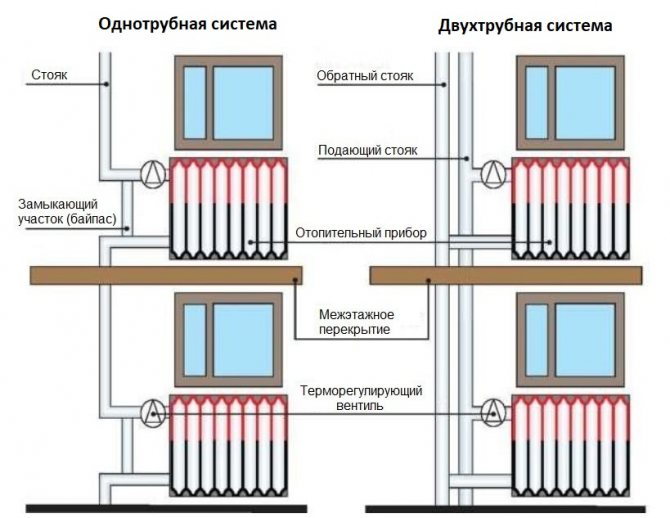
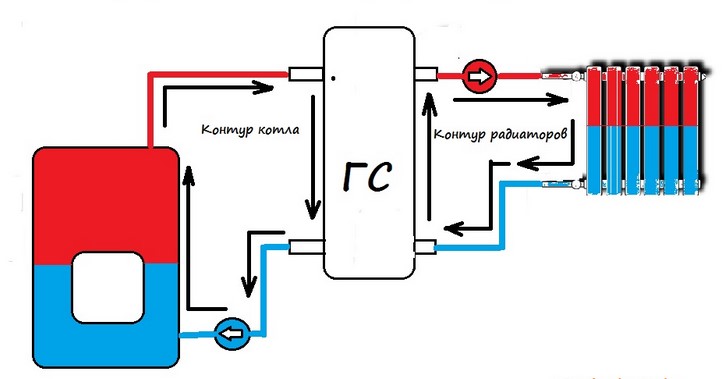
- Principle of operation
- Why choose such a system?
- The positive aspects of a one-pipe system
- Cons of a single pipe system
- Features of the installation of a single-pipe system
- Disadvantages of a single-pipe heating system
- Components and principle of operation
- Two wiring methods
- horizontal layout
- Vertical layout
- Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
- Closed system with gravity circulation
- Open system with gravity circulation
- Single pipe system with self-circulation
- How to choose a heating pump
- Advantages and disadvantages of heating with one pipe
- Connecting batteries to a one-pipe system - choose your option
- How to choose a heating pump
- How to calculate pipe diameter
- Vertical single pipe heating system
- Mounting order
- Benefits of Leningradka
- Disadvantages of "Leningradka"
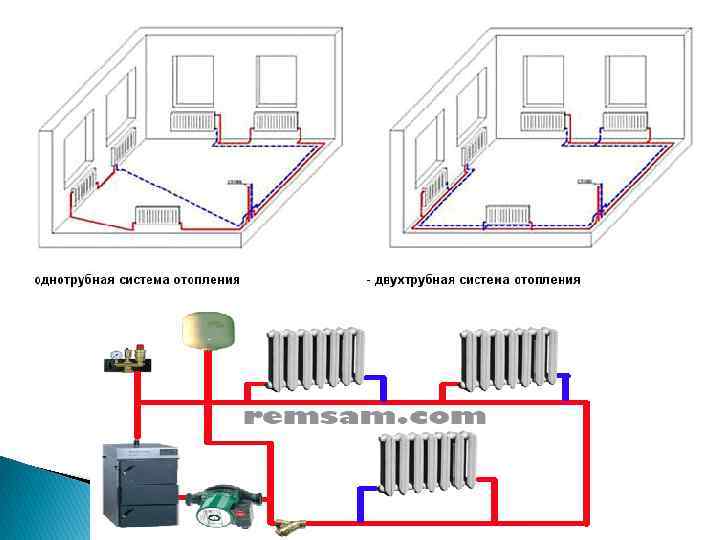
Principle of operation
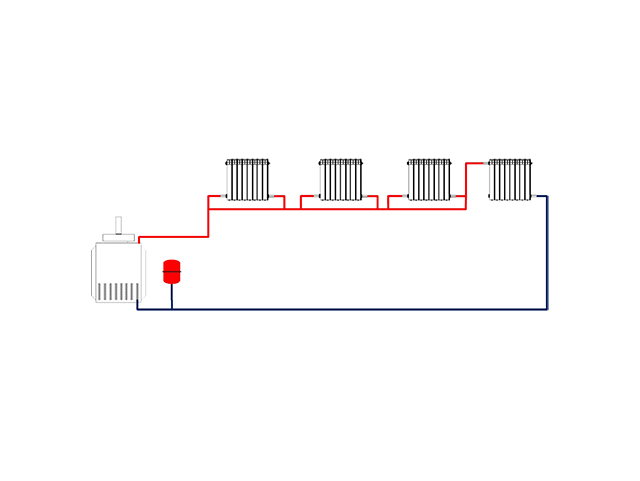
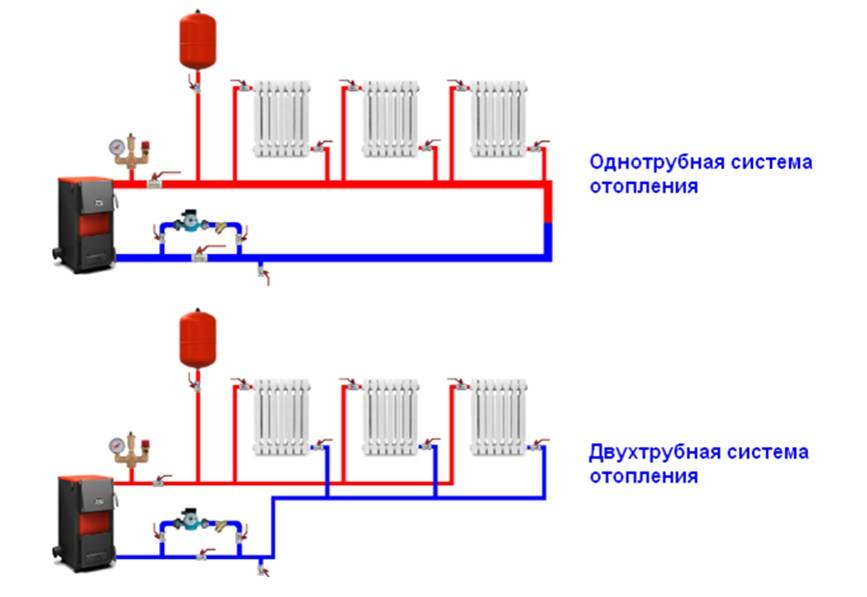
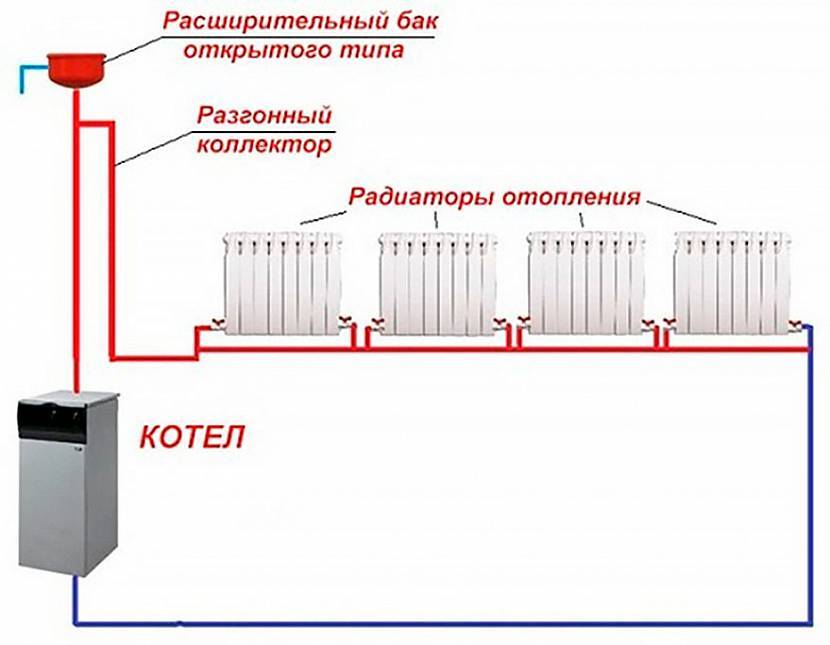
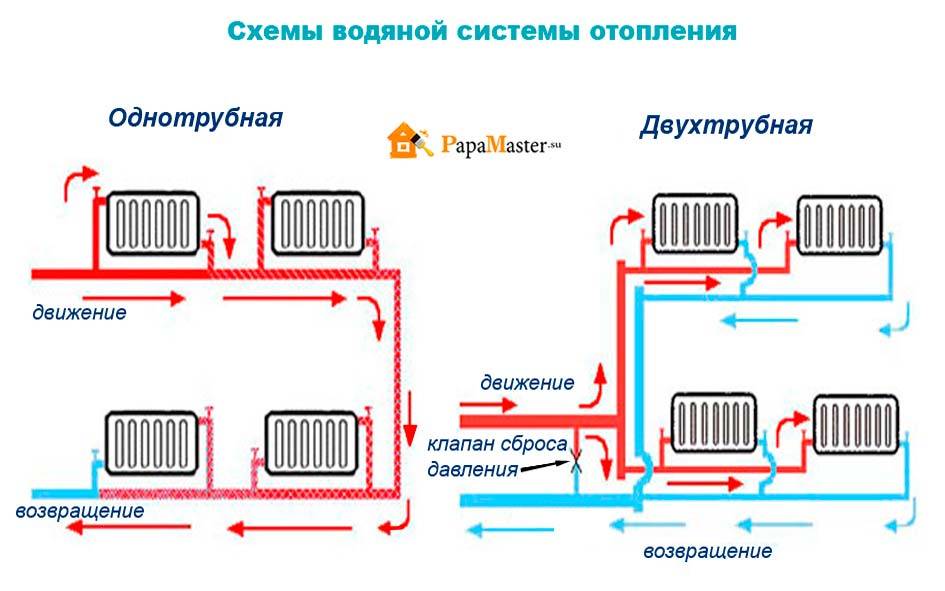
To solve the question of how to make single-pipe heating in a private house, it is necessary to study the principle of its operation. The main element of a single-pipe scheme is a gas or solid fuel boiler. With its help, water is heated, which later goes into the pipes and radiators of the heating system. In the process of moving, the coolant gradually cools down and returns to the boiler through the return pipe.
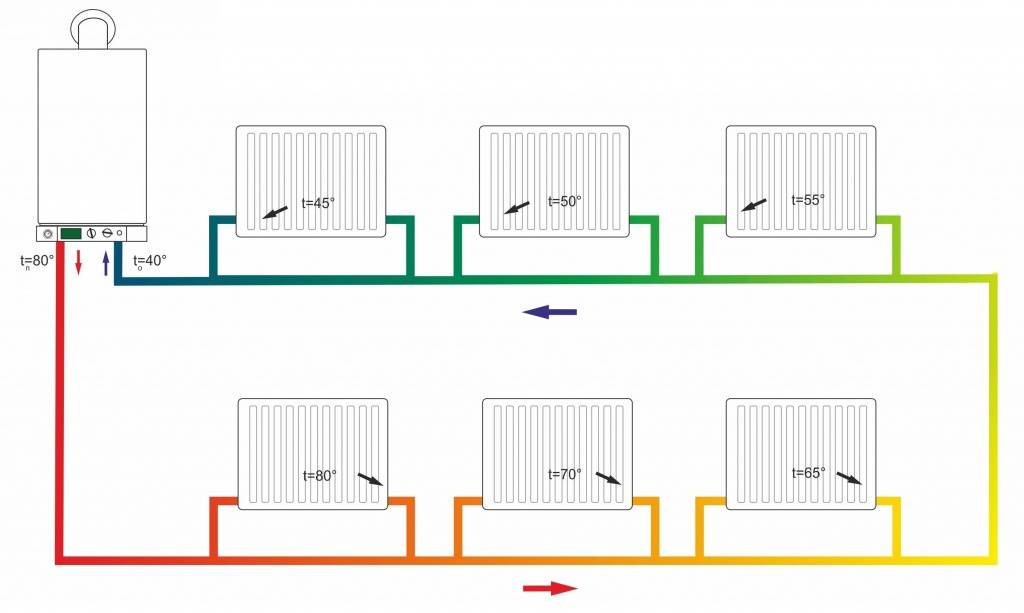
