- Smoke and fire ventilation
- Types and types of ventilation
- Norms for determining the parameters of air exchange
- Documents and acts of the Russian Federation
- Foreign ventilation quality standards
- Ventilation dampers for windows
- Air supply
- Examples of calculating the air exchange rate
- Features of designing a ventilation system for clean rooms
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
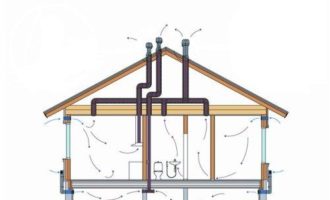
Smoke and fire ventilation
All ventilation equipment must be installed in accordance with fire regulations SP 7.13130.2013. It is impossible to neglect these simple rules when developing a circuit and installation. Any building, and even more public, must be equipped with fire and smoke ventilation of proper quality.
The spread of fire and smoke through the duct system is no small problem in a fire. To combat it, fire dampers with a temperature sensor are mounted in the air ducts.
Under normal conditions, it is constantly open. When the temperature rises to extreme, a sensor is triggered, which actuates the valve actuator. After closing, the seal applied to the edge of the valve expands, adhering as tightly as possible to the duct.
Smoke in the premises impedes evacuation and complicates the work of firefighters. It is impossible to completely get rid of smoke, but you can minimize its harm by installing fans for backwater and smoke removal.
Smoke exhaust fans are needed to remove the smoke-air mixture from the room. Modern models are able to work at a temperature of 400-600 ° C for about 2 hours
Smoke ventilation fans are necessary to provide people on the escape route with clean air. By forcing air in crowded places (evacuation corridors, stairwells), it increases pressure, preventing smoke from penetrating there.
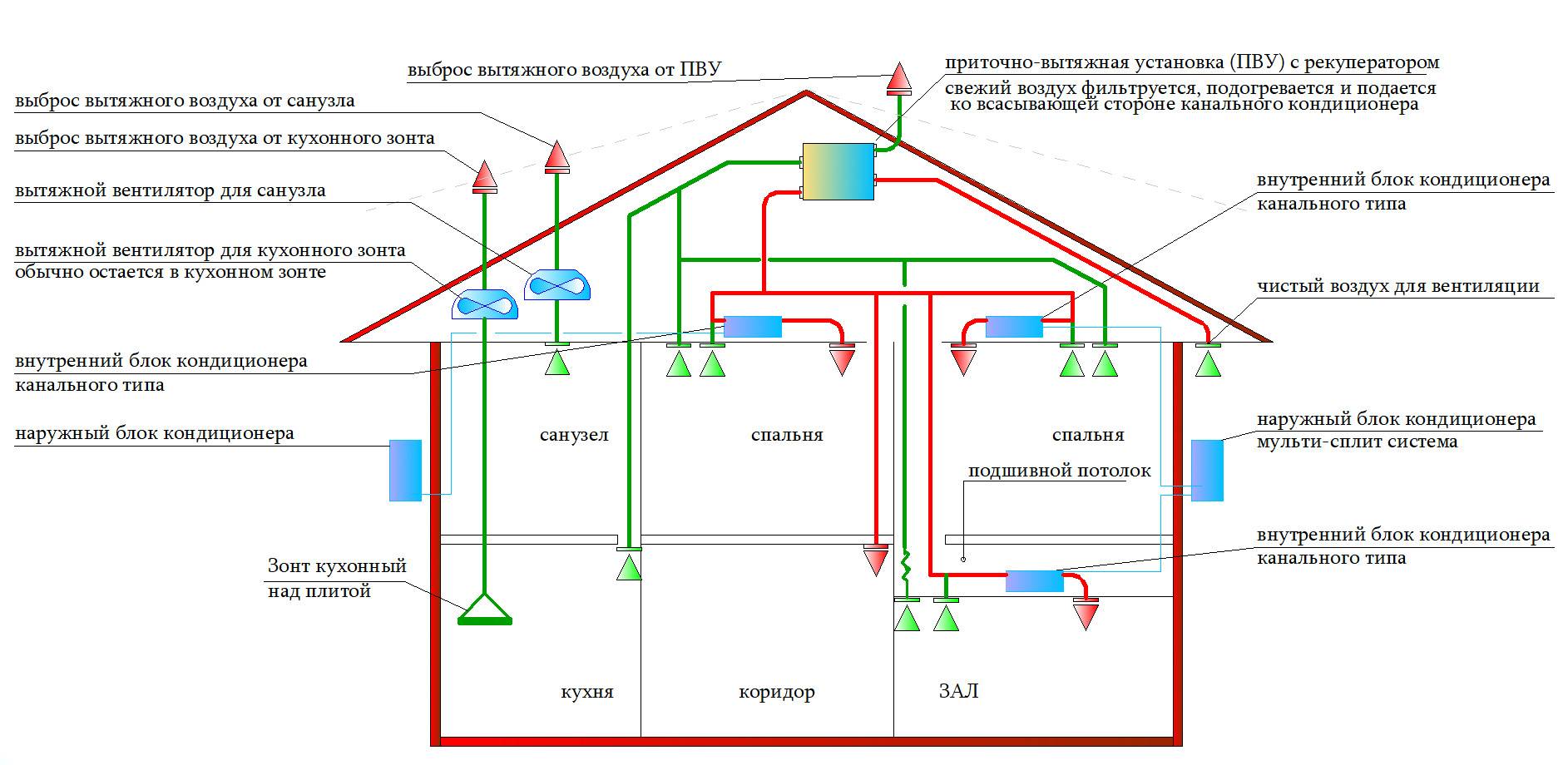
Types and types of ventilation
Before considering the classification of such systems, you should find out what ventilation is in scientific terms.
