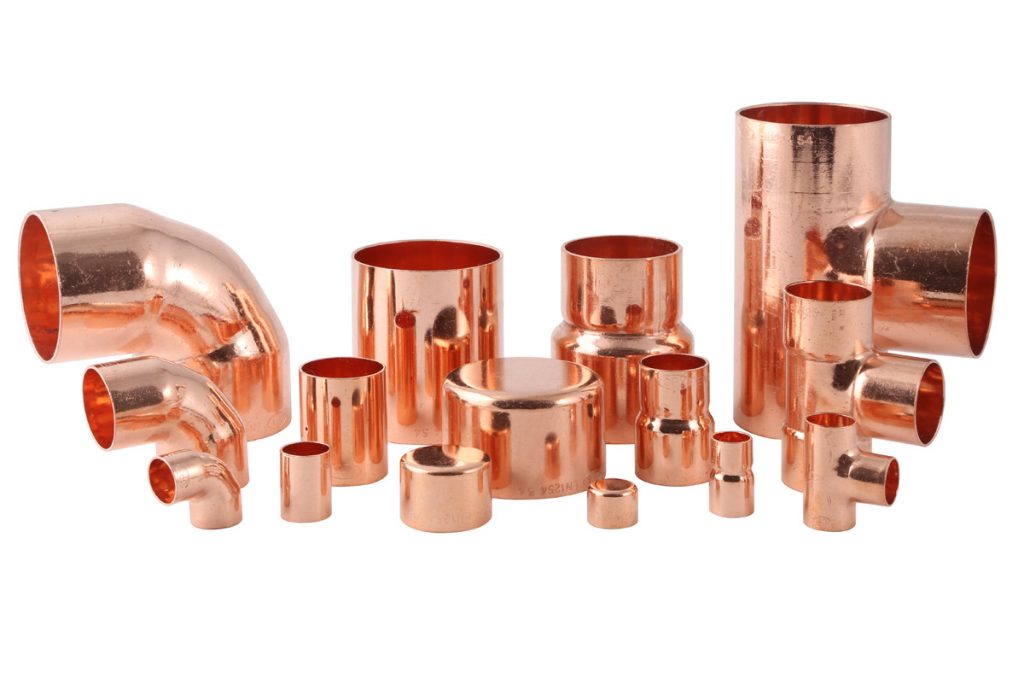
- Feature of installation of copper pipelines
- Capillary connectors
- Three main connection methods
- Option #1: Copper Pipe Welding
- Option #2: Capillary soldering
- Advantages of copper pipes over plastic pipes
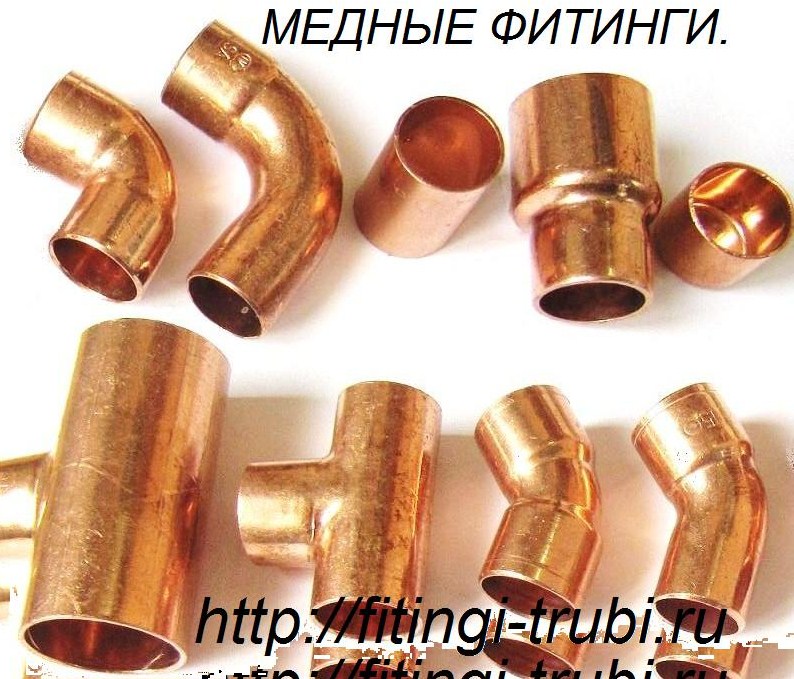
- Copper fittings and their types
- Fittings for connecting copper pipelines
- Solder fittings
- Collet connections
- Press connection
- The main advantages and areas of use of copper pipeline
- Elements for copper pipe connections
- Features of Brazed Copper Fittings
- 5 Myths and facts about copper pipes for water supply
- Characteristics of copper pipes
- Features of the installation of plastic pipes for gas
- Mounting methods
- Installation of copper pipes for water supply
- Necessary tools and materials
- Work progress
- Mounting Features
- Marking and cost
Feature of installation of copper pipelines
Before proceeding with the creation of a copper pipeline, the necessary measurements should be taken and the pipes cut into pieces. The cut of the product should turn out to be even and therefore use a special cutter. By the way, copper pipes are not threaded.
The connection of individual sections of the copper pipeline can be performed in the following ways:
- soldering method;
- pressing.
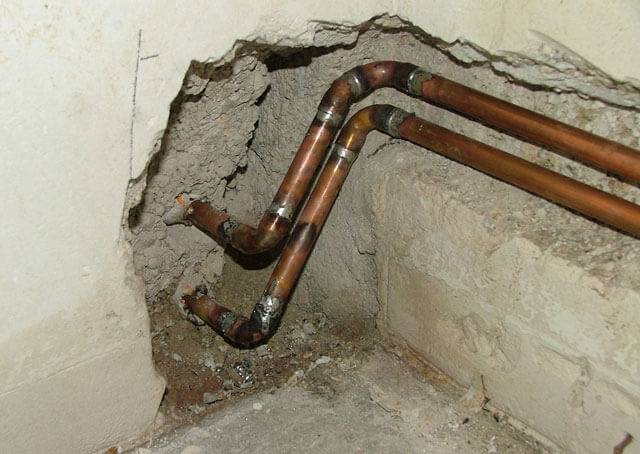

The most effective of them is docking using capillary soldering technology, so it has become more widespread. This method ensures reliability and absolute tightness of pipe joints. Copper products of square section are connected using capillary soldering, which is performed using fittings and sockets.
This method of laying pipelines from copper components is used when the pipeline is planned to be operated in conditions of extremely high temperatures.
Capillary connectors
They are more suitable than others for pipe products made of copper and steel. They have a very thin wire of copper, tin, or silver on the inside under the cut thread. This wire becomes the solder.
Video
The workpiece, which is covered with flux, is inserted into the fitting. The burner heats up the joint. Heating is carried out until the molten solder fills the space.

After that, the joint is left, it needs to cool. After some time, the joint is cleaned with special cleaners for working with copper.
Three main connection methods
Before connecting the pieces of copper pipes, they must be cut in accordance with the wiring diagram and prepared. You will need a pipe cutter or a hacksaw, a pipe bender and a file. And for cleaning the ends, fine-grained sandpaper will not hurt either.
Only having a diagram of the future pipeline system in hand, you can calculate the required amount of consumables. It is necessary to decide in advance where and what diameter the pipes will be mounted. It is also necessary to clearly understand how many connecting elements are required for this.
