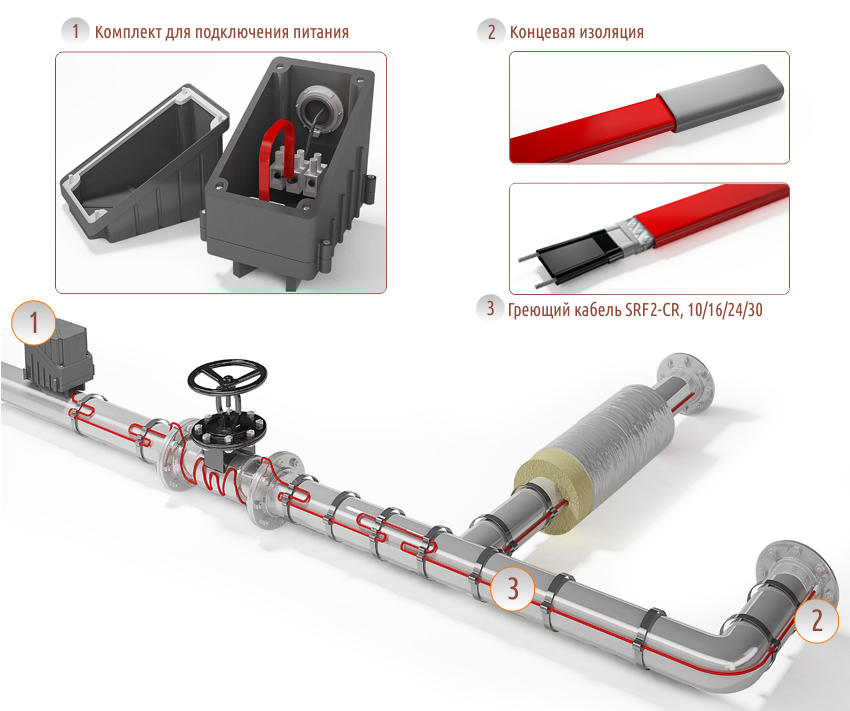
- Cable types
- resistive
- self-regulating
- 1. What is the heating cable for?
- What is it, application
- Types of heating cables for plumbing
- Types of heating cable
- Type #1 - resistive
- Type #2 - self-adjusting
- 7. Is subsequent insulation of the heated pipeline necessary?
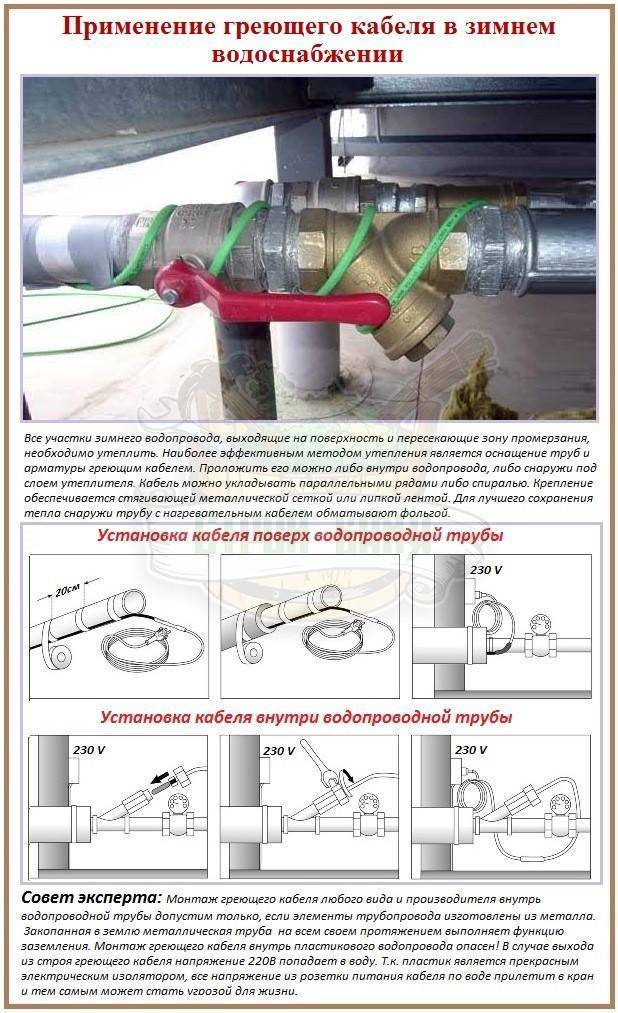
- Connection methods: inside or outside
- inside the pipe
- outdoor installation
- How to choose the right cable?
- 2. What parameters influence the choice?
- In what cases may it be necessary to install a heating cable?
- Heating cable power for water supply
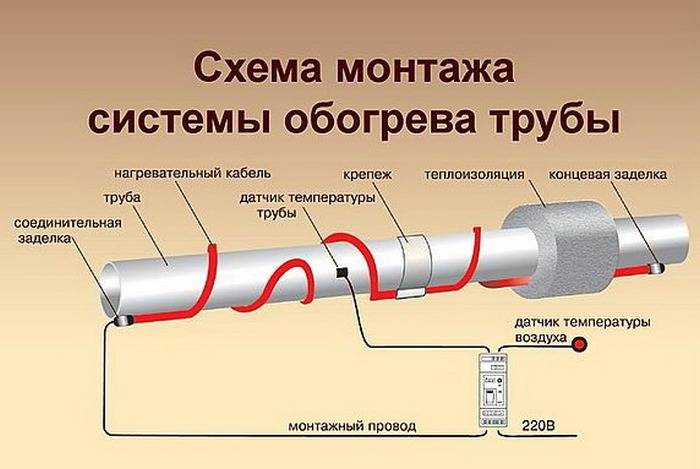
- Installation of a heating product
- Internal installation
- outdoor installation
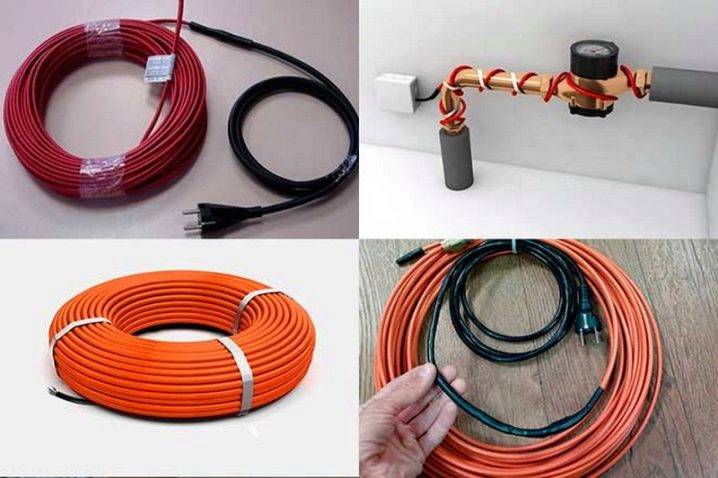
Cable types
Before installation, it is important to study what heating wires are and how to install them. There are two types of cables: resistive and self-regulating
There are two types of cables: resistive and self-regulating.
The difference between them is that when an electric current passes through the cable, the resistive one heats up evenly along the entire length, and the feature of the self-regulating one is the change in electrical resistance depending on temperature. This means that the higher the temperature of the self-regulating cable section, the lower the current strength will be on it. That is, different parts of such a cable can each be heated to the desired temperature.
In addition, many cables are produced immediately with a temperature sensor and auto control, which significantly saves energy during operation.
Self-regulating cable is more difficult to manufacture and more expensive. Therefore, if there are no special operating conditions, then more often they purchase a resistive heating cable.
resistive
A resistive-type heating cable for a water supply system has a budget cost.

Cable differences
It is divided into several varieties, depending on the design features. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages:
| cable type | pros | Minuses |
| single core | The design is simple. It has a heating metal core, a copper shielding braid and internal insulation. From the outside there is protection in the form of an insulator. Maximum heat up to +65°С. | It is inconvenient for heating pipelines: both opposite ends, which are far from each other, must be connected to the current source. |
| Two-core | It has two cores, each of which is isolated separately. An additional third core is bare, but all three are covered by a foil shield. External insulation has a heat-resistant effect. Maximum heat up to +65°C. | Despite the more modern design, it is not much different from a single-core element. The operating and heating characteristics are identical. |
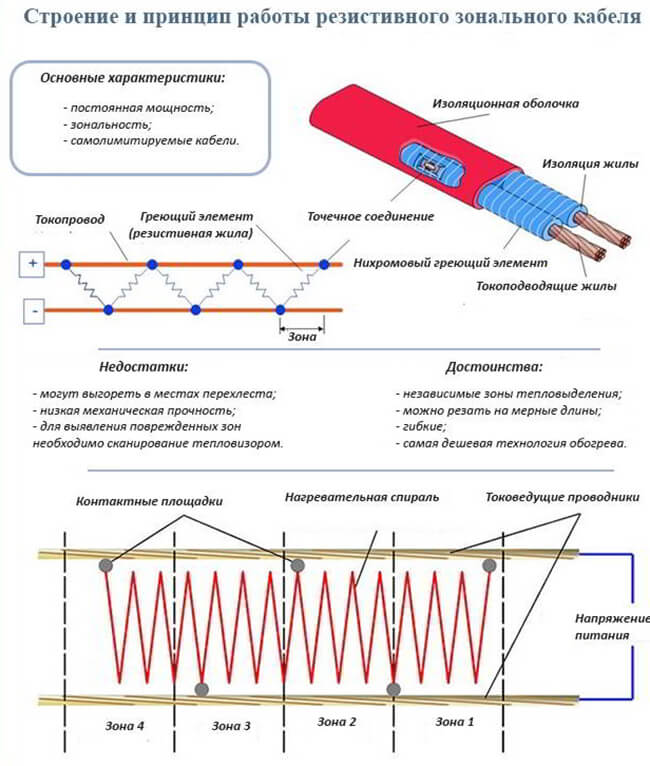
| Zonal | There are independent heating sections. Two cores are isolated separately, and a heating coil is located on top. The connection is made by means of contact windows with current-carrying conductors. This allows you to create heat in parallel. | No cons were found, if you do not take into account the price tag of the product. |
Resistive wires of various types
Most buyers prefer to lay the wire "the old fashioned way" and purchase a wire with one or two cores.
