- Choosing a place and method of installing a radiator
- Coolant circulation methods
- 5 Myths and facts about copper pipes for water supply
- Marking and cost
- Method #2: Grooving (Roll Groove)
- Preparing and making a knurled groove connection
- Testing the complete knurled system
- Tools you will need
- Varieties of copper products
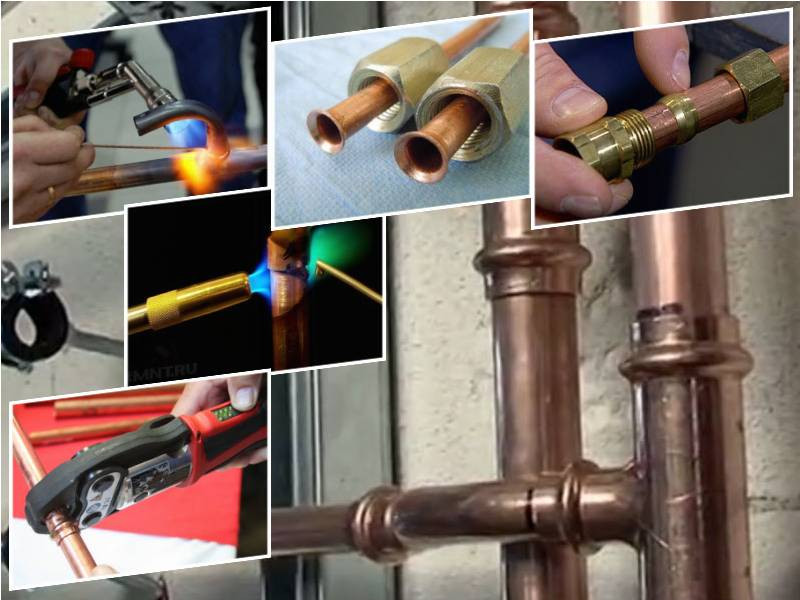
- Options for joining pipes made of copper
- Welding joint
- Flaring connection
- Press connection method
- Thread type connections
- Self assembly
- Classification by materials of manufacture
- Varieties of copper products
- By appointment
- According to the manufacturing method
- By section shape
- According to the degree of hardness
- Winding types
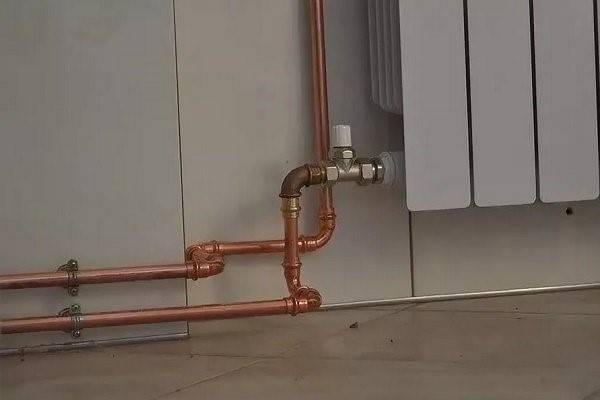
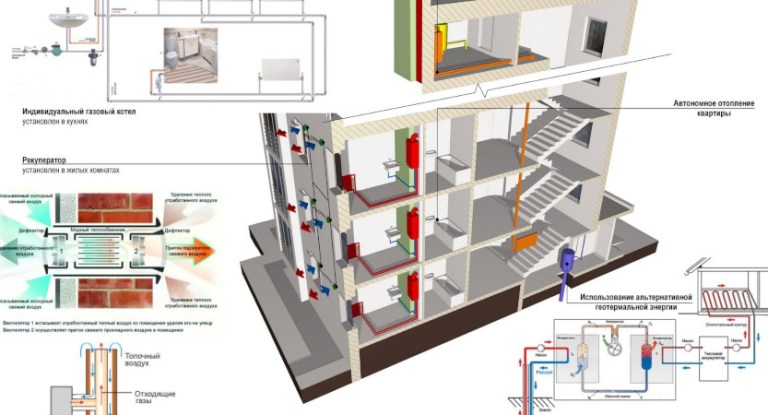
Choosing a place and method of installing a radiator
The options for connecting heating radiators depend on the general heating scheme in the house, the design features of the heaters and the method of laying pipes. The following methods of connecting heating radiators are common:
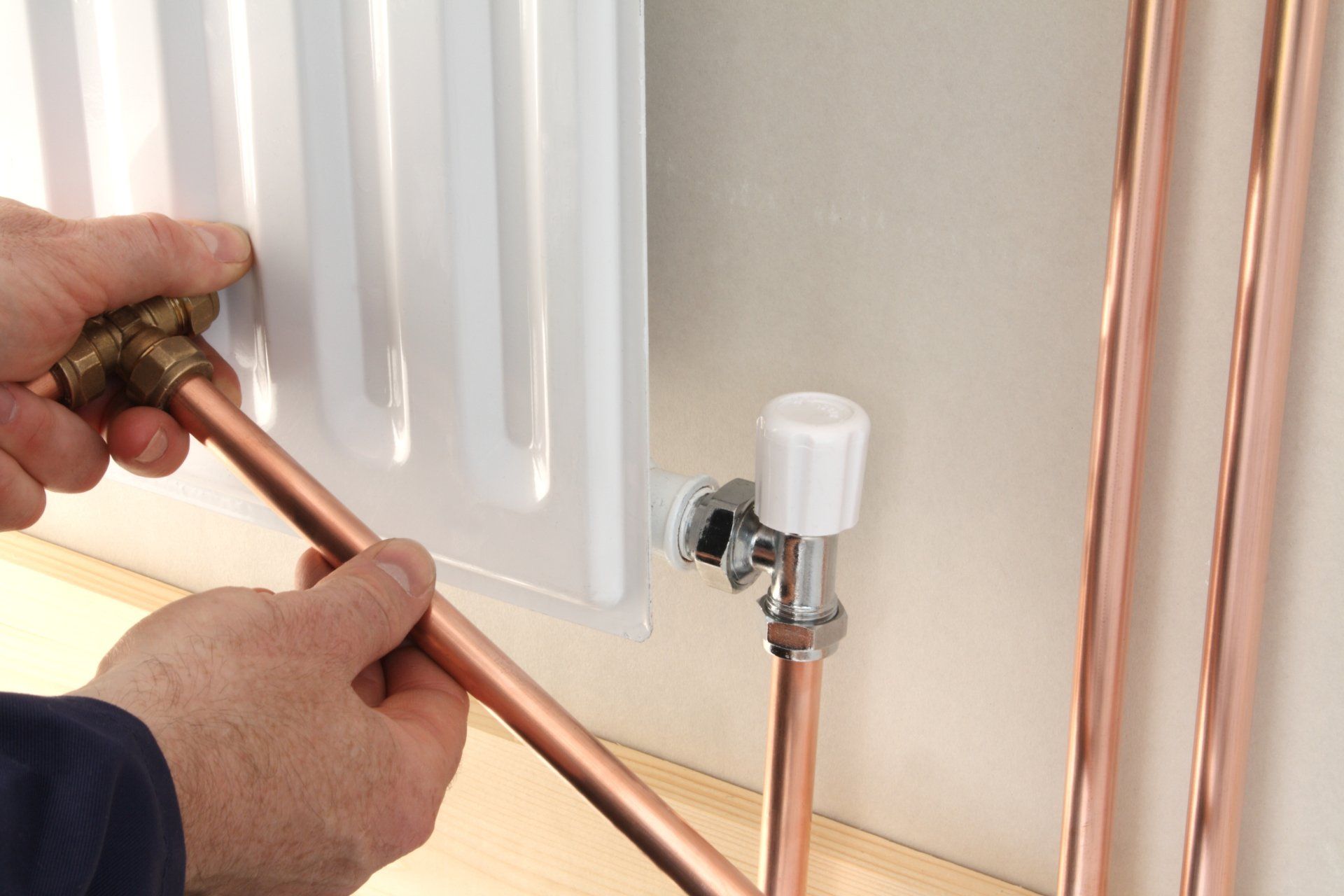
- Lateral (unilateral). The inlet and outlet pipes are connected on the same side, while the supply is located at the top. The standard method for multi-storey buildings, when the supply is from the riser pipe. In terms of efficiency, this method is not inferior to the diagonal one.
