- Microplastics in food: is it possible?
- The cycle of microplastics in nature
- Ready meals and food packaging
- Prevention
- What may contain
- Environmental pollution
- Stickies - annoying, but not dangerous
- Types of plastics and their applications in modern industry
- Sources of myroplast
- Air
- Water
- Food
- How microplastics affect human health
- First law against microplastics
- Which foods contain the most microplastics?
- Corals are dangerous if touched
- What can I do?
- Problems - trailer
- tea bags
- Prevention
- Diphyllobothriasis
- How microplastics enter the human body
- Water
- Fish
- How to reduce microplastics
- Backhorn - aggressive
Microplastics in food: is it possible?
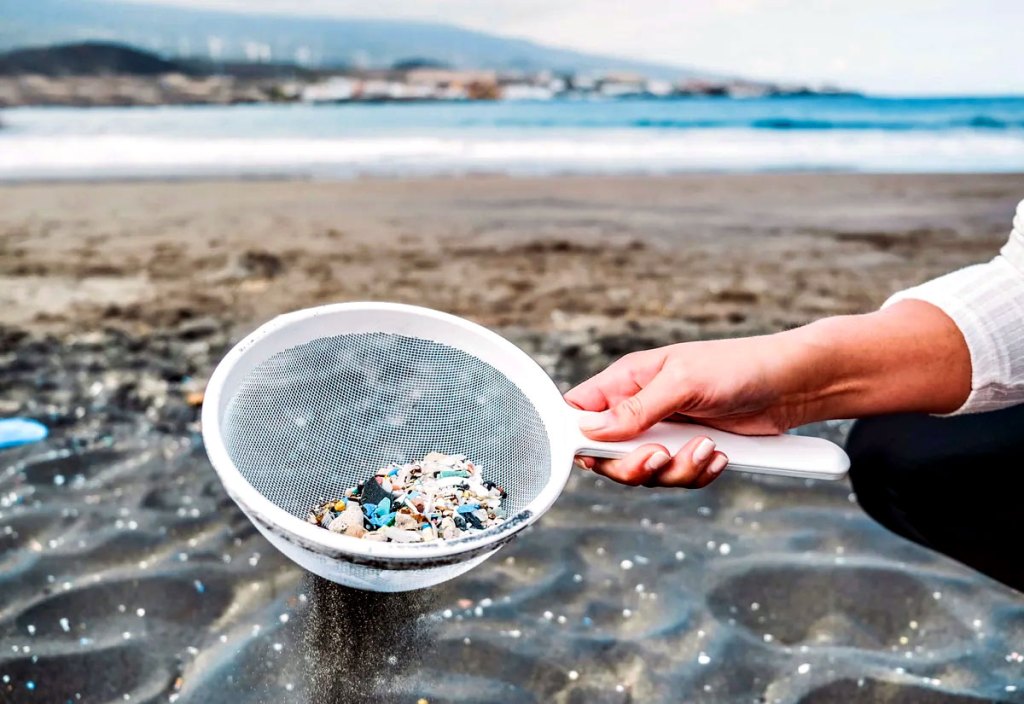
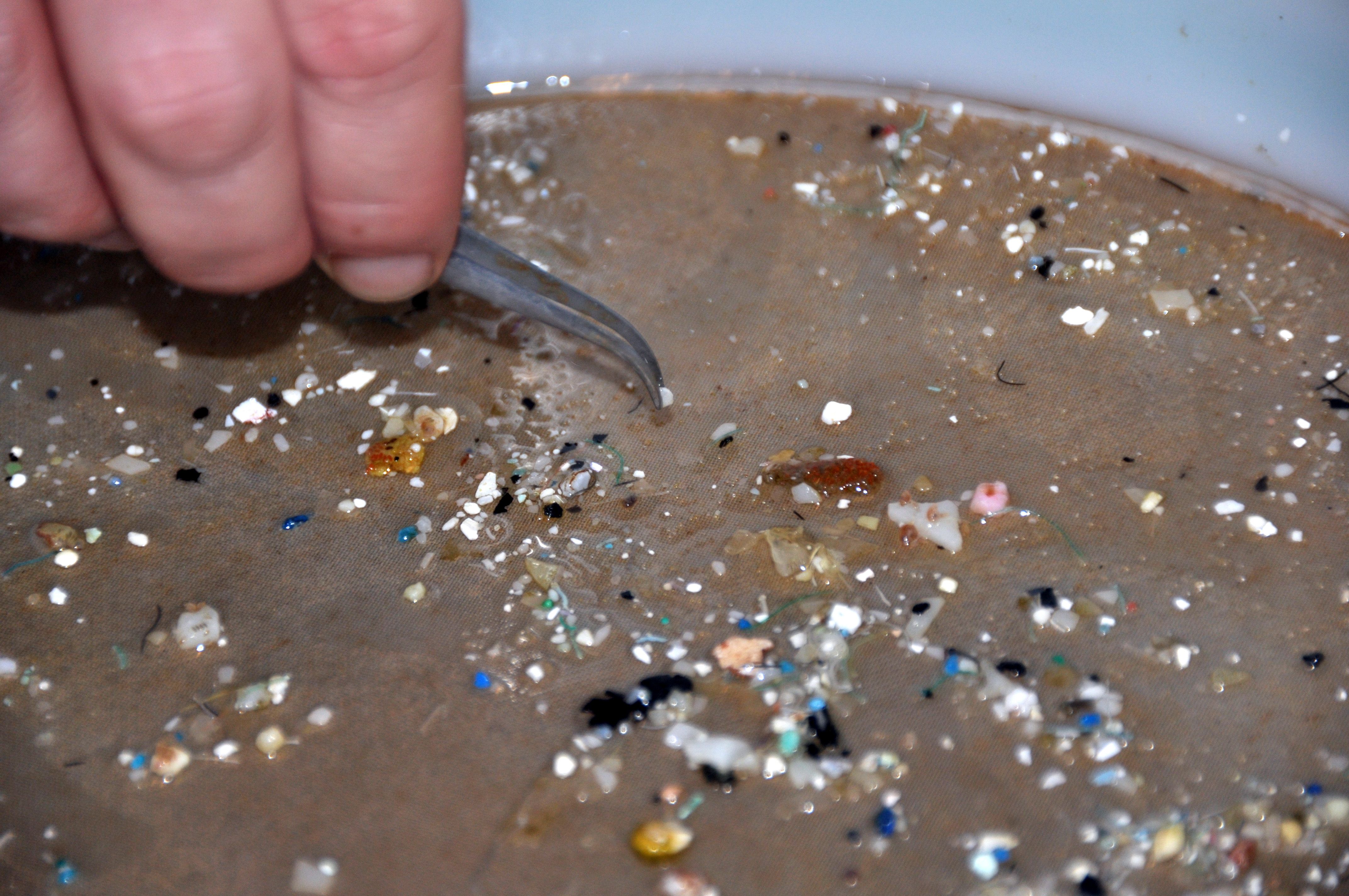
Researchers from the University of Vienna analyzed the composition of the faeces of 8 people from around the world (from Austria, Finland, Holland, Japan, Great Britain, Italy, Poland and Russia) for the presence of microplastic particles in them. During the week preceding the collection of biomaterial for laboratory analysis, the participants of the experiment kept a diary of food intake. None of the subjects were vegetarians, and 6 of them regularly ate sea fish.
