- Calculation of the number of radiator sections
- Scope of floor radiators
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Varieties of floor batteries
- Choosing a specific radiator model
- We calculate the thermal power
- Determine the required dimensions
- The final stage of the purchase of radiators
- Batteries in the floor: step by step instructions
- Convectors
- Cast iron batteries
- The device of a solid and sectional radiator
- Aluminum
- 4 Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum radiators
Calculation of the number of radiator sections
The thermal power of the radiator section depends on its overall dimensions. With a distance between the vertical axes of 350 mm, the parameter fluctuates in the range of 0.12-0.14 kW, with a distance of 500 mm - in the range of 0.16-0.19 kW. According to the requirements of SNiP for the middle band per 1 sq. meters of area, a thermal power of at least 0.1 kW is required.
Given this requirement, a formula is used to calculate the number of sections:
where S is the area of the heated room, Q is the thermal power of the 1st section and N is the required number of sections.
For example, in a room with an area of 15 m 2, it is planned to install radiators with sections of thermal power of 140 W. Substituting the values into the formula, we get:
N \u003d 15 m 2 * 100/140 W \u003d 10.71.
Rounding is done up. Given the standard forms, it is necessary to install a bimetallic 12-section radiator.
Important: when calculating bimetallic radiators, factors that affect heat loss inside the room are taken into account. The result obtained is increased by 10% in cases where the apartment is located on the first or last floor, in corner rooms, in rooms with large windows, with a small wall thickness (no more than 250 mm). A more accurate calculation is obtained by determining the number of sections not for the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, but for its volume
According to the requirements of SNiP, a thermal power of 41 W is required to heat one cubic meter of a room. Given these rules, get:
A more accurate calculation is obtained by determining the number of sections not for the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, but for its volume. According to the requirements of SNiP, a thermal power of 41 W is required to heat one cubic meter of a room. Given these rules, get:
where V is the volume of the heated room, Q is the thermal power of the 1st section, N is the required number of sections.
For example, a calculation for a room with the same area of 15 m 2 and a ceiling height of 2.4 meters. Substituting the values into the formula, we get:
N \u003d 36 m 3 * 41 / 140 W \u003d 10.54.
The increase is again carried out in the big direction. a 12-section radiator is required.
