- The subtleties of sewerage
- What is the security zone of the sewerage system according to SNiP?
- General concept of the sewer protection zone
- What is the risk of not following the rules?
- Sizes of sewer protection zones
- The specifics of laying communications in private homes
- 2.3. Determining the boundaries of the SSS belts of a surface source
- Protected water supply zones
- Belts of the water protection zone
- Standards for private housing construction
- General concept of the sewer protection zone
- What is the risk of not following the rules?
- Sanitary standards for water pipes
- Gas pipeline security zone
The subtleties of sewerage
Accidents on sewer networks are a frequent occurrence, and the reason for this is not only the natural wear of pipes and systems. Sewerage, like water supply, has a security zone, but it is not customary to designate it with signs and signs. The presence of sewer pipes and their location can be judged by wells closed with massive metal covers marked "K" or "GK".
Before starting excavation work in the sewer security zone, it is necessary to study the plans and schemes of engineering communications, obtain appropriate recommendations and expert advice.
Otherwise, it is easy to break a sewer pipe with one careless push of an excavator bucket, and then who will calculate the losses and material costs for restoration? And if there is a water supply nearby, then the damage and negative consequences increase many times over.

The letters "K" or "GK" on the cover of the sewer manhole indicate the sewer or city sewer, respectively, on the cover of the water well should be written "B"
The security zone of sewerage networks is established in proportion to the pipe section:
- up to 0.6 m in diameter - not less than 5 meters in both directions;
- from 0.6 to 1.0 m and more - 10-25 meters each.
It is necessary to take into account the seismological characteristics of the area, climate and average monthly temperatures, soil moisture and freezing, and soil features. The presence of adverse factors is a reason to increase the buffer zone
The distance to sewer networks located underground from such objects is also regulated:
- sewerage should be 3-5 meters away from any foundations (for pressure, the distance is greater than for gravity);
- from supporting structures, fences, overpasses, the indentation is from 1.5 m to 3.0 m;
- from the railway track - 3.5-4.0 m;
- from the road curb on the carriageway - 2.0 m and 1.5 m (standards for pressure and gravity sewerage);
- from ditches and ditches - 1-1.5 m from the near edge;
- street lighting poles, racks of contact networks - 1-1.5 m;
- supports of high-voltage power lines - 2.5-3 m.
The figures are reference, accurate engineering calculations allow you to get more reasonable data. If the intersection of water and sewer pipes cannot be avoided, the water supply should be placed above the sewer.When it is technically difficult to implement, a casing is put on the sewer pipes.
The space between it and the working pipe is tightly packed with soil. On loams and clays, the length of the casing is 10 meters, on sands - 20 meters. It is better to cross communications for various purposes at a right angle.
You can read more about sewer pipe slope calculations in our article.

In case of a large-scale sewer break, it is necessary to turn off the supply of tap water so that, if not stopped, then at least reduce the release of fecal water to the outside
When opening water and sewer pipes in connection with repairs, it is allowed to use equipment in earthworks to a certain depth. The last meter of earth above the pipe is removed carefully by hand without the use of a tool with shock and vibration action.
It is strictly forbidden during laying to touch the sanitary zones of water pipes with sewage, but in the city the requirements are less stringent.
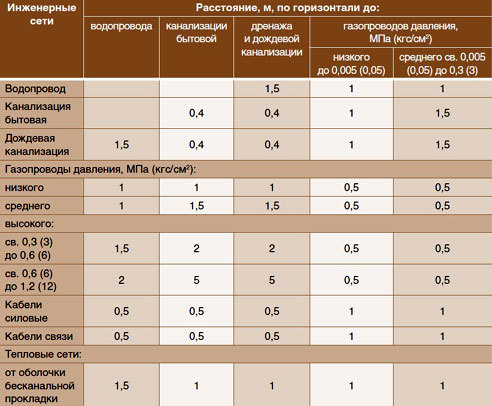
In urban conditions, with a forced parallel arrangement of main water and sewer pipes, it is necessary to maintain the following distances:
- 10 m for pipes up to 1.0 m in diameter;
- 20 m with a pipe diameter of more than 1.0 m;
- 50 m - on wet ground with any pipe diameter.
