- The principle of operation of water heating
- Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
- Closed system with gravity circulation
- Open system with gravity circulation
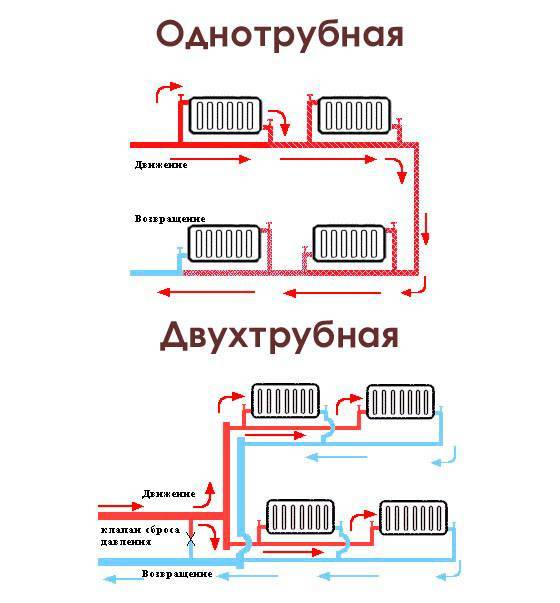
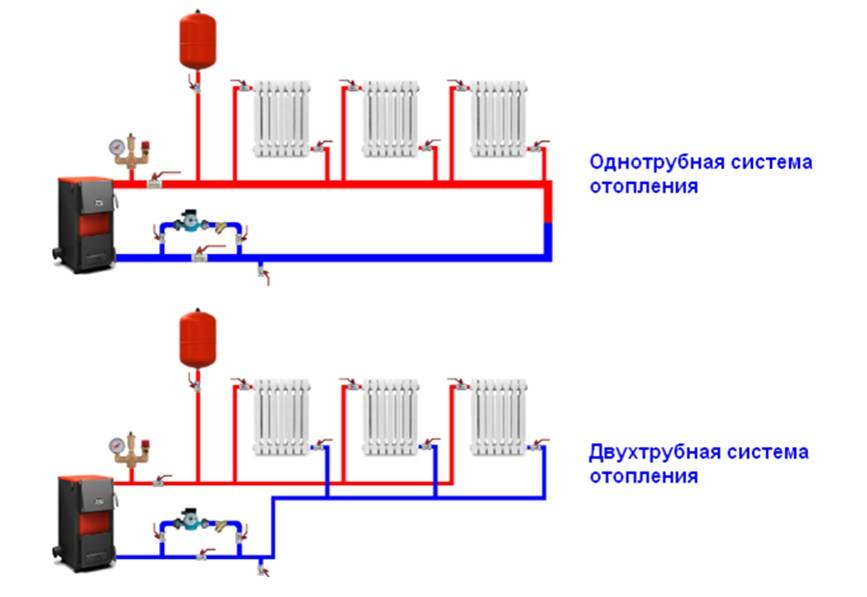
- Single pipe system with self-circulation
- What does a single-circuit flow heating scheme look like?
- pros
- Minuses
- Water heating devices
- Underfloor heating construction
- Skirting and floor convectors
- Single-column heating in individual construction
- The positive aspects of a one-pipe system
- Cons of a single pipe system
- Features of the installation of a single-pipe system
- Kinds
- According to the installation plan
- By type of wiring
- In the direction of the coolant
- Circulation
- Theoretical horseshoe - how gravity works
- Mounting Features
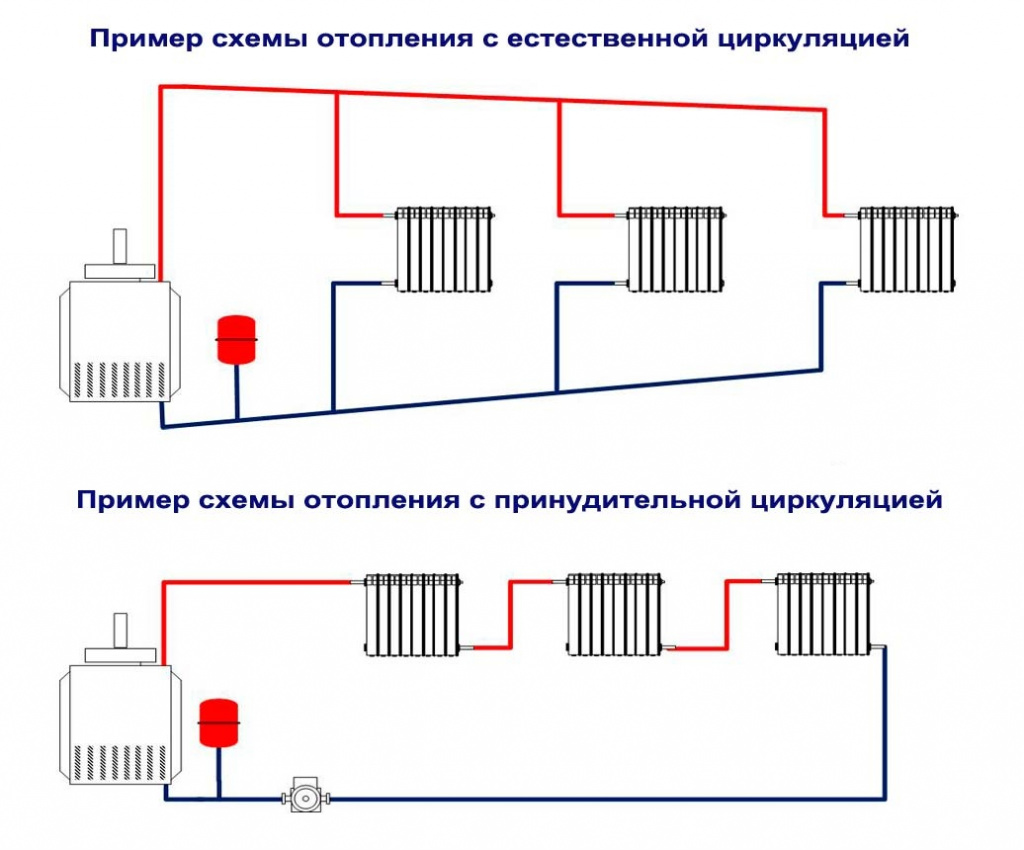
- What is forced circulation?
