- Positive and negative features
- Economy
- Life time
- Radiation quality
- The size
- Design
- Applications
- Advantages and disadvantages of light bulbs
- Advantages, disadvantages and scope
- Classification of modules with G4 base
- Features of capsule devices
- Distinctive features of models with a reflector
- MGL connection
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Design
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Operation of metal halide lighting devices
- MGL classification
- Application
- Fluorescent lamps
- Principle of operation
- The main types of halogen lamps
- With external flask
- Capsule
- With reflector
- Linear
- Halogen lamps with IRC coating
- Halogen chandeliers
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Positive and negative features
The design features and the materials used in the manufacture give the lamps certain pros and cons, which we will consider in terms of the main criteria for use.
Economy
The combination of factors such as high pressure, good metal performance and retention of a significant part of the radiant heat within the bulb (additional heating of the filament) endows halogen very good lamps light output - from 15 to 22 lm / W. For comparison, for "Ilyich's bulbs" this indicator does not exceed 12 lm / W.Simply put, a halogen lamp gives almost double the power advantage over classic counterparts.
As already mentioned, to improve performance by reducing losses, manufacturers use lamps with heavy inert gases and IR-blocking glass. The design of fixtures is regularly improved, due to which the advantages of their use become more obvious.
Life time
Partial restoration of the filament or filament during the tungsten-halogen process makes this type of lamp more durable. Today, a value of 2000-5000 working hours is considered quite a typical indicator. Despite the fact that halogen lamps have good competitors in the form of LED counterparts in this parameter, they win by a wide margin over classic tungsten incandescent lamps.
Radiation quality
Experts believe that halogen lamps give the radiation closest to natural light in terms of spectrum composition and other characteristics. Fluorescent and LED lamps also lose to them in this matter, because the shift of the spectrum towards blue “sins”. In halogen, this property also manifests itself with high heating, but it is less pronounced, and the color rendering remains within Ra 99-100.
The size
The ability to create efficient yet compact lamps has played a large role in the current popularity of halogen lamps. Conciseness in size allows them to meet the requirements of modern interior design, when lighting fixtures are installed in suspended ceilings, false ceilings and other structures with limited space.Compactness also makes it possible to effectively use halogen lamps in cars.
Additional advantages of this include good and simple compatibility with dimming equipment (light control) and safe operation in conditions of increased complexity, for example, with high humidity. In addition, lamps with an external bulb allow you to give the light flux different shades, which is valuable in design.
Design
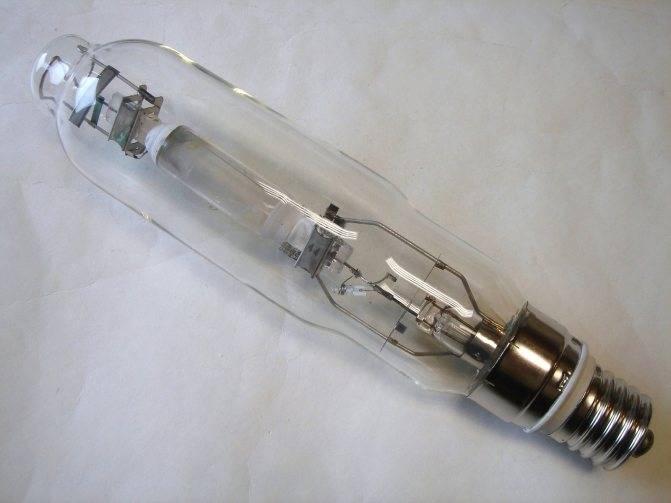
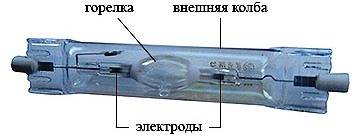
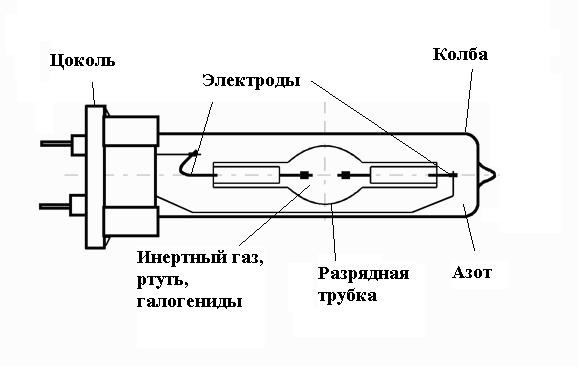
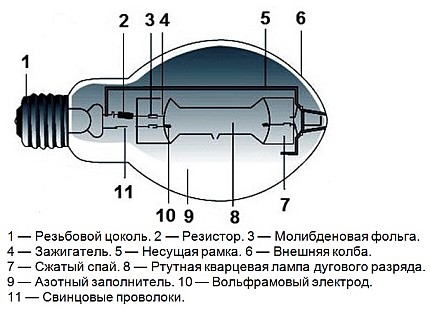
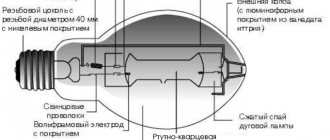
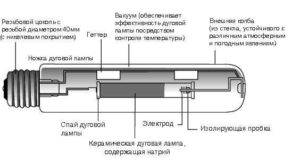
In its structure, haze does not differ much from mercury arc light sources. It also uses a burner made of ceramic or quartz. The flask plays a big role in ensuring the right temperature, reduces heat loss and cuts off ultraviolet radiation. The flask is made of borosilicate glass, which has increased strength and heat resistance. You should be aware that industrial models do not provide for an external flask; ozone-free quartz glass is used there.
Due to the fact that modern modifications are used in the lamp, metal halide lamps do not imply incandescent filaments, which ensures longer service life. There is also an easier start, due to the use of ignition electrodes.
Due to the fact that the flows of halide during the passage of the discharge depend on gravity, the lamp must be in the required position during operation. Lamps with two bases can only be operated in a horizontal position. Models with one base, for the most part, work with a vertical installation. There are separate models that are suitable for working in any position. Horizontal models are marked with the letters "BH" and vertical ones with "BUD". For any positions - "universal".
Applications
Different power and a wide color range of metal halide lamps make it possible to use them in the following areas:
- film studios;
- architectural structures;
- car lights;
- installations for lighting public buildings;
- scenes;
- railway stations;
- sports facilities, etc.