The peculiarity of such a system is that the first and second radiators will heat up more, and in the last batteries the water temperature drops significantly, therefore, it will be colder in this room.
In this case, it is important to understand how to properly make a one-pipe heating system.
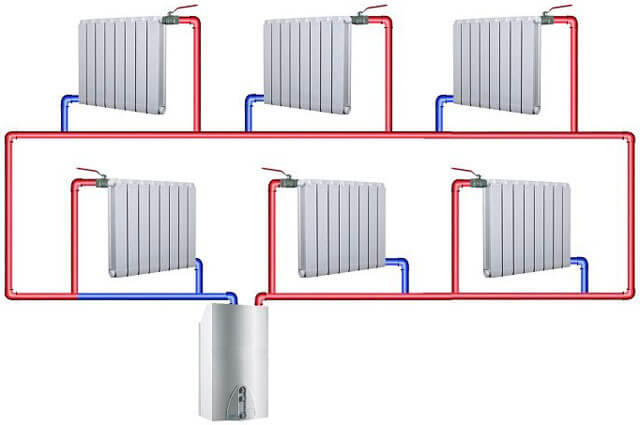
You can solve the problem in the following way:
- Increase the heat capacity of radiators located far from the boiler, which helps to increase heat transfer.
- Raise the temperature of the water leaving the boiler.
However, both options require significant material costs, which makes the entire heating system expensive.
Why choose such a system?
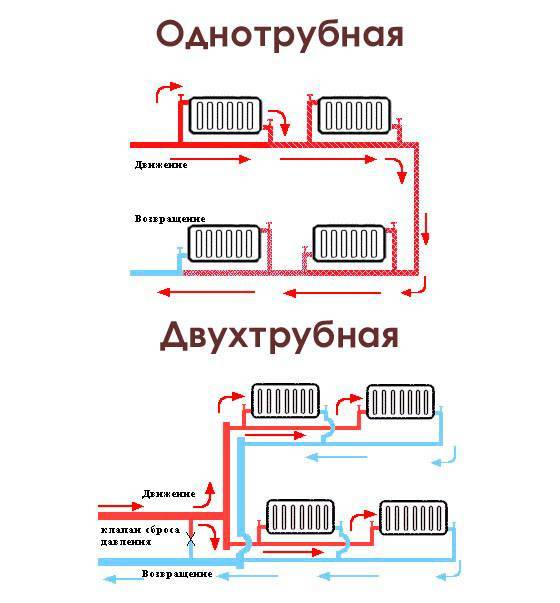
Two-pipe water heating is gradually replacing traditional single-pipe designs, since its advantages are obvious and very significant:
- Each of the radiators included in the system receives a coolant with a certain temperature, and for all it is the same.
- Possibility to make adjustments for each battery. If desired, the owner can put a thermostat on each of the heaters, which will allow him to get the desired temperature in the room. At the same time, the heat transfer of the remaining radiators in the building will remain the same.
- Relatively small pressure losses in the system. This makes it possible to use an economical circulation pump of relatively low power for operation in the system.
- If one or even several radiators fail, the system can continue to operate. The presence of shutoff valves on the supply pipes allows you to carry out repair and installation work without stopping it.
