current national standards and industry specifications. The main criterion in choosing the material for the body of any valve is its strength. The body is the basis for installing all other parts into it. It is like a foundation in construction - a supporting structure for the whole building.

The bodies of most pipeline locking devices are made of cast iron or steel. Sometimes other metal materials are also used for this: bronze, copper, aluminum and brass faucets and valves for household appliances are on sale.Reinforcement made of non-ferrous metals and their alloys has a good feature - it is not subject to corrosion and has a good appearance.

The most economical material for fittings is plastic, which combines under its common name products made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride), polypropylene, polyethylene and other artificial alloys of plastic material. But such fittings cannot withstand high pressure and temperatures, as they are not durable. But for pipes of small diameter and low pressures, this is a very suitable alternative to metal products. In addition to being cheap, plastic pipelines and fittings are valuable for their resistance to corrosion - the main scourge of steel devices of the same type.

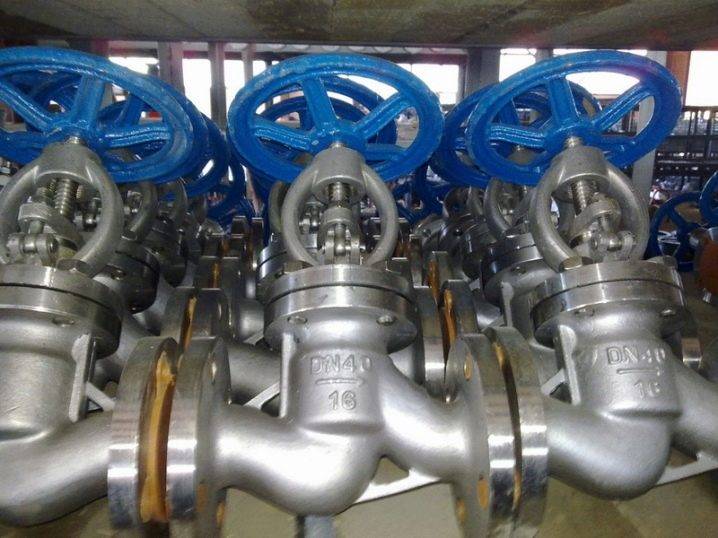
Malleable, gray or high-strength cast iron is used for casting valve bodies, depending on the area and conditions of use of a particular product. Due to their brittleness, fittings with a cast-iron body are not used at high pressures in pipelines, as well as where water hammer and sudden temperature changes are possible. In such situations, the cast iron housing can simply burst.
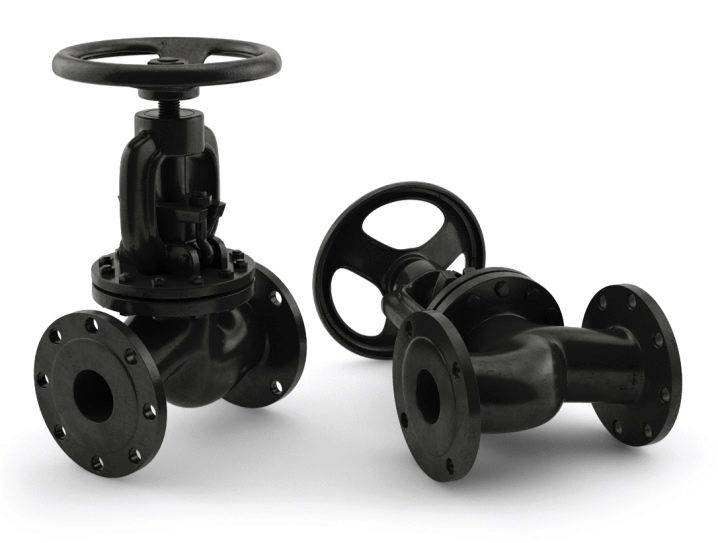