Option #1: Copper Pipe Welding
Automated or manual welding of copper pipes requires electrodes and gas to create a protective atmosphere (nitrogen, argon or helium). You will also need a DC welding machine and, in some cases, a torch. The electrode can be graphite, tungsten, copper or carbon.
The main disadvantage of this installation technology is the significant differences in the characteristics of the resulting seam and pipe metal. They differ in chemical composition, internal structure, electrical and thermal conductivity. If the welding is not performed correctly, the joint may subsequently even disperse.

Due to the alloying of copper as a result of the action of the deoxidizer present in the electrode, the weld in many respects differs greatly from the base metal being welded.
Welding copper pipes can only be correctly connected by a qualified craftsman. This requires certain knowledge and skills.
This installation option has a lot of technological nuances. If you plan to do everything yourself, but there is no experience with a welding machine, then it is better to use a different connection method.
Option #2: Capillary soldering
In domestic conditions, copper pipes are rarely connected by plumbing welding. This is too complex, requiring specialized skills and time consuming. It is easier to use the method of capillary soldering with using a gas burner or blowtorch.
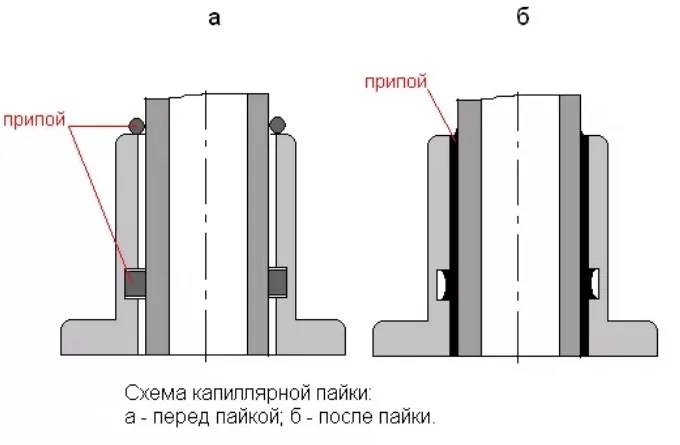
The technology of soldering copper pipes with solder is based on the capillary rise (leakage) of the latter after melting along the gap between two pressed metal planes
Soldering copper pipes happens:
- low-temperature - soft solders and a blowtorch are used;
- high-temperature - refractory alloys and a propane or acetylene torch are used.
These methods of soldering copper pipes do not have much difference in the end result. The connection in both cases is reliable and tensile. The seam with the high-temperature method is somewhat stronger. However, due to the high temperature of the gas jet from the burner, the risk of burning through the metal of the pipe wall increases.
Solders are used based on tin or lead with the addition of bismuth, selenium, copper and silver. However, if the pipes are soldered for a drinking water supply system, then it is better to refuse the lead version due to its toxicity.
Image gallery
To implement low-temperature welding, it is not necessary to have special equipment and special skills of the performer. You can do it on your own
Advantages of copper pipes over plastic pipes
Plumbing copper pipe, despite a very long history of its existence, successfully competes with modern products - plastic and metal-plastic products for plumbing. In many respects, it is noticeably superior to them:
- Copper is impervious to foul-smelling, harmful substances and even oxygen.
- Copper pipe, unlike plastic, is not subject to the damaging effects of chlorine, which is contained in tap water. More chlorine-resistant plastic pipes are supplied exclusively to the US market, where water is chlorinated in a similar way to Russia. Such products cost no less than copper. In Europe, the requirements for chlorine content are much lower, so plastic for low-chlorinated water that meets the European standard is common on the domestic market.
- Chlorine, being a strong oxidizing agent, contributes to the formation of a patina on the inner surface of the copper pipe - a durable, thin protective layer. Due to this, the service life of the pipeline is significantly extended.
- UV resistant. Plastic evaporates when exposed to sunlight.
- Insignificant, lower than that of plastic pipes, the roughness coefficient, which allows, under the same conditions, to use copper products of a smaller diameter. This is possible, among other things, due to the absence of overgrowing of the walls with colonies of microorganisms and corrosion products.
- Copes with long-term thermal loads much better.
- According to studies, plastic pipelines have the least reliable fittings and joints. For copper, on the contrary, these elements of the system are the most reliable.
- The quality of copper is almost stable and the same for different manufacturers, which is not typical for plastic products (there are many counterfeit products of dubious quality on the consumer market).
- It is characterized by antibacterial properties (pathogenic flora is suppressed). In plastic pipes, low-molecular organics are released, the walls become overgrown with biofilm over time.