Lighting devices of this type can have high power, therefore they are used in industry and landscape design. Often such attributes are used as street lighting at night in parks, squares, to illuminate buildings, monuments, etc.
In the stadium, metal halide lamps are indispensable devices. Circuses, shopping centers, advertising structures, arenas, office buildings are those structures that require powerful lighting.

Advantages and disadvantages of light bulbs
Like any other devices designed to create modern, practical and comfortable lighting systems for domestic, decorative and other purposes, halogen-type light bulbs equipped with a G4 base have certain advantages and disadvantages.

Due to their modest dimensions, G4 halogen lamps are ideal for installation in crystal chandeliers or sconces of the original design. The light emanating from the lamps shimmers beautifully in the pendants and gives the lighting fixture a spectacular, rich and catchy look.
The first category includes parameters such as:
- more economical consumption of electrical energy compared to classic incandescent lamps;
- optimal brightness of the light stream, which helps to increase concentration of attention, but does not cause additional eye strain in both adults and children;
- good light density and almost complete absence of distortion of the natural colors of human faces, furniture, interior and decorative elements located in the illuminated room;
- almost 100% stability of the luminous flux transmitted by the lamp throughout the entire operating period declared by the manufacturer;
- 30% more light supplied with the same power as the Edison lamp;
- compact dimensions, due to which the products can be used in open and closed lighting fixtures of various sizes, designed to organize spot, zone or background lighting;
- increased strength of the outer quartz bulb;
- extended service life - from 2000 hours subject to the basic rules of operation and up to 12,000 hours when organized in a soft start system;
- the presence in this segment of a large number of offers from recognized, reputable brands that have proven themselves in the market of lighting equipment and related elements.
All these criteria attract the attention of customers and make them prefer halogen modules when buying. Low voltage capsule lamps available in 10 W, 20 W and 35 W
It is not possible to manufacture products of this configuration, but with a brighter light flux on the G4 base. If enhanced radiation is required, it is worth using g4 reflector modules. They will give a glow with a power of 20 W, 35 W and 50 W