- Connecting radiators
The principle of operation of water heating
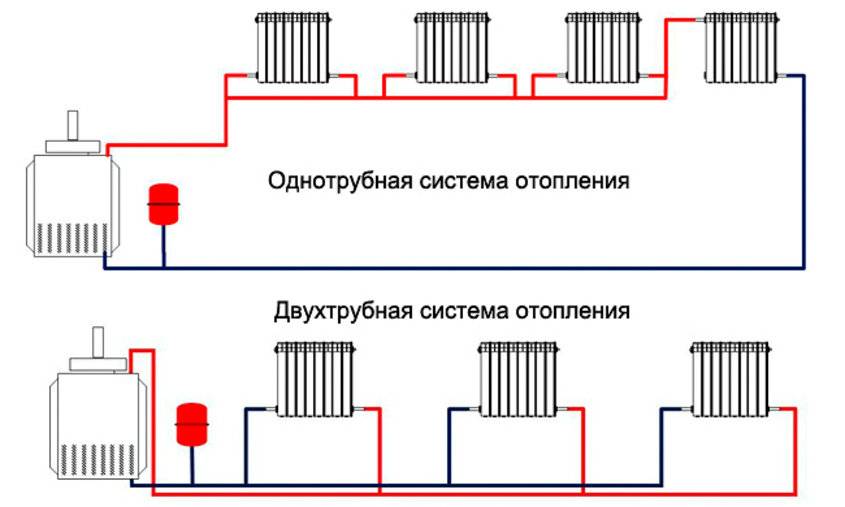
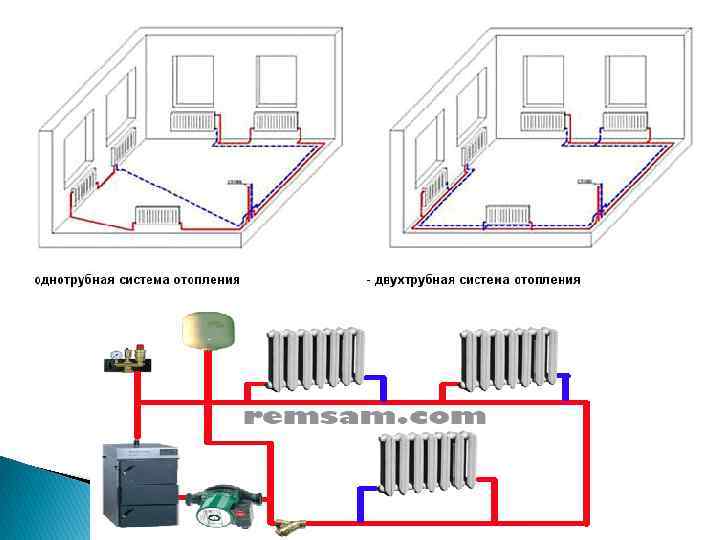
In low-rise construction, the most widespread is a simple, reliable and economical design with a single line. The single-pipe system remains the most popular way to organize individual heat supply. It functions due to the continuous circulation of the heat transfer fluid.
Moving through the pipes from the source of thermal energy (boiler) to the heating elements and back, it gives up its thermal energy and heats the building.
The heat carrier can be air, steam, water or antifreeze, which is used in houses of periodic residence. The most common water heating schemes.
Traditional heating is based on the phenomena and laws of physics - thermal expansion of water, convection and gravity. Heating up from the boiler, the coolant expands and creates pressure in the pipeline.
In addition, it becomes less dense and, accordingly, lighter. Pushed from below by heavier and denser cold water, it rushes upwards, so the pipeline leaving the boiler is always directed as far as possible upwards.
Under the action of the created pressure, convection forces and gravity, the water goes to the radiators, heats them up, and at the same time cools itself.
Thus, the coolant gives off thermal energy, heating the room. The water returns to the boiler already cold, and the cycle begins anew.
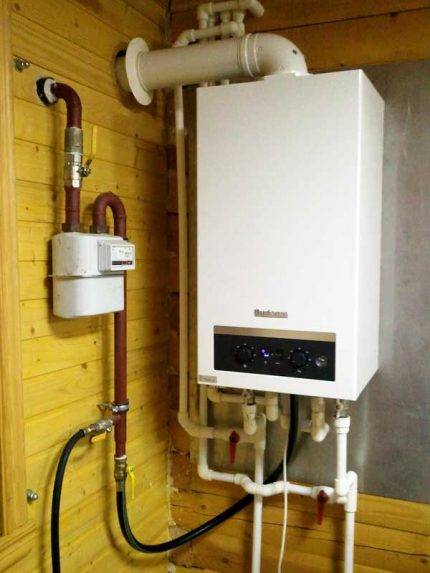

Modern equipment that provides heat supply to the house can be very compact. You don't even need a special room to install it.
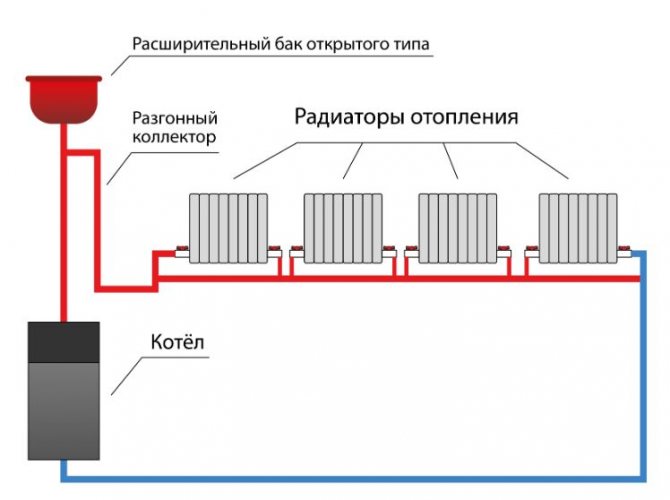
A heating system with natural circulation is also called gravity and gravity. To ensure the movement of liquid, it is necessary to observe the slope angle of the horizontal branches of the pipeline, which should be equal to 2 - 3 mm per linear meter.
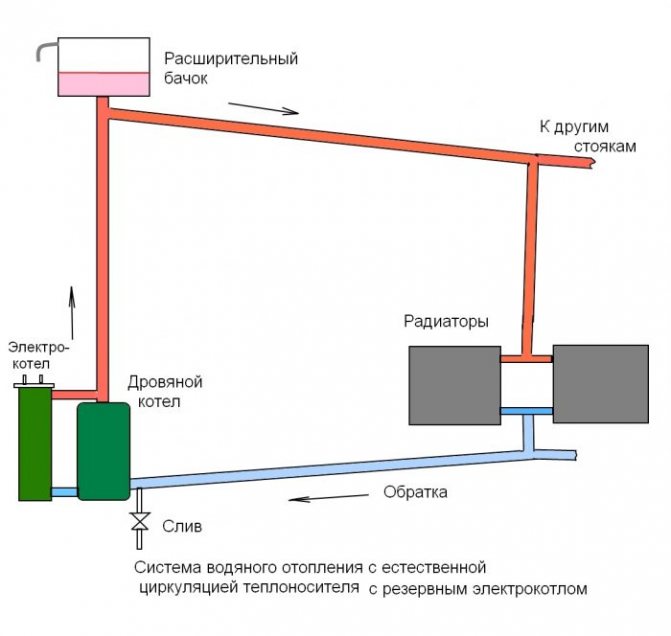
The volume of the coolant increases when heated, creating hydraulic pressure in the line. However, since water is not compressible, even a slight excess will lead to the destruction of heating structures.