Due to the fact that a cable with only two cores can be used for heating pipes, a single-core version of the resistive wire is not used. If the owner of the house unknowingly installed it, this threatens to close the contacts. The fact is that one core must be looped, which is problematic when working with a heating cable.
If you install the heating cable on the pipe yourself, then experts advise choosing a zonal option for outdoor installation. Despite the peculiarity of the design, its installation will not cause serious difficulties.

Wire design
Another important nuance in single-core and twin-core structures: already cut and insulated products can be found on sale, which eliminates the possibility of adjusting the cable to the optimal length. If the insulation layer is broken, then the wire will be useless, and if damage occurs after installation, it will be necessary to replace the system throughout the area. This disadvantage applies to all types of resistive products. Installation work of such wires is not convenient. It is also not possible to use them for laying inside the pipeline - the tip of the temperature sensor interferes.
self-regulating
Self-regulating heating cable for water supply with self-adjustment has a more modern design, which affects the duration of operation and ease of installation.
The design provides:
- 2 copper conductors in a thermoplastic matrix;
- 2 layers of internal insulating material;
- copper braid;
- external insulating element.
It is important that this wire works fine without a thermostat.Self-regulating cables have a polymer matrix
When turned on, carbon is activated, and during an increase in temperature, the distance between its graphite components increases.

Self-regulating cable
1. What is the heating cable for?
Someone will say that using a heating cable to prevent freezing of pipes is expensive and irrational. And it is much more logical to find out how deep the soil freezes at the lowest temperatures in your area, and simply deepen the trench to the desired amount. So it is, but it is not always possible to go deeper by 1.5-1.7 meters. For example:
- If you are digging trenches for pipe laying yourself to save money, or you just like to personally control everything, then a lot of physical effort will be required. After all, there is a difference - to go deeper by 0.5 meters or by 1.5?
- It is far from always that the soil on the ground is strong and homogeneous in its composition. You can stumble upon hard rocks in the process of work;
- If the area is swampy, then during the rainy season or snowmelt, the groundwater level can rise greatly, which will lead to flooding of communications. Moreover, this process will be regular, will adversely affect the condition of the water supply system and will certainly lead to its destruction;
- In regions where the temperature drops sharply in winter, even a significant deepening of the trench can not always prevent local freezing;
- The place where pipes enter the house will still remain unprotected;
- And, in the end, what if the water supply has already been finally installed and buried, and the problem has been discovered recently? It is much easier, and in this case cheaper, to install the heating cable inside the pipes than to dig everything out, dismantle, deepen and reassemble.
It follows that sometimes the use of a heating cable is an unavoidable necessity.
In general, the scope includes several main areas:
- For private needs - heating water pipes and sewers, preventing freezing of the roof. In the latter case, the cable is laid in places where icicles and ice cover form. Thanks to this, there is no need to regularly clean the roof. The main element of the "warm floor" system is also a heating cable;
- For commercial - heating pipes or fire extinguishing systems;
- For industrial - when high-risk work is carried out, or there is a need to heat various liquids in large tanks. For example, petroleum products or other chemical compounds.
What is it, application
The heating cable is a flexible conductor, which is a single-core, two-core or three-core wire. The main function of this type of cable products is to convert electrical energy into heat, which is made possible due to the resistivity of the metal.
The heating cable is designed for heating engineering systems
Cable heating is used not only to ensure the smooth functioning of pipelines. It can also be used to solve other problems.
- Install underfloor heating system.
- Lay along the perimeter of the roof, thereby preventing the formation of icicles.
- To heat the soil in country greenhouses and hotbeds.
- To carry out heating of stairs, ramps, outdoor areas and paths.
- Design anti-icing systems for ships, aviation and railway transport.
The main advantage of the heating wire is its flexibility. The wire can be laid on any curved surfaces. Attracts in this heating system and ease of installation. The cable intended for heating consists of several elements:
- central metal wire;
- polymer shell, which can be protected by a foil or copper braid screen (necessary to prevent short circuits and neutralize the effects of an electromagnetic field);
- hard outer shell made of PVC or stainless steel.
Types of heating cables for plumbing
There are two types of heating cables - resistive and self-regulating. In resistive, the property of metals is used to heat up when an electric current passes. In heating cables of this type, the metal conductor is heated. Their characteristic feature is that they always emit the same amount of heat.
It doesn’t matter if it’s +3°C or -20°C outside, they will heat up in the same way - at full capacity, therefore, they will consume the same amount of electricity. To reduce costs in a relatively warm time, temperature sensors and a thermostat are installed in the system (the same as used for electric underfloor heating)
The structure of the resistive cable
When laying resistive heating wires, they should not intersect or be located one next to the other (close to each other). In this case, they overheat and quickly fail.Pay close attention to this point during the installation process.
It should also be said that a resistive heating cable for water supply (and not only) can be single-core and two-core. Two-core ones are more commonly used, although they are more expensive. The difference in connection: for single-core, both ends must be connected to the mains, which is not always convenient. Two-core ones have a plug at one end, and a fixed ordinary electric cord with a plug on the second, which is connected to a 220 V network. What else do you need to know? Resistive conductors cannot be cut - they will not work. If you bought a bay with a length longer than necessary, lay it entirely.
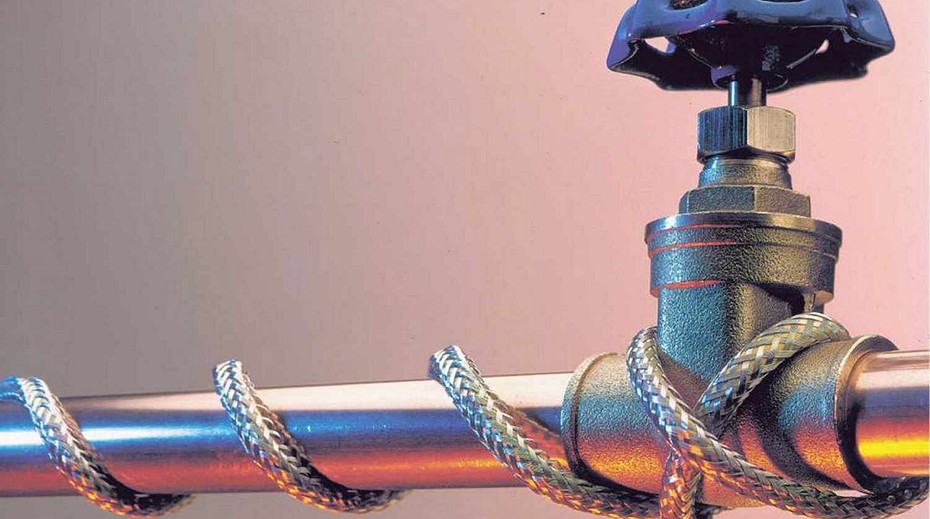
Approximately in this form they sell heating cables for plumbing
Self-regulating cables are a metal-polymer matrix. In this system, the wires only conduct current, and the polymer is heated, which is located between the two conductors. This polymer has an interesting property - the higher its temperature, the less heat it releases, and vice versa, when it cools down, it begins to release more heat. These changes occur regardless of the state of adjacent sections of the cable. So it turns out that he himself regulates his temperature, that's why he was called that - self-regulating.