The choice of the width of the bimetallic radiator for a private house is different from the apartment. The calculation takes into account the coefficients of thermal conductivity of each material used in the construction of the roof, walls and floor.
When choosing sizes, the requirements of SNiP for battery installation should be taken into account:
- the distance from the top edge to the window sill must be at least 10 cm;
- the distance from the bottom edge to the floor should be 8-12 cm.
For high-quality space heating, it is necessary to pay attention to the choice of sizes of bimetallic radiators.The dimensions of the batteries of each manufacturer have minor differences, which are taken into account when buying. Correct calculation will avoid mistakes
Correct calculation will avoid mistakes.
Find out what the correct dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators should be from the video:
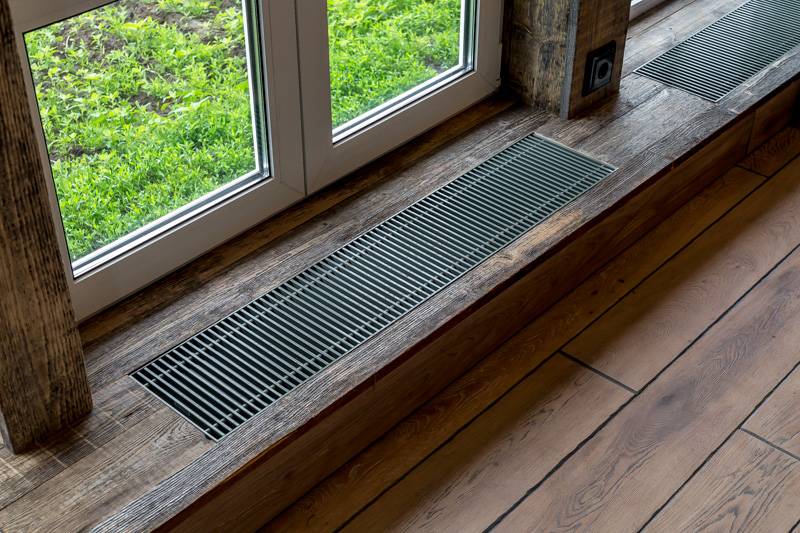
Scope of floor radiators
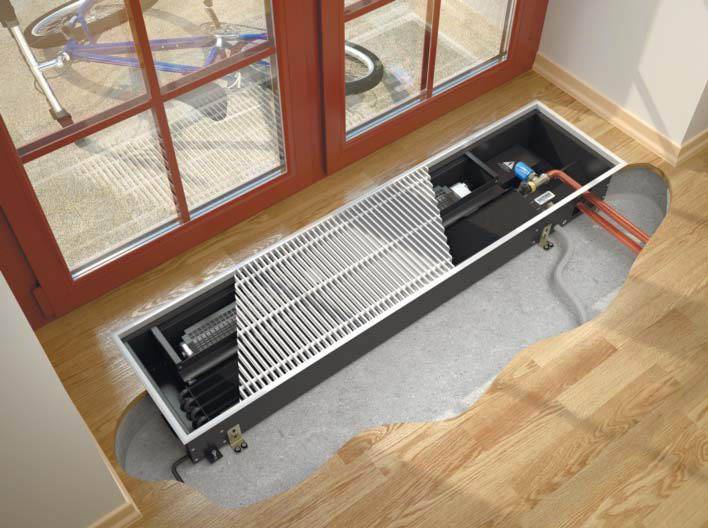
To begin with, let's figure out where they use heating devices that are installed on the floor.

Water floor heating batteries are advisable to use in such cases:
- In rooms where, for one reason or another, it is not possible to install traditional wall-mounted radiators. This often happens in houses where the walls are made of loose material (aerated concrete, foam concrete) or sheathed with drywall. Even light aluminum devices cannot be hung on them.
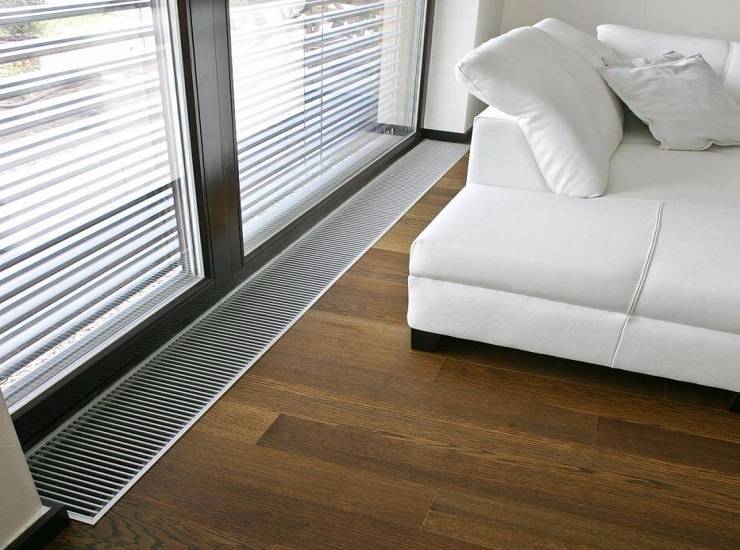
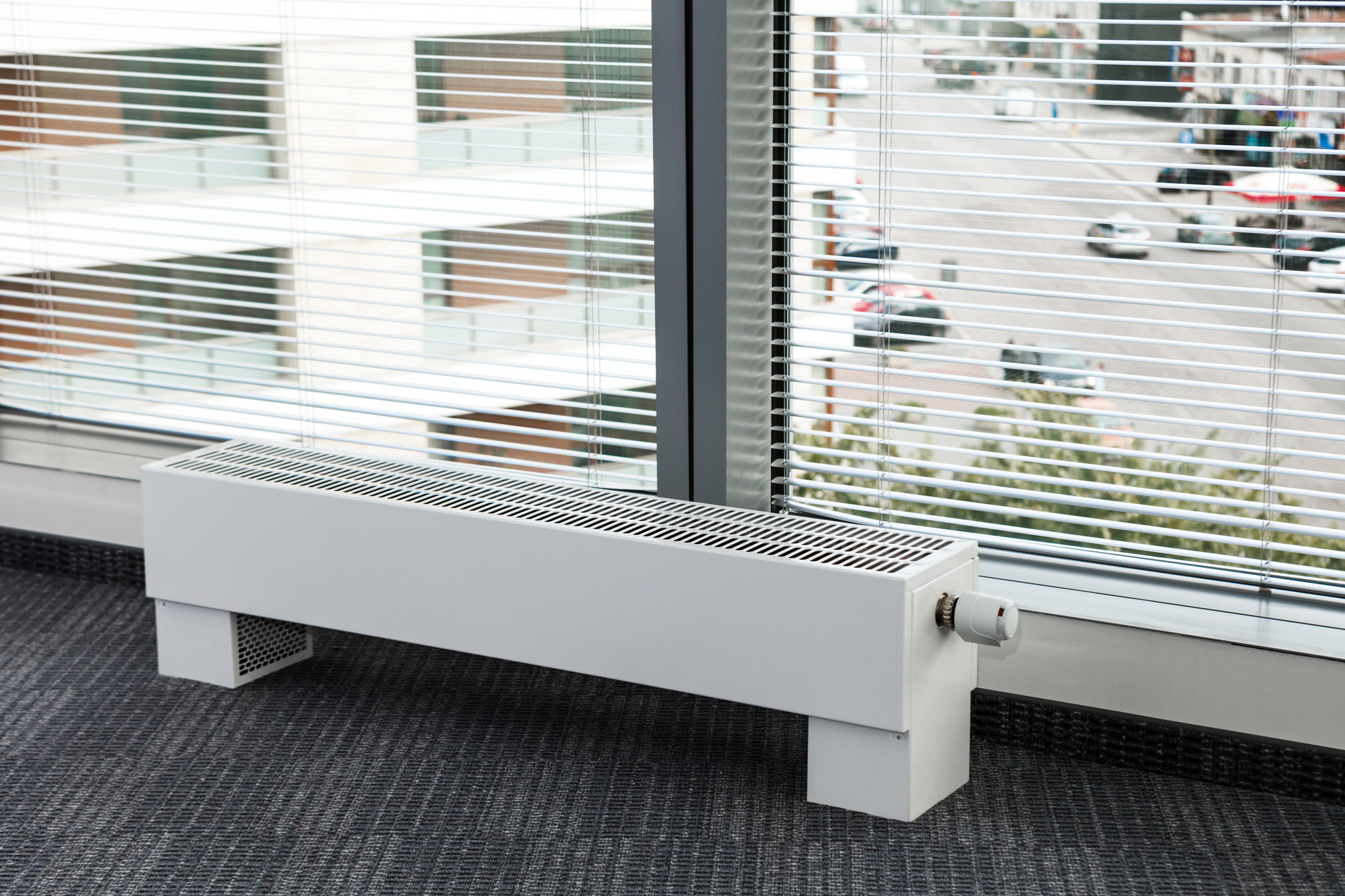