Therefore, in any heating system, a compensating device is installed - an expansion tank.
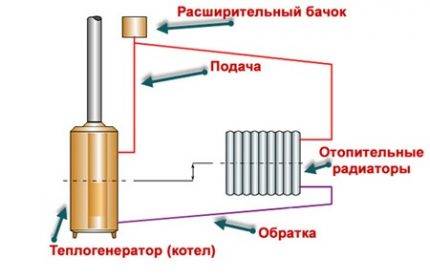
In a gravity heating system, the boiler is mounted at the lowest point of the pipeline, and the expansion tank is at the very top.All pipelines are sloped so that the coolant can move by gravity from one element of the system to another
Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
Despite the simple design of a water heating system with self-circulation of the coolant, there are at least four popular installation schemes. The choice of wiring type depends on the characteristics of the building itself and the expected performance.
To determine which scheme will work, in each individual case, you need to perform hydraulic system calculation, take into account the characteristics of the heating unit, calculate the diameter of the pipe, etc. You may need the help of a professional when doing the calculations.
Closed system with gravity circulation
Otherwise, closed-type systems work like other natural circulation heating schemes. As disadvantages, one can single out the dependence on the volume of the expansion tank. For rooms with a large heated area, you will need to install a capacious container, which is not always advisable.
Open system with gravity circulation
System open type heating differs from the previous type only in the design of the expansion tank. This scheme was most often used in old buildings. The advantages of an open system is the possibility of self-manufacturing containers from improvised materials. The tank usually has modest dimensions and is installed on the roof or under the ceiling of the living room.
The main disadvantage of open structures is the ingress of air into pipes and heating radiators, which leads to increased corrosion and rapid failure of heating elements.Airing the system is also a frequent "guest" in open circuits. Therefore, radiators are installed at an angle, Mayevsky cranes are required to bleed air.
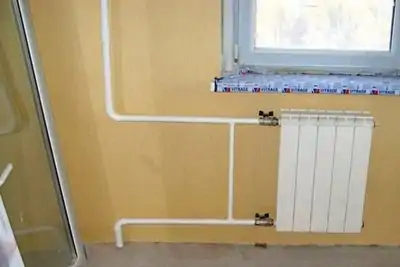
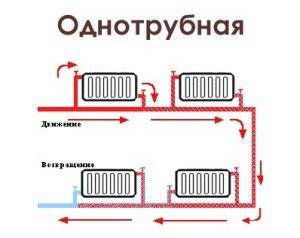
Single pipe system with self-circulation
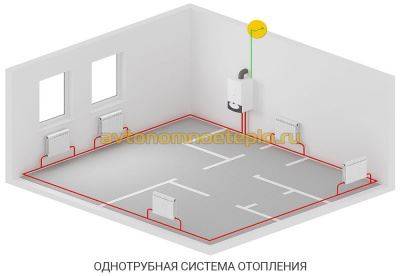
The heated coolant enters the upper branch pipe of the battery and is discharged through the lower outlet. After that, the heat enters the next heating unit and so on until the last point. The return line returns from the last battery to the boiler.
This solution has several advantages:
- There is no paired pipeline under the ceiling and above the floor level.
- Save money on system installation.
The disadvantages of such a solution obvious. The heat output of heating radiators and the intensity of their heating decreases with distance from the boiler. As practice shows, the single-pipe heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation, even if all slopes are observed and the correct pipe diameter is selected, is often redone (through the installation of pumping equipment).
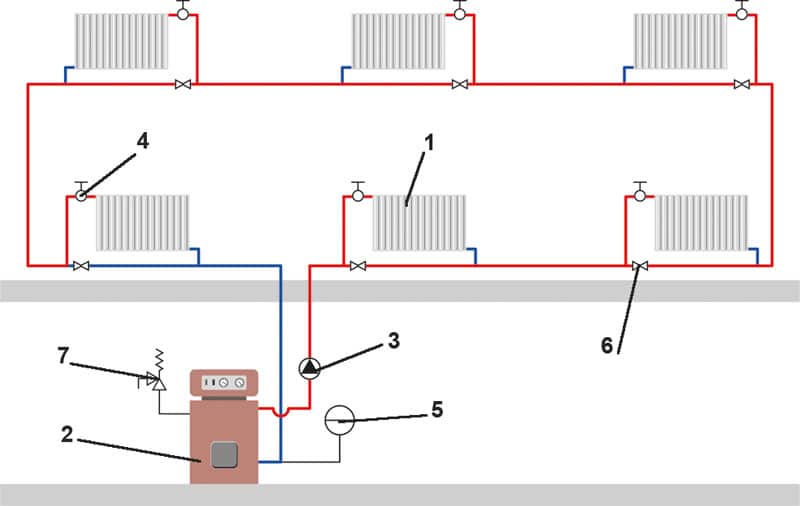
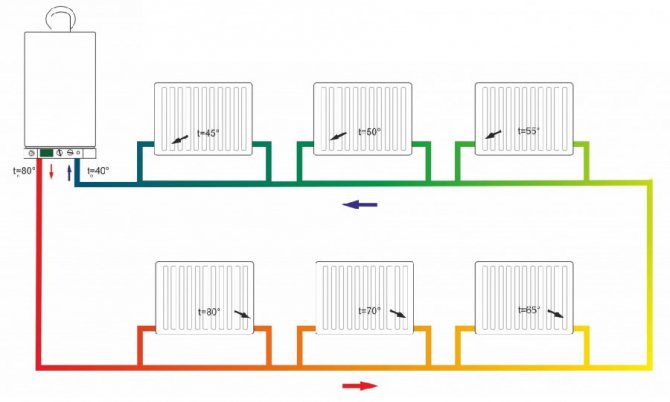
What does a single-circuit flow heating scheme look like?