Low-voltage capsule lamps have a power of 10 W, 20 W and 35 W. It is not possible to manufacture products of this configuration, but with a brighter light flux on the G4 base.If enhanced radiation is required, it is worth using g4 reflector modules. They will give a glow with a power of 20 W, 35 W and 50 W
But, despite the large number of positive qualities and progressive characteristics, halogen-type products also have their negative features. There are somewhat fewer of them than positive ones, but it is simply unreasonable not to take them into account when organizing a lighting system.
Among the cons, the following are most often mentioned:
- not too high level of efficiency, which is only 50-80%; such indicators are due to the expenditure of a large amount of energy for the basic heating of the product;
- insufficient strength of the device shell, vulnerable to mechanical damage;
- health hazard - in case of violation of the integrity of the design of the flask, a gas escapes into the atmosphere, which has a negative effect on a person and provokes migraines and severe headaches;
- high moisture susceptibility - limits the scope of use of halogens and makes it impossible to use them in the bathroom due to frequent temperature changes and the presence of constant condensate.
Modules that have served their time should not be thrown into a regular trash can. When broken, they emit vapors harmful to humans and the atmosphere.
It is recommended to send them to special containers intended for the processing of chemical waste or to hand them over to an enterprise that disposes of devices containing aggressive substances.

The compact G4 halogen pins are perfect for creating decorative lighting systems in residential and sanitary areas, shops, advertising and showrooms.
Of course, all these moments are not fatal and are not worth it to completely abandon the use of halogens.It’s just that before buying, you should think carefully about all the pros and cons in order to understand how to properly use the positive qualities of G4 lamps, and reduce the impact of negative ones to a minimum.
Advantages, disadvantages and scope
Experts and consumers note that the use of MGL bulbs has a lot of advantages. These include the following:
- greater durability than ordinary incandescent bulbs;
- high degree of light output;
- small power consumption;
- compactness;
- reliability of normal functioning even at low temperatures;
- good color rendering.
Metal halide lamps are not without drawbacks. Among them:
- the impossibility of adjusting the light flux;
- long warm-up;
- the need to use IZU;
- the inability to re-ignite the MGL lamp immediately after deactivation;
- sensitivity to sudden voltage drops.
Despite some disadvantages, metal halide type light bulbs are used in both conventional lamps and lighting equipment, due to the mass of useful properties.
Metal halide lamps are used in many areas:
- stage, studio and film lighting;
- decorative;
- architectural;
- utilitarian;
- lighting on the streets, in particular in quarries, railway stations, sports facilities, etc.
Among other things, metal halide lamps are often used for the production of headlights for motor vehicles and for industrial lighting.
Classification of modules with G4 base
This type of halogen is available in two versions: in the form of a small capsule or in the form of a truncated cone with a reflector.Each of the designs is designed for specific purposes and correctly provides the required light output in suitable conditions.
Features of capsule devices
Halogens G4, having an elongated elongated flask made of quartz glass, are called capsular or finger. The incandescent spiral in them is located longitudinally or transversely and, as a rule, in one layer.
The rear wall of the interior space is covered with a special reflective compound. The modules do not need additional external reflectors and protective elements.

The compactness of the products allows them to be used to illuminate furniture sets, ceiling space, shop windows and retail facilities. In everyday life, decorative sconces, chandeliers and lamps of the most unexpected shapes and configurations are completed with small light sources.
Being low voltage light sources, for a correct connection to a 220 W network, they need a transformer that lowers the base voltage.
Capsule-type devices mainly have a warm range of working light flux. However, compared to classic incandescent lamps, their tonality spectrum is much closer to the natural white glow that is characteristic of the natural environment.
G4 halogens, even at low power, have good brightness and almost without distortion convey the complexion of people in the room, and interior elements and pieces of furniture are illuminated with a pleasant neutral-warm light.