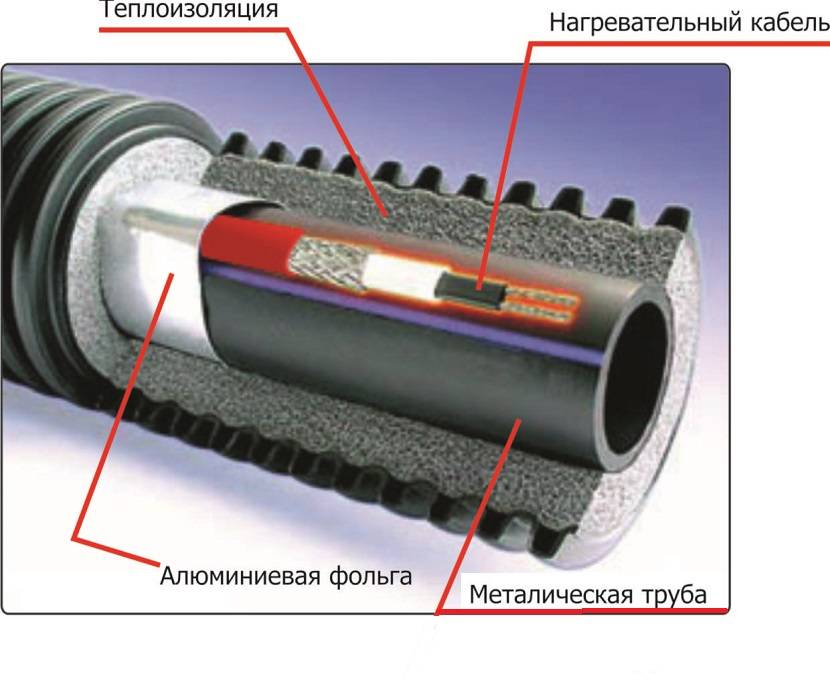
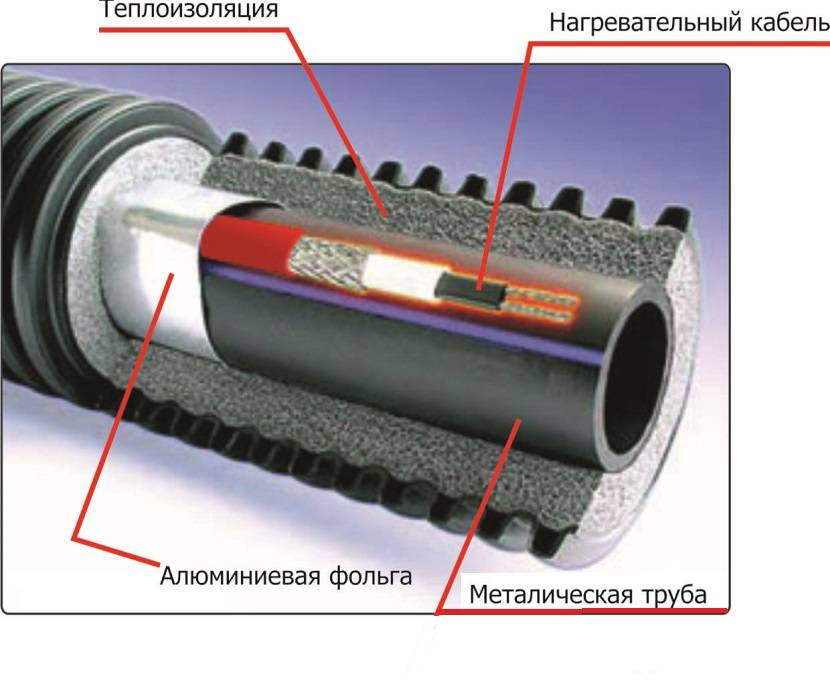
The structure of the self-regulating cable
Self-regulating (self-heating) cables have solid advantages:
- they can intersect and will not burn out;
- they can be cut (there is a marking with cut lines), but then you need to make an end sleeve.
They have one minus - a high price, but the service life (subject to the operating rules) is about 10 years. So these expenses are reasonable.
Using a heating cable for any type of water supply, it is desirable to insulate the pipeline.Otherwise, too much power will be required for heating, which means high costs, and it’s not a fact that the heating will cope with especially severe frosts.
Types of heating cable
All heating systems are divided into 2 large categories: resistive and self-regulating. Each type has its own area of application.
Suppose resistive ones are good for heating short sections of pipes of small cross section - up to 40 mm, and for extended sections of the water supply system it is better to use a self-regulating cable (in other words - self-regulating, "samreg").
Type #1 - resistive
The principle of operation of the cable is simple: a current passes through one or two cores located in an insulating winding, heating it. Maximum current and high resistance add up to a high heat dissipation coefficient.
On sale there are pieces of resistive cable of a certain length, having a constant resistance. In the process of functioning, they give off the same amount of heat along the entire length.
Single-core cable, as the name suggests, has one core, double insulation and external protection. The only core acts as a heating element
When installing the system, it must be remembered that a single-core cable is connected at both ends, as in the following diagram:
Schematically, the connection of a single-core type resembles a loop: first it is connected to an energy source, then it is pulled (wound) along the entire length of the pipe and comes back
Closed heating circuits are more often used to heat a roof drainage system or for a “warm floor” device, but an option applicable to plumbing also exists.
A feature of the installation of a single-core cable on a water pipe is its laying on both sides. In this case, only the external connection type is used.
For internal installation, one core is not suitable, since laying the “loop” will take up a lot of internal space, moreover, accidental crossing of wires is fraught with overheating.
A two-core cable is distinguished by the separation of the functions of the cores: one is responsible for heating, the second for supplying energy.
The connection scheme is also different. There is no need for a “loop-like” installation: as a result, the cable is connected at one end to the power source, the other is pulled along the pipe
Two-core resistive cables are used for plumbing systems as actively as samregs. They can be mounted inside pipes using tees and seals.
The main advantage of a resistive cable is its low cost. Many note reliability, long service life (up to 10-15 years), ease of installation.
But there are also disadvantages:
- high probability of overheating at the intersection or proximity of two cables;
- fixed length - can neither be increased nor shortened;
- the impossibility of replacing the burned-out area - you will have to change it completely;
- no power adjustment - it is always the same along the entire length.
In order not to spend money on a permanent cable connection (which is impractical), a thermostat with sensors is installed. As soon as the temperature drops to + 2-3°C, it automatically starts heating, when the temperature rises to + 6-7°C, the energy is turned off.
Type #2 - self-adjusting
This type of cable is versatile and can be used for various applications: heating of roofing elements and water supply systems, sewer lines and liquid containers.
Its feature is independent adjustment of power and intensity of heat supply. As soon as the temperature drops below the set point (assume +3°C), the cable starts to heat up without outside participation.
Scheme of a self-regulating cable. The main difference from the resistive counterpart is the conductive heating matrix, which is responsible for adjusting the heating temperature. Insulating layers do not differ
The principle of operation of the samreg is based on the property of the conductor to reduce / increase the current strength depending on the resistance. As the resistance increases, the current decreases, which leads to a decrease in power.
What happens to the cable when it cools down? The resistance drops - the current strength increases - the heating process begins.
The advantage of self-regulating models is the "zoning" of work. The cable itself distributes its “labor force”: it carefully warms up the cooling sections and maintains the optimum temperature where strong heating is not needed.
The self-regulating cable works all the time, and this is welcome in the cold season. However, during a thaw or in the spring, when frosts stop, it is irrational to keep it on (+)
To fully automate the process of turning on / off the cable, you can equip the system with a thermostat that is “tied” to the outside temperature.
7. Is subsequent insulation of the heated pipeline necessary?
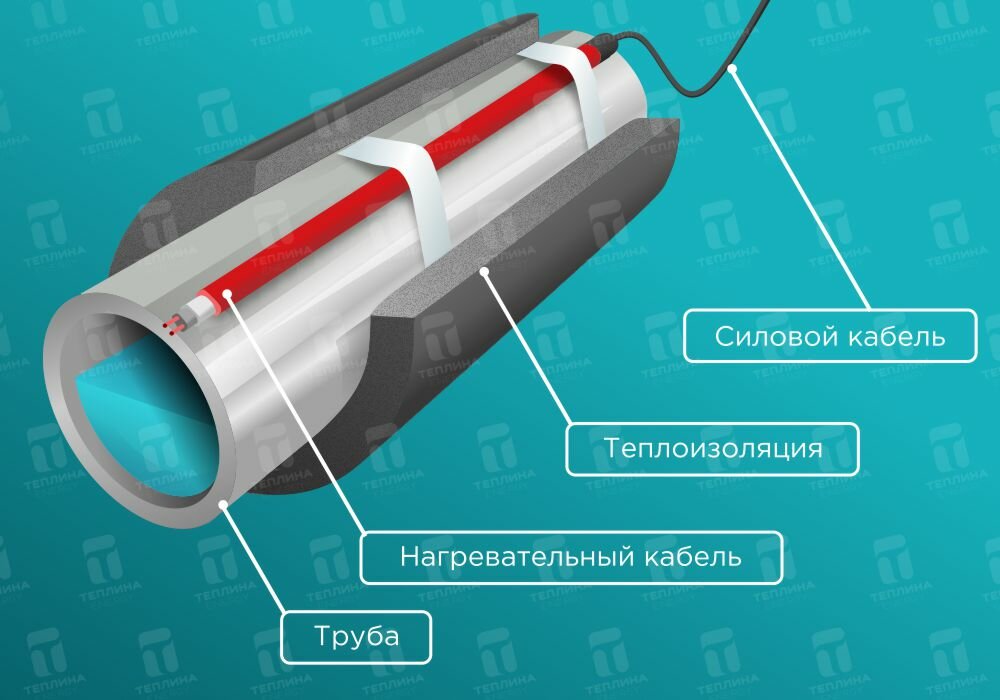
Another topical issue when organizing a pipe heating system is whether subsequent thermal insulation of the heated pipeline is needed? If you do not want to heat the air and operate the cable at maximum power, then insulation is definitely necessary. The thickness of the insulation layer is selected depending on where the pipes are located and what are the minimum temperatures typical for your region. On average, for the insulation of pipes that are located in the ground, a heater with a thickness of 20-30 mm is used. If the pipeline is above ground - at least 50 mm
It is very important to choose the “right” insulation that will not lose its properties even after several years.
