- Fluorescent lamps: description and device
- The principle of operation of a fluorescent lamp
- Why do you need a choke in a fluorescent lamp
- Working principle of fluorescent lamp starter
- Wiring diagram, start
- Breakdown detection and repair work
- Schemes with a starter
- Two tubes and two chokes
- Wiring diagram for two lamps from one throttle (with two starters)
- Principle of operation
- Repair of a rechargeable fluorescent lamp
- Malfunctions of luminaires with a choke
- Control gear
- Electronic ballast for fluorescent lamps
- Advantages
- Flaws
- We analyze the technical characteristics of different types of fluorescent lamps
- Versions
- Specifications: plinths, weight and color temperature
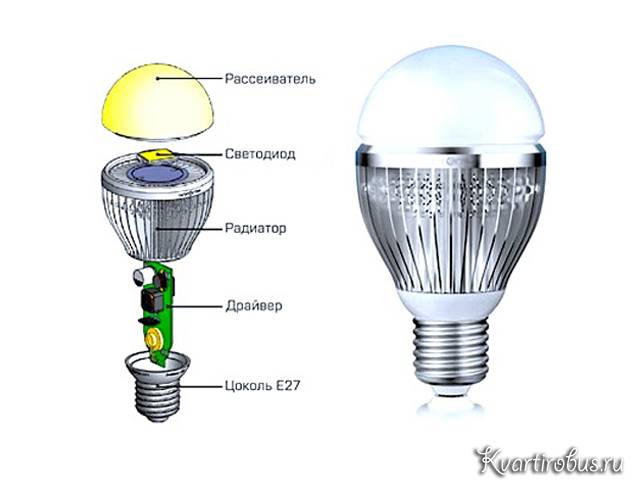
- Features of compact LL
Fluorescent lamps: description and device
Fluorescent lamps, in appearance, are a glass flask, of various shapes, white with connection contacts sticking out at the edges.
The shape of fluorescent lamps can be in the form of a rod (tube), torus, or spirals. During production, air is pumped out of the lamp bulb and an inert gas is pumped in. It is the behavior of an inert gas under the influence of electricity that causes the lamp to glow, creating streams of cold or warm light, which is commonly called "daylight".Hence the second name of these lamps, fluorescent lamps.
It is worth noting that the lamp could not shine if a phosphor had not been applied to the flask from the inside, and mercury would not have been in the lamp itself.
It was mercury that became the factor that displaces this type of lamp from the market. The danger of mercury pollution when breaking lamps raises many questions and environmentalists around the world.
The principle of operation of a fluorescent lamp
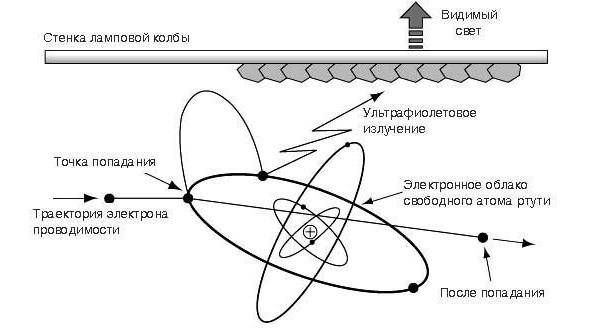
How does a fluorescent lamp work? First, freely moving electrons are formed. This occurs when the AC supply is switched on in the areas around the tungsten filaments inside the glass bulb.
These filaments, by coating their surface with a layer of light metals, create electron emission as they heat up. The external supply voltage is still not enough to create an electronic flow. During the movement, these free particles knock out electrons from the outer orbits of the atoms of the inert gas with which the flask is filled. They join the general movement.
At the next stage, as a result of the joint operation of the starter and the electromagnetic inductor, conditions are created for increasing the current strength and the formation of a glow discharge of gas. Now it's time to organize the light flux.
The moving particles have sufficient kinetic energy necessary to transfer the electrons of mercury atoms, which are part of the lamp in the form of a small drop of metal, to a higher orbit. When an electron returns to its former orbit, energy is released in the form of ultraviolet light. The conversion to visible light takes place in the phosphor layer covering the inner surface of the bulb.