- In shop windows and shopping malls, low floor heating radiators are used for panoramic windows. Such glazing cannot be left without a thermal curtain, because condensation will accumulate on the windows and frost will form.
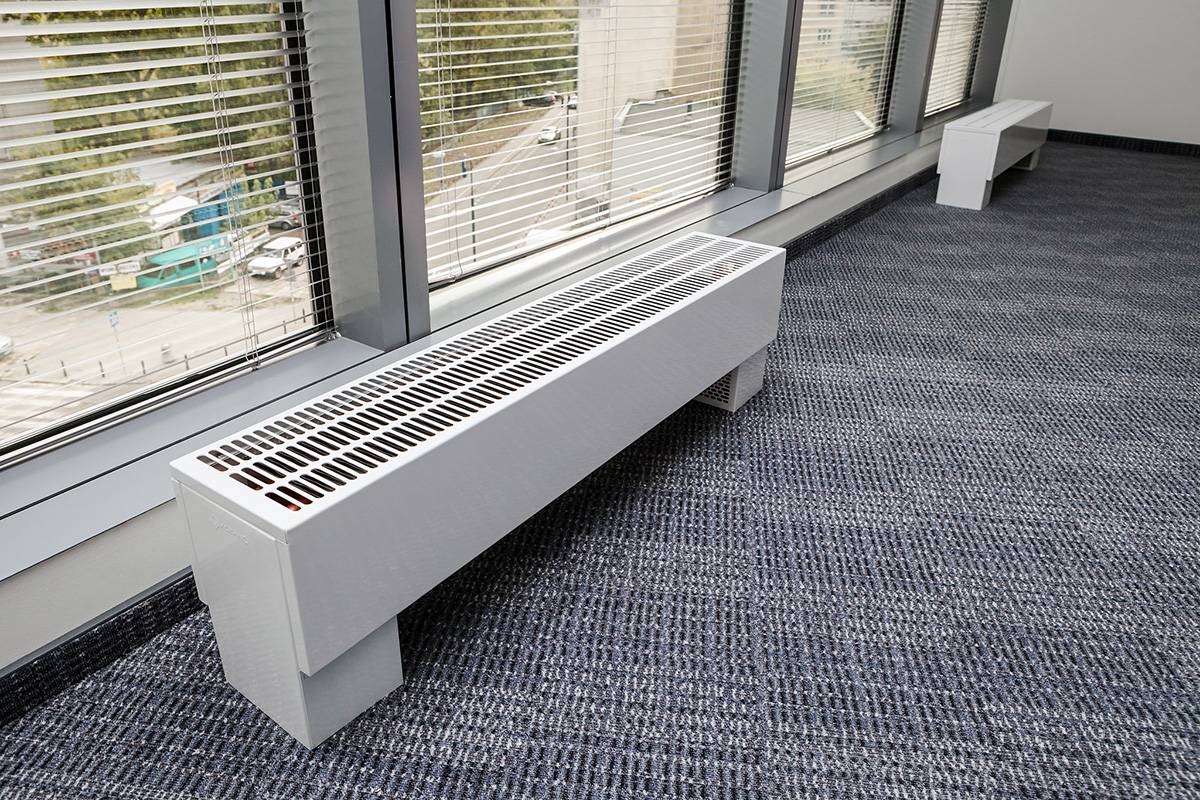
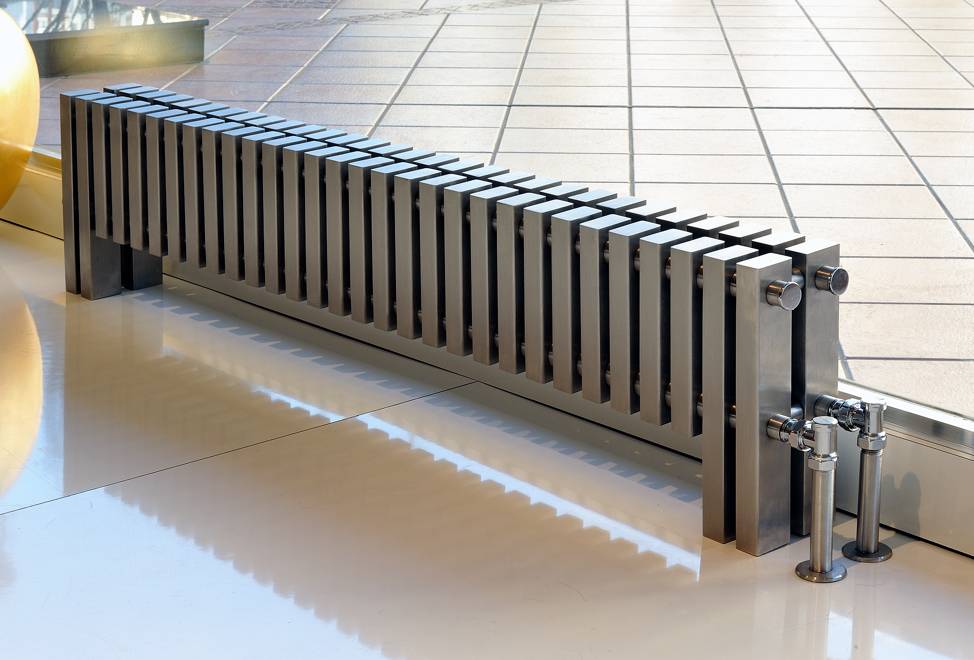
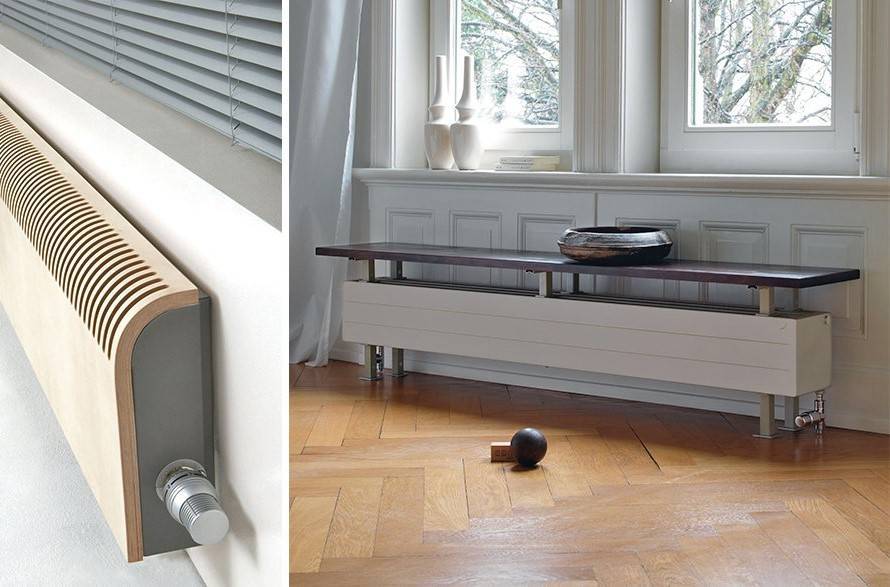
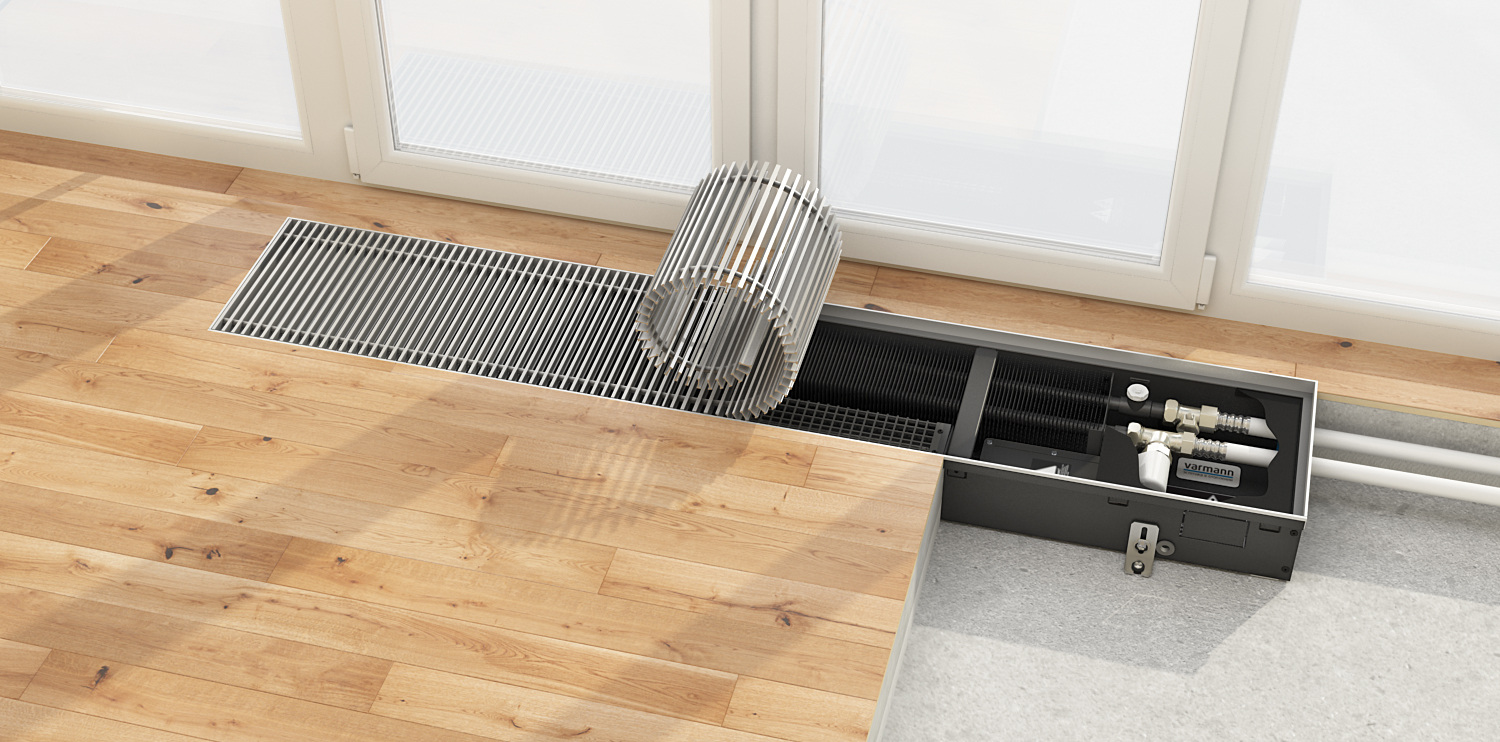
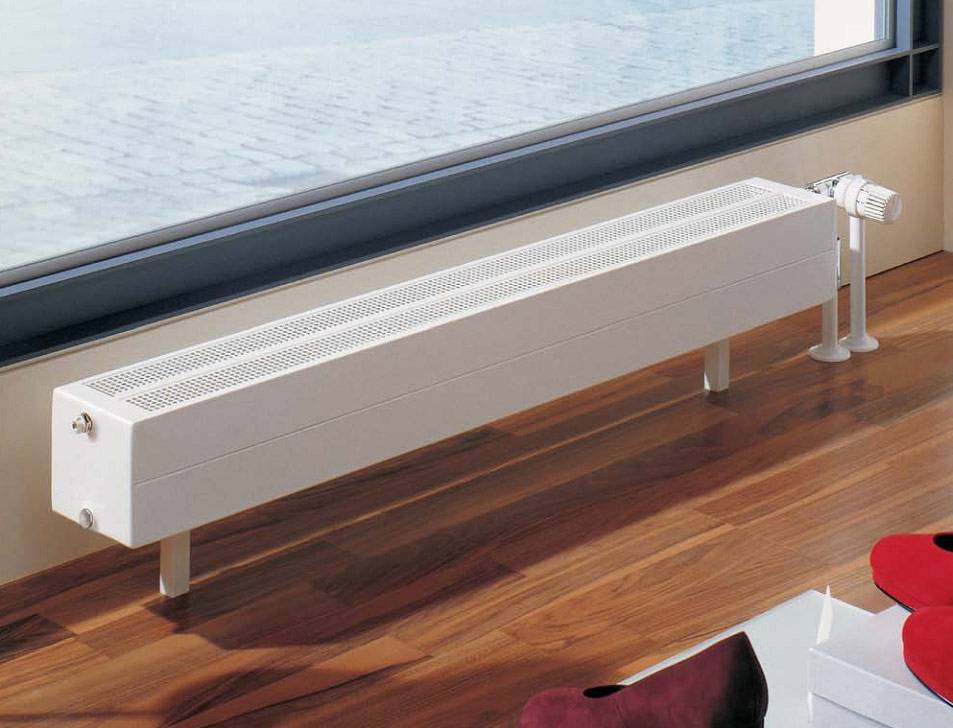
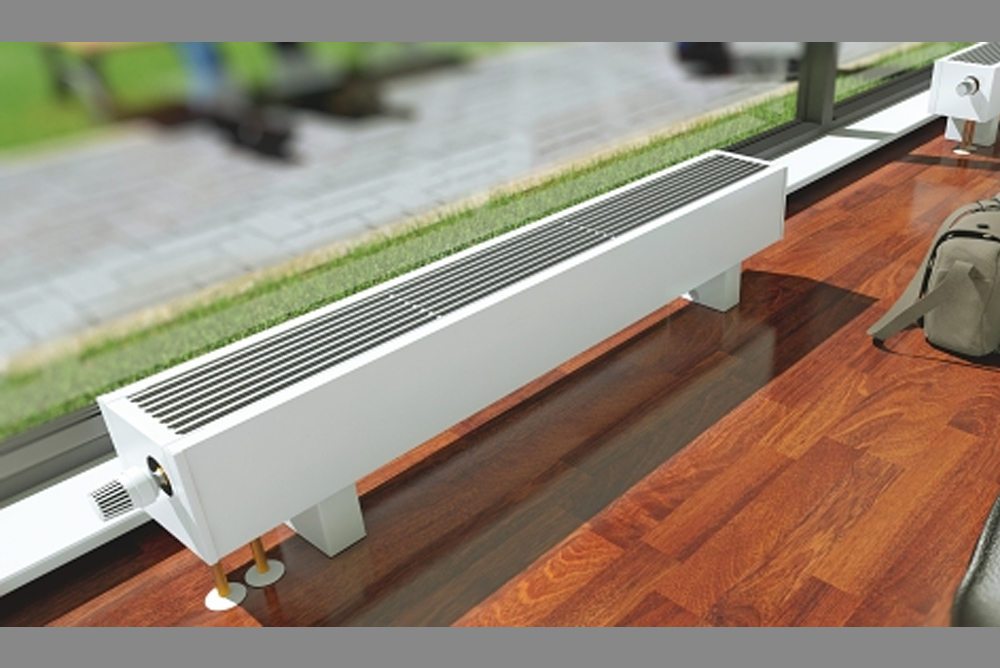
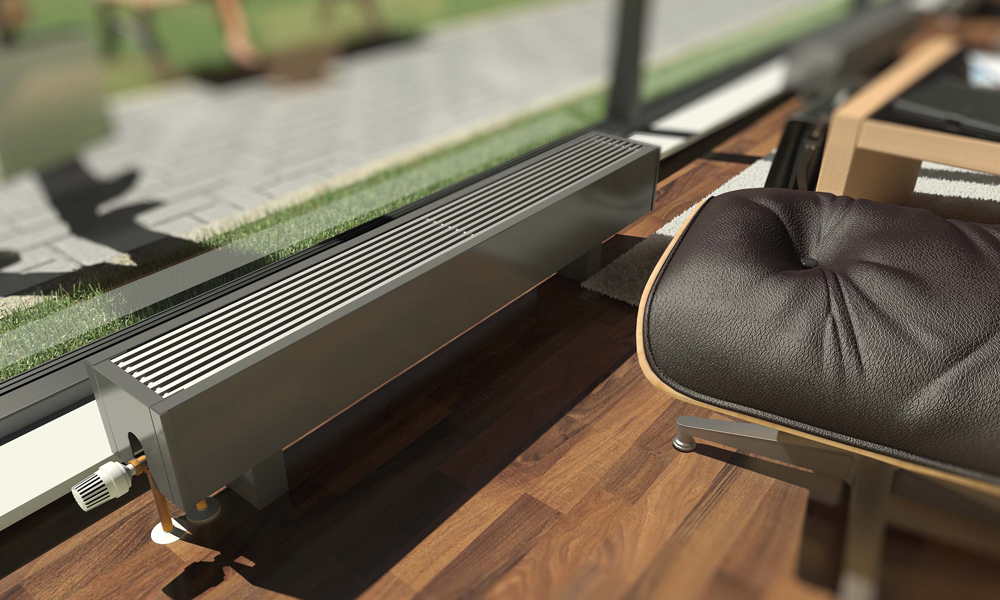
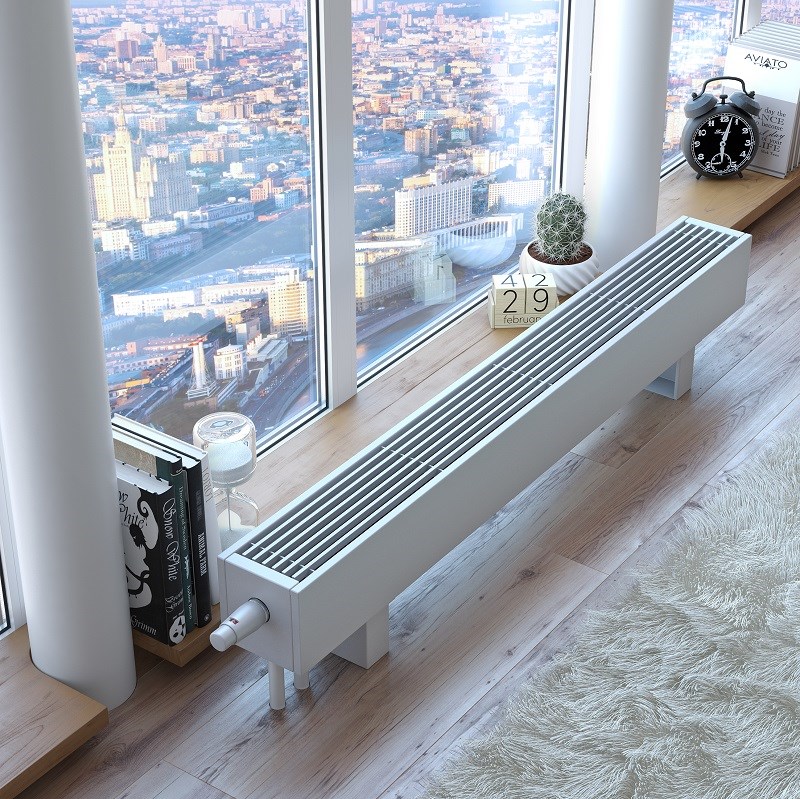
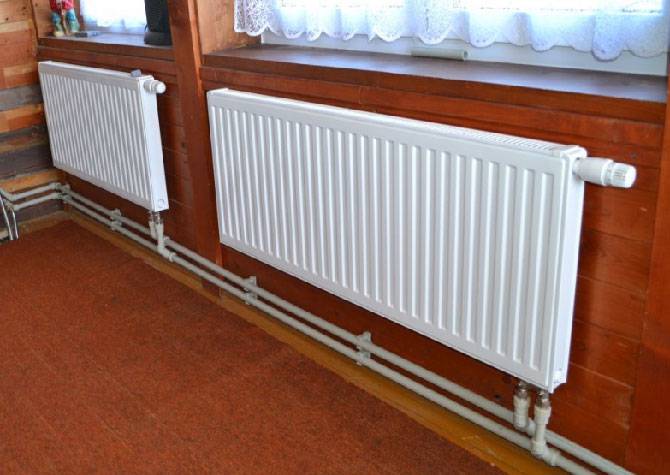
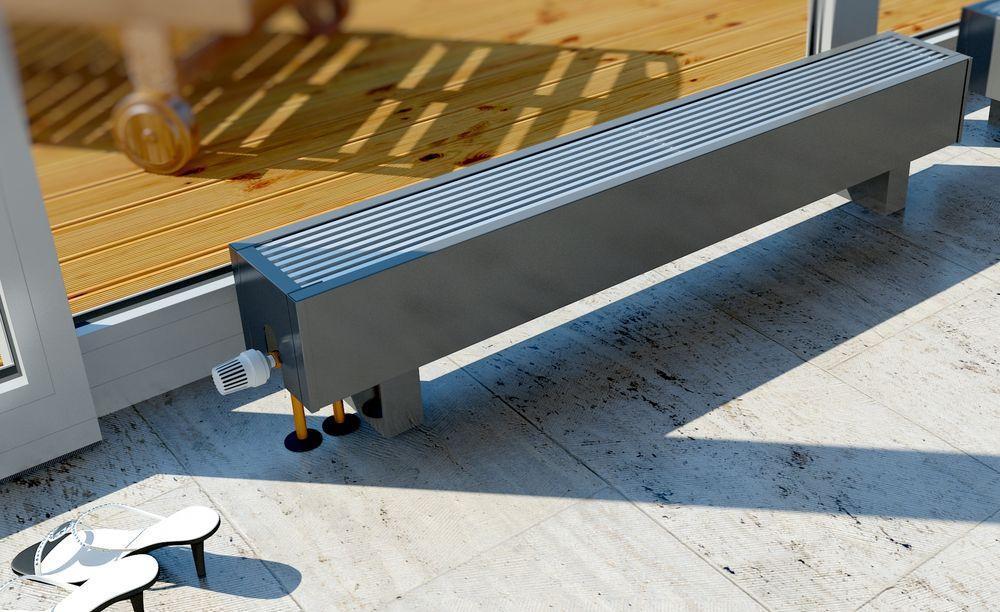
Unlike mounted heating units, floor batteries are installed only on the floor, they are not mounted on walls. The height of these devices is less than that of their sectional counterparts. The stand for the unit is rigidly attached to the floor.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages that low heating radiators have include the following:
- the unit can be mounted anywhere, regardless of the height of the windows;
- low heater saves space in the room;
- thanks to the stylish design and attractive appearance, the battery does not spoil the interior of the room, fits into any room design;
- can be mounted in a room with panoramic windows to create a thermal curtain in front of them;
- during installation, the material and strength of the walls does not matter, because the batteries are not attached to them.