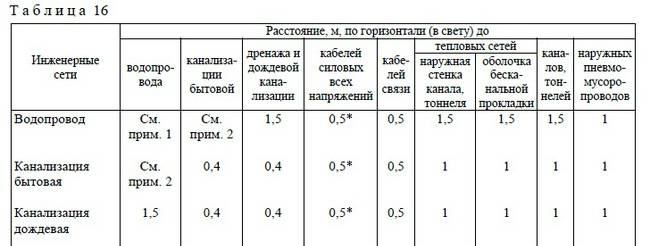
For thinner domestic sewer pipes, the distance to other underground utilities is determined by their own standards:
- to the water supply - from 1.5 to 5.0 m, depending on the material and diameter of the pipes;
- to rain drainage systems - 0.4 m;
- to gas pipelines - from 1.0 to 5 m;
- to cables laid underground - 0.5 m;
- to the heating plant - 1.0 m.
The last word on how to ensure the safe coexistence of water supply and sewerage, remains with the specialists of the water utilities. All controversial issues should be resolved during the design process and not come up at the operational stage.
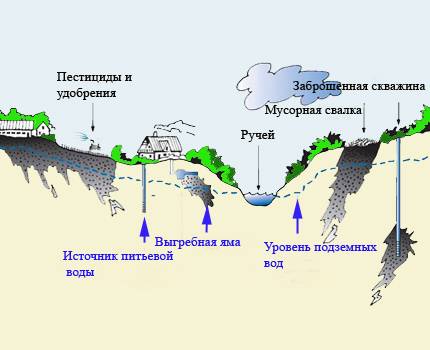 If you do not control domestic and industrial effluents, landfills, the amount of chemical fertilizers and poisons in the fields, water supplies will become unusable
If you do not control domestic and industrial effluents, landfills, the amount of chemical fertilizers and poisons in the fields, water supplies will become unusable
What is the security zone of the sewerage system according to SNiP?
Any sewerage system is a potential hazard to drinking water sources and the environment. Therefore, there is such a thing as a sewerage buffer zone - SNiP determine the size of the territory and the standards for its designation.
It is prohibited to build, plant trees and perform a number of other works in the protected area. Consider what rules for equipping security zones today are accepted in construction.
Surely, many have seen the installed signs, which indicate that a protected zone is located in this place. Such plates are placed, for example, in places where electrical cables are laid.
In the area covered by the established plate, it is forbidden to carry out unauthorized land work. There are also security zones for water supply and sewerage. They are designed to address two issues:
- For the purpose of environmental protection.
- To protect pipelines from damage.
General concept of the sewer protection zone
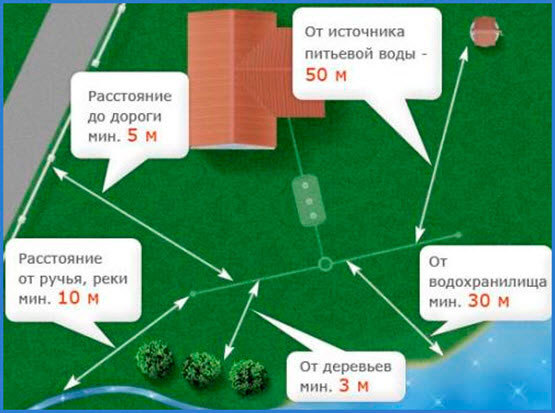
Territories that surround the buildings of sewer networks are called security areas. Within the sewer zones, the following actions should be refrained from:
- Planting trees;
- Digging trenches and pits;
- Storing firewood or any other materials;
- Landfill device.
- Planning the construction of some buildings, piling or blasting.
- Carrying out work that raises or lowers the level of the soil, that is, the production of sections of the soil or its backfilling.
- Reinforced concrete slab pavement, even if this road is temporary.
- The performance of any actions, as a result of which the passage to the sewer networks will be blocked.
As a rule, the boundaries of protected zones are prescribed in a decree issued by the Ministry of the Environment. Exact information about the size of the protection zones can be obtained from the local water utilities.