- It is not recommended to use mineral wool as an insulating material. They are not intended for use in conditions of high humidity, and when wet, they instantly lose their properties. In addition, if wet cotton wool freezes, then when the temperature rises, it crumbles and turns into dust;
- Also, materials that can compress under the influence of gravity are not always suitable. This applies to foam rubber or foamed polyethylene, which lose their properties when compressed. It is permissible to use such materials if the pipeline passes in a specially equipped sewer, where nothing simply can put pressure on it;
- If pipes are laid in the ground, rigid pipe-in-pipe insulation must be used. When another rigid pipe of a larger diameter is put on top of the heated pipes and the heating cable. For additional effect or in case of operation in harsh conditions, you can wrap the pipes with the same polyethylene foam, and then put on the outer pipe;
- It is permissible to use expanded polystyrene, which is fragments of pipes of different lengths and diameters. It has high thermal insulation properties, is not afraid of moisture and is able to withstand some loads, depending on the density. Such a heater is often called a "shell".
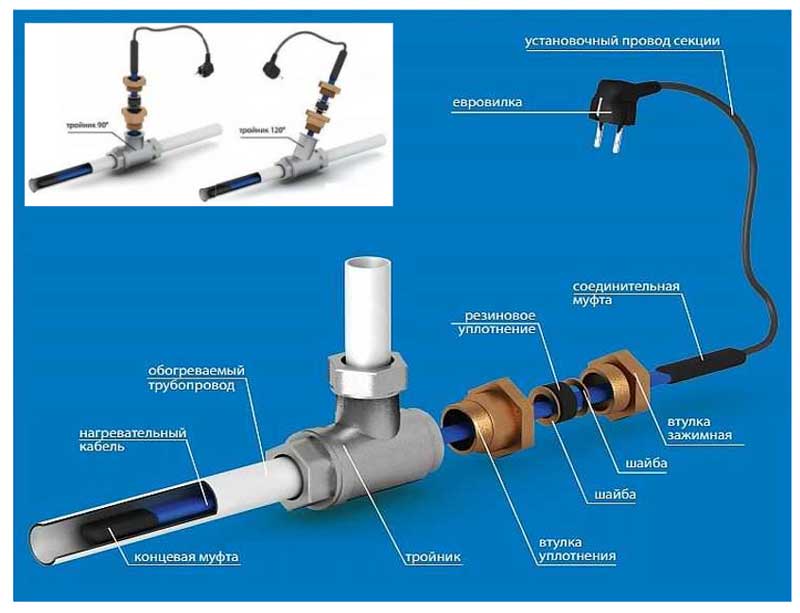
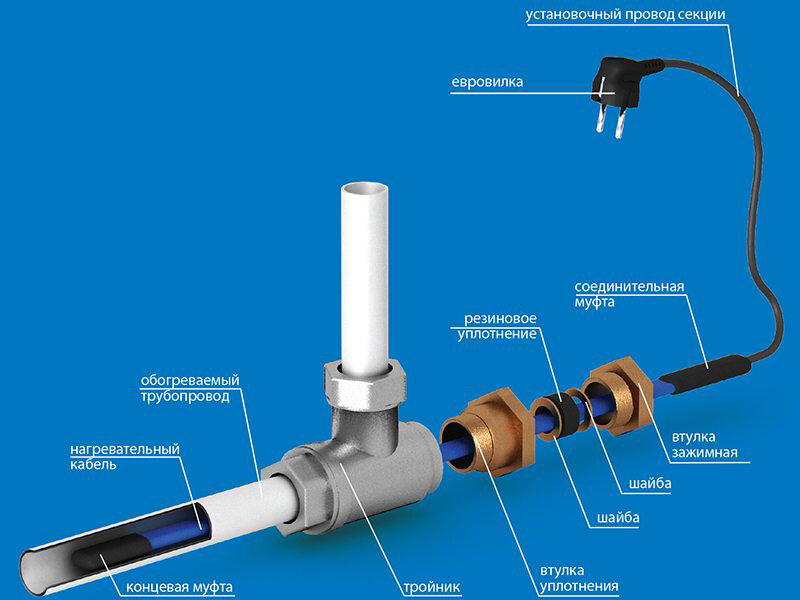
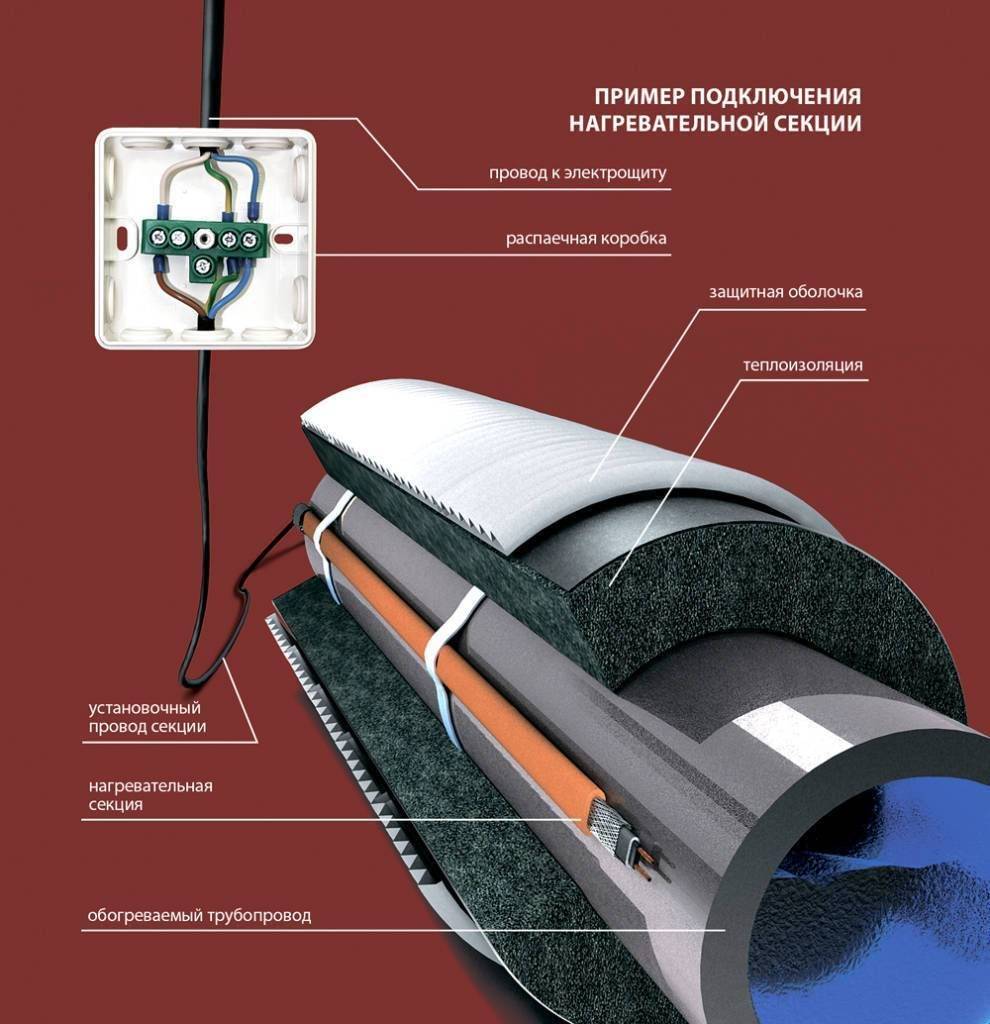
Connection methods: inside or outside
There are two ways to connect the heating cable: outside or inside the pipe. Each option has special types of wires - for outdoor use and for indoor installation, respectively. The recommended connection method is necessarily indicated in the technical specifications for the conductor.
inside the pipe
To install a heating element inside a water pipe, it must meet several requirements:
- the shell should not emit harmful substances;
- the degree of electrical protection must be at least IP68;
- sealed end sleeve.