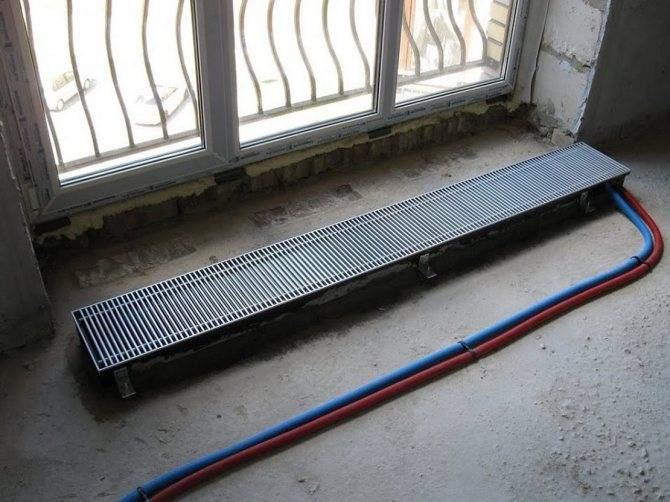

There are also disadvantages of such heating devices, they are as follows:
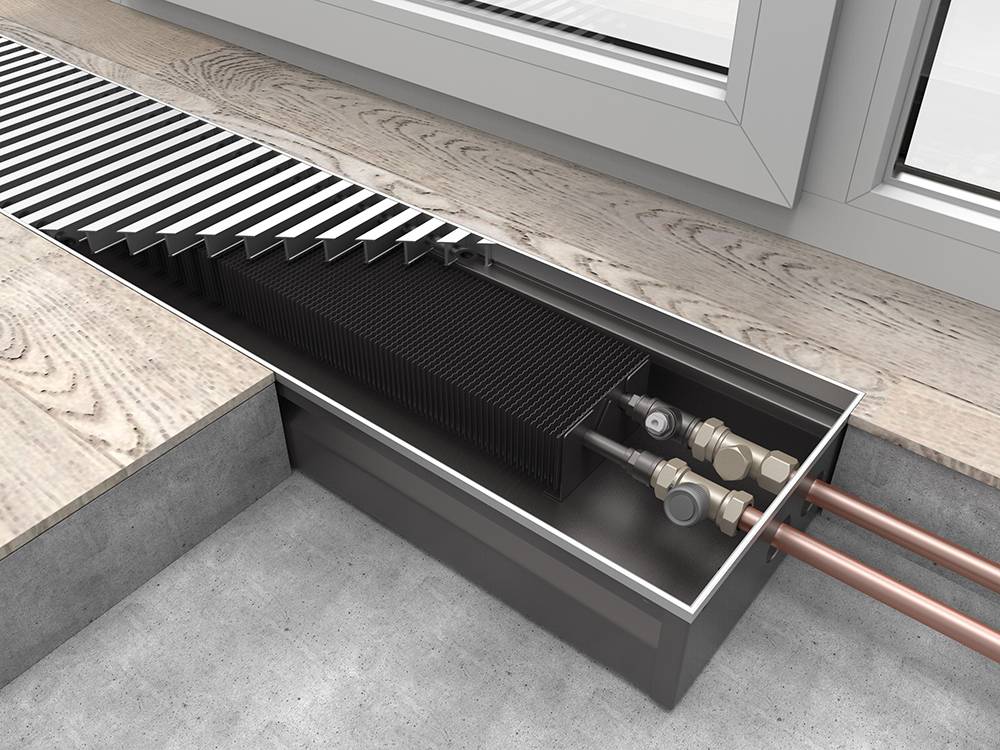
- To connect the battery to the heating system, you need to lay pipes in the floor screed, because they will interfere with the arrangement of furniture. Hidden laying of pipelines is considered not the best option, because it is more difficult to maintain and repair networks.
- The heat from these heating devices is distributed unevenly, so the unit is not suitable for heating rooms of considerable height. At the same time, some parts of the room may not be heated at all.
- Due to the hidden laying of pipelines, the floor screed in the room is made to a certain height, which creates difficulties when attaching radiators.
A significant disadvantage of floor heating units is that they are more expensive than sectional mounted batteries, and the room is heated worse.
Varieties of floor batteries
All horizontal heating radiators that are mounted on the floor are divided into several types depending on the material of execution:
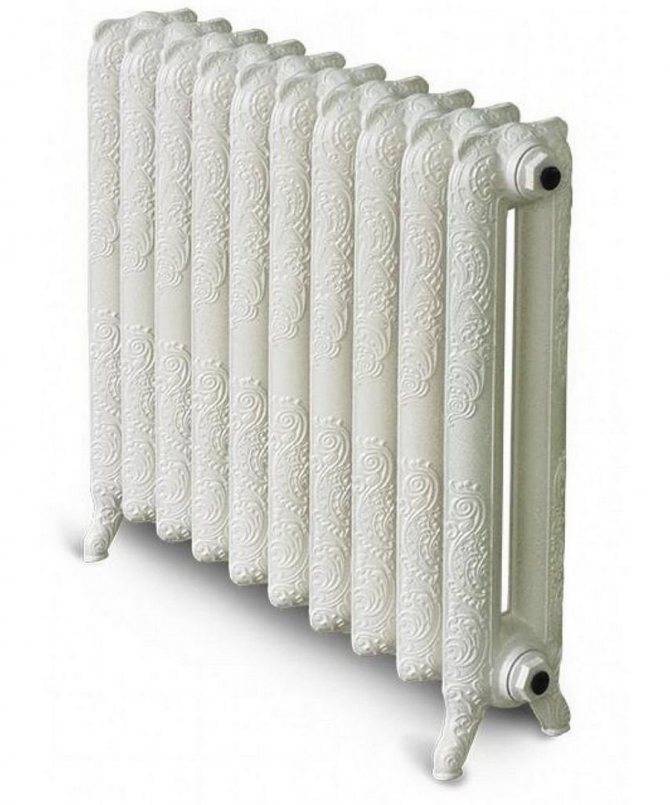
Cast iron batteries have been widely used in the last century, but they cannot boast of aesthetic appeal. Their main disadvantage is that the structure quickly silts up inside, so it needs to be cleaned regularly (about once every three years). Under mechanical stress, cast iron can crack. The same thing happens with hydraulic shocks.
Steel radiators are more popular today.They are quite durable and attractive in appearance. However, steel plate instruments often leak around the weld.
The most reliable and beautiful bimetallic units. Inside the aluminum case is a steel core. Due to this, the heat transfer of the device is quite high, and the optimal strength allows you to mount them in centralized networks with high pressure.
Aluminum batteries are the lightest, but they are not designed for high network pressure, therefore they are used only in autonomous systems.
It is important to carefully select the material of pipes and fittings, because aluminum forms galvanic couples with some metals.

By design, floor units are panel and sectional. Panel batteries are made only from steel, while sectional batteries are made from bimetal, cast iron or aluminum. In addition, all heaters come in different heights.
Choosing a specific radiator model
After you have decided on the type and type of heating radiators you need, it's time to calculate and select specific models of these radiators that will have the necessary technical parameters.
We calculate the thermal power
And how to choose the right heating radiators to achieve the proper level of warmth and comfort? To do this, you need to calculate the thermal power of the radiators planned for purchase. For certain standard conditions, a heat output of 0.09 to 0.125 kilowatts per square meter of space is required. It is this power that should be enough to create optimal climatic conditions in the room.
Now about what is meant by standard conditions.It's simple, it's a room that has a window with a wooden frame and three-meter (not higher) ceilings, as well as an entrance door. At the same time, hot water of a seventy-degree temperature flows through the heating pipes. If you have the same conditions, then multiplying 0.125 by the area of the room you will get the power of the radiator or radiators (if you need several) necessary for the room. Then it remains to look at the passport of specific radiators and, having learned there the thermal power of one section or the entire radiator, select the required model.
But this is a simple calculation, in fact, it is necessary to take into account some other factors that will have an influence in this case:
- You can reduce the power of radiators by 10 - 20% if you have plastic energy-saving double-glazed windows installed in your room, because they reduce the heat loss of the room by about that much.
- If there are not one, but two windows in the room, then you need to put a radiator under each of them. Their combined capacity should exceed the standard by 70%. We will do the same in the case of a corner room.
- With an increase or decrease in the temperature of hot water for every 10 degrees, the power of the device is also increased (or reduced) by 15-18%. The thing is that if the temperature of the coolant decreases, then the power of the heating radiators drops.
- If the ceilings are higher than three meters, the heat output must be increased again. The increase must be made as many times as many times higher for 3 meters the ceilings in the room. If the ceilings are lower, then you need to make a decrease.
When calculating, we will take into account how our radiators will be connected. Here are some recommendations for this:
- If the coolant enters the radiator from below and exits from above, then heat will be lost decently - from 7 to 10%.
- The lateral one-way connection makes it unreasonable to install radiators with a length of more than 10 sections. Otherwise, the last sections from the pipe will remain almost cold.
- Increases heat transfer by 10 to 15 percent by gluing a special reflective insulating material to the wall behind the radiator. For example, it may be a material such as Penofol.
Determine the required dimensions
When buying a radiator, you need to know exactly the following points:
- What type of eyeliner do you have - hidden or open;
- How pipes are connected to the radiator, from the floor, from the wall, from above, from the side, etc.;
- Diameter of heating pipes;
- Distance between pipes (centre distance).
We also provide for such a placement of the radiator so that the air can flow around it freely - otherwise the room will not receive 10 to 15% of the heat. The norms for the placement of radiators are as follows:
- The distance of the radiator from the floor is from 7 to 10 cm;
- distance from the wall - from 3 to 5 cm;
- distance from the window sill - from 10 to 15 cm.