- It has a very long service life: it does not deteriorate, does not age, retains its original strength. Copper pipes and fittings are used without replacement for as long as the building itself. Plastic products, with existing technologies, cannot yet occupy the niche of durable and high-quality pipelines.
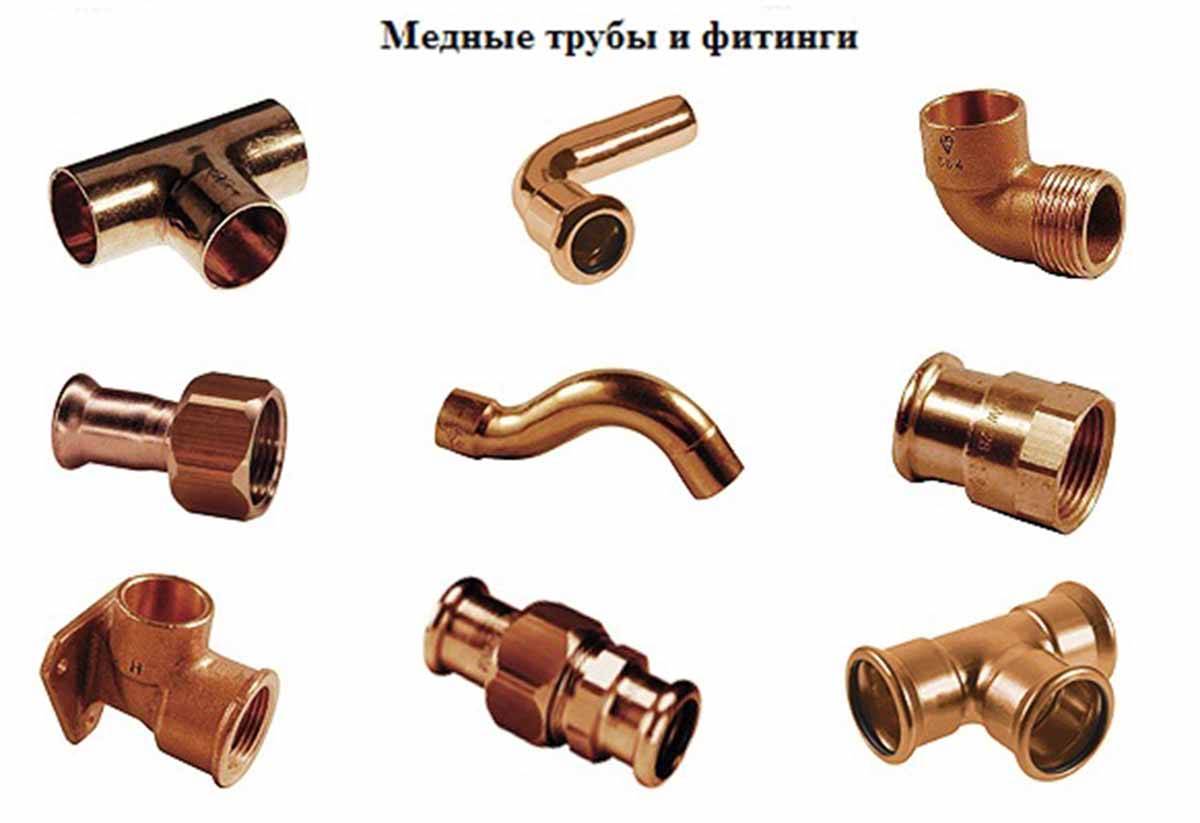
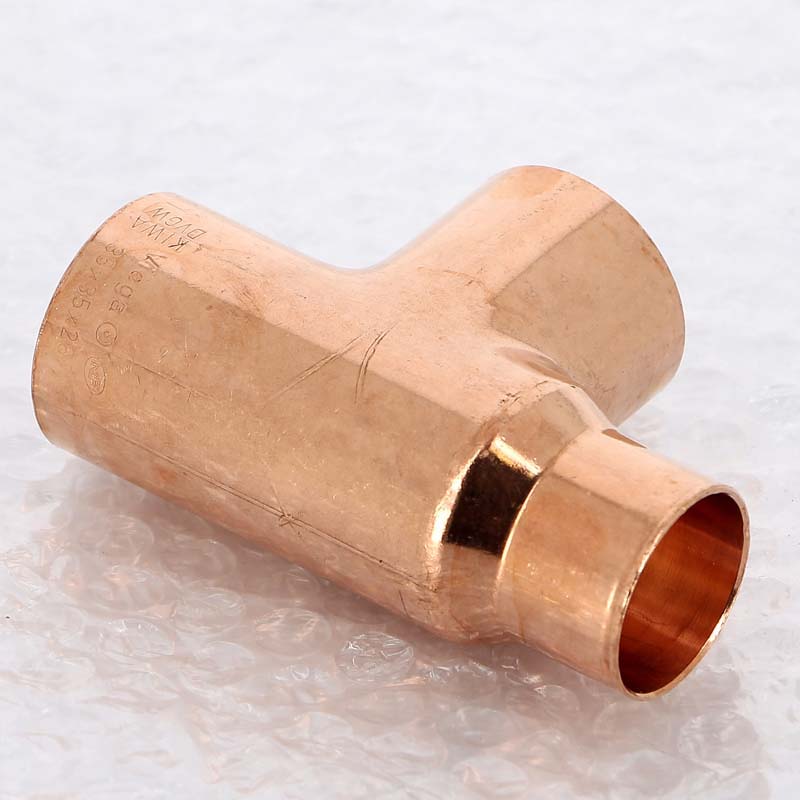
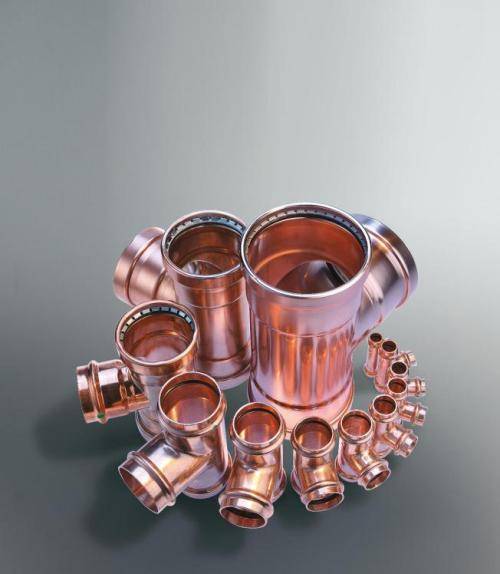
Copper fittings and their types

All engineering systems, which will include a copper pipeline, require high-quality fittings for installation.We are talking about fittings that are designed to connect pipes into one system with a guaranteed absence of leaks.
With the detachable connection option, the use of a threaded or compression fitting is acceptable. For a permanent connection, it is better to use capillary or press fittings. Their main task in a pipeline for any purpose is to provide branches, turns, connection of two pipes with the same or different diameters. Without fittings, a high level of sealing of the heating, air conditioning or plumbing system cannot be achieved. Just like pipes, they have high ductility and corrosion resistance, are easy to install and operate for a long time without needing repair.
By design and purpose, they distinguish: adapters and adapters, a 45 ° or 90 ° elbow, coal and arc bends with one or two sockets, a coupling, a bypass, a plug, a cross, a tee, an elbow, a union nut; reducing - tee, coupling and nipple.
Such a large assortment will allow you to find those products that will form the basis of communications. Depending on the mounting method, fittings for copper pipes can be:
- The NTM self-locking push-in copper push-in fitting revolutionizes piping installation. It is enough to insert pipes into it from both sides, and the installation is completed. Inside such structures there is a system of rings. One of them is equipped with teeth. When a special mounting key presses on the toothed element, it is firmly fixed in the adjacent ring, and a perfect connection is obtained. These fittings are recommended for temporary pipe connections and are indispensable for repair purposes.
- A threaded fitting differs from other varieties in that it has a thread with which the connection is made. The best option for the case when the pipeline is supposed to be disassembled and reassembled several times.
IMPORTANT! Usually, it is not necessary to apply sealant to the connected sections of copper pipes. But if it is still used for better contact, it is imperative to make sure that particles of the material do not get on the thread. Such fittings are used in those places where access is needed for constant monitoring of the reliability of the connection
Couplings, 45 and 90 degree elbows or elbows, outlet fittings, crosses, tees, caps and special plugs are used as suitable threaded elements.
Such fittings are used in those places where access is needed for constant monitoring of the reliability of the docking. Couplings, 45 and 90 degree elbows or elbows, outlet fittings, crosses, tees, caps and special plugs are used as suitable threaded elements.
- A compression or compression (collet) fitting has a rubber ferrule to achieve a tight connection. It is indispensable for water supply systems in which there are pipes of various cross sections. It is used for installation of underground and above-ground pipelines from soft and semi-solid thick-walled copper pipes. Unfortunately, such a connecting element is at risk of leakage. If the connection is untwisted for replacement, the ferrule can no longer be reused.
- Capillary fitting that is used for soldering. With this type of connection, it turns out to be one-piece, very reliable and durable. It is performed using copper or tin solder. The process is based on the capillary effect.This phenomenon ensures that the solder is evenly distributed over the surfaces that are being joined. For decades, it was soldering that was the main type of installation, although in recent years the choice of fitting connections has expanded.
- A press fitting connecting the elements of a copper pipeline is used very rarely. For installation, you need a special press, which is not cheap. It is acceptable only when it is not possible to connect pipes in another way.
In fact, copper pipes are easy to cut and bend, installation of fittings is simple, and wiring systems in the house does not take up much space. Copper pipes in heating and water supply systems are valued for their durability, reliability and resistance to corrosion. In addition, the water in such a system is protected from various kinds of negative influences. Knowing these points, consumers are ready to purchase expensive copper pipes and fittings in order to have extra-class pipelines.
