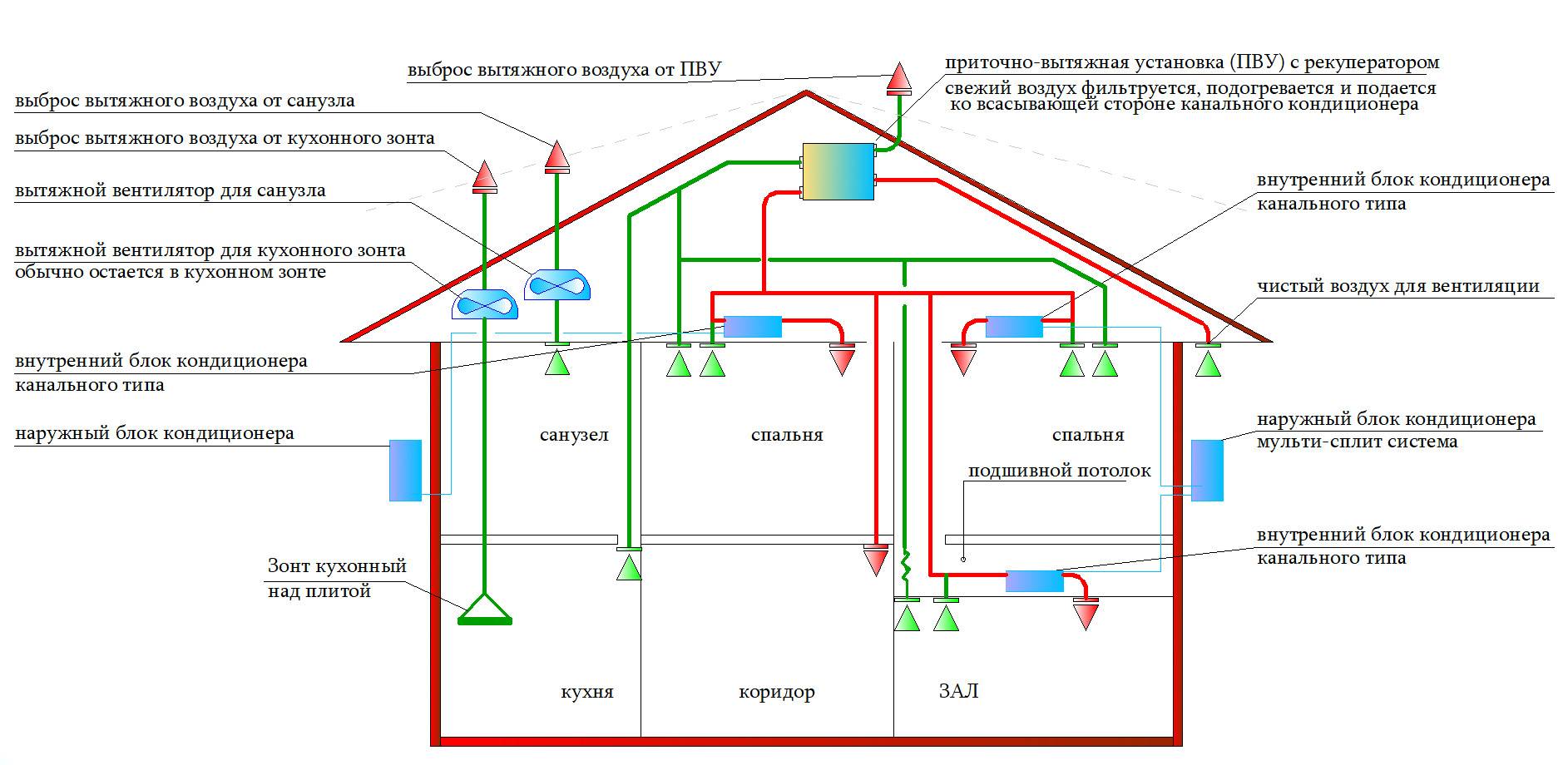
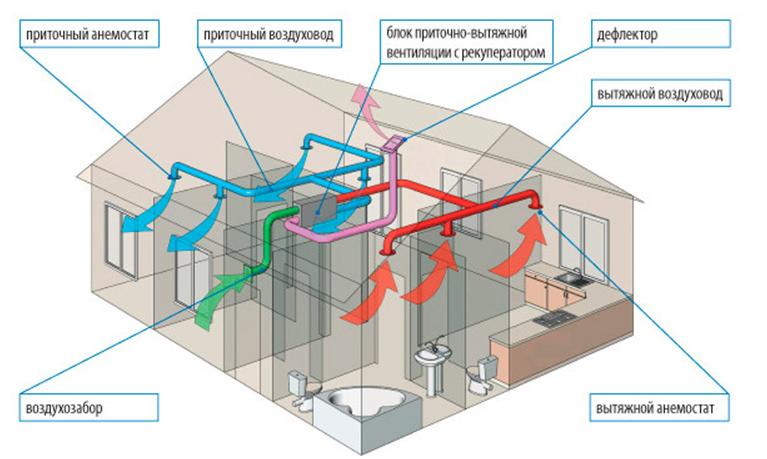
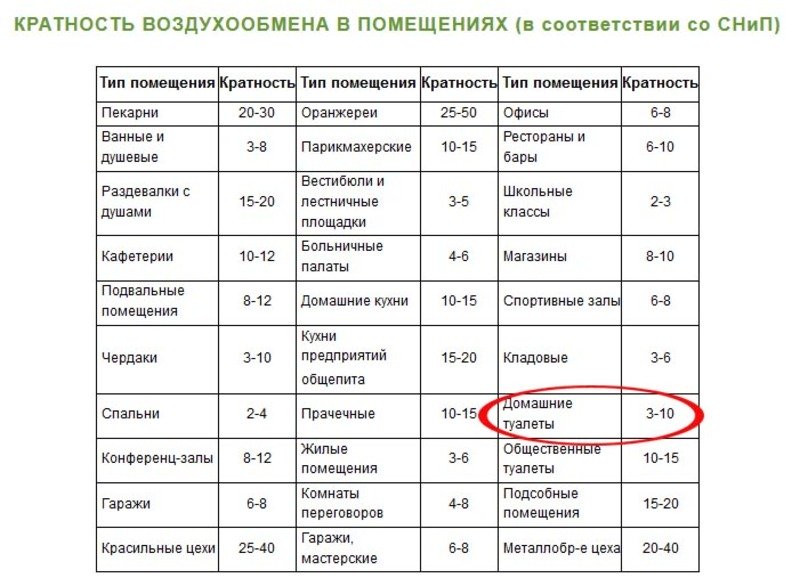
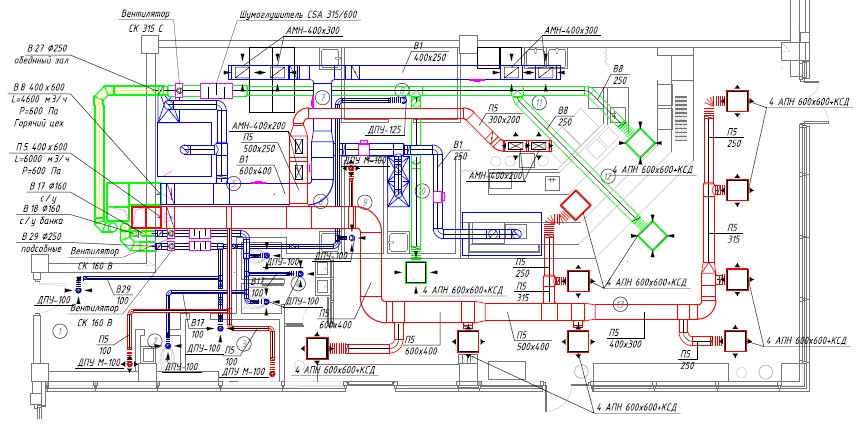
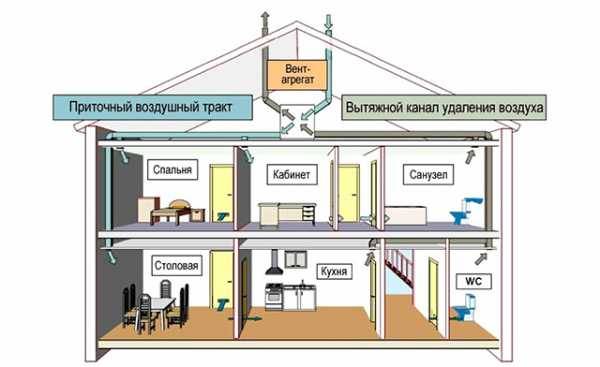
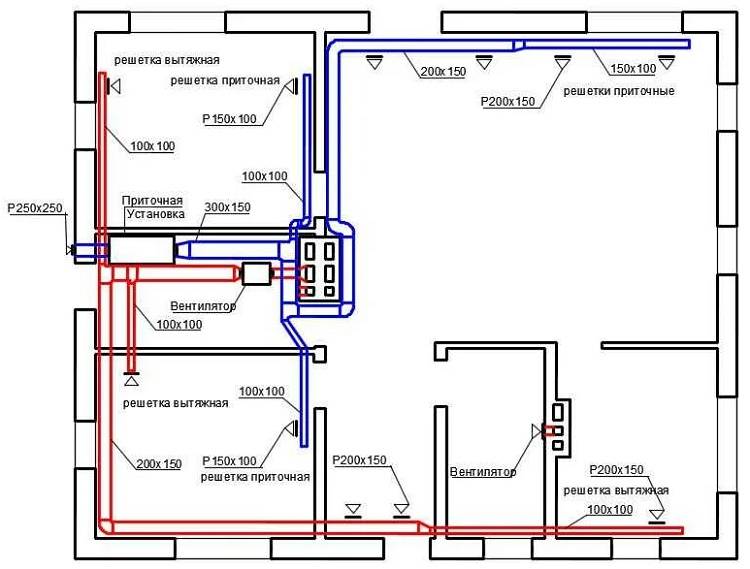
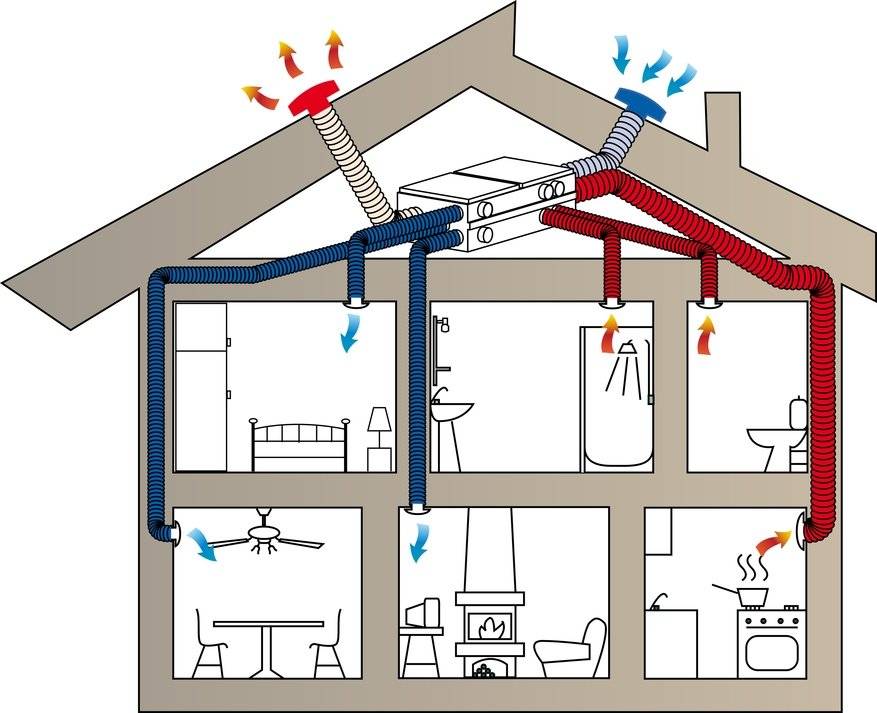
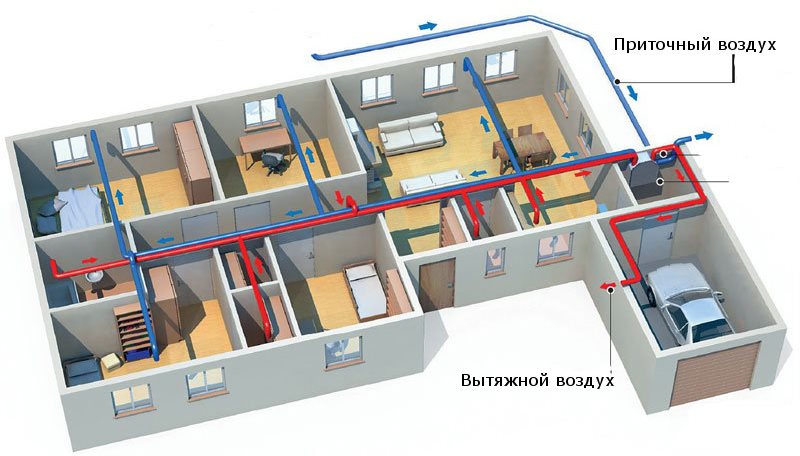
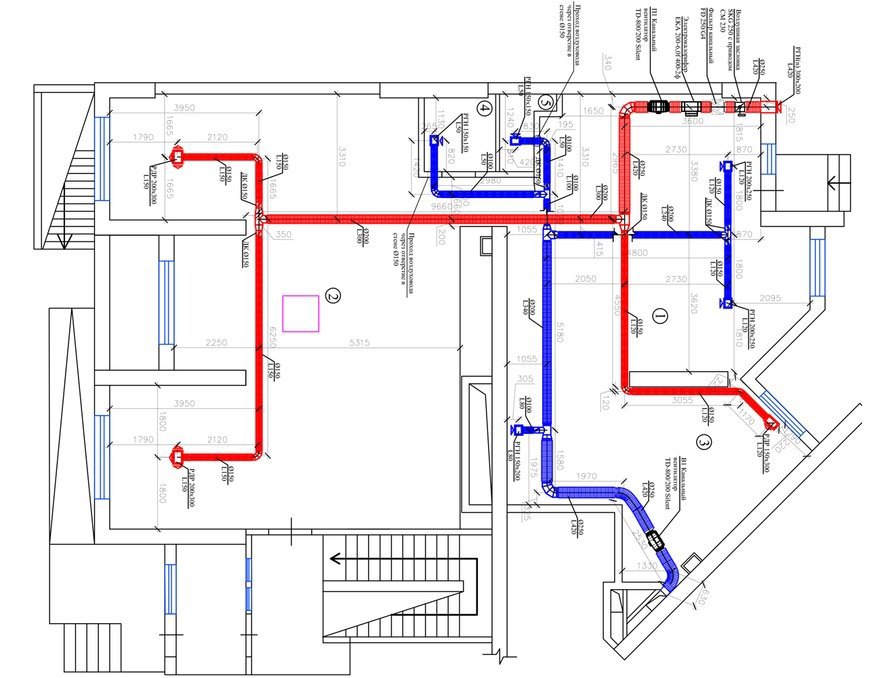
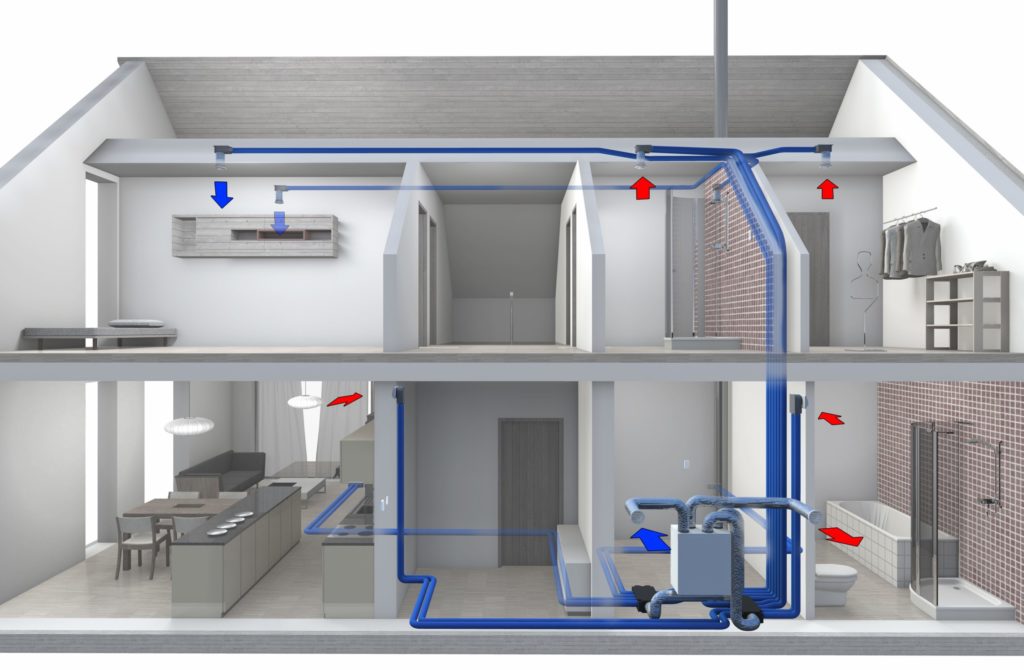
- Ventilation system design stages
- Pre-project proposals (PP)
- Recommendations
- On the design of natural ventilation in a house under construction
- For the modernization of ventilation in an already built house
- Norms of natural ventilation
- Microclimate in rooms of various types
- Selecting the type of ventilation system
- Air distribution
- Normative documents
- Ventilation design: how to correctly calculate air exchange in a private (country) house
- Calculation by the area of the object
- Calculation according to current sanitary standards
- Distribution of air masses by multiplicity
- How is the calculation carried out
- Regulation for the low-rise sector SP 55.13330.2016
- Tips for arranging natural ventilation
- in the bathroom
- In the bath
- In the boiler room
- In living rooms
- In the kitchen
- Design technology
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Ventilation system design stages
The scope and content of the project will vary depending on its complexity, but the main components will be approximately the same. So, at the preliminary stage, a technical project is drawn up, which, in fact, is a feasibility study (feasibility study).At this stage, specialists go to the site to record the initial information, including the purpose and functions of the building or premises, its area, and the number of residents/employees.