Basic rules for the placement of radiators.
The final stage of the purchase of radiators
Now, if you have autonomous heating, you can, taking these calculations with you, feel free to go to the store for heating appliances. But for residents of a high-rise building with a centralized CO, it makes sense to first go to the DEZ, having found out what the working pressure is in your heating system. We will build on this parameter, deciding which heating radiator is better to choose. The pressure indicated in the passport of the device must be higher than that named by the employees of the DEZ in order to get a certain margin.After all, do not forget that in each new season, heating devices are tested with pressure, which is 1.5 times more than the working one.
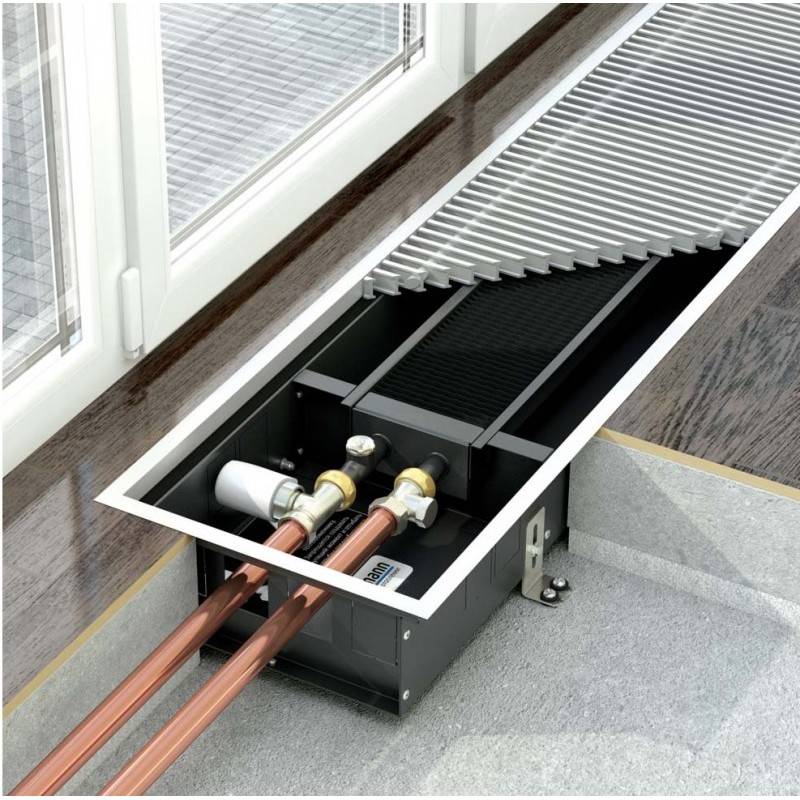
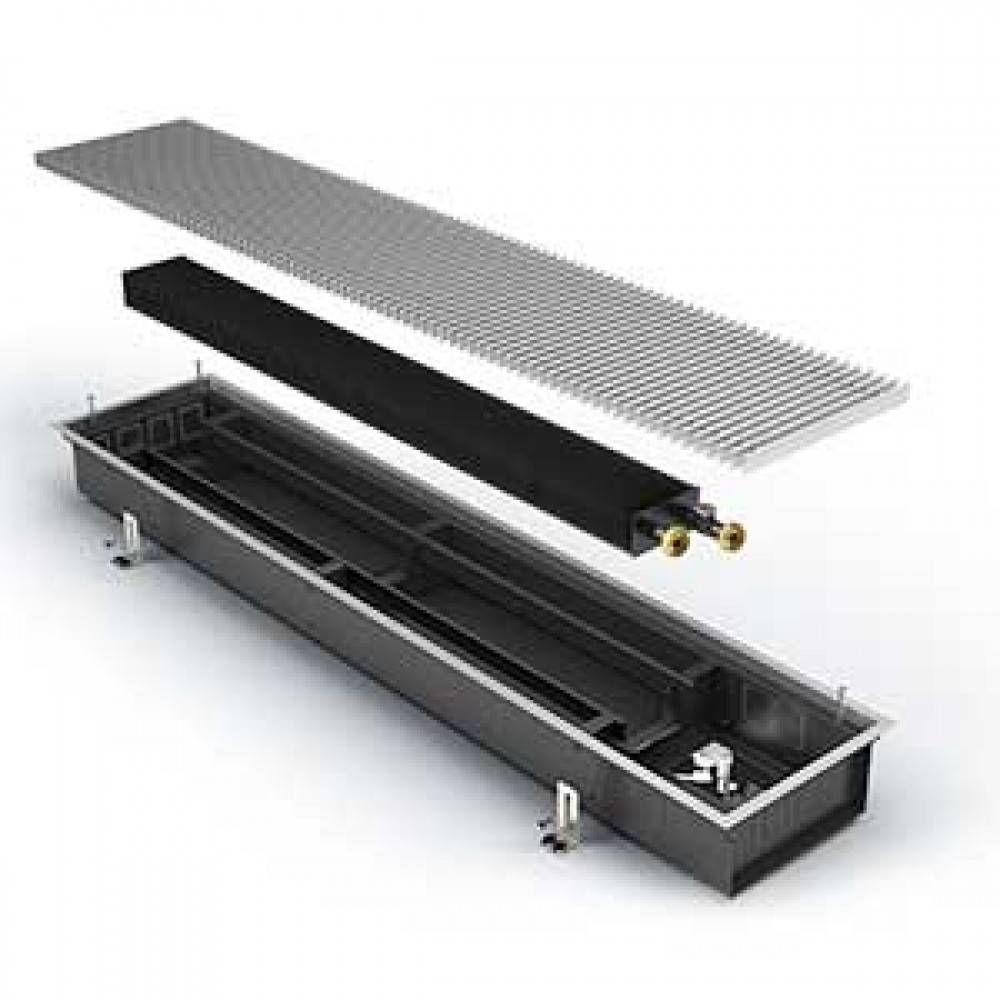
Batteries in the floor: step by step instructions

Before direct installation, you need to make sure that you have enough knowledge and experience to properly install, connect and configure everything. Typically, companies selling heating systems offer their specialists who will do everything with high quality, as well as with a guarantee.
When there is a desire to install, connect and configure the underfloor battery system, you can use the step-by-step instructions:
- Connect the heating medium (that is, pipes) or stretch the cable for the electric floor convector.
- Mount the channel-niche for the radiator;
- Fill the floor;
- Install batteries in the floor;
- Adjust its height with special bolts;
- Fix the entire structure, seal, and also isolate the space between the metal box and the channel walls;
- Mount the final finishing floor;
- Connect to the central heating system or power supply;
- Seal all cracks with silicone sealant;
- Close the battery with a grill.
When the installation work is completed, it remains to check the health of the heating system inside the floor, as well as adjust the heating temperature. When everything is done correctly, it will be felt immediately. If something does not work, then you need to find out what is wrong. And fix it!