Steel cases are made of various grades of steel: alloyed, heat-resistant and carbonaceous. Stainless steel with high resistance to corrosion is used for the manufacture of valve bodies that are installed on pipelines with aggressive substances or have a particularly clean working environment. Cases made of heat-resistant steel are used for fittings operating at elevated temperatures of the working medium. The use of a particular material, as well as the design and type of the flange, are determined by a number of factors, the main of which are the following:
- conditional diameter of pipelines;
- working environment pressure;
- flow direction;
- temperature conditions.
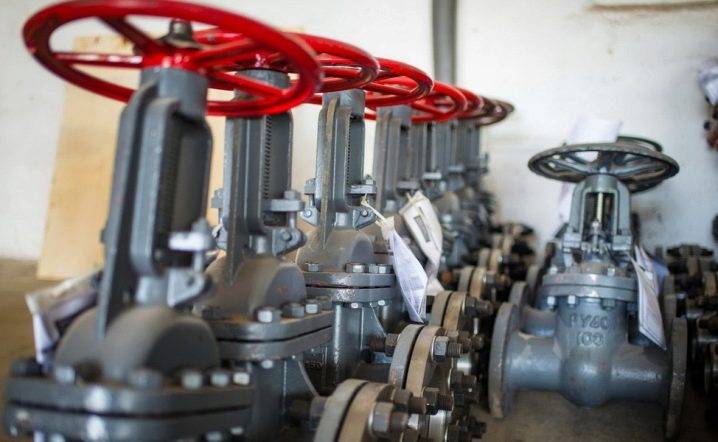

The sealing material is:
- metal products in the form of rings with corrosion resistance, anti-friction properties, well processed (steel, brass, bronze, monel);
- deposits from various hard alloys: stellite (cobalt alloy), sormite (iron-based alloys);
- non-metallic products (rubber and rubber-metal rings, polymer seals);
- sealing packings made of material of plant origin (cotton and linen fiber), talc, fiberglass;
- fluoroplastic and graphite for stuffing box seals in aggressive and high-temperature working environment;
- sheet rubber, paranit and fluoroplast for gaskets.
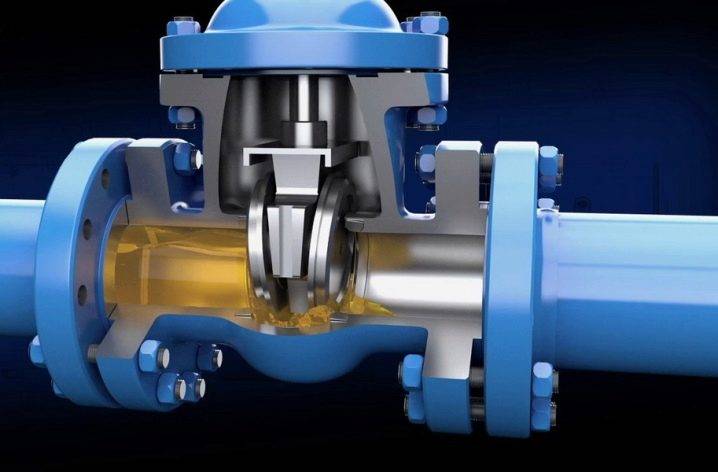