- Possibility of installation in a building of any height and area. It will only be necessary to choose the optimally suitable type of two-pipe system.
The disadvantages of such systems usually include the complexity of installation and the high cost compared to single-pipe structures. This is due to the double number of pipes that have to be installed.
However, it should be borne in mind that for the arrangement of a two-pipe system, pipes and components of small diameter are used, which gives certain cost savings. As a result, the cost of the system is not much higher than that of a single-pipe counterpart, while it provides much more advantages.
One of the significant advantages of a two-pipe heating system is the ability to effectively control the temperature in the room.
The positive aspects of a one-pipe system
Advantages of a one-pipe heating system:
- One circuit of the system is located around the entire perimeter of the room and can lie not only in the room, but also under the walls.
- When laying below floor level, pipes must be thermally insulated to prevent heat loss.
- Such a system allows pipes to be laid under doorways, thus reducing the consumption of materials and, accordingly, the cost of construction.
- The phased connection of heating devices allows you to connect all the necessary elements of the heating circuit to the distribution pipe: radiators, heated towel rails, underfloor heating. The degree of heating of the radiators can be adjusted by connecting to the system - in parallel or in series.
- A single-pipe system allows you to install several types of heating boilers, for example, gas, solid fuel or electric boilers. With a possible shutdown of one, you can immediately connect a second boiler and the system will continue to heat the room.
- A very important feature of this design is the ability to direct the movement of the coolant flow in the direction that will be most beneficial for the residents of this house. First, direct the movement of the hot stream to the northern rooms or those located on the leeward side.
Cons of a single pipe system
With a large number of advantages of a single-pipe system, some inconveniences should be noted:
- When the system is idle for a long time, it starts up for a long time.
- When installing the system on a two-story house (or more), the water supply to the upper radiators is at a very high temperature, while the lower ones are at a low temperature. It is very difficult to adjust and balance the system with such a wiring. You can install more radiators on the lower floors, but this increases the cost and does not look very aesthetically pleasing.
- If there are several floors or levels, one cannot be turned off, so when carrying out repairs, the entire room has to be turned off.
- If the slope is lost, air pockets may periodically occur in the system, which reduces heat transfer.
- High heat loss during operation.
Features of the installation of a single-pipe system
- Installation of the heating system begins with the installation of the boiler;
- Throughout the entire length of the pipeline, a slope of at least 0.5 cm per 1 linear meter of pipe must be maintained. If such a recommendation is not followed, air will accumulate in the elevated area and prevent the normal flow of water;
- Mayevsky cranes are used to release air locks on radiators;
- Shut-off valves should be installed in front of the connected heating devices;
- The coolant drain valve is installed at the lowest point of the system and serves for partial, complete draining or filling;
- When installing a gravity system (without a pump), the collector must be at a height of at least 1.5 meters from the floor plane;
- Since all wiring is made with pipes of the same diameter, they should be securely fastened to the wall, avoiding possible deflections so that air does not accumulate;
- When connecting a circulation pump in combination with an electric boiler, their operation must be synchronized, the boiler does not work, the pump does not work.
The circulation pump must always be installed in front of the boiler, taking into account its specifics - it works normally at a temperature not exceeding 40 degrees.
The wiring of the system can be done in two ways:
- Horizontal
- Vertical.
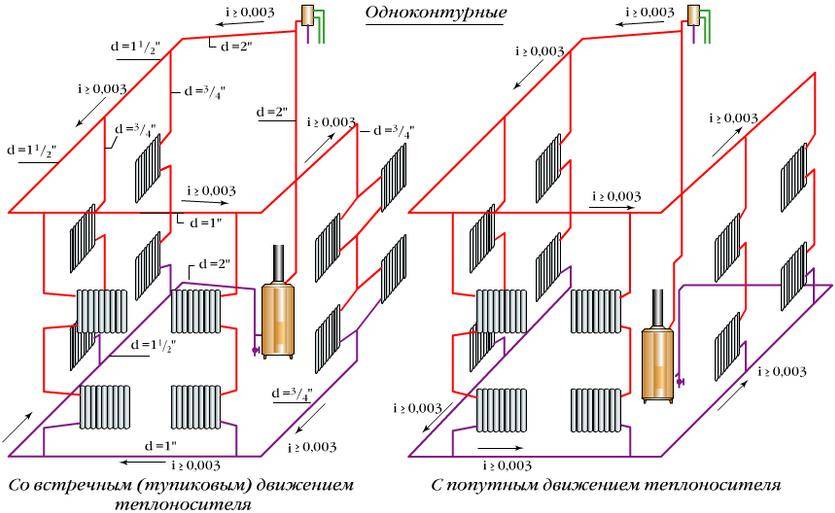
With horizontal wiring, a minimum number of pipes is used, and the devices are connected in series. But this method of connection is characterized by air congestion, and there is no possibility of regulating the heat flow.
With vertical wiring, pipes are laid in the attic and pipes leading to each radiator depart from the central line. With this wiring, water flows to radiators of the same temperature. Such a feature is characteristic of vertical wiring - the presence of a common riser for a number of radiators, regardless of the floor.
Previously, this heating system was very popular due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, but gradually, given the nuances that arise during operation, they began to abandon it and at the moment it is very rarely used for heating private houses.
Disadvantages of a single-pipe heating system
Such a sequence does not allow that during operation it is possible to regulate the heating of the radiator without affecting the rest of the system devices. If, for example, the temperature in one room is too high and if the valve is turned down a little, the temperature will drop in other rooms of the house.
Another disadvantage of a single-pipe heating system is that higher pressures are required during its operation. A single-pipe heating system is in dire need of installing a pump, since with an increase in its power, the costs associated with operation also increase.
The third disadvantage of such a system is the mandatory vertical spill. This is especially true for single storey buildings. An expansion tank in a one-story house can be installed in a room such as the attic of a house.
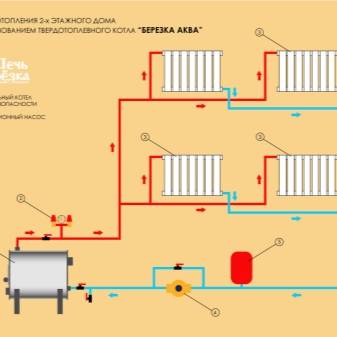
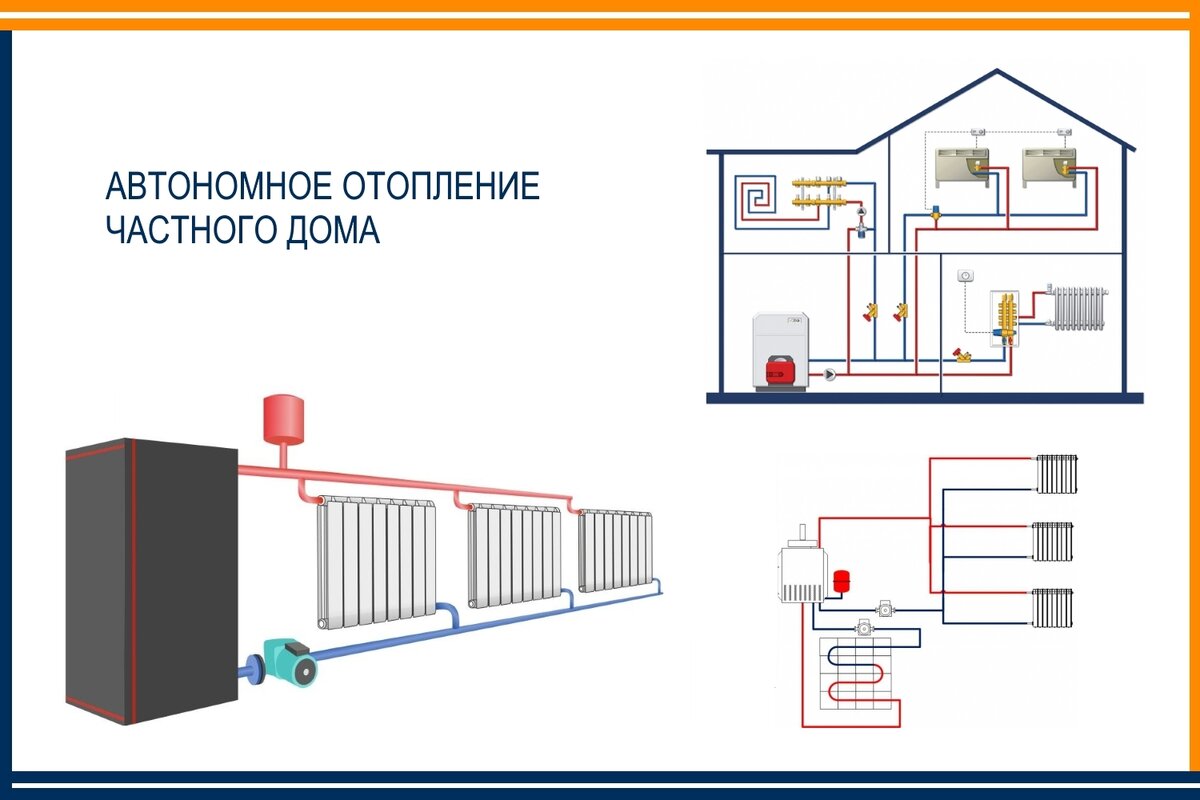
Components and principle of operation
Single-pipe heating systems of a private house consist of the following elements:
- boiler;
- a pipeline through which heated and cold liquid moves;
- shut-off and control valves;
- expansion tank;
- circulation pump (if necessary);
- connecting parts;
- security block;
- radiators or batteries.