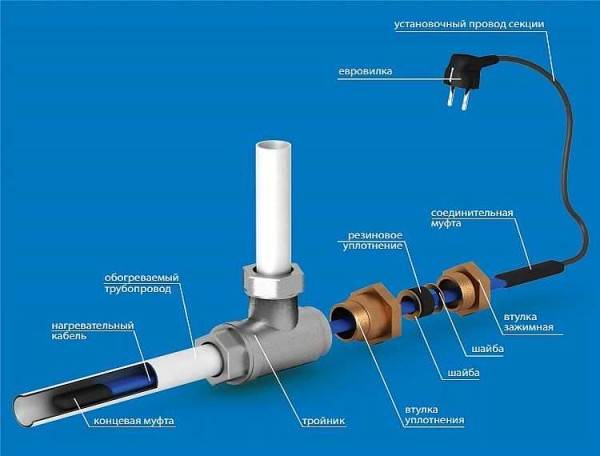
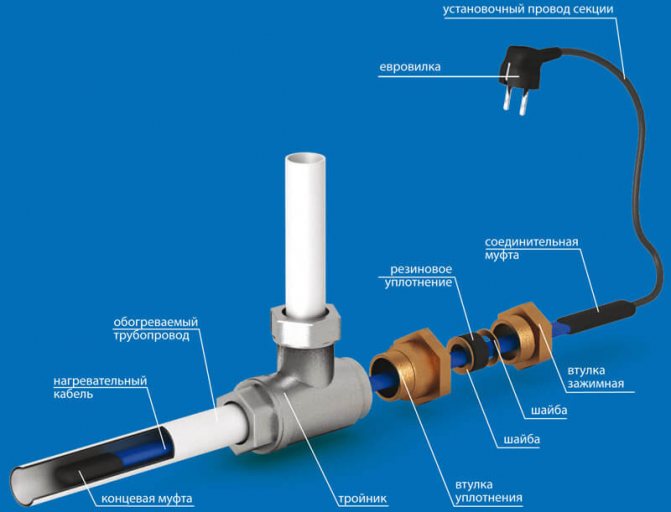
An example of installing a heating cable inside a pipe through a gland
A tee for mounting a heating cable inside a pipe can have different bend angles - 180°, 90°, 120°. With this method of installation, the wire is not fixed in any way. It's just put inside.

Types of tees for mounting a heating cable inside a water supply system
outdoor installation
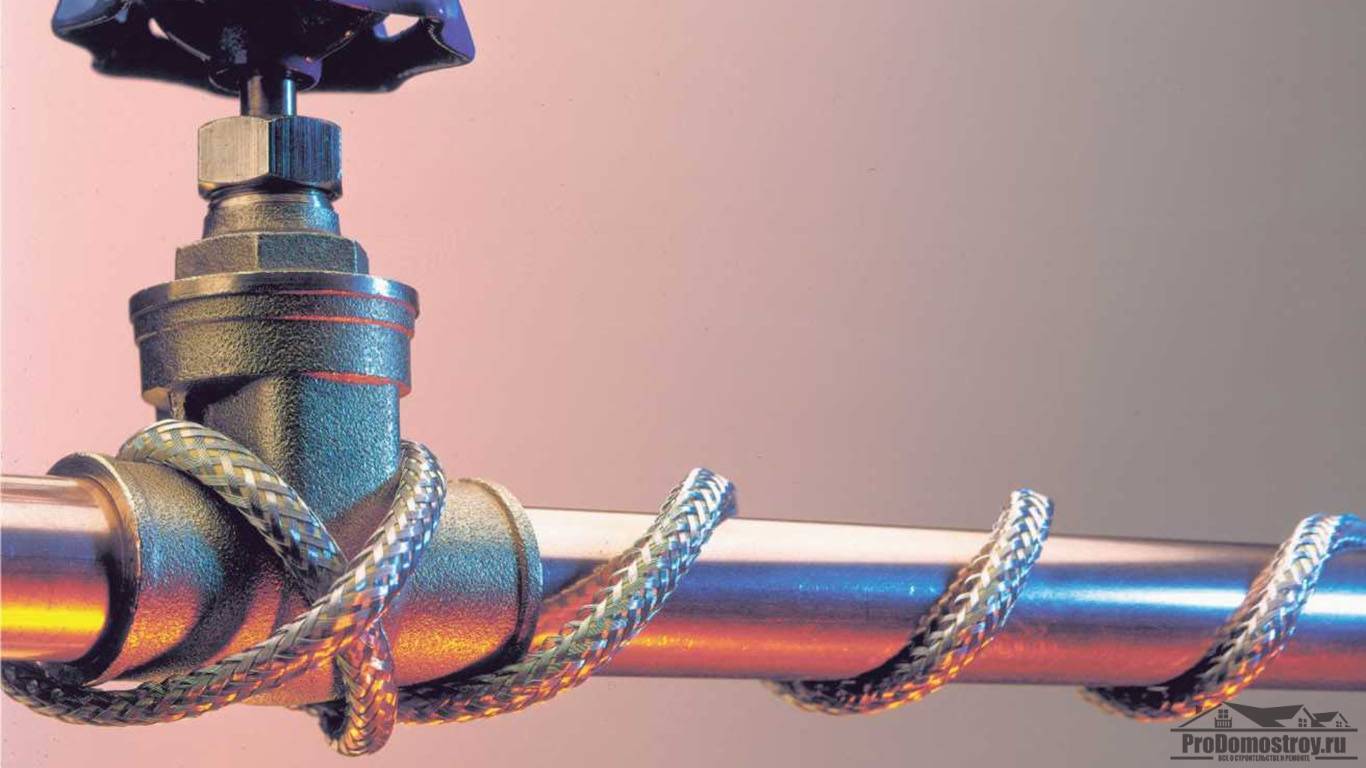
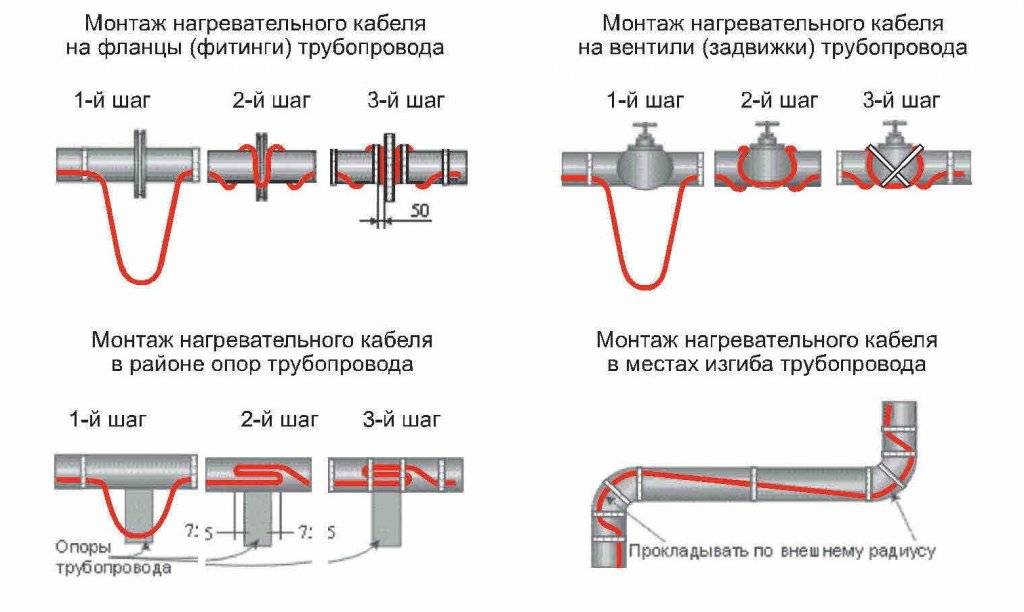
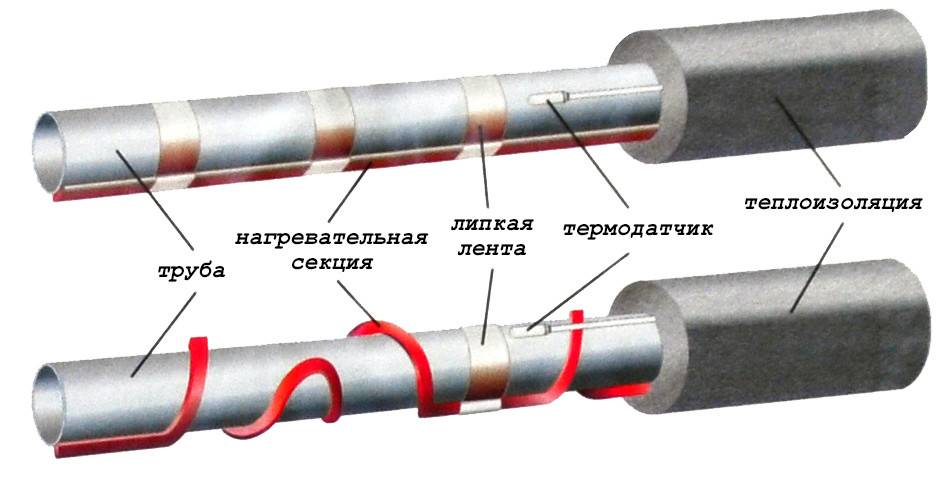
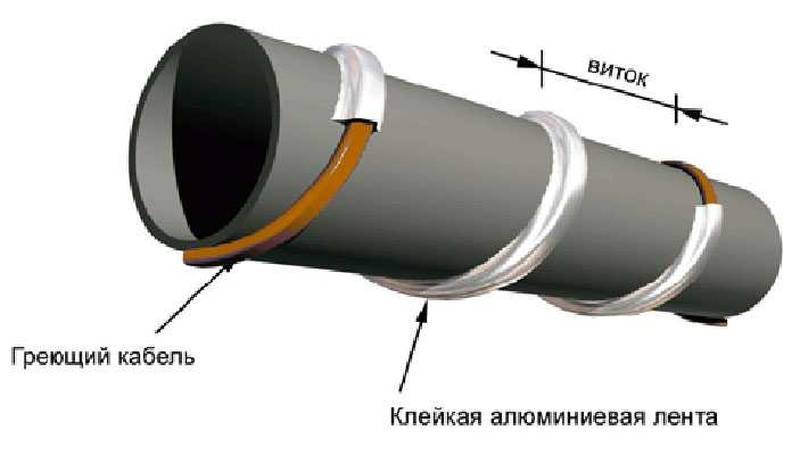
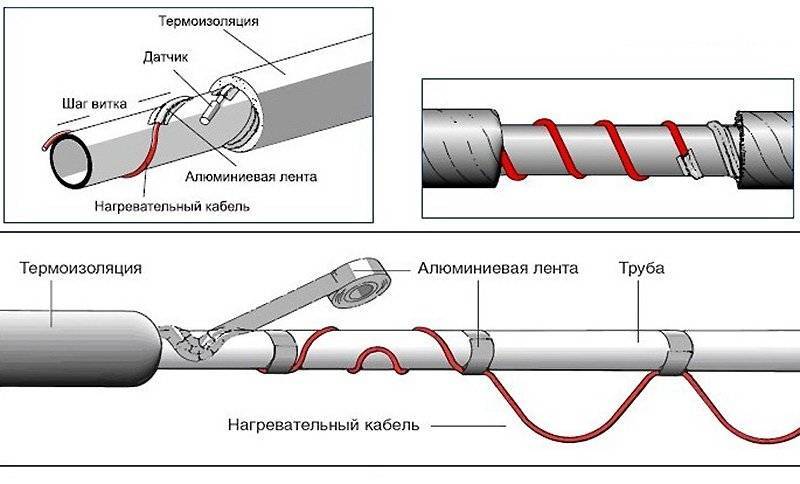
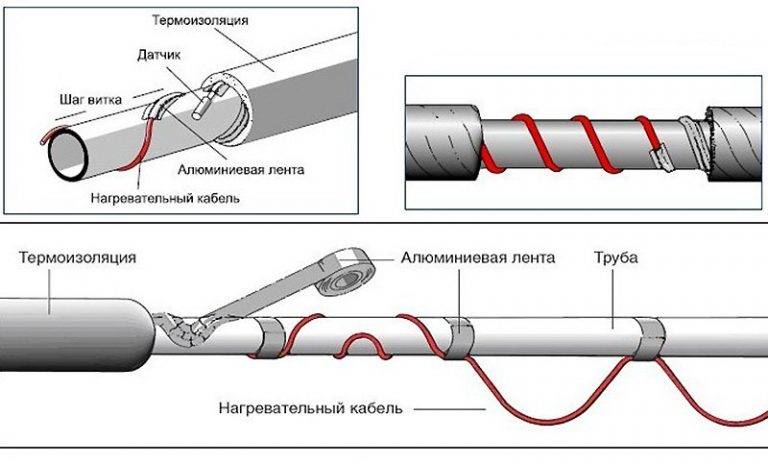
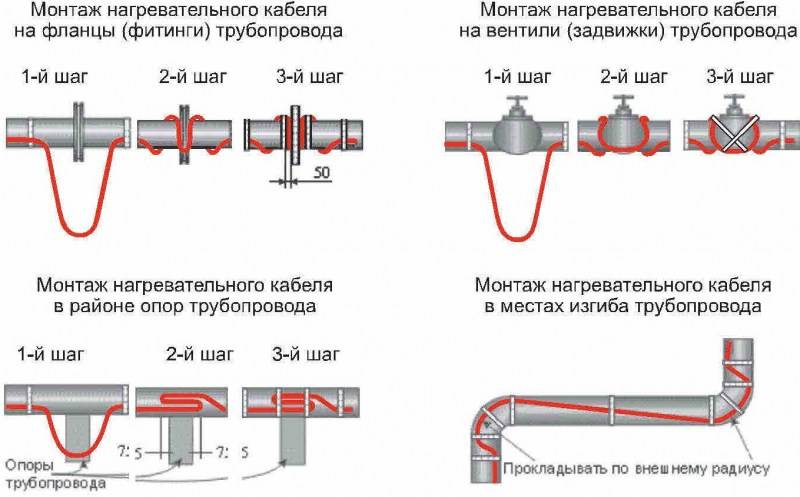
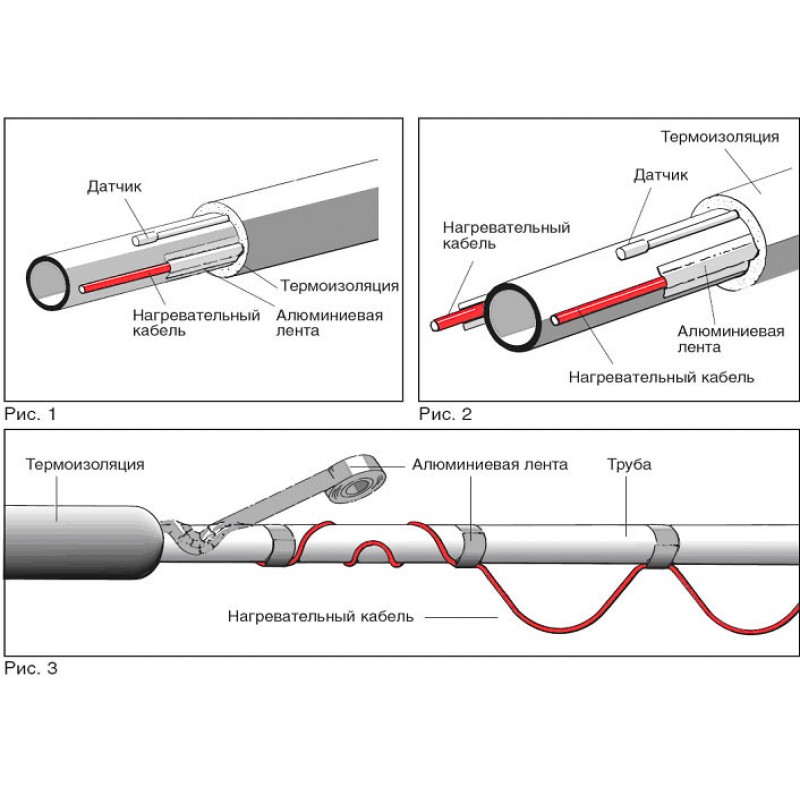
It is necessary to fix the heating cable for the water supply on the outer surface of the pipe so that it fits snugly over the entire area. Before installation on metal pipes, they are cleaned of dust, dirt, rust, welding marks, etc. There must not be any elements left on the surface that could damage the conductor.A rein is laid on clean metal, fixed every 30 cm (more often, less often not) using metallized adhesive tape or plastic clamps.
If one or two threads stretch along, then they are mounted from below - in the coldest zone, stacked parallel, at some distance from each other
When laying three or more wires, they are arranged so that most of them are at the bottom, but the distance between the heating cables is maintained (this is especially important for resistive modifications)