What is the risk of not following the rules?
It must be said that cases of damage to the sewer pipeline due to land works are not so rare. They happen even more often than damage to water pipes or power cables.
Random accidents are due to the fact that the work foreman simply does not know that a pipeline passes here. The point here is some discrepancy between the laws. So, for example, when laying power lines or building water pipes, the operating organization is obliged to install warning signs.
But the obligation to install a sign warning that there is a protected territory of the sewerage system is not regulated by law. That is, there is no clear indication that the owners of sewerage networks must mark the location of the buffer zone with signs, in the law.
Thus, if as a result of some work the sewer pipeline was damaged, then the responsibility will be borne by:
- In the absence of a warning plate - the operating organization.
- If the sign was present, but was ignored, then the responsibility lies with the contractor.
For damage to sewerage networks, the culprit bears administrative responsibility. If the accident caused damage to the environment, then the measure of responsibility will be different.
Advice! Before carrying out earthworks or other potentially dangerous work for the pipeline, it is necessary to study the area. Information on the location of sewer protection zones can be obtained from an organization that maintains water and sewer networks.
Sizes of sewer protection zones
Regulatory requirements regarding the size of buffer zones need to be known not only to the foremen. Indeed, today, quite often homeowners build their own local sewer systems, while it is necessary to comply with accepted norms and parameters that are regulated by SNiP.
Documents that regulate the rules for the construction of sewer systems:
- SNiP 40-03-99;
- SNiP 3.05.04-85;
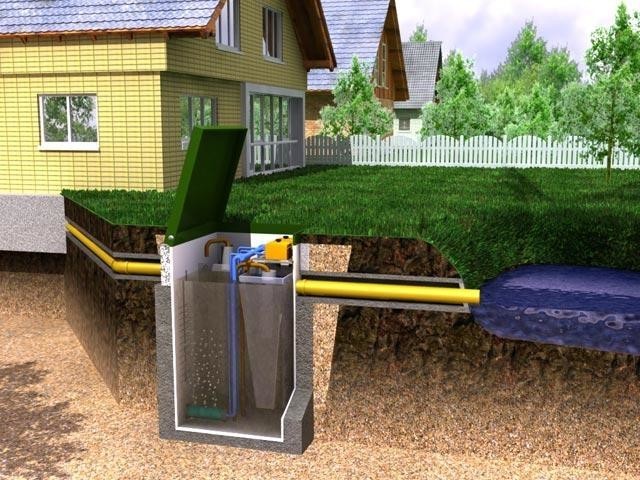
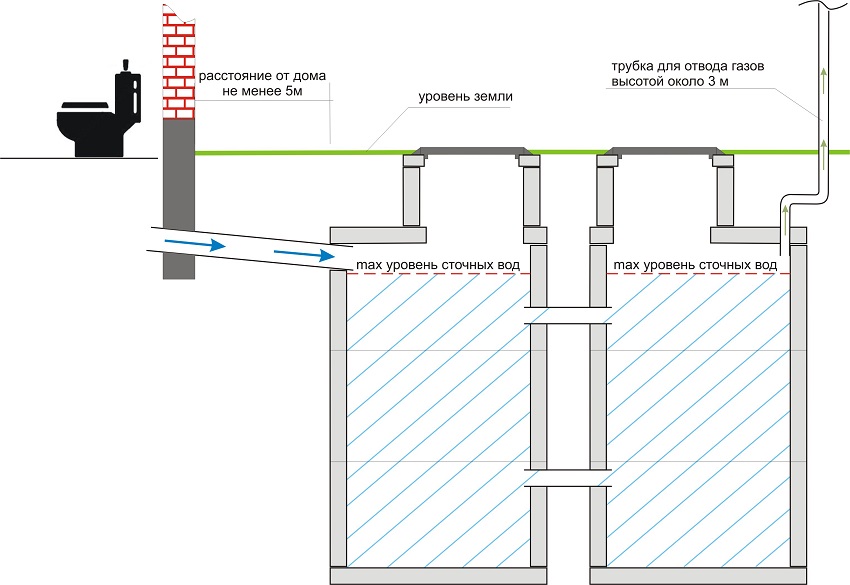
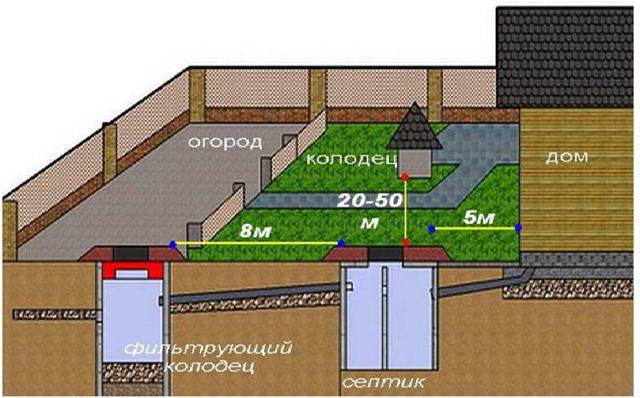
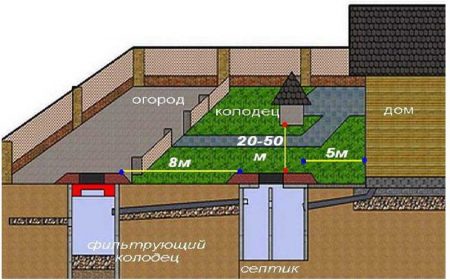
The specifics of laying communications in private homes
At
creating water supply and sewerage systems for a private house can be
different options were used - from connecting to centralized networks, to
creation of autonomous complexes. The most responsible cases include a fence
water from a well with the simultaneous use of a septic tank. Here it is necessary not
just keep the right distance
between sewerage and water supply pipelines, but also to the maximum
segregate water intake points with waste filtration areas. When creating a project