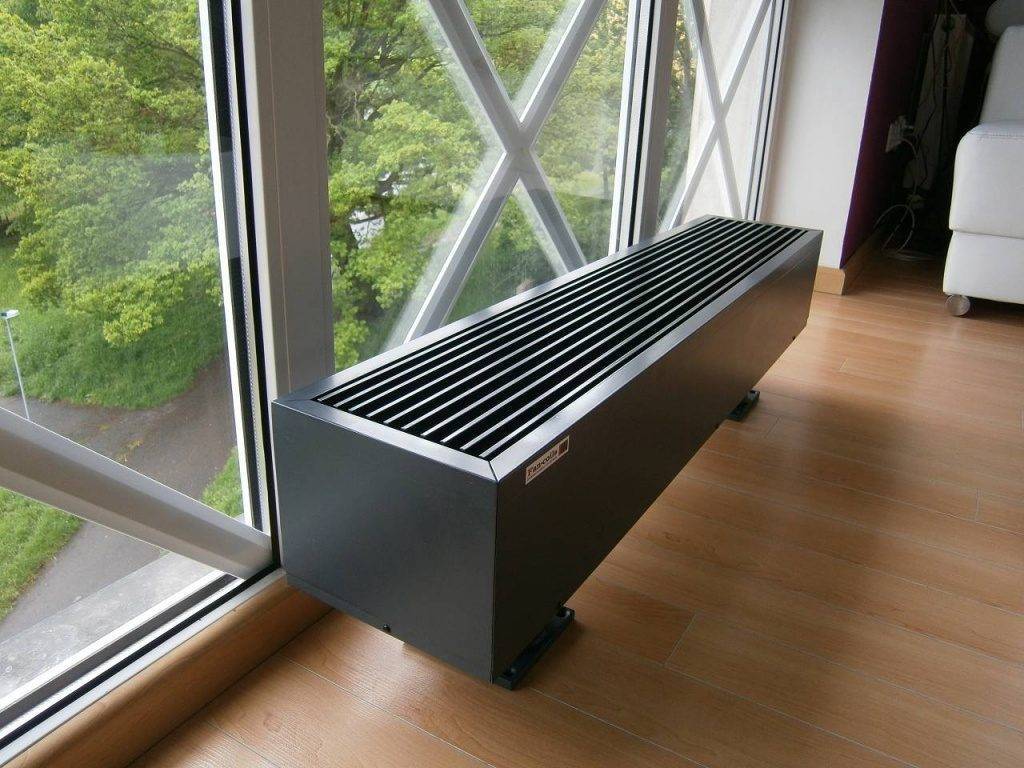
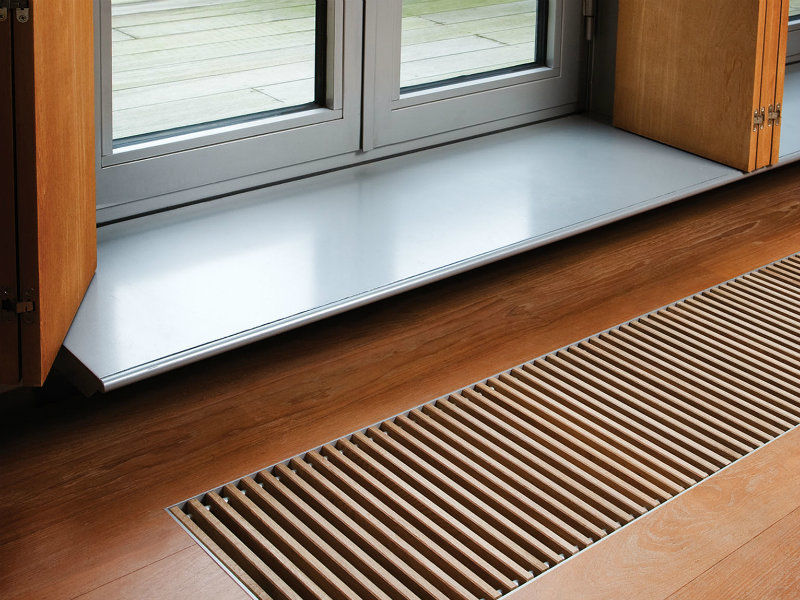
Convectors
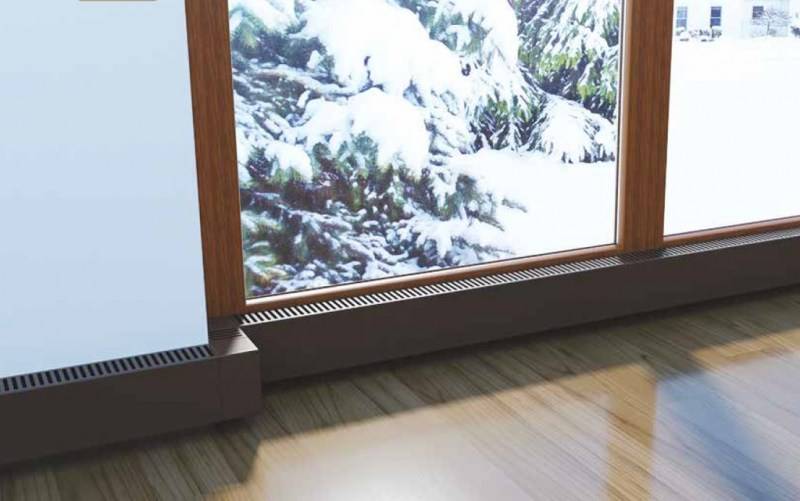
Recently, floor-to-ceiling glazing has become increasingly popular. Really beautiful, but what about the heating .... question.You can put low radiators on legs, but then all the chic is smeared. That's when floor convectors are used. Under them, a niche is made in the floor and the device itself is installed on the floor, closing it with a grate. In order to increase heat transfer at the same time (necessary for a period of cold weather), fans are built inside. The solution is aesthetic, but such systems cost decently. There is another nuance - fans, even the quietest ones, are noisy. This noise does not annoy someone, it bothers someone very much. In any case, there are more and less noisy models.

Floor convector - output for heating floor-to-ceiling French windows and glass doors
So, if you need to heat a French window from floor to ceiling, the best option is a convector built into the floor.
Cast iron batteries
The oldest of heating appliances. They are distinguished by high reliability, long service life, calmly tolerate overheating of the coolant (up to + 135 ° C), normally respond to water hammer. All because of the fact that they have thick walls. But the large thickness of the metal is not only pluses, there are also minuses. The first is a large mass. Not all modern building materials can support the weight of cast iron. Let today they are far from being as heavy as in the days of the USSR, but still much more massive than all the others. A large mass is also a difficulty in transportation and installation. Firstly, powerful hooks are required, and secondly, it is desirable to mount them together - the mass of a radiator for 6-7 sections is 60-80 kg. But that's not all. A large mass of metal means high heat capacity and significant inertia. On the one hand, this is a minus - until the batteries warm up, it will be cold in the room, but on the other - a plus, because they will cool down for a long time.There is one more minus in high inertia - cast-iron batteries are inefficient in systems with thermostats. All this together leads to the fact that cast-iron heating radiators are not installed very often today.

This is only a small part of modern cast iron radiators.
But they have their own scope - high-rise high-rise buildings. If the number of storeys is higher than 16, high pressure is created in such systems, which only cast iron and some types of bimetallic radiators (full bimetal) are able to withstand. Their properties are also optimal in heating systems of private houses and cottages with conventional solid fuel boilers without automation. These boilers have a cyclic principle of operation, then heating the coolant to a boiling point or even higher, then cooling down. Cast iron normally reacts to high temperatures, and also smooths out temperature differences due to inertia.
Until recently, cast-iron heating radiators had an unattractive appearance - the well-known and long-bored "accordion". Today there are models that look like aluminum or bimetallic ones - with smooth front edges, painted with powder enamel (most often white). There are many designer models, mostly on legs, decorated with cast ornaments. This option is generally available only in cast iron, all the rest have basically a more strict, ascetic design.
The device of a solid and sectional radiator
The device of the heating battery largely depends on what material was used:
classic cast iron radiators suggest the presence of 1 or 2 channels for the circulation of the coolant.They are produced, as a rule, sectional, individual sections are connected to each other through a nipple with left and right threads on different sides;

Cast iron batteries are also available in sectional
- aluminum models are distinguished by the fact that even each individual section can consist of several elements. Naturally, a greater number of joints is not in favor of durability;
- steel sectional radiator is characterized by high strength and the ability to withstand high pressure in the heating system. Also, the operating temperature of the coolant can be increased to a temperature above 100ᵒС. As for the types of construction, it can be sectional, panel and tubular (register), steel allows manufacturers to use practically the type of construction;
- Recently, bimetallic radiators have become popular, in which the coolant circulates through steel pipes, but the fins are made of aluminum pipes. A combination of copper + aluminum can also be found.

The photo shows that the aluminum fins are placed on top of the steel pipe.