- Lower.In this way, bimetallic radiators with a bottom connection or a steel radiator with a bottom connection are connected. The supply and return pipes are connected from below on the left or right side of the device and connected through the lower radiator connection unit with union nuts and shut-off valves. The union nut is screwed onto the lower radiator pipe. The advantage of this method is the location of the main pipes hidden in the floor, and heating radiators with a bottom connection harmoniously fit into the interior and can be installed in narrow niches.
- Diagonal. The coolant enters through the upper inlet, and the return is connected from the opposite side to the lower outlet. The optimal type of connection, providing uniform heating of the entire area of the battery. In this way, correctly connect the heating battery, the length of which exceeds 1 meter. Heat loss does not exceed 2%.
- Saddle. The supply and return are connected to the bottom holes located on opposite sides. It is mainly used in single-pipe systems when no other method is possible. Heat losses as a result of poor circulation of the coolant in the upper part of the device reach 15%.
WATCH VIDEO
When choosing a place for installation, several factors are taken into account that ensure the correct operation of heating devices. Installation is carried out in the places least protected from the penetration of cold air, under window openings. It is recommended to install a battery under each window. The minimum distance from the wall is 3-5 cm, from the floor and window sill - 10-15 cm. With smaller gaps, convection worsens and battery power drops.
Typical mistakes when choosing an installation location:
- Space for installation of control valves is not taken into account.
- A small distance to the floor and window sill prevents proper air circulation, as a result of which heat transfer decreases and the room does not warm up to the set temperature.
- Instead of several batteries located under each window and creating a thermal curtain, one long radiator is chosen.
- Installation of decorative grilles, panels that prevent the normal spread of heat.
Coolant circulation methods
The circulation of the coolant through pipelines occurs in a natural or forced way. The natural (gravitational) method does not involve the use of additional equipment. The coolant moves due to a change in the characteristics of the liquid as a result of heating. The hot coolant entering the battery, cooling down, acquires a greater density and mass, after which it falls down, and a hotter coolant enters in its place. Cold water from the return flows by gravity into the boiler and displaces the already heated liquid. For normal operation, the pipeline is installed at a slope of at least 0.5 cm per linear meter.
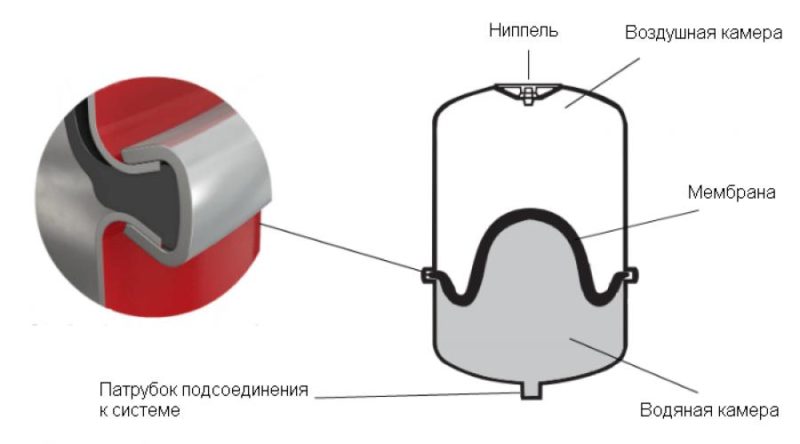
Scheme of coolant circulation in the system using pumping equipment
For forced supply of coolant, the installation of one or more circulation pumps is mandatory. The pump is installed on the return pipe in front of the boiler. The operation of heating in this case depends on the electrical supply, however, it has significant advantages:
- The use of pipes of small diameter is allowed.
- The main is installed in any position, vertically or horizontally.
- Less coolant required.
5 Myths and facts about copper pipes for water supply
Plumbing copper pipes have endowed with a number of shortcomings from the category of myths, due to competition and lack of awareness.
1. High cost of copper pipeline. This idea was formed thanks to the aggressive advertising of plastic pipes. Indeed, copper pipes are 2-3 times more expensive than plastic ones, but fittings made of copper cost 30-50 times less than those made of polymers. Given that the installation methods of the pipeline can be used the same, then the costs of installing systems from these materials are approximately equal. As a result, the cost of the completed pipeline is highly dependent on the topology of the system.
In the case of long and unbranched networks (main, for example), plastic pipelines are much cheaper. When using expensive, good plastics, which are designed for high levels of chlorination, but are not available on the Russian market, polymer systems will obviously be more expensive. Copper piping can be installed without the use of fittings, which makes it cheaper. And given the durability and high reliability of copper systems, the cost of their operation is an order of magnitude lower than plastic ones. In case of disposal of the used copper pipeline, the funds spent are returned.
2. Copper is poisonous. Completely unsubstantiated assertion. Poisonous are only special copper compounds produced by industry (dyes, blue vitriol, others) and not formed naturally in the pipeline. The oxides of this metal, which are mainly a protective film (patina) on its surface, are not poisonous.On the contrary, they and copper itself have a mild bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect, which, when using water from such a pipeline, ensures high infectious safety.
3. Chlorine. This substance in its pure form is a very strong oxidizing agent, prohibited for transportation through copper pipes. The impact of chlorine compounds, including those used for water disinfection, copper tolerates completely painlessly. On the contrary, interaction with these substances accelerates the formation of a protective web on the copper surface. Therefore, in the USA, during the technological flushing of a new pipeline, hyperchlorination is carried out in order to quickly obtain a protective layer.
The “chlorine problems” began with copper with the introduction of plastic pipes into the plumbing market. This is due to the fact that even chlorine compounds used to disinfect water have a rather detrimental effect on most plastics. And the golden rule of successful marketing, as you know, says: "Shift your blame to a competitor - let him justify himself."
4. Wandering currents. These are the currents that flow in the earth when it is used as a conducting medium. In this case, they lead to corrosion of metal objects in the ground. In this regard, stray currents have nothing to do with copper pipes, which are mostly internal.
It is forbidden to use both copper and steel systems as the main ground electrode. If this rule is strictly observed, then no electrical problems will arise (including stray currents). Grounding, operating in emergency mode, passes only short-term current, which will not harm the pipeline.Problems arise only when the fundamental rules for the design and operation of electrical installations are violated.
Marking and cost
Pipes for heating are made, marked according to GOSTs. For example, products with a wall thickness of 0.8–10 mm are manufactured according to GOST 617-90 standards. Another designation concerns the purity of copper, regulated by GOST 859-2001. At the same time, marks M1, M1p, M2, M2p, M3, M3 are allowed.
According to the marking, which is indicated on the manufactured products, you can find out the following information:
- cross section shape. Designated by the letters KR.
- Length - this indicator has different markings. BT - bay, MD - dimensional, KD - multiple dimensionality.
- The method of manufacturing the product. If the element is welded, the letter C is indicated on it. The letter D is placed on drawn products.
- Special operating features. For example, increased technical characteristics are indicated by the letter P. High plasticity index - PP, increased cut accuracy - PU, accuracy - PS, strength - PT.