it is necessary to draw up a detailed scheme for laying communications, in which
be reflected:
- pipe laying levels;
- distances between parallel channels;
- sections of pipeline crossings;
- points of entry of pipes into the house and into the external elements of the systems.
The internal part of the system is almost nothing
different from the sewerage device of an apartment building. the only
a feature is a relatively small number of plumbing fixtures,
falling on one riser.
This reduces the load on the pipeline, but does not remove any sanitary or
technical requirements for permissible distances.
An important factor is the material
which pipes are made. Requirements and standards for cast iron and plastic
species are significantly different from each other. If the area is small,
it is recommended to use modern polypropylene or PVC pipelines,
which can be placed much closer to each other. For example, the distance between a water pipe and
sewerage horizontally for cast-iron channels - at least 3 m, and for
plastic - 1.5 m.
2.3. Determining the boundaries of the SSS belts of a surface source
2.3.1. Borders of the first belt
2.3.1.1. The boundary of the first zone of the WSS of the water supply
with a surface source is established, taking into account specific conditions, in
the following limits:
a) for watercourses:
• upstream — at least 200 m from
water intake;
• downstream — at least 100 m from
water intake;
• along the bank adjacent to the water intake - not
less than 100 m from the water line of the summer-autumn low water;
• in the opposite direction from
water intake on the shore with a river or canal width of less than 100 m - the entire water area and
the opposite bank 50 m wide from the water line during summer-autumn
low water, with a river or canal width of more than 100 m - a strip of water area not wide
less than 100 m;
b) for reservoirs (reservoirs, lakes) the boundary
the first belt should be installed depending on local sanitary and
hydrological conditions, but not less than 100 m in all directions along the water area
water intake and along the bank adjacent to the water intake from the water line at
summer-autumn low water.
Note: at bucket type water intakes
the entire water area of the bucket is included within the limits of the first belt of the SZO.
2.3.2. The boundaries of the second belt
2.3.2.1. The boundaries of the second zone of the WSS of watercourses
(rivers, canals) and reservoirs (reservoirs, lakes) are determined depending on natural, climatic and hydrological conditions.