Automatic control eliminates human intervention (only during scheduled maintenance or repair).
Ventilation systems are divided into the following categories:
- Systems for maintaining a certain climatic comfort. They have higher installation requirements and are divided into:
• Natural. Ventilation of the premises occurs through natural phenomena, such as temperature or pressure changes (used: patient rooms and doctors' offices).
• Artificial. For constant circulation of the air flow, devices operating on the basis of mechanical, thermal or electrical energy are used. - Exhaust ventilation. The main function is the removal of exhaust air from the room. Such systems are often used in rooms with high humidity, to prevent the appearance of microorganisms hazardous to health (bacteria, microbes).
- Supply. It has the opposite principle of action - it brings fresh air to the room.They try to combine supply and exhaust ventilation, since high standards for indoor air quality are set in medical institutions (for example, intensive care units and treatment pools).
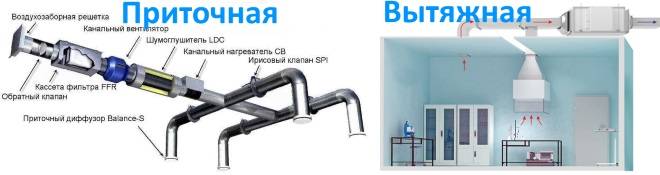
The classification of air circulation systems is also divided into the following groups:
- General exchange. Install high-power devices that can provide high-quality replacement of exhaust air throughout the room. Not used for individual zones or rooms.
- local value. The low power of such a system allows high-quality ventilation of the air in several squares specially designated for this.
- emergency type. Placed near possible sources of increased danger. Emergency ventilation must operate independently, and accordingly - have one or more separate power sources.
Norms for determining the parameters of air exchange
Since the ventilation system affects the quality of human life, its permissible parameters are prescribed in regulatory documents. Compliance with these requirements is mandatory in the case of commercial use of the premises, as well as when accepting multi-apartment buildings.
When designing ventilation inside an apartment or for a private house by the owner, they can be adopted at the level of recommendations.
Documents and acts of the Russian Federation
Russian legislation establishes various standards for ventilation and air conditioning, depending on the type and purpose of the premises. They are included in the codes of practice (SP), state standards (GOST) and sanitary rules and norms (SanPiN).
According to the rules, residential and domestic premises are ventilated to achieve the following goals:
- Maintenance of oxygen regime.A decrease in its concentration worsens a person's well-being. This problem is easiest to solve with the help of street air.
- Removal of unwanted gases and aerosols. Accumulation of carbon dioxide, combustion products or dust is hazardous to health.
- Regulation of microclimate parameters. Maintaining humidity in a given range with the help of ventilation is a common and effective method that is often used not only in residential areas, but also in warehouses and basements for various purposes.
In Russian standards, the calculation of the supply air flow is determined by many parameters, after which they take the highest possible rate. In practice, not all of them are often used, so this approach raises many questions among specialists.
There are 8 documents regulating air exchange rates, permissible microclimate parameters, as well as rules for the installation and operation of ventilation systems
Foreign ventilation quality standards
When installing a ventilation system for a cottage or your own apartment, it is not necessary to use the current Russian regulatory documents. Alternatively, you can apply in the calculations the provisions of foreign standards that regulate indoor air quality.
Founded in 1894, the ASHRAE engineering community has a wealth of scientific and practical experience in the field of ventilation and air conditioning.
ASHRAE has developed the following documents:
- ASHRAE 62.1 - requirements for ventilation and air conditioning systems;
- ASHRAE 55 - requirements for the microclimate and thermal comfort of the room.
Research by this American Society of Engineers is often used to calculate international and national quality standards.