- Manufacturing precision. The standard indicator is indicated by the letter H, increased - P.
To visually understand how to read the marking, you need to understand a simple example - DKRNM50x3.0x3100. Decryption:
- It is made of pure copper, designated by the M1 brand.
- The product is stretchy.
- The shape is round.
- Soft.
- External diameter — 50 mm.
- Wall thickness - 3 mm.
- The length of the product is 3100 mm.
European manufacturers use a special DIN 1412 marking system. They apply the EN-1057 designation to the elements of water supply and heating systems.It includes the number of the standard according to which the pipes are made, an additional element included in the composition - phosphorus. It is needed to increase the resistance to rust.
Copper pipes in a factory
Method #2: Grooving (Roll Groove)
Pipelines created by a connection with end grooves (knurling grooves) have been practiced for a long time on the construction of sprinkler (irrigation) fire systems. Since 1925, this completely reliable method of connecting pipes has been used on steel and iron pipelines for heating, ventilation, air conditioning and other systems.
Meanwhile, a similar knurled mechanical connection method is also available for copper pipes with a diameter of 50mm to 200mm. The knurled mechanical connection kit contains:
- couplings,
- gaskets,
- various fittings.
The mechanical knurling system offers a practical alternative to brazing larger diameter copper pipes. Accordingly, the groove method does not require additional heating (using an open flame), as in the case of brazing or soft soldering.
The knurling groove on the end of the copper pipe is one of the main elements of the “knurled groove” connection method. Measurement after rolling determines the suitable fitting
Groove connection is based on the ductility properties of copper and the increased strength of this metal during cold working. The design involves sealing the clamping system, for which a synthetic elastomer gasket (EPDM - Ethylene Propylene Diene Methylene) and a specially designed clamp are used.A number of manufacturers around the world offer tools for creating knurled joints - gaskets, clamps, fittings.
Fittings of various sizes and work clamps with gaskets are used in the design of connections made by the knurled groove method
Preparing and making a knurled groove connection
As with other solderless copper joining processes, proper preparation of the pipe end is of primary importance in creating a strong, leak-tight weld. The right choice of knurling tool for each type of copper pipe is also obvious. The manufacturer's recommendations must be followed to ensure safe, trouble-free preparation of these types of connections.
Table of permissible pressures and temperatures for this type of connection
| Connection type | Pressure range, kPa | Temperature range, ºC |
| Groove, D = 50.8 - 203.2 mm, type K, L | 0 — 2065 | minus 35 / plus 120 for K minus 30 / plus 80 for L |
| Roll groove, D = 50.8 - 101.2 mm, D = 50.8 - 203.2 mm type M | 0 — 1725 | minus 35 / plus 120 |
| 0 — 1375 | minus 30 / plus 80 |
Step-by-step process for assembling a knot with knurled grooves:
- Cut to size the ends of the copper pipes exactly perpendicular to the axis.
- Remove burrs after cutting and chamfer.
- Roll grooves to desired dimensions as required by the fitting manufacturer.
- Inspect fittings, gaskets, clamps for damage.
- Lubricate gaskets according to manufacturer's recommendations.
Prior to final assembly, inspect clamping surfaces for cleanliness and debris. Assemble the compound according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
Practically assembled fragment of the node using the "knurling groove" method.The elastic gaskets of the clamping bracket are treated with a small amount of lubricant before the final seating of the copper pipes.
The clamp nuts should be finally tightened to the required torque according to the manufacturer's recommendations. After tightening the screws, the clamp area should be re-examined to ensure that the assembly is properly assembled.
Testing the complete knurled system
Testing of a complete piping system may be performed by applying air or water pressure to the system. The hydropneumatic method is also not ruled out when a relatively high test pressure is applied.
However, it should be taken into account that the value of the test pressure should not exceed the maximum allowable working pressure specified by the manufacturer of the knurled groove system.
Tools you will need
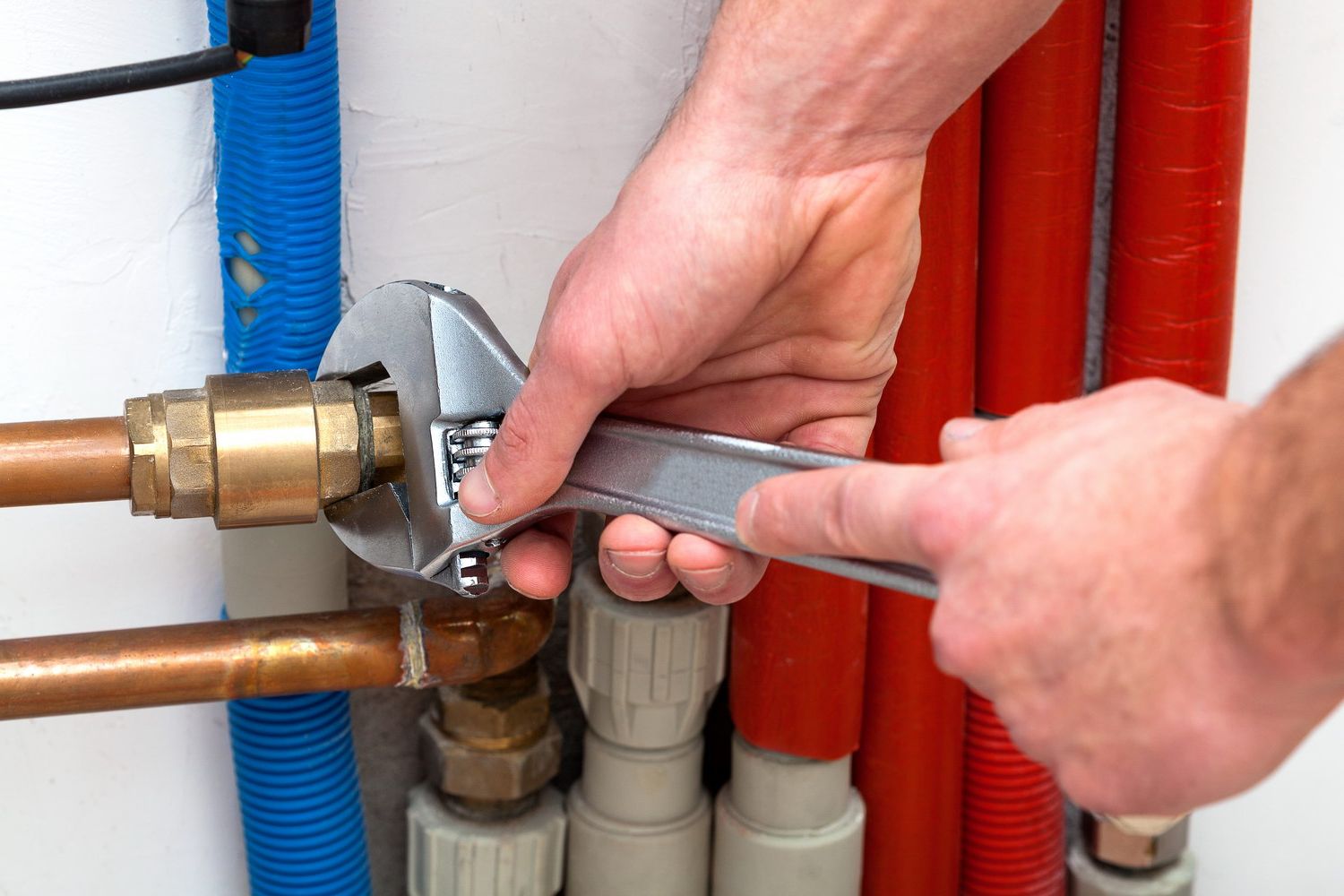
To carry out a competent installation, you must have the following tools:
- Pipe cutter - must be selected based on the specific type of pipe cross-section. Can be mechanical or manual;
- Sander - may well be replaced with sandpaper;
- Gas torch for soldering copper pipes or soldering iron with flux and solder.