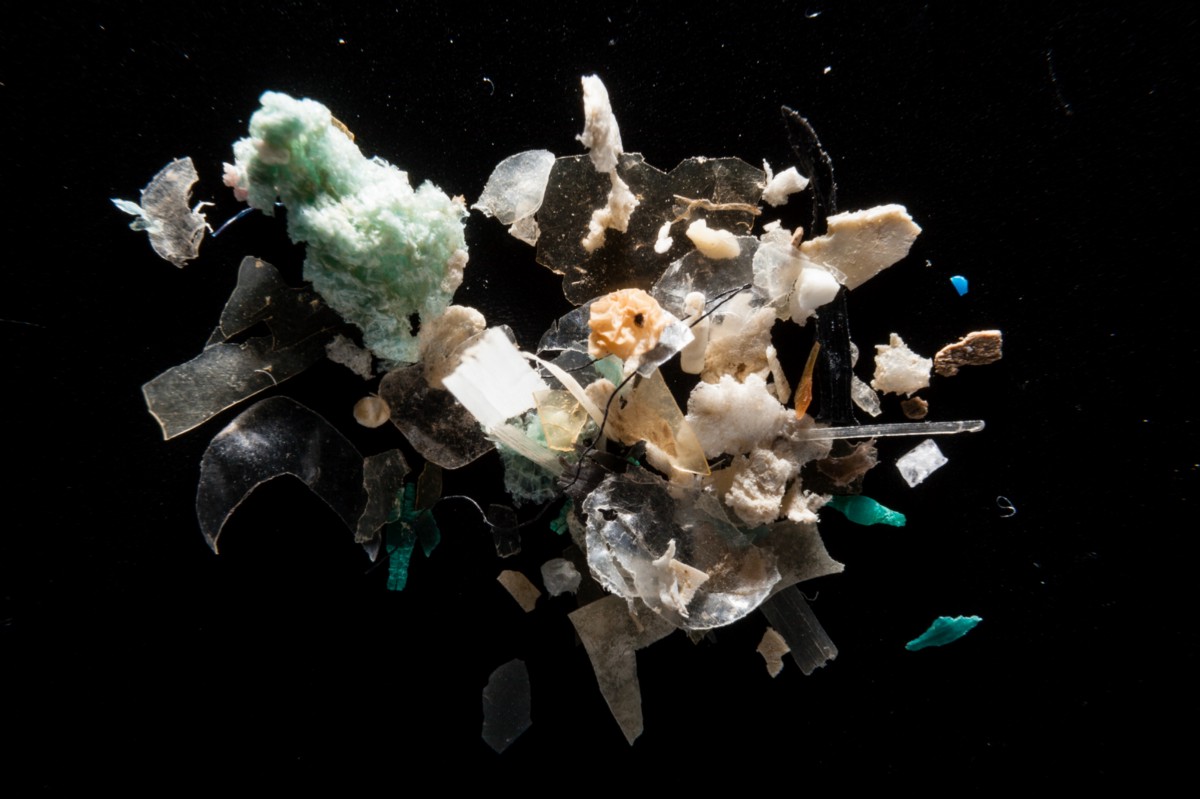
The results of the experiment surprised even scientists.Nine types of plastic were found in each stool sample. The fragments found were from 50 to 500 µm in diameter. The researchers calculated that, on average, there are about 20 microscopic plastic particles in every 10 g of feces. Most often it was polypropylene and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). The results of the study confirmed the guesswork of scientists that microplastics can also be found in human bodies. But how do microscopic plastic particles get into our bodies?
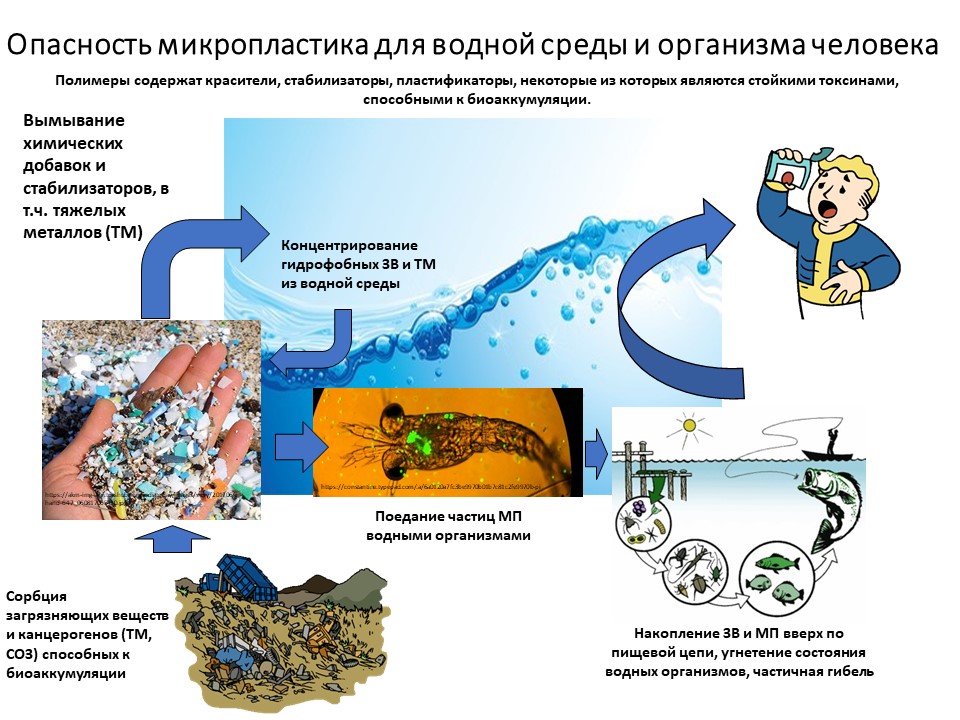
The cycle of microplastics in nature
For example, you bought a regular shampoo, where the manufacturer used polyquaternium to create a uniform consistency. It is a synthetic polymer in powder form. The manufacturer claims that the substance has a large molecule and cannot penetrate the body through the pores. Let's admit.
You washed your hair and washed the shampoo down the drain, from where the sewage flows either straight into the rivers or passes through the treatment plant along the way. But even they can’t filter out all the microplastics, so it goes free-swimming: it gets into the soil, becomes food for fish and other animals.
Sooner or later, these animals enter the human diet along the food chain and microplastics come back. This is just one of the possible scenarios.
Ready meals and food packaging
Most ready-to-eat meals, juices or hot drinks are sold in plastic packaging. Storing prepared meals and juices in plastic packaging leaches microplastics into food. The concentration of microplastics increases when food is heated in the microwave or at the production stage, when a raw dish is baked directly in the package.
Prevention
Even the so-called biodegradable plastic packaging, although it decomposes faster than usual, it also pollutes the environment faster. Buy ready meals in cardboard packaging (some manufacturers are moving away from plastic)
Please note that some cardboard containers may be lined on the inside or outside with plastic film. When heating, transfer food from packaging to glass or ceramic dishes
Most takeaway drinks are sold in cups with a plastic lid and an inner layer of polyethylene. Buy takeaway drinks in your own insulated cup made from a compostable material like bamboo. Buy a reusable metal straw, which often comes with a special brush for washing.