Standard 62.1 uses methodologies based on the following to determine minimum ventilation rates:
- air exchange rate (VRP), where the positions of the supply and exhaust devices are regulated and the power of the flows varies depending on the microclimate indicators;
- indoor air quality (IAQP), which suggests ways to reduce the concentration of unwanted aerosols by filtering them;
- dimensions and position of the openings for natural ventilation (NVP).
The integrated use of all three approaches can significantly reduce operating costs.
There are also works of the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) dedicated to the ventilation of buildings:
- standard EN 13779 - requirements for ventilation and air conditioning systems;
- standard EN 15251 - requirements for microclimate parameters;
- act CR 1752 - criteria for calculating the ventilation of buildings.
Both sets of standards relate directly to the health and comfort of users. The required volume of supply air is determined by the emission of carbon dioxide, since there are no other significant sources of pollution.
For technical premises, such as a gas boiler room, the calculation of the volume of air exchange is carried out from the position of ensuring safety, and not quality of life
You can order the calculation of the ventilation parameters of an apartment or house according to American or European standards. This will be reasonable, given the long foreign experience and more stringent requirements for the quality of life.
Ventilation dampers for windows
The natural ventilation scheme in the apartment is able to provide housing with oxygen through ventilation through windows, vents, cracks in the floor or doors. But these methods were relevant earlier, while modern windows are characterized by high tightness. Natural holes are replaced with special adjustable holes. These are small ventilation solutions with good functionality.
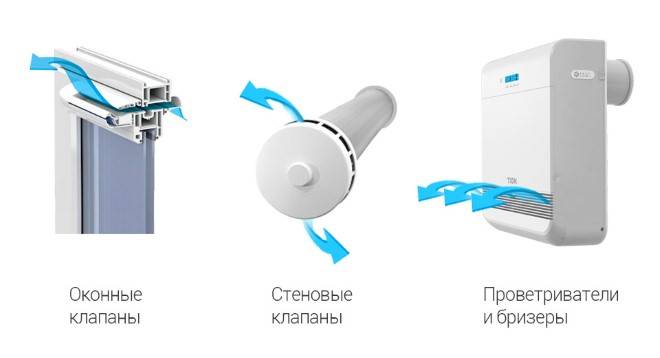
How effectively the holes work really feel only with the onset of cold weather. Cold streams, which are taken from the street, are mixed with the warm oxygen of the room inside the structure, and only after that it enters the housing.
Air supply
To create an airspace which meets hygienic and technological requirements, set the required air exchange rates. For a number of premises, it can be found in the codes of practice, for the rest it is determined by calculation.
In order to save money and ensure uninterrupted operation, ventilation is used with natural draft. The air supply is provided by supply devices air infiltration and through leaky doors. The direction of movement of air masses is organized by windows to the bathroom, bathroom and kitchen.
with air supply both the whole house and apartment spaces are faced not only by workers from organizations for the construction or operation of the building, but also by ordinary residents. For example, over time, the thrust in the channels disappeared. Or after the installation of plastic windows, an influx from the common house corridor was noticed. Of course, the tenant is looking for a solution to the problem.And it is absolutely necessary to take into account that there is a governing base of standards that regulates this area.
Before implementation in realitycomplex of project documents the object must pass a state or independent examination for compliance with the requirements of the Gosstroy of Russia. And only after a positive conclusion is developed a set of working drawings.
Examples of calculating the air exchange rate
Take for example a room with a height of 3.5 m and an area of 60 m², where 15 people work. We believe that the air becomes polluted only from an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide due to breathing.
First, we find the volume of the room: V = 3.5 m × 60 m² = 210 m³.
We take into account that 1 average person emits 22.6 liters of carbon dioxide per hour.
We get that harmful emissions can be calculated by the formula B = 22.6 × n, where n corresponds to the number of people in the room.
B = 22.6 l/h × 15 = 339 l/h
For premises, the maximum allowable concentration of carbon dioxide is 1/1000, or 0.1%. Let's translate this into 1 l / m³. There is about 0.035% carbon dioxide in pure air. We translate into 0.35 l / m³.
Let's calculate how much fresh air will be needed for all 15 people:
Q = 339 l/h : 1 l/m³ - 0.35 l/m³ = 339 l/h : 0.65 l/m³ = 521.5 m³/h. Cubic meters, in this case, have moved into the numerator, and hours, on the contrary, into the denominator.
In addition to the calculation for harmful substances, the air exchange rate is important when regulating the amount of moisture and heat in the room: the corresponding formulas are shown in this image.
We determine the frequency of air exchange:
N = 521.5 m³/h : 210 m³ = 2.48 times per hour. It turns out that with the change of air at the level of 2.48 times per hour, the concentration of carbon dioxide will remain within the normal range.