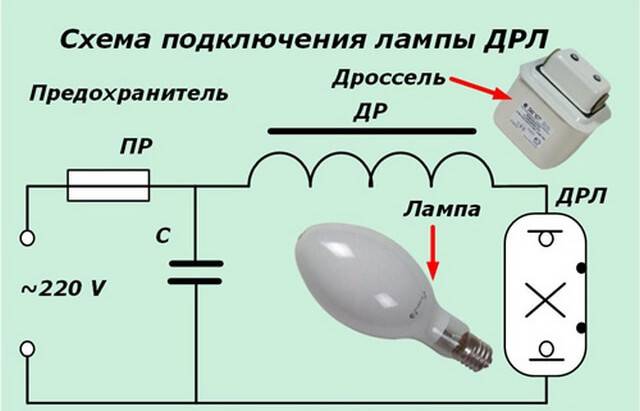
Why do you need a choke in a fluorescent lamp
This device works from the moment of start and throughout the entire glow process. At different stages, the tasks performed by him are different and can be divided into:
- switching on the lamp;
- maintaining normal safe mode.
At the first stage, the property of the inductor coil is used to create a voltage pulse of large amplitude due to the electromotive force (EMF) of self-induction when the flow of alternating current through its winding stops. The amplitude of this pulse directly depends on the value of the inductance. It, summing up with the alternating mains voltage, allows you to briefly create between the electrodes a voltage sufficient to discharge in the lamp.
With a constant glow created, the choke acts as a limiting electromagnetic ballast for the low resistance arc circuit. His goal now is to stabilize the operation to eliminate arcing. In this case, the high inductive resistance of the winding for alternating current is used.
Working principle of fluorescent lamp starter
The device is designed to control the process of starting the lamp into operation. When the mains voltage is initially connected, it is completely applied to the two starter electrodes, between which there is a small gap. A glow discharge occurs between them, in which the temperature increases.
One of the contacts, made of bimetal, has the ability to change its dimensions and bend under the influence of temperature. In this pair, he plays the role of a moving element. An increase in temperature leads to a rapid short circuit between the electrodes. A current begins to flow through the circuit, this leads to a decrease in temperature.
After a short period of time, the circuit breaks, which is a command for the EMF of the self-inductance of the throttle to enter into operation. The subsequent process has been described above. The starter will be needed only at the stage of the next inclusion.
Wiring diagram, start
The ballast is connected on one side to the power source, on the other - to the lighting element. It is necessary to provide for the possibility of installing and fixing electronic ballasts. The connection is made in accordance with the polarity of the wires. If you plan to install two lamps through the gear, use the option of parallel connection.
The schema will look like this:
A group of gas-discharge fluorescent lamps cannot work normally without a ballast. Its electronic version of the design provides a soft, but at the same time almost instantaneous start of the light source, which further prolongs its service life.
The lamp is ignited and maintained in three stages: heating of the electrodes, the appearance of radiation as a result of a high-voltage pulse, and maintaining combustion is carried out by means of a constant supply of a small voltage.
Breakdown detection and repair work
If there are problems in the operation of gas-discharge lamps (flickering, no glow), you can make repairs yourself. But first you need to understand what the problem is: in the ballast or in the lighting element. To check the operability of electronic ballasts, a linear light bulb is removed from the fixtures, the electrodes are closed, and a conventional incandescent lamp is connected. If it lights up, the problem is not with the ballast.
Otherwise, you need to look for the cause of the breakdown inside the ballast.To determine the malfunction of fluorescent lamps, it is necessary to “ring out” all the elements in turn. You should start with a fuse. If one of the nodes of the circuit is out of order, it is necessary to replace it with an analogue. The parameters can be seen on the burnt element. Ballast repair for gas discharge lamps requires the use of soldering iron skills.
If everything is in order with the fuse, then you should check the capacitor and diodes that are installed in close proximity to it for serviceability. The voltage of the capacitor must not be below a certain threshold (this value varies for different elements). If all the elements of the control gear are in working order, without visible damage, and the ringing also did not give anything, it remains to check the inductor winding.
Repair of compact fluorescent lamps is carried out according to a similar principle: first, the body is disassembled; the filaments are checked, the cause of the breakdown on the control gear board is determined. Often there are situations when the ballast is fully functional, and the filaments are burned out. Repairing the lamp in this case is difficult to produce. If the house has another broken light source of a similar model, but with an intact filament body, you can combine two products into one.