What may contain
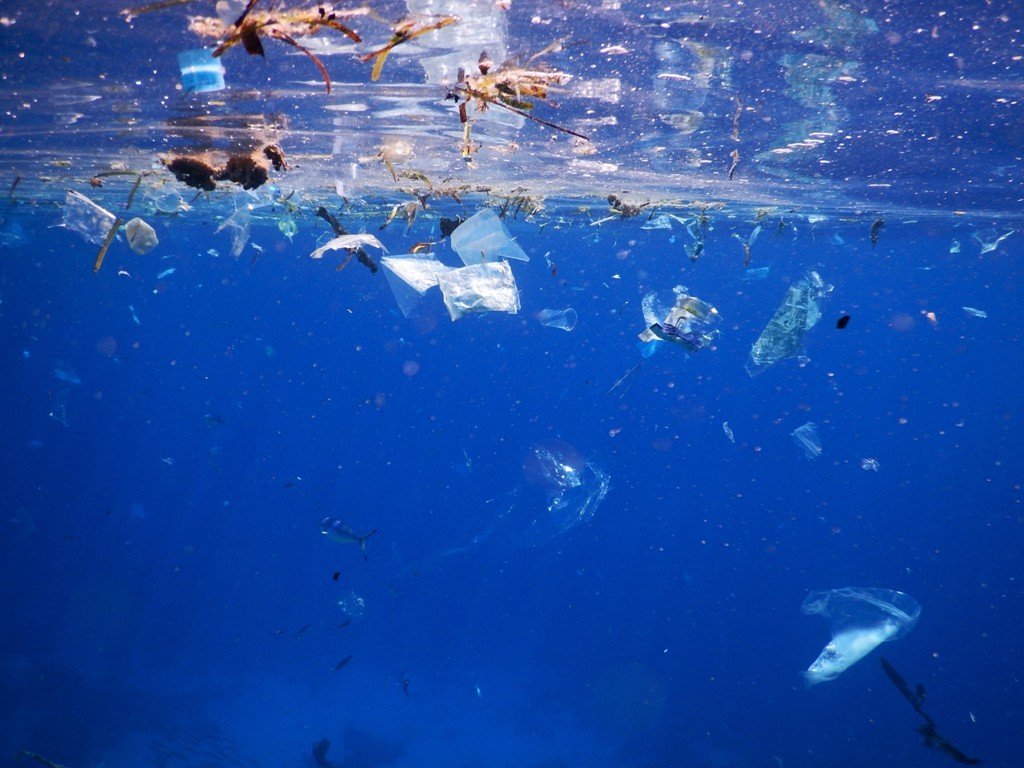
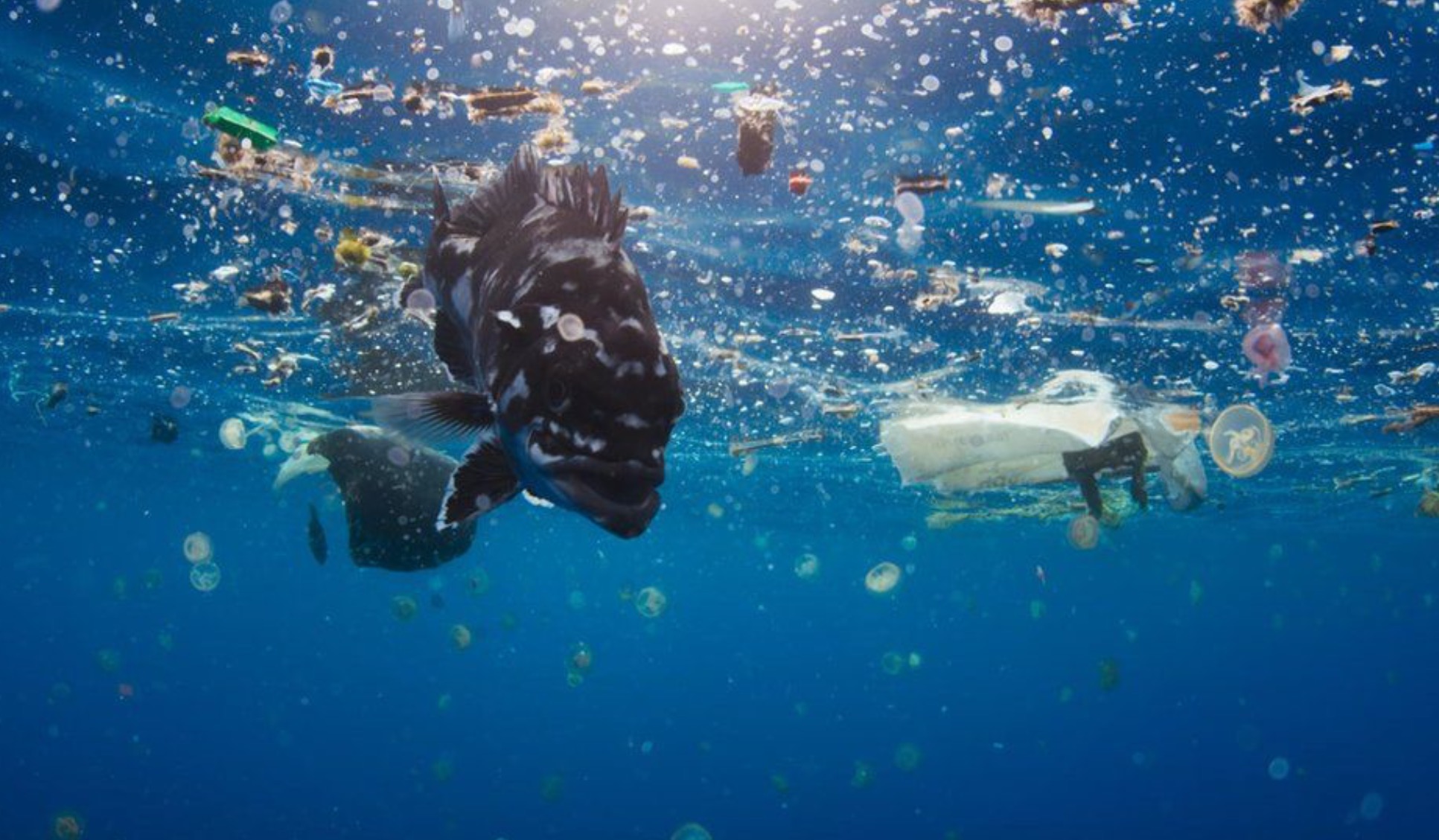
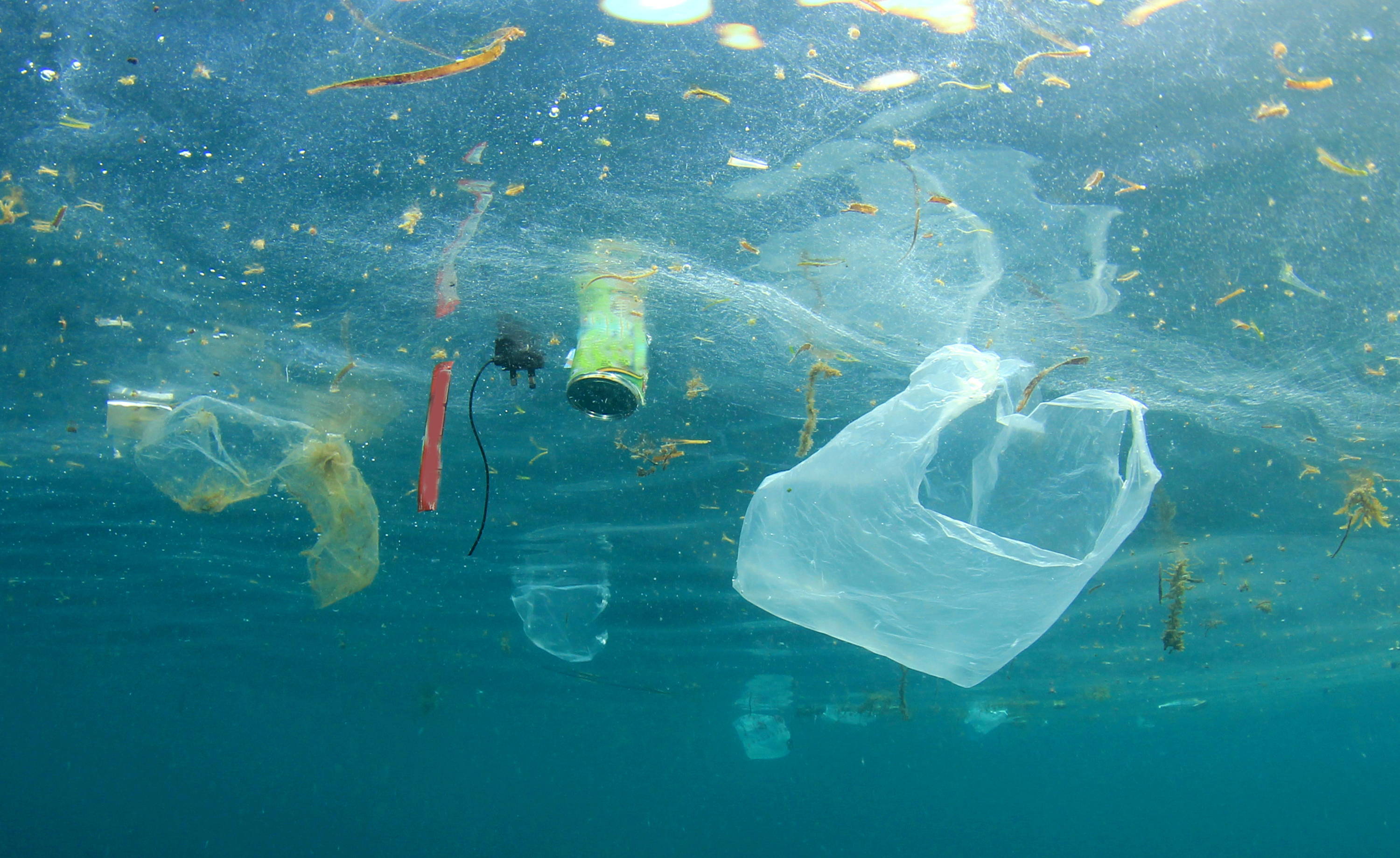
Figuratively speaking, the main vehicle for microplastics is water. So, during washing all synthetic microfibers end up in the water. In the case of plastic particles on roads and in the form of urban smog, they are washed away by rain. And there is also plastic garbage, which also decomposes into microparticles under the influence of chemical, biological and physical factors.