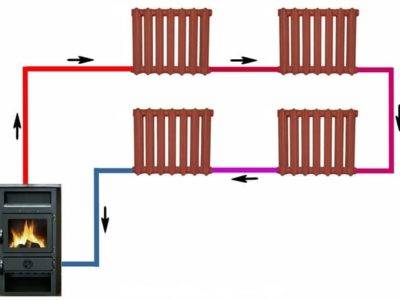
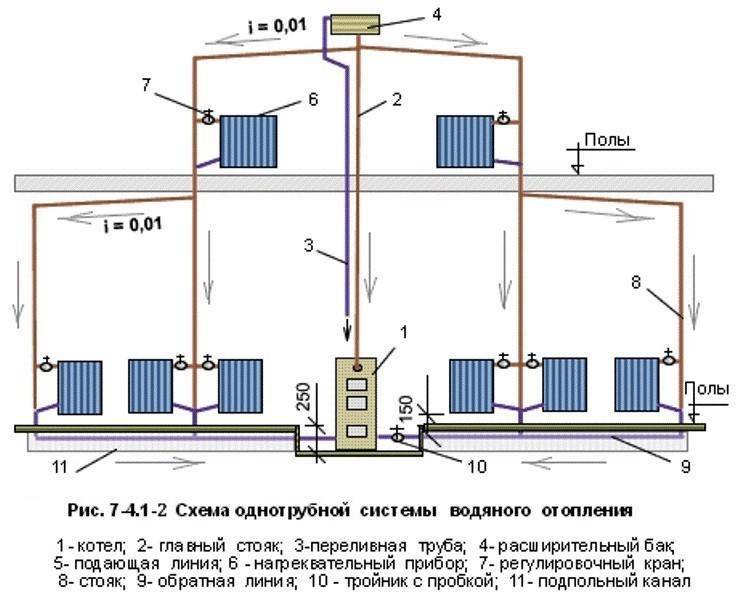
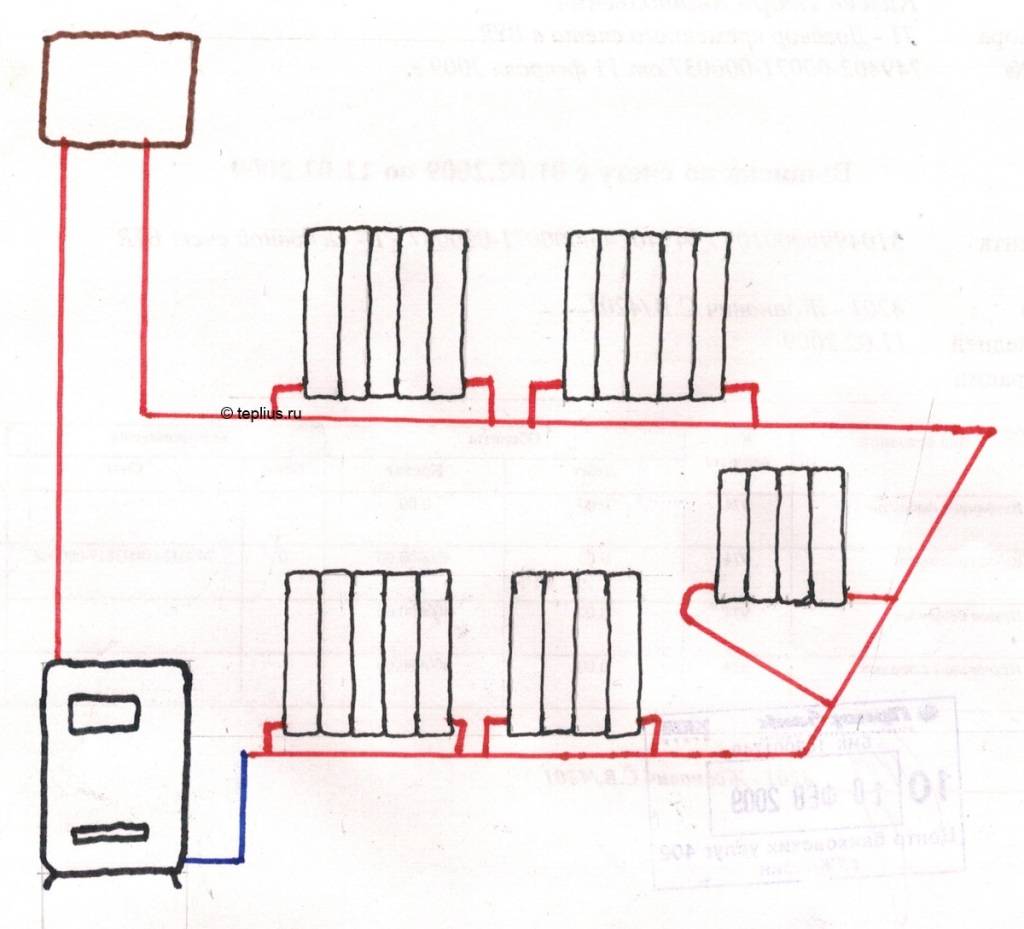
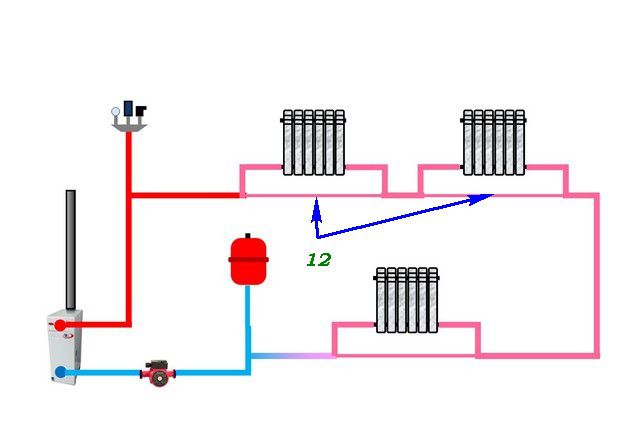
The principle of operation of the Leningradka is simple: the heated coolant entering the system from the boiler reaches the first radiator, where the tee is divided into several streams. Most of the liquid flows through the line, and the rest remains in the radiator. After the heat is transferred to its walls (the water temperature drops by 10-15 degrees), the coolant returns to the common collector through the outlet pipe.