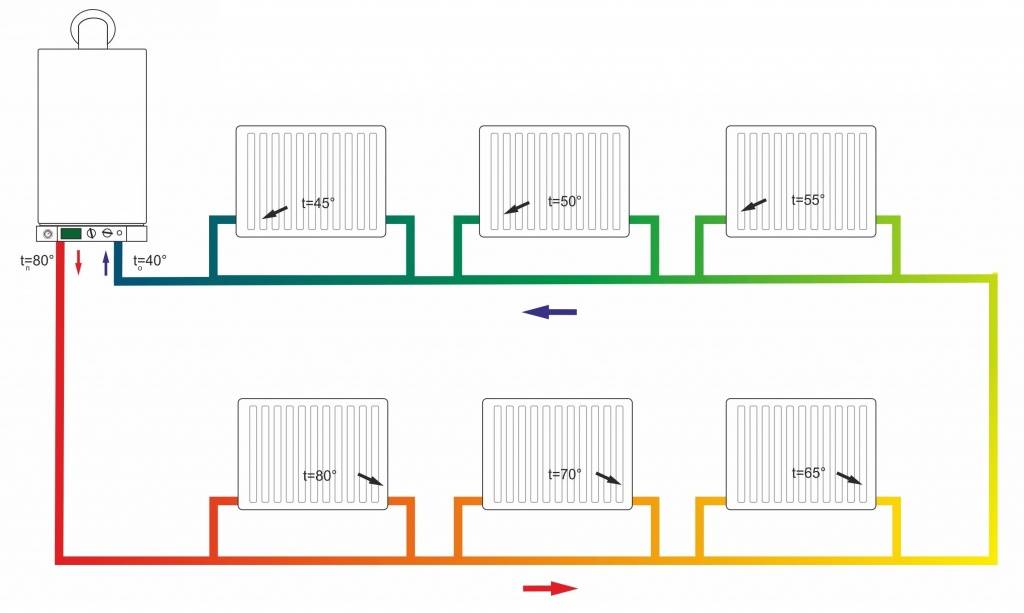
In multi-storey buildings for various purposes within the limits of the settlement, heating is carried out centrally, that is, the house has a heating main input and water valves, one or more heating units.
- the heating unit is located in a separate room, locked for safety;
Photo 1. A conditional image of what a single-circuit heating system looks like, indicating the temperature of the coolant throughout the entire circuit.
- water valves come first;
- after the valves, mud collectors are installed - filters in which foreign inclusions in the coolant are retained: dirt, sand, rust;
- then follow the DHW valves installed on the return and supply (or at the beginning and end of the circuit).
Their purpose is to provide hot water supply, which can be supplied from the supply or return. In winter, the coolant comes very hot, much more than 100 ° C (boiling does not occur due to high pressure in the pipeline).
Reference! In a single-pipe system, a similar principle is implemented by supplying hot water from the end of the circuit, where the water has already cooled to an acceptable temperature. Accordingly, if the temperature at the supply from the main is reduced, then the DHW changes the source to the beginning of the circuit.
Such water cannot be used for domestic needs, so the return flow is activated, where the temperature has already been reduced to an acceptable level. In the autumn-spring period, when the heating is less intense, the return water is too cold, so the DHW is supplied from the supply.

One of the convenient and common schemes is open water intake:
- boiling water from the CHPP enters the elevator unit, where it is mixed under pressure with water that already circulates in the system, resulting in water with a temperature of about 70 ° C, which enters the radiators;
- excess cooling coolant goes into the return line;
- heat distribution occurs with the help of valves or a collector with valves for each part of the house.
The return and supply are usually located in the basement, sometimes they are spaced apart: the return is in the basement, and the supply is in the attic.
pros
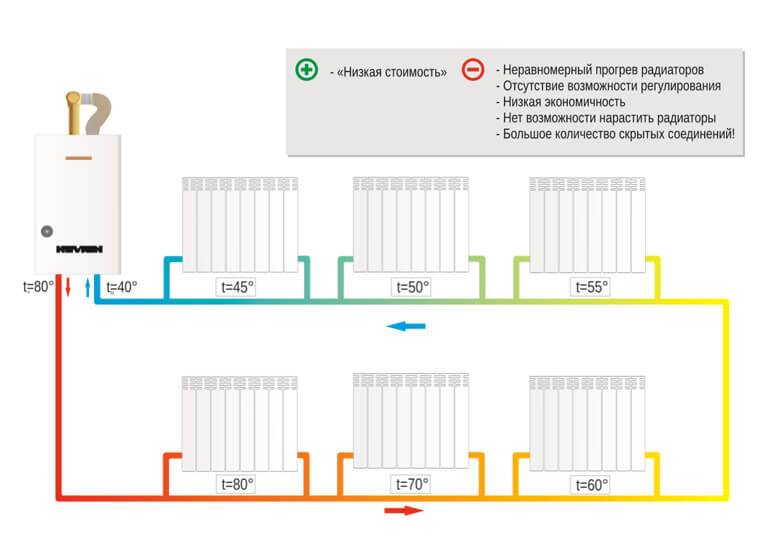
The advantage of a one-pipe system is considered cheap, and this is the only advantage of this system.With the spread and improvement of the two-pipe system, the one-pipe system in apartment buildings is used less and less.
In private homes, the economy and simplicity of design are rated higher - it can be assembled with your own hands, easily maintained and made non-volatile.
Minuses
There are more of them:
- the need to accurately calculate the diameters of the pipes of the main pipeline and branches;
- in the radiators at the end of the circuit, the temperature will be lower, so you will have to think about increasing the volume of heating devices;
- for the same reason, the number of radiators on one branch will be limited, since uniform heating of a large number is impossible.
Water heating devices
As heating elements of the premises can be:
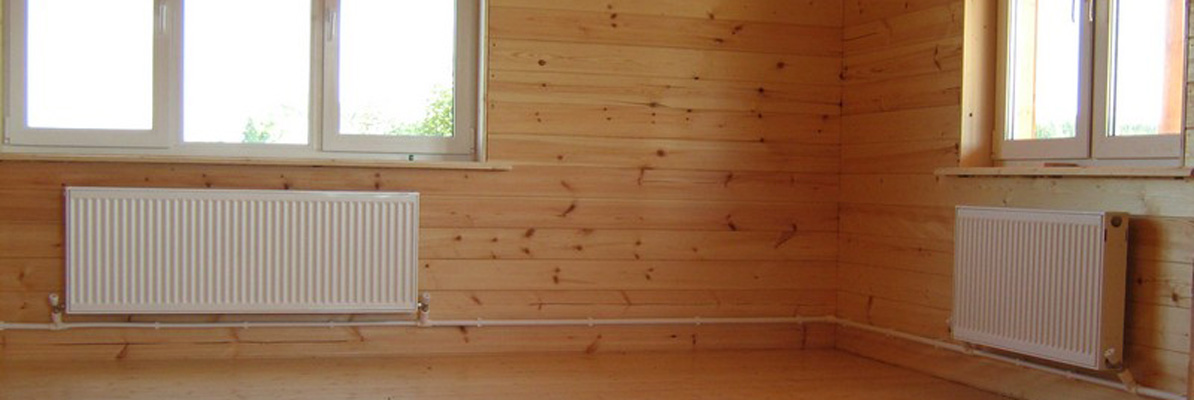
- traditional radiators installed under window openings and near cold walls, for example, on the north side of the building;
- pipe contours of floor heating, otherwise - warm floors;
- baseboard heaters;
- floor convectors.