Thus, electronic ballasts represent a group of advanced devices that ensure the efficient operation of fluorescent lamps. If the light source flickers or does not turn on at all, checking the ballast and its subsequent repair will extend the life of the bulb.
Schemes with a starter
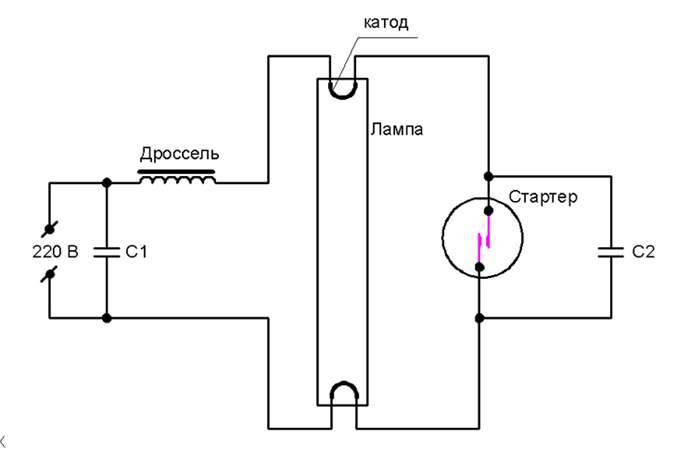
The very first circuits with starters and chokes appeared. These were (in some versions, there are) two separate devices, each of which had its own socket.There are also two capacitors in the circuit: one is connected in parallel (to stabilize the voltage), the second is located in the starter housing (increases the duration of the starting pulse). All this "economy" is called - electromagnetic ballast. The diagram of a fluorescent lamp with a starter and a choke is in the photo below.
Wiring diagram for fluorescent lamps with a starter
Here's how it works:
- When the power is turned on, the current flows through the inductor, enters the first tungsten filament. Further, through the starter it enters the second spiral and leaves through the neutral conductor. At the same time, the tungsten filaments gradually heat up, as do the starter contacts.
- The starter has two contacts. One fixed, the second movable bimetallic. In the normal state, they are open. When current is passed, the bimetallic contact heats up, which causes it to bend. Bending, it connects to a fixed contact.
- As soon as the contacts are connected, the current in the circuit instantly increases (2-3 times). It is limited only by the throttle.
- Due to the sharp jump, the electrodes heat up very quickly.
- The bimetallic starter plate cools down and breaks contact.
- At the moment of breaking the contact, a sharp voltage jump occurs on the throttle (self-induction). This voltage is sufficient for the electrons to break through the argon medium. Ignition occurs and gradually the lamp enters the operating mode. It comes after all the mercury has evaporated.
The operating voltage in the lamp is lower than the mains voltage for which the starter is designed. Therefore, after ignition, it does not work. In a working lamp, its contacts are open and it does not participate in its work in any way.
This circuit is also called electromagnetic ballast (EMB), and the operation circuit of an electromagnetic ballast is EmPRA. This device is often referred to simply as a choke.
One of the EMPRA
The disadvantages of this fluorescent lamp connection scheme are enough:
- pulsating light, which negatively affects the eyes and they quickly get tired;
- noise during start-up and operation;
- inability to start at low temperatures;
- long start - from the moment of switching on, about 1-3 seconds pass.
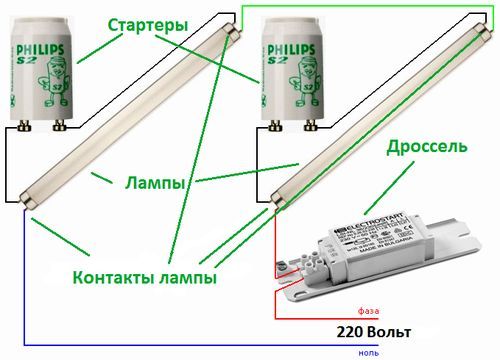
Two tubes and two chokes
In luminaires for two fluorescent lamps, two sets are connected in series:
- the phase wire is fed to the inductor input;
- from the throttle output it goes to one contact of the lamp 1, from the second contact it goes to the starter 1;
- from starter 1 goes to the second pair of contacts of the same lamp 1, and the free contact is connected to the neutral power wire (N);
The second tube is also connected: first the throttle, from it - to one contact of the lamp 2, the second contact of the same group goes to the second starter, the starter output is connected to the second pair of contacts of the lighting device 2 and the free contact is connected to the neutral input wire.