Fittings for connecting copper pipelines
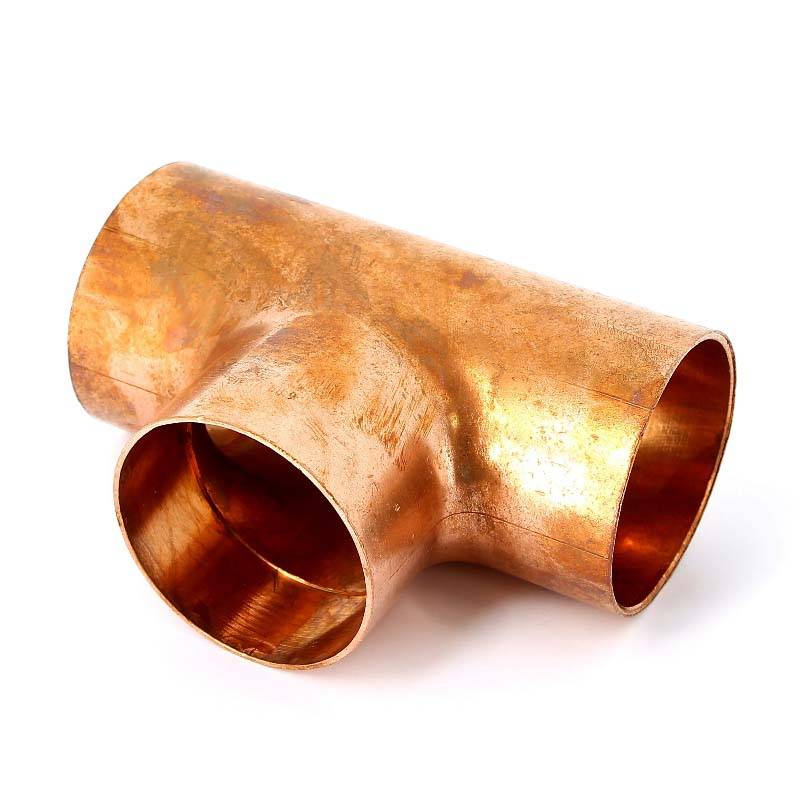
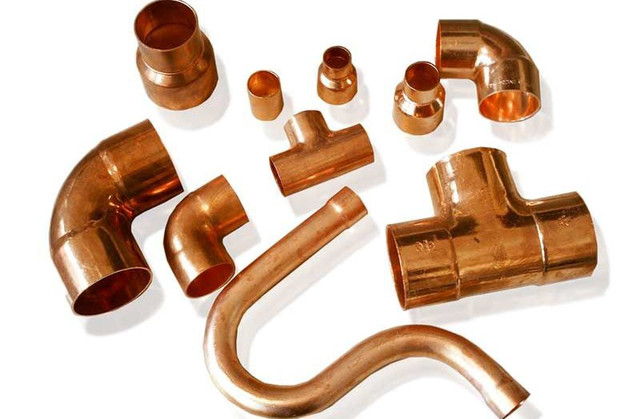
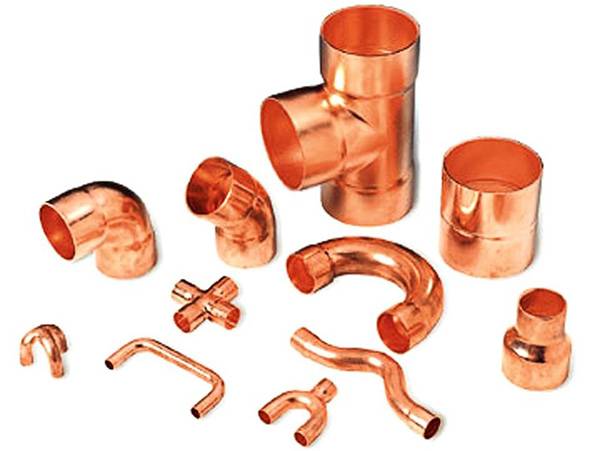
Copper fittings are shaped elements by means of which individual sections of the pipeline are joined together. Copper pipe fittings are available in the following configurations:
- parallel couplings;
- tees;
- squares (at 45 and 90 degrees);
- crosses.
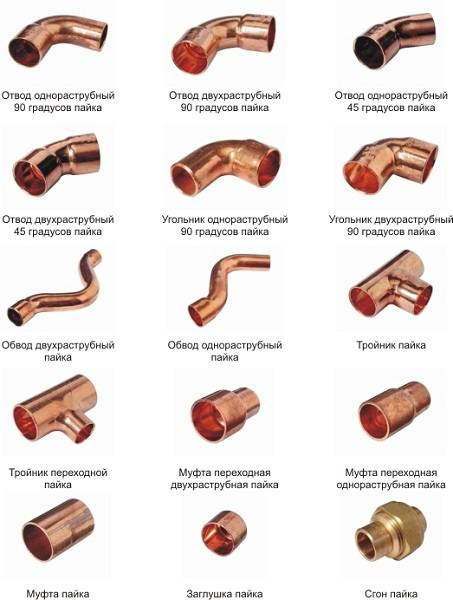
Varieties of copper fittings
The above copper fittings can be one-dimensional - for connecting pipes of the same diameter, or transitional - for connecting pipeline sections of different sizes.
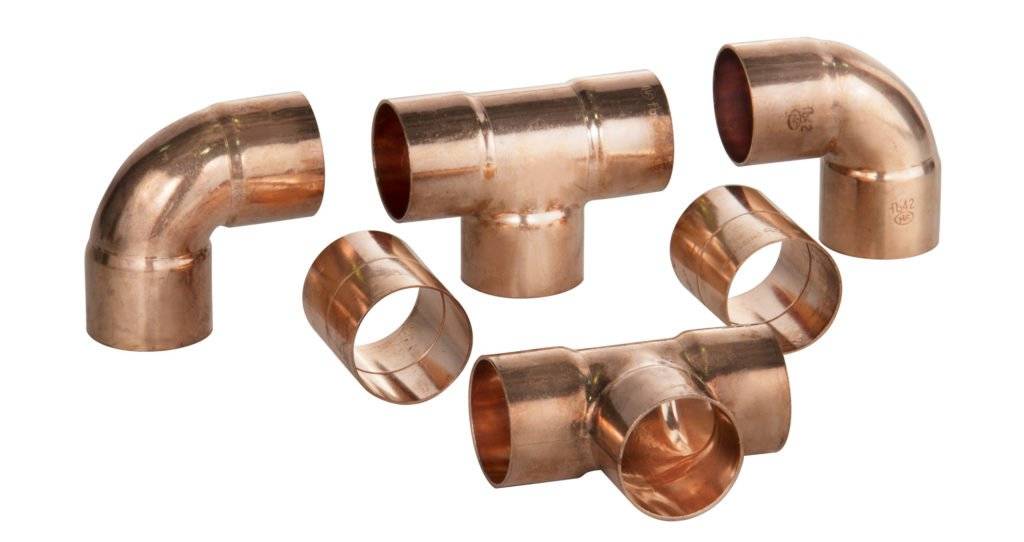
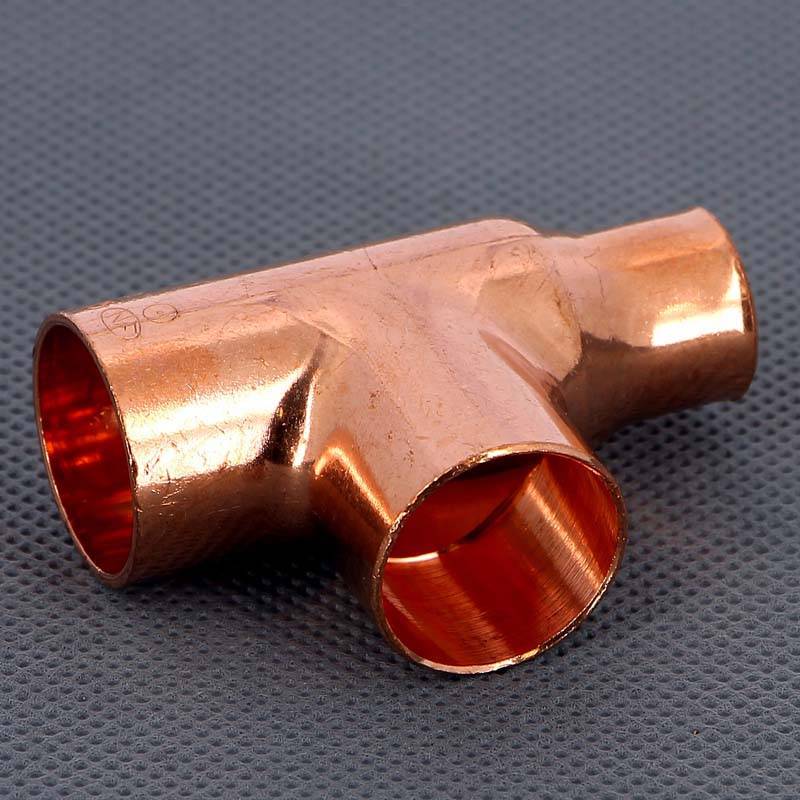
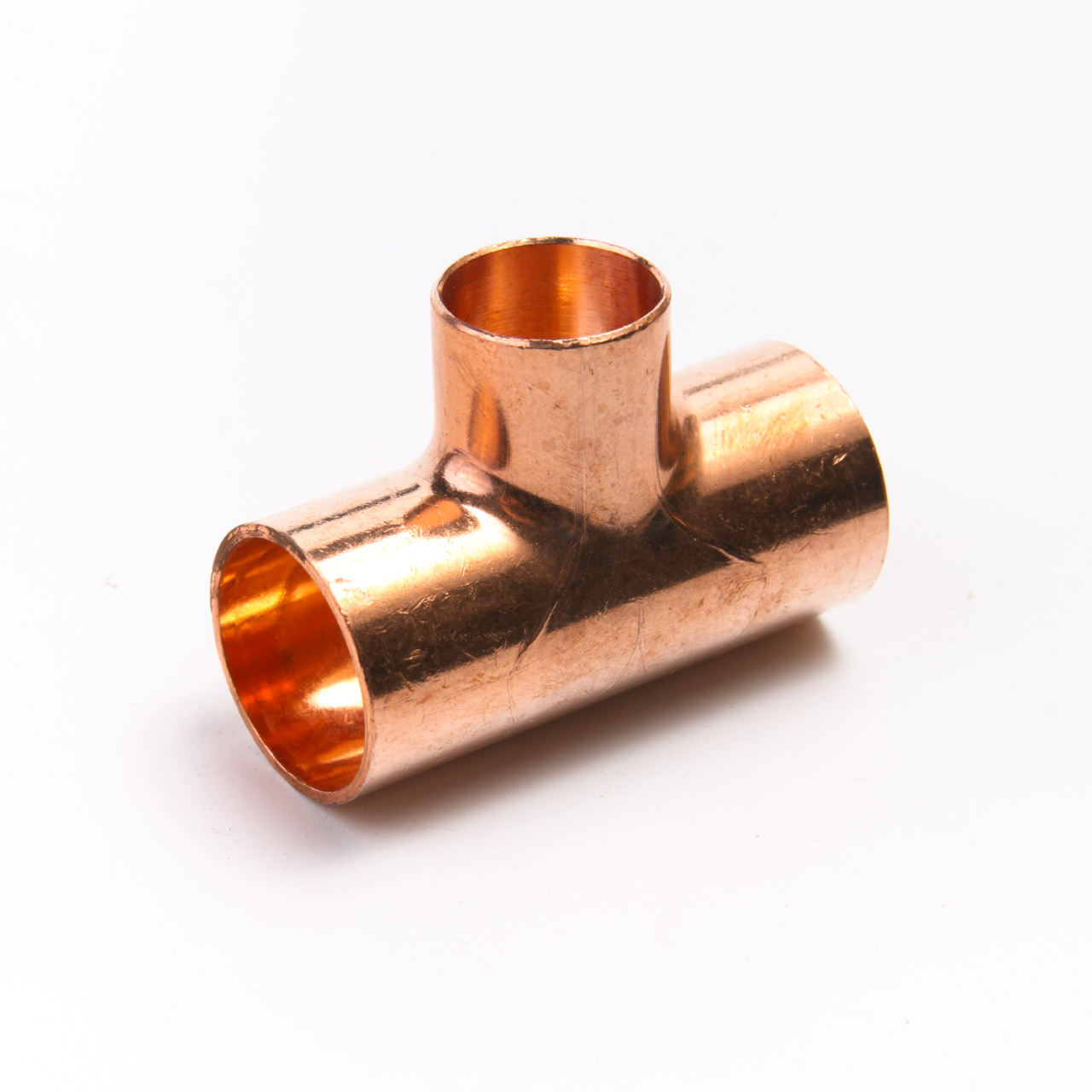
Solder fittings
Connecting products intended for joining by soldering are called capillary. Their inner walls are covered with a thin layer of tin solder - molten solder fills the gap between the walls of the connecting products and, after hardening, firmly links them together.