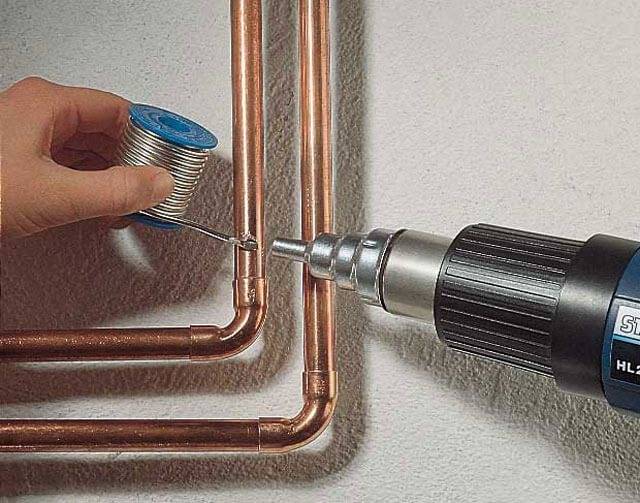
Work begins with drawing up a plan for the heating system with the obligatory designation of places where batteries are planned to be installed. The next step is cutting the pipe into cut lengths. It should be borne in mind that the ends must be strictly perpendicular. The cut specimens must be free of burrs. The joints must be cleaned with fine-grained sandpaper.
A flux is applied to the cleaned end of the pipe, after which it (the end) is inserted into the radiator or fitting until it stops. After that, solder is applied to the joint for soldering copper heating pipes.The mating parts at the junction are heated with a gas burner. Care must be taken to ensure that the flame does not touch the solder. But, at the same time, it must melt to fill the gaps between the fitting and the pipe.
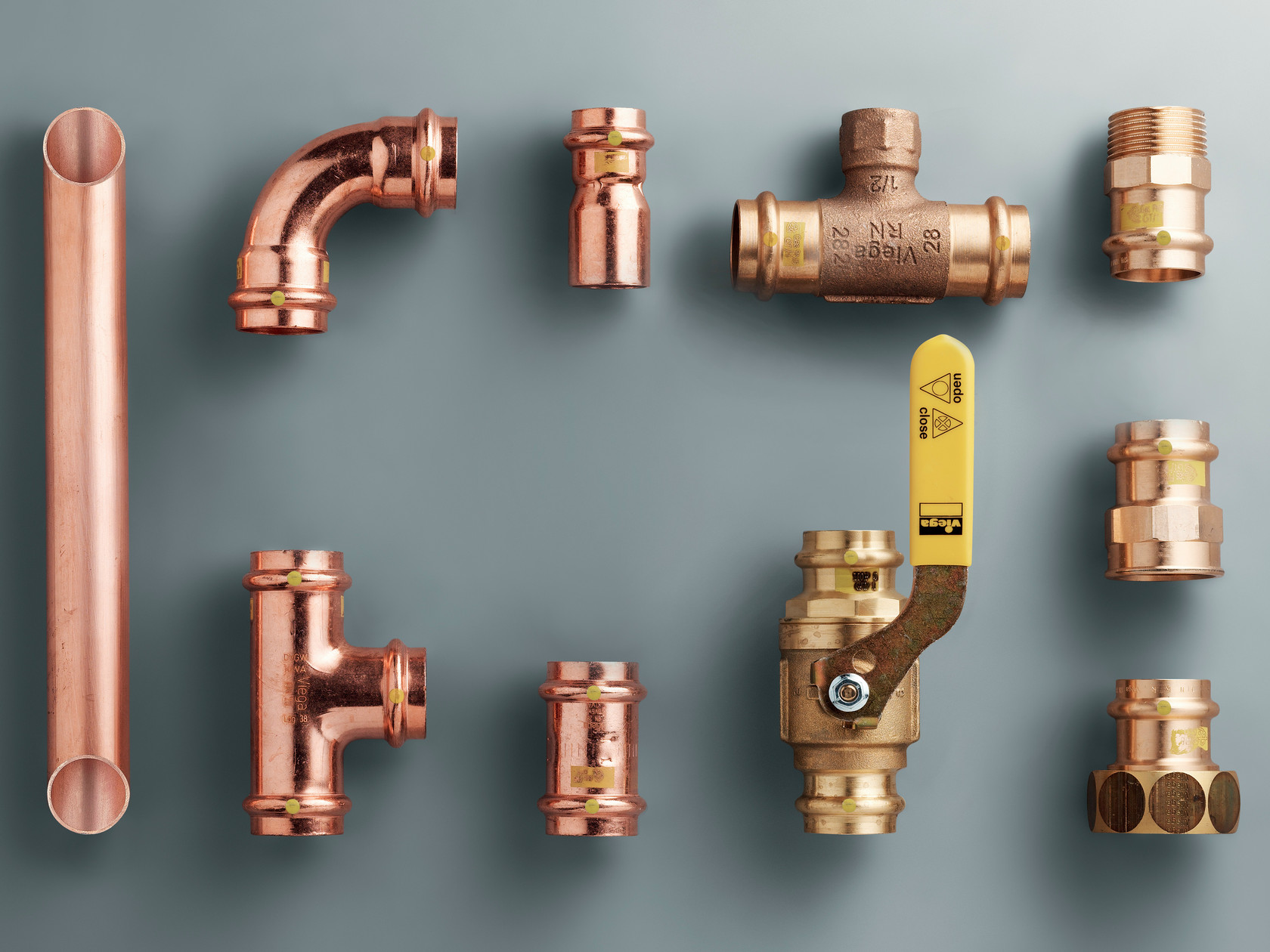
Varieties of copper products
There are several classifications of copper pipes. Let's consider some of them. According to the method of manufacture, products are distinguished:
- Unannealed. They are made from pure metal by stamping or rolling. They are characterized by high tensile strength, which is about 450 MPa. In this case, the ductility of the metal decreases, which creates certain restrictions on the use of parts.
- Annealed. They differ in special processing technology. The pipes are heated to 700C and then gradually cooled. As a result, the products somewhat lose their strength, but become more ductile. Such pipes stretch perfectly, just before the break, the length of the element can increase one and a half times. Annealed products are softer, which simplifies their installation.
The shape of the section distinguishes between round and rectangular elements. The latter are distinguished by a higher cost, which is due to the complexity of their manufacture. They are used for the production of conductors in stator windings of electrical equipment cooled by a liquid method. Standard sizes of non-insulated copper products in terms of outer diameter vary from 12 to 267 mm. In addition, each of the standard sizes can have a different wall thickness, which is in the range from 0.6 to 3 mm. For gas supply, products with a minimum thickness of 1 mm are used. In plumbing, the most commonly used sizes are 22, 18, 15, 12 by 1 mm, 52 by 2 mm and 42, 35, 28 by 1.5 mm.
Annealed copper pipes lose some strength, but acquire special plasticity and softness, which facilitates the process of their installation.
GOST 52318-2005 regulates the manufacture of copper parts in three types, differing in the degree of hardness, operational and mechanical properties:
- Soft. Designated M or W, obsolete r or F22. Withstand expansion without cracks and breaks in the process of increasing the outer diameter by 25%. Can be subjected to bending and fitting-free cold connection. Products are used for arranging heating and water supply systems with a beam distribution of piping to heating and plumbing fixtures, as well as for heat pumps, floor and panel heating.
- Semi-solid. Marking P or HH, obsolete version z. Parts withstand expansion in the process of increasing the diameter of the pipe by 15%. Less ductility than soft products requires the use of heat for a fittingless connection. For bending you will need a pipe bender.