Mixing, the water cools by 1.5 degrees and flows into the next radiator. At the end of the circuit, the cooled liquid is sent to the boiler, where it is heated again. The last battery receives a not so hot coolant, so the room is heated unevenly. To eliminate this drawback, you can install a more powerful battery at the end of the circuit, increase the performance of the circulation pump or the diameter of the pipe.
Two wiring methods
Horizontal wiring is characterized by the fact that it is necessary to artificially maintain the movement of the coolant with the help of a circulation pump.
Vertical wiring can work both with natural circulation of the coolant and with forced circulation.
In low-rise private houses, both options are used.
horizontal layout
Among the people, a single-pipe horizontal heating system was called "Leningradka".
The presence of a circulation pump in a horizontal circuit for pumping the coolant is mandatory.
The horizontal system is laid above the floor or directly in the floor structure. Radiators are installed at the same level, and the line itself is made with a slight slope in the direction of the coolant.
 Photo of the horizontal scheme
Photo of the horizontal scheme
The disadvantages of the horizontal wiring diagram are the same as those of the vertical one.To balance the system, pipes of small diameter are used (as they move away from the distributor or riser).
To prevent heat loss, it is necessary to make thermal insulation of pipes. An overview of pipe insulation materials is available on this page.
The disadvantages of a single-pipe heating system abound, however, this does not mean at all that it should not be used.
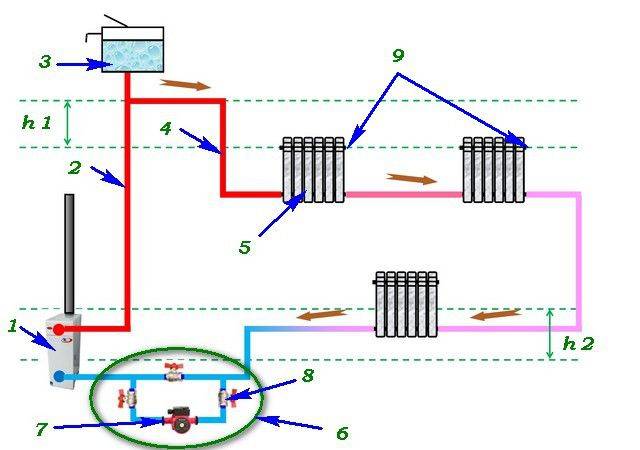
Vertical layout
The vertical single pipe system has found wide application due to its low pipe consumption and ease of installation. It can be successfully used in systems with natural and forced circulation of the coolant.
The heated coolant rises to the upper floor through the supply line and enters the heating devices located above through the risers. Then he goes down the supply risers to the heating devices located on the lower floor.
 Scheme of a vertical single-pipe heating system
Scheme of a vertical single-pipe heating system
The main disadvantage of such a scheme: on the lower floors of the house, the coolant has a much lower temperature than on the upper ones.
To reduce the temperature difference of the coolant, it is necessary:
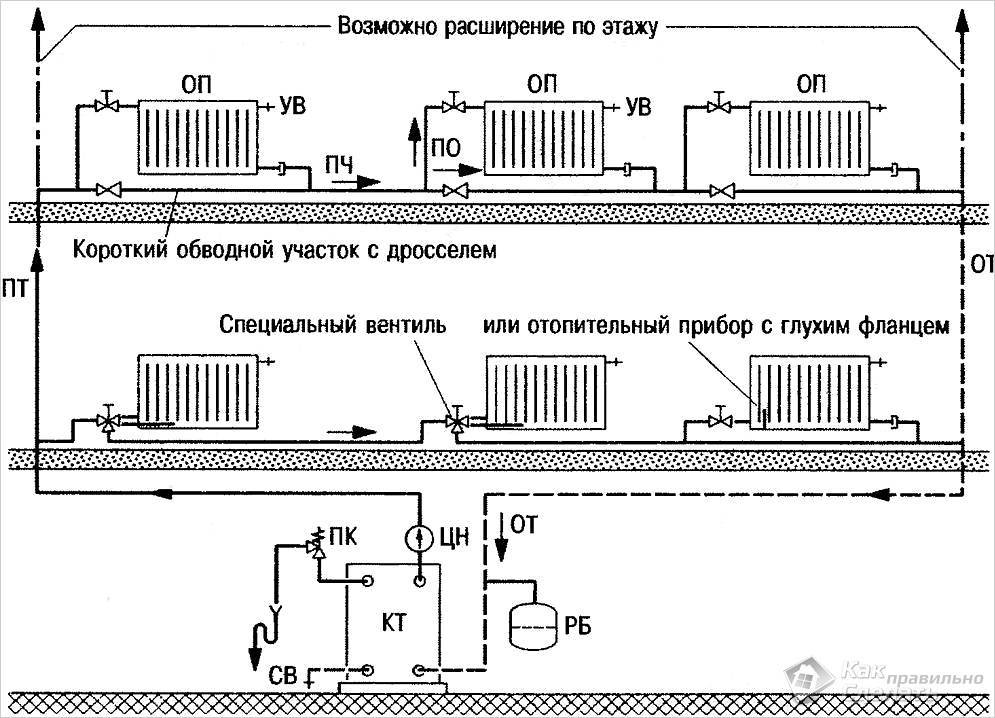
- install closing sections when connecting radiators;
- use the associated movement of the coolant.
Since the distance from the boiler to the radiators is the same during passing traffic, heating of the radiators is carried out more evenly.
The main thing is to choose the right boiler and radiators, correctly carry out the heat engineering and hydraulic calculation of the heating system, and adhere to the rules for plumbing work during the installation of equipment.
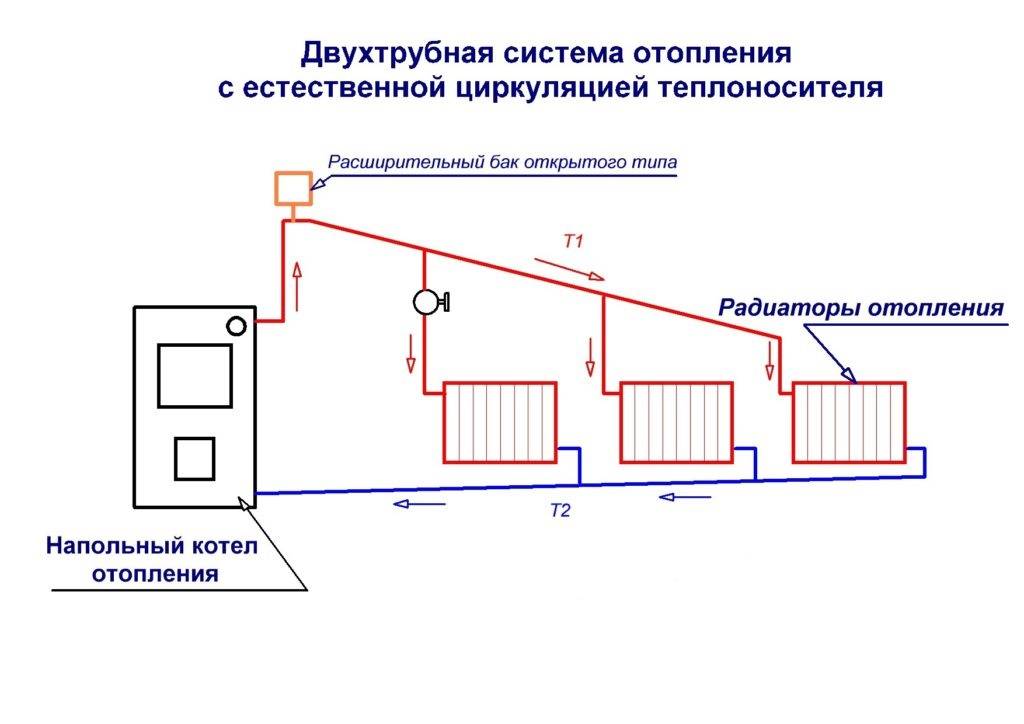
Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
Despite the simple design of a water heating system with self-circulation of the coolant, there are at least four popular installation schemes. The choice of wiring type depends on the characteristics of the building itself and the expected performance.