On illuminated surfaces, capsule devices create an attractive glossy effect, while maintaining the natural tonality inherent in objects.
This lighting option allows you to convey the overall color orientation of the interior, emphasizing its most catchy and original elements.
Distinctive features of models with a reflector
G4 halogen devices with a reflector have a specific shape resembling a truncated cone and are called reflex devices. They give a directional light stream at different angles.
Inside the flask of such devices is a special element that reflects light and distributes it more clearly and evenly.
The reflector is usually of two types:
- interference;
- aluminum.
The first type has a translucent texture and actively removes the generated heat back, which significantly enhances the basic light intensity, but makes its flow diffuse and wide.
The second option redirects the resulting heat forward and creates a narrower, brighter and more concentrated beam of light.
There are also some differences in the design of the bulbs. Different manufacturers produce modules with a G4 base, both with and without a protective glass cover. The configuration of products is determined by the intended purpose.

The angle of dispersion of G4 halogen reflective bulbs ranges from 8 to 60 degrees. This quality allows you to mount light sources with reflectors in devices that provide directional illumination of goods and exhibits.
Modules with external protection against damage are suitable for use in open luminaires of any configuration. Halogens without a cover are mounted only in closed fixtures, where there is no direct access to the surface of the bulb.
MGL connection
Since this light source cannot be connected directly to the network, there are certain auxiliary devices that allow you to start. Since the burner cannot ignite itself, it needs a high-quality high-voltage discharge.For this, a ballast control gear is provided, which is otherwise called ballast. They are electromagnetic and electronic. It is best to choose electronic ballasts, as they can significantly extend the service life and provide an even glow at start-up. The advantage is ballasts that have a built-in IZU, which can not only ignite the burner, but also limit the current. Another advantage is their size, as they are more compact and lighter. To extend the service life and save electricity, it will not be superfluous to install a capacitor.