Water radiator heating is the most reliable and cheapest option among those listed. It is quite possible to install and connect the batteries yourself, the main thing is to choose the right number of power sections. Disadvantages - weak heating of the lower zone of the room and the location of the devices in plain sight, which is not always consistent with the interior design.
All commercially available radiators are divided into 4 groups according to the material of manufacture:
- Aluminum - sectional and monolithic. In fact, they are cast from silumin - an alloy of aluminum with silicon, they are the most effective in terms of heating rate.
- Bimetallic. A complete analogue of aluminum batteries, only a frame made of steel pipes is provided inside.Scope of application - multi-apartment high-rise buildings with central heating, where the heat carrier is supplied with a pressure of over 10 bar.
- Steel panel. Relatively cheap monolithic type radiators made of stamped metal sheets plus additional fins.
- Pig-iron sectional. Heavy, heat-intensive and expensive devices with an original design. Due to the decent weight, some models are equipped with legs - it is unrealistic to hang such an "accordion" on the wall.
In terms of demand, the leading positions are occupied by steel appliances - they are inexpensive, and in terms of heat transfer, thin metal is not much inferior to silumin. Following are aluminum, bimetallic and cast iron heaters. Choose which ones you like best.
Underfloor heating construction
The floor heating system consists of the following elements:
- heating circuits made of metal-plastic or polyethylene pipes, filled with cement screed or laid between logs (in a wooden house);
- distribution manifold with flow meters and thermostatic valves to control the water flow in each loop;
- mixing unit - a circulation pump plus a valve (two- or three-way), maintaining the temperature of the coolant in the range of 35 ... 55 ° C.
The mixing unit and the collector are connected to the boiler by two lines - supply and return. Water heated to 60 ... 80 degrees is mixed in portions with a valve into the circuits as the circulating coolant cools down.
Underfloor heating is the most comfortable and economical way of heating, although installation costs are 2-3 times higher than the installation of a radiator network. The optimal heating option is shown in the photo - floor water circuits + batteries regulated by thermal heads.
Warm floors at the installation stage - laying pipes on top of the insulation, fastening the damper strip for subsequent pouring with cement-sand mortar
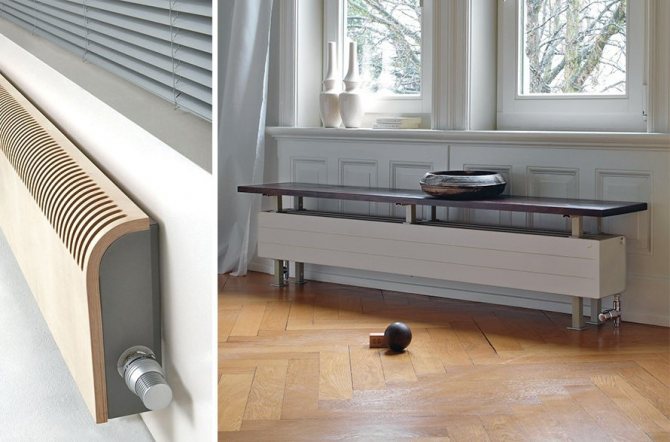
Skirting and floor convectors
Both types of heaters are similar in the design of the water heat exchanger - a copper coil with thin plates - fins. In the floor version, the heating part is closed with a decorative casing that looks like a plinth; gaps are left at the top and bottom for the passage of air.
The heat exchanger of the floor convector is installed in a housing located below the level of the finished floor. Some models are equipped with low-noise fans that increase the performance of the heater. The coolant is supplied through pipes laid in a hidden way under the screed.
The described devices successfully fit into the design of the room, and underfloor convectors are indispensable near transparent outer walls made entirely of glass. But ordinary homeowners are in no hurry to purchase these appliances, because:
- copper-aluminum radiators of convectors - not a cheap pleasure;
- for full heating of a cottage located in the middle lane, you will have to install heaters around the perimeter of all rooms;
- floor heat exchangers without fans are inefficient;
- the same products with fans emit a quiet monotonous hum.
Baseboard heating device (pictured left) and underfloor convector (right)
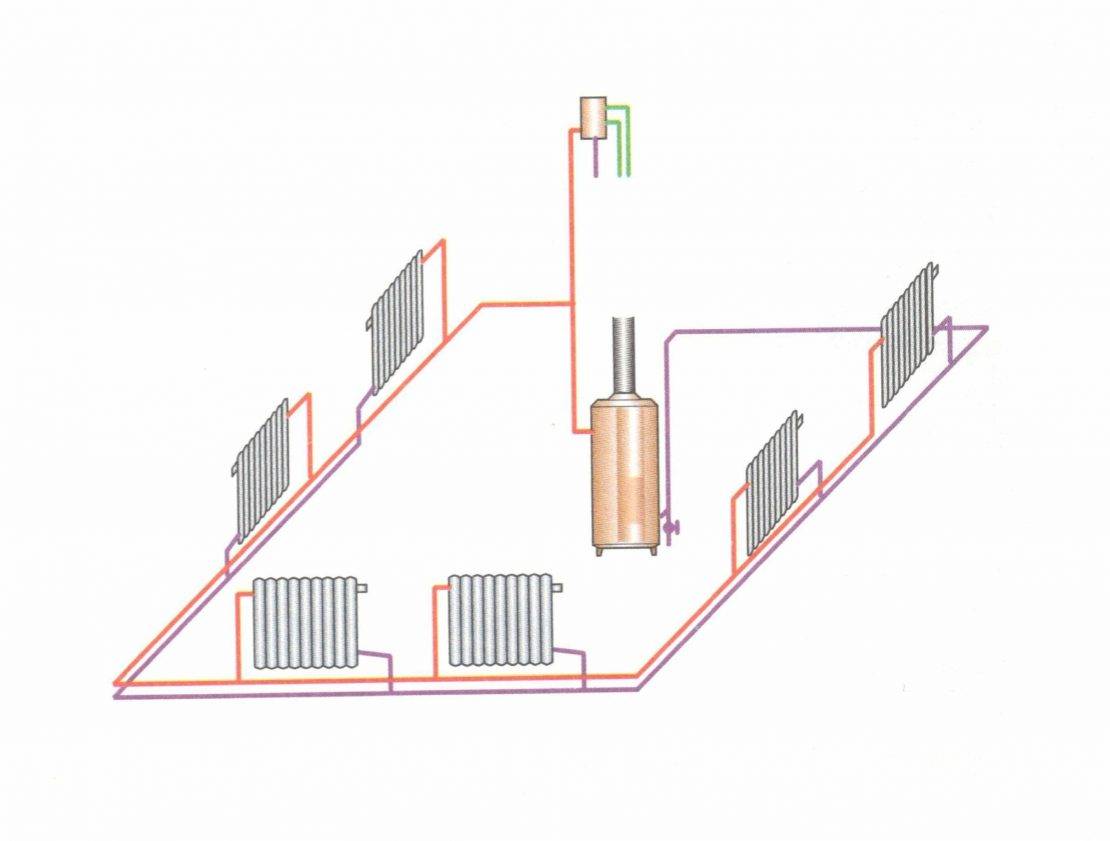
Single-column heating in individual construction
If heating with one main riser is installed in a one-story building, then it will be possible to get rid of at least one significant drawback of such a scheme - uneven heating.