To determine which scheme will work, in each individual case it is required to perform a hydraulic calculation of the system, take into account the characteristics of the heating unit, calculate the pipe diameter, etc. You may need the help of a professional when doing the calculations.
Closed system with gravity circulation
Otherwise, closed-type systems work like other natural circulation heating schemes. As disadvantages, one can single out the dependence on the volume of the expansion tank. For rooms with a large heated area, you will need to install a capacious container, which is not always advisable.
Open system with gravity circulation
The open type heating system differs from the previous type only in the design of the expansion tank. This scheme was most often used in old buildings. The advantages of an open system is the possibility of self-manufacturing containers from improvised materials. The tank usually has modest dimensions and is installed on the roof or under the ceiling of the living room.
The main disadvantage of open structures is the ingress of air into pipes and heating radiators, which leads to increased corrosion and rapid failure of heating elements. Airing the system is also a frequent "guest" in open circuits. Therefore, radiators are installed at an angle, Mayevsky cranes are required to bleed air.
Single pipe system with self-circulation
The heated coolant enters the upper branch pipe of the battery and is discharged through the lower outlet. After that, the heat enters the next heating unit and so on until the last point. The return line returns from the last battery to the boiler.
This solution has several advantages:
- There is no paired pipeline under the ceiling and above the floor level.
- Save money on system installation.
The disadvantages of such a solution are obvious. The heat output of heating radiators and the intensity of their heating decreases with distance from the boiler. As practice shows, the single-pipe heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation, even if all slopes are observed and the correct pipe diameter is selected, is often redone (through the installation of pumping equipment).
How to choose a heating pump
Best suited for installation are special low-noise centrifugal-type circulation pumps with straight blades. They do not create excessively high pressure, but push the coolant, accelerating its movement (the working pressure of an individual heating system with forced circulation is 1-1.5 atm, the maximum is 2 atm). Some models of pumps have a built-in electric drive. Such devices can be installed directly into the pipe, they are also called "wet", and there are devices of the "dry" type. They differ only in the rules of installation.
When installing any type of circulation pump, an installation with a bypass and two ball valves is desirable, which allows the pump to be removed for repair / replacement without shutting down the system.
It is better to connect the pump with a bypass - so that it can be repaired / replaced without destroying the system
The installation of a circulation pump allows you to adjust the speed of the coolant moving through the pipes.The more actively the coolant moves, the more heat it carries, which means that the room heats up faster. After the set temperature is reached (either the degree of heating of the coolant or the air in the room is monitored, depending on the capabilities of the boiler and / or settings), the task changes - it is required to maintain the set temperature and the flow rate decreases.
For a forced circulation heating system, it is not enough to determine the type of pump
It is important to calculate its performance. To do this, first of all, you need to know the heat loss of the premises / buildings that will be heated
They are determined based on losses in the coldest week. In Russia, they are normalized and installed by public utilities. They recommend using the following values:
- for one- and two-story houses, losses at the lowest seasonal temperature of -25 ° C are 173 W / m 2. at -30 ° C, losses are 177 W / m 2;
- multi-storey buildings lose from 97 W / m 2 to 101 W / m 2.
Based on certain heat losses (denoted by Q), you can find the pump power using the formula:
c is the specific heat capacity of the coolant (1.16 for water or another value from the accompanying documents for antifreeze);
Dt is the temperature difference between supply and return. This parameter depends on the type of system and is: 20 o C for conventional systems, 10 o C for low-temperature systems and 5 o C for underfloor heating systems.
The resulting value must be converted into performance, for which it must be divided by the density of the coolant at operating temperature.
In principle, when choosing the pump power for forced circulation of heating, it is possible to be guided by averaged norms:
- with systems that heat an area up to 250 m 2. use units with a capacity of 3.5 m 3 / h and a head pressure of 0.4 atm;
- for an area from 250m 2 to 350m 2, a power of 4-4.5m 3 / h and a pressure of 0.6 atm are required;
- pumps with a capacity of 11 m 3 / h and a pressure of 0.8 atm are installed in heating systems for an area from 350 m2 to 800 m2.
But you need to take into account that the worse the house is insulated, the greater the power of the equipment (boiler and pump) may be required and vice versa - in a well-insulated house, half of the indicated values \u200b\u200bmay be required. These data are average. The same can be said about the pressure created by the pump: the narrower the pipes and the rougher their inner surface (the higher the hydraulic resistance of the system), the higher the pressure should be. Full calculation is a complex and dreary process, which takes into account many parameters:
The power of the boiler depends on the area of the heated room and heat loss.
- resistance of pipes and fittings (read how to choose the diameter of heating pipes here);
- pipeline length and coolant density;
- number, area and type of windows and doors;
- the material from which the walls are made, their insulation;
- wall thickness and insulation;
- the presence / absence of a basement, basement, attic, as well as the degree of their insulation;
- type of roof, composition of the roofing cake, etc.
In general, heat engineering calculation is one of the most difficult in the region. So if you want to know exactly what power you need a pump in the system, order a calculation from a specialist. If not, choose based on average data, adjusting them in one direction or another, depending on your situation. It is only necessary to take into account that at an insufficiently high speed of movement of the coolant, the system is very noisy.Therefore, in this case, it is better to take a more powerful device - the power consumption is small, and the system will be more efficient.
Advantages and disadvantages of heating with one pipe
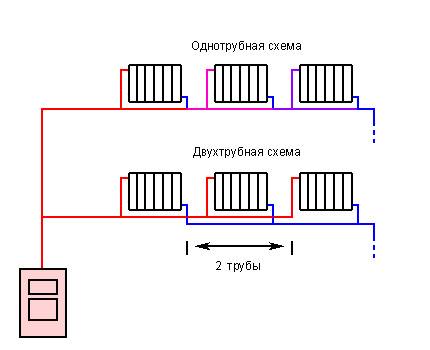
Single-pipe heating (also called "Leningradka") is characterized by the supply of fluid to the radiators and its removal from them in series.
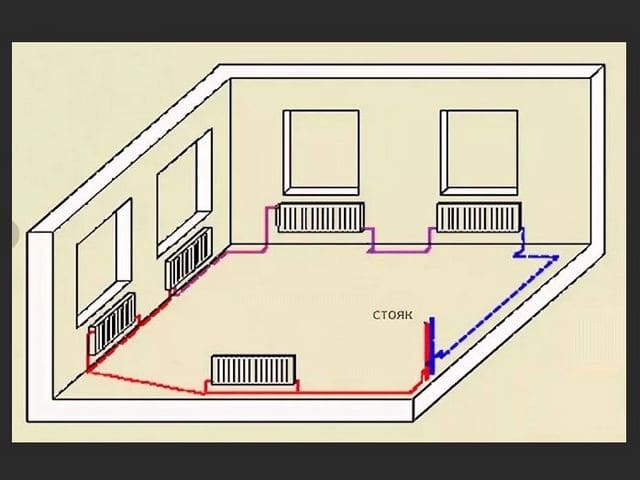
It has such advantages:
- reduction of time and labor intensity of installation;
- the highway can be hidden in the walls, which improves the aesthetic properties of the room;
- it is possible to organize the gravity flow of the coolant in buildings on 2-3 floors;
- comparative cheapness of pipe laying;
- if the system is closed, then its adjustment is carried out automatically, by means of thermostatic radiator valves.
However, Leningradka is characterized by such disadvantages:
- as the liquid moves to the distant batteries, it cools down, so at the end the circuit does not provide the required heating of the room;
- hydraulic instability (when the valve is closed on one radiator, the others will start to overheat, which will create an unpleasant microclimate in the rooms);
- for good movement of water with a closed type of system, the installation of full-bore fittings on the branches is required;
- a single-pipe design with vertical wiring is more expensive than a two-pipe one;
- balancing the system is not easy.