2.3.2.2. The boundary of the second belt on the watercourse in
for microbial self-purification purposes should be removed upstream of the water intake
so that the travel time along the main watercourse and its tributaries, at
water flow in the watercourse 95% security, it was at least 5 days - for IA, B, C and D, as well as IIA climatic regions, and at least 3 days -
for ID, IIB, C, D, as well as III climatic region.
The speed of water movement in m / day is taken
averaged over the width and length of the watercourse or for its individual sections at
sharp fluctuations in the flow rate.
2.3.2.3. Boundary of the second zone of the WSS of the watercourse
downstream should be determined taking into account the exclusion of the influence of wind
reverse currents, but not less than 250 m from the water intake.
2.3.2.4. Lateral boundaries of the second zone of the ZSO from
the water's edge during the summer-autumn low water should be located at a distance of:
a) with a flat terrain - not less than
500 m;
b) in mountainous terrain - to the top
the first slope facing the source of water supply, but not less than 750
m with a gentle slope and at least 1,000 m with a steep one.
2.3.2.5. The border of the second zone of the ZSO on water bodies
should be removed along the water area in all directions from the water intake at a distance of 3
km - in the presence of surge winds up to 10% and 5 km - in the presence of surge winds
more than 10%.
2.3.2.6. Border 2 zones of the ZSO on reservoirs along
territory should be removed in both directions along the coast for 3 or 5 km in
in accordance with paragraph 2.3.2.5 and from the water's edge at a normal retaining level (NSL)
at 500-1,000 m in accordance with clause 2.3.2.4.
2.3.2.7. In some cases, considering
specific sanitary situation and with appropriate justification, the territory
the second belt can be increased in agreement with the center of the state
sanitary and epidemiological supervision.
2.3.3. Borders of the third belt
2.3.3.1. Borders of the third zone of the ZSO
surface sources of water supply on the watercourse upstream and downstream
coincide with the boundaries of the second belt. Side borders should run along the line
watersheds within 3-5 km, including tributaries. Borders of the third belt
surface source on the reservoir completely coincide with the boundaries of the second
belts.
Protected water supply zones
Work on the construction of security zones near the water supply is carried out in order to provide protection from various kinds of pollution of the source of drinking water.
At the same time, during the construction of the system, measures are taken to prevent situations, the occurrence of which would affect the quality of the water supplied to residential buildings.
Belts of the water protection zone
 The protected area around the water pipeline consists of three belts.When it is arranged, it is necessary to first develop a zone project, which then must be agreed with the sanitary and epidemiological service, the water utility enterprise, and besides other organizations interested in this.
The protected area around the water pipeline consists of three belts.When it is arranged, it is necessary to first develop a zone project, which then must be agreed with the sanitary and epidemiological service, the water utility enterprise, and besides other organizations interested in this.
The first belt, which is part of the protected area, is a circle, the center of which is located at the water intake point. If the project of the water supply network provides for several sources of water intake, then in this case it is necessary to allocate several protection zones. If you need to reduce the radius of one belt, then in this case you should contact the sanitary and epidemiological control service, since such a question is within the competence of this body.
The second zone is the territories, the use of which is mainly associated with the prevention of pollution of water sources. By carrying out hydrodynamic calculations, the dimensions of the second belt are determined
During their implementation, take into account the time during which the water source can reach the infection. Also, the size of this belt may depend on climatic conditions, soil characteristics, soil water.
The third belt is mainly used to protect the water supply from chemical contamination.
The width of the zone along the pipeline system that is used to transport water is determined based on the type of soil.
If a water pipe is laid in dry soil, then the size of the zone in each direction is 10m. If the pipe diameter is less than 1000 mm, then in this case the security zone should extend to 10 m on each side. At 20m, it should pass when installing large diameter pipelines.
When laying a water supply network in soil with high humidity, the length of the security zone in each side should be 50m
Such a factor as the diameter of the pipe used is not taken into account. If the water supply is laid in territories that are already built up, then in this case it is allowed to reduce the size of the security zones
But this can be done only after this issue is agreed and approved by the SES.
The protected area should not have:
- garbage bins;
- it is forbidden to conduct water supply through the territory of landfills and filtration fields;
- it is unacceptable to conduct them in cattle burial grounds and cemeteries.