We note the Sanha fittings for high-quality solder products. This company produces copper fittings of all common sizes according to German quality standards from CW024A grade alloy. Connections are able to withstand pressure in the range of 16-40 bar and an operating temperature of 110 degrees.
The technology for connecting copper pipelines by soldering is quite simple in execution:
- The mating surfaces of the pipes and fittings are cleaned of contaminants, degreased and processed with fine-grained sandpaper.
- A layer of low-temperature flux up to 1 mm thick is applied to the pipe walls.
- The connecting elements are joined together, after which the joint is heated with a hot air gun or gas burner to a temperature of 4000 for 10-15 seconds.
- The joint is cooled down, after which the flux residues are cleaned with a rag.
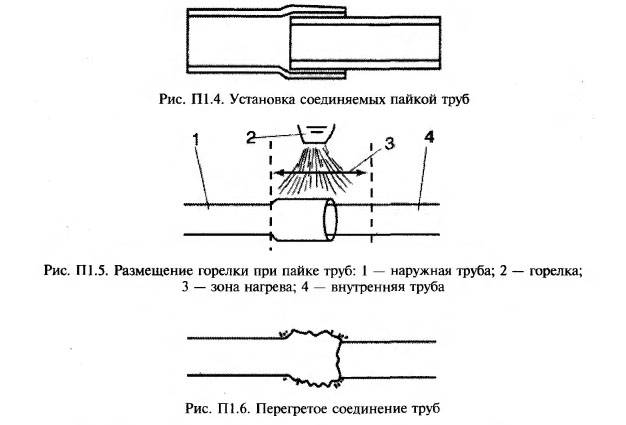
Scheme for soldering copper pipes
It is necessary to carry out soldering in a ventilated room, since during the melting of solder and flux, gases harmful to the body are released.