If the design is gravity flow, then it is necessary to ensure a large diameter of the pipes. Moreover, they are laid with a certain slope - up to 5 mm per 1 running meter.
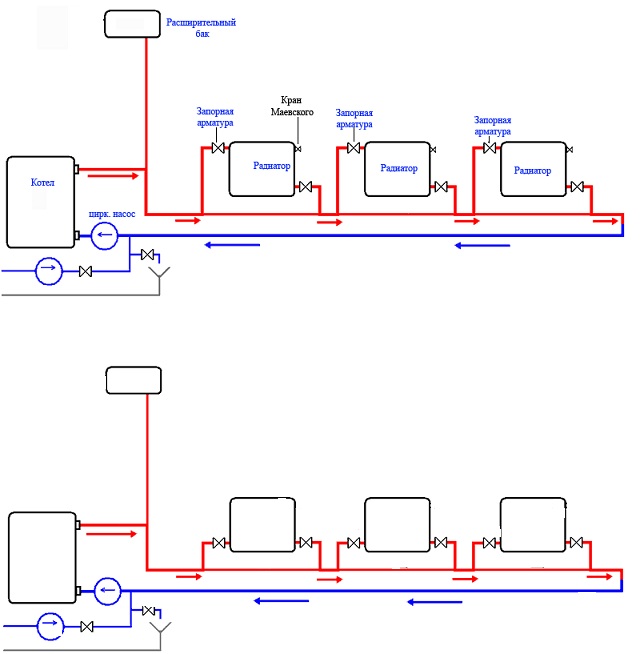
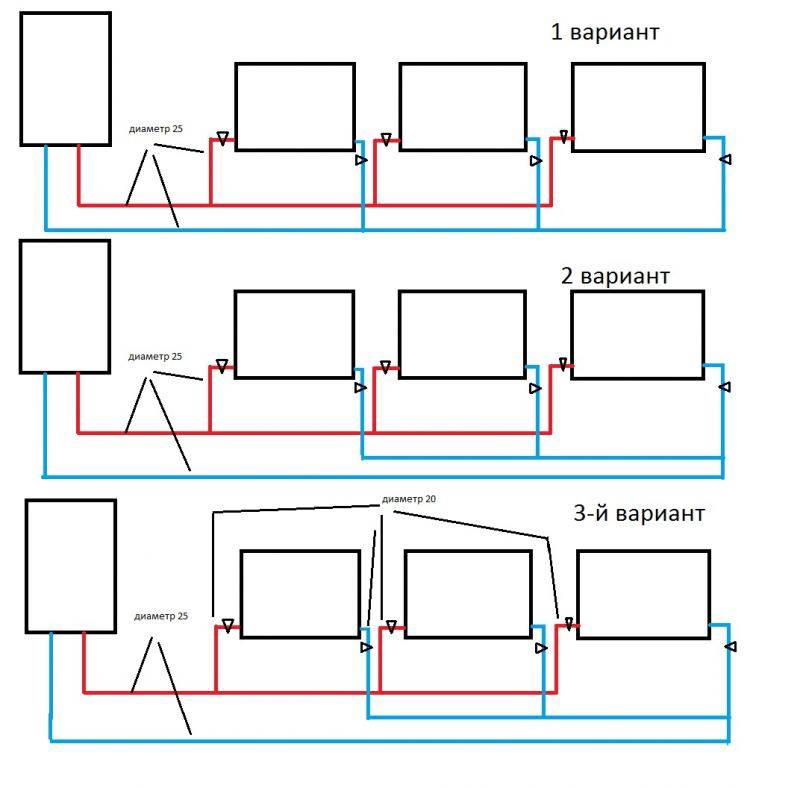
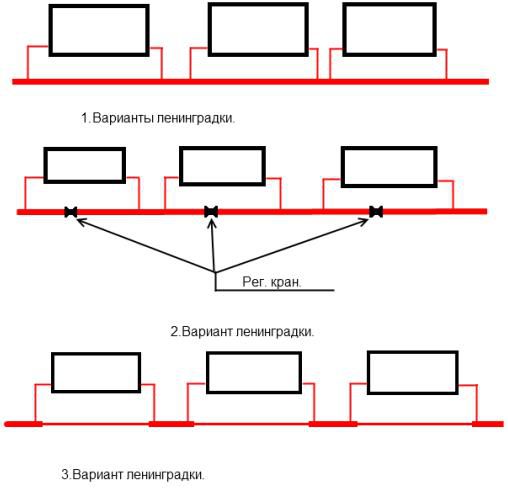
Connecting batteries to a one-pipe system - choose your option
When installing heating with one main, you can connect radiators in two ways: according to the Leningradka scheme or according to an unregulated standard scheme.The second option involves the use of a small amount of materials. You will need to connect the battery to the line in two places - at the outlet and at the entrance. Everything is simple. But remember - the usual scheme will not allow you to regulate the operation of the heating system, as well as turn off individual radiators if necessary.
The Leningradka scheme is more efficient, it provides uniform heating of all heating batteries in the house. Do-it-yourself installation is not much more complicated than connecting radiators using the usual method. You will need to additionally put two faucets at the outlet of the battery and at the entrance to it.
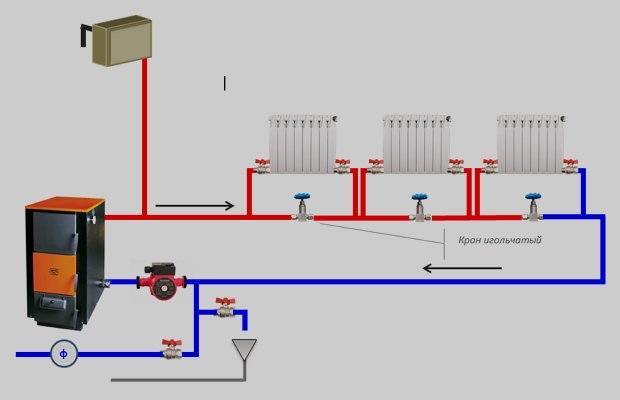
Heating scheme "Leningradka"
With their help, if necessary, you can easily shut off the supply of hot water to a specific battery or adjust the coolant flow to certain parameters. In addition, a special bypass should be installed to bypass the battery. They also put a faucet on it. It allows you to direct all hot water directly through the battery.
Leningradka, thus, simplifies the process of adjusting the heating temperature for each individual room in the home. Therefore, experts advise connecting radiators in this way.
How to choose a heating pump
Best suited for installation are special low-noise centrifugal-type circulation pumps with straight blades. They do not create excessively high pressure, but push the coolant, accelerating its movement (the working pressure of an individual heating system with forced circulation is 1-1.5 atm, the maximum is 2 atm). Some models of pumps have a built-in electric drive. Such devices can be installed directly into the pipe, they are also called "wet", and there are devices of the "dry" type.They differ only in the rules of installation.
When installing any type of circulation pump, an installation with a bypass and two ball valves is desirable, which allows the pump to be removed for repair / replacement without shutting down the system.
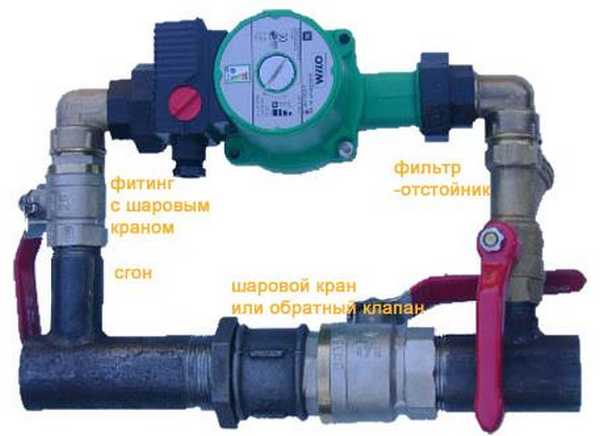

It is better to connect the pump with a bypass - so that it can be repaired / replaced without destroying the system
The installation of a circulation pump allows you to adjust the speed of the coolant moving through the pipes. The more actively the coolant moves, the more heat it carries, which means that the room heats up faster. After the set temperature is reached (either the degree of heating of the coolant or the air in the room is monitored, depending on the capabilities of the boiler and / or settings), the task changes - it is required to maintain the set temperature and the flow rate decreases.