The initial stage ends with the selection of equipment, consideration of the main characteristics and properties. Optimization decisions are made on interaction with other engineering systems. And the calculation of the air exchange of each specific room is carried out in accordance with the technical conditions, construction and sanitary standards.
Next, a scheme is developed for calculating the diameter and area of air ducts and the noise level is determined. The drawings are sent for approval. The project designer or direct customer can make changes.
At the next stage, after agreement, a package of documents on plumbing, construction work and electrical power is prepared.
Only after completion of all the above stages, ventilation is installed and launched.
Ceiling height plays an important role in the design of the ventilation system. The low-lying ceiling significantly complicates the task, as a rule, this is found in the living room, bedroom and kitchen, if the corridor is completely adjacent to the wall of the living room
Of no small importance in the design is also the rational distribution of funds intended for the purchase of equipment and materials. On the modern market there is a huge range of equipment and devices from various manufacturers of different price categories.
For the purchase of equipment, special calculations will be required:
- With the help of the area and purpose of the premises indicated in the floor plan of the structure, the required performance is determined. The indicator is calculated in m3 / h.
- Taking into account the performance, the value of the air temperature at the outlet of the ventilation system and the minimum ambient temperature determine the power of the air heater. The duct heater is used exclusively in the cold season as a building heater.
- The characteristics of the fan depend on the length and complexity of the route. To calculate the required power, the type and diameter of the duct, diameter transitions, and the number of bends are used.
- Calculation of air flow velocity in air ducts.
- The air speed affects the noise level.
The project budget is calculated after the completion of all calculations, drawing on the building plan of the proposed ventilation ducts. The prepared TOR must be approved by the customer and departmental structures.
In a private house, a project for a ventilation system should be in hand even before the foundation is laid. All details must be thought out in advance to the smallest detail, which will ensure an effective air exchange system.
Pre-project proposals (PP)
At the stage of pre-project proposals, initial permit documentation is drawn up and relevant documents are developed that are approved by various authorities. Documentation development The development of documentation at the stage of pre-project proposals includes the following items:
- general explanatory note (contains a brief description of the state of the object, the main technical and economic indicators and the results of calculations of the economic efficiency of design solutions, data on the volume of construction and installation work, etc.);
- calculation of loads (determination of thermal loads and basic loads of an object for connection to networks);
- schematic diagrams of engineering systems (principal solutions for engineering support - equipment for ventilation, air conditioning, heating, dispatching, automation and management of engineering systems);
- technological solutions (drawings, plans, specification of equipment and materials with reference, etc.);
- engineering systems and equipment (examination of the possibilities of installation of engineering systems and equipment at the construction stage of the facility, changes in the quality of engineering and technical support during the reconstruction of the facility, replacement of engineering networks during the overhaul of the facility).
 |
Recommendations
When equipping natural ventilation in a private house with your own hands, it is advisable to take into account the features of a comfortable air exchange device for buildings under construction and existing buildings.
On the design of natural ventilation in a house under construction
The main principle of drawing up a scheme of natural ventilation in a private house during the construction process is the location of the mines. They are arranged exclusively in internal partitions to ensure that the main part of the pipe is kept warm. This principle makes it possible to obtain sufficient exhaust power, especially at negative outdoor air temperatures.
Plumbing plastic pipes are used as pipes for the air duct, because. when using corrugated products, there are weak, but perceived by human hearing, noises.

When removing ventilation pipes through an unheated attic floor to the roof, it is recommended to take care of additional insulation of the air duct in this room.
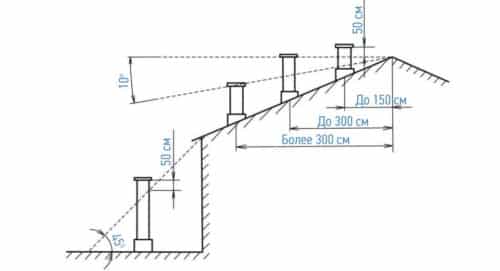
When installing the exhaust pipe, it is recommended to maintain verticality, if this condition cannot be maintained, bypass slopes should be made with a deviation angle not exceeding 30 degrees. Each transition with an offset from the main vertical axis takes about 10% of the power.
You should carefully consider the docking nodes of the duct. Inaccurate articulation of individual elements, foreign objects, roughness - complicate the process of efficient operation of the hood.

Recommended height of ventilation ducts above the roof.
For the modernization of ventilation in an already built house
To increase the traction power and provide additional protection against the penetration of insects and dust into the building, it is desirable to install a deflector at the end of the duct. This device helps to increase power by 20%.
 The deflector on the exhaust pipe.
The deflector on the exhaust pipe.
In rooms with high humidity, it is recommended to install exhaust fans. This measure turns the natural system into a combined one, but at the same time, the dependence on weather conditions disappears. In addition, the installed devices will balance the humidity and temperature conditions in these places and prevent materials from rotting.
When the building is equipped with plastic windows and in frosty weather, ventilation is rarely carried out, in order to save heat, the efficiency of air mass circulation drops sharply. In such a situation, it is recommended to equip windows with special ventilation valves, which make it possible to organize the flow of outside air, and at the same time arbitrarily regulate the flow.
 Vent valve in the window.
Vent valve in the window.
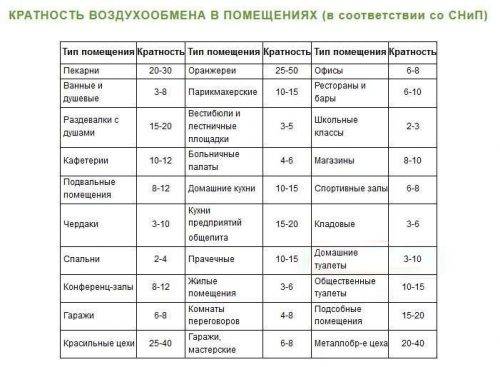
Norms of natural ventilation
Modern SNIPs regulate the norms of ventilation of residential premises based on the value of the total air exchange in the building, and is measured in the number of times or cubic meters per hour.