Advantages and disadvantages
The most important advantage of a metal halide lamp is a wide and uniform emission spectrum. Its light almost completely corresponds to the sun, and the color rendition reaches 95%. Such accurate color reproduction is not provided by any artificial light source that exists today, including LED lamps.
The second important advantage is high energy efficiency. A metal halide lamp of even low power is capable of producing a luminous flux of up to 70 lm per watt of power consumption
And starting from a kilowatt and above, the light output of the device can reach 95 lm / W. This is almost the same as for real cost LED lamps (diodes with a light output of 120 - 150 lm / W exist, but their production is unreasonably expensive).
Let's add to the advantages a relatively low cost (tens of times cheaper than LED sources of the same power) and a service life, which, depending on the power, ranges from 10,000 to 15,000 hours.For comparison: the average life of sodium lamps is 10,000-20,000 hours, and LEDs, whose MTBF is considered fantastic, are 15,000-30,000 hours.
Metal halide light sources have the following disadvantages:
- High operating temperature. Like any other arc light source, metal halide gets very hot. The temperature of the burner can reach 1200, and the outer flask (if provided by the design) - 300 degrees Celsius. This, of course, requires the adoption of special security measures.
- Long time to work. After switching on, it takes 10-15 minutes for the device to enter the operating mode - it flares up. Also, once turned off, the lamp will not start until it cools down. This drawback is a constraint for the use of metal halide lamps in everyday life, where it is quite difficult to wait 10-30 minutes until the lamp starts to shine.
- Contains toxic substances. The burner of a metal halide lamp is filled with metallic mercury, so it cannot be taken and thrown into the trash. MGL must be disposed of at special points.
- The need for additional equipment. In order to run a metal halide lamp, you need a ballast and IZU, which are often larger in size than the lamp itself and, of course, cost a lot of money.
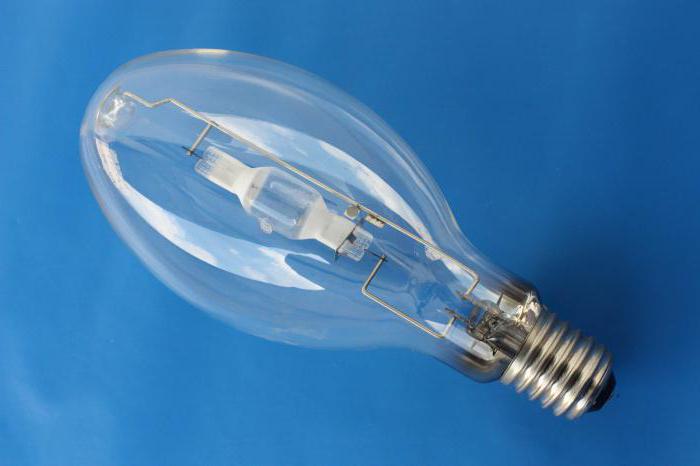
Design
Due to the fact that modern modifications are used in the lamp, metal halide lamps do not imply incandescent filaments, which ensures longer service life. There is also an easier start, due to the use of ignition electrodes.
Due to the fact that the flows of halide during the passage of the discharge depend on gravity, the lamp must be in the required position during operation.Lamps with two bases can only be operated in a horizontal position. Models with one base, for the most part, work with a vertical installation. There are separate models that are suitable for working in any position. Horizontal models are marked with the letters "BH" and vertical ones with "BUD". For any positions - "universal".
Advantages and disadvantages
The electrical parameters of metal halide products can vary quite a lot, the choice on the market is large. The quality of the bulbs and increased light output make MGL products very popular.
 Aquarium Lighting Devices
Aquarium Lighting Devices
Light bulbs are small, powerful, suitable for the light source, and will be the best replacement for classic arc fluorescent products today, because of the safe spectrum for people.
The luminosity of the MHL is 3 times greater than that of the LN, and the light output will generally be 70-90 lm/watt.
Color temperature can be:
- 6500 K (cold shade);
- 4500K (daylight) or 2500K (warm).
They can be obtained with a color rendering of about 90-95%, the efficiency will exceed 6 times an incandescent bulb.
The power range is from 15 W to 3500 W for one lamp, also the temperature in the room does not legally affect the operation of the light bulb. MHL serve for a long time, on average 10,000 hours of uninterrupted operation.
Operation of metal halide lighting devices
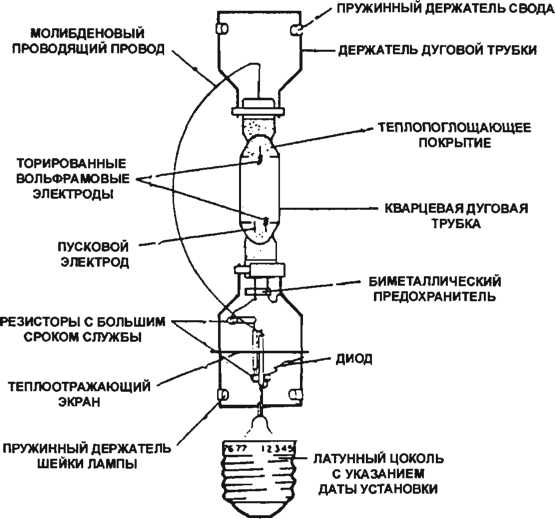 The discharge is initiated by means of auxiliary ignition electrodes or by means of a pulse gap. The start of the lighting device is possible due to the use of ballast (ballast). With its help, the values \u200b\u200bof the supply voltage from the power source and the parameters of the lamp are coordinated.
The discharge is initiated by means of auxiliary ignition electrodes or by means of a pulse gap. The start of the lighting device is possible due to the use of ballast (ballast). With its help, the values \u200b\u200bof the supply voltage from the power source and the parameters of the lamp are coordinated.
If the lamp was turned off and it became necessary to turn it on again, the start will occur only after the lamp has cooled down, it takes 10 minutes. If you try to turn on the lamp before this time, it may burn out. A special sensor is provided in the design of the luminaire to protect against unauthorized start-up and quick re-closing. It protects the device from the supply of voltage to the lamp that has not had time to cool down.
MGL classification
Initially, they are divided into:
- single-ended;
- Double-ended. Otherwise, double-ended ones are called soffit;
- Without plinth.
Plinth type: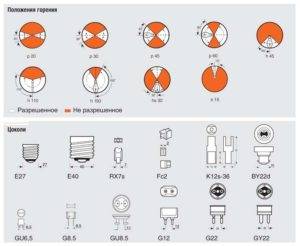
- E27;
- E40;
- RX7s;
- G8.5;
- G12;
This light source has 3 emission spectra:
- Warm spectrum, with a light temperature of 2700K;
- Neutral spectrum, with a light temperature of 4200K;
- Cold spectrum, with a light temperature of 6400K.
By marking:
- D - arc;
- P - mercury;
- Y - iodide.
By power.
- 220V - 20, 35, 50, 70, 150, 250, 400, 700, 1000 W;
- 380V - over 2000 watts.
Types of luminaires may differ according to the type of installation:
- Recessed - when the luminaire can be fixed in suspended ceiling structures;
- Consignment note - when the device is attached to a wall or ceiling;
- Track - when the lamp has a special reflector that can accentuate the glow radius;
- Suspended - when the luminaire can be suspended from the ceiling or ceiling lintels.
Application
MHL is a compact, powerful and efficient light source (IS), which is widely used in lighting and light-signal devices for various purposes.Main applications: motion picture lighting, utilitarian, decorative and architectural outdoor lighting, car headlights (the so-called "xenon" car headlight bulbs are actually metal halide), lighting installations (OU) of industrial and public buildings, stage and studio lighting, Op-amps for illuminating large open spaces (railway stations, quarries, etc.), lighting sports facilities, etc. In op-amps for technological purposes, MGLs can be used as a powerful source of visible and near ultraviolet radiation. The compactness of the luminous body of the MGL makes them a very convenient IC for projector-type lighting devices with catoptric and catadioptric optics.
Fluorescent lamps
Fluorescent light bulbs work on a completely different principle: it is not a tungsten filament that burns in a glass bulb, but mercury vapor under the influence of current. The gas discharge emits ultraviolet, the eye practically does not distinguish it. Ultraviolet causes the glow of the phosphor covering the walls of the tube.
The threaded cartridge is replaced in fluorescent lamps by 2 pins on both sides of the tube. To mount them, you need to insert them into the cartridge and turn.
The advantage of such light bulbs is their low operating temperature, so they can be installed anywhere. Due to the large surface of the glow, an even diffused light is obtained, imitating daylight. Moreover, the color of the radiation can be adjusted by changing the phosphor.
Fluorescent lamps last 10 times longer than incandescent lamps. However, they have a significant disadvantage - the need for special ballasts to connect to the mains, which is explained by the physical nature of the glow.
The light that a fluorescent lamp emits is indicated by a special marking:
- LB - white;
- LD - daytime;
- LE - natural;
- LHB - cold;
- LTB - warm.
After the letters in the marking, numbers are indicated: the first indicates the color rendering, the second and third indicate the glow temperature. For example, marking LB840 means that the temperature is 4000 K (daylight color).