For a forced circulation heating system, it is not enough to determine the type of pump
It is important to calculate its performance. To do this, first of all, you need to know the heat loss of the premises / buildings that will be heated. They are determined based on losses in the coldest week
In Russia, they are normalized and installed by public utilities. They recommend using the following values:
They are determined based on losses in the coldest week. In Russia, they are normalized and installed by public utilities. They recommend using the following values:
- for one- and two-story houses, losses at the lowest seasonal temperature of -25 ° C are 173 W / m 2. at -30 ° C, losses are 177 W / m 2;
- multi-storey buildings lose from 97 W / m 2 to 101 W / m 2.
Based on certain heat losses (denoted by Q), you can find the pump power using the formula:
c is the specific heat capacity of the coolant (1.16 for water or another value from the accompanying documents for antifreeze);
Dt is the temperature difference between supply and return. This parameter depends on the type of system and is: 20 o C for conventional systems, 10 o C for low-temperature systems and 5 o C for underfloor heating systems.
The resulting value must be converted into performance, for which it must be divided by the density of the coolant at operating temperature.
In principle, when choosing the pump power for forced circulation of heating, it is possible to be guided by averaged norms:
- with systems that heat an area up to 250 m 2. use units with a capacity of 3.5 m 3 / h and a head pressure of 0.4 atm;
- for an area from 250m 2 to 350m 2, a power of 4-4.5m 3 / h and a pressure of 0.6 atm are required;
- pumps with a capacity of 11 m 3 / h and a pressure of 0.8 atm are installed in heating systems for an area from 350 m2 to 800 m2.
But you need to take into account that the worse the house is insulated, the greater the power of the equipment (boiler and pump) may be required and vice versa - in a well-insulated house, half of the indicated values \u200b\u200bmay be required. These data are average. The same can be said about the pressure created by the pump: the narrower the pipes and the rougher their inner surface (the higher the hydraulic resistance of the system), the higher the pressure should be. Full calculation is a complex and dreary process, which takes into account many parameters:

The power of the boiler depends on the area of the heated room and heat loss.
- resistance of pipes and fittings (read how to choose the diameter of heating pipes here);
- pipeline length and coolant density;
- number, area and type of windows and doors;
- the material from which the walls are made, their insulation;
- wall thickness and insulation;
- the presence / absence of a basement, basement, attic, as well as the degree of their insulation;
- type of roof, composition of the roofing cake, etc.
In general, heat engineering calculation is one of the most difficult in the region. So if you want to know exactly what power you need a pump in the system, order a calculation from a specialist. If not, choose based on average data, adjusting them in one direction or another, depending on your situation. It is only necessary to take into account that at an insufficiently high speed of movement of the coolant, the system is very noisy. Therefore, in this case, it is better to take a more powerful device - the power consumption is small, and the system will be more efficient.
How to calculate pipe diameter
When arranging dead-end and collector wiring in a country house with an area of up to 200 m², you can do without scrupulous calculations. Take the cross section of highways and piping according to the recommendations:
- to supply the coolant to radiators in a building of 100 square meters or less, a Du15 pipeline (outer dimension 20 mm) is sufficient;
- battery connections are made with a section of Du10 (outer diameter 15-16 mm);
- in a two-story house of 200 squares, the distributing riser is made with a diameter of Du20-25;
- if the number of radiators on the floor exceeds 5, divide the system into several branches extending from the Ø32 mm riser.
Gravity and ring system is developed according to engineering calculations.If you want to determine the cross-section of pipes yourself, first of all, calculate the heating load of each room, taking into account ventilation, then find out the required coolant flow rate using the formula:
- G is the mass flow rate of heated water in the section of the pipe supplying the radiators of a particular room (or group of rooms), kg/h;
- Q is the amount of heat required to heat a given room, W;
- Δt is the calculated temperature difference in the supply and return, take 20 °С.
Example. To warm up the second floor to a temperature of +21 °C, 6000 W of thermal energy is needed. The heating riser passing through the ceiling must bring 0.86 x 6000 / 20 = 258 kg / h of hot water from the boiler room.
Knowing the hourly consumption of the coolant, it is easy to calculate the cross section of the supply pipeline using the formula:
- S is the area of the desired pipe section, m²;
- V - hot water consumption by volume, m³ / h;
- ʋ – coolant flow rate, m/s.
Continuation of the example. The calculated flow rate of 258 kg / h is provided by the pump, we take the water velocity of 0.4 m / s. The cross-sectional area of the supply pipeline is 0.258 / (3600 x 0.4) = 0.00018 m². We recalculate the section into diameter according to the circle area formula, we get 0.02 m - DN20 pipe (outer - Ø25 mm).
Note that we neglected the difference in water densities at different temperatures and substituted the mass flow rate into the formula. The error is small, with a handicraft calculation it is quite acceptable.
Vertical single pipe heating system
A vertical wiring scheme works much more efficiently if a circulation pump is included in it. Forced circulation of the coolant will allow, even with a smaller diameter of the main pipeline, to achieve fairly rapid heating.
When calculating the vertical gravity scheme, it is necessary to provide pipes of a larger diameter in order to ensure sufficient throughput of the entire heating system. In this case, the installation should be carried out at a slight angle so that the circulation of water in the riser is better.
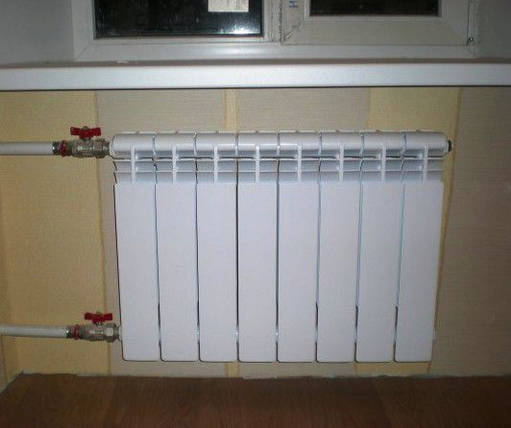

Photo of a radiator connected to a network with vertical wiring
Mounting order
Do-it-yourself Leningradka is installed quite simply, subject to the installation sequence:
- A pipe with a diameter of one and a half to two inches is laid around the perimeter of the room from the boiler;
- Directly at the boiler, a technological insert is made, where a vertical line will then be welded;
- An expansion tank is attached to this segment from the very top;
- After that, batteries and radiators are connected.

Stage of installation inside the floor
A video of the installation of one-pipe heating can be viewed here:
Benefits of Leningradka
- Simplicity and accessibility;
- Price;
- Cheapness and acquisition of individual elements;
- Repairability.
Important! When installing radiators in all rooms, the last heaters in the chain should have a large heat transfer area (batteries should have more sections). This will improve the heating of the room
Disadvantages of "Leningradka"
- For installation on your own, you need a welding machine and the ability to use it (if the main pipeline is made of steel pipes);
- It is necessary to provide for the possibility of increasing the pressure inside the system to improve the circulation of the coolant;
- The impossibility of using heated towel rails and "warm floor" systems in the horizontal one-pipe heating system "Leningradka";
- Some non-aesthetics in the interior of the room (due to large diameter external pipes);

Vertical riser section
- Restrictions on the total length of the chain or riser;
- The need after installation to check the tightness of the joints at the welding site.
- This scheme makes it possible to "upgrade" the system during operation;
- When connecting bypasses - bypass pipes with taps or valves - it becomes possible to replace and repair individual batteries without turning off the heating, right during operation;