The norms for one-story residential buildings are:
- residential premises of permanent residence - 1 full exchange per hour;
- kitchen - from 60 m3 / hour (hood);
- bathroom - at least 25 3 / hour (hood);
- other premises - 0.2 full exchange per hour.
The norms of natural ventilation in a multi-storey building take into account the presence of additional premises:
- laundry - 90 3 / hour;
- gym - 80 3/hour;
- dressing room - 0.2 full exchange per hour;
- gas boilers - 1 full exchange per hour + 100 3 / hour.
There are special requirements and standards for ventilation equipment in basements, technical floors and attics.
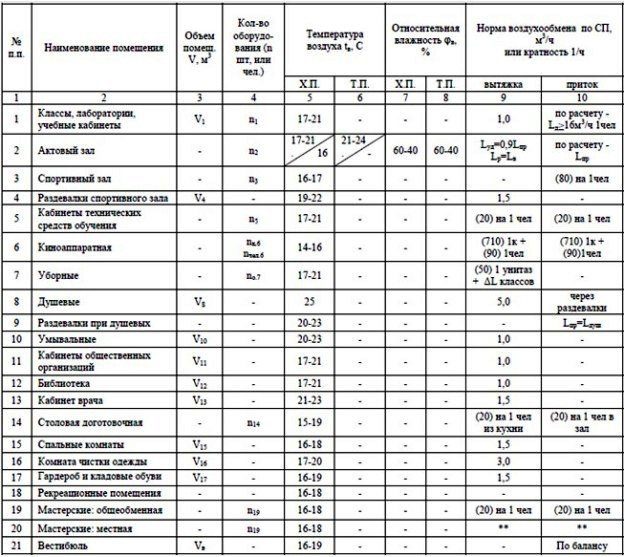
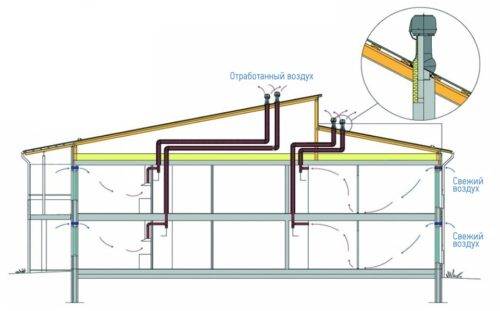
Microclimate in rooms of various types
The scheme of the ventilation system is developed during the design of the building. Engineers and designers take into account the specifics of the structure, architectural features, the difference in the climatic regime in the premises.
 Before being supplied to the room, the air in the cold season must be heated. For this, duct heaters are used in supply ventilation systems.
Before being supplied to the room, the air in the cold season must be heated. For this, duct heaters are used in supply ventilation systems.
Regulatory documents come to the aid of specialists that establish the limits of microclimate limit values:
- SP 7.13130.2013;
- SP 60.13330.2016;
- SP 252.1325800.2016.
Before starting work on the design of the air conditioning and ventilation system of public buildings, it is necessary to determine which category the building belongs to.
According to GOST 30494-2011, categories are distinguished:
- 1 category.It includes all rooms in which people are in a state of rest and rest, lying or sitting.
- 2 category. The building is intended for mental work or study.
- 3a. The premises are characterized by a massive stay of people without warm outerwear, mostly sitting.
- 3b. In the premises there are people in street clothes, usually sitting.
- 3c. In the premises there are people in street clothes, standing.
- 4th category. Places for active sports.
- 5th category. Premises of this type suggest the presence of people in a half-dressed form (pools, gyms).
- 6 categories. The category includes premises where people stay for a short time (pantries, bathrooms, lobbies, corridors).
Engineers have a rather difficult task to ensure optimal parameters in each room.
 Installing a rooftop supply fan is an example of space management in a public building that saves space in the room
Installing a rooftop supply fan is an example of space management in a public building that saves space in the room
According to the norms, 20-30 m3 of fresh air per person should be constantly supplied to the room. Now around this value there are disputes. With such an influx, a draft can occur, which is very unpleasant in the cold season, when the heating elements of the ventilation simply do not have time to warm the air flow to a comfortable temperature.
Another method for calculating the required air exchange is based on the formula:
V = 3 m3 * S,
where S is the area of the room.
Accordingly, there are 3 cubic meters of air per square meter. This method is used, as a rule, to calculate the required inflow in a residential building, but SNiP 31-05-2003 allow such a calculation for offices in an administrative public building.
In calculations for some premises, such as a toilet, a smoking room, a kitchen, the air exchange rate is used as a value that determines the parameters of the ventilation system.
This is a value that characterizes how many times the entire volume of air in the room will be replaced within one hour. For the kitchen, the minimum allowable value is 3 rpm, for the toilet - 5 rpm, for the smoking room - 7 rpm. Such a calculation is only suitable for small rooms in which people stay for a short time.
For small branches of general ventilation, it is more rational to use round duct fans, they can be installed in any position
Selecting the type of ventilation system
In addition to careful calculation of the parameters of the ventilation complex, it is necessary to pay attention to the selection of its type. To do this, pay attention to the following features:
- air pressure from outside;
- the need for heating the inflow in winter;
- the required power of this heating;
- the total need for air intake and removal.

In turn, these parameters are selected according to the size, purpose, location, workload of the serviced premises. The natural type of ventilation is simple, which attracts people in most cases. You can create it without the use of special equipment, so its failure is initially excluded. Even if the electricity is turned off, the system will freshen the air in the rooms or work areas regularly. But at the same time, its productivity is limited, and the dependence on external conditions is too great.