Unfortunately, even the most modern treatment facilities cannot catch this type of pollution, so most microplastic particles end up in rivers, and then into the seas and oceans. According to experts, the world's oceans can contain from 93,000 to 268,000 tons of microplastics. About 40 tons of microplastics enter the Baltic Sea alone every year. According to other estimates, from 2% to 5% of the plastic produced in the world penetrates into the water.
It is difficult for scientists to determine the exact amount of plastic in the oceans, as some of these materials are heavier than water and sink to the bottom, which complicates the calculations. And the one that remains on the surface accumulates heavy metals and other toxic substances contained in sea water.
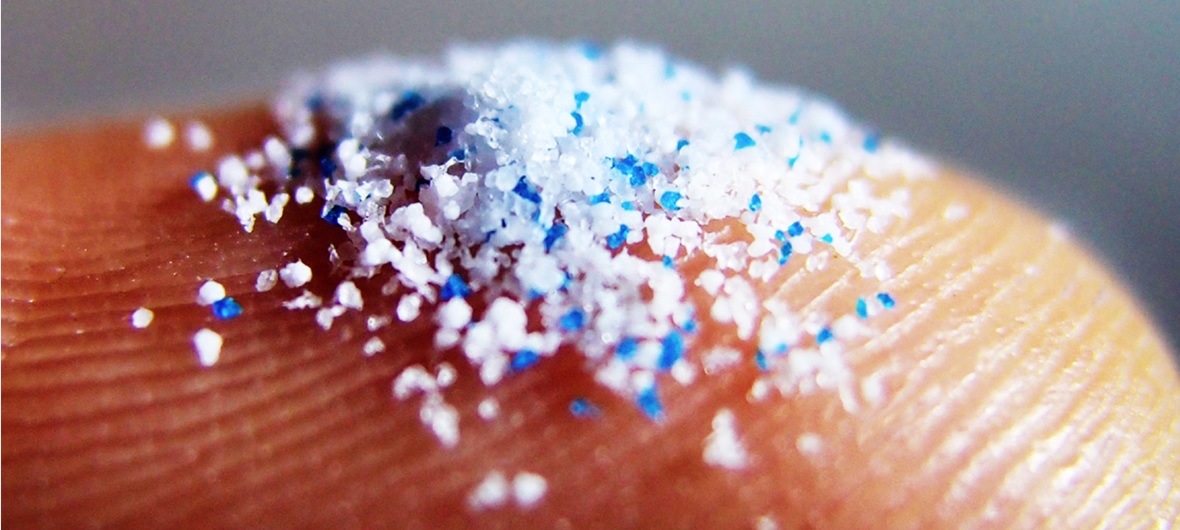
But microplastics are not only found in water. It is also present in the air - the so-called plastic dust that we inhale. Microplastics enter the soil from oxo-biodegradable foil, which is broken down into microparticles under the influence of the sun. Microplastics are increasingly being added to cosmetic products such as body lotions, face creams, make-up products, toothpastes, scrubs, and shampoos. In different types of products, the proportion of microplastics can range from 1% to 90%.
Environmental pollution
Cigarettes against the oceans
Nowadays, many people have the misconception that plastic bags are the main source of plastic waste in the oceans. Against this background, many countries around the world are joining a large-scale campaign calling for an end to the production of plastic bags.
Of course, bags are among the leaders in terms of pollution, however, if compared in quantitative terms with garbage, then they would drown in mountains of cigarette butts. In 2014, a group of volunteers from a litter-free world collected more than two million cigarette butts from the beaches of the United States of America.
Most people are unaware that a cigarette filter is, in fact, a plastic called cellulose phcetate. Sunglasses are made from the same material.The filter of a single cigarette is capable of disintegrating into thousands of microplastic particles that pollute the environment.
And even if we assume that in the future cigarette filters will be widely manufactured from materials subject to microbiological degradation, it doesn't improve the situation much. The fact is that even after smoking, cigarette butts still contain a variety of toxins that can pollute both the land and the ocean.
It is for this reason that some researchers advocate that cigarettes around the world be made without filters. And not only because the "gobies" represent the biggest threat to ocean life. Another reason, which has nothing to do with the pollution of the seas and oceans, is that the tobacco companies have created a false image in the minds of the inhabitants, according to which the filter makes cigarettes safe.
In this context, the results of one study are noteworthy, according to which many smokers would rather quit smoking altogether than switch to unfiltered cigarettes. In this way, would be able to improve the ecological situation in the oceans, and save the health of many people, and save the huge amounts of money that different countries spend every year to combat smoking and its consequences.
100% contaminated mussels
In 2018, a group of researchers from a UK university collected a number of “wild” mussels from eight coastal regions of the country to study. The scientists also bought this popular seafood from eight different local supermarkets.
As subsequent studies showed, absolutely all mussels contained microplastics (even those that were artificially grown on various farms). It is noteworthy that freshly caught bivalve clams contained fewer plastic particlesthan those bought frozen or already cooked.
This can only mean that microplastic pollution has long assumed planetary proportions. And the method of cooking mussels has absolutely nothing to do with it. The "wild" mussels, which were collected alive from eight different coastal areas, were all "infected" with microplastics.
And even in industrially grown mussels in the UK, about 70 microparticles of plastic and other waste were found. (for example, cotton and rayon) for every hundred grams of product. All this garbage ended up inside the mussels for the reason that these bivalves filter sea water through themselves in the process of feeding.
Some scientists put forward the assumption that plastic does not pose any risks to the human body, since it passes undissolved through our body. However, other experts believe that the negative impact of microplastic particles (especially nanoparticles) is still very poorly understood.
Stickies - annoying, but not dangerous

Sticks are large, gray, parasitic fish commonly found on the lateral surfaces of sharks, rays, and other large species. Stickies are not dangerous for their owners. They simply attach themselves to a larger animal and swim with it. The fish attached to the host absorbs leftover food and waste from the larger creature.In some cases, the sticks cleanse the host body of bacteria and small parasites.
Non-attached stickies can be a nuisance to divers. They have been known to cling to a diver's equipment or body. As long as the diver is covered by a wetsuit, sticking will not cause harm. Most encounters with free-swimming fish are comical as they mistakenly try to suck on the diver's equipment and limbs. However, fish that attach directly to a diver's skin can scratch them. This is another reason to wear a wetsuit when diving.
Types of plastics and their applications in modern industry
Often we see abbreviations of plastic types instead of full names. Let's decipher these abbreviations and look at the most common types of plastics in the industry:
- PEHD or HDPE - HDPE is low pressure polyethylene, high density polyethylene. Scope of application - production of flasks, bottles, semi-rigid packaging. It does not pose a risk for use in the food industry and is considered safe.
- PET or PETE - PET, PET is polyethylene terephthalate (lavsan). It is used for the production of packaging, upholstery, blisters, liquid food containers, in particular beverage bottles.