Standards for private housing construction

CH Directory
456-73 considers only trunk lines and sewers. It does not apply to
plots allocated for IZHS. Fulfill the requirements of SN 456-73 and comply with the norms for the removal of sewage
and water supply in the conditions of private housing construction is impossible, since the dimensions
lanes under highways are too large. In addition, the size of the plots depends on
several factors:
- the region in which the construction is being carried out;
- building density;
- availability of sanitary or security zones;
- ground conditions.
In addition, other factors are taken into account:
- demand for plots;
- the amount of free land;
- the procedure for settling areas;
- general development of the region, needs, level
the life of the population.
Based on these factors, the sizes of the plots are accepted by local governments. Therefore, there is no standard in this matter. The minimum size is 3 acres, the maximum can reach several tens of hectares. It is impossible to use the same normative document in such conditions.Norms of land acquisition for local sewerage cannot be determined, since the entire system is located on the area of the site, it does not go beyond its limits. Therefore, in such cases, only allowable distances to buildings, drinking water supply facilities, other structures or infrastructure are considered. For local water supply lines, the standards are more lenient, but very stringent requirements are imposed on sewerage or disposal systems. This is due to the specifics of the operation of autonomous treatment facilities, their potential danger to drinking wells or wells. At the same time, the construction of private systems is carried out within the framework of one site, so the use of standard standards becomes inappropriate. The only condition is the observance of distances to objects, structures, as well as the correct installation of containers, pipes.
General concept of the sewer protection zone
Territories that surround the buildings of sewer networks are called security areas. Within the sewer zones, the following actions should be refrained from:

- Planting trees;
- Digging trenches and pits;
- Storing firewood or any other materials;
- Landfill device.
- Planning the construction of some buildings, piling or blasting.
- Carrying out work that raises or lowers the level of the soil, that is, the production of sections of the soil or its backfilling.
- Reinforced concrete slab pavement, even if this road is temporary.
- The performance of any actions, as a result of which the passage to the sewer networks will be blocked.
As a rule, the boundaries of protected zones are prescribed in a decree issued by the Ministry of the Environment.Exact information about the size of the protection zones can be obtained from the local water utilities.
What is the risk of not following the rules?
It must be said that cases of damage to the sewer pipeline due to land works are not so rare. They happen even more often than damage to water pipes or power cables.
Random accidents are due to the fact that the work foreman simply does not know that a pipeline passes here. The point here is some discrepancy between the laws. So, for example, when laying power lines or building water pipes, the operating organization is obliged to install warning signs.
But the obligation to install a sign warning that there is a protected territory of the sewerage system is not regulated by law. That is, there is no clear indication that the owners of sewerage networks must mark the location of the buffer zone with signs, in the law.
Thus, if as a result of some work the sewer pipeline was damaged, then the responsibility will be borne by:
- In the absence of a warning plate - the operating organization.
- If the sign was present, but was ignored, then the responsibility lies with the contractor.

For damage to sewerage networks, the culprit bears administrative responsibility. If the accident caused damage to the environment, then the measure of responsibility will be different.
Sanitary standards for water pipes
According to sanitary norms and rules, the sanitary zone is the distance that must be observed from any pipe in which water is transported.Moreover, regardless of its personal or state affiliation, occupancy from underground or aboveground sources.

Since SanPiN, which defines the protective territory, was created on the basis of Federal Law No. 52, non-compliance with the requirements threatens with serious troubles for violators of existing rules. In this regard, it is worth noting the following:
- absent or created in violation of existing norms, the protected area and the sanitary zone of the water supply system are punishable by a fine, often quite significant for the budget;
- the operation of communications, in accordance with existing regulations, is regulated by the Code of Administrative Offenses (CAO);
- violation of the sanitary zones of reservoirs and other sources of water supply can be up to 40 thousand rubles for legal entities, and up to 2 thousand rubles for individuals. and more, depending on the severity of the offense committed;
- the water supply zone cannot be used for any type of construction or reconstruction, unless we are talking about structures that are of direct importance for its functioning or protective measures of a sanitary and epidemiological orientation;
- the water supply zone assumes the absence in the close neighborhood of sewage, sewage, agricultural land in which pesticides are used;
- Strict restrictions are imposed on the proximity to garbage dumps, the burial of any kind of waste, and even on logging, unless it is sanitary.