Connection diagram for two fluorescent lamps
The same connection diagram for a two-lamp fluorescent lamp is shown in the video. It might be easier to deal with the wires this way.
Wiring diagram for two lamps from one throttle (with two starters)
Almost the most expensive in this scheme are chokes. You can save money and make a two-lamp lamp with one throttle. How - see the video.
Principle of operation
Let's take a look at what a fluorescent lamp is and how it works.It is a glass tube that starts working due to a discharge that ignites the gases inside its shell. A cathode and an anode are installed at both ends, it is between them that a discharge occurs, which causes a starting fire.
Vapors of mercury, which are placed in a glass case, when discharged, begin to emit a special invisible light, which activates the work of the phosphor and other additional elements. It is they who begin to radiate the light that we need.
The principle of the lamp
Due to the different properties of the phosphor, such a lamp emits a wide range of different colors.
Repair of a rechargeable fluorescent lamp
The given diagram of the Ultralight System luminaire is similar in circuitry to similar devices from other companies.
A diagram and a brief description may be useful during repair and operation.
The rechargeable luminescent luminaire is designed to provide evacuation and backup
lighting, as well as a network table lamp.
Power consumption in charging mode - 10W.
Operating time from the internal battery at a full charge, not less than 6 hours. (with one lamp and 4 hours with two lamps).
Time to fully charge the battery, at least 14 hours.
Check the operation of the lamp, in most cases it is possible to identify malfunctions without even opening
luminaire housing, guided by the brightness of the LOW and HIGH LEDs.
To do this, the mode switch must be switched from OFF to DC LED LOW or HIGH and the lamp lamps must
light up. When the lamps do not light up, we switch the switch to AC mode and connect it to the network, if after
this lamp does not work, you need to look at the control board and lamps.
Important
If the lamp is working normally from the mains, we switch the switch to DC mode, press the TEST button,
the lamp should light up. Even 1.5-2V lamps dimly light up when the TEST button is pressed. Hence the conclusion
battery voltage is less than 5V. The LOW LED shines brightly when the battery voltage is 5.9V,
when the voltage decreases, the brightness will drop and at 2V it turns off, this indicates a low battery.
The glow of the HIGH indicator indicates the voltage on the battery is 6.1V or higher. At a voltage of 6.4V
the LED should shine brightly, with a decrease in voltage, the brightness of the LED drops, at 6.0V the indicator
turns off.
When the battery is at 6.0V, both LOW and HIGH indicators will turn off.
Frequent lamp defects.
Battery charging does not work.
Check power cord. Invalid power supply. Often the problem of failure of the normal operation of the unit
the power supply is very poor installation. It is necessary to check all soldering suspicious to solder. Verify
Advice
power supply transistors, if one of them is not working, you need to change the other immediately.
Practice shows that a previously unreplaced transistor will be the culprit of the re-repair.
In AC mode it works, DC does not work.
LOW / HIGH LEDs do not light, the fuse is blown.
In most cases, a break in the connecting conductors of the board, or a battery failure
or its complete discharge.
Management fee.
Useful links …
Charging device “IMPULSE ZP-02” Flashlight en electronic model: 3810
Repair of the relay voltage stabilizer Uniel RS-1/500 Repair of stabilizers of the LPS-хххrv series
Malfunctions of luminaires with a choke
So, if the previous steps are completed, and the lamp still does not work, you need to start checking all the nodes of the lighting fixture circuit, i.e., directly start repairing fluorescent lamps.
Scheme of serial connection of fluorescent lamps
A visual inspection can tell a lot of things, sometimes breakdowns, dents and other reasons why the lamp does not light up are visible to the naked eye.
As with any repair, you first need to check the elementary. It makes sense to change the starter to a known working one, after which the lamp should light up, and then this malfunction of the fluorescent lamp can be eliminated. However, it is not always at hand that a starter suitable in terms of parameters may be at hand, but it is somehow necessary to check the one that is, what if the reason is not in it?
Everything is quite simple. You will need a regular lamp with an incandescent bulb. Power must be supplied to it like this - turn on the sequentially checked starter in the gap of one of the wires, and leave the second intact. If the lamp lights up or blinks, then the device is operational and the problem is not in it.