If such heating is implemented in a multi-storey building, then the upper floors will be heated much more intensively than the lower floors. This will lead to a situation where it is cold on the first floors of the house, and hot on the upper floors.
A private house (mansion, cottage) is rarely more than two or three stories high. Therefore, the installation of heating, the scheme of which was described above, does not threaten that the temperature on the upper floors will be much higher than on the lower floors.
The positive aspects of a one-pipe system
Advantages of a one-pipe heating system:
- One circuit of the system is located around the entire perimeter of the room and can lie not only in the room, but also under the walls.
- When laying below floor level, pipes must be thermally insulated to prevent heat loss.
- Such a system allows pipes to be laid under doorways, thus reducing the consumption of materials and, accordingly, the cost of construction.
- The phased connection of heating devices allows you to connect all the necessary elements of the heating circuit to the distribution pipe: radiators, heated towel rails, underfloor heating. The degree of heating of the radiators can be adjusted by connecting to the system - in parallel or in series.
- A single-pipe system allows you to install several types of heating boilers, for example, gas, solid fuel or electric boilers. With a possible shutdown of one, you can immediately connect a second boiler and the system will continue to heat the room.
- A very important feature of this design is the ability to direct the movement of the coolant flow in the direction that will be most beneficial for the residents of this house.First, direct the movement of the hot stream to the northern rooms or those located on the leeward side.
Cons of a single pipe system
With a large number of advantages of a single-pipe system, some inconveniences should be noted:
- When the system is idle for a long time, it starts up for a long time.
- When installing the system on a two-story house (or more), the water supply to the upper radiators is at a very high temperature, while the lower ones are at a low temperature. It is very difficult to adjust and balance the system with such a wiring. You can install more radiators on the lower floors, but this increases the cost and does not look very aesthetically pleasing.
- If there are several floors or levels, one cannot be turned off, so when carrying out repairs, the entire room has to be turned off.
- If the slope is lost, air pockets may periodically occur in the system, which reduces heat transfer.
- High heat loss during operation.
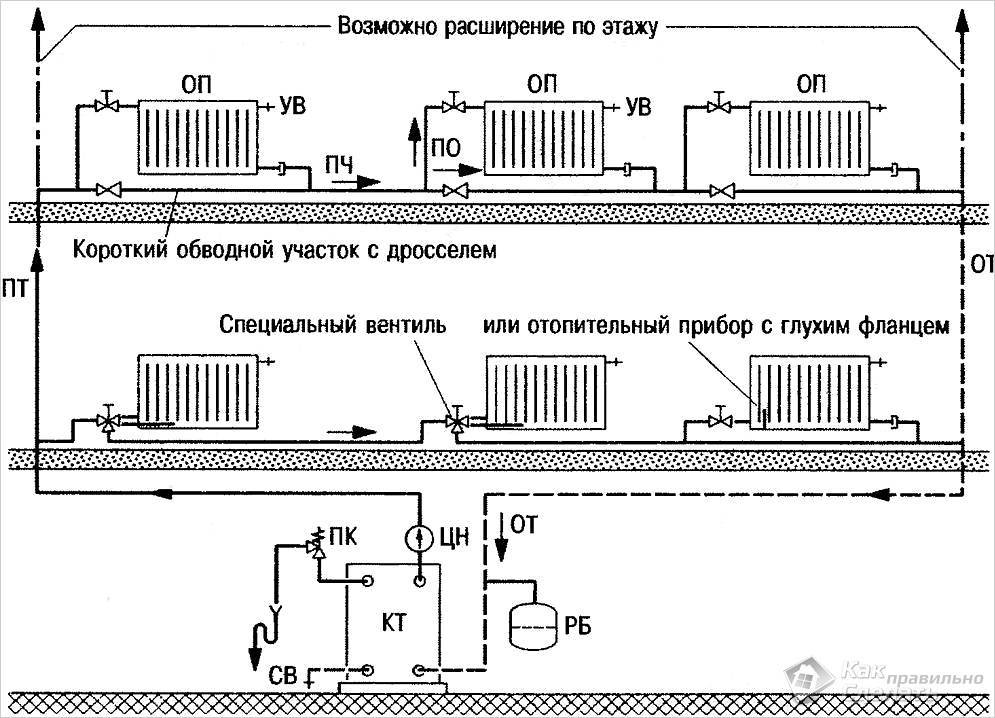
Features of the installation of a single-pipe system
- Installation of the heating system begins with the installation of the boiler;
- Throughout the entire length of the pipeline, a slope of at least 0.5 cm per 1 linear meter of pipe must be maintained. If such a recommendation is not followed, air will accumulate in the elevated area and prevent the normal flow of water;
- Mayevsky cranes are used to release air locks on radiators;
- Shut-off valves should be installed in front of the connected heating devices;
- The coolant drain valve is installed at the lowest point of the system and serves for partial, complete draining or filling;
- When installing a gravity system (without a pump), the collector must be at a height of at least 1.5 meters from the floor plane;
- Since all wiring is made with pipes of the same diameter, they should be securely fastened to the wall, avoiding possible deflections so that air does not accumulate;
- When connecting a circulation pump in combination with an electric boiler, their operation must be synchronized, the boiler does not work, the pump does not work.
The circulation pump must always be installed in front of the boiler, taking into account its specifics - it works normally at a temperature not exceeding 40 degrees.