- Solid. Designation T or H, obsolete z6 or F30. During installation, the expansion of the pipe occurs only during the heating process. A pipe bender is used to bend the part. Solid, as well as semi-solid, elements are used for arranging highways without frequent changes in direction of movement and turns. In addition, such products are used for pipelines that require increased mechanical strength.
Some manufacturers produce special pipes with additional options that are in demand for heating and water supply systems:
- Insulated with a polyethylene thin-walled sheath, the thickness of which is 2-2.5 mm.The material is resistant to chemical and mechanical stress, applied to pipes with a diameter of 12 to 54 mm. The sheath reduces heat losses present in heating systems and prevents the formation of condensate on cold water pipes.
- With protective insulation 2.5 to 3 mm thick. The inner side of the polyethylene shell is equipped with small longitudinal teeth that form air channels. Thus, the thermal insulation characteristics are improved, and it becomes possible to carry out thermal expansion of the monolithic pipe with temperature fluctuations.
- With a thermal insulation shell made of foam materials: synthetic rubber, polyethylene foam, soft polyurethane foam, etc. The width of the insulation layer can exceed 30 mm. The shell is used to reduce high heat transfer in hot water and heating systems.
If necessary, you can purchase special parts for sheltering and thermal insulation of installed pipelines.
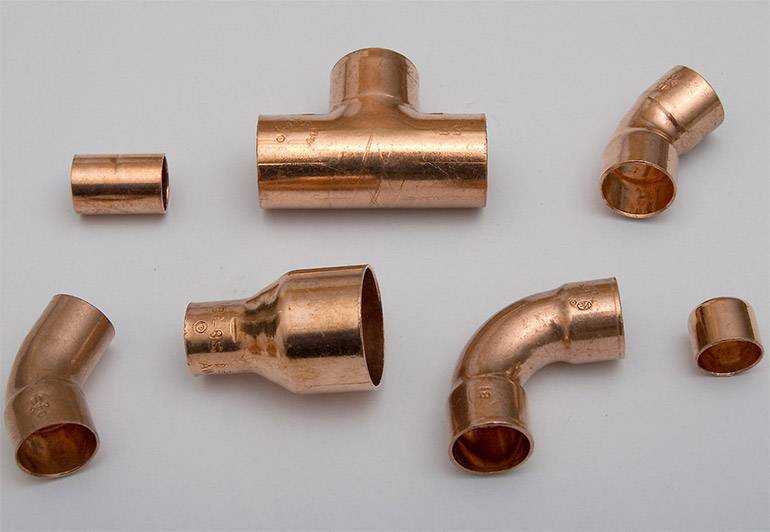
Fittings are used to connect copper parts. Their range is very wide. They differ in shape and are designed to make various types of connections.
Options for joining pipes made of copper
When assembling heating, various installation methods are used. So, the docking of copper pipes is carried out by a collapsible and non-collapsible method. In the first case, flanges, threaded fasteners, fittings are used, which are fixed automatically. When designing a non-separable heating system, pressing, soldering and welding are used.
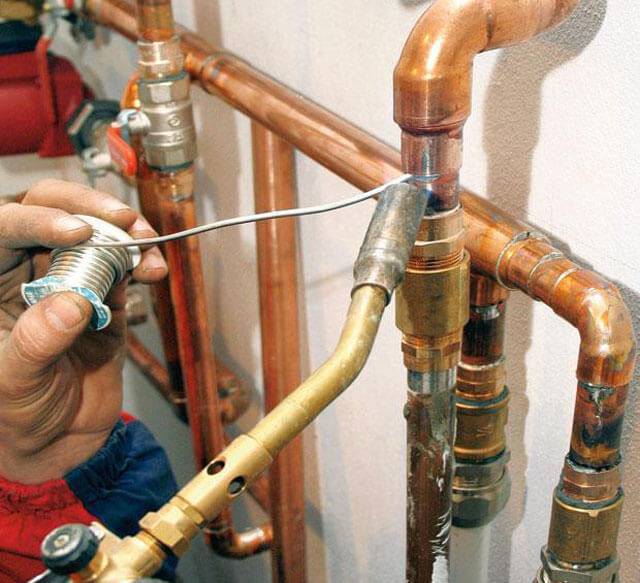
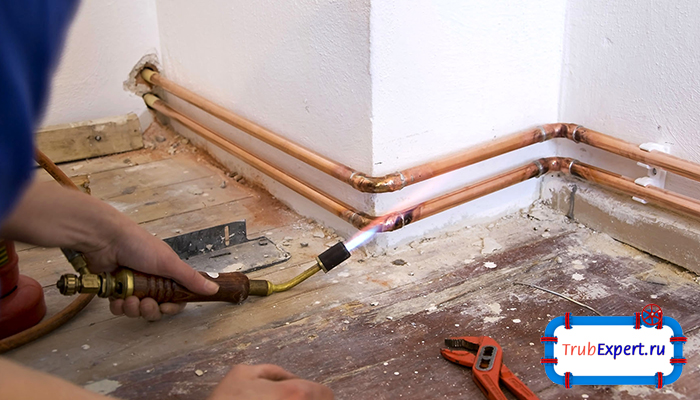
Welding joint
Let's take a look at the process of welding copper pipes. This docking technique is applied to pipes with a diameter of 108 mm or more.The wall thickness of the heating material must be at least 1.5 mm. To carry out welding work, in this case, it is only necessary to butt, while the proper temperature should be 1084 degrees. It is worth adding that this option for installing heating is not recommended to be done by hand.
To date, builders use several types of welding:
- Gas welding using oxy-acetylene type burners.
- Welding with consumable electrodes, performed in an inert gas environment - argon or helium.
- Welding in which non-consumable electrodes are used.
In most cases, the arc welding method is used to join copper elements. If the pipes that are planned to be used to assemble the pipeline are made of pure copper, then it is necessary to use non-fusible tungsten electrodes in an argon, nitrogen or helium environment. When welding copper elements, the process must be fast. This will prevent the formation of various oxidations on the metal base of the pipe.
Welding joint of copper pipes
To give strength to such a connection, upon completion of the docking work, it is recommended to carry out additional forging of the resulting joints.
Flaring connection
It happens that the use of welding torches during the installation of heating systems creates some inconvenience. In this case, it is recommended to resort to flaring copper pipe joints. This installation method will turn out to be detachable, which will play a positive role in the event of a forced heating assembly.
An operation of this kind will require the obligatory presence of a flaring device.We will try to describe in detail how to connect heating pipes by flaring:
- to begin with, the tip of the pipe is cleaned in order to remove from its surface the scuffs and burrs formed during the sawing of the material;
- a coupling is fixed on the pipe;
- then the pipe is inserted into a clamping device, with the help of which further expansion is performed;
- then you should begin to tighten the screw of the tool until the angle of the end of the pipe reaches 45 degrees;
- after the pipe area is ready for connection, a coupling should be brought to it and the nuts should be tightened.
You can learn more about the process in the video below.