Cast iron and steel fittings equipped with flanges have undeniable advantages in terms of tightness, maintainability and strength of the pipeline network compared to flangeless fittings. But the mass and dimensions of such reinforcement sometimes reach large values (in tons and several meters, respectively). To this, you still need to add control devices (handwheel, electric drive or pneumatic drive, hung on the valve). Flanges lead to increased metal consumption and labor intensity in their manufacture.
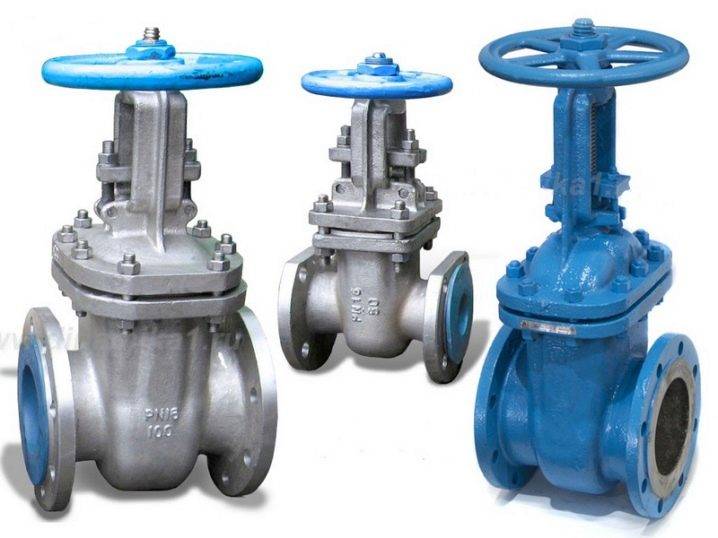

Shut-off devices on gas pipelines: types of valves and features of its installation
It's no secret that gas distribution systems in settlements, as well as in multi-apartment and private houses, are a source of constant danger. The slightest leak of blue fuel can lead to serious problems, up to an explosion
And you must admit that in order for this not to happen, it is extremely important to carefully and constantly monitor the condition of gas pipes and fittings on them.
One of the main shut-off elements here is a valve or valve, which, if necessary, turns off the gas in the pipe.
And in order for these disconnecting devices on gas pipelines to work properly, their selection and installation should be approached with all due attention. Next, we will analyze all types of such equipment and the rules for its installation.
Types of fastening structures
Bearing fastening structures are divided into the following types:
- Fixed supports. When using this fastener, angular or linear movement of the fixed sections is not allowed.
- Guide supports. The use of this design allows displacement in only one direction. As a rule, only along the horizontal axis.
- Rigid pendants. Movements are allowed, but only in the horizontal plane.
- Spring hangers and supports. Both vertical and horizontal movements are possible.
Types of fastening pipelines to the wall
Requirements for supports and hangers
If fixation occurs between two fixed supports, movements that may occur as a result of temperature changes, mounting braces or displacement of supports must be self-compensating. But such a compensating ability, as calculations show, is sometimes not enough. In this case, special compensators must be installed.
Pipe clamp equipped with screw/bolt
They are made from pipes of the same type and diameter as the structure as a whole. Most often they are performed in the form of the letters "P" or "G".
If the structure is fixed fixedly, the fasteners must withstand the weight of the pipeline itself, the fluid that moves through it, as well as axial loads generated by thermal deformation, vibrations and hydraulic shocks. When mounting products made of polymers, movable supports are most often used.
If the installation is carried out in fixed supports, restrictive rings or segments 10-20 mm wide are welded to the pipes, which are made from pieces of pipes of the same plastic. These segments or rings should be located on both sides of the support.
Choice of fasteners
Suitable fasteners are selected taking into account many factors. The choice depends on the location of the installation site, on the purpose of a particular system, and so on.
Plastic pipe fixing
Sometimes the pipe must be insulated from the source of cold or heat. If you use a simple clamp that fixes the area, then it will not provide the gap from the adjacent surface necessary to solve the problem. But, for example, an annular support, which has a threaded extension and a plate for fixing to the supporting surface, will completely eliminate the problem.
If you have to fix heavy cast-iron pipes, then use special fasteners that can withstand heavy loads. For vertically located systems, it is installed on floors. Horizontally oriented systems are fixed not even one by one, but by groups of pipes laid on the console.
A competent approach to the selection and placement of fasteners allows for a long and efficient operation of the pipeline without fear of emergency situations.But do not forget about the economic component of this problem. After all, exceeding the required and sufficient number of elements can lead to an unjustified increase in the cost of the structure and complicate installation work.