The higher the degree of luminescence, the more comfortable the lighting for the eyes:
- 2700 K - super warm white;
- 3000 K - warm white;
- 4000 K - natural white or white;
- more than 5000 K - cold white.
Modern fluorescent energy-saving light bulbs are compact in size, differ in power and discharge tube shapes. The control gear (ballast) is built into the base, so no electronic ballast is needed.
There are also fluorescent bulbs without control gear, which are used in luminaires with built-in electronic ballast.
Another type of fluorescent lamps is high-pressure mercury arc lamps, which operate due to an arc discharge in mercury vapor. They are ballast-driven and have a high light output of up to 60 lumens per watt.
The main disadvantage of fluorescent lamps is unnatural light that hurts the eyes, which is why they are often used in cobra-type street lamps. In addition, such lamps start up for a rather long time - from several seconds to several minutes, and during their operation, the hum of the electronic ballast is heard. Fluorescent bulbs can work at low temperatures, but at -10 degrees they begin to shine dimly. Frequent turning on and off leads to a quick failure of the devices.
Principle of operation
Halogen lamps are more advanced modifications of conventional incandescent lamps.
This design consists of several main components:
- Tungsten filament. This element is made in the form of a spiral, which allows to increase the working area of the system. In this way, much more light is obtained than a straight filament would generate. The appearance of light radiation occurs due to the passage of current through tungsten. This causes the metal to generate photons, which are released into the external environment.
- filler gas. As already mentioned, in such lamps substances of the halogen series are used. This component solves several problems at once. First of all, the gas prevents the rapid evaporation of the tungsten filament, which can eventually lead to its destruction. Also, the filler "forces" the evaporated tungsten to be deposited again on the spiral. This is achieved through special chemical reactions in which the components enter.
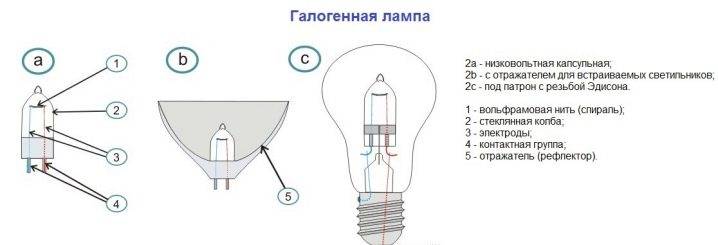
At the same time, gas under high pressure can be pumped into small flasks. This, in turn, also extends the life of the product several times.
The main types of halogen lamps