The apparent disadvantages of a mechanical ventilation system for designers are not too significant, if only taken seriously.Professional selection of key components minimizes the risk of breakage. And the number of options and flexible settings only have a positive effect on the microclimate of the room. Having dealt with the natural or artificial method of work, you need to further make a choice about what ventilation will be:
- only to ensure the flow of air from the outside;
- only throw out polluted air;
- combine these two tasks.

There is no need to rush when making such a decision. It is required to analyze a number of factors: how the room is planned, how many people use it, what is the danger of harmful substances, how large is their intake, and so on. Both supply and combined ventilation systems in Russia can work normally only if there is an air preparation complex. The fact is that its temperature, humidity, chemical composition and other parameters with direct air collection on the street are not always ideal. When all these parameters are determined, one more decision needs to be made - how exactly the ventilation system will be controlled.

If there are no special wishes, and you just need to “make a good microclimate”, you need to stop at the proven option - the supply and exhaust configuration. She will definitely cope with all the tasks assigned. An additional advantage is that the occurrence of pressure drops between the street and the house, between the individual parts of the building, is completely eliminated. But complex treatment systems need to be installed only at industrial and energy facilities. In residential buildings, unless the ecological situation is close to catastrophic, you can do without them.

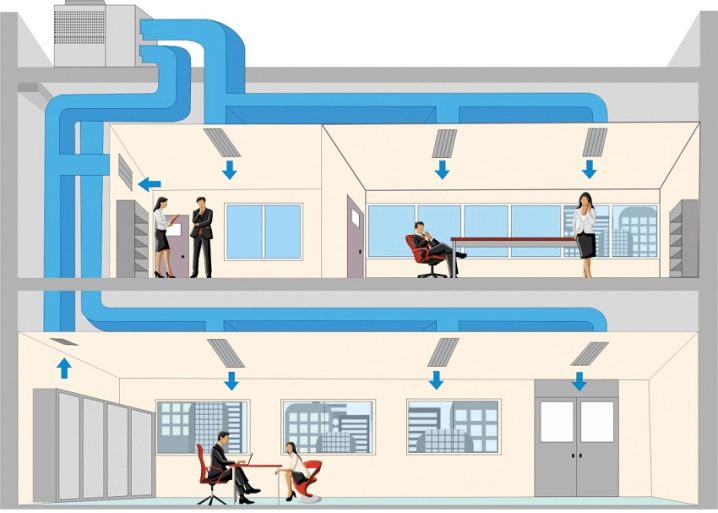
Air distribution
Ventilation should not easily supply a certain amount of air inside. Its goal is to deliver this air directly to where it is needed.
When planning the distribution of air masses, the following indicators are taken into account:
- daily regimen of their application;
- annual cycle of use;
- heat input;
- accumulation of moisture and unnecessary components.
Any room where people are constantly deserves fresh air. But if the building is used for public needs or solving administrative problems, about half of it can be sent to neighboring rooms and corridors. Where there is an increased concentration of moisture or a lot of heat is released, it is required to ventilate the areas of water condensation on the enclosing elements. It is unacceptable to move air masses from areas with increased pollution to places with a less polluted atmosphere. The temperature, speed and direction of air movement should not contribute to the appearance of a foggy effect, water condensation.
Normative documents
It is undoubtedly important to personally verify the compliance of design materials with the established requirements. But it is still supposed to be approved by the supervisory authorities, although there is not always a need for such a procedure.
It can be abandoned if only the reconstruction of existing ventilation is carried out without a fundamental change in its parameters. It is usually practiced to coordinate all project documentation for construction or repair in the form of a single package.Separate submission of working materials on the design of ventilation for approval is required only in case of departure from the general design solutions.
If the project is submitted for approval, it must have a strictly defined structure and set of blocks. Their standard list is as follows:
- the title page, where the name is given, the initiator and performer are mentioned;
- terms of reference, in which the customer sets out everything that he considers necessary to implement, and it also describes how to achieve this;
- a set of drawings in accordance with the requirements for design schemes;
- explanatory material, which describes which fans will be installed, what will be the flow power and what multiplicity is being achieved, how control will be organized;
- a set of specifications for the installed equipment;
- confirmation of the coordination of these materials with designers and architects.
In addition to these materials, the explanatory block is supplemented by calculations of a special kind. These include the calculation of the scale of heat losses attributable to the enclosing elements, and the calculation of the aerodynamic parameters of the ventilation complex. Only structures listed in registered self-regulatory organizations have the right to compile all project materials. Thus, according to the law, constant mutual control of work efficiency is maintained. Now designers are required to use SP 60.13330.2012, as well as comply with all those standards, references to which are given in this document.
Regulations provide a clear boundary between natural and forced ventilation. But regardless of the use of one or another option, it is required to ensure the tracking of the slightest deviations of the normalized indicators.According to official requirements, mechanical ventilation should be installed only where there is no natural way to ensure safety. So, special fans help maintain normal temperature and humidity, if it is impossible to take them otherwise. According to the requirements of regulatory documents, it is also supposed to provide air overpressure on flights of stairs and inside elevator shafts.
If these requirements are not met, the project will be denied approval.
When calculating natural ventilation, it is necessary to pay attention, first of all, to the difference in densities of external and internal air. The air exchange rate must correspond to the conditions in a particular room
If in a residential building or in a wardrobe there is enough renewal of the air environment 2–3 times per hour, then in paint shops, petrochemical industries, and so on, this figure should be 5–6 times higher. In any case, the regulations prescribe a balance in the exchange of air: you can not remove it more than pump it in.
The general (sometimes called general exchange - these are equivalent names) system is designed to provide air to the building as a whole. Those ventilating communications that are designed to supply air to separate zones or separate workplaces are considered local. It is strictly forbidden to pass general ventilation through a number of fire compartments. For any of them, it must be created separately. It is also forbidden to merge in one branch of complexes providing recuperation, and systems in which it is not provided.
The standards provide for power take-off and the main characteristics of all components, taking into account the frequency of air exchange, its losses
Additionally, attention is paid to natural pumping due to leaky walls. When analyzing indicators, they pay attention only to the information that is reported by the enterprises that manufacture the equipment.
It makes no sense to overpay for explosion-proof ventilation systems. Anyway, they are not needed in residential premises.