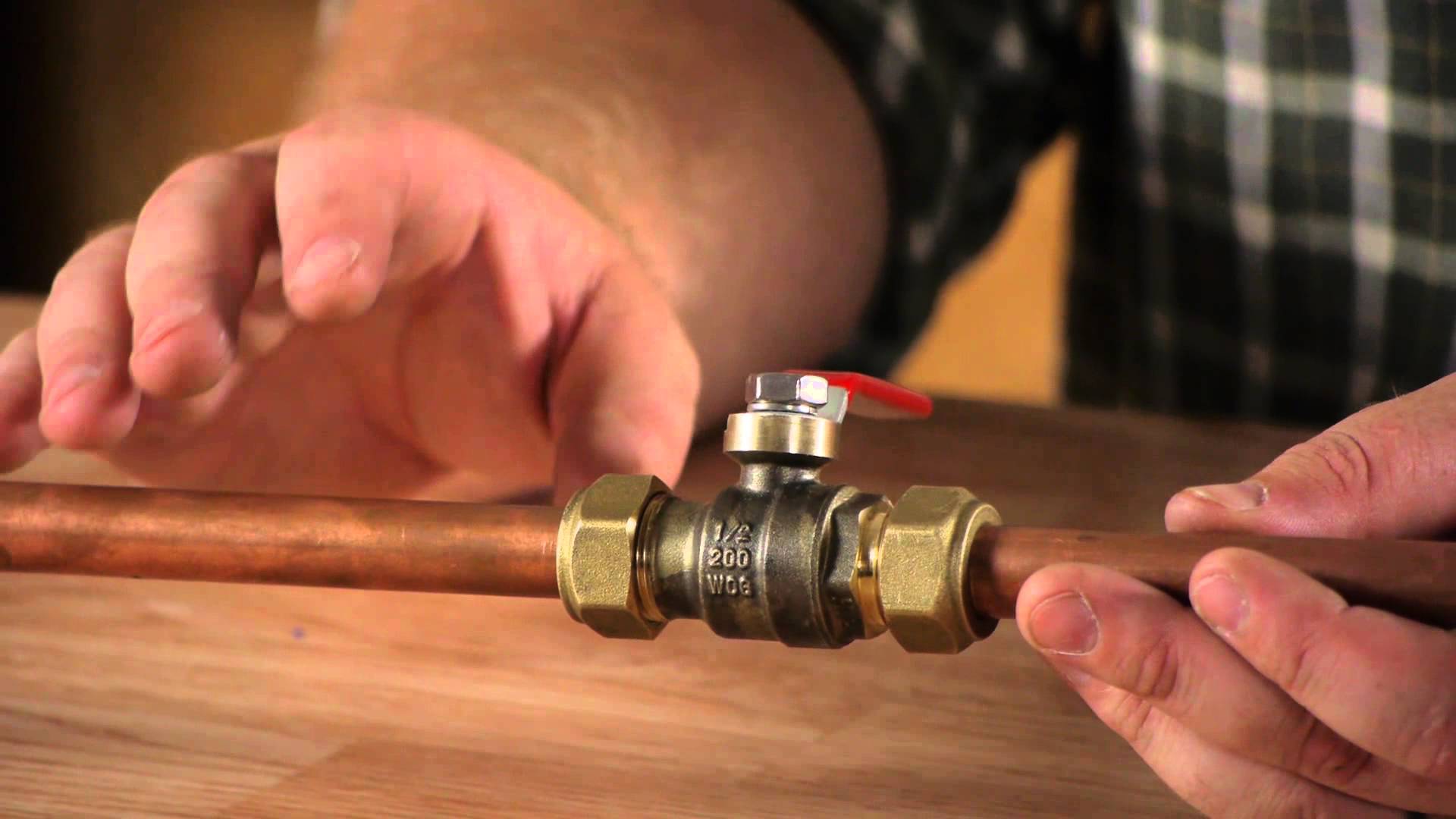
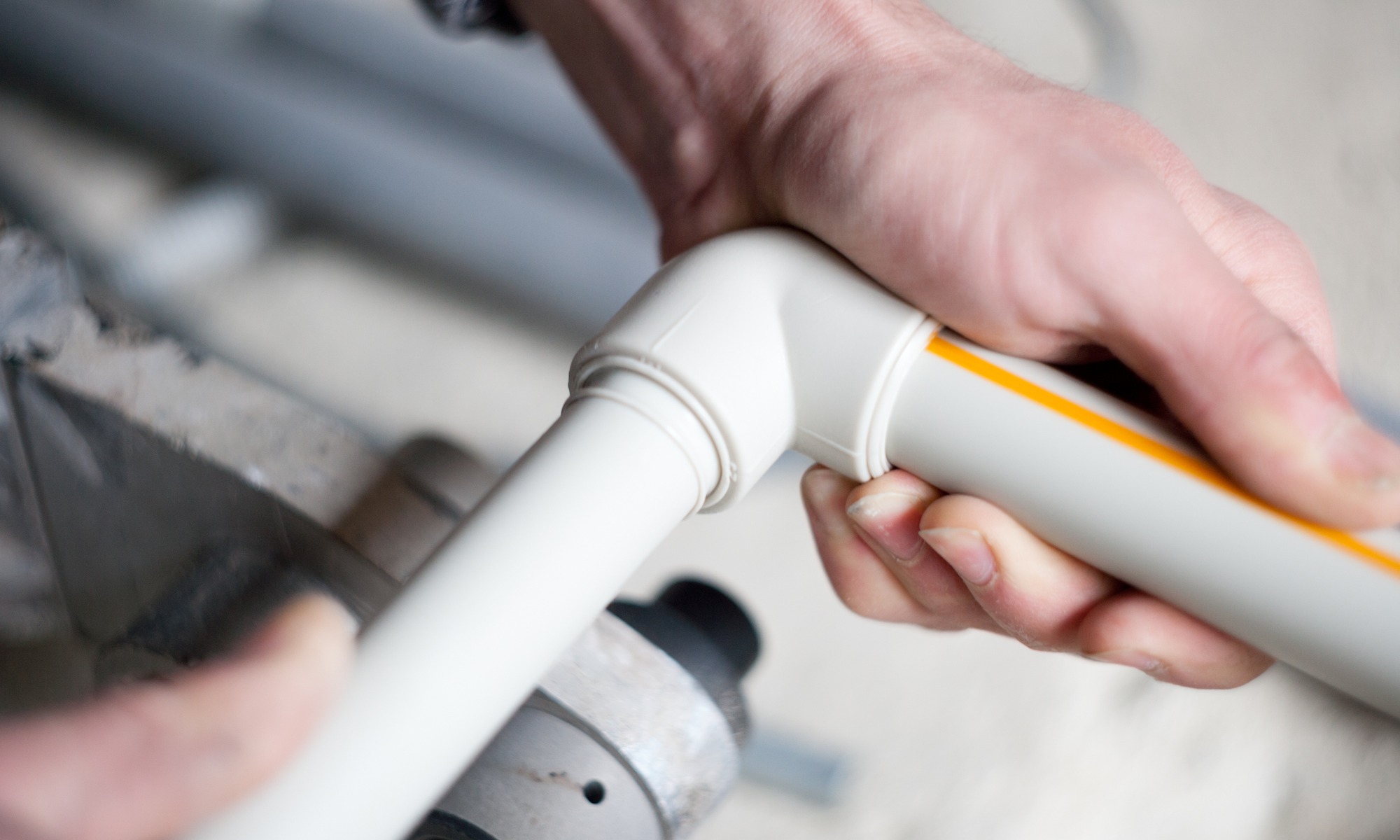
Press connection method
In addition to all of the above methods for installing heating pipes, there is also a pressing technique. To join the copper elements in this case, it is necessary to insert the previously prepared end of the pipe into the coupling until it stops. After this, the use of a hydraulic or manual press will be required, through which the pipes will be fixed.
If the heating is planned to be assembled from thick-walled pipes, press fittings with special compression sleeves will be required. These elements make it possible to compress pipes and fittings for heating from the inside, while external seals will provide excellent tightness of the structure.
Thread type connections
Unfortunately, it is impossible to find copper pipes with threaded connections on the market, and therefore it is customary to use fittings that have a union nut to join parts of a heating system.