Next, check the input and output voltage at the inductor. A working tester should show the current at the output. If necessary, this circuit assembly must be replaced.
If, after this, the lamp does not light up, then you will have to ring all the wires of the lamp for integrity, and also check the voltage at the contacts of the cartridges.
Control gear
Any type of gas discharge lamps cannot be directly connected to the mains.When cold, they have a high level of resistance and require a high voltage pulse to create a discharge. After a discharge appears in the lighting device, a resistance with a negative value arises. To compensate for it, it is impossible to do simply by turning on the resistance in the circuit. This will lead to a short circuit and failure of the light source.
To overcome energy dependence, ballasts or ballasts are used together with fluorescent lamps.

From the very beginning and until now, electromagnetic type devices - EMPRA - have been used in lamps. The basis of the device is a choke with inductive resistance. It is connected together with a starter that provides switching on and off. A capacitor with a high capacitance is connected in parallel. It creates a resonant circuit, with the help of which a long pulse is formed, which lights the lamp.
A significant disadvantage of such a ballast is the high power consumption of the throttle. In some cases, the operation of the device is accompanied by an unpleasant buzz, there is a pulsation of fluorescent lamps, which adversely affects vision. This equipment is large and heavy. It may not start at low temperatures.
All negative manifestations, including the pulsations of fluorescent lamps, were overcome with the advent of electronic ballast - electronic ballast. Instead of bulky components, compact microcircuits based on diodes and transistors are used here, which made it possible to significantly reduce their weight.This device also provides the lamp with electric current, bringing its parameters to the desired values, reducing the difference in consumption. The required voltage is created, the frequency of which differs from the mains one and is 50-60 Hz.
In some areas, the frequency reaches 25-130 kHz, which made it possible to eliminate blinking, which negatively affects vision, and reduce the ripple coefficient. The electrodes are warmed up in a short period of time, after which the lamp immediately lights up. The use of electronic ballasts significantly increases the shelf life and normal operation of luminescent light sources.
Electronic ballast for fluorescent lamps
Electronic ballast circuits for fluorescent lamps are as follows: On the electronic ballast board is:
- EMI filter that eliminates interference coming from the mains. It also extinguishes the electromagnetic impulses of the lamp itself, which can negatively affect a person and surrounding household appliances. For example, interfere with the operation of a TV or radio.
- The task of the rectifier is to convert the direct current of the network into an alternating current suitable for powering the lamp.
- Power factor correction is a circuit responsible for controlling the phase shift of the AC current passing through the load.
- The smoothing filter is designed to reduce the level of AC ripple.
As you know, the rectifier is not able to perfectly rectify the current. At the output of it, the ripple can be from 50 to 100 Hz, which adversely affects the operation of the lamp.
The inverter is used half-bridge (for small lamps) or bridge with a large number of field-effect transistors (for high-power lamps).The efficiency of the first type is relatively low, but this is compensated by driver chips. The main task of the node is to convert direct current to alternating current.
Before choosing an energy-saving light bulb. it is recommended to study the technical characteristics of its varieties, their advantages and disadvantages
Particular attention should be paid to the installation location of the compact fluorescent lamp. Very frequent on-off or frosty weather outside will significantly reduce the duration of the CFL
Connecting LED strips to a 220 Volt network is carried out taking into account all the parameters of lighting devices - length, quantity, monochrome or multicolor. Read more about these features here.
A choke for fluorescent lamps (a special induction coil made of coiled conductor) is involved in noise suppression, energy storage and smooth brightness control.
Voltage surge protection - not installed in all electronic ballasts. Protects against mains voltage fluctuations and erroneous start without a lamp.
Advantages
Production technologies are constantly being improved. In modern energy-saving fluorescent lamps, the luminescent layer is used with increasing quality. This made it possible to reduce their power, while at the same time increasing the efficiency of the luminous flux, and also the diameter of the glass tube decreased by 1.6 times, which also affected its weight.
Consider the advantages of fluorescent lamps, these are:
- high efficiency, economy, long service life;
- a variety of color shades;
- wide spectral range;
- availability of colored and special flasks;
- large coverage area.