Let us now find the specific rate of air replacement per 1 person and per 1 m². In this case, the volume of the room must be at least 210 m³, and the ceiling height - from 3.5 m.
521.5 m³/h : 15 people = 34.7 m³/h per person
521.5 m³/h : 60 m² = 8.7 m³/h per 1 m² area
Harmful emissions (B) are also calculated using the formula:
B = a × b × V × n, where:
a is the infiltration coefficient; b is the concentration of carbon dioxide, l/m³ for 1 hour; V is the volume of the room, m³; n is the number of people.
The content of substances can be measured in grams, not liters - it will be better for safety.
Features of designing a ventilation system for clean rooms
Design and installation of ventilation systems and air conditioning of clean rooms requires skills in working with special equipment, as well as knowledge of the standards and requirements for clean rooms.
There are three schemes for organizing air exchange in clean rooms:
- all air streams move in parallel;
- disordered direction - the supply of clean air occurs in different directions;
- mixed direction - observed in large rooms, when in one part the air moves in parallel, and in the other part - randomly.
Depending on the size of the room and the location of the working area, the optimal design of the ventilation system is chosen, but the most optimal solution is ventilation with a unidirectional flow of clean air.
For clean rooms, an exclusively supply and exhaust ventilation and air conditioning system is used. Its essence is as follows: from above, under pressure, a stream of clean air is supplied at a certain speed, which “squeezes out” the polluted air in the room down to the air intakes.
The cooled air is supplied at a low velocity, usually to the upper part of the room (about 1/4 of the room volume) through the ceiling panels. It seems to flow around the space, lowering the dust down to the hood, while creating a minimum level of irritation. With such ventilation, drafts and whirlwinds of dust that have settled on the floor do not appear. In addition, the supply air is pretreated to the required temperature and humidity.
You can get a draft design of clean room ventilation free of charge
Go
The basis of the ventilation and air conditioning system is a supply and exhaust unit with recirculation, consisting of the following elements:
- frame;
- filters;
- humidifier;
- heat exchangers;
- fans. General diagram of the ventilation system of clean rooms.
Special requirements apply to filters. The filtration system consists of three groups of filters through which the air flow passes in sequence:
- coarse filter (first degree of filtration) - removes mechanical impurities from the air;
- fine filter (second degree of filtration) - removes bacteria and other microorganisms;
- HEPA and ULPA microfilter with absolute cleaning (removes 99.999995% of microorganisms).
Coarse and fine filters are located in the central air conditioner, and HEPA and ULPA filters are located directly in the air distributors. HEPA and ULPA filters
Depending on the size of the room, air pressure, method of furniture placement, the number and characteristics of air intakes and air distributors are determined.
There are a number of rules to consider when designing cleanroom exhaust ventilation:
It is necessary to maintain a positive imbalance of air pressure in cleanrooms.
The pressure difference must be at least 10 Pa with the doors closed.
At the design stage, it is important to consider the height of the ceilings. If they are higher than 2.7 m, then it is more rational to use the method of local ventilation of the workplace
In this case, the flow of clean air enters directly into the place where a person works.
For rooms up to 4.5 m long, instead of the raised floor, wall gratings are installed at a height of 0.6 m to 0.9 m.
"Clean" rooms should be located near those rooms in which the level of cleanliness is as high as possible.
For the construction of clean rooms, only ecological materials with high tightness are used, which will allow maintaining stable air circulation.
In clean rooms, it is necessary to use HEPA filters and CAV regulators: the former provide high quality cleaning of the supplied air, and the latter determine the portioning of its supply.
Below are the most optimal ventilation and air conditioning systems for clean rooms.
A) Unidirectional flow is supplied through the ventilation grille.
B) Air is supplied in different directions due to diffusers located on the ceiling.
C) Unidirectional flow enters the room through a perforated panel on the ceiling.
D) Air is supplied directly to the working area through an air distributor located on the ceiling.
E) The flow of clean air moves in opposite directions due to the equipment of annular air hoses.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How to deal with a heavy indoor atmosphere:
We examined the mandatory and permissible microclimate parameters in some categories of buildings, as well as in which rooms there should be, and what kind of ventilation. As you can see, in most cases they are different. The only requirement is that wherever they are, they must comply with current regulations. Compliance with the rules is a guarantee of the safety of life and health of people.
Of course, we have given you only general ideas, it is impossible to voice all the exact requirements in one article for each item. Moreover, they are often individual in terms of the dimensions of the buildings, their geometry, the location of the halls, and so on. If you need to develop high-quality ventilation or air conditioning, you should contact experienced companies with a license, as well as in order to prove that your rights to a comfortable microclimate are infringed in any way.
Have you experienced microclimate problems? Or maybe they designed an air exchange system? Share your experience and ask your questions in the comments.