For joining copper pipes with pipes made of other materials, bronze or brass threaded fittings are used. Their use eliminates the possibility of galvanic corrosion.In the event that the pipes differ in diameter, resort to the help of special expanders.
Considering the types of seals used today for copper heating systems, there are two types of threaded connections:
- Consolidations of conical type ("American"). These elements are recommended for heating installation in conditions of high temperature indicators.
- Flat type connections. Such materials include in their design seals made of polymeric materials of various colors. Gaskets are painted in different colors to indicate the temperatures at which you can work with such elements.
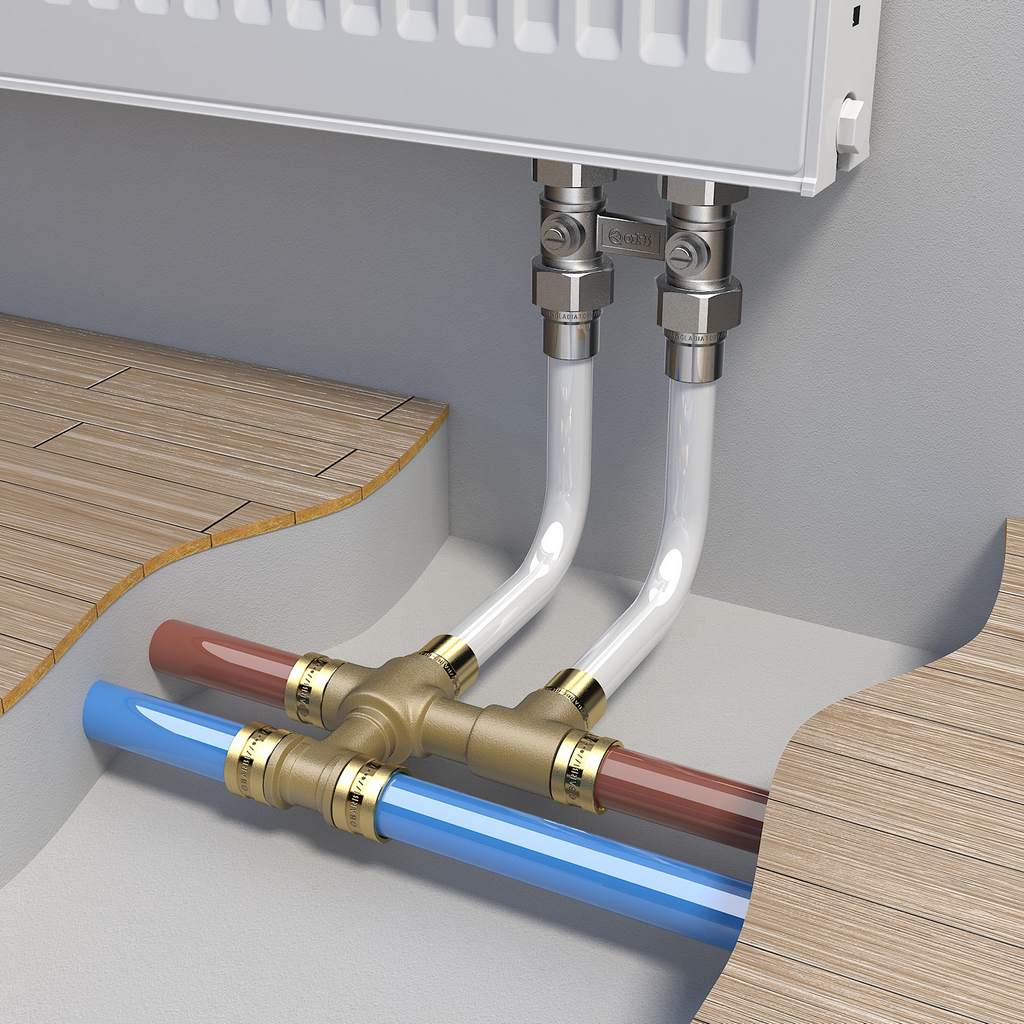
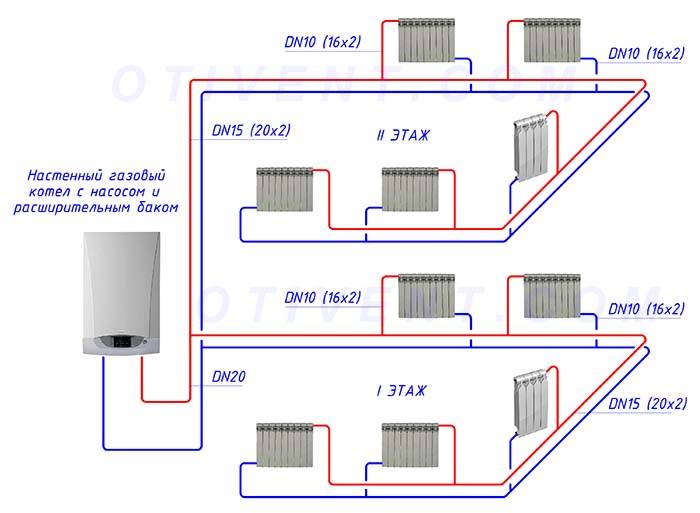
Connection diagram for copper pipes
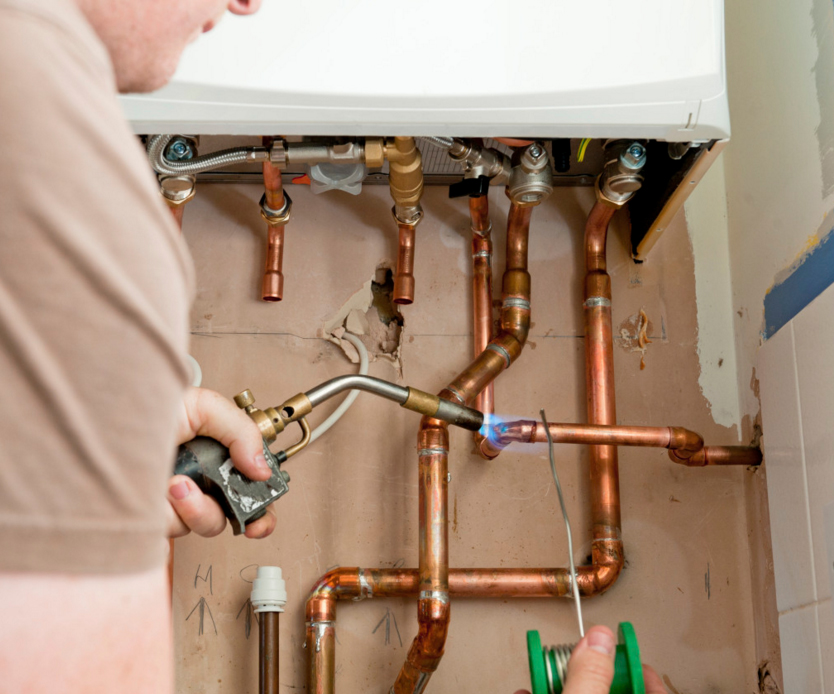
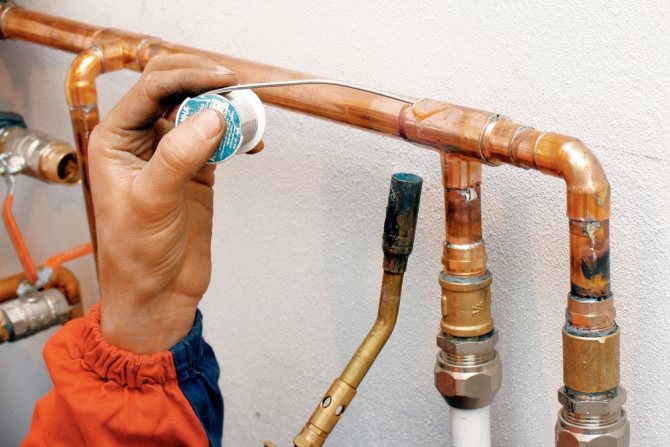
Self assembly
Installation of the pipeline using copper pipes is quite feasible with your own hands. To do this, use a gas burner and solder, which is of two types - hard and soft. Hard solder is used for high-temperature soldering in communications for water supply, gas and heating. Soft - for soldering at lower temperatures in domestic conditions.