Depending on the appearance and method of application, halogen lamps are divided into several main types:
- with an external flask;
- capsular;
- with reflector;
- linear.
With external flask
With a remote or external bulb, a halogen lamp is no different from standard Ilyich bulbs. They can be connected directly to a 220 volt network and have any shape and size. A distinctive feature is the presence in a standard glass bulb of a small halogen bulb with a bulb made of heat-resistant quartz.Halogen lamps with a remote bulb are used in various lamps, chandeliers and other lighting devices with an E27 or E14 base.

Capsule
Capsular halogen lamps are miniature in size and are used to organize interior lighting. They have low power and are often used with sockets G4, G5 in a 12 - 24 volt DC network and G9 in a 220 volt AC network.
Structurally, such a lamp has a filament body located in a longitudinal or transverse plane, and a reflective substance is applied on the rear wall of the bulb. Such devices, due to their low power and size, do not require a special protective bulb and can be mounted in open-type luminaires.

With reflector
Reflector devices are designed to emit light in a directed manner. Halogen lamps may have an aluminum or interference reflector. The most common of these two options is aluminum. It redistributes and focuses the heat flux and light radiation forward, due to which the light flux is directed to the desired point, and excess heat is removed, protecting the space and materials around the lamp from overheating.
The interference reflector conducts heat inside the lamp. Halogen reflector lamps come in a variety of shapes and sizes, as well as different light emission angles.
Linear
The oldest type of halogen lamp, which has been used since the mid-60s of the 20th century. Linear halogen lamps have the form of an elongated tube, at the ends of which there are contacts. Linear lamps come in various sizes as well as high wattage, and are mainly applied to various spotlights and street lighting fixtures.
Halogen lamps with IRC coating
IRC-halogen lamps are a special kind of this kind of lighting devices. IRC stands for "infrared coverage". They have a special coating on the flask that freely transmits visible light, but prevents the passage of infrared radiation. The composition of the coating directs this radiation back to the filament, which increases the efficiency and efficiency of the halogen lamp, improves the uniformity of the glow and light output.
The use of IRC technology makes it possible to reduce the consumption of electrical energy by such devices by up to 50% and significantly affects the energy efficiency of the lighting device. Another advantage is the increase in service life by almost 2 times, in comparison with standard halogen lamps.
Halogen chandeliers
Halogen chandeliers are one-piece devices that are based on many halogen lamps connected in parallel to each other. Such chandeliers have a completely different appearance and configuration, and due to the small size of halogen lamps, they have an aesthetic appearance and a uniform glow.
In stores, you can find halogen chandeliers powered by 220 volts AC, as well as low-voltage options for use in DC systems or using with power supplies.

Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1 Overview of characteristics of metal halide luminaires:
Video #2 Checking the operation of a metal halide spotlight:
Video #3 Connecting a metal halide lamp:
Metal halide luminaires continue to be used in many areas despite a number of design flaws.A diverse spectrum of radiation allows you to select them for various needs of economic activity. Therefore, MGLs will remain competitive in the industrial lighting niche for a long time to come.
Please write comments in the block below, ask questions, post photos on the topic of the article. Share your own guidelines for choosing a metal halide light bulb. Tell us why you chose this device.