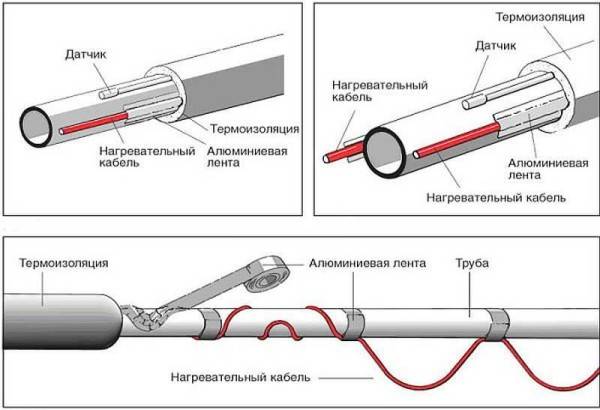
Ways to fix the heating cable on the pipe
There is a second mounting method - a spiral. It is necessary to lay the wire carefully - they do not like sharp or repeated bends. There are two ways. The first is to unwind the coupling gradually winding the released cable onto the pipe. The second is to fix it with sagging (lower picture in the photo), which are then wound and secured with metallized adhesive tape.
If a plastic water pipe is heated, then metallized adhesive tape is first glued under the wire. It improves thermal conductivity, increasing heating efficiency. Another nuance of installing a heating cable on a water supply system: tees, valves and other similar devices require more heat. When laying, make several loops on each fitting. Just keep an eye on the minimum bend radius.
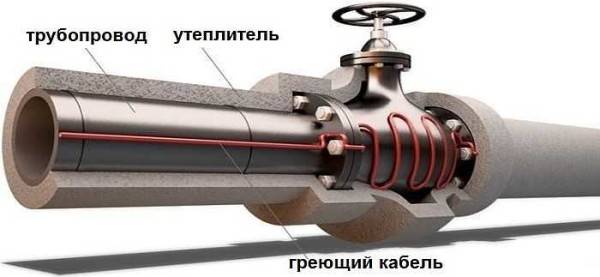
Fittings, taps need to be warmed up better
How to choose the right cable?
When choosing a suitable hot cable, it is necessary to determine not only its type, but also the right power.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account such parameters as:
- the purpose of the structure (for sewerage and water supply, calculations are performed differently);
- the material from which the sewerage is made;
- pipeline diameter;
- features of the area to be heated;
- characteristics of the heat-insulating material used.