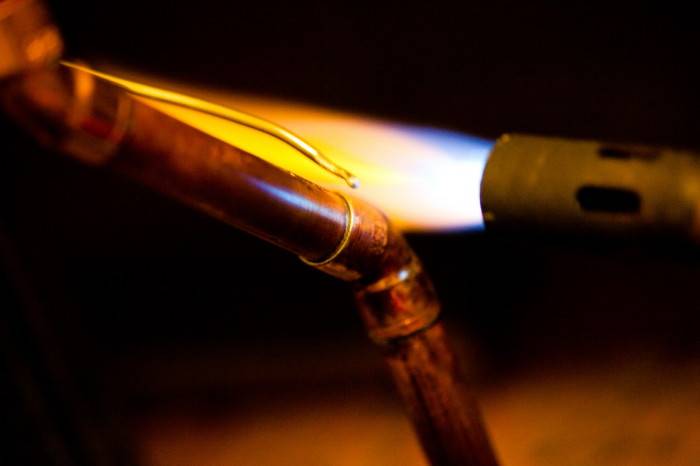

- brushing and sanding the inside of the joint;
- application of flux paste inside and out;
- heating the connection point with a gas burner.
Take advantage of these tips. Do not remove the burrs after trimming the edges of the pipes with sandpaper. One of the ends of the pipes must be expanded with a pipe expander so that they fit into each other
When applying the flux paste, make sure that there is not too much of it and it does not get into the lumen of the pipe when soldering.
It is important not to overheat the junction, 15-20 seconds are enough to get the effect.Heating is stopped when the flux acquires a silver color.
Before starting the finished system, it is advisable to rinse it with a large pressure of water in order to remove all particles from the installation process.
Working with open flames requires safety precautions. Life and health are worth taking care of during these works.
Copper pipelines, due to their excellent properties, have shown themselves to be a reliable option for a heating system, along with the possibility of hot and cold water supply.
Classification by materials of manufacture
The choice of material depends on the operational loads - pressure, fluid flow, (sometimes also on its density), as well as on the level of hydraulic resistance. After all, a fitting is an additional flow barrier caused by various adjacent elements - gaskets and design features of the product itself - the presence of tides, ledges, curvature radii, transition sections, etc.
The materials that are recommended for the manufacture of the parts in question are also selected taking into account the manufacturability of their production:
- Cast iron. Cast irons with nodular graphite (grade VCh100) are more often used, which have sufficient strength and satisfactory ductility. Quite often there are adapters made of ductile iron grades SCH30 or SCH35, as well as ductile iron grades KCh35-10 or KCh 37-12. In some cases, finished products are galvanized to improve their presentation.
- Steel. Mostly stainless steel grade 08X18H10 is used, as well as its foreign counterparts. Other brands are used in systems designed for pumping corrosive media at elevated temperatures, which are contaminated with abrasive particles.Here steel type 45X is used. 40HN. 40HNM and the like.
- Brass. When using plastic deformation technology, they are guided by the brands of deformable brass: ordinary from L70, multicomponent - LA-77-2, LN 65-5. From casting brass - LTs40S, LTs25S2, etc.
- Metal-plastics based on deformable aluminum and polyethylene grades PE-X or PE-RT.
- Low pressure polyethylene (HDPE). At low operational loads, polymers are used, manufactured according to the technical requirements of GOST 16338-85.

Fittings for HDPE pipes: types of fittings and options for connecting pipelines In construction, pipelines made of HDPE are increasingly used. That is why the demand for reinforcement elements is also increasing. With their help, pipe installation becomes easy and fast ...
Varieties of copper products
At the moment, there are several varieties of copper tubes. Below are the main ones.
By appointment
The following tubes are used for their intended purpose:
- for furniture - made of chrome - 25 mm;
- for commercial equipment - an oval product - 25 mm;
- in the manufacture of furniture supports - 50 mm (bar);
- for the kitchen room - 50 and 26 mm (railing and bar).
In the manufacture of furniture, furniture chrome-plated pipe is used. It is used in the main furniture structure - as a metal bar. Unlike round, it has a rectangular cross section. The most commonly used profile is 40*100, 40*80, 50*50.
It is installed only on a flat surface, and also used in repairs and in car factories - when creating a strong frame.
According to the manufacturing method
Depending on the manufacturing method, such copper tubes are used as:
Unannealed copper piping.It is made of pure metal using stamping.
It has high tensile strength. In this case, the metal becomes less ductile, after which there are some restrictions on the use of such a tube.
Annealed copper pipes are plastic, this quality facilitates the installation process
Annealed copper pipe. It goes through a special processing technology. It is heated to 700 degrees Celsius and then cooled down. In this case, the pipeline elements become less strong, but more flexible.
In addition, they stretch well - before breaking, their length increases by 1.5 times.
Annealed piping products are softer, so their installation is faster and easier.
By section shape
According to the shape of the section, they distinguish:
- round water pipes;
- pipeline elements having the shape of a rectangle. They are used to create conductors in the stator winding of electrical equipment, which is cooled by a liquid method.
The dimensions of copper pipes can be determined by the outer diameter, which is 12–267 mm. In this case, any pipe size has a certain wall thickness equal to 0.6–3 mm.
When conducting gas into houses, pipes are used that have a thickness of at least 1 mm.
When installing plumbing, in many cases a copper plumbing pipe is used, which has such sizes as: 12, 15, 18, 22 by 1 mm, 28, 35, 42 by 1.5 mm and 52 by 2 mm.
According to the degree of hardness
According to the degree of hardness copper tubes are used, such as:
Soft. The designation is M or W. They are able to withstand expansion without cracking and tearing when the outer diameter expands by 25%.
Such pipeline products are used when a heating system is being created or pipelines are being laid for the water supply of consumers. At the same time, a beam distribution of the piping to plumbing and heating devices is made.
Soft pipeline elements in most cases are used in the construction and repair of water pipes. Their connection is considered the simplest - docking can be done without the use of additional equipment.
Copper pipes can withstand the high temperature of the liquids transported through them
Semi-solid. They have the following designations - P or NN. Such pipeline products are able to withstand expansion with a diameter increase of 15%.
When they are installed, heating is used to connect the tubes without the use of fittings. For bending or unbending semi-solid products, a pipe bender for copper pipes is used.
Solid. They are designated by the following letters - T or H. When they are installed, distribution is done only during heating. In order to bend the pipe, use a pipe bender.
The last 2 types of copper products are used in the construction of various highways.
Also, such parts are used in the construction of a pipeline, which should have increased mechanical strength.
The sealing of such tubes is considered an important process. After all, their undocking can occur at any time - for example, when the sealant is depleted. In the event of such a situation, it will be necessary to completely redo the joints.
Winding types
Manufacturers use different types of windings for copper pipes:
- FUM tape. This tape is used in all types of threaded connections;
- curing sealant for plumbing. Such material is used both at various enterprises and in everyday life;
- homemade sealant for plumbing.The pipes that are installed in the houses of the 1940s do not leak.
Also, this method can be applied if it is necessary to make heating from copper pipes.
If red lead is not available, then ordinary PF paint should be used.
Sealing when working with fluid-conducting systems is mandatory