Read also: Malfunctions of the steam regulator in the gc 2048 iron
They consume 5-7 times less electricity than ordinary incandescent lamps. For example, a 20W fluorescent lamp will give as much light as a 100W incandescent lamp. In addition, they have a very long service life. In this regard, only an LED light bulb can compare with them and exceed these readings, but it has its own characteristics. And also they make it possible to select flasks that will give the desired level of illumination. And its variety of color shades will make it easy to decorate the room.
Fluorescent lamps are used in medicine, being used as good lamps and as ultraviolet and bacterial devices. This possibility is widely used in the food industry.
Very important is the fact that such a lamp can illuminate a fairly solid area, so it has become indispensable for large rooms. Its minimum service life is 4800 hours, 12 thousand hours are indicated above in the technical specification - this is an average value, the maximum is 20,000 hours, but it depends on the number of on and off, so it will last less in public places.
Flaws
Despite such great advantages of fluorescent lamps, they can be harmful to health, so such lamps are not recommended for installation at home or on the street. If such a device breaks, it can poison the room, terrain and air over a long distance. The reason for this is mercury. That is why used flasks must be handed over for recycling.
Another disadvantage of fluorescent bulbs is their flicker, which is easily caused by the slightest malfunction. It can adversely affect vision and cause headaches.Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the timely elimination of the malfunction or change the tube to a new one.
A choke is needed to start the lamp, which complicates the design and affects the price.
36W fluorescent lamps are economical, give high quality bright color and create a pleasant working atmosphere, their prices are low and start from 60 rubles
When choosing them, buyers pay more attention to the need for lighting the room. Lamps for them are also very cheap, so when buying a lamp, they pay more attention to the desired quality, and not to the price.
Lamps are supplied in boxes of 25 pieces - this is the minimum lot. You can buy one or more in retail stores, where they are packed in original boxes. A unit of goods weighs only 0.17 kg
The flask is very light, long and fragile, so care must be taken when transporting it.
Fluorescent lamps are low pressure mercury vapor lamps. Power 36 W.
It is applied where high requirements to a color rendition are not put forward. Mains voltage 23..
It is applied where high requirements to a color rendition are not put forward. Mains voltage 22..
It is applied where high requirements to a color rendition are not put forward. Mains voltage 22..
It is applied where high requirements to a color rendition are not put forward. Mains voltage 22..
It is applied where high requirements to a color rendition are not put forward. Mains voltage 22..
It is applied where high requirements to a color rendition are not put forward. Mains voltage 22..
It is used for general lighting of industrial facilities and offices. They can work as in conventional s..
It is used for general lighting of industrial facilities and offices. They can work as in conventional s..
It is used for general lighting of industrial facilities and offices. They can work as in conventional s..
Mercury gas-discharge low pressure. It has a better color reproduction than the usual..
Mercury gas-discharge low pressure. It has a better color reproduction than the usual..
It is used for general lighting of industrial facilities and offices. They can work as in conventional s..
It is mainly used for lighting plants and for lighting aquariums. Due to the increased...
We analyze the technical characteristics of different types of fluorescent lamps
At present, it would not be a mistake to say that fluorescent lamps are the most common type among all lamps used in lighting. Back in the 1970s. they changed incandescent lamps in industrial premises and various public institutions. Being energy efficient, they made it possible to illuminate large areas with high quality: corridors, foyers, classrooms, wards, workshops, offices.
Further improvement in the production technology of fluorescent lamps made it possible to reduce their size, increase the brightness and quality of the emitted light. Since the 2000s these lamps are beginning to actively penetrate into households and are used where "Ilyich's bulbs" used to shine. Fluorescent lamps are attractively priced, save energy, and provide the ability to choose the color temperature of the light.
Versions
There is a wide variety of electroluminescent lamps, but all of them can differ in:
- execution form;
- type of ballast;
- internal pressure.
The form of execution can be like that of conventional fluorescent lamps - a linear tube or a tube in the form of the Latin letter U. Compact versions were added to them, made under the usual base using various spiral flasks.
The ballast is a device that stabilizes the work of the product. Electronic and electromagnetic types are the most common switching circuits.
Internal pressure determines the area of use of products. For domestic purposes or public places, low-pressure lamps or energy-saving designs have been used. In industrial premises or places with reduced requirements for color reproduction, high-pressure specimens are used.
To assess the ability of lighting, the indicator of lamp power and its light output is used. Many more different classification parameters and options can be cited, but their number is constantly increasing.