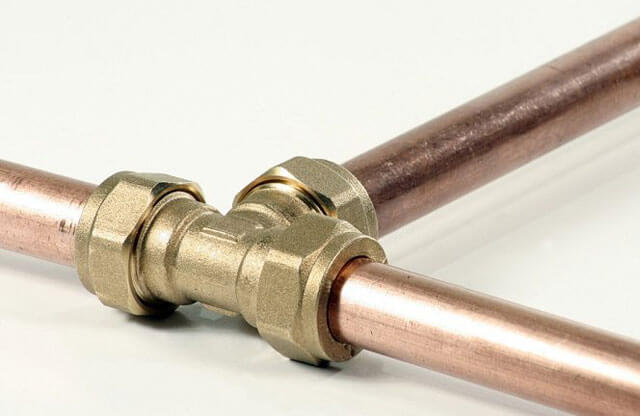
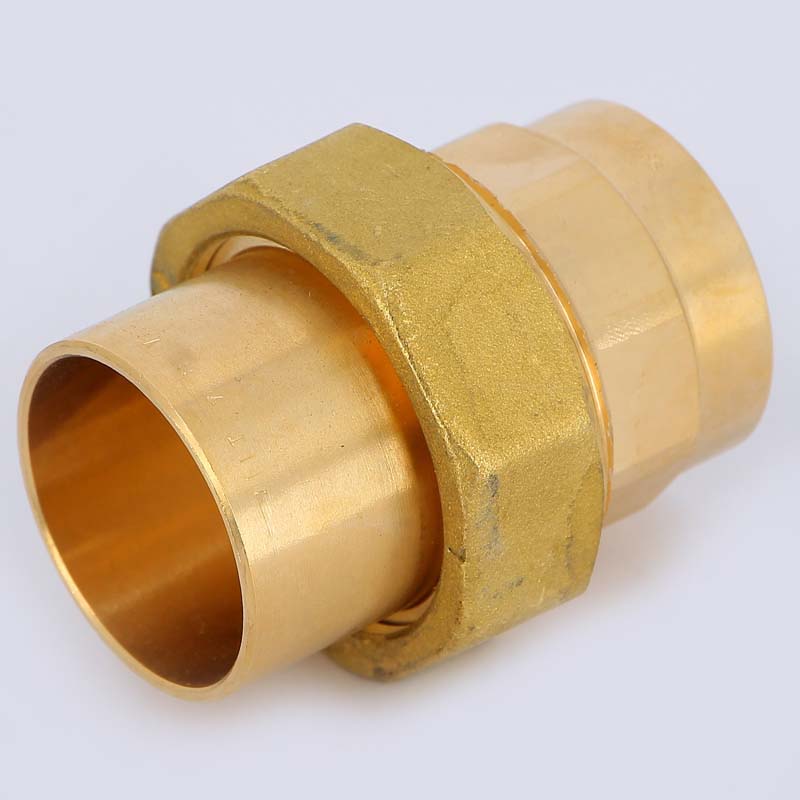
Collet connections
Collet, they are also compression fittings for copper pipes, perform a serviced connection to be dismantled. All push-in fittings are classified into two groups:
- "A" - for products made of solid and semi-solid copper;
- “B” - for soft copper pipes.
They differ in that class “B” fittings have an inner sleeve - a fitting, on which the connected sections of the pipeline are mounted. The fitting acts as a support element that prevents deformation of the copper walls during crimping.

Compression copper fitting
Connection mounting technology:
- A union nut and a split ring are put on the pipe.
- The ring is placed at a distance of 1 cm from the cut.
- The pipe is pushed onto the fitting nipple.
- The union nut is manually tightened until it stops, after which it is tightened with an adjustable or open-end wrench.
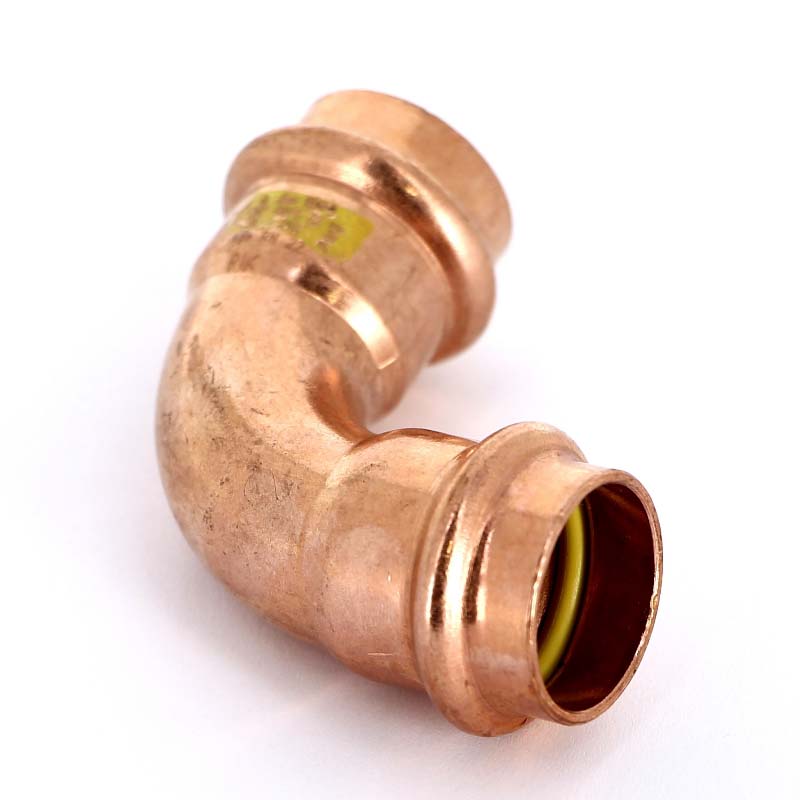
Press connection
Press fittings for copper pipes consist of a body, a fitting and a compression sleeve. Their installation takes a minimum of time - the connecting sections of the pipeline are inserted into the seat on the fitting, after which the sleeve is crimped using press tongs. This tool can be rented at a plumbing store or bought, prices start at 3 thousand rubles.
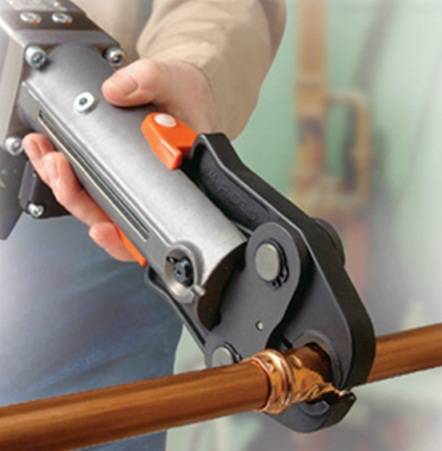

Press fitting installation
Such a connection is maintenance-free, unlike a collet joint, you cannot dismantle it without violating the integrity of the fitting. In the event of leakage, it is necessary to replace the connecting element. Note that press fittings are the most reliable and durable, their service life reaches 30 years.
The main advantages and areas of use of copper pipeline
Copper pipes have a working temperature from -200 to +250 degrees, as well as a low linear expansion, which allows them to be successfully used for such systems:
- heating;
- Plumbing;
- Conditioning;
- Gas transportation;
- Obtaining alternative energy, for example, solar systems.