Based on this information, heat losses are calculated for each meter of the structure, the type of cable, its power are selected, and then the appropriate length of the kit is determined. Calculations can be performed using a special formula, according to calculation tables or using an online calculator.
The calculation formula looks like this:
Qtr - heat loss of the pipe (W); - coefficient of thermal conductivity of the heater; Ltr is the length of the heated pipe (m); tin is the temperature of the contents of the pipe (C), tout is the minimum ambient temperature (C); D is the outer diameter of communications, taking into account the insulation (m); d - outer diameter of communications (m); 1.3 - safety factor
When heat losses are calculated, the length of the system should be calculated. To do this, the resulting value must be divided by the specific power of the cable of the heating device. The result should be increased, taking into account the heating of additional elements. The power of the cable for sewerage starts from 17 W / m and can exceed 30 W / m.
If we are talking about sewer pipelines made of polyethylene and PVC, then 17 W / m is the maximum power. If you use a more productive cable, then there is a high probability of overheating and damage to the pipe. Information about the characteristics of the product can be found in its technical data sheet.
Using the table, choosing the right option is a little easier. To do this, you first need to find out the diameter of the pipe and the thickness of the thermal insulation, as well as the expected difference between the temperature of the air and the contents of the pipeline. The latter indicator can be found using reference data depending on the region.
At the intersection of the corresponding row and column, you can find the value of heat loss per meter of pipe. Then the total length of the cable should be calculated. To do this, the size of the specific heat loss obtained from the table must be multiplied by the length of the pipeline and by a factor of 1.3.
The table allows you to find the size of the specific heat loss of a pipe of a specific diameter, taking into account the thickness of the heat-insulating material and the operating conditions of the pipeline (+)
The result obtained should be divided by the specific power of the cable. Then you need to take into account the influence of additional elements, if any. On specialized sites you can find convenient online calculators. In the appropriate fields, you need to enter the necessary data, for example, pipe diameter, insulation thickness, ambient and working fluid temperature, region, etc.
Such programs usually offer the user additional options, for example, they help to calculate the required diameter of the sewer, the dimensions of the thermal insulation layer, the type of insulation, etc.
Optionally, you can choose the type of laying, find out the appropriate step when installing the heating cable in a spiral, get a list and the number of components that will be needed for laying the system.
When choosing a self-regulating cable, it is important to correctly consider the diameter of the structure on which it will be installed. For example, for pipes with a diameter of 110 mm, it is recommended to take the Lavita GWS30-2 brand or a similar version from another manufacturer
For a 50 mm pipe, the Lavita GWS24-2 cable is suitable, for structures with a diameter of 32 mm - Lavita GWS16-2, etc.
Complex calculations will not be needed for sewers that are not used often, for example, in a summer cottage or in a house that is used only occasionally.In such a situation, they simply take a cable with a power of 17 W / m with a length corresponding to the dimensions of the pipe. A cable of this power can be used both outside and inside the pipe, while installing a gland is not necessary.
When choosing a suitable option for a heating cable, its performance should be correlated with the calculated data on the likely heat loss of the sewer pipe
For laying a heating cable inside a pipe, a cable with special protection against aggressive effects, for example, DVU-13, is selected. In some cases, for installation inside, the brand Lavita RGS 30-2CR is used. This is not entirely correct, but a valid solution.
This cable is designed for heating roofs or storm drains, so it is not protected against corrosive substances. It can only be considered as a temporary option, since with prolonged use in inappropriate conditions, the Lavita RGS 30-2CR cable will inevitably break.
2. What parameters influence the choice?
Before you purchase the right amount of cable, you need to clearly determine which type is right for your needs. The whole variety of this product differs in five main features:
- By type - the cable can be self-regulating or resistive. At the same time, the principle of operation for both heaters is the same. Heating occurs due to the current that flows through the internal veins;
- According to the material of the outer insulation. The possibility of application under certain conditions depends on this criterion. For example, to organize a heating system for sewers or drains, it is necessary to choose cables with a polyolefin coating.Fluoropolymer insulation is available for cable that will be installed on the roof or used in industrial applications where additional UV protection is needed. If the cable is laid in the inner cavity of the water pipes, then it is better to choose a food-grade coating, that is, fluoroplast insulation. This will prevent the change in taste of the water, which is sometimes the case;
- Absence or presence of a screen (braid). The braid makes the product stronger, more resistant to various mechanical influences, in addition, the screen performs the function of grounding. The absence of this element indicates that you have a product that belongs to the budget category;
- According to the temperature class - there are low-, medium- and high-temperature heaters. This indicator is very important in the arrangement of the heating system for water supply and drainage. Low-temperature elements are heated up to +65°C, power does not exceed 15 W/m and is suitable for heating pipes of small diameter. Medium-temperature conductors are heated up to a maximum of +120 ° C, the power reaches 10-33 W / m, they are used to prevent freezing of pipes of medium diameter or to heat the roof. High-temperature thermal cables are capable of heating up to +190°C and have a specific power from 15 to 95 W/m. This type is advisable to use for industrial purposes or in the presence of pipes of large diameter. For domestic use, such conductors are considered too powerful and expensive;
- By power. The power characteristics of the coolant must be taken into account without fail. If you pick up a low power conductor, you simply will not achieve the desired result.Exceeding the required indicator can lead to too high a level of energy consumption, which in practice will be unjustified. The choice of the required power level primarily depends on the diameter of the heated pipe. According to the recommendations of experts, for pipes with a diameter of 15-25 mm, a power of 10 W / m is sufficient, for a diameter of 25-40 mm - 16 W / m, for a pipe with a size of 60-80 mm - 30 W / m, for those that exceed 80 mm in diameter, - 40 W / m.
In what cases may it be necessary to install a heating cable?
In principle, in order for the water supply or sewerage not to freeze, they must be laid at a depth of 1.1 - 1.3 m (more accurate indicators can be found in the corresponding tables for each region of Russia). However, it is not always possible to lay a pipeline at such a depth - here are a few reasons for this:
- High concentration of communications. In large cities, on many plots of land, there is a high density of already existing communications, for example, electrical cables, gas and water supply, as well as sewerage and communication communications. Because of this, digging in these places is prohibited, and where it is allowed, it will not be possible to dig deep. Therefore, it may be necessary to lay the pipe above the freezing depth of the soil, which carries with it the possibility of freezing the liquid inside the pipe.
- High soil density. If it is not possible to dig with an excavator, but only manually, but the soil is very hard, then you may have to lay the pipe higher.
- Entering the house above the freezing level of the soil. Even if the entire pipe is deep, the entrance to the house may still be located above the freezing depth of the soil, so there is a possibility of ice formation.
- The pipeline was installed before you at insufficient depth. If the problem of freezing of the pipeline was discovered recently and it is impossible to dig out and shift the line, then it is possible to lay the heating cable inside the product.
In fact, there can be many more reasons for using a heating cable. What is the best heating cable for plumbing and sewerage? This will be discussed further.
Heating cable power for water supply
It is rather difficult for a user even with an engineering education to determine exactly how much power is required for the efficient operation of a resistive or self-regulating heating cable - the calculation formulas are too cumbersome and the calculation takes a long time. The task is within the power of only qualified specialists, and its solution in everyday life was carried out by manufacturers and distributors of heating electrical cable products.
For domestic HDPE water pipes with a standard diameter of one or one and a half inches, the optimal thickness of the insulation shell is 30 mm; when using sewerage, you will need a higher power cable of about 20 W per meter or spiral winding, with a heater thickness of 50 mm.
For outdoor heating, the power of the heating cable is linearly related to the ambient temperature and the state of the heated elements, for pipelines its average value is about 20 W per linear meter, on roofs and in downpipes powerful resistive electric cables up to 60 W per linear meter are used.