- PVC - PVC - polyvinyl chloride. The scope of application is quite wide. It is used to produce garden furniture, window profiles, electrical tape, floor coverings, blinds, electrical insulation, oilcloth, pipes, detergent containers.
- PP - PP - polypropylene. It is used in the manufacture of toys, in the automotive industry (bumpers, equipment), in the food industry (mostly in the manufacture of packaging). For food use, PP is considered safe.Polypropylene pipes are common for the manufacture of water supply networks.
- LDPE or PELD - LDPE is low density polyethylene, high pressure polyethylene. It is used in the production of bags, flexible containers, tarpaulins, garbage bags, films.
- PS - PS - polystyrene. The scope of its application is quite wide: it is used to make packaging material for food products, thermal insulation boards for buildings, dishes, cutlery and cups, pens, CD boxes, toys, as well as other packaging materials (foam materials and food film). Due to its styrene content, this material is considered potentially hazardous, especially when flammable.
- Others. This group includes any other plastics not included in the groups listed above. Most often, it is polycarbonate used to make reusable dishes, for example, baby horns. Polycarbonate may contain bisphenol A, which is hazardous to humans.
Today, scientists face the main task - to study the influence of chemical and physical effects on the reproductive function of organisms, their growth, as well as the susceptibility of an organism affected by microplastics to diseases.
In March, a study was published that indicated that not only did fish exposed to microplastics reproduce fewer fry, but their offspring, which were not adversely affected by plastic particles, also repeated the parental experience. These studies have led scientists to speculate that the negative effects of microplastics may affect future generations.
There are organisms, for example, freshwater crustaceans, which are called amphipods, did not react in any way to microplastics, but this is for now.Martin Wagner, an ecotoxicologist at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology who took part in the study, said:
Perhaps this is because they can process natural indigestible materials such as pieces of stone.
Chelsea Rohman, a University of Toronto researcher, has been experimenting with several types of living beings and studying the toxic effects of exposure to microplastics. It was found that the negative impact came only from certain types of plastic.
A significant part of the research on the negative impact of microplastics was carried out in laboratory conditions. The experiments were designed for a short time, and only one type of plastic with larger particles was used. Or the studies were conducted in conditions of increased concentration of microplastics compared to their content in the environment.
Wagner stated that the studies "will not tell us about the long-term environmental impacts that occur at low concentrations of microplastics." Wagner is among the researchers moving beyond past measurements, matching animals to the pollutants and polymers they are most likely to deal with in real life.
In Wagner's words, real-world features are being taken into account, in which microplastics "won't be the only stressor." For species that are also subject to other pressures such as poaching, chemical pollution, climate change, microplastics may be the last straw.
“It's very difficult,” says Wagner.
Sources of myroplast
There are three sources of microplastics entering the human body: air, water, food.In everyday life, a person constantly releases microplastics. For example:
- Throwing plastic bottles into water or on the ground - under the influence of moisture and the sun they disintegrate;
- Using the car: tires are erased on asphalt, forming fine plastic dust;
- Washing - Synthetic clothing releases microplastic particles during washing;
- Washing your face and brushing your teeth - a large number of cosmetics contain a large amount of microplastic granules.
Air
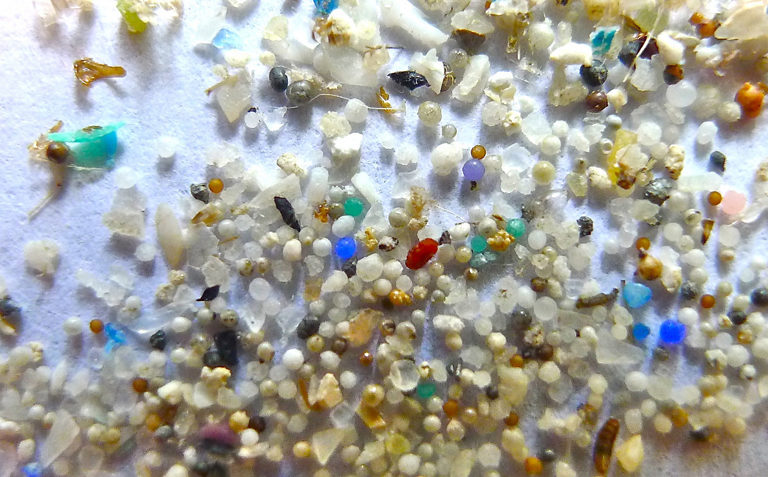
Microplastics enter the air with the help of wind currents from ground sources, such as landfills, landfills, etc. Due to the fact that microplastics are very small and have almost no mass, the wind can carry them thousands of kilometers from the source. So, in May, French scientists found particles of plastic less than a tenth of a millimeter in size in the Pyrenees. Also, plastic was in the snow, rainwater and on the surface of the soil. On average, over 300 fragments (fibers and small particles) were located per square meter
It is important that due to the very small volume, not every respirator will be able to protect against plastic entering the body through the lungs.
Water
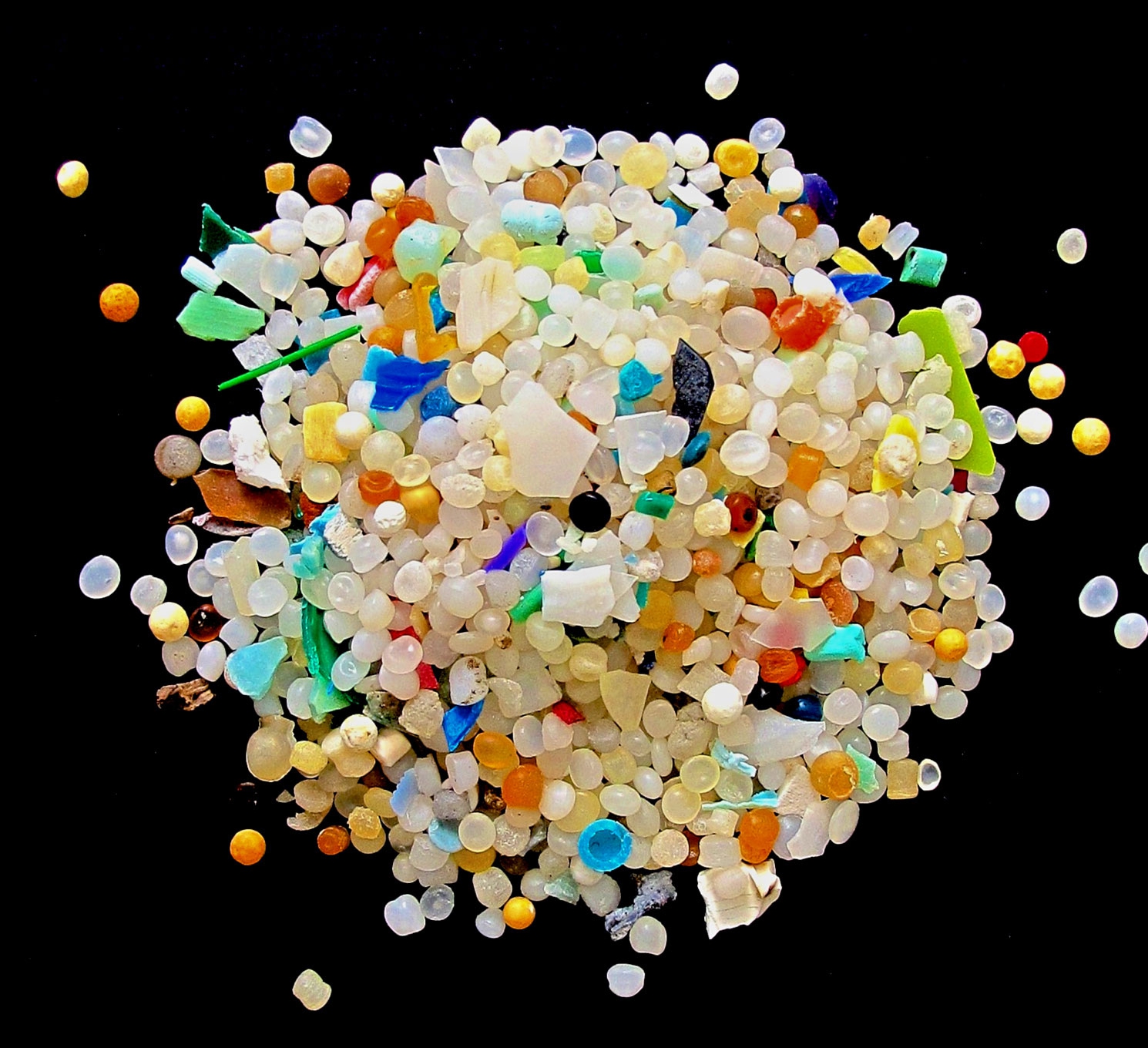
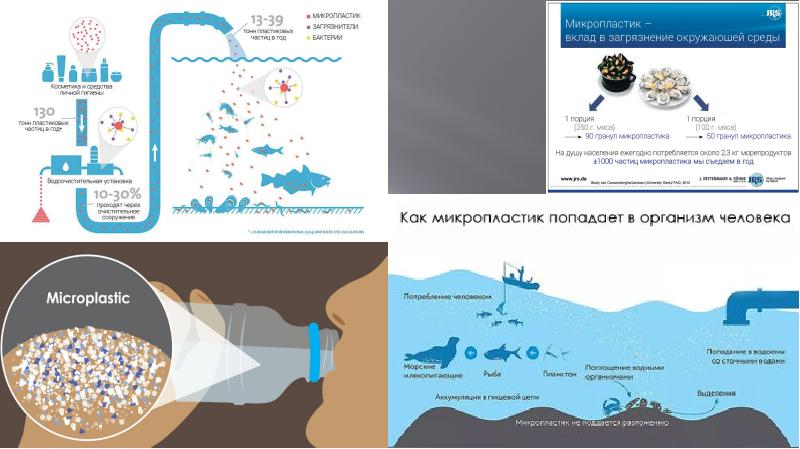
Water is one of the main sources of microplastics in the world. This is due to the fact that a huge amount of plastic garbage is dumped into the water. Already, the diameter of the garbage island in the Pacific Ocean exceeds 1.5 thousand kilometers and, like an iceberg, goes under water. Note that annually humanity produces 400 million tons of plastic, but only a fifth of it is sent for recycling. The bulk is sent to landfills and decomposed into small particles.