Copper pipeline
When installing copper pipelines for supplying cold and hot water, you do not have to worry about overgrowing or silting of the internal section. Also, they are not destroyed by chlorine, which is added to tap water in high concentrations. On the contrary, chlorine creates the thinnest protective layer on the inner wall of pipelines, which significantly extends the life of the pipelines.In turn, a small amount of copper is released into drinking water, which has a beneficial effect on human health.
Elements for copper pipe connections
Copper fittings, which are used to connect copper pipes, are presented on the modern market in a wide variety of sizes and designs. The most well-known types of such connecting elements are:
- threaded fittings for copper pipes;
- self-locking connecting elements;
- compression or crimp type fittings;
- so-called press fittings;
- connecting fittings of capillary type.
Of all the listed types of connecting elements, press fittings for copper pipes are the least commonly used in our time, which is explained by the following reasons: their installation requires the use of complex and expensive equipment: special presses. The design of press fittings was originally developed in order to connect plastic and metal-plastic pipes with their help, so their use for mounting copper products is not always advisable.
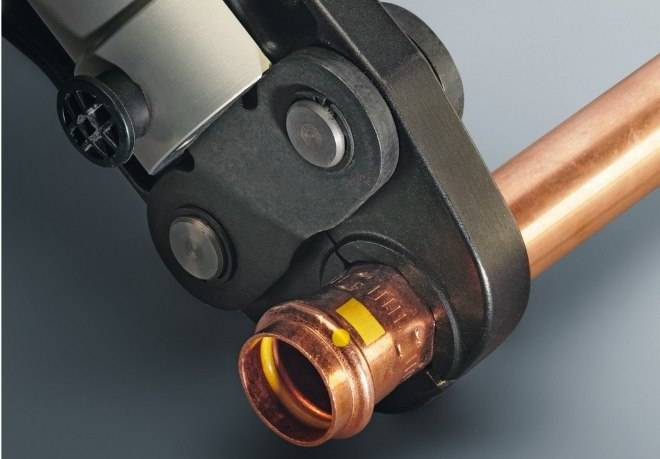

Press fitting pliers
In order for the pipeline, in the arrangement of which copper parts are used, to serve as long as possible and be highly reliable, it is advisable to use elements of homogeneous materials during its installation. Connecting copper pipes with fittings that are made from other raw materials should only be done in rare exceptions.
If it is not possible to avoid the use of fittings made of dissimilar materials during the installation of pipelines, then such a process must be carried out, adhering to the following simple rules:
- copper pipes in communications, for the creation of which elements from different materials are used, are always installed after ferrous metal products: in the direction of the liquid;
- copper parts of pipelines cannot be connected to fittings made of galvanized and non-alloy steel, failure to comply with this requirement will cause electrochemical reactions to operate in such systems, which will significantly accelerate the corrosion process of steel parts;
- copper elements of pipe structures can be connected to parts made of acid-resistant steels, but if possible, it is better to replace such parts with fittings made of polyvinyl chloride.
Features of Brazed Copper Fittings
One of the simplest and most durable connections of pipelines from copper components is soldering.
Unlike polymer products, copper fittings, like pipes, are considered eternal in terms of service life, they serve for at least a century, do not deteriorate under the sun, do not melt from high temperatures and do not crack in the cold, therefore they are used where the tightness and strength of pipeline highways are subject to increased requirements.
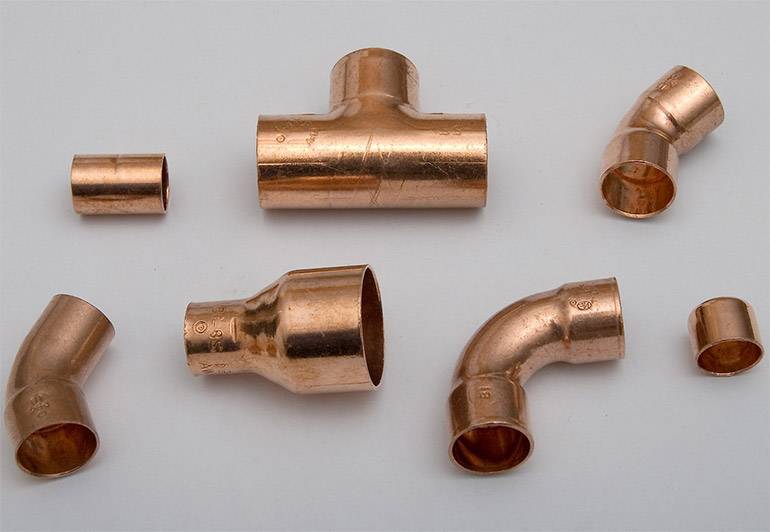

The popularity of copper fittings is due to the special characteristics of the metal:
- copper is a well-known antiseptic that protects pipes from the development of bacteria and fungi;
- installation of communications consisting of copper components is easier than connecting pipeline systems made of cast iron and steel;
- it is possible to damage copper pipes or fittings only under a pressure of more than 200 atm, but such pressure simply cannot exist in communication systems.
5 Myths and facts about copper pipes for water supply
Plumbing copper pipes endowed with a number of shortcomings from the category of myths, which is due to competition and lack of awareness.
1. High cost of copper pipeline. This idea was formed thanks to the aggressive advertising of plastic pipes. Indeed, copper pipes are 2-3 times more expensive than plastic ones, but fittings made of copper cost 30-50 times less than those made of polymers. Given that the installation methods of the pipeline can be used the same, then the costs of installing systems from these materials are approximately equal. As a result, the cost of the completed pipeline is highly dependent on the topology of the system.
In the case of long and unbranched networks (main, for example), plastic pipelines are much cheaper. When using expensive, good plastics, which are designed for high levels of chlorination, but are not available on the Russian market, polymer systems will obviously be more expensive. Copper piping can be installed without the use of fittings, which makes it cheaper. And given the durability and high reliability of copper systems, the cost of their operation is an order of magnitude lower than plastic ones. In case of disposal of the used copper pipeline, the funds spent are returned.

2. Copper is poisonous. Completely unsubstantiated assertion. Poisonous are only special copper compounds produced by industry (dyes, blue vitriol, others) and not formed naturally in the pipeline. The oxides of this metal, which are mainly a protective film (patina) on its surface, are not poisonous.On the contrary, they and copper itself have a mild bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect, which, when using water from such a pipeline, ensures high infectious safety.
3. Chlorine. This substance in its pure form is a very strong oxidizing agent, prohibited for transportation through copper pipes. The impact of chlorine compounds, including those used for water disinfection, copper tolerates completely painlessly. On the contrary, interaction with these substances accelerates the formation of a protective web on the copper surface. Therefore, in the USA, during the technological flushing of a new pipeline, hyperchlorination is carried out in order to quickly obtain a protective layer.

The “chlorine problems” began with copper with the introduction of plastic pipes into the plumbing market. This is due to the fact that even chlorine compounds used to disinfect water have a rather detrimental effect on most plastics. And the golden rule of successful marketing, as you know, says: "Shift your blame to a competitor - let him justify himself."
4. Wandering currents. These are the currents that flow in the earth when it is used as a conducting medium. In this case, they lead to corrosion of metal objects in the ground. In this regard, stray currents have nothing to do with copper pipes, which are mostly internal.
It is forbidden to use both copper and steel systems as the main ground electrode. If this rule is strictly observed, then no electrical problems will arise (including stray currents). Grounding, operating in emergency mode, passes only short-term current, which will not harm the pipeline.Problems arise only when the fundamental rules for the design and operation of electrical installations are violated.