Ventilation design: how to correctly calculate air exchange in a private (country) house
The concept of air exchange is understood as the frequency of oxygen change within the living space for a given period of time. The relevant norms are clearly regulated by the normative documentation. Traditionally, 3 methods of calculation are used. In this article, we will consider the most accessible methods suitable for our own implementation.
Calculation by the area of the object
To calculate the parameter in question, one should be guided by the current standards - for residential real estate, oxygen must be replaced by 3 m3 hourly, at the rate of each square meter. For example, for a 15 m2 room, the corresponding value would be 45 m3/h. Almost all examples of ventilation projects in modern apartment buildings are implemented according to this standard.
Calculation according to current sanitary standards
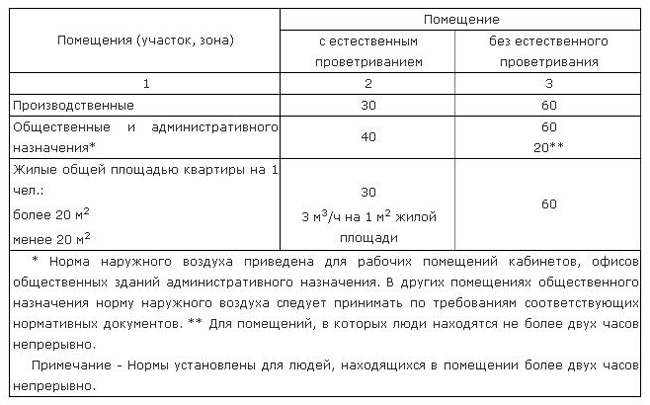
For the design of an air exchange system, it is easiest to use the current hygiene standards. These norms are taken into account when implementing new housing construction. Taking into account the current sanitary and hygienic standards, the average need for pure oxygen for each person is at least 60 m3 / h, if we are talking about a room where he is constantly.
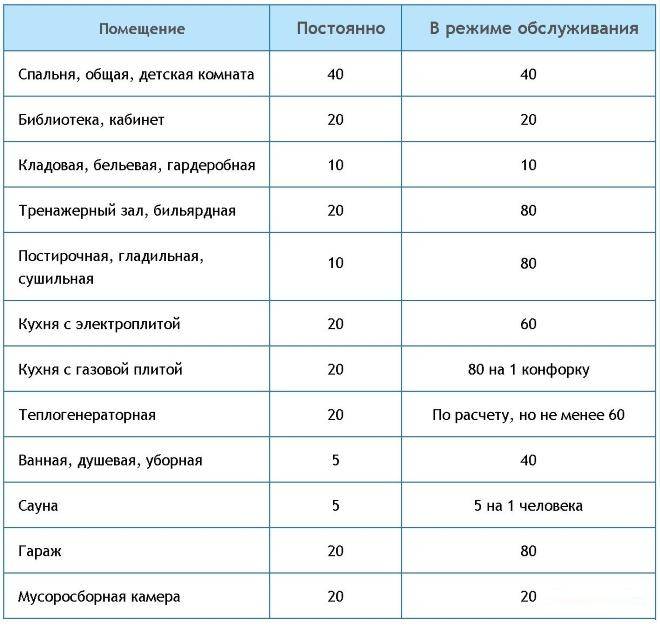
Air exchange rate, m 3 / h, not less than
Needs for clean air are most fully regulated and are accordingly presented in SNiPs 2.04.05-91.
Distribution of air masses by multiplicity
The concept of multiplicity refers to the frequency of air changes in a particular room.
The indicator under consideration involves taking into account such an important indicator as the volume of the room. For this purpose, tabular data for residential buildings are provided (we are talking about MGSN 3.01-96)
At the first stage, the terms of reference for the installation are drawn up. On the second - the TK is loaded into the program, data on the parameters of the room are entered. At the third stage, ventilation design is carried out.
List of current tabular data for private country houses, cottages and city apartments:
- bathroom - an influx of pure oxygen 3 cubic meters per hour for every 1 m2 of area, the hood should ensure the removal of 25 cubic meters of dirty masses every hour;
- bathroom - inflow - up to 3 cubic meters of clean air for each 1 m2 of the room, exhaust capacity - from 90 m3 / h;
- dining room and kitchen - inflow up to 3 cubic meters, with a discharge of 90 m3 / h;
- living room - inflow rate - from 1;
- change houses - supply - up to 3 cubic meters, extract with a multiplicity of 1.5.
Before starting the preparation of project documentation for a particular house or certain rooms of it, it is important to analyze the available system. Ventilation design takes a lot of time, and most importantly - financial resources
For the same kitchen, only an air supply unit may be required to provide the interior space with fresh oxygen.
The final data must fully comply with sanitary and fire safety standards, not to mention economic feasibility.
How is the calculation carried out
Generally speaking, the volume of oxygen is initially calculated for each room, and then for the whole house. This is done in a simple way: the length, width and height are multiplied. The program allows you to automate this process.

Formulas for calculating aerodynamic performance
- The optimum level of air exchange is calculated for each room. Everything is carried out according to a simple formula: L \u003d n * V, where V is the volume of a room or any room, n is the oxygen exchange rate.
- The data from paragraph 1 are calculated for all premises of the apartment, both in terms of the value of the hood and the inflow. Specialized programs do all the calculations automatically.
- Ideally, the preparation of technical specifications with balanced values ∑ Lpr = ∑ Lout.
Only after this is the design of the ventilation system carried out either manually or by means of a program.
Regulation for the low-rise sector SP 55.13330.2016
This is one of the main sets of rules applied to the design development of residential buildings with one apartment. The standards for ventilation of a private house collected in it relate to the design of autonomously located residential buildings, the height of which is limited to three floors.
A comfortable microclimate is created in the interior of the building with the help of ventilation equipment. Its characteristics are given by GOST 30494-2011.
In most cases, an individual house is heated by an autonomous heating boiler. It is installed in rooms with good ventilation on the first or basement floors. Possibility of accommodation in the basement of the cottage.With a heat generator power of up to 35 kW, it can be installed in the kitchen.