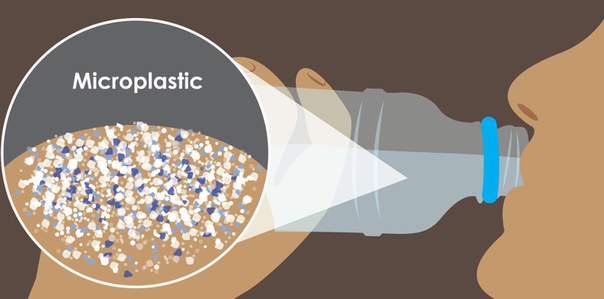
Interestingly, microplastic particles have been found not only in the world's oceans, but also in bottled water.According to research by American scientists, every liter of liquid that enters the human body from plastic containers contains 325 microplastic particles.
For the study, scientists purchased drinking bottled water from 27 different batches in 9 countries in Europe, Asia, Africa and America. A total of 259 bottles of 11 brands were purchased, with only 17 of them containing no traces of microplastics. As a percentage, it turns out that 93% of water bottles contain microscopic particles of plastic.
The particle diameter ranges from 6 to 100 micrometers, which is comparable to the thickness of a human hair. The structure of microplastics from bottled water looked like this:
- 54% - polypropylene, from which bottle caps are made;
- 16% - nylon;
- 11% - polystyrene;
- 10% - polyethylene;
- 6% - a mixture of polyester and polyethylene terephthalate;
- 3% - other polymers.
Food
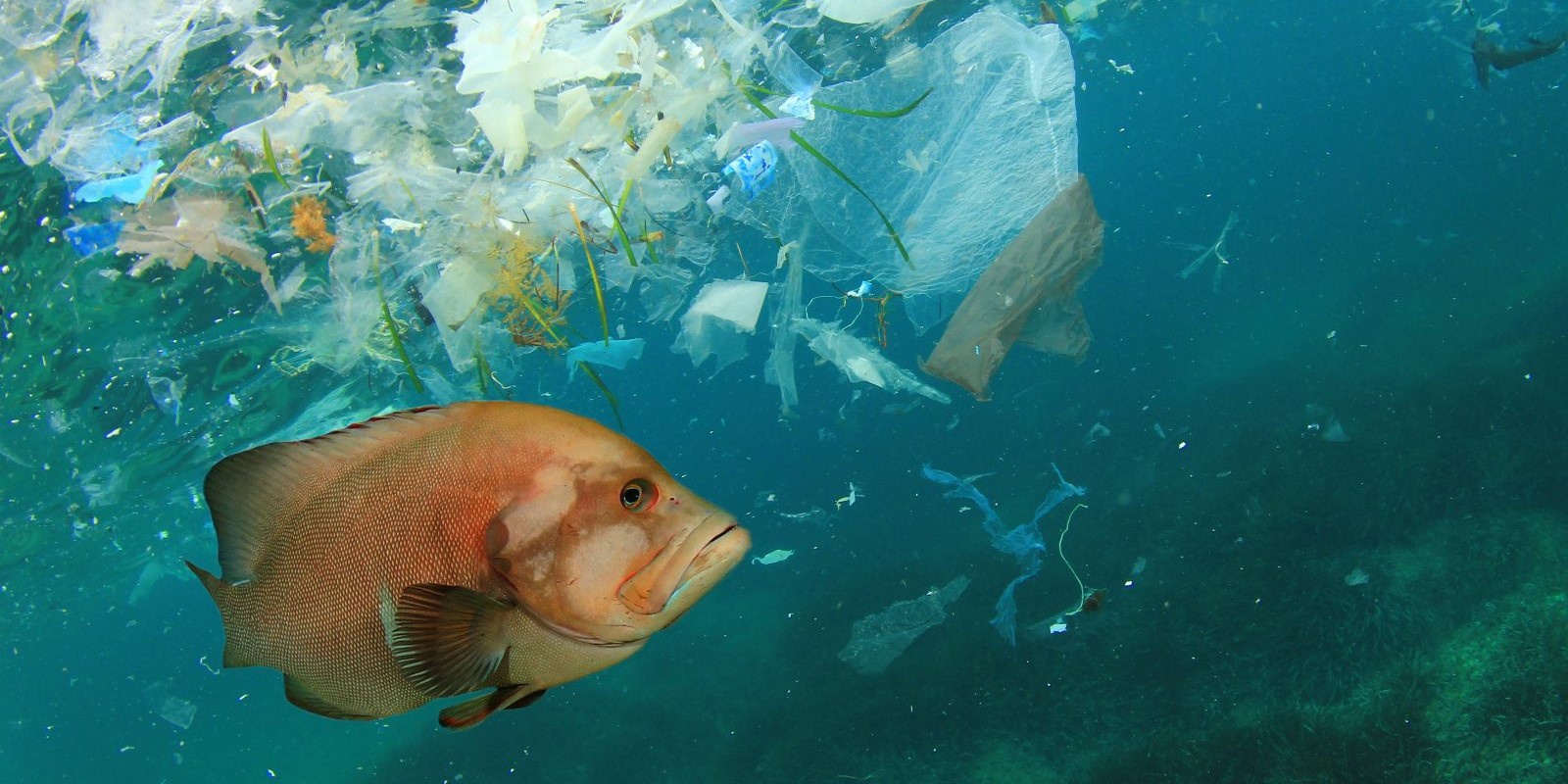
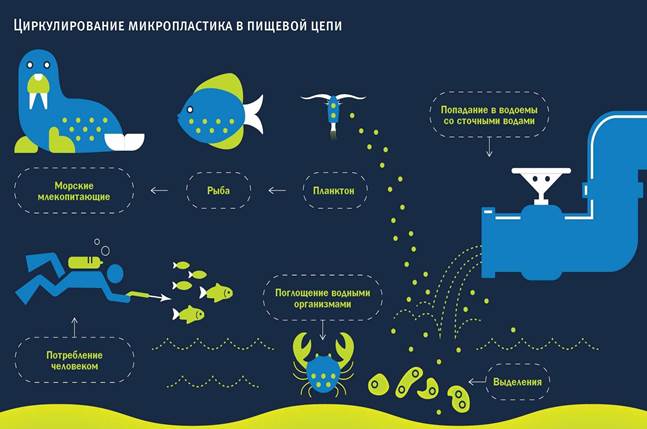
Another source of microplastics entering the human body is food. A few years ago, scientists discovered microplastics in plankton, which means they are already in the lowest levels of the food chain, where they reach the human table. Most plastic is found in fish and seafood, especially oysters and mussels. They contain 360-470 particles per kilogram.