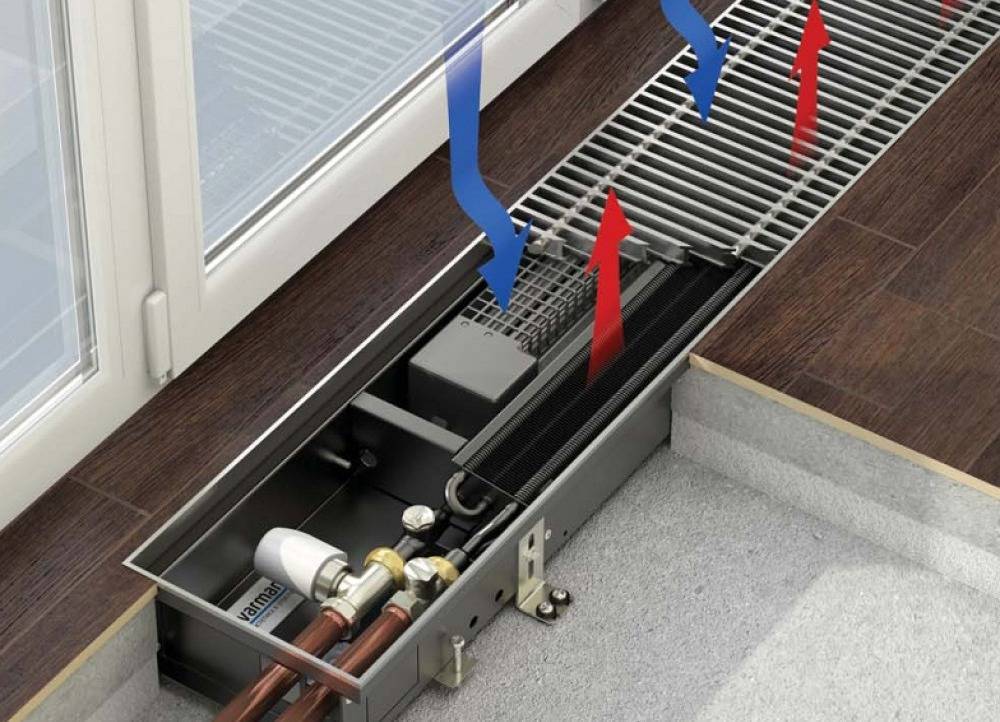
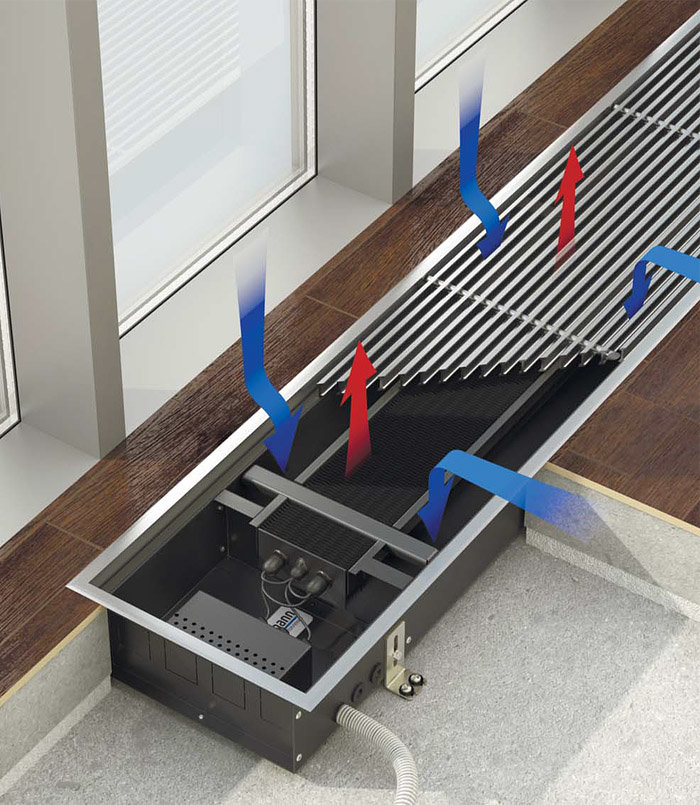
The use of aluminum fins allows to reduce weight and ensure fast heating of the radiator. In modern models, the design of the fins is optimized so that the air moves in the direction from bottom to top. That is, cold air is taken in at the bottom, and already heated air comes out at the top.
Air movement pattern
Of the design features, the presence of additional stiffeners between aluminum plates can be noted.Manufacturers write this down as an advantage of their radiators, but in fact there is no particular benefit from this innovation, and the price increases slightly. Still, most batteries simply hang on the wall and do not experience significant mechanical stress during operation, so high structural rigidity is simply not needed.
Aluminum
Aluminum heating radiators are not made of pure aluminum, but of an alloy based on it. This metal was not chosen by chance, as it has one of the highest heat transfer coefficients - 4-4.5 times better than cast iron and 5 times better than steel.
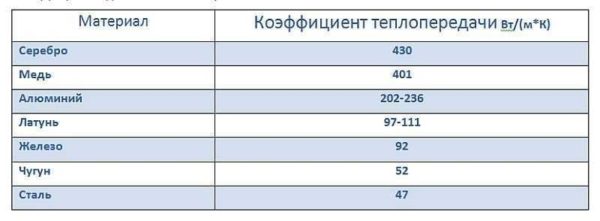
Table with thermal conductivity coefficients of different metals
Therefore, aluminum radiators are distinguished by high power (180-190 W per section), at least a high heating rate and low inertia. They work very effectively in tandem with thermostats, allow you to maintain a stable temperature with an accuracy of one degree. The advantages of aluminum radiators include their low weight (one section weighs 1.5-2 kilograms), which facilitates delivery and installation. Another positive point is that the shape is designed in such a way that it has a large cross-section of channels for the coolant (slightly smaller than that of cast-iron "accordions"). This is good, since there is a low probability that these channels will become clogged and the radiator will stop heating.
Now about the disadvantages of aluminum radiators. They are related to the properties of aluminum. As you know, it is a reactive metal. It actively interacts with most of the chemical table, and reacts especially violently with copper. And in modern heating systems, copper parts are common.Such a neighborhood threatens the rapid exit of the copper parts of the system and system, as well as increased gas formation. They learned how to deal with gases - they put automatic gas vents (valves) in the systems, and they save copper by not putting it close to aluminum appliances. The process, of course, still goes on, but not with such intensity.

Aluminum radiators look modern
The chemical activity of aluminum is also manifested in the demands on the quality of the coolant. Not in the sense of its contamination, but in the sense of its acidity. Aluminum radiators work normally in systems with a coolant acidity not higher than 7 (Ph 7).
The softness of aluminum is not very good for the operation of the heating system. In the alloy, from which heating radiators are made, there are additives that increase its rigidity, but, anyway, they do not work in high pressure networks. Typical working pressure is 8-16 atm depending on the type and manufacturer.
Based on the foregoing, an area looms where aluminum radiators will be the best. These are individual heating systems with boilers controlled by automation. They also feel good in apartments, but only in low-rise buildings (up to 10 floors), in which a coolant with Ph 7-8 circulates.
4 Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum radiators
Autonomous types of heating in private houses are most often made in the form of a system of pipes and radiators, where hot water acts as a coolant. Such systems are called water heating. If you have just such a system installed at your home, it is better to stop at aluminum heating radiators for a private house. They have benefits such as:
- light weight, which will allow you to install radiators even on fragile plasterboard walls;
- aesthetic appearance;
- high level of heat transfer;
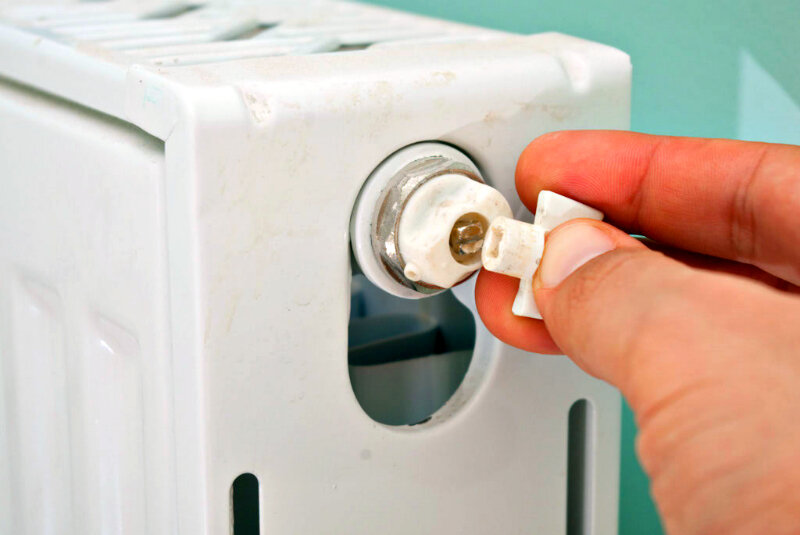
- the ability to regulate the temperature with special taps.
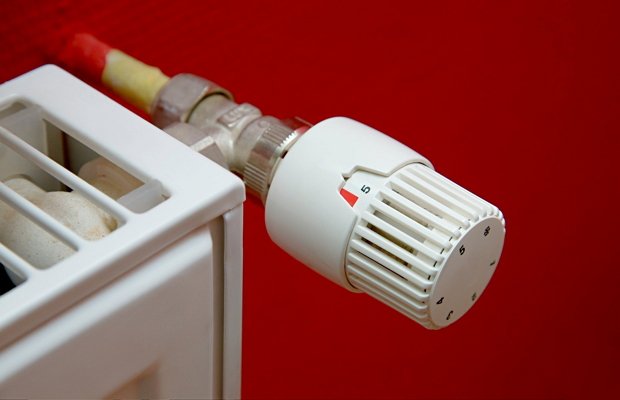

Temperature control tap for aluminum radiator
However, aluminum products have some drawbacks that it is desirable to know about in advance. So, for example, the coolant in such radiators must be free from chemical additives and solid particles that can destroy the material. In addition, aluminum radiators are known for not having the highest quality threaded connections, which increases the risk of leaks.