The design of any building, regardless of its area, number of storeys, purpose, without fail includes the section "Ventilation" with the development of a scheme, calculations and recommendations for construction
If the heating unit is running on gas or liquid fuel in the boiler house, measures are taken to insulate equipment and pipelines under the terms of SP 61.13330.2012.
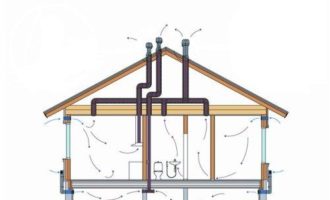
The collection offers three principles for ventilation:
- The exhaust air is removed from the premises by natural draft through the ventilation ducts. The influx of fresh air occurs due to the ventilation of the rooms.
- Supply and removal of air mechanically.
- The intake of air in a natural way and the same removal through the ventilation ducts and the incomplete use of mechanical force.
In individual houses, air outflow is most often arranged from the kitchen and bathrooms. In other rooms it is organized on demand and need.
The flow of air from kitchens, bathrooms, latrines with strong and not always pleasant odors is removed immediately to the outside. It must not enter other rooms.
For natural ventilation, windows are equipped with vents, valves, transoms.
An important advantage of the supply and exhaust system is the stability of operation, which does not depend on temperature and air density within the room and outside the window.
The efficiency of ventilation equipment is calculated taking into account a single change of air for one hour in rooms with a constant presence of people.
Minimum volume of air escape in operating mode:
- from the kitchen - 60 m3 / hour;
- from the bathroom - 25 m3 / hour.
The air exchange rate for other rooms, as well as for all ventilated rooms with ventilation, but when it is turned off, is 0.2 of the total cubic capacity of the space.

Air ducts laid in an open way are fixed to building structures using brackets. To reduce sound vibrations, the holders are equipped with noise-absorbing elastomer gaskets.
Cylindrical or rectangular air ducts are attached to building structures using various devices: hangers, brackets, eyes, brackets. All fastening methods must ensure the stability of the ventilation lines and exclude deflection of the ventilation pipes or ducts.
The surface temperature of the air ducts is limited to 40°C.
Outdoor appliances are protected from low negative temperatures. All structural parts of the ventilation system are provided with free passage for routine inspection or repair.
In addition, there are also collections of standards such as NP ABOK 5.2-2012. These are instructions for regulating the air circulation in the premises of residential buildings. They were developed by specialists of the non-commercial partnership ABOK in the development of the normative acts discussed above.
Tips for arranging natural ventilation
Each room in country buildings or a country house has features that must be taken into account when installing ventilation devices.
in the bathroom
For a toilet and a bathroom in a suburban building, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of micro-ventilation through windows or doors.
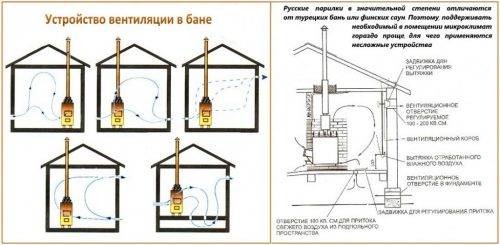
In the bath
When equipping ventilation in the bath, it is necessary to place the supply channel at the installation site of the furnace. Outdoor air penetrates from below, gradually displacing warm air to the ceiling, heating itself.The exhaust valve in the steam room is installed under the ceiling.
I open the valves if necessary to quickly dry the steam room or washing room.
In the boiler room
If a country house is heated by gas, it must provide a separate room for placing equipment. A gas boiler is an object of increased danger, therefore, the requirements for equipping a boiler hood are quite serious.
The ventilation of the boiler room is mounted separately and does not cut into a common exhaust pipe; most often, an external pipe is used to get rid of smoke and gas.
Supply air devices are used to deliver outside air to boiler rooms. The weak point of the natural type supply and exhaust system in boiler rooms is the dependence on wind power. In quiet, calm weather, it is impossible to provide good traction.
 Turning the ventilation ducts reduces efficiency by 10%.
Turning the ventilation ducts reduces efficiency by 10%.
In living rooms
To ensure efficient air circulation between individual rooms in the house, it is necessary to arrange small holes or gaps between the door leaf and the floor in the lower part of the door panels.
In the kitchen
When installing an exhaust ventilation grille above the stove, it is necessary to place this device at a distance of 2 meters from the floor. This position of the hood allows you to effectively remove excess heat, soot and odors, preventing them from spreading around the room.
Design technology
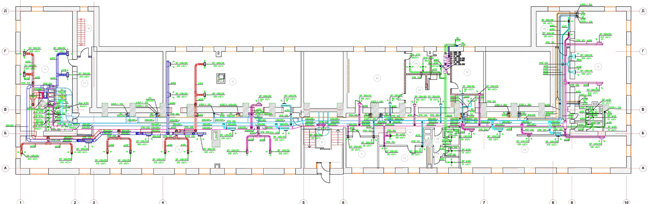
The technology of network design with the creation of an electronic database is used, which significantly reduces time, costs and risks in the development of projects.
Such organization of the process contributes to the optimization of the full range of works: design, assembly, shipment, installation, integration and programming, documentation.
The documentation development process is carried out using advanced software technologies and allows the maximum automation of thermal, hydraulic, aerodynamic and acoustic calculations and optimization of technical solutions to achieve high quality and reliability.
The project is carried out in accordance with the requirements:
- sanitary requirements
- building and architectural requirements
- fire safety requirements
- operational requirements
- equipment reliability
- economic efficiency
All design solutions are carried out in accordance with the requirements of building codes and regulations, GOSTs, sanitary and hygienic, fire and other standards in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.
| enlarge + |
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
With specificity air exchange system devices according to the natural scheme, the following video will introduce:
Normal air exchange has a positive effect on human health, increases the efficiency of the brain, counteracts the onset of symptoms of lethargy, weakness and sleepiness, and also prevents the appearance of dampness, fungus and mold in the house.
Do you want to talk about how you arranged the ventilation system of your own house or cottage? Do you want to share useful information on the topic of the article? Please leave comments in the block form below, post photos and ask questions.