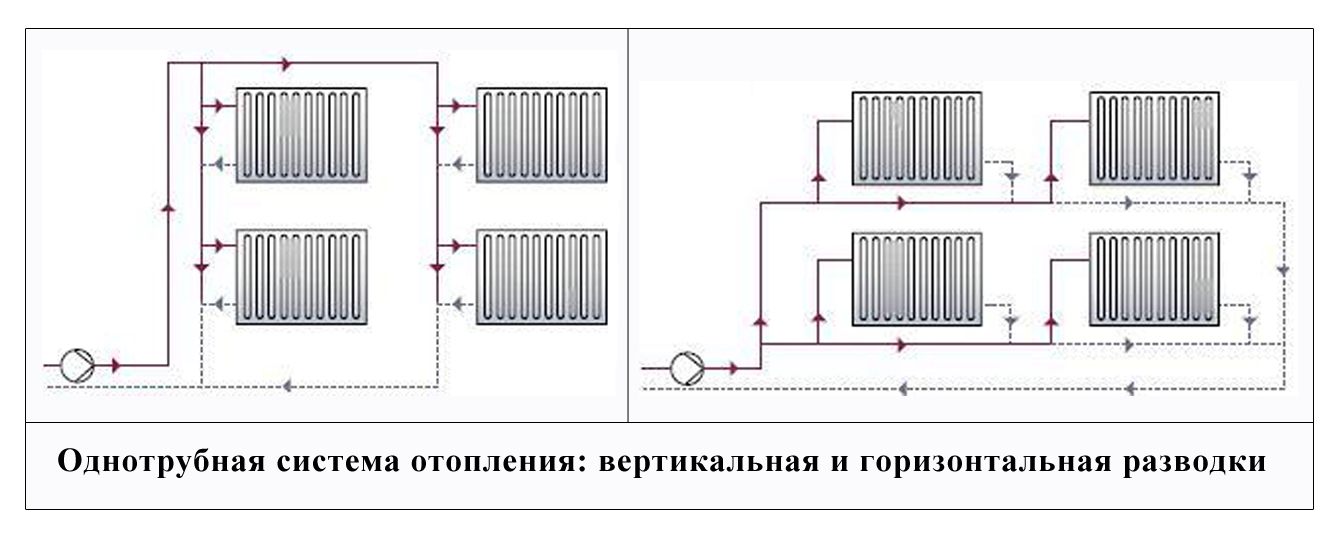
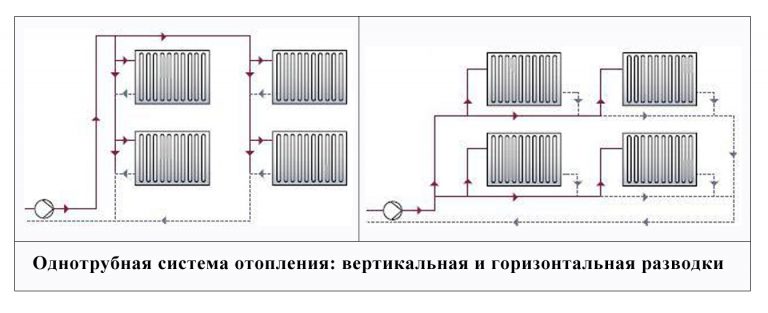
The wiring of the system can be done in two ways:
- Horizontal
- Vertical.
With horizontal wiring the minimum number of pipes is used, and the devices are connected in series. But this method of connection is characterized by air congestion, and there is no possibility of regulating the heat flow.
With vertical wiring, pipes are laid in the attic and pipes leading to each radiator depart from the central line. With this wiring, water flows to radiators of the same temperature. Such a feature is characteristic of vertical wiring - the presence of a common riser for a number of radiators, regardless of the floor.
Previously, this heating system was very popular due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, but gradually, given the nuances that arise during operation, they began to abandon it and at the moment it is very rarely used for heating private houses.
Kinds
There are several varieties of two-pipe heating structures that differ in the installation scheme, type of wiring, direction of movement of the coolant and circulation.
According to the installation plan
According to the installation scheme, heating systems from two circuits are divided into two subspecies:
- Horizontal. In such a system, the pipes through which the water moves are laid horizontally, creating a separate subcircuit for each floor. Such a scheme is more suitable for one-story houses or buildings of several floors, but of great length in length.
- Vertical. This scheme assumes the presence of several risers arranged vertically, each of which is connected to radiators located in space one above the other. This method is more suitable for two- or more-story houses of a small area.
By type of wiring
There are also two varieties here.
- Top wiring. It is used if the heating boiler and expansion tank are located in the upper part of the house, for example, in an insulated attic. With this type of wiring, the pipes of both circuits are carried out at the top, under the ceiling, and descents are made from them to the radiators.
- Bottom wiring. In cases where the heating element is installed below the main circuit of the system (for example, in the basement), it is more advisable to run pipes between the floor and window sills, which will simplify the connection of radiators.
In the direction of the coolant
- With the opposite movement. As the name suggests, in this case, the water moves along a straight circuit in the opposite direction to that along which the chilled water returns to the boiler. A feature of this type is the presence of a "dead end" - the final radiator, in which the most remote points of both circuits are joined.
- With passing traffic. In this design, the coolant in both circuits moves in the same direction.
Circulation
Systems with natural circulation. Here, the movement of the coolant along the circuits is ensured by the temperature difference in the circuits and the slope of the pipes. Such systems are characterized by a low heating rate, but do not require the connection of additional equipment.
Currently, this option is used more in houses for seasonal living.
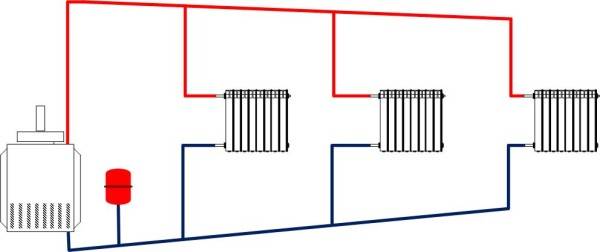
Systems with forced circulation. A circulation pump is built into one of the circuits (most often the return one), which ensures the movement of water. This approach provides faster and more uniform heating of the room.
Theoretical horseshoe - how gravity works
The natural circulation of water in heating systems operates due to gravity. How does this happen:
- We take an open vessel, fill it with water and begin to heat it up. The most primitive option is a pan on a gas stove.
- The temperature of the lower liquid layer rises, the density decreases. The water becomes lighter.
- Under the influence of gravity, the upper heavier layer sinks to the bottom, displacing the less dense hot water. The natural circulation of fluid begins, called convection.
Example: if you heat 1 m³ of water from 50 to 70 degrees, it will become 10.26 kg lighter (below, see the table of densities at various temperatures). If heating continues to 90 °C, then the cube of liquid will lose 12.47 kg, although the temperature delta remains the same - 20 °C. Conclusion: the closer the water is to the boiling point, the more active the circulation occurs.
Similarly, the coolant circulates by gravity through the home heating network. The water heated by the boiler loses weight and is pushed up by the cooled coolant that has returned from the radiators.The flow velocity at a temperature difference of 20–25 °C is only 0.1…0.25 m/s versus 0.7…1 m/s in modern pumping systems.
The low speed of fluid movement along highways and heating devices causes the following consequences:
- The batteries have time to give off more heat, and the coolant cools down by 20–30 °C. In a conventional heating network with a pump and a membrane expansion tank, the temperature drops by 10–15 degrees.
- Accordingly, the boiler must produce more heat energy after the burner starts. Keeping the generator at a temperature of 40 ° C is pointless - the current will slow down to the limit, the batteries will become cold.