2 id="tehnicheskie-harakteristiki-tsokoli-ves-i">Specifications: plinths, weight and color temperature
The base serves to attach the lamp to the lamp socket and to supply power to it. The main types of plinths:
- Threaded - are designated (E). The flask is screwed into the cartridge along the thread. Diameters according to GOST 5 mm (E5), 10 mm (E10), 12 mm (E12), 14 mm (E14), 17 mm (E17), 26 mm (E26), 27 mm (E27), 40 mm (E40) are used ).
- Pin - are designated (G). The design includes pins. The plinth type expression includes the distance between them. G4 - distance between pins 4 mm.
- Pin - are designated (B). The base is connected to the cartridge with two pins located along the outer diameter. Marking depends on the location of the pins:
- VA - symmetrical;
- VAZ - displacement of one along the radius and height;
- BAY - offset along the radius.
The number following the letters indicates the base diameter in mm.
Information about the weight of the fluorescent lamp is required for proper disposal. Do not dispose of used light sources in household waste. They are handed over for destruction to special organizations. Waste material is taken from the population by weight. The average weight of the lamp is 170 g.
The color temperature is indicated on the lamp, the unit of measure is the degree Kelvin (K). The characteristic shows the proximity of the glow of the lamp to sources of natural light. It is divided into three ranges:
- Warm white 2700K - 3200K - lamps with this characteristic emit white and soft light, suitable for residential premises.
- Cold white 4000K - 4200K - suitable for workspaces, public buildings.
- Day white 6200K - 6500K - emit white light of cold tones, suitable for non-residential premises, for streets.
The temperature of the light affects the color of the surrounding objects. The color temperature of fluorescent lamps depends on the thickness of the phosphor. The greater the thickness, the lower the color temperature of the lamp in Kelvin.
Features of compact LL
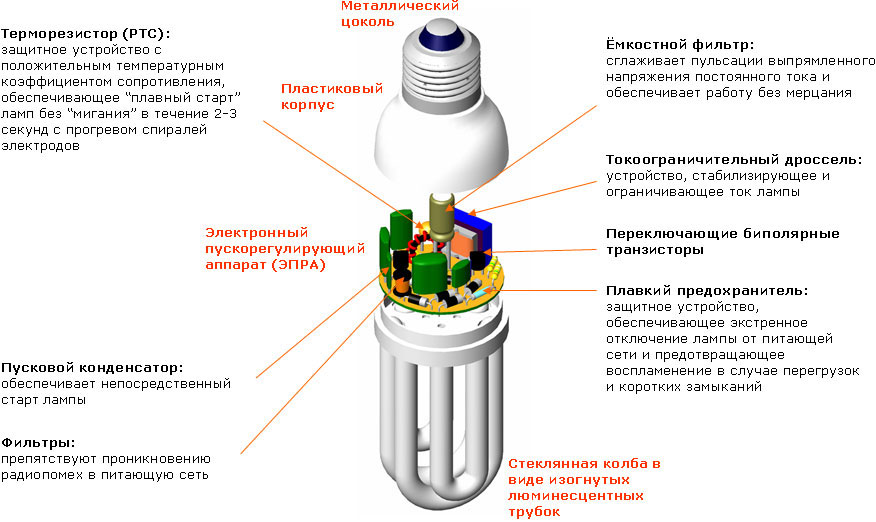
Compact-type LLs are hybrid products that combine some of the specific distinguishing features of incandescent lamps and the characteristics of fluorescents.
Thanks to advanced technologies and expanded innovative capabilities, they have a small diameter and medium-sized dimensions characteristic of Ilyich light bulbs, as well as a high level of energy efficiency, characteristic of the LL line of devices.

Compact-type LLs are produced for traditional E27, E14, E40 socles and are very actively replacing classic incandescent lamps from the market by providing high-quality light with significantly lower power consumption
CFLs are in most cases equipped with an electronic choke and can be used in specific types of lighting fixtures. They are also used to replace simple and familiar incandescent lamps in new and rare lamps.
With all the advantages, compact modules have such specific disadvantages as:
- stroboscopic effect or flickering - the main contraindications here relate to epileptics and people with various eye diseases;
- pronounced noise effect - in the process of prolonged use, an acoustic background appears that can cause some discomfort to a person in the room;
- smell - in some cases, products emit pungent, unpleasant odors that irritate the sense of smell.