Note that according to the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), 21 grams of plastic enters the human body per week - this is equivalent to a credit card. About 250 grams are accumulated per year - this is one and a half smartphones. According to WWF, most microplastics enter the body with drinking water.
How microplastics affect human health
To date, experts have no scientific evidence that microplastics are dangerous to humans, since serious studies on this topic have not yet been conducted. However, many scientists suggest that the consumption of plastic, even in the form of microfibers, can lead to gastrointestinal disorders, tissue inflammation, liver problems, endocrine disorders, and even malignant cell transformation. Together with plastic, toxic chemicals and other pathogens can enter the human body. According to scientists, only the largest particles of microplastics enter the intestines, smaller ones can penetrate the bloodstream, lymphatic system, and even reach the liver.
In 2016, Dr. Una Lonnstedt, together with colleagues from Uppsala University (Sweden), studied the behavior and health of perches kept in a reservoir contaminated with plastic. Scientists have found that 15% fewer fry hatch from eggs in a polluted environment than in a clean reservoir. In addition, the inhabitants of waters rich in microplastics grow smaller, they are slower and die faster. And most interestingly, the habitat affects the food preferences of fish. Residents of polluted water bodies, choosing between plankton and microplastics, often choose the latter. And although this study only concerns fish, scientists saw a threat to humans in its results.
First law against microplastics
If you don’t surprise anyone with the prohibitions on the use of disposable tableware, plastic bags, straws, then it’s more difficult with microplastics. The European Union has pioneered legislation regarding the use of microplastics by manufacturers.
At the beginning of 2019, the Government banned the addition of all types of plastic to products.To a greater extent, this applies to the cosmetic industry. Brands will have to replace this component with a biological alternative.
We hope that this legislative initiative will be successfully implemented and become an example for other countries. And if we also connect personal control of funds on our shelf and clothes in the closet, we can achieve good results and reduce our eco-footprint.
Which foods contain the most microplastics?
In the modern world, it is impossible to avoid getting polymers into the body. Most of them are found in the air. Even in the Pyrenees, 365 particles per square meter were recorded. m. In bottled water there are 325, in apples - 195.5. Microplastics enter fruits and vegetables through water and soil. According to the World Wildlife Fund, every week we eat 5 grams of polymers (the weight of a credit card) or 250 grams per year (the weight of a small tablet).
Particles are found not only in plant and animal foods. They are found in clothing, cosmetics, shampoos and other household chemicals.
According to the UN, more than 9 billion tons of plastic have been produced in the world. This is about 1 ton per person. And the pandemic has only made things worse. The journal Environmental Science and Technology estimates that, in addition to ordinary waste, the COVID-19 pandemic is causing 129 billion face masks and 65 billion gloves, which are also made from polymers, to be thrown away every month.

Corals are dangerous if touched
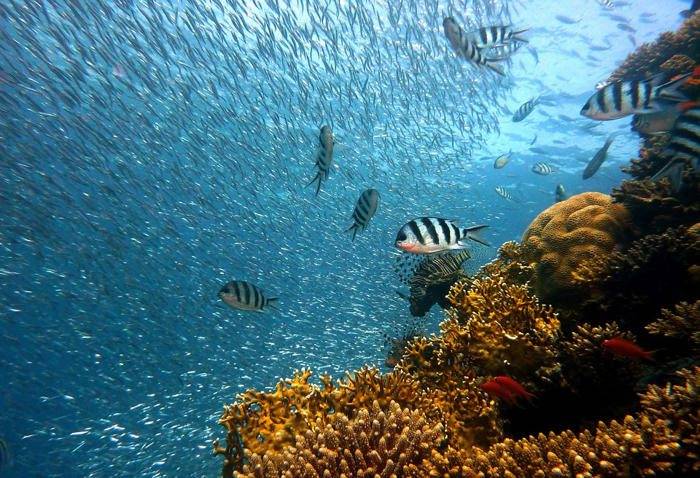

The most common marine injury during scuba diving is believed to be from corals. Coral is a hard structure covered with thousands of tiny coral polyps.A person who swims near a coral reef may be cut by sharp limestone or stung by coral polyps. Depending on the type of coral, these injuries range from minor scratches to severe burns. Of course, you can completely avoid injury by staying away from the reefs.
Contact with corals is dangerous not only for humans, but also for corals. Even a slight touch can kill coral polyps. A person who touches the reef does more damage to the corals than they do to him.
What can I do?
- Reduce the individual release of microplastics into the environment: wash less often and do not buy clothes made of synthetic fabrics, refuse to use household chemicals and cosmetics with microplastics, give plastic waste for recycling.
- Limit your consumption of seafood and mussels in particular.
- Invest in a water filter that removes even the smallest microplastic particles and try not to drink bottled water.
LIST OF USED LITERATURE
- Diogo Peixoto, Carlos Pinheiro, João Amorim, Luís Oliva-Teles, Lúcia Guilhermino, Maria Natividade Vieira. Microplastic pollution in commercial salt for human consumption: A review. ()
- Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity. Marine debris: understanding, preventing and mitigating the significant adverse impacts on marine and coastal biodiversity. ()
- Greenpeace. Microplastics found in drinking water sources in St. Petersburg. ()
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood. ()
- Jiana Li, Christopher Green, Alan Reynolds, Huahong Shi, Jeanette M. Rotchell.Microplastics in mussels sampled from coastal waters and supermarkets in the United Kingdom. ()
- Wieczorek Alina M., Morrison Liam, Croot Peter L., Allcock A. Louise, MacLoughlin Eoin, Savard Olivier, Brownlow Hannah, Doyle Thomas K. Frequency of Microplastics in Mesopelagic Fishes from the Northwest Atlantic. ()
- S.L. Wright, F.J. Kelly. Plastic and human health: a micro issue? ()
- Sherri A. Mason, * Victoria G. Welch, and Joseph Neratko. Synthetic Polymer Contamination in Bottled Water. ()
- European Parliament News. Microplastics: sources, effects and solutions. ()
- Liebmann, Bettina & Köppel, Sebastian & Königshofer, Philipp & Bucsics, Theresa & Reiberger, Thomas & Schwabl, Philipp. Assessment of microplastic concentrations in human stool — final results of a prospective study. ()
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Microplastics in fisheries and aquaculture: status of knowledge on their occurrence and implications for aquatic organisms and food safety. ()
- United Nations News. ‘Turn the tide on plastic’ urges UN, as microplastics in the seas now outnumber stars in our galaxy. ()
- Plastics Europe, Operation Clean Sweep Report. ()
- Matthew Cole, Pennie Lindeque, Claudia Halsband, Tamara S. Galloway. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. ()
- Julien Boucher, Damien Friot. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: a Global Evaluation of Sources. International Union for Conservation of Nature. ()
Problems - trailer
Microplastics can turn into the whole Universe, just some kind of space. For some reason, it attracts representatives of marine flora and fauna: algae, bacteria.