Characteristics of copper pipes
Such products do not enter into chemical reactions with working fluids such as oil, water and herbicides. They almost do not form growths, limescale and other substances, both organic and inorganic. Such pipes are made of copper from 3 to 400 hundred mm in diameter, and the wall thickness can be from 0.8 to 12 mm.
Of the main characteristics can be distinguished:
- Functioning in a wide temperature range, it varies from +250 to -200°С. Products have a small coefficient of thermal expansion and are resistant to temperature changes. Thanks to these qualities, copper pipes for water supply are not afraid of liquid freezing, they will remain intact and tight.
- Resistance to corrosive processes. With dry air, oxidation does not occur, and under the influence of carbon dioxide or moisture, the surface of the pipeline is covered with a green coating - patina.
- Durability. The service life of copper pipes is about 80 years.
Features of the installation of plastic pipes for gas

The recommendations are simple and related to the characteristics of the material:
- PE pipes do not tolerate direct sunlight. The circuit is protected from the sun or laid underground. This requires preparation: marking, digging trenches, backfilling.
- The mechanical strength of plastic is inferior to steel, so the gas pipeline is installed in secluded places.
- Unlike metal, the coefficient of thermal expansion of plastic is much higher.This does not affect the functionality of the gas pipeline, but it obliges to lay pipes in an open area. Installation under the floor or in walls is undesirable.
- Plastic attracts with its flexibility and the ability to build a complex system. It should be noted that the fewer bends and turns in the system, the better it functions.
- Every 2-3 meters, the pipe, both vertical and horizontal, must be supported with additional fastening or support.
Mounting methods
Connect plastic pipes by welding. The method is very simple, since the welding temperature is low, even a novice master can handle docking.
The most popular 3 methods are:
- Butt - fastening is performed butt-to-butt. So extend the pipe or make a branch.
- Socket - when connecting, an additional layer of polymer is welded to the junction. The method is recommended for pipes with a diameter of more than 15 mm.
- Electrofusion - gas pipelines are connected by welding through a fitting. So they change the direction of the pipeline, make branches or merge.
All methods provide a tight connection. Electrofusion - the most convenient and fastest.
Installation of copper pipes for water supply
Before starting work, you need to draw up a diagram of the future plumbing structure and, on its basis, calculate the footage of rolled pipe and the number of connecting elements (press couplings, tees, bends, adapters, etc.).
Necessary tools and materials
To perform the installation of pipe rolled copper alloy, you need to prepare a set of tools, consisting of:
- Hacksaws for metal or pipe cutter.
- Pliers.
- Manual calibrator.
- Wrenches or a gas burner (for heating the pipe section when connecting parts by soldering).
- File.
For joining pipe sections, depending on the selected connection method, the following materials will be required:
- Fitting.
- FUM - tape for sealing joints of detachable fittings.
- Solder and flux (in the case of soldering products).
Precautionary measures
Soldering copper products is carried out when they are heated to high temperatures, so when working it is necessary to wear protective clothing and use a fire shield. It is necessary to remove rubber or plastic braids from the parts to be joined in the contact zone. The valve to be installed must be unscrewed so that the sealing rings do not melt.
When soldering copper products in an already installed pipeline system, all shut-off valves should be opened so that the pressure level in the pipes does not exceed the permissible values due to the heating of some sections.
Work progress
Docking of pipe segments using fittings is performed in the following sequence:
- Cut pipe sections to the required size.
- If the water supply is assembled from copper pipes with PVC insulation, then this layer should be removed at the ends of the products.
- Clean the cut line with a burr file.
- Remove bevel.
- Put on the prepared part alternately the union nut and the compression ring.
- Connect the fitting to the nut and tighten the threads first by hand and then with a wrench.
- In places where a transition fitting is being installed from a copper pipe to a steel pipe, the tightness of the joints is ensured by the use of FUM - tape.
When connecting pipes by soldering with your own hands, you must follow the precautions described above and have certain skills. The preparation process and the soldering itself includes the following steps:
- Cutting the required lengths of pipes with a pipe cutter or a hacksaw.
- Removal of the heat-insulating layer (if any) and the resulting burrs at their ends.
- Removal of the oxide film in the soldering zone with a fine abrasive sandpaper.
- Fitting sanding.
- Lubrication of the outer surface of parts with flux.
- Inserting the end of the pipe into the fitting in such a way that a gap of no more than 0.4 mm remains between the parts.
- Warming up the contact zone of the gas burner elements (pictured below).
- Inserting solder into the gap between the fitting and the end of the copper pipe.
- Solder seam.
- Flushing the system from flux particles.
The process of soldering copper pipe rolled products can be viewed on the video:
Mounting Features
Mounting by soldering forms one-piece connections that do not need maintenance and are considered the most reliable in operation. But in order to solder copper plumbing, you must have sufficient experience in this type of work and relevant knowledge. Beginners can use the following recommendations:
- Cleaning copper products should not be done with abrasive cleaners, coarse sandpaper or a wire brush, as they will scratch the copper. Deep scratches on the surface interfere with the solder joint.
- Flux is a fairly aggressive substance with high chemical activity. Apply it in a thin layer using a brush. If there are excesses on the surface, at the end of the process of joining the parts, then they must be removed immediately.
- The contact zone should be warmed up sufficiently, but not excessively, so as to prevent the metal from melting. The solder itself should not be heated.It should be applied to the heated surface of the part - if it starts to melt, then you can start soldering.
- Pipes must be bent in such a way as to prevent creases and twisting.
- Installation of copper products should be carried out in front of aluminum or steel sections in the direction of water flow in order to prevent rapid corrosion of the latter.
- For the transition from copper pipes to sections of other metals, it is recommended to use fittings made of brass, bronze or stainless steel.
Marking and cost
Pipes for heating are made, marked according to GOSTs. For example, products with a wall thickness of 0.8–10 mm are manufactured according to GOST 617-90 standards. Another designation concerns the purity of copper, regulated by GOST 859-2001. At the same time, marks M1, M1p, M2, M2p, M3, M3 are allowed.
According to the marking, which is indicated on the manufactured products, you can find out the following information:
- cross section shape. Designated by the letters KR.
- Length - this indicator has different markings. BT - bay, MD - dimensional, KD - multiple dimensionality.
- The method of manufacturing the product. If the element is welded, the letter C is indicated on it. The letter D is placed on drawn products.
- Special operating features. For example, increased technical characteristics are indicated by the letter P. High plasticity index - PP, increased cut accuracy - PU, accuracy - PS, strength - PT.
- Manufacturing precision. The standard indicator is indicated by the letter H, increased - P.
To visually understand how to read the marking, you need to understand a simple example - DKRNM50x3.0x3100. Decryption:
- It is made of pure copper, designated by the M1 brand.
- The product is stretchy.
- The shape is round.
- Soft.
- External diameter — 50 mm.
- Wall thickness - 3 mm.
- The length of the product is 3100 mm.
European manufacturers use a special DIN 1412 marking system. They apply the EN-1057 designation to the elements of water supply and heating systems. It includes the number of the standard according to which the pipes are made, an additional element included in the composition - phosphorus. It is needed to increase the resistance to rust.
 Copper pipes in a factory
Copper pipes in a factory





















