- To deliver the required amount of heat to the radiators, it is necessary to increase the flow area of the pipes.
- Fittings and fittings with high hydraulic resistance can worsen or completely stop gravity flow. These include non-return and three-way valves, sharp 90° turns and pipe constrictions.
- The roughness of the inner walls of pipelines does not play a big role (within reasonable limits). Low fluid velocity - low resistance from friction.
- A solid fuel boiler + gravity heating system can work without a heat accumulator and a mixing unit. Due to the slow flow of water, condensate does not form in the firebox.
As you can see, there are positive and negative moments in the convection movement of the coolant. The former should be used, the latter should be minimized.
Mounting Features
Installation of equipment, subject to the features of the scheme of a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation of the coolant, is not difficult. Initially, the heating unit is mounted, they are divided into several types:
- on gas fuel;
- on diesel fuel;
- with the use of solid fuel;
- combined.
The boilers are connected to the chimney system, as well as to the heating main. In this case, two outputs are produced in the heating apparatus. The carrier enters the system through the upper one, and the cooled liquid returns through the lower one.
All structural elements are connected using high-pressure polypropylene, metal or polyethylene pipes.
A forced circulation pump, shut-off equipment, Mayevsky taps, as well as a protection unit are connected to the line. Pipes are connected in different ways, depending on the material from which they are made.
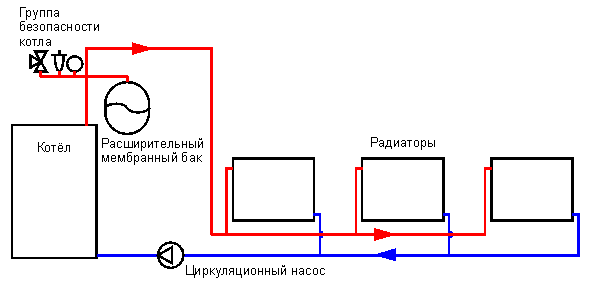
What is forced circulation?
In natural systems, in order for the carrier to evenly distribute heat in radiators, pipes are mounted with a slope. In one-story private houses, such conditions are easy to comply with. When installing pipes along a large perimeter and on several floors, air jams may occur in the system. In addition, the liquid cools down and the extreme radiators do not receive energy.
With an air lock, the coolant stops moving, which will lead to overheating and premature failure of some devices of the heating boiler. To eliminate such problems and malfunctions, it is necessary to use a circulation pump. With it, you can reduce heat loss and speed up the movement of fluid in the system.
 Forced circulation pump
Forced circulation pump
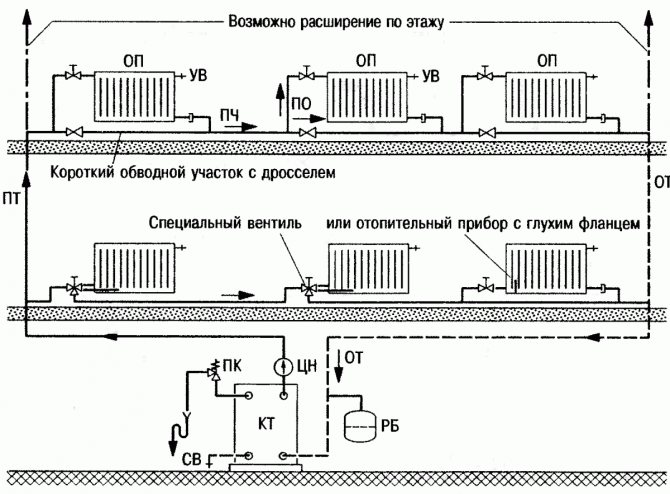
Connecting radiators
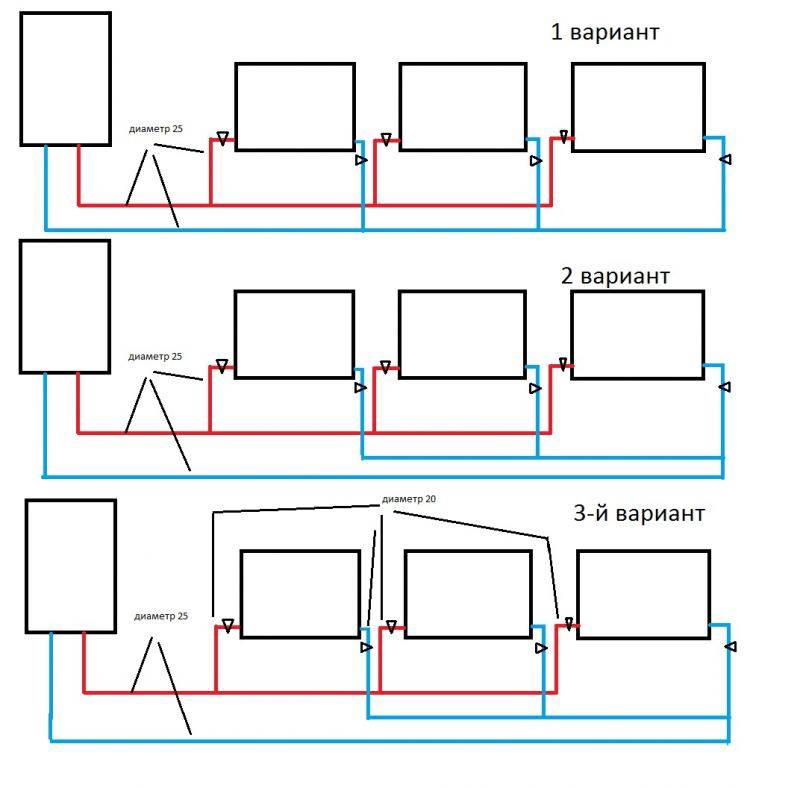
The choice of how to connect them depends on their total number, method of laying, length of pipelines, etc. The most common methods are:
• diagonal (cross) method: the straight pipe is connected to the side of the battery at the top, and the return pipe is connected to its opposite side below; this method allows the heat carrier to be distributed over all sections as evenly as possible with minimal heat loss; used with a significant number of sections;
• unilateral: also used with a large number of sections, a pipe with hot water (straight pipe) and a return pipe are connected on one side, which ensures sufficient uniform heating of the radiator;
• saddle: if the pipes go under the floor, it is most convenient to attach the pipes to the lower pipes of the battery; due to the minimum number of visible pipelines, it looks attractive outwardly, however, the radiators heat up unevenly;
• bottom: the method is similar to the previous one, the only difference is that the straight pipe and the return pipe are located almost at the same point.
To protect against the penetration of cold and create a thermal curtain, the batteries are located under the windows. In this case, the distance to the floor should be 10 cm, from the wall - 3-5 cm.