“Especially for some reason they love polystyrene, expanded polystyrene.If you take a fragment that has been in the sea, you can see a whole ecosystem: it is all overgrown, inside the passages of some aquatic insects. What is the risk? Biologists look at this with apprehension. So far, no scary things have been found, but plastic is very easily transported, especially by currents in the ocean from Africa to Europe. What microorganisms, what biology, viruses can be brought? It’s not clear,” says Irina Chubarenko.
The scientist explains: plastic itself is absolutely inert, a good durable material - it takes 500-700 years to decompose, and sometimes the range is from 450 to 1000 years (you know, no one has checked this yet). "Material of the 21st century", as they said in the middle of the 20th century.
Why does he live so long? Yes, he does not need anyone! says the expert. - Only as a carrier, a collector, and animals, fish, birds take it for food. Of course, this is not helpful. Even worse, when large animals get entangled in marine debris, they die because their stomachs are filled with plastic instead of normal ordinary food. But plastic itself is just a hydrocarbon, a natural element. That is, a person has managed to make such long molecules that now cause concern. When various products are made from plastic, dyes, plasticizers, UV stabilizers are added to it, that is, there are many other chemicals that are harmful in themselves.

Remains of an albatross chick fed plastic trash by its parents
“Microplastic particles take on well various toxicants: organochlorine, organobromine. All this moves around the world, forming a new plastisphere, ”says a Greenpeace representative.
tea bags
Researchers at McGill University in Canada found that when tea bags are immersed in a cup of near-boiling water (95°C), about 11.6 billion microplastic particles and 3.1 billion smaller nanoplastic particles are released into the liquid. This number is significantly higher than the estimated number of microplastic particles consumed by a person throughout the year. Four different types of plastic commercial tea bags were tested, taken from shops and cafes in Montreal. The tea bags were cut, washed and then immersed in near-boiling water for five minutes and then analyzed by electron microscopes and spectroscopy.
Prevention
Brewing and drinking loose leaf tea is tastier and healthier than tea bags. Tea bags are a substandard low quality product that does not bring any benefit to the body, including the danger of toxins and plastic microparticles.
Diphyllobothriasis
Diphyllobothriasis is a helminthic disease that affects the digestive organs. The causative agent is a wide ribbon. This is the largest of the human helminths, its length can reach 10, and sometimes 20 meters. The parasite consists of a head, neck and body. The head is an oblong oval shape, flattened laterally and has on its narrow sides two longitudinal suction slots (bothria), with which the tapeworm is attached to the intestinal wall. The body consists of many segments, and the width is much greater than the length, which is due to the name of the parasite (wide tapeworm). The number of segments can reach 3000-4000 pieces. The tapeworm lives in the upper sections of the small intestines, feeds on the entire surface of the body, while absorbing various nutrients, including Bi2 vitamins and folic acid.Lentets wide-hermaphrodite. During the day, up to 2 million eggs are excreted in the external environment with feces. The number of parasites can reach up to 100 copies. Lifespan parasites in the human body reach the age of 28.
For the development of a wide tapeworm, like opisthorchiasis, the presence of three owners is necessary.
The final host is man, domestic and wild animals. Everyone secretes eggs, which fall into reservoirs with melt water. Diphyllobothriasis cannot be transmitted through water.
Intermediate hosts are cyclops (crustaceans). Eggs are swallowed by crustaceans (cyclops) and larvae develop in their body. Cyclopes are swallowed as food by freshwater predatory fish.
An additional host are fish of predatory species: pike, burbot, perch, ruff, pike caviar is especially dangerous.
Attached to the wall of the intestines, the parasites infringe the mucous membrane of the intestines with bothria and can be one of the reasons for its necrosis. Sometimes there is blockage of the intestines.
Diphyllobothriasis occurs in a mild or severe form, which is associated with the intensity of invasion, the presence of concomitant diseases and the general condition of the body. Sometimes the disease is asymptomatic.
With a mild course, patients complain of general weakness, poor appetite, nausea, pain and rumbling in the abdomen, intestinal disorders, and decreased ability to work.
In severe cases, intestinal obstruction occurs. In 2-3% of patients, a severe form of anemia (anemia) occurs. Patients complain of weakness, drowsiness, dizziness. Bright red spots, cracks appear on the tongue. The skin becomes pale with a yellowish tint; the liver and spleen may be enlarged. Body temperature reaches 36-38 degrees.
The diagnosis of these diseases is established on the basis of the detection of eggs of a wide tapeworm and opisthorch in feces.
How microplastics enter the human body
Plastic enters the human body with food. Scientists have found that its microparticles can be found in fish and seafood, sea salt, beer, and even bottled water.
Water
Scientists say microplastics are ubiquitous, including plumbing. But if someone believes that only tap water is dangerous, then they are deeply mistaken. In 2017, specialists in different parts of the world purchased 250 bottles of drinking water from 11 global brands. Their task was to study how safe bottled water is to drink. In 93% of the samples tested, scientists found microplastics. Moreover, it turned out that in bottled water, the amount of microplastics is almost 2 times higher than that recorded in tap water. In some samples, the amount of plastic reached 10,000 molecules per 1 liter of water. It is impossible to see these plastic particles with the naked eye, since their size for the most part does not exceed 100 microns, which is comparable to the diameter of a hair. Scientists have suggested that plastic containers may be the source of plastic in drinking water.
Fish
One food that also contains microplastics is marine fish. In addition, microplastics have been found in all types of marine organisms, from plankton to birds and mammals, in the same food chain.
Microscopic particles of plastic enter the fish with food and are stored in its digestive system.In most cases, plastic in fish is not terrible for humans, since no one eats the insides of fish, although it harms the fish itself. But researchers have found that, in some cases, the plastic enters the fish's bloodstream, and thus into its meat. And such a product is no longer the safest for humans. Experts suggest that at least half of the world's population absorbs microscopic plastic fibers with food.
How to reduce microplastics
It is most likely impossible to exclude microplastics from food, water, soil, air. But we can reduce its amount around us. Given the sources of microplastics and reasons for its appearance, there are three ways to reduce the toxic pollutant.
-
Give preference to clothes made from natural fabrics: linen, silk, organic cotton, wool, etc.
-
Sort the trash. If plastic waste ends up in recycling, rather than landfills and then into the environment, then it will not become a source of microplastics.
-
Read the composition of cosmetics and household chemicals. It is necessary to exclude from use funds with the following components:
Acrylates/C10-30
Acrylates Crosspolymer (ACS)
Alkyl Acrylate Crosspolymer
Carbomer
Ethylene-Vinylacetat-Copolymer
Nylon-6
Nylon-12
Polyacrylate
Polymethyl Methacrylate
Polyquaternium
Polyquaternium-7
Polyethylene (PE)
Polypropylene (PP)
Polyothylenteraphthalat (PET)
Polyurethane (PUR)
Polyurethane-2
Polyurethane-14
Polyurethane-35 etc.
That leaves Nylon, Carbomer and Ethylen, making the list shorter and easier to remember.
However, innovations aimed at combating microplastics have already begun to emerge.In the UK, Guppyfriend has patented a synthetic laundry bag that keeps microplastics from our clothes from ending up in the sewer and then into the environment. The invention is made of the smallest polyamide mesh, which acts as a filter. After use, the bag must be shaken out and the collected microplastic fibers must be disposed of. Manufacturers are asking customers to send them their bags that have become unusable for recycling.
This is interesting: How to wash if the washing powder is over - in the washing typewriter machine and hands
Backhorn - aggressive

Some species of triggerfish are friendly, while others defend their territory from intruders. An example of a highly active triggerfish is the blue-finned balisthodes, common in the Indo-Pacific region. They are quite large - about 75 cm long - and have specialized teeth and powerful jaws. Blue-finned balisthodes are highly protective of their nests and territory, and will bite intruders.
These fish are known to seriously injure divers and should not be taken lightly. Many experienced divers are more nervous to see bluefin balistodes than any other fish. Diving in the habitats of these dangerous creatures usually includes a clear explanation of how to identify these triggerfish and what actions to take if an aggressive individual is found. Stay with your diving guide and follow his advice. In many cases, guides can help divers avoid dangerous areas.