The Russian government has adopted a number of resolutions and documents that show that the concept of "security zone" refers not only to water intake.Protective measures are subject to the entire route of water transportation through the pipeline, starting from the source and further along the entire length.
However, from a legal point of view, the Sanitary Protection Zone (or ZSO), created during the implementation of water supply, depends on several components.
In particular, the source of water - underground or aboveground, the level of natural protection available in a particular case. As well as the epidemiological and environmental situation and hydrogeological conditions at the site or in a particular area.

Gas pipeline security zone
Russian legislation distinguishes two gas pipeline security zones: the zone of gas distribution networks and the zone of main gas pipelines.
The RF LC provides for a security zone for pipelines (including gas pipelines) (clause 6, article 105 of the RF LC), as well as a zone of minimum distances to main or industrial pipelines (including gas pipelines) (clause 25, article 105 ZK RF).
Clause 2 of the Rules for the protection of gas distribution networks, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 20, 2000 N 878, establishes that these Rules are valid throughout the territory of the Russian Federation and are mandatory for legal entities and individuals who are owners, owners or users of land plots located within the security zones of gas distribution networks, or designing civil and industrial facilities, engineering, transport and social infrastructure facilities, or carrying out any economic activity within the boundaries of these land plots.
Subparagraph "e" of paragraph 3 of the Rules determines that the security gas distribution network zone is a territory with special conditions of use, established along the routes of gas pipelines and around other objects of the gas distribution network in order to ensure normal conditions for its operation and exclude the possibility of its damage.
In order to prevent their damage or violation of the conditions of their normal operation, restrictions (encumbrances) are imposed on land plots included in the security zones of gas distribution networks, which prohibit the persons specified in paragraph 2 of the Rules, including: appointments; enclose and block security zones, prevent the access of personnel of operating organizations to gas distribution networks, maintenance and elimination of damage to gas distribution networks; make fire and place sources of fire; dig cellars, dig and cultivate the soil with agricultural and reclamation tools and mechanisms to a depth of more than 0.3 m (paragraph 14 of the Rules).
The procedure for protecting main gas pipelines from 20.09.2017 is regulated by the Rules for the protection of main gas pipelines, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 08.09.2017 N 1083. Clause 2 of the Rules establishes that the concept of "main gas pipeline" includes: the linear part of the main gas pipeline; compressor stations; gas measuring stations; gas distribution stations, units and gas reduction points; gas cooling stations; underground gas storage facilities, including pipelines connecting underground gas storage facilities, and clause 3 of the Rules establishes security zones for gas pipeline facilities.
These Rules impose a number of obligations on the owner (or other legal owner) of the land plot on which the main gas pipeline facilities are located, and also establish prohibitions (clause 4 of the Rules) and some restrictions on the use of land plots - in particular, mining, explosive, construction, installation, land reclamation, loading and unloading and other works and activities is allowed only with the written permission of the owner of the main gas pipeline or the organization operating the main gas pipeline (clause 6 of the Rules).
The limitations established by the federal legislator on the actual use of land plots on which gas supply system facilities are located, due to the explosive and fire hazardous properties of gas transported through gas distribution networks, and the special conditions for the use of these land plots provided for in this regard and the regime for exercising economic activity on them are not aimed at only to ensure the safety of gas supply system facilities during its operation, maintenance and repair, but also to prevent accidents, disasters and other possible adverse consequences and thereby protect the life and health of citizens, to ensure their safety (Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of 06.10.2015 N 2318-O “On the refusal to accept for consideration the complaint of citizen Osipova Lyudmila Vladislavovna about the violation of her constitutional rights by the provisions of clause 6 of article 90 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, part six of article 28 and part four of article 32 of the Federal of the Federal Law “On Gas Supply in the Russian Federation”).