Connection diagram for single-core and two-core cables
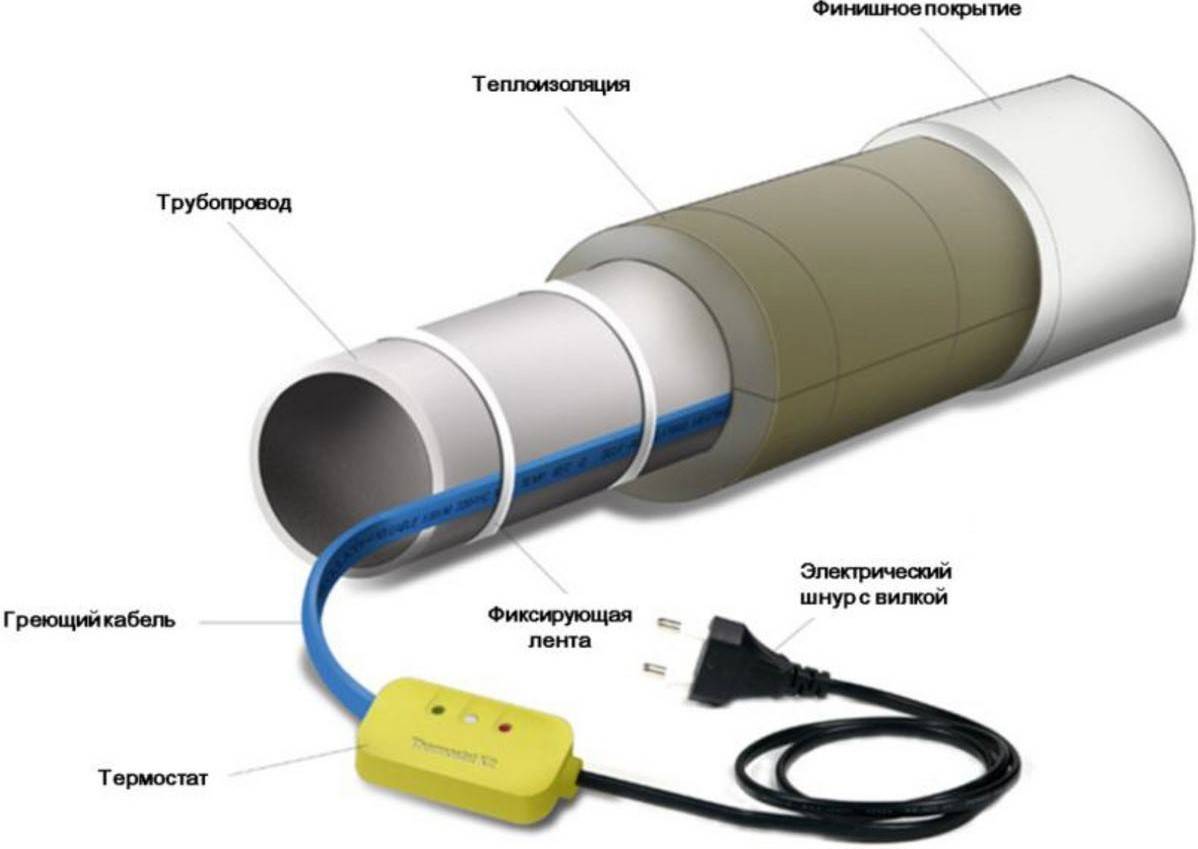
Installation of a heating product
The heating cable can be laid inside the pipeline or fixed outside. Each of these mounting methods has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- It is possible to lay the cable inside only if the diameter of the pipeline allows it. This technique is applicable when it is not possible to equip external heating (communications are covered with bitumen or concrete mortar). Single-core resistor-type products are not suitable for arranging internal heating.
- The main advantage of outdoor installation is the simplicity and convenience of performing work, as well as practicality. In this case, you can use any type of heating cables.
Consider each of the installation methods in more detail.
Internal installation
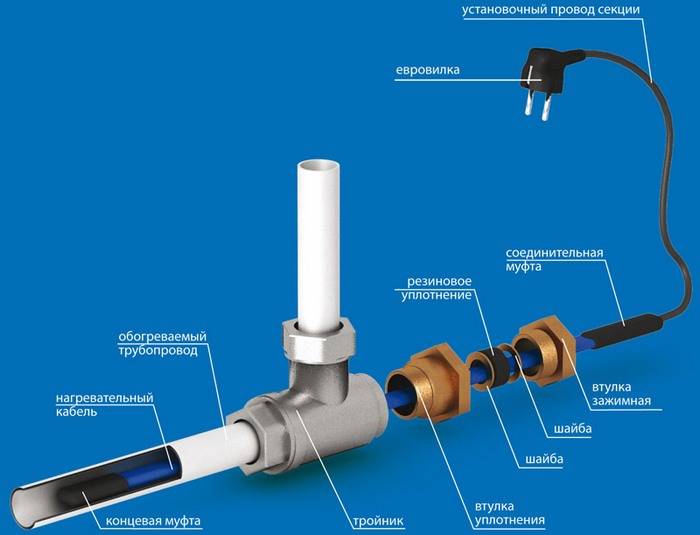
For indoor installation, a special moisture-resistant cable is suitable, which, in addition, must be resistant to acidic environments
For indoor installation, a special moisture-resistant cable is suitable, which, in addition, must be resistant to acidic environments. You do not need full access to the pipeline to perform the installation. For this, a special coupling is used, through which the cable is inserted into the plumbing system to the required length. After that, the other end of the wire is connected to the electrical network. In fact, a coupling is a special tee that is screwed onto the pipeline at the exit point.
Worth knowing: the efficiency of this heating method is 2 times higher than that of the external gasket. Therefore, it is allowed to use a heating device of lower power. In addition, for the insulation of such a pipeline, a smaller layer of heat-insulating material will be needed.
The disadvantages of this method of warming include the following:
- This method is not suitable for heating sewer pipes. In this case, only external mounting of the heating device is permitted.
- If the pipeline section has branches, taps and bends at an angle of 90 degrees or more, then this method is not suitable.
- Since the internal clearance of the pipe is slightly reduced due to the laid cable, the water pressure is reduced.
- It is quite difficult to perform installation on long sections.
- Over time, the wire can become overgrown with plaque, which will lead to clogging of small diameter pipes.
outdoor installation
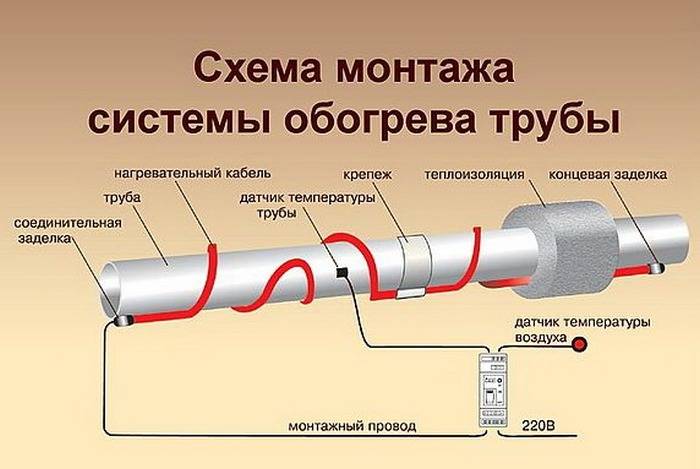
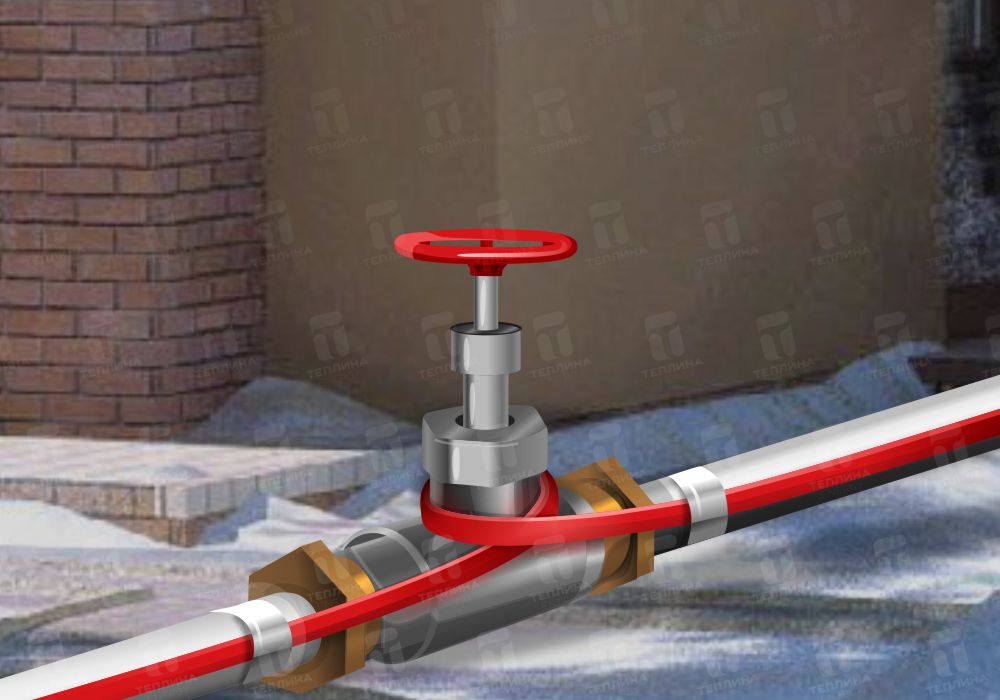
The wire is wrapped around the pipeline or placed under it and fixed with aluminum foil.
This method of installing a heating product is quite simple. The wire is wrapped around the pipeline or placed under it and fixed with an aluminum film. In addition to fixing, this film effectively reflects heat rays. Then the pipe is wrapped with a layer of heat-insulating material.
This method of installing a heating product can be done by hand. At the same time, the clearance of the pipes does not decrease, and the damaged heating product is easy to replace. In this case, you can use two ways of laying the cable:
- The cable is fixed with adhesive tape on one side of the pipe. At the same time, to increase the contact area and heat transfer, the product is laid in a wave. After that, the pipe is insulated.
- Pipes laid in climatic regions with severe winters are best wrapped with cable. In this case, the turn pitch is 50 mm. For more reliable fixation, the product is attached in several places with the help of foil tape.
After performing any method of laying the cable, the entire pipe is tightly wrapped with tape. This will protect the heat-insulating material from strong heating, since exposure to high temperatures can be detrimental to it.
Attention: the resistive product is connected by means of a thermostat. It will provide uniform heating and will not allow excessive consumption of electricity. If a self-regulating cable is installed, connection through a thermostat is not required.
If a self-regulating cable is installed, connection through a thermostat is not required.